Abstract
Comparing data objects is at the heart of machine learning. For continuous data, object dissimilarity is usually taken to be object distance; however, for categorical data, there is no universal agreement, for categories can be ordered in several different ways. Most existing category dissimilarity measures characterize the distance among the values an attribute may take using precisely the number of different values the attribute takes (the attribute space) and the frequency at which they occur. These kinds of measures overlook attribute interdependence, which may provide valuable information when capturing per-attribute object dissimilarity. In this paper, we introduce a novel object dissimilarity measure that we call Learning-Based Dissimilarity, for comparing categorical data. Our measure characterizes the distance between two categorical values of a given attribute in terms of how likely it is that such values are confused or not when all the dataset objects with the remaining attributes are used to predict them. To that end, we provide an algorithm that, given a target attribute, first learns a classification model in order to compute a confusion matrix for the attribute. Then, our method transforms the confusion matrix into a per-attribute dissimilarity measure. We have successfully tested our measure against 55 datasets gathered from the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Machine Learning Repository. Our results show that it surpasses, in terms of various performance indicators for data clustering, the most prominent distance relations put forward in the literature.
1. Introduction
Comparing data objects is at the heart of machine learning, for most data mining and knowledge discovery techniques rely on a way to measure the similarity of objects. For continuous data, object similarity is usually fixed to some object distance relation (e.g., Minkowski [1]); however, for categorical data, there is not a universally accepted relation. This is because the values that a categorical attribute may take can be ordered in several different ways.
Most of the existing similarity measures characterize the distance among the values an attribute may take using precisely the number of different values the attribute takes (the attribute space) and the frequency at which they occur. This approach yields three main kinds of distance relation. One is based on probability, which includes similarity relations that are information-theoretic centered, for example [2,3,4,5,6]; the next is based on the attribute space, for example [7,8,9]; and the other amounts to a specialization of a standard measure, such as Euclidean or Manhattan distance. All these measures overlook attribute interdependence, which, as noted in [10], may provide valuable information when capturing per-attribute object similarity.
In this paper, we introduce a novel object dissimilarity measure that we call Learning-Based Dissimilarity, for comparing categorical data. (In passing, we note that per-attribute value dissimilarity is a complementary relation of similarity. In our discussion, we will switch freely between these two notions, according to the context.) This measure characterizes the dissimilarity between two categorical values of a given attribute in terms of a proportion as to how likely such values are confused or not when the remaining attributes are used to predict them. To that end, we provide an algorithm that, given a target attribute, first learns a classification model in order to compute a confusion matrix for the attribute. Then, our method transforms the confusion matrix into a per-attribute dissimilarity measure. Iterating on each attribute for a given dataset, our method builds the complete dissimilarity measure for all categorical data in the set.
We have extensively experimented with Learning-Based Dissimilarity in the context of clustering. We have successfully tested our measure against 55 datasets gathered from the UCI Machine Learning Repository [11]. Our results show that it surpasses, in terms of various performance indicators for data clustering, the most prominent distance relations put forward in the literature, namely: Goodall, Gambaryan, Eskin, Manhattan, Euclidean, Lin, occurrence frequency, and inverse occurrence frequency.
Our results suggest that one should attempt to exploit any correlation among object attributes to characterize object dissimilarity in the context of categorical data. This opens two new lines of investigation, namely: the discovery of new inter-attribute comparison measures and the discovery of novel similarity measures that combine both inter- and intra-attribute comparison measures.
In summary, our contributions are as follows.
- We identify a means of defining a relation for categorical data (dis)similarity, which captures a meaningful characterization of value distance in terms of inter-attribute value dependency.
- We provide an algorithm that, given a target attribute, computes a per-attribute similarity relation, using a prediction relation provided by the values of other object attributes in a given entire dataset.
- We open further lines of investigation to study similarity relations that may simultaneously exploit inter-attribute value dependency and intra-attribute value space.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 gives an overview of the most popular similarity measures for categorical data and also introduces symbols and notation. Section 3 is the core of our paper, as it introduces Learning-Based Dissimilarity and provides an example application of it. Then, Section 4 describes our experimental framework and Section 5 outlines our main findings, including an analysis of them. Finally, Section 6 gives an overview of the conclusions drawn from this research and provides directions for further research.
