Abstract
The influence of the electrospinning parameters on the diameter of the polyethersulfone (PES) nanofibers was demonstrated using response surface methodology. The electrospinning parameters studied were lithium chloride (LiCl) concentration, PES concentration, feed rate, and tip-to-collector distance. The average fiber diameter was correlated to these factors by using a second-order polynomial function at a 95% confidence level. The statistical analysis indicated that LiCl concentration, PES concentration, and feed rate had the significant connection with the fiber diameter, and LiCl concentration was the most important factor in determining the fiber diameter. When LiCl concentration increased, the fiber diameter decreased, because with more LiCl that is added, more applied voltage is needed to overcome the electrostatic attractions. The interactive effect between PES concentration and feed rate, the interactive effect between PES concentration and tip-to-collector distance, and the quadratic coefficients of LiCl concentration were also found to be significant. The adjusted determination coefficient (Radj2) of the model was calculated to be 0.9106. The water flux measurements showed that the decrease in the fiber diameter of the membrane caused the decrease in the initial pure water flux. The retention tests with 0.6 μm polystyrene (PS) suspension indicated that as the fiber diameter decreased, the pore sizes decreased and the particle removal efficiency increased.
1. Introduction
Many researchers have recently been interested in the fabrication of ultrafine and uniform fibers using various materials such as organics, inorganics, and composites [1]. Electrospinning is one of the versatile methods for producing the nanofibers, which have one-dimensional nanostructures [2]. The interconnected nanostructuring of nanofibers in distinction from the conventional nonwoven media can show unique properties. Thus, electrospun nanofibers have been applied in the field of electronics, catalysis, drug delivery, tissue engineering, and filtration [3,4,5,6]. Electrospun nanofiber membranes (ENMs) were widely applied for the particle separation from water. Thus, they can be used for treatment of wastewater prior to the treatment by UF (Ultrafiltration), NF (Nanofiltration) and RO (Reverse osmosis) [7,8,9,10]. Fiber diameter is a very important factor in determining the performance of ENMs and is dependent on the electrospinning parameters. The electrospinning parameters are comprised of solution properties, operating conditions, and ambient conditions. Parametrization is a mathematical process consisting of expressing the state of a system, process, or model as a function of some independent quantities called parameters. The state of the system is generally determined by a finite set of coordinates, and the parametrization thus consists of one function of several real variables for each coordinate. The parametrization study is important to fabricate the desired fiber morphology. However, there are few reports related to the salt effect on the diameter of PES nanofibers, and the methods of predicting the fiber diameter from information of one parameter alone does not currently exist because the parameters interact simultaneously in the electrospinning process. Therefore, the experimental investigation of individual parameters and interactions between parameters acting simultaneously was carried out, introducing the response surface methodology (RSM) [1]. The fiber diameter influences various properties of the electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs) (i.e., morphology, specific surface, water treatment performance, and so on). To fabricate electrospun nanofibers which have the desired fiber diameter and morphology, it is necessary to adjust various processing parameters (i.e., flow rate, tip-to-collector distance, and so on) and solution parameters (i.e., salt concentration, polymer concentration, and so on). Response surface methodology (RSM) is a collection of mathematical and statistical techniques used to analyze the experimental data acquired in the experimental design and to develop the suitable model.
In this study, the PES solution, including lithium chloride (LiCl), was used to produce electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs). The electrospinning parameters considered were solution properties (i.e., salt concentration, polymer concentration) and operating conditions (i.e., flow rate, tip-to-collector distance), and the response in the experiment was the average fiber diameter. A mathematical model of the fiber diameter was obtained during the RSM process. Since the fiber morphology can have a direct effect on the membrane structure, a thorough understanding of the electrospinning parameters is needed for the wide application of nanofibers [11]. When applied to filters for removing the particulate contaminants in air or water, ENMs provide many advantages, such as the high porosity for higher permeability, the interconnected pores for lower fouling, and the high surface area for larger particle retention [12]. The permeability tests and the filtration tests with micro-particles presented in water were conducted to demonstrate the effect of electrospinning parameters on filtration properties. The membranes for the filtration experiments were manufactured utilizing the information obtained in response surface models.
The objectives of this study were to observe the morphology change of PES nanofibers through blending LiCl and investigate the influence of electrospinning parameters on the fiber diameter systematically by the RSM. We also identified the properties of particulate removal according to the morphology of nanofibers in liquid filtration and evaluated the applicability of PES ENMs as filters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Polyethersulfone (PES, Gafone™ 3000P) was obtained from Solvay in Belgian. N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP, anhydrous, 99.5%) and lithium chloride (LiCl, ACS grade) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Polystyrene (PS) micro-particles of a 0.6 μm mean diameter were also purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). All chemicals were used as received. The polymer solutions were prepared at various PES concentrations (28–32% (w/v)) and LiCl concentrations (0–0.10% (w/v)) which can be in a fabricated condition without polymer beads. The desired amount of LiCl was dissolved in NMP at room temperature using a rotator from Labtech (Gwangju, Korea). Then, the desired amount of PES was added to the pre-prepared LiCl solution. The mixture was dissolved for more than 12 h at room temperature to become homogeneous using a rotator.
