Abstract
Car horns were originally installed in vehicles for safety. However, many urban areas in several countries face noise problems related to the use of car and motorbike horns. To propose measures to suppress the use of horns, relationships between horn use and factors including driver awareness and behavior, traffic environment, and the transportation system should be investigated. The present study therefore conducted surveys to grasp the current circumstances of horn use and traffic at urban intersections in Taiwan. The relationship between horn use and the traffic volume of standard-sized vehicles was found. According to an analysis of horn use during traffic signal cycles, in many cases, horns were honked after entering intersections to turn left. In particular, horns were honked when the driver waited more than 4 s for the car in front to start moving after the green light allowing left turns was turned on. An analysis of noise levels at intersections showed that the maximum noise level value (LAmax) could be reduced if vehicle horns were not used. Multiple regression analysis also indicated that LAmax values increased with the frequency of horn use. The equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure level (LAeq,10min) did not change with driver horn use, and increased with the traffic volume of motorcycles.
1. Introduction
The effects of transportation noises such as road traffic noise (RTN), railway noise and aircraft noise on humans have long been recognized, and the relationships between noise exposure and human responses have been investigated [,]. Out of these transportation noises, the road traffic noise generated by vehicles was one of the major sources. Many studies have revealed that RTN induces adverse effects on human responses such as annoyance [,,,,,,,,,,,,], sleep disturbance [,,,,,,,,], and other non-auditory reactions [,,,,]. Of course, among the RTN, the noise of travelling vehicles is dominant, and it comprises honking sounds as well. Several countries face noise problems caused by horn use. A report on the RTN in urban areas of Vietnam, for example, showed frequent horn honking as a major factor of RTN []. A report on the RTN at urban rotaries in India found that heavy vehicles and their honking more significantly affected the equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure level (LAeq) than other vehicle types did []. Another study in India also revealed that frequent honking increased from 2 to 5 dB in LAeq []. According to research on the RTN in Iran, the model estimating LAeq using factors including traffic flow, vehicle speed, and horn noise indicated that the honking frequency contributed to the increasing LAeq and maximum noise level value (LAmax) [].
The situations in which drivers should use horns are stated in the traffic regulations of various countries. Road Traffic Act in Japan [], for instance, states that a vehicle horn should be used only in an emergency or in dangerous locations where there is a sign allowing horn use, such as on a blind curve. However, there are many situations in which a horn is used other than those mentioned above. Although this is not a serious problem in Japan, such horn use evokes negative reactions from pedestrians and residents.
Horns were originally installed in vehicles for safety. Horn sounds are therefore designed with high sound pressure levels to alert drivers of danger in noisy environments. However, vehicle interior and exterior noises are quieter than they used to be when standards stating the acoustic characteristics of horn sounds were established. Horn sounds should therefore fulfil functions even if they have lower sound pressure levels. Concerning the current sound pressure level of a horn sound, the Automobile Standard Harmony World Forum in 2014 proposed regulations on the acoustic characteristics of horn sounds [] in which the upper limit of the sound pressure level was maintained while the lower limit was reduced. Such a revision of the regulations will not mitigate noise problems relating to honking because horn sounds with high sound pressure levels will still be generated on roads. As long as the current horn system is used, in which the horn sound is emitted outside a vehicle at a sound level loud enough to be heard by drivers inside their vehicles, the noise problem will not be improved by the acoustic design of a horn. Therefore, the control of horn use is supposed to be more effective to drastically improve the noise problem of horn use. To reduce the RTN, including horn sounds in urban areas of Indonesia, the ridesharing or car-pooling policy to reduce the number of vehicles, and the similar policy for motorcycles and the prohibition of vehicle horn use, were examined for actual measurement results of the RTN []. Through the combined application of these programs, the maximum reduction in LAeq,10min was estimated to be 3.9 dB. The result revealed that the prohibition of horn use was not so effective.
In controlling driver horn use, it is necessary to identify the factors affecting driver horn use. Various intrinsic and extrinsic factors are assumed to influence driver horn use. Driver horn use is considered an indicator of driver aggression []. In Scandinavia, the use of horns is generally regarded as a manifestation of driver aggression, whereas the threshold for horn use is lower and not necessarily regarded as such in Southern Europe []. Fujii has proposed a socio-psychological model representing driver traffic behaviors []. In this model, a certain traffic behavior is assumed to be caused by behavioral intention, which is related to psychological factors such as personal norm and moral obligation. From these studies, driver horn use can be considered one of the traffic behaviors and is influenced by the intrinsic (psychological) factors of the driver. A study conducted in South Korea investigated the relationship between driver awareness of their horn use and the manner of its use []. It was suggested that drivers who do not normally use horns are reluctant to use them, and that they sound a short horn when necessary to warn other drivers of danger or for the purpose of alerting them.
Furthermore, another study conducted in Japan reported that the honking patterns of horn use were related to location and traffic volume []. The results suggested that driver horn use is influenced by extrinsic factors (i.e., situations). Based on these findings, we assumed a similar behavioral model in which intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence behavioral intentions and induce specific traffic behaviors, including the use of a horn. To address the horn noise issue, a comprehensive understanding of the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that lead drivers to use their horns is needed.
