Abstract
Asphalt rubber (AR) is often described as an environmentally friendly material due to the incorporation of recycled rubber from used tires and its improved service life. Its field application is influenced by many factors. In order to evaluate the impact of different factors such as crumb rubber (CR) content, stabilizer and the production method on the performance of rubber powder modified asphalt, two different matrix asphalts were prepared, the basic experiments, control variable methods and several related tests were thereafter conducted. The results showed that a moderate amount of CR could enhance the pavement performance. The suitable CR content was 20–25% for 90# matrix asphalt and 22–26% for 70# matrix asphalt. The stabilizer had a positive impact on the AR’s high temperature behavior and was beneficial to the storage of AR, but it did not make a significant influence on low temperature behavior. In addition, different methods brought certain performance differences. Though AR produced with the heat fusion method had better high-temperature performance, the rubber particles would easily disperse and melt in the asphalt during the shearing process, which gave AR more balanced physical performance. This study identifies the shearing method as the optimal choice for site construction and provides a wider application range for asphalt rubber in the road construction field. The selection of parameters depends on the construction areas and performance requirements.
1. Introduction
With the development of China’s social economy in recent years, the number of motor vehicles has increased significantly, resulting in a sharp increase in the number of used tires. China became the world’s largest tire producer in 2006, and the tire production increased from 190 million units in 2003 to 816 million units in 2018 with more than 10 million tons of used tires are accumulated every year [1,2,3,4,5]. The large number of used tires has caused severe environmental and ecological safety problems, known as “black pollution”, and resulted in the accumulation of large quantities of used tires in the suburbs of large cities [6,7,8,9]. What is worse, not proper storage of the tires may lead to fires [10,11,12].
Recycling these tires can create economic benefits while addressing the environmental issues. The processing of used tires into rubber powder by mechanical means for asphalt modification or asphalt mixture modification is recognized as a harmless treatment method for used tires [13]. Since rubber and asphalt are both polymeric organic materials, and have a natural affinity, which means they are easy to react, thus, the use of waste rubber powder to modify asphalt (asphalt rubber) have a bright application prospect [14,15,16,17,18]. Asphalt rubber (AR) can significantly improve the performance of the road surface against rutting, high temperature performance, reflection cracks, water stability and fatigue cracking. In addition, AR also has the characteristics of reducing road maintenance, improving anti-sliding and reducing road noise [19,20,21,22,23].
Xie Bangzhu [24] found that the mesh number of rubber powders could significantly affect the dispersion of rubber powder in asphalt during the initial miscibility process. In the later reaction process, the reaction temperature was the key influencing factor responsible for rubber powder swelling and desulfurization degradation. Ghavibazoo [25,26,27] established that temperature was the most important factor affecting the dissolution rate of rubber powder, and that the performance of asphalt changed with the influence of rubber powder in asphalt. Ge Xuanrui [28] showed that the fatigue life of the asphalt rubber mixture increased with the crumb rubber content increasing, but only to a certain point before it started to decrease again, meaning that there was an optimal crumb rubber content. Maccarrone [29] proposed that the most ideal state of rubber powder distribution in asphalt rubber was that where the macroscopic dispersion was uniform, and the microadhesive powder and asphalt components absorbed and cross-linked each other. In addition, the poor compatibility caused the rubber powder particles to flocculate, granular and even caused delamination, which significantly affects the performance of asphalt rubber. Han Shufeng [30] found that the asphalt rubber produced under different mixing modes had little difference except for the viscosity. When examining these mixing methods, the asphalt rubber produced by the high-speed shear method had the worst viscosity, while the asphalt rubber produced by the high-speed stirring method had better viscosity. When examining the different stirring temperatures, the indexes changed significantly, showing that higher or lower production temperature was not conducive to the performance of asphalt rubber. The AR performance produced at 180–200 °C provided the best results.
Therefore, the production temperature, different crumb rubber content, the mesh number and the different production method all have a certain effect on the performance of the asphalt rubber. However, it is not clear how exactly these different factors affect the performance properties of AR, which in their turn have an effect on its wide range of use. Compared to the previous studies, most of the researchers focused on the performance improvement of AR with different additives. All the produced samples were in accordance with the related specifications, which made the preparation process and parameters not concerned. From the feedback of site construction of AR, the production method, crumb rubber content and stabilizer were the most obvious influencing factors affecting its performance because of the huge usage. Though the performance of AR had met the requirements, the adjustment of a certain preparation parameter would bring about the performance change and huge economic loss, which was also an important reason for this study to focus on the preparation process. In order to meet the requirements under limited site conditions, the stabilizers was chosen, which could maintain asphalt rubber stable performance and prevent its decomposition. For this reason, different stabilizers were selected in this study and their effect on the performance of asphalt rubber through a combination of macro tests and micro observations was evaluated.
To achieve this objective, two different asphalts (70# and 90#), two different production methods, different crumb rubber (CR) contents and stabilizer addition were selected to evaluate performance differences of asphalt rubber. The basic properties, rheological properties and micromorphology were investigated to illustrate the different influence degrees to ensure the quality of asphalt rubber and increase its fields of application. It could bring more stable performance to asphalt rubber through more appropriate parameter control of production method, CR content and stabilizer addition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt
The SK90#, SK70# and AH70# matrix asphalts were used in the experiment. Their main physical and technical properties are shown in Table 1. All of their performance indicators met the standards for the asphalt pavements in the “Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements” (JTG F40-2004).