2.2. PES ENMs Fabrication by Electrospinning
A custom-built electrospinning instrument was used to fabricate the PES nanofibrous mats. The prepared solutions were injected with a 10 mL syringe (Kovax-Syringe®, Korea Vaccine, Korea) with a 19-gauge stainless-steel needle. The voltage in the 13.0–22.5 kV range was applied with a high-voltage power supply. The tip-to-collector distance varied in the 20–30 cm range. The polymer solution placed in the syringe was ejected by the syringe pump, producing a feed rate in the 0.3–0.5 mL/h range. The nanofibers were collected on the plate and covered with aluminum foil. The synthesized PES nanofibrous mats were immersed in de-ionized water (18.2 MΩ cm, Milli-Q, Millipore, Burlington, VT, USA) to remove the remaining solvent. To produce PES electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs) with different fiber diameters, the LiCl concentrations were adjusted to 0, 0.01, and 0.10% (w/v) in NMP. Then, 30% (w/v) PES solutions were prepared in each LiCl solution. The synthesized PES ENMs were immersed in de-ionized water (18.2 MΩ cm, Milli-Q, Millipore, Burlington, VT, USA) to remove the remaining solvent. The three resultant membranes were called ENM 30, ENM 30-0.01, and ENM 30-0.10, respectively. The specific fabrication conditions of the PES ENMs are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Fabrication conditions of the three different polyethersulfone (PES) electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs).
2.3. Characterization of PES ENMs
The surface structures of the PES nanofibrous mats and ENMs were analyzed with a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) (S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The average diameter of the nanofibers was measured using FE-SEM images and Image J 1.48v software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). To calculate the average diameter in each sample, 30 nanofibers were randomly selected within three images. The thickness of PES ENMs was measured using a dial thickness gauge (Mitutoyo 7301, Mitutoyo, Kanagawam Japan). Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy (Varian 660-IR, Bruker, Billerica, USA) was utilized to identify the chemical surface property of the PES ENMs according to the LiCl addition.
To compare the pore structures of the PES ENMs with the different fiber diameters, the pore size distribution of the PES ENMs was evaluated using a capillary flow porometer (Porous Materials Inc., New York, NY, USA). The PES ENMs were soaked with the wetting liquid, GalwickTM (Welcron, Seoul, Korea) and then put in the test sell with an effective diameter of 1.5 cm. Nitrogen gas was injected to overcome the capillary force of the liquid in the pores and flowed through the pores, increasing the differential pressure slowly. The relation between pore size and the corresponding gas pressure is obtained by the Young-Laplace Equation (1):
where r is the radius of the pore, ∆P is the differential gas pressure, γ is the surface tension of the wetting liquid, GalwickTM (15.9 × 10−5 N/cm = 15.9 dyn/cm), and θ is the wetting angle. The bubble point pore diameter represents the largest pore size in the membrane. The mean flow pore diameter indicates that half of the gas flow passes through pores larger than the mean pore size and that the remaining half of the gas flow passes through pores smaller than the mean pore size [13]. The porosity measurements of the PES ENMs were performed using a mercury porosimeter (AutoPore III 9420, Micrometrics, Norcross, GA, USA).
2.4. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
A Box-Behnken design in response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to study the influence of electrospinning parameters on the applied voltage and the average fiber diameter. Applied voltage was selected as the dependent variable for the response surface analysis in this study, compared to other studies. The reason was that the applied voltage responded to other parameters sensitively, using the conductive polymer solutions due to the addition of LiCl. LiCl concentration, PES concentration, feed rate, and tip-to-collector distance was selected as independent variables because these mainly influence to fiber-diameter which determine the pore size of ENMs. The four independent variables were LiCl concentration (X1), PES concentration (X2), feed rate (X3), and tip-to-collector distance (X4). The experimental range and coded levels of the independent variables are listed in Table 2. A total of 27 experimental points were needed to fit in the four variable Box-Behnken design (Table 3). In this study, a second-order polynomial model was used to describe the correlation between factors X and response Y. Applied voltage (Y1) and average fiber diameter (Y2) were set as the responses:
where b0 is the constant coefficient and means the response when none of the factors work. bi, bii, and bij are the linear, quadratic, and interaction coefficients, respectively. ε is the statistical error.