2. Related Work
The aim of this section is twofold. First, it provides a general discussion of the rationale behind both existing similarity relations and a new interpretation where the distance among two values that a categorical piece of data may take can be modeled taking into account the entire context of a dataset, as opposed to only the composition of the image of the data. Second, this section gives a definition of the similarity measures that we have used for comparison purposes throughout our study.
2.1. An Account for Per-Attribute Similarity Measures
Let be an arbitrary categorical attribute that may take different values. Then, existing similarity relations are defined so as to exploit three key observations. First, two distinct attribute values model two distinctive aspects of the real world and should be considered dissimilar events. Second, the larger , the number of distinct values may take, the less separable the values are, and so they should be deemed to be more similar. Third, the more similar the frequency at which two attribute values occur, the more dissimilar they become. These observations can be used to yield a well-defined similarity relation; however, the output relation may be anything but intuitive. This is because these relations characterize attribute value similarity in terms of the structure of that attribute space. However, it is difficult to argue that such structure captures a similarity meaning among the distinct values that the attribute takes. Further, the structure of the attribute space is something that can be manipulated externally; that is, we may induce a different similarity relation just by changing the construction of the dataset, making the entire process error-prone.
By way of comparison, our approach to per-attribute similarity considers that every element in a dataset corresponds to a reading of a system or an aspect of the world. Each reading ought to be consistent, even though we do not neglect or overlook the possibility of a noisy observation. Typically, an object (that is, an observation about the world) is given in terms of the readings of several sensors, inputs, or other attributes, but together, across the dataset, the attribute values are in a way coherent; one would not expect to watch a Jaguar jumping over a hill in Juneau. If one is able to accurately predict two distinct attribute values from the other attributes’ values in a number of objects, then we deem the two target attribute values to be highly separable and thus highly dissimilar.
There are, of course, several wrinkles to reify our similarity relation. One is to identify a prediction function that suitably captures any form of inter-attribute value dependability. There are several options worth exploring, although in this paper we focus only on implementing prediction through the use of a classification ensemble. Another issue is how to map a similarity value out from a prediction function, for it has to be done in a way that correctly expresses subtle differences between attribute values. In our understanding, if two attribute values cannot be crisply separated, then we take them to be similar, for one might be taken to be a noisy capture of a reading of the other.
However, the benefit of following our approach is that a suitable prediction function gracefully degrades, yielding properties seen in an intra-attribute space similarity relation. For example, the larger the number of distinct values may take, the more difficult value prediction becomes, and so attribute values will be considered to be more similar to one another. In addition, in the presence of an imbalance as to the frequency at which an attribute value occurs, the more likely that attribute value will be considered similar to other attribute values of more frequent occurrence.
We believe that our paper may open several lines of investigation. One, for example, would attempt to identify better abstractions of counts of value predictions. Others would consider interesting combinations of these two approaches. We can see our approach is philosophically rather distinct in nature from previous ones.
2.2. Per-Attribute Similarity Measures for Categorical Data
According to Boriah et al. [9], there are two notions of similarity: one is neighborhood-based, and so it is used to define the neighborhood of an object; the other is instance oriented, and so it is used to compute the similarity between two object instances. As in [9], our study considers the latter notion only, for it can be thought of as being a key part to define neighborhood-based similarity.
We now introduce some notation in order to overview the types of similarity relations that will be considered in our study. Let be a finite, categorical dataset, containing n objects, . The properties of each object in are described in terms of a fixed set of attributes, . Each attribute, , is defined over an intended domain , examples of which include and . An instance, , is given by a tuple .
Take any two objects, . Then, the similarity of the object pair and , in symbols , is defined as the pairwise similarity between the two values of both objects’ attributes [12]:
where stands for the weight assigned to attribute , and where is the per-attribute similarity between , for some attribute , defined over .
As in [12], our work considers . Now, evaluating essentially amounts to building a symmetric matrix. Let , then:
where, in addition, , for all and .