Table 1.
Main property of the matrix asphalt.
2.1.2. Crumb Rubber
Crumb rubber used in the study was recycled from waste tires produced in Hancheng city, Shaanxi Province. Close-up photos and a SEM photo are shown in Figure 1, the main physical and chemical properties of the CR are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.
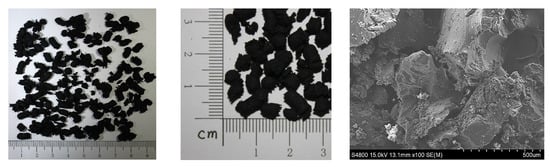
Figure 1.
Close-up photos and SEM photo of regular rubber particle.

Table 2.
Physical properties of crumb rubber.

Table 3.
Chemical properties of crumb rubber.
2.1.3. Stabilizer
The function of the stabilizer in the asphalt rubber is to improve the segregation performance for it not only has physical thickening effect, but also has a steric hindrance effect. Three stabilizers ZB-01, HMD-1 and HMD-2 were selected and recorded as 1#, 2# and 3#. Their parameters are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Parameters of different stabilizers.
2.2. Sample Preparation
In this study, the heat fusion method and shearing method were selected to produce asphalt rubber (to illustrate performance differences) using an X-blade mixer and a high-speed shear. Auxiliary equipment included temperature control heaters, mixing pots, electronic scales, thermometers and glass rods. The steps of preparation are as follows and the preparation process is shown in Figure 2.
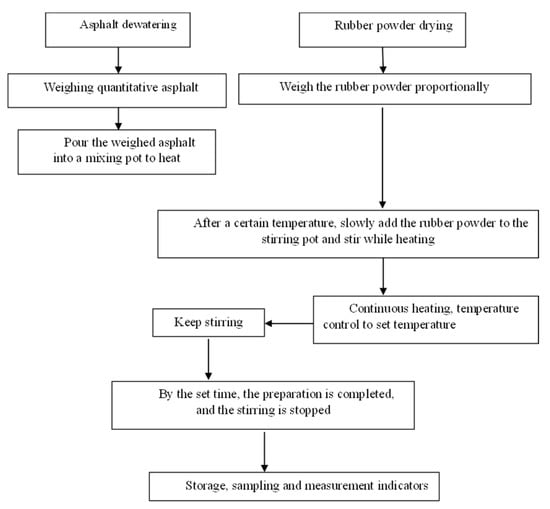
Figure 2.
Asphalt rubber preparation process.
The samples for the shearing method were prepared as follows:
(1) The matrix asphalt was placed in an oven, the temperature was set to 150 °C and the asphalt was removed after heating to a fully liquefied state.
(2) The rubber particle was heated and dried in a small oven at 110 °C. Worth noting that if the temperature is too low, the moisture in the rubber powder cannot be easily removed, and if the temperature is too high, the space network of the rubber powder will be destroyed and affect the properties of AR.
(3) The mixer was set to a speed of 300 r/min the mixer was operated until the temperature rose to 150 °C to stir the asphalt.
(4) The rubber particle was added during the stirring process slowly and stirred at 170–180 °C continuously for 30 min to prevent asphalt aging caused by overheating.
(5) After the completion of the stirring, the sample was placed on a shearing machine and subjected to high speed shearing at a speed of 4000 r/min, the shearing time was 1 h and the shearing temperature was controlled in the range of 170–180 °C.
(6) After the completion of the shearing, the sample was taken out and stirred for 1 h (reaction time), and the sample was stirred at 170 °C for 1 h.
The heat fusion method was to directly put the rubber powder into the reaction tank under the same process parameters, and to produce it only by stirring.
After completion, it was poured into a test container for the follow-up experiments for both methods.
2.3. Experimental Methods
Physical properties test
In order to test the basic physical properties of asphalt binder, the penetration at 25 °C, softening point, ductility at 5 °C, elastic recovery and rotational viscosity at 180 °C, tests were conducted in accordance with the JTG E20 T0604-2011, JTG E20 T0606-2011, JTG E20 T0605-2011, JTG E20 T0662-2000 and JTG E20 T0625-2011, respectively, which are similar to ASTM D5, ASTM D36, ASTM D113 and ASTM D4402.
Stabilizer effect test
In this study, two types of matrix asphalt were used to make asphalt rubber samples and three stabilizers were added respectively. The physical characteristics were tested to compare the effects of asphalt rubber with and without stabilizers. Asphalt A and Asphalt B were SK- 70# (A) and AH-70# (B) and AR was 30-mesh waste tires CR with 20% of matrix asphalt (external blending).