Table 2.
Experimental range and coded levels of the independent variables for fabricating PES nanofibers.

Table 3.
Experimental responses of the dependent variables for the applied voltage (Y1) and the average PES nanofiber diameter (Y2) in the Box-Behnken design. X1: LiCl concentration (% (w/v)), X2: PES concentration (% (w/v)), X3: Feed rate (mL/h), X4: Tip-to-collector distance (cm). The real values of the independent variables are listed in Table 2.
Determination coefficient (R2) evaluated the coincident extent between observed response values and the model equation. R2 ranges from 0 to 1. The lower values of R2 indicate that the observed response values do not fit the model equation well; however, a high value of R2 does not necessarily ensure the adequacy of the regression model. When additional factors are included in the model equation, R2 will always increase. Therefore, an adjusted R2 (Radj2) is induced as follows:
where n is the number of experiments and p is the number of coefficients in the regression model [14,15]. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a t-statistic of responses were conducted to judge the statistical significance using Minitab 17.0 software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA). The level of confidence was set to 0.05.
2.5. Pure Water Flux and Retention Test
The initial pure water flux of PES ENMs was determined using a dead-end filtration cell (AMICON 8200, Millipore, Burlington, VT, USA). The filtration cell was connected to a 5 L reservoir. The wetted PES ENM with a diameter of 63.5 mm was put in the filtration cell, and de-ionized water (18.2 MΩ cm, Milli-Q, Millipore, Burlington, VT, USA) in the reservoir was supplied to the membrane under the feed pressure of 0.2 bar. The mass of water that permeated through the membrane during 5 s was recorded, and the pure water flux was obtained by Equation (4):
where J is the pure water flux (L/(m2 h)), Q is the volume of the permeated water (L), A is the effective membrane area (m2), and ∆t is the sampling time (h).
Retention tests of 0.6 μm PS particles were performed at 0.2 bar on the simple dead-end filtration setup. The feed of 400 mL PS suspension (20 mg/L) in the reservoir was passed through the wetted PES ENM. The PS concentration of the permeated solutions was determined by a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Optizen 2120UV, Mecasys, Daejeon, Korea) at the wavelength of 450 nm. The separation factor (S.F.) was calculated as follows:
where Cf and Cp are the PS concentration of the feed solution (mg/L) and permeated solution (mg/L), respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameters Optimization in Fabricating PES Electrospun Nanofibers
To determine the effect of electrospinning parameters on applied voltage and average polyethersulfone (PES) nanofiber diameter, the dependent variables were observed in a total of 27 experimental points, including three replications of the central point, by the Box-Behnken design. The results are represented in Table 3.
3.1.1. Response Surface Model Analysis for Applied Voltage
The model adequacy checks indicated that the applied voltage was best described with the quadratic polynomial model (Table S1). The quadratic polynomial model involves linear, quadratic, and interaction terms. The significance probability (p-value) for the quadratic model (p = 0.000) was less than 0.05, and the adjusted determination coefficient (Radj2) for the quadratic model was the closest to 1 (Radj2 = 0.9627) of the considered models. The results suggest that the quadratic model fits the responses for applied voltage well. The p-value for lack of fit was not calculated because the pure error was 0. The analysis of the variance (ANOVA) in the quadratic model for applied voltage is shown in Table S2. The regression model for applied voltage reacted to linear and quadratic terms significantly at p < 0.05, whereas there were no interactive effects among the electrospinning parameters on the response of applied voltage at p > 0.05.
The measured voltages from the experiments and the predicted voltages from the model are distributed in Figure 1a. The good accordance between the measured values and the predicted values demonstrated that the estimated model was suitable. The regression coefficients in the quadratic model for the applied voltage are shown in Table 4. We found that all linear coefficients of the LiCl concentration (X1), PES concentration (X2), feed rate (X3) and tip-to-collector distance (X4) affected the applied voltage significantly at p < 0.05. One of the quadratic coefficients, X12, also affected the applied voltage significantly.
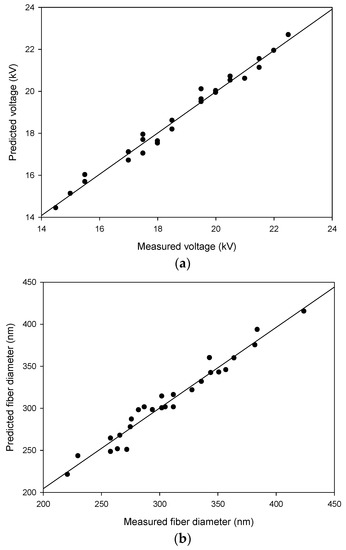
Figure 1.