We are now ready to define the standard taxonomy (see, for example, [9,12]) for per-attribute similarity measures, which is then easily extended in the usual way to object similarity measures, see Equation (1). Based on the symmetric matrix defining , Equation (2), the similarity measures studied in this paper can be classified as follows:
- Type DEO: those that fill the diagonal entries only (DEO); that is, similarity measures that assign a non-zero value for the similarities where a value match occurs, and a zero otherwise:
- Type OEO: those that fill the off-diagonal entries only (OEO); that is, similarity measures that assign a value of one for the similarities in which a value match occurs, and a value otherwise:
- Type DOE: those that fill both diagonal and off-diagonal entries (DOE); that is, similarity measures that assign values , with , when a value match or mismatch occurs:
2.3. Per-Attribute Similarity Measures Used in Our Study
In this study, for comparison purposes, we shall consider eight per-attribute similarity measures: Eskin, Lin, occurrence frequency (OF), inverse occurrence frequency (IOF), Goodall, Gambaryan, Euclidean, and Manhattan. The rationale behind our choosing is severalfold. First, we consider at least one relation for each different type DEO, OEO, and DOE: Goodall, Gambaryan, Manhattan, and Euclidean are of type DEO; Eskin, OF, and IOF are of type OEO; and Lin is of type DOE. Second, these measures are the de facto standard for comparison purposes (see, for example, [9,12]). Third, they have been extensively studied.
To provide formal definitions of these similarity measures, we first introduce more notation:
- : the amount of distinct values the kth attribute takes in the dataset ;
- , frequency in which attribute takes the value x in the dataset . Note that, in particular, for any ;
- , frequency of value x in the dataset ;
- , probability that attribute takes the value x in the dataset , given by
- , estimated probability that attribute takes the value x in the dataset , given by
We are now ready to define the similarity measures under consideration.
2.3.1. Goodall Similarity
The Goodall similarity [2], of type DEO, is defined as follows. Let be a partial order over , the domain of attribute , given as follows: if and only if , under the proviso of . We extend to in the expected manner. Then, we define the cumulative estimated probability out of the partially ordered set of the domain of attribute , and , up to a value , as follows:
Then, Goodall is given by
Clearly, Goodall gives a high similarity measure to objects if both the pairwise values of and are equal, and such values, with respect to the corresponding attribute, do not frequently occur in .
2.3.2. Gambaryan Similarity
The Gambaryan similarity measure [3], of type DEO, is defined pretty much the same as the entropy of a value x, . Put in terms of an attribute , we define both and . Then, Gambaryan is given as follows:
Unlike Goodall, Gambaryan gives a high similarity measure to objects , if both the values of and are pairwise equal, and such values frequently occur in , with respect to the corresponding attribute.
2.3.3. Manhattan Distance
In our study, we also consider similarity measures that are standard extensions to their original definition for vectors of numbers. For example, the per-attribute Manhattan similarity measure is defined as follows:
Manhattan is of type DEO and yields a number in ; the maximum value is obtained when the two objects under comparison are all attribute-wise equal.
2.3.4. Euclidean Distance
The Euclidean similarity measure, of type DEO, is defined as the square root of the Manhattan similarity measure. So, instead of applying Equation (1), we now have
where, as before
2.3.5. Eskin Similarity
The Eskin similarity measure [8], of type OEO, is given by
It follows that Eskin deems the occurrence of different values for an attribute to be non-interesting, whenever that attribute takes a large amount of distinct values, ; this is because if . In the opposite case, when the attribute takes a few values, the mismatch becomes paramount; note that for the minimum value that may take (namely 2), Eskin will assign to a mismatch.
2.3.6. Occurrence Frequency (OF) Similarity
OF, a similarity measure of type OEO, is defined as follows [9]:
Therefore, OF gives a high per-attribute similarity measure to a mismatch, if such values occur frequently often in . The range of , whenever is . The measure yields the minimum value when and occur only once in ; that is, and . By contrast, OF yields the maximum one when and are the only values for in X and they occur with the same frequency; that is, and .
2.3.7. Inverse Occurrence Frequency (IOF) Similarity
The IOF similarity measure [7] is also of type OEO; it is given by
As the name suggests, IOF is defined in terms of inverse frequency. However, as it stands, it exploits the fact that the frequency in which attribute takes the value x, , is approximately equal to that in which x occurs in dataset , . This is, in turn, approximately equal to the frequency in which x appears, no matter how many times, in every attribute , the so-called inverse occurrence frequency of x in .
From the definition it follows that, unlike OF, IOF gives a low per-attribute similarity measure to a mismatch, see , whenever and occur frequently often in .