Sample Preparation
The matrix asphalt was heated to 150 °C and placed in a mixer for stirring. The CR was gradually added during the mixing process, and the total amount of the CR reached 20% of the mass of the asphalt. The prepared stabilizer was added after the stirring was completed and the heating was continued during the following stirring process (the temperature was maintained between 170 and 180 °C). The mass of the stabilizer was 3‰ of the total amount of AR, and stirring continued for 1 h after its addition. Afterwards, the sample was poured into the test vessel for the tests. The AR sample preparation summary is shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Asphalts rubber sample preparation scheme.
Different Stirring methods on AR
In order to study and verify the influence of the stirring method on the performance of the asphalt rubber systematically, the ordinary heat fusion method and the high-speed shearing method were used in laboratory tests. For the shearing method, the sample was subjected to high-speed shearing at 4000 r/min, the shearing time was 1 h and the shearing temperature was controlled within a temperature range of 170–180 °C. Under the same process parameters, the mixing of the asphalt rubber with different dosages was carried out. The results of both mixing methods were compared to analyze the effect of hot melt and shear on the performance of asphalt rubber.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
In order to evaluate the performance of asphalt with crumb rubber, the microscopic aspects should first satisfy the conditions for the firm bonding of the asphalt to the surface of the filler. Studies showed that the irregular shape and distribution characteristics of fine particles in asphalt could affect the mechanical properties of the asphalt binder [31]. In this paper, asphalt with different crumb rubber contents was investigated by SEM.
Rheological properties test
To investigate the effect of crumb rubber on rheological behavior, matrix asphalt and asphalt with 20% dosage crumb rubber were tested using the bending beam rheometer (BBR) test and the strain-controlled dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) test.
(i) The stiffness modulus S and creep rate m measured by the BBR test could reflect the low temperature crack resistance of the asphalt. In this paper, BBR was carried out to test the low temperature creep of asphalt rubber. The asphalt binder beams (125 mm in length, 6.25 mm in width and 12.5 mm in height) were prepared in molds. The measured temperatures of the asphalt samples of this test were set to −6 °C, −12 °C and −18 °C. The beam specimens were removed from the mold after cooling the mold assembly in the freezer for 10 min. The beam was then kept in the test bath for 60 ± 5 min before the test. After the preloading procedures, a 100-g load was applied to the beam for a total period of 240 s.
(ii) The relaxation of shear stress of asphalt rubber was tested in a DSR followed by ASSHTO TP5. The parallel plate’s geometry with a diameter of 8 mm and gap size of 1 mm were used in the test at different temperatures (46 °C, 52 °C, 58 °C, 64 °C, 70 °C and 76 °C). The target shear strain was set up to 1%, and the range of the time to reach the target strain was 60 s. Relaxation time was 1000 s. After the asphalt binder sample was sandwiched between the fixed plate and the spindle, the desired test temperature was controlled at 0.1 °C using a water bath. The resulting strain was monitored and recoded when the spindle was oscillated back and forth with constant stress.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Different CR Content on the Performance of AR
3.1.1. 90# Matrix Asphalt
In order to clarify the influence of different CR proportions on the asphalt rubber performance, five contents of CR (15%, 17.5%, 20%, 22.5% and 25%) were selected for comparison tests with SK90# matrix asphalt. All the AR samples were then produced with a heat fusion method. The basic physical performances of all samples were obtained through laboratory tests (Table 6). The results from Table 6 are graphically reproduced in Figure 3.

Table 6.
Basic physical properties of different asphalt rubber (AR).
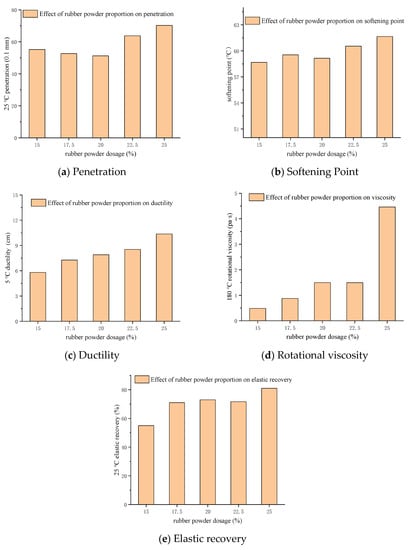
Figure 3.
Effect of crumb rubber (CR) content on conventional tests result for 90# asphalt.
As shown in Figure 3a, when the CR content increased from 15% to 20%, the penetration degree gradually decreased as the rubber powder absorbed the oil in the asphalt and indirectly changed the colloidal structure. The rubber powder was evenly distributed in the asphalt after swelling, and so were the micelles gradually changing from the free phase to the double continuous phase, and then from the double continuous phase to the rubber powder continuous phase and the free asphalt discontinuous phase [32]. This process resulted in a decrease of the asphalt rubber viscosity and penetration. As the amount of rubber powder increased from 20% to 25%, the rubber powder began to desulfurize and degrade, the long-chain structure formed was destroyed, and the asphalt became soft, resulting in gradual increase of the penetration degree. Therefore, the penetration of the AR, its flexibility and low-temperature performance can be significantly improved by increasing its CR content in the test blending range.