Parity plot of the measured applied voltage and predicted applied voltage (a), the measured fiber diameter and predicted fiber diameter (b).

Table 4.
The regression analysis in the fitted quadratic polynomial model for applied voltage based on the t-statistic. R2 = 0.9828, Radj2 = 0.9627.
The response surface function for the applied voltage was obtained as follows, eliminating insignificant terms:
Y1 = 19.5 + 2X1 − 0.292X2 + X3 + 2.125X4 − 0.813X12
Equation (6) indicates the independent correlations between the applied voltage and each of the considered electrospinning parameters. The LiCl concentration and the tip-to-collector distance in particular have more noticeable effects on the applied voltage because their predicted coefficients are relatively high. These results suggest that the applied voltage indirectly affects the average fiber diameter included in the other electrospinning parameters [16,17]. Therefore, we propose that the applied voltage may be excluded from the independent variables regarding the average nanofiber diameter in this study.
3.1.2. Effects of Electrospinning Parameters on Applied Voltage
The effects of the electrospinning parameters on the applied voltage were considered physicochemically based on the response surface function for applied voltage obtained. A droplet of polymer solution in the tip is exposed to the capacitor-like electrical field during the electrospinning process. When the tip-to-collector distance is much larger than the needle diameter, the electrical field strength applied to the charges in the droplet can be estimated as follows [18]:
where E is the electrical field strength, V is the applied voltage, and d is the tip-to-collector distance. Equation (7) indicates that more applied voltage is needed for stable electrospinning as the tip-to-collector distance increases. This supports our statistical finding that the linear coefficient of the tip-to-collector distance (2.125) was positive in Equation (6) and had the highest value. Our previous statistical analysis indicates that the LiCl concentration exerts the corresponding influence on the applied voltage compared with the tip-to-collector distance. Since the linear coefficient of the LiCl concentration (2) was positive in Equation (6), the applied voltage increases with an increasing LiCl concentration. Many researchers have reported the interactions of LiCl and polar aprotic solvents, such as N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), dimethylformamide (DMF), and dimethylacetamide (DMAc), with polymers [19,20,21]. When LiCl is dissolved first in NMP, Li+ cations form the positive charged complexes with the amide groups in NMP under the solvation process. Li+ cations may also form the positive charged complexes with the sulfone groups in PES following the addition of PES in the LiCl-NMP system. In other words, the addition of LiCl changes the solution environment, inducing the bulky solvated NMP molecules and the electrostatic interactions among the formed complexes and Cl− anions. As a result, the two chemical reactions improve the viscosity of the mixed solvent [21]. This phenomenon means that the more LiCl that is added, the more applied voltage is needed to overcome the electrostatic attractions.
3.1.3. Response Surface Model Analysis for Average Fiber Diameter
The model adequacy checks indicated that the average fiber diameter was also best described in the quadratic polynomial model (Table S3). The p-value for the quadratic model (p = 0.000) was less than 0.05, and the Radj2 for the quadratic model was the closest to 1 (Radj2 = 0.9106) of the considered models. In addition, the p-value for lack of fit (p = 0.496) was insignificant at p > 0.05. The results suggest that the quadratic model fits the responses for the average fiber diameter appropriately. The analysis of the variance (ANOVA) in the quadratic model for the average fiber diameter is shown in Table S4. The regression model for the average fiber diameter reacted to linear, quadratic, and interaction terms significantly at p < 0.05.
The measured fiber diameters from the experiments and predicted fiber diameters from the model are distributed in Figure 1b. The good accordance between the measured values and the predicted values demonstrated that the estimated model was suitable. The regression coefficients in the quadratic model for the average fiber diameter are shown in Table 5. We found that three linear coefficients of the LiCl concentration (X1), PES concentration (X2), and feed rate (X3) affected the average fiber diameter significantly at p < 0.05. One quadratic coefficient of X12 and two interaction coefficients of X2X3 and X2X4 also affected the average fiber diameter significantly.

Table 5.
The regression analysis in the fitted quadratic polynomial model for the average fiber diameter based on the t-statistic. R2 = 0.9587, Radj2 = 0.9106.
The response surface function for the average fiber diameter was obtained as follows, eliminating insignificant terms:
Y2 = 301.33 − 51.67X1 + 20.92X2 + 34.33X3 − 18.71X12 − 26.5X2X3 − 19.75X2X4
The LiCl concentration, PES concentration, and feed rate have a direct relevance to the average fiber diameter, as shown in Equation (8). The LiCl concentration in particular is the most decisive parameter in controlling the average fiber diameter because the absolute value of the predicted coefficient is the highest. This observation is consistent with the previous studies which found that the addition of ionic salt has a stronger influence on the fiber diameter than other electrospinning parameters [22,23]. In addition, the feed rate makes a larger contribution to the average fiber diameter than the PES concentration because the coefficient of the feed rate is higher than that of the PES concentration. This result is not consistent with other studies in which the polymer concentration affected the average fiber diameter significantly compared with the feed rate [1,24].