The main purposes of the present study were to find the extrinsic factors of driver horn use, such as the behavior of other drivers and the traffic environment, and to propose the countermeasure to reduce driver horn use. Although the actual road conditions and situations surrounding drivers are complicated and change continuously, the relationship between the occurrence of horn use and the traffic environment was investigated. As a case study, measurements and recordings of horn use and the current circumstances of traffic were conducted at urban intersections in Taiwan []. We found traffic features at intersections and relationships between the extrinsic factors, such as traffic count and traffic signals, and driver use of horns. A microscopic analysis was then conducted to examine the quantitative parameters of the traffic environment related to driver horn use []. As a further study, this paper analyzes the effects of vehicle horn use and the traffic environment on the acoustic environment around intersections, i.e., LAeq and LAmax at the measured point at intersections. Furthermore, based on the results obtained, countermeasures to improve the acoustic environment and to reduce drivers’ use of their horns will be discussed. To approach these points, important data on the vehicular environment [,] are restated in this paper.
2. Procedures
2.1. Surveyed Sites and Equipment
Measurement surveys were carried out in Taipei City, Taiwan, where we observed frequent horn use during an onsite inspection. Motorcycles account for a high proportion of the traffic volume in Taiwan. Similar trends have been observed in several areas of Southeast Asian countries. In such areas, it has been regarded as being effective to create high road transport capacity by means of personal transportation []. Taiwanese traffic regulations include regulations on vehicle horn use []. For instance, when compared with Japanese regulations [], in both countries, a vehicle horn is allowed in an emergency or in dangerous situations, such as when taking a blind corner. Additionally, it is necessary for a driver to use the horn when overtaking another vehicle in Taiwan. Moreover, the manner of honking is mainly limited to short honking. In particular, a horn should be honked twice when overtaking and no more than twice in other situations.
We conducted measurement surveys at three intersections in Taipei City. The surveyed intersections are shown in Figure 1. Intersection 1 was located southeast of Taipei main station and was the largest intersection of the study subjects. Intersection 2 was located near Taipei main station, with a nearby bus terminal and large taxi stop. Intersection 3 was located north of Taipei main station and was the smallest intersection of the study subjects. Table 1 shows the characteristics of intersections (i.e., the number of lanes in each direction). The numbers in parentheses are the numbers of lanes available for turning left. Figure 2 displays a view of the three intersections. In Taiwan, vehicles drive on the right-hand side of the road.
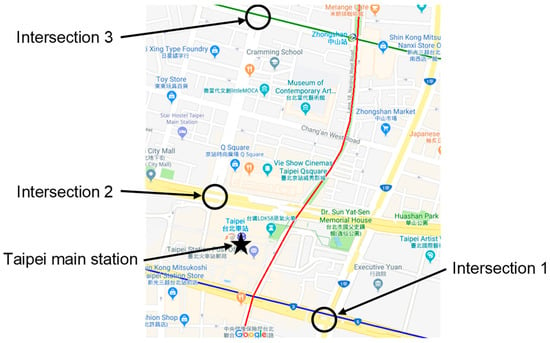
Figure 1.
Map of the surveyed sites.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the targeted intersections.
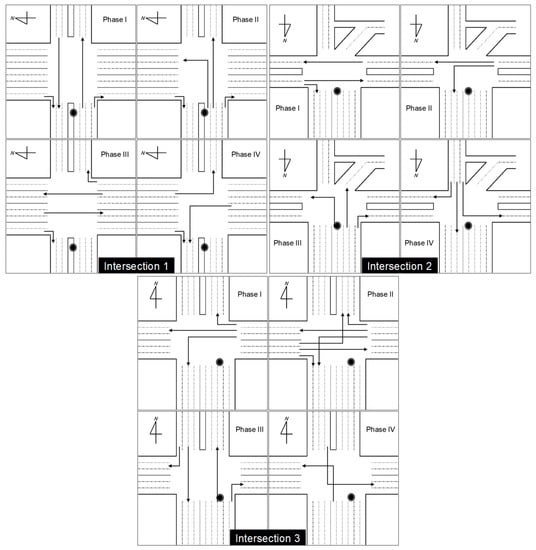
Figure 2.
Traffic flow in each of four green light phases (phase I to phase IV) during traffic signal cycles and the measurement point at each intersection (black circles).
Traffic signal timing was analyzed at each intersection. In all three intersections, four green light phases (from phase I to IV) were assigned to the traffic signal cycles, as shown in Figure 2. For example, at Intersection 2, phases I to IV allowed east–west traffic flow and right turn movements to the north (phase I), vehicle traffic from west to east and left turn movements to the north (phase II), entry into the intersection from the north only (phase III), and entry into the intersection from the south only (phase IV), respectively. Table 2 represents the durations of each green light phase and traffic signal cycle at each intersection. These durations differed depending on the day (weekday or weekend) and time of day.

Table 2.
Durations of each green light phase and traffic signal cycle.
At each intersection, the A-weighted sound pressure level of the RTN was measured with a sound level meter (RION NL-52) over a 12 h period (7:00 a.m.–7:00 p.m.) on one weekday and one weekend day. At the same time, all vehicles passing through the intersection were recorded by two camcorders (SONY HDR-CX560V and SONY HDR-CX370). These instruments were installed on pedestrian bridges near intersections. In particular, the sound level meter was installed at a height of 1.5 m on a pedestrian bridge that would be directly above the road, as seen in Figure 2.