As shown on Figure 3b, the softening point curve of AR increased with the increment of CR blending ratio, but overall, the softening point did not change significantly. In the range of 15–20%, the change of softening point was not obvious. In the range of 20–25%, the penetration curve showed a rapid growth trend with the increment of CR content. This was mainly because the rubber powder absorbed the light components in the asphalt and the cross-linking effect after the rubber powder particles swell [33]. Therefore, in the test blending range, the increment in CR content did not significantly change the softening point of the AR, however, it slightly increased the viscosity of the AR, which, in its turn improved the high temperature resistance to permanent deformation (to some extent only).
As shown on Figure 3c, the ductility curve of AR increased with the increment of CR content. When the CR content was in the range of 15–25%, the ductility curve of AR continued to rise and the ductility index increased by nearly 80%. This was because the rubber molecular segment in the asphalt rubber was gradually increasing, which enhanced the low temperature flexibility of the asphalt, and the cross-linking, affected between the rubber powder in the AR, was gradually enhancing. Therefore, it can be concluded that the low temperature ductility will increase when the rubber powder content increases.
From Figure 3d, the viscosity curve of AR continued to rise with the increment of CR content. This would cause difficulties in handling the AR and aggregate and increase the operation time during construction. Based on the domestic and international research experience on the requirements of AR, the 180 °C Brookfield viscosity (Pa·s) of AR should be between 1 and 4 (Pa·s). When the CR content was more than 25%, the viscosity of the AR exceeded that which was recommended in the standard (to ensure satisfactory construction performance). In a certain range, asphalt has better high temperature stability when viscosity is higher, so the increment in the viscosity of the AR increased its high temperature stability.
As shown on Figure 3e, the elastic recovery of AR increased with the increase of CR content. When the rubber powder content was between 15% and 17.5%, the elastic recovery increased noticeably, when the content was between 17.5% and 22.5%, the elastic recovery remained basically unchanged. When the CR content was between 22.5% and 25%, resilient recovery continued to grow. As shown in research and practice, satisfactory elastic recovery performance could reduce the residual deformation of pavement material under load, improve the fatigue strength of pavement and reduce the damage of roads [34].
In this research, different contents of CR were added to SK90# matrix asphalt. It can be seen from the analysis above that the indexes of matrix asphalt were improved with the increase of the addition ratio of CR. According to the low temperature ductility test results of the AR, the low temperature ductility of the AR was difficult to reach the requirement of 10 cm. However, all other indexes except for the low temperature ductility index had met the requirements. Therefore, the comprehensive test results suggested that, in practice, the 5 °C ductility technical standard should be revised and, depending on the actual project, a consideration should be made to reduce this index requirement.
Based on the analysis of results above, it was finally determined that the optimal CR addition ratio of AR based on 90# matrix asphalt was 20–25% (external blending).
3.1.2. 70# Matrix Asphalt
Similar tests were conducted with SK70# matrix asphalt for comparison purposes. The upper limit ranges of CR contents were expanded to 16%, 18%, 20%, 22%, 24%, 26% and 28%. The preparation and test methods were the same as previously described. The tests results were shown in Table 7, as following:

Table 7.
Basic physical properties of different AR.
Compared with the test results of 90# matrix asphalt, the trend of SK70# matrix asphalt with CR content between 16% and 26% was basically the same as that of 90# with CR content between 15% and 25% when it comes to rotational viscosity and elastic recovery (Figure 3d,e compared to Figure 4d,e respectively). It is worth noting that the 90# matrix asphalt did not show peaks in 15–25% range, while the 70# matrix asphalt had peaks in the penetration, elastic recovery and ductility index when the CR content was between 24% and 26%. When the CR content continued to increase to 28%, the softening point and viscosity index kept increasing, however, the penetration, elastic recovery and ductility index all showed a downward trend. This indicated that there was an optimum dosage in the range of 22–26% that the AR decreased after the index reached the peak.
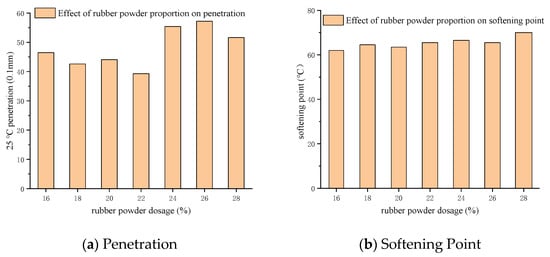
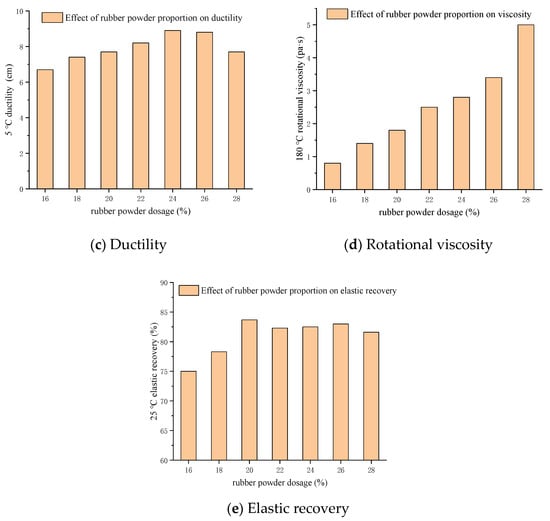
Figure 4.