The interactive effect of the PES concentration and the feed rate on the average fiber diameter is presented in Figure 2a. To minimize their influences on the average fiber diameter, the LiCl concentration and tip-to-collector distance were fixed at low levels of 0.01% (w/v) and 20 cm, respectively. This contour plot suggests that the responses in the average fiber diameter rely on the feed rate at a lower PES concentration. When the feed rate increased at a low PES concentration of 28–30% (w/v), the average fiber diameter increased in a wide range of <330 to >430 nm; however, the feed rate exerted little influence on the average fiber diameter at a higher PES concentration. This is because the increased viscoelastic effect of the PES concentration counteracted the mass flow effect of the feed rate.
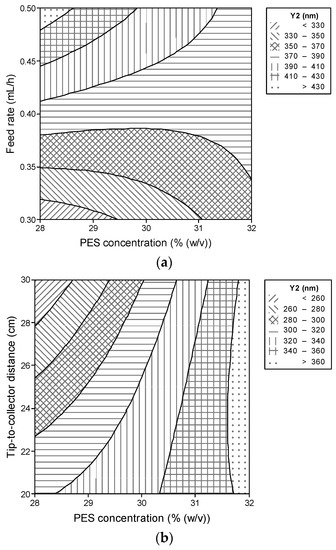
Figure 2.
Contour plot for the average fiber diameter (Y2, nm) as a function of feed rate and PES concentration at an LiCl concentration of 0.01% (w/v) and a tip-to-collector distance of 20 cm (a); as a function of the tip-to-collector distance and the PES concentration at an LiCl concentration of 0.01% (w/v) and a feed rate of 0.3 mL/h (b).
The interactive effect of the PES concentration and the tip-to-collector distance on the average fiber diameter is presented in Figure 2b. To minimize their influences on the average fiber diameter, the LiCl concentration and feed rate were fixed at low levels of 0.01% (w/v) and 0.3 mL/h, respectively. We found that the increase of the tip-to-collector distance caused the decrease of the average fiber diameter at a low PES concentration of 28–29% (w/v) in this contour plot; however, the tip-to-collector distance exerted little influence on the average fiber diameter at a high PES concentration of 30–32% (w/v).
3.1.4. Effects of the Electrospinning Parameters on the Average Fiber Diameter
The effects of the electrospinning parameters on the average fiber diameter were considered physicochemically based on the response surface function for the average fiber diameter obtained. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the morphology and the average diameters of the nanofibers electrospun in 30% (w/v) PES solutions with different LiCl concentrations. The PES nanofibers were fabricated at each optimal voltage, the feed rate of 0.5 mL/h, and the tip-to-collector distance of 20 cm. The average fiber diameter decreased considerably with an increasing LiCl concentration in a range of 0–0.10% (w/v). The observations coincide with our statistical result that the linear coefficient of the LiCl concentration (−51.67) was negative in Equation (8) and had the highest absolute value. The addition of LiCl increases the electrical conductivity of the solution, bringing about a higher surface charge density of the polymer jet. When more charges move in the polymer jet, a greater elongation of the jet occurs due to the electrostatic repulsion among charges [11,22]. This elongation effect increases the period or the nanofibers to exist in the instability region, causing a reduction in the diameter of the resultant nanofibers.
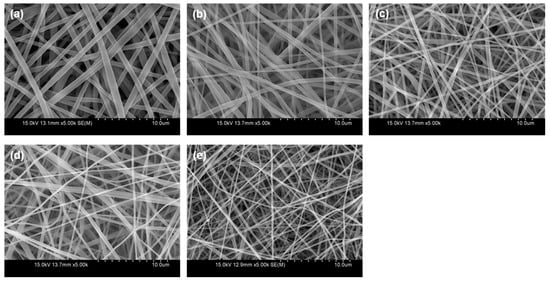
Figure 3.
FE-SEM images (5000×) of 30% (w/v) PES nanofibers with different LiCl concentrations at each optimal voltage, the feed rate of 0.5 mL/h, and the tip-to-collector distance of 20 cm. (a) 0% (w/v)/13.0 kV, (b) 0.01% (w/v)/15.5 kV, (c) 0.03% (w/v)/17.5 kV, (d) 0.05% (w/v)/19.5 kV, (e) 0.10% (w/v)/22.0 kV.