2.3.8. Lin Similarity
The Lin similarity measure [4] is of type DOE and is based on information theory. It relies on the similarity theorem, which states that the similarity between x and y is given by the ratio between the information one needs to describe the commonality of x and y, and the information needed to completely describe x and y; in symbols:
For our case, when defining the per-attribute similarity measure for , we drop off the denominator, for it is the same regardless of or . Finally, if we define
we then arrive at the standard formulation of the Lin similarity:
According to [9], Lin gives a higher per-attribute similarity measure to matches on frequent values, but lower ones to mismatches on infrequent values.
We now introduce our notion of similarity.
3. Learning-Based Dissimilarity
This section is the core of this paper. We introduce a novel dissimilarity measure that we call Learning-Based Dissimilarity. The rationale behind our measure is that two object attribute values should be rendered dissimilar whenever one cannot be taken to be the other. To verify when two attribute values are not distinguishable, we exploit the fact that attributes might depend on one another. In particular, to compute Learning-Based Dissimilarity, we make a classifier to infer an attribute value using the values of the others. Two attribute values will be taken to be more similar whenever the associated classifier is more likely to misleadingly classify one of these values to be the other. Note that this implies that Learning-Based Dissimilarity is anti-symmetric. This, we believe, is crucial as it captures that many wolves can pass as a dog; this statement, however, does not reverse in general (consider, for example, a chihuahua exemplar).
3.1. Per-Attribute Learning-Based Dissimilarity
Roughly, take and consider the kth attribute. Now, take to be a dataset, where each element belongs to one of either of possible classes, one for each . Then, train a classifier so as to infer the class from , which is as , except that for every , we have , with , and . Then, two elements, and , are learning-based similar (written in symbols ) if and only if:
Therefore, it follows that Learning-Based Similarity is of type OEO. As expected, the Learning-Based Dissimilarity of and , in symbols , is given by
We now proceed to provide the inner procedural workings of our relation.
3.2. Learning-Based Dissimilarity, the Algorithm
For computing per-attribute Learning-Based (Dis)similarity, we follow a two-step approach. Given and a target attribute, , in the first step, our algorithm extracts and then trains a classifier for so as to compute a confusion matrix for it. Then, in the second step, our algorithm transforms the confusion matrix into a (dis)similarity measure. This procedure is applied repeatedly to , according to m, the number of attributes of each object in .
Figure 1 depicts a flow diagram of Learning-Based Dissimilarity. It is worth noting that, to avoid any kind of bias, in the first step (cf. inner loop), instead of using a single classifier, we rather use an ensemble of different classifiers. Then, for the attribute under consideration, we set the confusion matrix to be the one output by the classifier with the highest area under the receiver operational characteristic curve (AUC, for short). The rationale behind using a classification ensemble is as follows. Supervised classifiers make assumptions about the structure of data for a ‘correct’ generalization. We address this issue following [13], using an ensemble of distinct supervised classifiers and then applying a max combination rule. In our experimentation, we use Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, Bayesian Networks, Bagging, Simple Logistic, and KStar, as implemented in the Weka data mining tool [14].
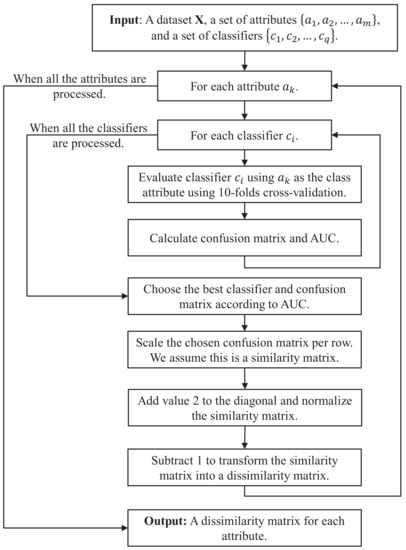
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for the procedure of computing Learning-Based Dissimilarity.
Next, to transform the confusion matrix into a per-attribute (dis)similarity measure, we proceed as follows. Take an attribute, , with different values. Then:
- Normalize each row of the confusion matrix, i.e.,
- Set the element of the diagonal to be equal to one ; and
- Normalize the rest of the row elements again as follows:
With this, we obtain a similarity matrix for ; to transform it into a dissimilarity matrix, we simply let . We apply this procedure, repeatedly, for each attribute in .
As expected, to compute Learning-Based Similarity, we apply Equation (1), accordingly:
where, for now, we have set , for . In the remainder of this section, we show an example application of Learning-Based Similarity.