Effect of CR content on conventional tests result for 70# asphalt.
3.2. Effect of Stabilizers on the Performance of AR
The test results of asphalt rubber properties with three different stabilizers are shown in Figure 5. It can be seen that the physical properties of AR with different types of stabilizers changed significantly. In Figure 5b, the softening point of A-2 and B-2 were 65.7 °C and 72.1 °C, respectively, which was significantly higher than that of the base AR. This indicated that AR with stabilizer 2# could provide higher stiffness to resist long-term traffic and environmental impact. In comparison, stabilizer 1# and 3# did not result in obvious increase in stiffness and achieved similar results to that of the base AR. In terms of penetration (Figure 5a) it could be concluded that the value of A-2 and B-2 were 44.5 and 34.2 dmm, respectively, which was significantly lower than that of the base AR (62.6 and 40.2 dmm). The incorporation of stabilizer 2# resulted in an obvious improvement in penetration. Considering these test results, the stabilizer 2# and 3# could help asphalt rubber obtain better high-temperature property.
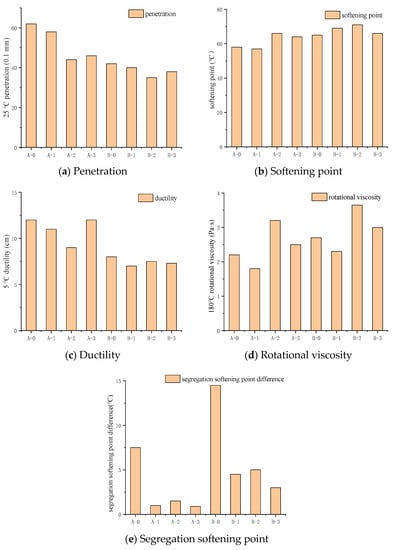
Figure 5.
Effect of three stabilizers on the conventional test of AR of A and B.
Figure 5c–e shows the ductility of the two types of AR decreased slightly after the stabilizers were added. The 180 °C viscosity had an opposite trend with ductility, which increased significantly with stabilizers, in particular, stabilizer 2#. This indicated that all stabilizers could affect the low-temperature property. When the stabilizers were added in the AR, a stable phase interface adsorption layer was formed between the polymer phase in the AR and the virgin asphalt phase, the surface tension of the phase interface was lowered and the two phases were increased [35]. In terms of storage stability, the A type AR had much better stability than that of B. This indicated that B type could only be mixed and applied on site. On the contrary, all the softening point difference of A type AR with stabilizers were less than 1 °C, which was much smaller than the standard requirements. Judging from the results, A type AR could be stored. When the stabilizer was added in the AR, it swelled and promoted the expansion of the volume of the rubber powder particles, which improved the stability and the dynamic viscosity of the asphalt rubber.
Based on these results, the stabilizer produced active radicals, which were cross-linked and grafted with polymer molecular chains such as rubber powder and asphalt functional groups under certain thermal conditions, which influenced the asphalt properties [36]. The stable colloidal system formed between the powder and the asphalt could improve the high-temperature property. It provides a wider range and long-distance transportation of usage for AR. The final choice of stabilizers depends on the construction areas and performance requirements.
3.3. Effect of Different Production Methods on AR
Conventional performance tests were conducted on asphalt rubber using different stirring methods. The test results of 25 °C penetration, softening point, 5 °C ductility, 25 °C elastic recovery and 180 °C viscosity are all shown in Figure 6. It can be seen from Figure 6a,b that a dosage of 20% was a turning point. When the CR content was less than 20%, the AR penetration of the two production methods decreased gradually from 59 and 55 to 53 and 52 cm, respectively. The AR produced by the high-speed shearing method had higher penetration than that of the heat fusion method. When the CR content was more than 20%, the trend changed, and the penetration increased gradually with the CR content increasing. Meanwhile, the AR produced by the heat fusion method had higher penetration and a faster recovery speed. For the softening point, AR had a much higher softening point than that of the asphalt and increased remarkably with increasing the CR content. For the two different methods, the heat fusion method showed a higher softening point, which brought a good high temperature performance to the AR.