2.2. Traffic Volume at Intersections
We analyzed the traffic volume using video data, which was recorded over 10 min spans in every hour by the camcorders. First, we investigated whether the traffic volume for 1 h could be estimated from the 10 min recording for each hourly time zone. The total traffic volume in each time zone for a weekday (i.e., 12 h) was similar, with values estimated from the traffic volume during the 10 min recordings (i.e., 10 min traffic volume × 6) (error ratios: 0.48% to 6.23%) []. The 10 min traffic volume data thus approximately represent the hourly traffic volumes. In the subsequent analysis, therefore, we employed traffic volume data recorded over 10 min for each hourly time zone.
For the purpose of tabulation, we categorized vehicles into motorcycles, standard-sized vehicles, and large-sized vehicles. Large-sized vehicles included buses, mixer trucks, and other specialized vehicles. Other vehicles, such as mini-buses and light trucks, were classified as standard-sized vehicles.
Table 3 presents the range of total traffic volumes at each intersection during the measurement time period (10 min per h) analyzed in each measurement day. The total traffic volumes at Intersection 2 were higher than those at other intersections.

Table 3.
Range of total traffic volumes during the measurement time period analyzed in each measurement day.
2.3. Analysis of Horn Honking
From the noise data recorded by the sound level meter, the times at which drivers used their horns were obtained using an application for data management (RION AS-60). Data of horn honking were analyzed for the periods (10 min in each hourly time zone) during which the traffic volume was counted.
3. Results
Figure 3 shows the total traffic volume at each measured hour in each intersection. Table 4 presents similar results for each vehicle type in each intersection. The results for weekdays revealed peaks in the total traffic volume representing rush hours around 8:00 in the morning and around 17:00 or 18:00 in the evening. Meanwhile, there were no similar peaks in the total traffic volume on the weekend. The total traffic volume gradually increased from morning to evening. These characteristics of total traffic volume were found at all intersections.
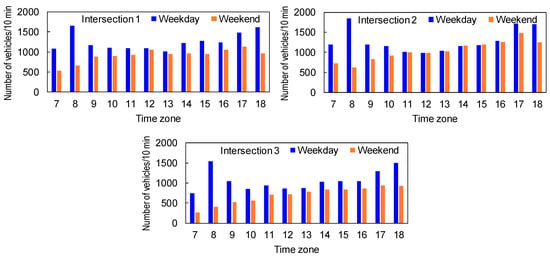
Figure 3.
Total traffic volume at each measured hour in each intersection.

Table 4.
Temporal variation of traffic volume for each type of vehicle.
Table 4 indicates that the traffic volume of motorcycles was very high during rush hours (i.e., around 8:00 in the morning and 17:00 or 18:00 in the evening) on weekdays at all intersections, while that on the weekend gradually increased from morning to evening. The large number of motorcycles on weekdays appears to affect the total traffic volume. On weekend days, the traffic volume of motorcycles gradually increased from morning to evening. Similar results were found in the traffic volume of standard-sized vehicles on weekend days. On weekdays, a peak in the traffic volume of standard-sized vehicles due to the morning rush was found only at Intersection 1. At other intersections, the traffic volume monotonously increased during the measurement period. The traffic volume of large-sized vehicles was the lowest of all vehicle types, and there does not appear to be much difference in traffic volume for this vehicle type between morning and afternoon.
4. Analysis
4.1. Relationship between Traffic Volume and Horn Honking
The macroscopic analysis using the traffic counts were firstly carried out []. Correlation analysis between the total traffic volume and the frequency of horn use was examined at each intersection on each day of measurement. On weekdays, there was no significant correlation at any surveyed site (Intersection 1: r = 0.16, Intersection 2: r = 0.28, and Intersection 3: r = 0.02). On the weekend, significant correlations were obtained at two sites (Intersection 1: r = 0.72, p < 0.01; Intersection 2: r = 0.57, not significant; and Intersection 3: r = 0.90, p < 0.01).
Table 5 presents the coefficient of correlation between the traffic volume of each vehicle type and the frequency of horn use. The results show significant correlations between the standard-sized vehicle traffic volume and the frequency of horn use on the weekend at all intersections and on the weekday at Intersection 2. The traffic volume of motorcycles significantly correlated with the frequency of horn use only at Intersection 3 (r = 0.90, p < 0.01). On weekdays, however, there was no relationship other than that for standard-sized vehicles at Intersection 2.

Table 5.
Correlation coefficient between the traffic volume of each type of vehicle and the frequency of horn use.
Figure 4 shows scatter diagrams of the total traffic volume and the frequency of horn use during the measured 10 min in each hourly time zone, where the numbers next to data points represent time zones from 7:00 to 19:00. The frequency of horn use approximately increased as the total traffic volume increased at all surveyed sites. Such tendencies become clearer when removing the data for rush hours on weekdays (i.e., 8:00 and 17:00 or 18:00), in particular, at Intersections 1 and 3. As mentioned above, a high traffic volume during rush hours is supposed to relate to a high volume of motorcycles. The correlation between the total traffic volume and the frequency of horn use was analyzed using the data for weekdays and weekends with the data for rush hours eliminated (i.e., data for 9 h on a weekday and 12 h during the day on a weekend). Significant relationships were obtained for Intersections 1 and 3 (Intersection 1: r = 0.71, p < 0.01; Intersection 2: r = 0.35, not significant; and Intersection 3: r = 0.77, p < 0.01).
