Abstract
During the basketball training for beginner children, sensors are needed to count the number of times the basketball hits the target area in a certain period of time to evaluate the training effect. This study proposes a self-powered basketball training sensor, based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. The designed sensor with a rectangular floor shape will output a pulse signal with the same frequency as the basketball impact to achieve the measurement function through the mutual contact of the internal copper (Cu) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Test results show that the working frequency of the sensor is 0 to 5 Hz, the working environment temperature should be less than 75 °C, the working environment humidity should be less than 95%, and which has high reliability. Further tests show that the maximum output voltage, current, and power of the sensor can reach about 52 V, 4 uA, and 26.5 uW with a 10 MΩ resistance in series, respectively, and the output power can light up 12 light-emitting diode (LED) lights in real-time. Compared with the traditional statistical method of manual observation, the sensor can automatically count data in a self-powered manner, and also can light up the LED lights in real-time as an indicator of whether the basketball impacts the target area, to remind beginner children in real-time.
1. Introduction
Basketball has many advantages, such as fitness, confrontation, collective, viewing, and fun [1,2], and which is also meaningful for children because it can not only strengthen the body, but also cultivate the teamwork spirit [3]. For beginner children, the basic training contents are “bounce the ball in situ” and “two-hand chest pass the ball”, which can be seen in Figure 1a. The “bounce the ball in situ” refers to that a child continuously slaps a basketball bounced from the ground with one hand in situ, and the landing point must be kept within a certain target area, so the number of balls dropped into the target area can reflect the effect of basketball training. Similarly, the “two-hand chest pass the ball” usually allows young children to pass the ball to a fixed target area on the wall, so the number of balls dropped into the target area can also reflect the effect of basketball training. However, there is no professional equipment to detect it at present, and the current statistical method that only relies on the naked eye of the coach has the disadvantages of larger error, larger workload, and inability to simultaneously observe multiple children at the same time, so there is an urgent need to develop a sensor that can automatically record the number of basketball impacts, thereby evaluating the training effect and formulating the next training plan for beginner children.
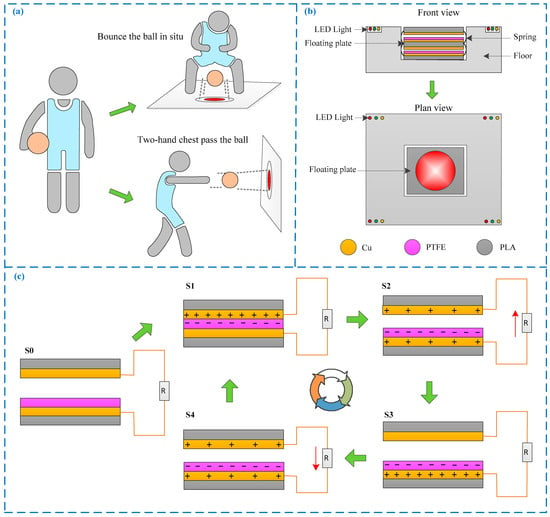
Figure 1.
Composition and working principle. (a) Schematic diagram of “bounce the ball in situ” and “two-hand chest pass the ball”; (b) schematic diagram of the sensor structure; (c) schematic diagram of the sensor working steps. PTFE, polytetrafluoroethylene.
In addition, if the sensor used for detection is powered by batteries, the frequent batteries replacement will cause the sensor to be taken out multiple times, which will undoubtedly increase labor intensity. On the other hand, if cables are used to power the sensor, cables must be laid during the construction of the basketball stadium, which will increase construction costs and have potential safety hazards. Therefore, sensors with the self-powered function will undoubtedly be more suitable for basketball training environments. For self-powered sensors, the current results on power generation methods, including piezoelectric generators, electromagnetic generators and solar nano-antennas [4], etc., can solve the power supply problem of the sensor, but the basketball training grounds for children are not exposed to sunlight because the training venues are generally indoor gymnasiums, and the costs of piezoelectric and electromagnetic power generation are relatively higher, so other self-powered methods may be more suitable for indoor basketball training conditions.