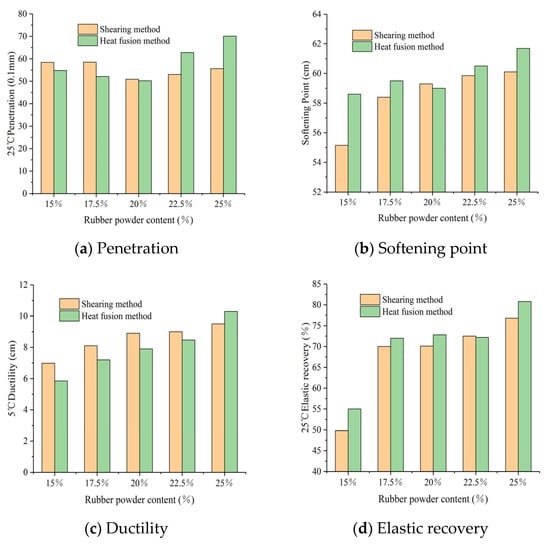
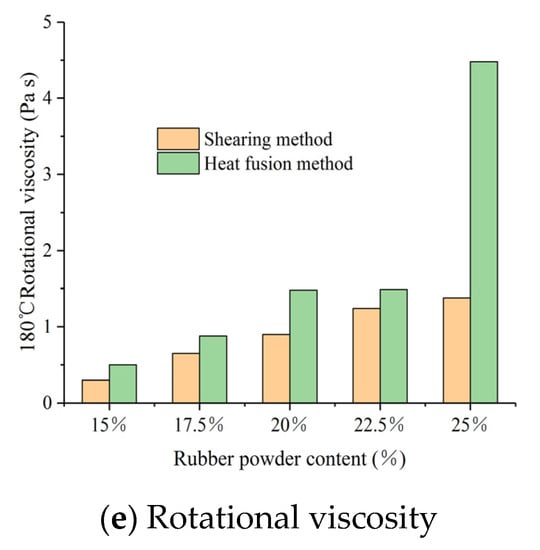
Figure 6.
Effect of two stirring methods on the conventional test of AR.
It can be seen from Figure 6c that the change of ductility was not apparent with the rubber powder content increasing. Almost all the values of ductility were less than 10 cm. When the rubber powder content was less than 25%, the asphalt rubber produced by the shearing method had larger ductility values, and the trend changed only when the content reached 25%. If the rubber powder content was less than 25%, the shearing method was a better choice for obtaining good low temperature properties. According to the test data, the hot melt method was better than the shearing method when the content was higher than 25%. However, good ductility came at the expense of high temperature performance, which led to asphalt aging and influenced the asphalt properties. Overall, the shearing method would be the first choice for AR in the road construction. Based on Figure 6d, the heat fusion method received better elastic recovery with the content less than 15%, which reflected better swelling of rubber powder. Nevertheless, with the content higher than 15%, the shearing method showed its superiority and elastic recovery increased obviously. A similar problem with ductility occurred at 25% content, the elastic recovery with the hot melt method was better than that of the shearing method. It required much higher temperature to swell the rubber powders, which lead to asphalt aging. The test of viscosity highlighted the difference between the two methods. From Figure 6e, the viscosity values with the heat fusion method were always larger than that with the shearing method. Higher viscosity increases the difficulty of road construction and also affects its quality and progress. When the rubber powder content reached 25%, the AR with the heat fusion method had both better elasticity and low temperature property, but the fluidity of AR became very poor.
To conclude, it is possible to improve the elasticity and high temperature property of AR with the heat fusion method. However, the shearing method can further make the rubber particles finer and give better melt reaction with the asphalt, which is more favorable for the large-scale engineering application of AR.
SEM Test of AR
In order to characterize the micromorphology and rheological properties of asphalt rubber in the previous test results, SK90# asphalt with crumb rubber content of 20% was selected. Scanning electron microscopy and rheological properties testing were conducted.
The SEM test was conducted for virgin asphalt and AR, and the results are shown in Figure 7a,b, respectively. It could be clearly seen that the surface of virgin asphalt was very smooth. The asphalt appearance became uneven after mixing it with rubber powder. The rubber powder was completely covered by asphalt. Compared to virgin asphalt, many solid rubber particles were observed in asphalt rubber, indicating that most of the rubber powder particles were completely present in the asphalt, and the irregularly shaped rubber particles could be completely covered by the asphalt medium. Crumb rubber particles around 1 mm and contacting with each other were clearly observed in the AR. It proved the swelling of crumb rubber particles in asphalt. Due to this phenomenon, the light components of asphalt were absorbed by crumb rubber forming a thick gel film around crumb rubber particles. The solid crumb rubber particles got into contact with each other by the ambient gel film. The package was evenly dispersed and formed a stable whole with the asphalt. The presence of the rubber powder particles was the main reason for the significant decrease in the ductility after the modification of the asphalt.
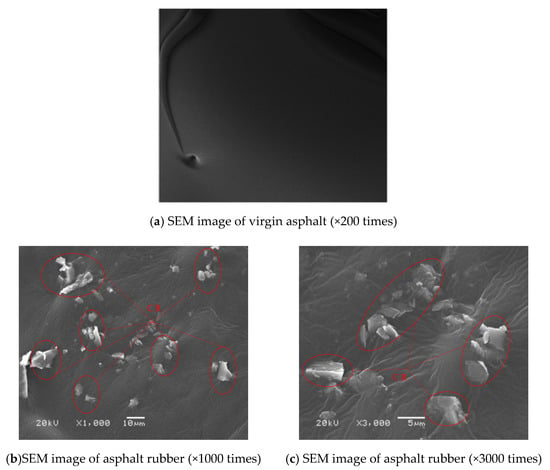
Figure 7.
SEM images of asphalt and asphalt rubber.
3.4. Rheological Properties of AR
BBR test
According to the previous research [37], there were several criterions on the stiffness modulus and m-value in the BBR tests. Creep stiffness should be smaller than 300 MPa and the m-value should be larger than 0.30. The small creep stiffness or the large m-value would lead to a better low-temperature performance.