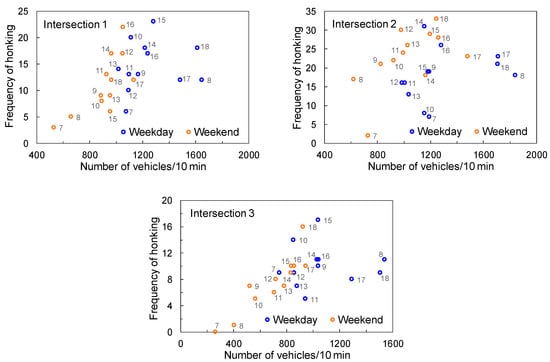
Figure 4.
Relationship between the total traffic volume and frequency of horn use during the recorded 10 min in each time zone.
To investigate the effect of the characteristics of the intersections on horn use, the relationship between the total traffic volume per lane at each intersection (i.e., the total traffic volume during the recorded 10 min of each hourly time zone was divided by the number of lanes entering the intersection) and the frequency of horn use was examined. Figure 5 shows scatter diagrams for the total traffic volume per lane and the frequency of horn use during the recorded 10 min in each hourly time zone. The result for the total measurement time, including rush hours, is displayed in Figure 5a, while the result obtained when removing the data for rush hours on weekdays is displayed in Figure 5b. These figures in Figure 5 show positive relationships between the frequency of horn use and the traffic volume per lane. Both relationships were statistically significant (Figure 5a: r = 0.63, p < 0.01; and Figure 5b: r = 0.74, p < 0.01). However, the linear relationship of the result for which the data of rush hours were eliminated in Figure 5b was clearer than that for the total measurement time.
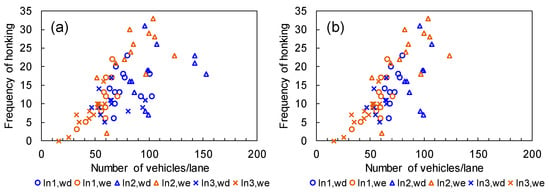
Figure 5.
Relationship between the traffic volume per lane and frequency of horn use. (a) Data of all measurement times. (b) Data without measurements during rush hours on weekdays.
The linear relationship between the traffic volume and the frequency of horn use would suggest that horn use should be frequent during rush hours, but in fact, horn use was not as frequent. The results suggest that the situations in which drivers need to use their horn are unlikely to occur during rush hours.
Furthermore, scattered data for each intersection are distributed within a certain range of the traffic volume in Figure 5b. The results for Intersection 2 (indicated by triangles) are distributed at large numbers of horn use and high traffic volumes. Conversely, the results for Intersection 3 (indicated by crosses) are oppositely distributed in the figure. This suggests that the characteristics of the intersections, such as locations in the city, connections with roads, and the number of lanes, affect horn use.
4.2. Horn Honking during Traffic Signal Cycles
The situations in which horn sounds were generated during the traffic signal cycle were analyzed []. Table 6 shows the frequencies of horn use, which were observed during each green light phase for all measured time periods (the total duration of each green light phase during a 10 min × 12 h period). The horn honking was generally more frequent on weekdays than on weekends. At Intersection 1, drivers used their horns more frequently in phases I and II. At Intersection 2, they used horns more frequently in phases other than phase II. At Intersection 3, horns were used more frequently in phases II and III than in other phases.

Table 6.
Frequencies of horn use during each green light phase for all measured time periods.
The duration of the green lights varied by phase, date of measurement, and intersection (Table 2). Therefore, the duration of horn sounds counting was equalized to 10 min periods. The frequency of horn use during the 10 min periods was estimated from the frequency of horn use within 1 s span measures that were averaged in each of the four green light phases throughout all measured time periods and measurement days (a 10 min × 12 h × 2 day period), as shown in Figure 6. Table 7 gives the estimated frequencies of horn use. At Intersection 1, the frequency of horn use is high in phases I and II. At Intersection 2, horn use frequency is higher in phases other than phase I. The overall frequency of vehicle horn use at Intersection 3 was low, but relatively high in phases I and IV compared to other phases.
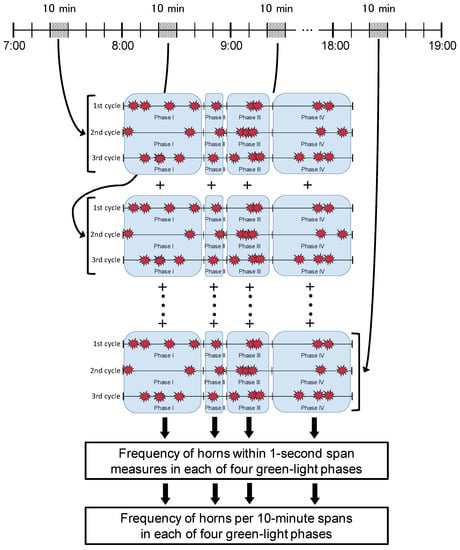
Figure 6.