Fortunately, the triboelectric nanogenerator brings hope to solve the above-mentioned problems. The triboelectric nanogenerator with a basic principle of triboelectricity and electrostatic induction [5] was proposed in 2012 [6], and has been widely used in the fields of energy harvesting and sensors. For example, in the field of energy harvesting, the triboelectric nanogenerator can collect low-frequency and low-density weak energy, and theoretically can convert most of the physical energy into electrical energy, so it had been widely used in biological energy harvesting [7,8], rainwater energy harvesting [9,10], vibration energy harvesting [11,12,13], wave energy harvesting [14,15,16], environmental mechanical energy harvesting [17], and wind energy collection [18,19], etc. On the other hand, in the field of sensors, sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators have a self-powered function, so it had been widely used in areas where traditional power supply methods are inefficient, such as human physiological monitoring [20,21,22], vibration monitoring [23,24], wind monitoring [25,26], acceleration monitoring [27], sports monitoring [28,29,30], force or pressure monitoring [31,32,33], and speed monitoring [34,35], etc. In summary, the triboelectric nanogenerator has advantages for developing self-powered sensors, so this research proposes a self-powered sensor that can be used for beginner children basketball training based on the triboelectric nanogenerator.
This research is expected to have the following innovations. Firstly, the sensor can automatically record the slap times of the beginner children, which can reduce the error caused by the traditional statistical method of visual observation. Secondly, the sensor will have a self-powered function, so the extra power generated during the sensing process can light up the light-emitting devices, which can use lights to remind beginner children whether the target is hit. Thirdly, the sensor can normally work without an additional power supply, which means that the sensor can effectively avoid the increase in labor intensity caused by traditional power supply methods. The structure of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the composition, fabrication, and working principle of the sensor. Section 3 introduces the test situation of the sensor, including sensor measurement performance tests, sensor environmental adaptability tests, and sensor output power performance tests. Section 4 are the conclusions.
2. Composition and Working Principle
As shown in Figure 1b, the sensor is mainly composed of a floor, springs, floating plates and LED lights, etc. The floating plate with a size of 200 mm × 200 mm is installed in the floor with a size of 400 mm × 400 mm × 80 mm, and any two adjacent floating plates are supported by springs to form a vertical contact model triboelectric nanogenerator. The upper surface of the floating plate are successively pasted with 0.05 mm thick copper (Cu) and 0.03 mm thick polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the electrode layer and friction layer, respectively, while the lower surface is pasted with 0.05 mm thick Cu both as the friction layer and the electrode layer.
The fabrication of the sensor are as follows. The floor is an ordinary wooden floor purchased. According to the design requirements, the installation space of the floating plate is cut with a saw blade, and the cut part is the floating plate. Further, through holes are drilled around the floor to install LED lights, and the wires of LED lights under the floor. Then, blind holes with a size of 60 mm are drilled on the floor and the floating plate to install the springs. Finally, a floor-shaped striped paper is glued on the surface for beautification after the entire sensor is assembled.
The sensor is installed on the floor or wall when used for the basketball training of “bounce the ball in situ” and “two-hand chest pass the ball”. If the training posture of the beginner children is correct, the sensor can be impacted by a basketball, which will cause the friction layers between different floating plates to rub against each other to generate corresponding triboelectric signals, to realize the function of measurement. Meanwhile, the LED lights at the four corners of the sensor will be lit once in real-time when the sensor was impacted because the working process of the sensor is also the process of generating electricity, so the beginner children can also observe whether the LED lights are lit to judge whether their training activities are standard.
The working principle of the sensor is further explained in conjunction with Figure 1c. Assuming that the simplified initial state of the two floating plates, as shown in step S0, and there is no charge at this stage because the two floating plates are not in frictional contact. When the floating plate is impacted by a basketball, the two floating plates will contact each other and reach the stage of S1. At this stage, positive and negative charges are generated in the two friction plates because of the triboelectricity, and the Cu friction layer is positively charged while the PTFE is negatively charged because Cu is easier to lose electrons than PTFE [36]. When the basketball impact force disappears, the two floating plates will gradually separate, due to the spring force, that is, the S2 stage. During this process, the change of the induced electromotive force will cause the electrons in the upper floating plate to transfer to the lower, thereby generating a short-circuit current. Then the S3 stage is reached when the separation distance between the two floating plates reaches the maximum, and the charge transfer is completed at this state. Finally, the floating plate will be returned to the new initial stage S4 by the spring restoring force and gravity. At this stage, the reverse movement of the two plates causes the reverse transfer of charges, thereby generating a reverse short-circuit current. In summary, it can be seen that the sensor will output a voltage pulse signal or an alternating current pulse signal during a working cycle, and the signal frequency is proportional to the frequency of the basketball impacting the sensor, so the effect of beginner children basketball training can be measured and evaluated by counting the number of output pulse signals.