3.3. Learning-Based Dissimilarity, a Working Example
Consider Balloons, one of the datasets available at the UCI Machine Learning Repository [11]. A snapshot of this dataset appears in Table 1. In this case, ; then, consider that we are to compute the per-attribute Learning-Based Similarity measure of Color.

Table 1.
A snapshot of the Balloons Dataset. We omitted the class attribute since it is not used for clustering.
First, we train our ensemble of classifiers to learn how to predict Color out of objects from Balloons, containing Size, Age and Act only. Having done so, we compute the AUC and then apply the max rule on AUC in order to identify the classifier that better separates Color. In this case, SimpleLogistic happens to output the highest AUC (0.75); the corresponding confusion matrix is shown in Table 2. This completes the first step of our algorithm (cf. Figure 1).

Table 2.
Confusion matrix associated with the classifier that rendered the highest area under the receiver operational characteristic curve (AUC).
To transform the output confusion matrix into a similarity measure, we execute the three transformations of the second step of our algorithm, as shown in Table 3. This completes the second step, and the sub-table (c) of Table 3 is the per-attribute Learning-Based Similarity of Color. This process is applied on the remaining attributes, namely: Size, Age and Act.

Table 3.
An example application of the second step of per-attribute learning-based similarity.
Now, consider objects and , given by:
Then, assuming , clearly:
This completes our description of Learning-Based Similarity. In what follows, we describe an experimental analysis of this similarity measure.
4. Experimental Framework
We now describe our experimental framework, as well as the results we have obtained throughout our investigation. Since, in our study, we have chosen to use clustering as the data mining task for evaluating Learning-Based Dissimilarity, we have set KMeans++ [15] to be our basis clustering algorithm. The rationale behind this selection decision is that KMeans++ is guaranteed to find a solution that is competitive to the optimal standard KMeans solution, which is the most popular clustering algorithm.
We have modified KMeans++ so as to make it parametric of a similarity (dissimilarity) relation (the source code for our proposal is available at https://github.com/edjacob25/DissimilarityMeasures, accessed on 13 April 2021). We considered nine different relations, including learning-based, yielding nine algorithm variants. We made each KMeans++ variant run in 55 datasets, fixing k, the number of clusters to be formed, according to that of the classes provided in the corresponding dataset (the source code for batch processing is available at https://github.com/edjacob25/DissimilarityAnalysis, accessed on 13 April 2021). To compare the behavior of each variant, and hence of the corresponding similarity relation, we selected the external quality indexes F-measure [16] and Adjusted Rand Index [17] as the performance measures (the source code for computing the performance measures is available at https://github.com/edjacob25/MeasuresComparator, accessed on 13 April 2021). We confirmed our results, to be discussed in the next section, using a statistical hypothesis test.
4.1. Cluster Analysis and Datasets
For comparatively evaluating Learning-Based Dissimilarity, we chose cluster analysis, although other data mining tasks, such as anomaly detection, could have been chosen. Since the behavior of a similarity relation affects the output of, but does not depend on, the cluster analysis technique, we picked KMeans++ [15]. The rationale behind this decision is that KMeans++ is, perhaps, the most popular clustering algorithm, for it has been thoroughly studied [18], and has found a number of applications. The key problem with KMeans++ is that it needs to be given k, the target number of problems to be found. However, in our case, this is not a problem, since, as shall be described later, we have turned a classification problem into a clustering one, and so each dataset contains both objects and their intended class, and so is taken as the ground truth.
We used 55 datasets collected from the UCI Machine Learning Repository [11]. Our datasets were split into two groups. The first group contains 26 datasets, where each object’s properties were originally described using only categorical attributes. The second group, however, contains 29 datasets that were artificially made to satisfy the above property; put differently, every object in a dataset of this kind is as it was originally asserted, except that we have removed from it any attribute that is not categorical. The rationale behind this pre-processing decision is to get away from whatever possible negative impact there may be for these kinds of variable in our results. Table 4 lists the datasets used in our investigation, together with key properties thereof.

Table 4.
Datasets, as well as some characteristics thereof, used in our experimentation. They were all taken from the UCI Machine Learning Repository [11]. Columns #Ob and #Ft, respectively, stand for number of objects and number of categorical features.