Based on BBR tests at low temperatures, the cracking parameters including creep stiffness (S) and creep rate (m) were measured and results are shown in Figure 8. Overall, it can be deducted from these figures that the asphalt rubber had higher m-value and lower S at different temperatures, and that all obtained data satisfied the requirements. The results showed that the stiffness (S) of both virgin asphalt and asphalt rubber increased and that the creep rate (m) decreased with temperature decreasing. The stiffness (S) of AR with crumb rubber content increasing indicated that this addition enhanced the cracking potential of asphalt. It is well known that the higher the creep rate (m), the quicker the stress could be released, and hence the better the cracking resistance of the asphalt rubber. Therefore, the crumb rubber would improve the cracking resistance of asphalt, and this was consistent with the low-temperature creep stiffness analysis.
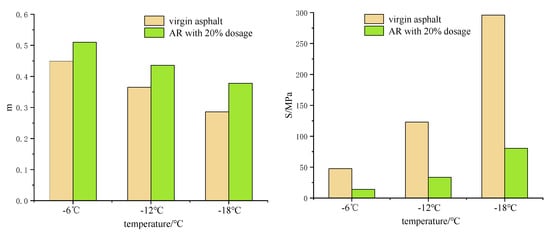
Figure 8.
Creep S and m of asphalt rubber.
DSR test
The asphalt rutting factor (G*/sin (δ)) was developed by the SHRP in the 1990s and was mainly used as an index in performance evaluation at high temperatures. A criterion specified by Superpave was G*/sin (δ) was higher than 1 kPa for fresh asphalt binders. The asphalt rutting factor (G*/sin (δ)) of different types of asphalt binder at different temperatures is shown in Figure 9. It could be noticed that the asphalt rubber experienced higher G*/sin (δ) than the virgin asphalt. When the temperature was greater than 65 °C, virgin asphalt did not meet the criterion, and high temperature performance was not satisfactory. Meanwhile, the asphalt rutting factor (G*/sin (δ)) of asphalt rubber remained higher than 1 kPa and satisfied the requirement, showing a better high temperature performance. Therefore, the addition of crumb rubber could significantly improve the rutting resistance of the asphalt and make positive improvement to its high temperature performance.
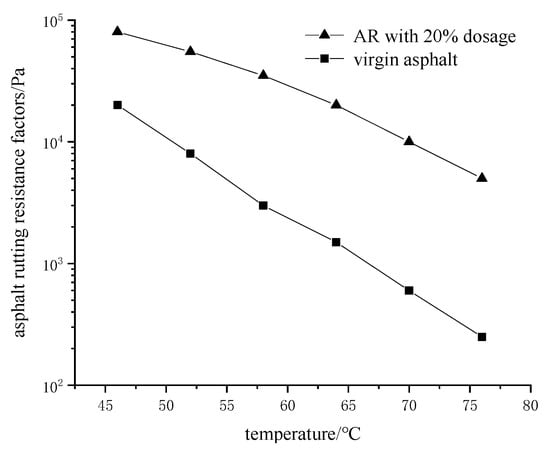
Figure 9.
Rutting resistance factors of virgin asphalt and asphalt rubber at different temperatures.
4. Conclusions
The experimental results of this study showed the effect of different factors on the AR properties. The main conclusions drawn based on the test results are as follows:
(1) The CR dosage was a crucial element towards the improvement of the AR characteristics. The CR content of 20–25% (external blending) was optimal for the physical properties of SK90# matrix asphalt, while 22–26% was better for SK70# matrix asphalt. The addition of crumb rubber could significantly improve the high temperature performance of the asphalt, and its cracking and rutting resistance. The variation of asphalt performance within the dosage range was basically consistent in the same interval.
(2) The addition of stabilizers could significantly improve the high temperature stability of asphalt rubber, but only slightly affect its low temperature performance. In addition, the stabilizers used in this study could all reduce the segregation softening point, which was benefit to the storage of asphalt rubber.
(3) The production modes could significantly affect the physical properties of AR due to different fusion states. The rubber particles are further shredded during the shearing process and would easily disperse and melt in the asphalt, which had much lower viscosity than that of the hot melt method. The AR produced by the shearing method was the optimal choice for site construction because of the more balanced physical performance.