3. Tests
The test equipment is shown in Figure 2a. During the tests, the output signal of the sensor is sequentially connected to the data acquisition card (USB5632, ART Technology Co., LTD., Beijing, China) and the electrometer (6514, Keithley Co., LTD., Solon, OL, America), and finally connected to the computer. The computer is installed with software written by LabVIEW language, so the sensor output signal can be processed in real-time. It can be seen from Figure 2b,c that the sensor can output two obvious voltage and current pulse signals when impacted by a basketball twice in succession, and the amplitude are respectively 52 V and 4 uA, so both voltage and current output signals can be selected as the sensor detection signal. But the anti-interference ability of the voltage signal is stronger because the voltage signal amplitude is much larger than the noise signal; this research selected the voltage pulse as the detection signal of the sensor.
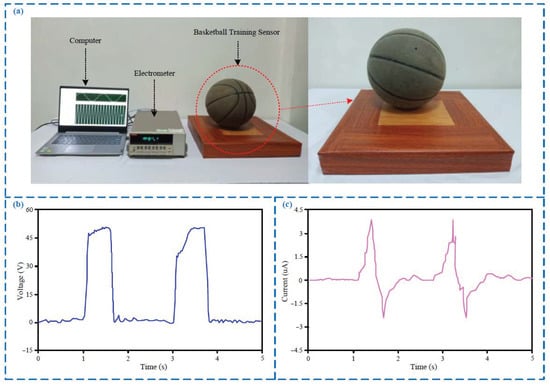
Figure 2.
The output signal of the sensor. (a) Pictures about the test devices and the sensor; (b) output voltage signal of the sensor; (c) output current signal of the sensor.
During the children’s basketball training, the more times the basketball impacts the target area per unit time, the stronger the basic basketball ability of the children—that is, the working frequency of the sensor needs to meet the actual needs. Through experiments and investigations, it can be known that the frequency of slap basketball will not exceed 5 Hz, so we tested the output signal characteristics of the sensor in the frequency range of 0 to 5 Hz, and the results are shown in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3a,b, the amount of transferred charge gradually decreases as the impact frequency increases, which results in a gradual decrease in the output voltage. The reason may be insufficient frictional contact during high-frequency impact, which further results in a reduction in the frictional contact area, and ultimately a reduction in output. But the output voltage amplitude of the sensor is still about 46 V at the working frequency of 5 Hz, and the amplitude is still much larger than the noise signal, so the sensor can work normally within the working frequency of 0 to 5 Hz. In addition, the output current gradually increases with the increase of the impact frequency, which can be seen in Figure 3c, and the reason may be that the number of impacts per unit time increases, resulting in an increase in the total amount of cumulative output current.
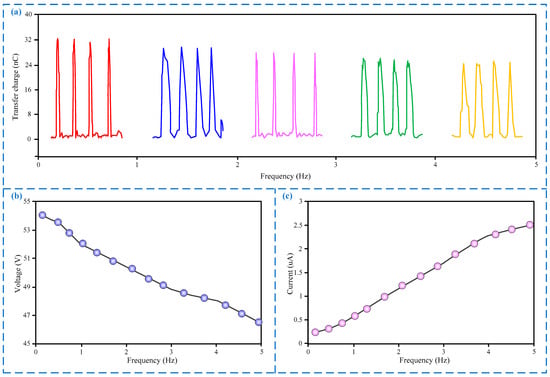
Figure 3.
The output signal characteristics of the sensor under different frequencies. (a) Transferred charge under different frequencies; (b) output voltage under different frequencies; (c) output current under different frequencies.