Estimation of the frequency of horn use if the duration of each green light phase is 10 min. The upper part shows 10 min spans in every hour. The middle part shows the counting procedure of the frequency of horn use in each of the four green light phases.

Table 7.
Estimated frequency of horn use if the duration of each green light phase is 10 min.
During the green light phases, where the estimated frequency of horn use was higher, left-turn traffic was allowed, as was straight traffic, as shown in Figure 2. Video data analysis revealed many instances where vehicles entering the intersection to make a left turn during a green light phase began honking their horns. Therefore, we examined in detail the causes of horn use in green light phases when left turns were possible.
4.3. Analysis of Causes of Horn Use in Green Light Phases When Left Turns Were Possible
To explore measures to reduce horn honking, we conducted a microscopic analysis of how drivers use their horns []. Video data were analyzed in detail for instances where horns were used during signal phases allowing left turns (specifically, phase II at Intersections 1 and 2 and phase IV at Intersection 3). First, we categorized the situations in which vehicle horns were used into four types: (1) cutting in line, (2) slowness, (3) sudden stops, and (4) stopping state. Situation (1) is a circumstance in which a driver of a car who interrupted the line to make a left turn was honked at by the driver of another car. Situation (2) refers to a circumstance where a driver of a car driving slowly was honked at by another driver. Situation (3) is a circumstance in which a driver had to stop suddenly because the vehicle in front of them stopped, and they used their horn. Situation (4) refers to a circumstance in which a driver honked at another car that remained stopped at the stop line even though he/she could turn left after the green light turned on. Table 8 shows the number of these situations in which drivers used their horns during the above phases of the entire measurement period. Excluding the situation where the cause of horn use was unclear (situation (5)), horn use was frequently found in situation (4) (stopping state situations) at each intersection.

Table 8.
The number of each situation with and without horn use in green light phases when left turns were possible.
Next, regarding situation (4), the duration from when the light turned green until the car in front of the stop line started moving (the start delay time) was measured using video data, and then the start delay times were compared between when a horn was used and when a horn was not used. Intersection 1 had two lanes for left turns. Therefore, the same analysis was performed in each lane at this intersection. Table 9 presents the mean start delay times with and without horn use at each intersection. The mean start delay times were over 4 s when horn use occurred, but only about 2 s when horn use did not occur. T-test results revealed significant differences of the mean start delay times. The results suggest that delayed departure of the vehicle in front is one of the major causes of driver horn use at intersections.

Table 9.
Mean start delay times with and without horn use.
4.4. Noise Level in Situations with and without Honking
A previous study employed the noise prediction model to estimate the effects of honking on the acoustic environment []. However, in the present study, a single-point measurement was conducted because it was considered that such a simple measurement would be sufficient to approximately determine the impact of horn use on the acoustic environment near intersections (or the difference between when the horn use occurred and when it did not occur) without using noise maps or other prediction methods.
To determine the impact of horn use on the acoustic environment around intersections, we calculated the equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure level (LAeq,10min) and the maximum noise level (LAmax) of the RTN, both with and without the use of horns, by vehicles. Data management software (RION AS-60) was employed to calculate the LAeq,10min and LAmax without the use of horns. The data for horn sounds were removed from the initial data, and then both acoustic indices were recalculated. Figure 7 displays the variations in total traffic volume and LAeq,10min during the measurement time for each intersection and each measurement day. The similar results for LAmax are displayed in Figure 8.
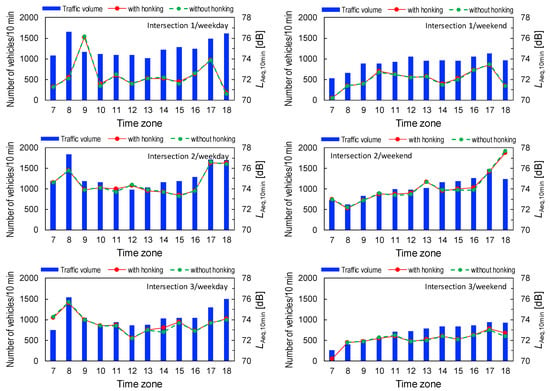
Figure 7.
Temporal variations of the total traffic volume and LAeq,10min.
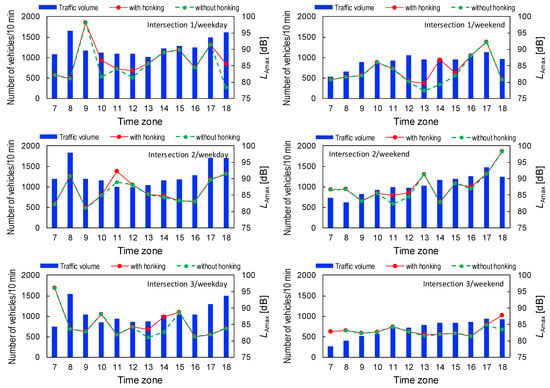
Figure 8.
Temporal variations of the total traffic volume and LAmax.
