Abstract
Ultrastructural observation of biological specimens or nanogranules usually requires the use of electron microscopy. Electron microscopy takes a lot of time, requires many steps, and uses many chemicals, which may affect the native state of biological specimens. A novel microchip (K-kit) was used as a specimen kit for in situ imaging of human platelet granules in an aqueous solution using a transmission electron microscope. This microchip enabled us to observe the native human platelet granules very quickly and easily. The protocols included blood collection, platelet purification, platelet granule isolation, sample loading into this microchip, and then observation by a transmission electron microscope. In addition, these granules could still remain in aqueous solution, and only a very small amount of the sample was required for observation and analysis. We used this microchip to identify the native platelet granules by negative staining. Furthermore, we used this microchip to perform immunoelectron microscopy and successfully label α-granules of platelets with the anti-P-selectin antibody. These results demonstrate that the novel microchip can provide researchers with faster and better choices when using a transmission electron microscope to examine nanogranules of biological specimens in aqueous conditions.
1. Introduction
The ultrastructure of biological specimens is usually examined using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). To obtain high-resolution images of the ultrastructure, traditional TEM requires several complicated steps, including sample fixation, dehydration, infiltration, embedding, ultrathin sectioning, and staining [1]. If one of these steps is not done well, the ultrastructural image may show many artifacts. Therefore, it takes a lot of time and high-level techniques to observe the ultrastructure of biological samples using traditional TEM. In addition, because most biological specimens are soft and rich in water, samples need to be fixed, dehydrated, infiltrated, and embedded with many chemicals before ultrathin sectioning can be performed. These chemicals likely affect the original ultrastructure [2]. Therefore, many morphologists are actively looking for faster and more effective materials and methods to observe nanoscale biological samples without affecting their ultrastructure.
Liu et al. [3] developed a microchip (called the K-kit), which can directly observe nanoparticles in an aqueous solution, providing an impressive method to observe the ultrastructure of biological specimens. This microchip contains a sample chamber, which consists of SiO2 nanomembranes with an observation window. Specimens in aqueous solution can be loaded into the chamber and then examined by an electron microscope. Previously, images of non-biological particles and living bacteria were successfully demonstrated with this microchip [3,4,5]. Sample preparation steps of this microchip are simpler and faster than those of traditional TEM. In addition, no chemicals are required for fixation, dehydration, infiltration, or embedding, so biological specimens can be kept in their native state. Although the microchip was used to quantify nanoparticles in plasma [6], it still has not been confirmed whether granules of living human platelets in an aqueous solution can be examined with this microchip. In this study, we performed negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy to quickly identify specific granules of human platelets using this microchip.
Platelets are small, anucleated blood cells that execute many important functions in the clotting of blood under physiological and pathological conditions. They play an initial role in maintaining the integrity of blood vessels and are the first line of defense against hemorrhaging by forming a thrombus. The coagulation cascade is initiated by thrombin production induced by activation of platelets and release of granules [7,8]. Functional roles of platelets have expanded in recent years to include processes such as inflammation, innate immunity, growth and development, angiogenesis, wound healing, and cancer metastasis [9,10,11]. The exocytosis of platelet granules is important to platelet function and participates in platelet activities [12]. Platelets contain at least three major types of granules: α-granules, dense granules, and lysosomes. These different membrane-bound granules contain specific mediators and molecules and create various functions of platelets [13,14].
α-Granules are the most abundant granules and the major protein storage compartment in platelets. They contain some membrane-associated receptors (for example, P-selectin) and several soluble substances (for example, platelet factor 4, fibrinogen, thrombospondin, platelet-derived growth factor, etc.) [15,16]. Exocytosis of α-granules is evaluated primarily through plasma membrane expression of P-selectin as assessed by flow cytometry or estimating the release of granule substances [17]. More recent work using serial block face-scanning electron microscopy for a 3D ultrastructural analysis showed that α-granules in resting human platelets are ovoid with a generally homogeneous matrix [18]. Several studies explored homogeneity in the size, shape, and composition of α-granules [19,20,21].
Dense granules (also known as δ-granules) are another important type of granule in platelets. Under an electron microscope, their ultrastructure consists of extremely electron-dense cores surrounded by clear spaces enclosed by a single membrane [22]. Dense granules contain many biologically active molecules (for example, adenosine diphosphate, adenosine triphosphate, guanosine 5’-triphosphate, guanosine 5’-diphosphate, calcium, and serotonin) [23,24]. External membrane of a dense granule contains lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP 2), cluster of differentiation 63 (CD63 also known as LAMP 3), and multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) [25,26].