Further, we tested the output signal characteristics of the sensor under different working conditions, and the results are shown in Figure 4. As shown in Figure 4a, the output voltage gradually increases with the increases of the impact pressure of the basketball on the sensor, but it will remain at the maximum value of about 52 V when the impact pressure is greater than 10 N. During actual basketball training, the impact pressure is much greater than 10 N, due to the combined effect of basketball gravity and slap force, which means that the sensor can output the maximum voltage in actual application. As shown in Figure 4b, the output voltage is inversely proportional to the temperature, and it will reduce to about 50 V when the temperature reaches 75 °C, but the value of 50 V is still much larger than the noise signal, which means that the sensor can work normally within the temperature range of less than 75 °C.
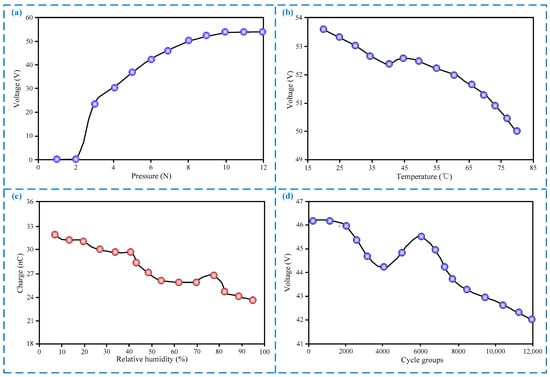
Figure 4.
Output signal characteristics of the sensor at different working conditions. (a) Output voltage under different pressures; (b) output voltage under different temperatures; (c) transfer charge under different relative humidity; (d) output voltage under different cycles.
Relative humidity will also affect the output of the sensor, so we conducted tests, and the results, shown in Figure 4c, show that the output of the sensor decreases by about 28% as the relative humidity increases to 95%. Although the output after the decrease is still greater than the noise signal—that is, the sensor can work normally in the relative humidity range of less than 95%, it is still necessary to seal as much as possible to avoid relative humidity interference. For the sealing methods, the overall sealing can be performed by adding a sealing tape on the floor frame or by covering the floor surface with a flexible sealing film. In addition, we conducted the tests, shown in Figure 4d, to test the reliability of the sensor, and the results show that the output voltage attenuation is only 4 V after the sensor is cycled for 12,000 times, which indicate that the sensor has high reliability because the output voltage after attenuation is much larger than the noise signal. However, the aging of triboelectric nanomaterial is the core issue of the large-scale promotion of the sensor, so the next research will be to look for new anti-aging materials in the hope of solving the aging problem.
The LED lights carried by the sensor will be lit when the beginner children slap the basketball to the target area, so we tested the power generation characteristics of the sensor, and the results are shown in Figure 5. It can be seen from Figure 5a,b that the output voltage gradually increases and the output current gradually decreases as the external load resistance increases, which are consistent with Ohm’s law. Then we detected the output power of the sensor under different load resistances, and the results, shown in Figure 5c, show that the output power can reach a maximum of 26.5 uW when the external load is about 10 MΩ, and it can light up 12 LED lights in real-time, as shown in Figure 5d, which can be used to indicate the basketball training posture and effect in real-time. In addition, related theoretical knowledge had confirmed that the output power of the triboelectric nanogeneratora is also related to the surface morphology of nanomaterials and the length of nanowires [37]. The rougher the surface of nanomaterials and the longer the nanowires, the larger the effective friction contact area, and therefore, the greater the output power.
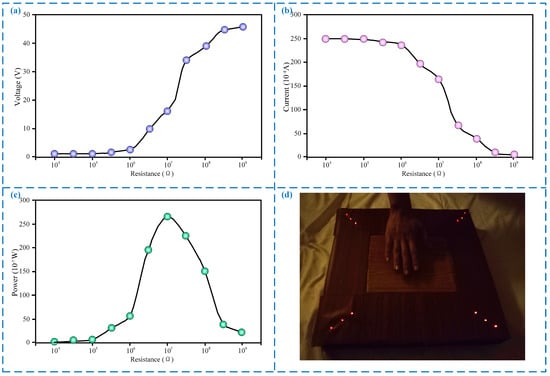
Figure 5.
Power generation characteristics of the sensor. (a) Output voltage under different load resistance; (b) output current under different load resistance; (c) output power under different load resistance; (d) a picture shows the LED lights are lighted in real-time.