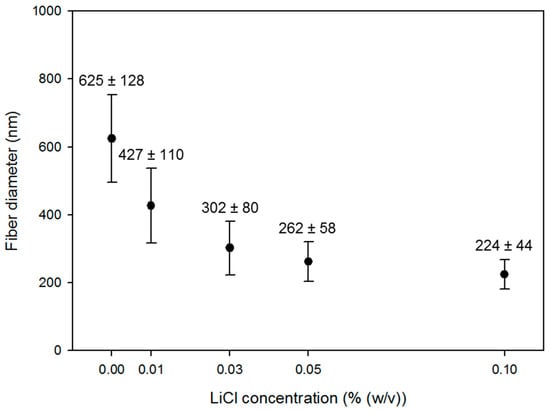
Figure 4.
The LiCl concentration effects on the average diameter of 30% (w/v) PES nanofibers at each optimal voltage, the feed rate of 0.5 mL/h, and the tip-to-collector distance of 20 cm.
Our previous statistical analysis indicates that the PES concentration and the feed rate have secondary impacts on the average fiber diameter compared with the LiCl concentration. Since the linear coefficients of the PES concentration (20.92) and the feed rate (34.33) were positive in Equation (8), the average fiber diameter increases with increasing PES concentration and feed rate. The increased PES concentration is closely associated with the increased viscosity of the solution [1,5]. This is because of the higher entanglement among the increased polymer chains in the solution [25]. The viscoelastic effect increases the diameter of the resultant fibers. The feed rate is related to the mass flow of the polymer. When the feed rate increases, more polymers transfer from the needle tip to the collector in a faster stream of the polymer jet [12,26]. This results in an increment of resultant fibers.
3.2. Particulate Removal of PES Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes in Liquid Filtration
Wang et. al. report the effects of electrospun nanofibrous structures on the filtration performance, a series of nanofibrous membranes with different fiber diameters. They observed that smaller fiber diameters led to smaller pores with more uniform distribution, and the membrane pore size has a direct relation with the permeability and particle rejection efficiency of membrane [27].
3.2.1. Characterization of the PES ENMs
The surface structures of the PES electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs) are shown in Figure 3. According to the previous results, the LiCl concentration and the feed rate have more direct impacts on the fiber diameter. Therefore, the PES solutions with different LiCl concentrations of 0, 0.01, and 0.10% (w/v) were electrospun to produce PES ENMs with different fiber diameters and the feed rate was optimized accordingly. ENM 30-0.10 had the smallest fiber diameter and was prepared from the PES solution with the highest LiCl concentration of 0.10% (w/v). All membranes possessed relatively uniform nanofibers without beads or spindles. The basic characteristics of the PES ENMs are tabulated in Table S5. To minimize the effect of membrane thickness on liquid filtration performance, the thicknesses of the PES ENMs were similarly set.
The PES ENMs with different LiCl concentrations were characterized by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy (Figure S1). There was no particular distinction among the spectra of PES ENMs, regardless of whether or not LiCl was added in the membranes. We observed that the PES ENMs only had the chemical properties of PES compared with the reported band assignments of the PES membrane by Belfer et al. [28]. Although the peak at 1671 cm−1 is related to the carbonyl vibrations of the N–C=O group in NMP, this peak was not observed. Therefore, the results propose that the chemical properties of the PES ENMs do not change with the addition of LiCl because the solvent NMP that mainly forms the complex with a Li+ cation is completely removed during the electrospinning process and the immersion process in water.
3.2.2. Pore Characterization of the PES ENMs
The average pore sizes (Table S6) of the PES ENMs were obtained by the capillary flow porometer. It was observed that the pore size ranges of the PES ENMs belonged to microfiltration (MF) scale [29]. After linking these results with the fiber diameters of the PES ENMs shown in Table S5, it was found that the fiber diameter plays an important role in determining the pore structure of the PES ENMs. When the fiber diameter decreases, the pore sizes and the pore size distribution also decrease.
The porosities of the PES ENMs were obtained by the mercury porosimeter. It was found that the porosity of the PES ENMs increased slightly with a decrease in the fiber diameter. In conclusion, the porosity was insignificantly affected by the fiber diameter in our study.
3.2.3. Pure Water Flux and PS Retention Test
The pure water flux test was carried out to investigate the relationship between the fiber diameter and the water permeability of the PES ENMs. The initial pure water fluxes of ENM 30, ENM 30-0.01, and ENM 30-0.10 were obtained as 15,900, 11,400, and 10,800, respectively (Figure 5a). This decline tendency is similar to the results of other research groups [30,31]. We found that three PES ENMs exhibited higher pure water fluxes compared with the commercial GSWP 0.22 μm membrane and had a pure water flux of 9155 L/(m2 h bar) at 0.17 bar [32].