Functional analysis of platelets requires isolation and purification of membrane-bound granules and cellular compartments. Protocols of sucrose density gradient separation or an immunomagnetic sorting method for purification and determination of the types of isolated platelet granules takes 1–2 days to complete [27]. In this study, we used the recently developed microchip (K-kit) to quickly observe and identify types of isolated platelet granules in an aqueous solution by negative staining. In addition, we also used this microchip to perform immunoelectron microscopy to distinguish and confirm the α-granules using an anti-P-selectin antibody. Results of this study can provide an advanced method and technology for faster observation of the ultrastructure of nanoscale biological specimens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Collection and Platelet Preparation
Human platelet suspensions were prepared as previously described [28]. In brief, fresh whole blood was collected from healthy volunteers who had taken no medications during the preceding 2 weeks. Fresh blood was immediately mixed with an acid citrate-dextrose (ACD) solution (9:1, v/v; 0.1 M citric acid, 0.2 M sodium citrate, and 0.4 M dextrose; pH 6.8), which functioned as an anticoagulant and antistimulant for platelets. After centrifugation (at 2200 rpm for 10 min), the supernatant (platelet-rich plasma) was collected and supplemented with EDTA (2 mM) and heparin (6.4 U/mL). Washed platelets were centrifuged (at 3500 rpm for 8 min) and then suspended in Tyrode’s solution containing bovine serum albumin (BSA; 3.5 mg/mL). The final concentration of Ca2+ in Tyrode’s solution was 1 mM. This study conformed to the directives of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Taipei Medical University (TMU-JIRB-N201812024). An informed consent form was provided to all human blood donors involved in the study.
2.2. Platelet Granules Isolation
Procedures of platelet granules isolation were based on methods published by Jena et al. [29]. In brief, 1 mL of purified platelet preparation was added to 3 mL of ice-cold double-distilled (dd) H2O and gently mixed for 2 min to make a hypotonic platelet lysis solution. Next, 0.5 mL of ice-cold 10× phosphate-buffered saline (10 × PBS; 1370 mM NaCl, 27 mM KCl, 100 mM Na2HPO4, and 18 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4) was added and mixed to make iso-osmotic suspension medium. The lysed platelet suspension was centrifuged at 14,000× g for 6 min, and the resultant suspension was the total remaining vesicle preparation containing platelet granules for observation and immunoelectron microscopy.
2.3. Conventional TEM
To investigate the internal ultrastructure of platelets and granules, we observed the morphology using conventional TEM. Purified platelets in Tyrode’s solution were resting or activated by collagen (1 ng/mL) for 10 min at 37 °C, and then incubated with a mixed aldehyde solution composed of 2% paraformaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) for 30 min at 4 °C. Subsequently, samples were centrifuged (at 3500 rpm for 8 min), and then the pellets were postfixed using 1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2). After dehydration in an ethanol series, samples were infiltrated with propylene oxide and embedded in Epon according to standard procedures. Ultrathin sections were cut and double-stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and then examined in a Hitachi H-600 electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. Negative Staining of Isolated Platelet Granules with the K-kit Microchip
A microchip (called K-kit) was used to observe isolated platelet granules in aqueous condition according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Materials Analysis Technology Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan). The K-kit microchip provides a narrow chamber (300 μm long, 25 μm wide, and 2 μm high) suitable for observing isolated platelet granules. In negative staining, the sample solution (10 μL) was mixed with 1% uranyl acetate (10 μL) before loading. After that, the mixture was placed on paraffin paper and then loaded into the narrow chamber of the microchip by capillary suction for 2 min at room temperature. After loading the sample, the sample chamber was sealed at both ends with Torr Seal Kit (containing epoxy resin and hardener), and then the microchip containing the sample was adhered to a copper grid by the mounting medium. The copper grid with the microchip was placed on the holder, and then examined in an electron microscope.
2.5. Immunoelectron Microscopy Using the K-kit Microchip
In order to confirm the presence of specific platelet granules, we performed immunoelectronic microscopy with a specific antibody. First, we used a poly-L-lysine solution (0.1% w/v) to promote adhesion of isolated platelet granules to the sample chamber to carry out immunostaining. The microchips were coated with poly-L-lysine solution for 20 min, and then dried at 37 °C for 1 h. After that the isolated platelet granules were loaded into the poly-L-lysine-coated sample chamber for 30 min at room temperature to allow the adhesion of platelet granules. Samples were then fixed with 0.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffer (PB, pH 7.4) for 10 min. After washing with PB, non-specific binding was blocked using 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 30 min at room temperature. Samples were then incubated with the primary antibody (mouse monoclonal anti-P-selectin antibody) for 2 h at 37 °C. The anti-P-selectin (CD62P, clone AK-6) antibody was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). After washing with PB, samples were reacted with a secondary antibody (6-nm gold-conjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody) for 2 h at 37 °C. The secondary antibody was purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch Inc. (West Grove, PA, USA). After washing with PB, the chamber of the microchip was sealed, adhered to a copper grid, and then examined in the electron microscope.