In addition, the processing circuit of the sensor are also explored in this research. Figure 6a shows the traditional energy harvesting circuit for triboelectric nanogenerator [38,39], in which the output of the sensor is processed by the rectifier bridge, inductors, and capacitors to directly supply power to the load. For working conditions that require low input voltage, the output of the sensor can also be stepped down by a DC-DC module to supply power to the load, which can be seen in Figure 6b. Some scholars have also studied AC-to-DC and high-voltage dual-input converters in the energy harvesting process [40,41], and the results can not only provide protection for the high-voltage input, but also track the maximum power point, which also applies to the triboelectric nanogenerators because the low power impedance matching algorithm is applied [42,43]. Meanwhile, the nonlinear optimization electrical interfaces can be considered when modeling to harvest energy from shocks because the sensor output power is generated under the impact of the basketball [44,45], to obtain a more energy harvesting effect.
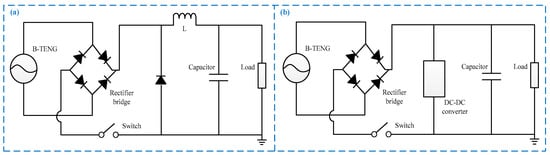
Figure 6.
The output circuit of the sensor. (a) Energy processing circuit; (b) low-voltage output energy processing circuit.
4. Conclusions and Discussions
This research proposes a self-powered basketball training sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator, and which can automatically count the number of basketball impacts in a self-powered model. Test results show that the working frequency of the sensor is 0 to 5 Hz, the working environment temperature should be less than 75 °C, the working environment humidity should be less than 95%, and which has high reliability. Further tests show that the maximum output voltage, current, and power of the sensor can reach about 52 V, 4 uA, and 26.5 uW with a 10 MΩ resistance in series, respectively, and the output power can light up 12 LED lights in real-time. Therefore, children can judge whether they impact the target area correctly according to whether the LED lights are lit during training, and then adjust their training posture.
The designed sensor meets the basic requirements for beginner children basketball training, but the energy harvesting efficiency is low, resulting in a small amount of output power and unable to meet the higher demands, as follows. The current output power of the sensor can only light up 12 LED lights in real-time—that is, the sensor lights up 12 LED lights once if a basketball impacts the sensor once, but the brightness of the 12 LED lights is low and which is easily misjudged by beginner children as not being lit when the light is brighter in the day. Therefore, the next step can start from increasing the number of friction layers and synthesizing nanowires to increase the output power of the sensor, to light up more high-brightness LED lights in real-time to meet the needs under different light conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and C.W.; methodology, C.W. and Q.Z.; investigation, Z.Z. and Q.Z.; data curation, Z.Z. and Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., C.W. and Q.Z.; funding acquisition, C.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2019A1515110634); Open Foundation of Hubei Intelligent Geological Equipment Engineering Technology Research Center (DZZB202004).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stojanović, E.; Stojiljković, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Milanović, Z. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basket-ball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.L.; Scanlan, A.T.; Stanton, R. A review of player monitoring approaches in basketball: Current trends and future direc-tions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, O.V.; Alexandrovich, N.A.; Dmitriy, V. Sports Game Radial Basketball in Physical Education of Preschool Children. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 4, 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- Citroni, R.; Di Paolo, F.; Livreri, P. Evaluation of an optical energy harvester for SHM application. Aeu Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 111, 152918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lin, M.-F.; Lee, P.S. Skin-touch-actuated textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with black phosphorus for durable biomechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; Jang, S.; Ra, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D.; Choi, D. Universal biomechanical energy harvesting from joint movements using a direction-switchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 71, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Park, S.-C.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.-Y.; Song, I.; Choi, D.; Lim, H.; Kim, D.S. Biomimetic anti-reflective triboelectric nanogenerator for concurrent harvesting of solar and raindrop energies. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Yan, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Integrated multi-unit transparent triboelectric nanogenerator harvesting rain power for driving electronics. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving vibration energy harvesting and self-powered sensing by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Wen, G. Pagoda-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator With High Reliability for Harvesting Vibration Energy and Measuring Vibration Frequency in Downhole. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13999–14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Rana, S.S.; Salauddin, M.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Kim, H.; Cho, H.; Park, J.Y. A highly miniaturized freestanding kinetic-impact-based non-resonant hybrid-ized electromagnetic-triboelectric nanogenerator for human induced vibrations harvesting. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Super-robust and frequency-multiplied triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting water and wind energy. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Si, Y.; Li, T. Multi-grating triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting low-frequency ocean wave energy. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. High Power Density Tower-like Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Arbitrary Directional Water Wave Energy. Acs Nano 2019, 13, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, Y.; Jia, X.