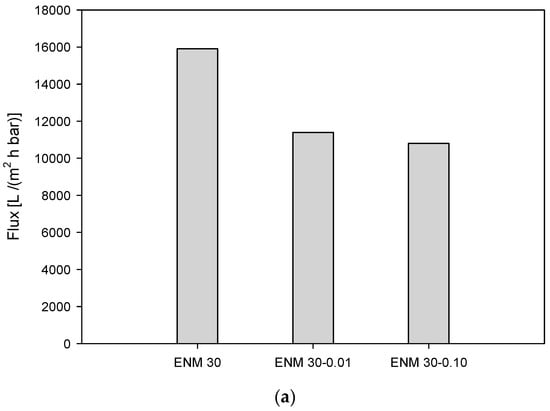
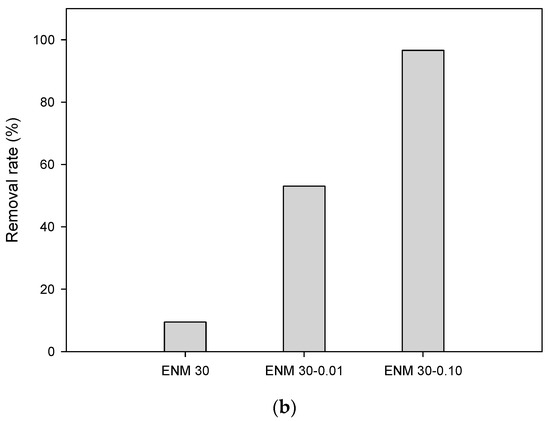
Figure 5.
Water permeation (a) and 0.6 μm PS suspension filtration (b) performance of the PES ENMs.
On the basis of Darcy’s law [33,34], the pure water flux through a MF membrane can be estimated as follows:
where J is the water flux (m3/s), ε is the porosity (–), r is the pore radius (m), ∆P is the pressure difference across the membrane (Pa), μ is the dynamic viscosity (Pa s), τ is the tortuosity (–) and ∆x is the membrane thickness (m).
Equation (9) implies that the pore size is a very effective factor in determining the initial pure water flux because the porosities and the thicknesses of the PES ENMs have little difference in our study. It should be noted from Figure 3 that the number of nanofibers per unit area is arranged in the order of ENM 30-0.10 > ENM 30-0.01 > ENM 30. Thus, smaller pore size and more nanofibers can make the transfer route of water molecules complicated in the membrane. This results in the reduction of pure water flux.
The retention test was carried out to investigate the relationship between the fiber diameter and the liquid filtration properties of the PES ENMs. On the basis of the pore size characteristics of the PES ENMs, 0.6 μm polystyrene (PS) suspensions were selected as target particles. The separation factors in ENM 30, ENM 30-0.01, and ENM 30-0.10 were obtained as 10%, 53%, and 97%, respectively (Figure 5b). The membranes composed of thinner nanofibers had smaller pore sizes and a narrower pore size distribution. They can also have a high specific surface area for particle adsorption and a large interconnection among nanofibers [13]. This results in the improvement of liquid filtration performance.
4. Conclusions
The influence of the electrospinning parameters on the diameter of the polyethersulfone (PES) nanofibers was demonstrated using response surface methodology (RSM). The preliminary factors consisted of a lithium chloride (LiCl) concentration, PES concentration, applied voltage, feed rate, and tip-to-collector distance. The applied voltage was left out because it was found that the applied voltage responded to other parameters sensitively in the conductive polymer solution. A quadratic model on the average fiber diameter was fitted through the analysis of the variance (ANOVA). The responses in the model indicated that the LiCl concentration was the most important factor in determining the average fiber diameter and that the tip-to-collector distance had no connection with the average fiber diameter. This work shows the possibility of predicting the fiber diameter in specific conditions and producing PES nanofibers with the desired diameter. The properties of the PES solutions with LiCl loadings also need to be observed for proving the effects of the LiCl concentration in a chemical aspect.
Based on the parametrization, three PES electrospun nanofibrous membranes (ENMs) with different fiber diameters were fabricated. The synthesized membranes were used for the liquid filtration application. It was observed that the pore sizes and the pore size distribution also decreased as the fiber diameter decreased. The pure water flux test and the retention test were performed to identify the relationship between fiber diameter and filtration performance. When the fiber diameter decreased, the initial pure water flux decreased, and the removal rate of the micro-particles increased due to a denser membrane structure. This study demonstrates the possibility of producing various size selective membranes through the adjustment of the fiber diameter; however, further research is required to thoroughly understand the liquid filtration mechanism and to identify the structural and mechanical integrity of PES ENMs in membrane processes for water treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/20/7295/s1, Figure S1: ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) ENM 30, (b) ENM 30-0.01, and (c) ENM 30-0.10, Table S1: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) in various mathematical models for the applied voltage, Table S2: Analysis of the variance (ANOVA) in the fitted quadratic polynomial model for applied voltage, Table S3: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) in various mathematical models for the average fiber diameter. Table S4: Analysis of the variance (ANOVA) in the fitted quadratic polynomial model for the average fiber diameter, Table S5: Fiber diameter and membrane thickness of the PES ENMs, Table S6: Pore properties of the PES ENMs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B. and H.K.; methodology, H.K.; software, H.K; formal analysis, H.K.; data curation, S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, H.K.; writing—review and editing, J.B.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, K.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT), grant number 20200451-001.