4.2. Evaluation Protocol
Our evaluation protocol was as follows. First, remove the class label from every object in the given dataset, D, and set k, in KMeans++, to the original number of classes in D. Then, execute nine KMeans++ variants (one for each dissimilarity measure) on the 55 datasets. Next, for each executing output, compute the F-Measure and Adjusted Rand Index comparing the output clusters against the classes annotated in the original dataset. Finally, form a rank per dataset, out of these performance results, and compute the average output performance per algorithm.
As is known, the F-measure [19] is a combination of precision and recall, ranging from 0 (no matching pair of sets of clusters, in our case) to 1 (two identical sets of clusters). Hence, for a given dataset, the closer to 1 the F-measure associated with a KMeans++ variant run, the higher that variant’s rank. When calculating an F-Measure, we conducted a pairwise comparison between the original dataset and an output clustering. We are not required to have groups in the same order to obtain an accurate result and get away from problems in relation to cluster size.
The Adjusted Rand Index [17] is a measure used to compute the similarity between two given partitions (clusterings) for a set of elements. It is much stricter than F-measure, as it requires the two clusterings to be practically equal for a high measure (one).
To assess whether the population’s mean ranks of two given matched variants’ performance outputs had a significant difference, we used a statistical test, namely Wilcoxon, as described in [20], with a significance level of . Following this proposed evaluation protocol, the best possible outcome for a given algorithm is to have an average rank of 1, which would indicate that the algorithm indisputably obtained first place in all datasets. If, in addition to this, the result for that algorithm has a p-value less than 0.05, then it would indicate that it is significantly better than the rest.
In what follows, we overview our main findings and discuss their relative significance.
5. Findings and Discussion
In our study, we used KMeans++ [15], as implemented in the Weka toolbox for machine learning and data science [21]. We slightly modified it so that, apart from k (the target number of clusters to form), it is given the dissimilarity relation as an input parameter. For each dissimilarity measure, we executed KMeans++ in all datasets, as explained previously, and computed the F-measure and Adjusted Rand Index. In passing, we note that, on any application of KMeans++, we used inputting; that is, for every dataset, any time we found that a value was missing for an object attribute, we set that value to be the mode of that object attribute.
Figure 2 provides, via a box plot, a graphical description for each group of F-measures, one for every dissimilarity relation under study. In general, the greater the median of a group of F-measures, the better the associated dissimilarity relation; a similar remark applies when the size of the box is short and when the box appears closer to the right-hand side of the figure. Note how, in particular, Learning-Based Dissimilarity appears right at the top of the figure and most to the right. While this looks like a good first impression for our proposed method, we must stand on a sound, statistical method if we are to draw strong conclusions.
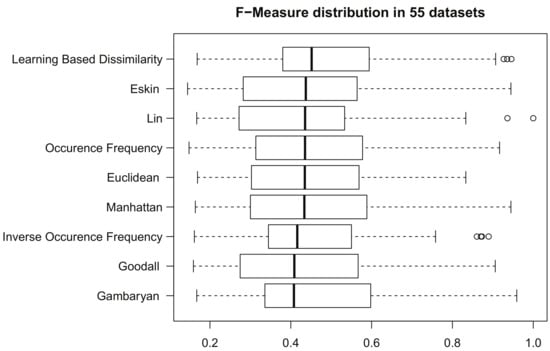
Figure 2.
Box and whisker diagrams of all groups of F-measures [16]. Each F-measure group is associated with a dissimilarity measure and gathers the output of KMeans++ [15] having made a run on every dataset selected for our experimentation. Box and whisker diagrams are shown following a descending ordering, considering the associated F-measure median.
We used the Wilcoxon signed-rank test [22] to conduct a one-to-one comparison of Learning-Based Dissimilarity against all the other dissimilarity measures under investigation. Table 5 summarizes our comparison results: on each row, we display a dissimilarity measure, the median, and the standard deviation of the group of F-measures output by KMeans++ for it, and the p-value output by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, rejecting the null hypothesis. From this, we conclude that the results of K-Means++ are significantly better when using Learning-Based Dissimilarity according to F-measure.

Table 5.
Statistical results, according to F-measure [16], for KMeans++ using all the dissimilarity measures, considering all the tested datasets. The last column corresponds to the p-value obtained when comparing Learning-Based Dissimilarity against the other dissimilarity measures using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test [22]. The results are sorted from top to bottom in descending order of the associated F-measure group median.