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Natural Leaf Made Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Environmental Mechanical Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, B.; Xia, Y.; Deng, Z.; Dai, H.; Hagedorn, P.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L. Galloping triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting under low wind speed. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Leaves based triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) and TENG tree for wind energy harvest-ing. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, K.; Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator enabled body sensor network for self-powered human heart-rate moni-toring. Acs Nano 2017, 11, 8830–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hou, X.; He, J.; Cui, M.; Wang, C.; Geng, W.; Mu, J.; Han, B.; Chou, X. Ultra-flexible and high-sensitive triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for self-powered hu-man physiological signal monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X. Air-flow-driven triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered real time respiratory monitor-ing. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6156–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, H.; Li, R.; Fan, C. Research on the potential of spherical triboelectric nanogenerator for collecting vibration energy and measuring vibration. Sensors 2020, 20, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yin, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. A Fully Self-Powered Vibration Monitoring System Driven by Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogener-ators. Acs Nano 2020, 14, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Tcho, I.W.; Choi, Y.K. Triboelectric nanogenerator based on rolling motion of beads for harvesting wind energy as active wind speed sensor. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Pan, L.; Wu, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, L.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Wind Sensor System for Detecting Wind Speed and Direction Based on a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 3954–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Chun, F.; Pan, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, W.; et al. Self-powered acceleration sensor based on liquid metal triboelectric nanogenerator for vi-bration monitoring. Acs Nano 2017, 11, 7440–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Q. Bolt-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Rock-Climbing Training Trajectory Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Q. Research on the Folding Spring Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Rock Climbing Trajectory and Time Monitoring. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155086–155092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.-C.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Smart Insole for Multifunctional Gait Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, T.; Cao, X.; Xiong, J.; Jie, Y.; Willander, M.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Self-sterilized flexible single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and dy-namic force sensing. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Wei, G.; Wu, J.M.; Han, W.; Yang, Y. Polyimide/Graphene Nanocomposite Foam-Based Wind-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Du, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerator based on paper and as a self-powered velocity and force sensor. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 13, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Han, C.B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. A ball-bearing structured triboelectric nanogenerator for nondestructive damage and rotating speed measurement. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Pang, Y.; Bu, T.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Self-Powered Hall Vehicle Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wu, C.; Wen, G. Development of gas–liquid two-phase flow pattern sensor of coalbed methane based on the principle of triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 195501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Niu, S.; Zi, Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerator; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks Integrated with Power Management Module for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.; Pang, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Guo, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Universal power management strategy for triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 37, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes, A.; Morel, A.; Juillard, J.; Lefeuvre, E.; Badel, A. Maximum power point of piezoelectric energy harvesters: A review of optimality condition for electrical tuning. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 29, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Maeng, J.; Shim, M.; Jeong, J.; Kim, C. A High-Voltage Dual-Input Buck Converter Achieving 52.9% Maximum End-to-End Efficiency for Triboelectric Energy-Harvesting Applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2019, 55, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Quelen, A.; Berlitz, C.A.; Gibus, D.; Gasnier, P.; Badel, A.; Pillonnet, G. 32.2 Self-Tunable Phase-Shifted SECE Piezoelectric Energy-Harvesting IC with a 30nW MPPT Achieving 446% Energy-Bandwidth Improvement and 94% Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–20 February 2020; pp. 488–490. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Manoli, Y. A piezoelectric energy-harvesting interface circuit with fully autonomous conjugate impedance matching, 156% extended bandwidth, and 0.38 μW power consumption. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Confer-ence-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A.; Quelen, A.; Gasnier, P.; Grezaud, R.; Monfray, S.; Badel, A.; Pillonnet, G. A Shock-Optimized SECE Integrated Circuit. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2018, 53, 3420–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.C.; Huang, P.H.; Shu, Y.C. Self-powered SECE-based piezoelectric energy harvesting for sensor supply under shock exci-tations, Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems XIV. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2020, 11376, 1137609. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).