Acknowledgments
Authors are very grateful for the funds [Project # 20200451-001] provided by “Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology” (KICT).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Neo, Y.P.; Ray, S.; Easteal, A.J.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Quek, S.Y. Influence of solution and processing parameters towards the fabrication of electrospun zein fibers with sub-micron diameter. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, C645–C651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Nizar, S.; Balamurugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Advancement in electrospun nanofibrous membranes modification and their application in water treatment. Membranes 2013, 3, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhate, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, C1–C8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bromberg, L.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Catalytic hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate by electrospun polyacrylamidoxime nanofibers. Polymer 2007, 3, C4675–C4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Preparation of continuous alumina nanofibers via electrospinning of PAN/DMF solution. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ma, Z.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous filtration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 281, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussawasathien, D.; Teerawattananon, C.; Vongachariya, A. Separation of micronto submicron particles from water: Electrospun nylon-6 nanofibrous membranes as pre-filters. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 315, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Novel nanofibrous scaffolds for water filteration with bacteria and virus removal capability. J. Electron. Microsc. 2011, 60, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Barhate, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Hot pressing of electrospun membrane and its influence on separation performance on thin film composite nanofiltrtion membrane. Desalination 2011, 279, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabola, K.P.; Moutloali, R.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters on the morphology and diameter of poly(vinyledene fluoride) nanofibers- effect of sodium chloride. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous materials and their applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Feng, C.Y.; Chan, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Tabe, S.; Matsuura, T. Electrospun nanofibrous polysulfone membranes as pre-filters: Particulate removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, H.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Criscenti, G.; Moroni, L.; Dijkstra, P.J. The influence of process parameters on the properties of electrospun PLLA yarns studied by the response surface methodology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukigara, S.; Gandhi, M.; Ayutsede, J.; Micklus, M.; Ko, F. Regeneration of Bombyx mori silk by electrospinning—Part 1: Processing parameters and geometric properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 5721–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, A.G.; Altay, A.S.; Altay, F. Effect of voltage on morphology of electrospun nanofibers. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 1–4 December 2011; pp. I-324–I-328. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcinkaya, B.; Yener, F.; Jirsak, O.; Cengiz-Callioglu, F. On the nature of electric current in the electrospinning process. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 538179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrova, A.K.; Glazunov, V.B.; Papkov, S.P. Interaction in the system polymer-dipolar aprotic solvent-salt. Fibre Chem. 1987, 18, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Won, J.; Lee, H.; Kang, Y.S. Solution properties of poly (amic acid)–NMP containing LiCl and their effects on membrane morphologies. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 196, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Idris, A.; Pa, N.F.C. Novel method of synthesizing poly(ether sulfone) membranes containing two solvents and a lithium chloride additive and their performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wang, S.-Y. Interior structure of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers with LiCl. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1325–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Ho, K.-H.; Chiang, Y.-P.; Wu, K.-W. Fabrication of electrospun poly (methyl methacrylate) nanofibrous membranes by statistical approach for application in enzyme immobilization. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.P. Polymer entanglements. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro- and Nanostructured Surface Morphology on Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for high flux microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfer, S.; Fainchtain, R.; Purinson, Y.; Kedem, O. Surface characterization by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy of polyethersulfone membranes-unmodified, modified and protein fouled. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 172, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Influence of electrospun fiber size on the separation efficiency of thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Baek, I.; Choi, H. Mechanically enhanced PES electrospun nanofiber membranes (ENMs) for microfiltration: The effects of ENM properties on membrane performance. Water Res. 2016, 105, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High-flux microfiltration filters based on electrospun polyvinylalcohol nanofibrous membranes. Polymer 2013, 54, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Dutrê, B.; Persson, K.M.; Trägårdh, G. Water permeability in ultrafiltration and microfiltration: Viscous and electroviscous effects. Desalination 1997, 113, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.S.; Buhr, K.; Ebert, K. Polyethersulfone electrospun nanofibrous composite membrane for liquid filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).