Significant relationships between LAeq,10min and total traffic volume were found for all measurements, except one weekday at Intersection 1 (Intersection 1: rweekday = −0.05, not significant; rweekend = 0.81, p < 0.01; Intersection 2: rweekday = 0.87, p < 0.01; rweekend = 0.76, p < 0.01; and Intersection 3: rweekday = 0.62, p < 0.05; rweekend = 0.85, p < 0.01). Although the values of LAeq,10min when the noise level data of honking were removed were very similar to those when such data were not removed, LAmax sometimes decreased when the noise level data of honking were removed in situations when LAeq,10min values were relatively low.
4.5. Relationship between Noise Level and the Traffic Environment
To clarify the effects of vehicle horn use and traffic environment on the acoustic environment around intersections, multiple regression analysis was performed with LAeq,10min as the dependent variable and the honking frequencies, as well as the traffic environmental factors, such as the traffic volumes of the three vehicle types, total number of entry lanes, and total number of exiting lanes in each intersection, as the independent variables.
As a result, an index of multicollinearity suggested that the variable “total number of entry lanes” was correlated with the other variables. Therefore, this variable was excluded from the independent variables and an analysis was conducted using five variables. Table 10 presents the obtained result. According to this table, the variable “traffic volume of motorcycles” was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The result reveals that LAeq,10min increases with the traffic volume of motorcycles. Neither the traffic count of standard-sized vehicles nor their horn use appears to have any effect on the acoustic environments of intersections.

Table 10.
Result of multiple regression analysis for LAeq,10min.
A similar analysis was conducted for LAmax. The dependent variable was LAmax and the independent variables were the honking frequencies and the traffic environmental factors mentioned above. As a result, because multicollinearity problems also arose in this analysis, the variable “total number of entry lanes” was excluded. Table 11 shows that the significant variable is the “honking frequency” only and suggests that LAmax increases with the frequency of honking.

Table 11.
Result of multiple regression analysis for LAmax.
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship between the Acoustic Environment around Intersections and Horn Honking and the Traffic Environment
The analysis of the LAeq,10min and LAmax of the RTN with and without honking at intersections indicates that LAmax values sometimes decreased when the noise level data of honking were removed in situations with low LAeq,10min values. As electric cars and hybrid vehicles become more prevalent in the future, the acoustic environment near roads will improve, but as it is, the current horn system will prevent that improvement.
The values of LAeq,10min obtained by excluding the noise level data for horn use was almost the same as those obtained from the original data, as shown in Figure 7. The relationship between the number of honks per minute and the increment of the RTN indicated that LAeq did not increase when horn events occurred less than twice per minute []. In the present result, the maximum numbers of honks per minute were estimated as 2.3 at Intersection 1 and 3.3 at Intersection 2 (Figure 4). Therefore, the sound energy of honks was not supposed to affect the LAeq,10min values.
The acoustic environment around roads should generally be influenced by traffic volume []. In the surveyed sites, small motorcycles are commonly used for commuting (Table 4). To improve the acoustic environment of the surveyed sites, it is necessary to address the heavy motorcycle traffic.
The LAeq,10min values at Intersection 1 were lower than those at other intersections, especially during rush hours (8:00 and 18:00); nevertheless, traffic volume was very high (Figure 7). The measurement point at Intersection 1 was located on the pedestrian bridge on the west side of this intersection (Figure 2). This measurement point was located on the outside of the intersection, slightly away from the road, with many lanes in the north–south direction, which serves as an arterial road connecting Taipei City and its suburbs. Therefore, noise from the north–south traffic flow was not fully reflected in the noise level values. On the other hand, the LAeq,10min values were higher at 9:00 and 17:00 than at other time zones due to ambulance sirens. These may be the reasons why the correlation between noise level and traffic volume was not significant (r = −0.05) only at Intersection 1 on weekday.
This analysis also confirmed that horn honking did not significantly affect the noise levels (LAeq,10min) at the surveyed sites. However, the multiple regression analysis for LAmax indicated that the maximum noise level increased with honking frequency. It may suggest that the more frequent the honking is, the more likely it is to be reflected in the maximum values of noise levels. Therefore, a reduction of deafening horn sounds should be effective in improving the acoustic environment around intersections.
5.2. Relationship between Horn Honking Use and Traffic Volume
To investigate the factors affecting a driver’s horn use, relationships with the vehicular environment were analyzed. Although the total traffic volume was mainly constructed with those of motorcycles and standard-sized vehicles, correlation analysis indicates that the frequency of horn use was related to the standard-sized vehicle traffic volume (Table 5). The frequency of horn use, especially on the weekends, increased with the number of standard-sized vehicles. The increase in the number of standard-sized vehicles at intersections might create dangerous and frustrating situations that may induce drivers to use their horns.
Figure 5 shows that the frequency of horn use differs among intersections, and that the traffic volume of Intersection 2 was higher than that of other intersections. Intersection 2 is located near Taipei Main Station and is an important traffic hub. These characteristics may have influenced the traffic volume and the frequency of honking.