In an attempt to show that the above result holds independently of what performance measure is used, we ran a similar experiment but this time using the Adjusted Rand Index [17]. As in Figure 2, Figure 3 provides a box plot for each group of Adjusted Rand Index measures, one for every dissimilarity relation under study. Boxes are to be compared similarly as before. Again, note how, in particular, Learning-Based Dissimilarity appears right at the top of the figure and most to the right. In addition, we proceed similarly relying on the statistical method so as to draw strong conclusions.
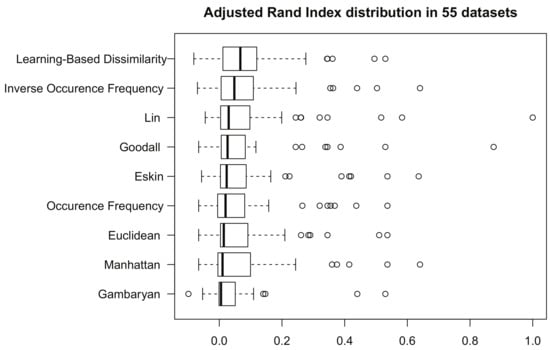
Figure 3.
Box and whisker diagram according to Adjusted Rand Index [17], for KMeans++ [15] using all the dissimilarity measures, considering all the tested datasets. The results are sorted from top to bottom in descending order of the median.
Table 6 summarizes our comparison results: on each row, we display a dissimilarity measure, the median, and the standard deviation of the group of Adjusted Rand Index measures output by KMeans++ for it, and the p-value output by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. These results indicate no evidence supporting our proposal’s statistically significant difference compared to inverse occurrence frequency and Lin, but our proposal exhibits a higher median. With this, we provide further evidence that Learning-Based Dissimilarity is a better relation for clustering categorical values using KMeans++.

Table 6.
Statistical results, according to Adjusted Rand Index [17], for KMeans++ [15] using all the dissimilarity measures, considering all the tested datasets. The last column corresponds to the p-value obtained when comparing our proposal (Learning-Based Dissimilarity) with the other dissimilarity measures using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test [22]. The results are sorted from top to bottom in descending order of the median.
Learning-based dissimilarity, as it stands, is time-consuming, for we are required to learn the dissimilarities for the categorical values. Recall that this process involves performing cross-validation with several supervised classifiers, and this is a time-consuming task. Figure 4 shows that our proposal is, on average, between two and one orders of magnitude slower than the rest of the dissimilarity measures. From these results, we suggest performing undersampling before computing Learning-Based Dissimilarity on large datasets.
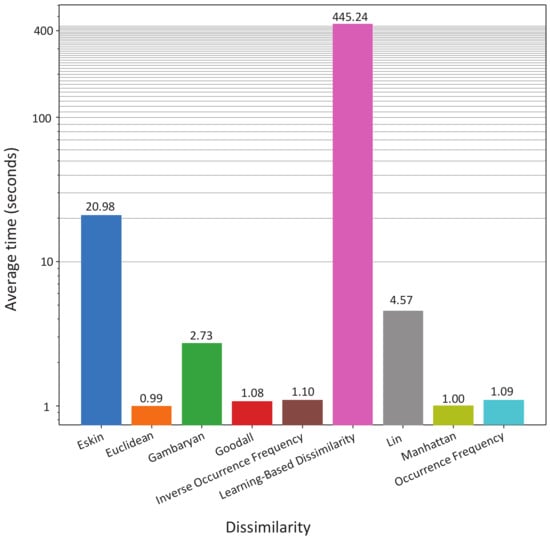
Figure 4.
Average time of clustering with KMeans++ [15] using all the dissimilarity measures, considering all the tested datasets. The vertical axis is on a logarithmic scale.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this paper, we have seen how to characterize the similarity of the values of a categorical attribute through the correlation each of these attribute categories maintains with the other attributes of all the objects of a dataset. Further, we have seen that this attribute correlation can be learnt via supervised classification. We have shown that by exploiting such attribute correlation one can induce a similarity relation, which helps distinguish better what cluster one object should be associated with. We believe that our similarity relation can help similarly in other machine learning tasks, such as classification, knowledge discovery, etc.
We have shown that Learning-Based Dissimilarity outperforms, in terms of various performance indicators for data clustering, relevant distance relations that are popular in the literature. This result can be explained by the fact that existing similarity relations compute the similarity between attribute values in terms of the structure of the space of such target attributes. However, this sort of syntactic notion of similarity may not be meaningful and it is open to external manipulation, for one can easily change the composition of a dataset by simply changing some of its constituents.