(4) The production method, preparation process, crumb rubber content and stabilizer will all affect the distribution of rubber powder and properties of asphalt rubber. Though the heat fusion method can improve the elasticity and high temperature property of asphalt rubber, shearing method can give better melt reaction with asphalt, which is more favorable for large-scale engineering applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L.; methodology, H.L.; validation, H.L. and Q.M.; formal analysis, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.L.; writing—review and editing, A.A.T. and G.Z.; supervision and project administration, Q.M. and D.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Project of Henan Department of Transportation (2020J-2-3), Science and Technology Project of Shanxi Department of Transportation (No.17-32T, No.17-05K, No.19-10K, No.19-28K), and Rising Tech Star Project of Shanxi Department of Science and Technology (No.2019KJXX-035).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, O.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z. Pavement Performance of Asphalt Mixtures with Economical Low Content Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. J. Chongqing Jiao Tong Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 5, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q. Thoughts on High Quality Development of Recycled Rubber in China. China Rubber. 2018, 12, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Ali, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Hafeez, I. Performance Evaluation of Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt Mixtures Based on Laboratory and Field Investigations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Dong, B.; Zhao, D. Physical, Rheological and Stability Properties of Desulfurized Rubber Asphalt and Crumb Rubber Asphalt. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5043–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.P.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.Y.; Su, N.Y.; Hou, X.D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. Mechanism and Research Development of Noise Reduction Technology of Rubberized Asphalt Pavement. China J. Highw. Transp. 2019, 32, 73–91. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.; Guo, S.; Chen, S.; You, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q. Strength and durability of dry-processed stone matrix asphalt containing cement pre-coated scrap tire rubber particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Jiao, L.; Ni, F. Evaluation of plastic–rubber asphalt: Engineering property and environmental concern. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, H.; Geng, J.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, R. Production and performance of desulfurized rubber asphalt binder. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Liu, K.; Wu, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, Z. Effect of LDHs on the aging resistance of crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Holikatti, S.; Vacura, P. Caltrans use of scrap tires in asphalt rubber products: A comprehensive review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 1, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Wang, J.G.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Imaninasab, R. Investigating the effectiveness of Vacuum Tower Bottoms for Asphalt Rubber Binder based on performance properties and statistical analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.H.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, D.Y. Experimental study of stable crumb rubber asphalt and asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souliman, M.I.; Eifert, A. Mechanistic and Economical Characteristics of Asphalt Rubber Mixtures. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2016, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venudharan, V.; Biligiri, K.P.; Das, N.C. Investigations on behavioral characteristics of asphalt binder with crumb rubber modification: Rheological and thermo-chemical approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z. Study on the road performance of warm mixed rubber asphalt mixture gradations. J. Xian Univ. Archit. Technol. 2018, 50, 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.K.; Qi, C.P.; Zheng, K.J.; Zhao, M.Z. Test on Low-temperature Performance for High-temperature Pyrolytic Rubber Modified Asphalt. China J. Highw. Transp. 2017, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Fang, C. Dynamic stability of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer/crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. China Highw. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Huang, W.; Xiao, F. Chemical and rheological investigation of high-cured crumb rubber-modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, S.; Kutay, M.E. Use of crumb rubber in lieu of binder grade bumping for mixtures with high percentage of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikarimi, P.; Rahi, M.; Nejad, F.M. Comparing different rutting specification parameters using high temperature characteristics of rubber-modified asphalt binders. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertloypanyachai, P.; Thongsang, S. Improving the mechanical properties of rubber floor tiles by rock powder particle as filler in natural rubber. Mater. Today: Proc. 2018, 5, 14907–14911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-yan, L.I.; Lu, P.I.; Hai-nian, W.A.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhan-ping, Y.O. Performance test of rubber asphalt based on domestic and abroad test methods. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2015, 15, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.Z.; Du, S.J.; Cai, L.; Mu, J.Q.; Wang, H. Research on the Influences of Mesh Number of Rubber Powder and Temperature on the Performance Properties of the Rubber Asphalt. North. Commun. 2018, 9, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavibazoo, A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Ragab, M. Changes in composition and molecular structure of asphalt in mixing with crumb rubber modifier. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2016, 17, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavibazoo, A.; Abdelrahman, M. Composition analysis of crumb rubber during interaction with asphalt and effect on properties of binde. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavibazoo, A. Characterization of activities of crumb rubber in interaction with asphalt and its effect on final properties. Diss. Theses Gradworks 2014, 17, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Xuanrui, G. Research on the influence factors of asphalt rubber mixture fatigue performance. In Proceedings of the C. 2016 IEEE International Conference of Online Analysis and Computing Science (ICOACS), Chongqin, China, 28 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Egami, K.; Kimura, M.; Hamaguchi, T. Effect of Crumb Rubber Modifier Dissolution on Storage Stability of Crumb Rubber–Modified Asphalt. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2370, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S. Effect of stirring method and stirring temperature on the performance of rubber asphalt. Highw. Automot. Appl. 2013, 11, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Qin, J. Study on Rheological Properties of Microwave Activated Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2018, 42, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, G.T.; Ye, F. Study on rheological and microscopic properties of rubber asphalt based on activation temperature. Highw. Eng. 2019, 44, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.D. Study on anti cracking performance of crumb rubber asphalt. Highw. Transp. Technol. (Appl. Technol. Ed.) 2019, 15, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.N.; Zhao, L.; Han, J.W.; Sun, G.N. High temperature rheological properties and microstructures of asphalt under salt freezing cycles. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2017, 34, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Omari, A.; Taamneh, M.; Khasawneh, M.; Al-Hosainat, A. Effect of crumb tire rubber, microcrystalline synthetic wax, and nano silica on asphalt rheology. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Fan, W.; Yang, G.; Han, L.; Xing, B.; Lv, X. Influence of crumb rubber particle size and SBS structure on properties of CR/SBS composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Hao, P.W. Rheological properties and modification mechanism of RET compound rubber modified asphalt. Mater. Rev. 2016, 30, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).