5.3. Relationships between Driver Horn Use and Various Factors on Vehicular Environment
A detailed analysis of the situations in which horns were honked revealed that vehicle horn use was more frequent during traffic signal phases allowing a left turn and in “stopping states” situations. There were many cases where a vehicle on the stop line did not immediately start moving after the green light was turned on to allow a left turn, and the driver of the following vehicle then used their horn for the purpose of requesting that the vehicle start moving. Vehicle start delay is considered to be one of the causes of driver horn use. The significant difference in mean start delay time between when the horn occurred and when it did not occur at a green light allowing a left turn also supported this consideration (Table 9).
Video data analysis revealed that drivers sometimes did not realize a green light signal and delayed starting to move their vehicle. When the start delay time exceeded 4 s, drivers of the following vehicles used their horns. Behavioral experiments for drivers have shown that during rush hours and on weekends, their reaction time to horn use was 2 to 4 s when blocked by another car after a green light []. If drivers’ response delays to traffic signals could be prevented, their horn use would decrease. To achieve drivers’ immediate responses to traffic signals, it is necessary to install traffic signals in locations where drivers can easily see them. It may be also effective in directing the driver’s attention to the traffic signal by displaying the time remaining before the traffic signal turns green while the vehicle is stopped.
A previous study [] that applied a logit model to predict the probability of driver horn use reported that the probability significantly increased with the departure delay time and the standard-sized vehicle traffic volume. Furthermore, it was suggested that the probability tended to increase with a shorter green light signal duration that permitted a left turn (p = 0.063). Traffic signal optimization would be effective for not only better managing traffic flow [,], but also for reducing the use of horns.
6. Conclusions
Our measurements and recordings of horn use and current circumstances of traffic at three intersections in Taipei city, Taiwan suggested that LAmax significantly increased with frequency of honking, although no effect of horn honking on LAeq was found. In terms of LAeq, driver horn use did not affect the acoustic environment at the surveyed sites. Here, reducing the amount of small motorcycle traffic would be most effective. However, horn sounds are audible when noise levels are relatively low. Therefore, reducing the use of deafening horn sounds could be effective for improving the acoustic environment around intersections.
The present study indicates the relationship between standard-sized vehicle traffic volume and frequency of horn use. The results also suggest that the characteristics of the intersections, such as connections with roads and number of lanes, were related to horn use. An analysis of honking frequency during traffic signal cycles showed that honking was more frequently observed during the green light phases allowing left turns than in other phases. Video data analysis regarding the instances of honking during such green light phases appeared to show that horn use was frequently found in “stopping state” situations in which a vehicle at a stop line did not immediately start moving after a green light was turned on to allow a left turn, inducing another driver’s horn use. In such situations, the mean start delay times when drivers used their horns were significantly longer than those when they did not. To prevent vehicle start delays and reduce driver horn use, measures to direct the attention of stopped drivers to traffic signals would be necessary.
If the next-generation mobility (e.g., self-driving vehicles) is widely introduced into society and traffic conditions improve, the current horn system may no longer be needed. However, until such a dream is realized, the current system will be maintained. This study is expected to provide useful information for such current situations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T. and Y.O.; methodology, M.T., T.I., K.-H.K., K.Y. and Y.O.; formal analysis, M.T., S.T., K.H. and Y.O.; investigation, M.T., S.T., K.H., T.I. and K.-H.K.; resources, M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T. and S.T.; writing—review and editing, M.T. and S.I.; visualization, M.T. and S.T.; supervision, M.T., Y.O. and S.I.; project administration, M.T.; funding acquisition, M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by JSPS KAKENHI grant number JP17H00812.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Glenn Pennycook for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kryter, K.D. The Handbook of Hearing and the Effects of Noise; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Luxon, L.M.; Prasher, D. (Eds.) Noise and Its Effects; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, F.J. Noise nuisance caused by road traffic in residential areas, Part I. J. Sound Vib. 1976, 47, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, F.J. Noise nuisance caused by road traffic in residential areas, Part II. J. Sound Vib. 1976, 47, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambart, R.; Myncke, H.; Cops, A. Study of annoyance by traffic noise in Leuven (Belgium). Appl. Acoust. 1976, 9, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, R.; Sörensen, S.; Kajland, A. Traffic noise exposure and annoyance reactions. J. Sound Vib. 1976, 47, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.L.; Tayler, S.M. Predicting community response to road traffic noise. J. Sound Vib. 1977, 52, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T.J. Synthesis of social surveys on noise annoyance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 377–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryter, K.D. Community annoyance from aircraft and ground vehicle noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 72, 1222–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Vos, H. Exposure-response relationships for transportation noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Oudshoorn, C.G.M. Annoyance from transportation noise: Relationships with exposure metrics DNL and DENL and their confidence intervals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Tamura, A. Road traffic noise mitigation strategies in Greater Cairo, Egypt. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.A.; Tarrero, A.; González, J.; Machimbarrena, M. Exposure–effect relationships between road traffic noise annoyance and noise cost valuations in Valladolid, Spain. Appl. Acoust. 2006, 67, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.Y.T.; Yano, T.; Phan, H.A.T.; Nishimura, T.; Sato, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Community responses to road traffic noise in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Lam, K.C.; van Kamp, I. Quantification of the exposure and effects of road traffic noise in a dense Asian city: A comparison with western cities. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet, M.; Gagneux, J.M.; Blanchet, V.; Favre, B.; Labiale, G. Long term sleep disturbance due to traffic noise. J. Sound Vib. 1983, 90, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrström, E.; Skånberg, A. Sleep disturbances from road traffic and ventilation noise—Laboratory and field experiments. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 271, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrström, E.; Skånberg, A. Longitudinal surveys on effects of road traffic noise: Substudy on sleep assessed by wrist actigraphs and sleep logs. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 272, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrström, E. Longitudinal surveys on effects of changes in road traffic noise: Effects on sleep assessed by general questionnaires and 3-day sleep logs. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 276, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griefahn, B.; Marks, A.; Robens, S. Noise emitted from road, rail and air traffic and their effects on sleep. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 295, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, J.; Lim, C.; Kim, K.; Lee, S. The effects of long-term exposure to railway and road traffic noise on subjective sleep disturbance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristovska, G.; Lekaviciute, J. Environmental noise and sleep disturbance: Research in Central, Eastern and South-Eastern Europe and Newly Independent States. Noise Health 2013, 15, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regecová, V.; Kellerová, E. Effects of urban noise pollution on blood pressure and heart rate in preschool children. J. Hypertens. 1995, 13, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babisch, W.; Fromme, H.; Beyer, A.; Ising, H. Elevated catecholamine levels in urine in traffic noise exposed subjects. Proc. Inter. Noise 96 1996, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Babisch, W. The NaRoMI-Study: Executive summary—Traffic noise. In Chronic Noise as a Risk Factor for Myocardial Infarction, The NaRoMI Study; Umweltbundesamt: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. I-1–I-59. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Nordsborg, R.B.; Jensen, S.S.; Lillelund, K.G.; Beelen, R.; Schmidt, E.B.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Road traffic noise and incident myocardial infarction: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basner, M.; Babisch, W.; Davis, A.; Brink, M.; Clark, C.; Janssen, S.; Stansfeld, S. Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014, 383, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.Y.T.; Yano, T.; Sato, T.; Nishimura, T. Characteristics of road traffic noise in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, K.; Chowdary, V. Influence of honking on the road traffic noise generated at urban rotaries for heterogeneous traffic. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2020, 24, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, R.; Sharma, A.; Chakrabarti, T.; Gupta, R. Assessment of honking impact on traffic noise in urban traffic environment of Nagpur, India. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, P.; Dehrashid, S.A.; Hashemi, M.; Shalkouhi, P.J. Traffic noise prediction and the influence of vehicle horn noise. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2013, 32, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. Road Traffic Act; Japanese Law Translation; Ministry of Justice: Tokyo, Japan, 2021; Chapter 3.
- Economic and Social Council of United Nations. Proposal for Amendments to Regulation No. 28; ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRB/2014/4; The International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA): Paris, France, 2014.
- Hustim, M.; Fujimoto, K. Road traffic noise reduction using TDM-TMS strategies in Makassar city, Indonesia. J. Environ. Eng. (Trans. AIJ) 2013, 78, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shinar, D. Aggressive driving: The contribution of the drivers and the situation. Transp. Res. Part. F 1998, 1, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajunen, T.; Parker, D.; Summala, H. The Manchester Driver Behaviour Questionnaire: A cross-cultural study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2004, 36, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S. Social psychological approach of travel behavior. In Modeling of Travel Behavior; Kitamura, R., Morikawa, T., Eds.; Gihodo Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 2002. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Takada, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kim, K.H.; Shin, J.H.; Iwamiya, S. Driver’s vehicle horn and its effects on other drivers and pedestrians: A case study in South Korea. Mech. Eng. J. 2017, 4, 16–00433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Fukuda, Y.; Iwamiya, S. Questionnaire survey on vehicle horn use and its effects on drivers and pedestrians. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Inada, T.; Takada, M.; Oeda, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Kim, K.H.; Iwamiya, S. Survey on vehicle horn use at intersections in Taipei City, Taiwan. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, InterNoise 18, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 3170–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, M.; Tsunekawa, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Inada, T.; Oeda, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Kim, K.H.; Iwamiya, S.I. Analysis of vehicle horn use and factors at intersections in an urban area of Taiwan. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Acoustics: Integrating 4th EAA Euroregio, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019; pp. 7188–7195. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii, T.; Shimoi, Y.; Kitamura, R. Capacity analysis of mixed traffic flow with motorcycles. Int. Assoc. Traffic Saf. Sci. 2004, 29, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Transportation and Communications. Road Traffic Safety Regulations; Laws and Regulations Database of the Republic of China (Taiwan): Taipei, Taiwan, 2021; Chapter 4. (In Chinese)
- Kalaiselvi, R.; Ramachandraiah, A. Honking noise corrections for traffic noise prediction models in heterogeneous traffic conditions like India. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Jerrett, M.; Ross, Z.; Coogan, P.F.; Seto, E.Y.W. Assessment of traffic-related noise in three cities in the United States. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, D.; Okada, A.; Matsumori, T.; Aihara, K.; Yoshida, H. Traffic signal optimization on a square lattice with quantum annealing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lee, M.; Jun, C.; Han, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. Traffic signal optimization for multiple intersections based on reinforcement learning. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).