We have turned the computation of inter-attribute value dependency into a classification task, where one makes use of the information provided by other attributes to predict the values of a target attribute. However, there are other ways of reifying value prediction. In addition, as mentioned previously, our approach is at least one order of magnitude more computationally expensive than standard approaches for computing per-attribute dissimilarity, and one should strive towards achieving more efficient means.
We believe that this research opens up further avenues of investigation that are worth exploring. First, one might find other ways of capturing and using attribute dependency (for example, through an attribute selection mechanism). Second, one might find new and more precise means of combining the use of attribute dependency and the underlying structure of the space of a target attribute.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.J.R.R., M.A.M.-P. and M.S.L.-C.; methodology, M.A.M.-P. and M.S.L.-C.; software, E.J.R.R.; validation, E.J.R.R., M.A.M.-P., M.S.L.-C. and R.M.; formal analysis, E.J.R.R., M.A.M.-P., M.S.L.-C. and R.M.; investigation, E.J.R.R., M.A.M.-P., M.S.L.-C.; resources, E.J.R.R.; data curation, E.J.R.R. and M.A.M.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M. and M.A.M.-P.; writing—review and editing, M.A.M.-P. and M.S.L.-C.; visualization, E.J.R.R. and M.A.M.-P.; supervision, M.A.M.-P., M.S.L.-C. and R.M.; funding acquisition, E.J.R.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly supported by the National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study appear in http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml accessed on 1 April 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DEO | Diagonal entries only |
| OEO | Off-diagonal entries only |
| DOE | Diagonal and off-diagonal entries |
| OF | Occurrence frequency |
| IOF | Inverse occurrence frequency |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operational characteristic curve |
References
- Merigó, J.M.; Casanovas, M. A New Minkowski Distance Based on Induced Aggregation 342 Operators. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2011, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodall, D.W. A new similarity index based on probability. Biometrics 1966, 22, 882–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, P. A mathematical model of taxonomy. Izvest. Akad. Nauk Armen. SSR 1964, 17, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D. An Information-Theoretic Definition of Similarity. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, Madison, WI, USA, 24–27 July 1998; pp. 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Cheung, Y.; Liu, J. A New Distance Metric for Unsupervised Learning of Categorical Data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 27, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheung, Y.; Tan, K.C. A Unified Entropy-Based Distance Metric for Ordinal-and-Nominal-Attribute Data Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, K.W.; Gale, W.A. Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): A Measure of Deviations from Poisson. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Very Large Corpora, VLC@ACL 1995, Cambridge, MA, USA, 30 June 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Eskin, E.; Arnold, A.; Prerau, M.J.; Portnoy, L.; Stolfo, S.J. A Geometric Framework for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection. In Applications of Data Mining in Computer Security; Advances in Information Security; Barbará, D., Jajodia, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriah, S.; Chandola, V.; Kumar, V. Similarity Measures for Categorical Data: A Comparative Evaluation. In Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, SDM, Atlanta, GA, USA, 24–26 April 2008; pp. 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheung, Y. An Ordinal Data Clustering Algorithm with Automated Distance Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 6869–6876. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, A.; Asuncion, A. UCI Machine Learning Repository: School of Information and Computer Science; University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2010; Volume 213, Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Dos Santos, T.R.L.; Zárate, L.E. Categorical data clustering: What similarity measure to recommend? Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, J.; Medina-Pérez, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.E.; Monroy, R.; Terashima-Marín, H. Cluster validation using an ensemble of supervised classifiers. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 145, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Frank, E.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA data mining software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2009, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. k-means++: The Advantages of Careful Seeding. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, LA, USA, 7–9 January 2007; pp. 1027–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, D.; Christen, P. A note on using the F-measure for evaluating record linkage algorithms. Stat. Comput. 2018, 28, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, L.; Arabie, P. Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 1985, 2, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K. Data Clustering: 50 Years Beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, E.; Gonzalo, J.; Artiles, J.; Verdejo, F. A comparison of extrinsic clustering evaluation metrics based on formal constraints. Inf. Retr. 2009, 12, 461–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demšar, J. Statistical Comparisons of Classifiers over Multiple Data Sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Derrac, J.; García, S.; Molina, D.; Herrera, F. A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2011, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).