3. Results
3.1. The Structure and Instructions of the K-Kit Microchip
The structure of the microchip was mainly composed of silicon. The shape of the microchip was an octagonal cuboid block at 1.7 mm in the long-axis, 1.4 mm in the short-axis, and 0.8 mm in height; a schematic diagram is shown on Figure 1A. The sample chamber is a long, narrow, flat canal, located in the middle of the microchip. The sample chamber wall was composed of SiO2 membrane. There was a hollow observation window (300 μm × 25 μm × 2 μm) located in the center of the sample chamber of the microchip. The electron beam could pass through the observation window and then pass through the sample. If a specimen is electron-dense, the electron beam will be blocked or shifted, so a darker image was displayed. Since the sample chamber is a narrow channel, the sample can be loaded into the chamber through capillary suction. By touching the aqueous solution with the opening of sample chamber (located on both ends), the specimen can be drawn into the sample chamber (as shown by the oval circle in Figure 1A). After the specimen enters the sample chamber, both ends of the sample chamber were sealed with a Torr Seal Kit (containing epoxy resin and hardener), and then the entire microchip was placed on and adhered to a copper grid (with an outside diameter of 3 mm and inside diameter of 1 mm). The copper grid with the microchip was placed in the sample holder and examined in the electron microscope (Figure 1B).
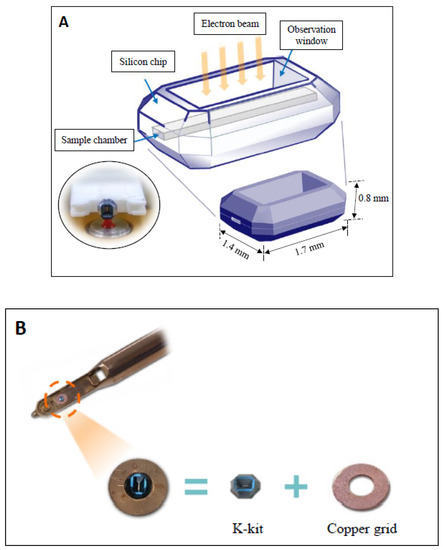
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the K-kit microchip. (A) The three-dimensional structure of the K-kit microchip, which is composed of silicon metal, appeared as an octagonal cuboid-like block (1.7 mm × 1.4 mm × 0.8 mm). There are two small sample chamber openings on the left and right ends of the long axis of the microchip. The liquid specimen can naturally enter the sample chamber by touching the specimen through the openings (as shown in the ovoid circle). The upper and lower sides of the microchip are depressed to form an observation window. Only the area of the observation window allows the electron beam of electron microscope to pass through the specimen to generate a high-resolution image of the specimen. (B) After the K-kit microchip is loaded with the liquid specimen, the two ends of the sample chamber are sealed, and the microchip is placed and fixed in the center of a copper grid (3 mm in diameter with a 1 mm diameter hole in the center). The grid combined with the microchip can be directly placed on the grid holder of a traditional electron microscope for ultrastructural examination.
3.2. Images of Platelets and Granules by Traditional TEM
Isolated resting platelets were round or ovoid biconvex discoid and had an average diameter of 2–3 μm in the long axis. In a traditional EM, we could identify the mitochondria, vacuoles, and several membrane-bounded granules in the cytoplasm (Figure 2A). There were two major types of membrane-bounded granules. α-Granules were abundant, homogeneous pale-staining, and about 200–300 nm in diameter. Dense granules were darkly stained and smaller than α-granules. Since there were fewer dense granules, they were not as easily visible in sections. The platelet also contained round or elongated membrane-bounded vesicles or vacuoles that represented sections of the open canalicular system (OCS), the opening of which is located on the surface of the platelet (Figure 2A).
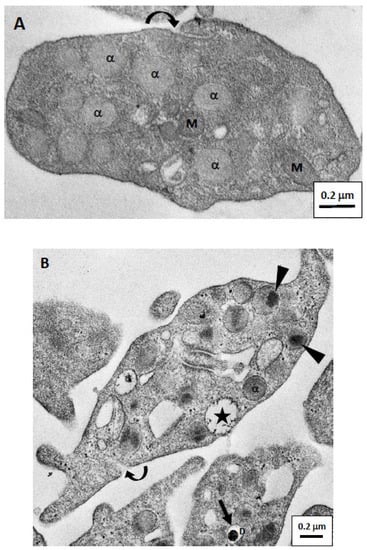
Figure 2.
Electron micrographs of resting and active human platelets. (A) A resting platelet is oval (with a long axis length of about 2 µm), and filled with many membrane-bound granules. Most of these granules were α-granules of about 200 nm in diameter that contained gray homogeneous substances. In addition, we could identify mitochondria and small vesicles in the cytoplasm. However, no dense granule was observed in this figure. The curved arrow indicates an opening of an open canalicular system (OCS) on the surface membrane of the resting platelet. (B) The active platelet showed the extended pseudopods. The α-granules in the active platelets had a more-dense electron core (indicated by arrowheads) after activation. The curved arrow also indicates an opening of OCS on the surface membrane of the active platelet. In addition, we observed that granule substances were released from the membrane because the granule was in contact with the membrane and liquid substances were exuded (indicated by asterisk). A dense granule with a high-density core surrounded by a stain-free rim (indicated by arrow) can be seen in another platelet below the picture. α, α-granule; D, dense granule; M, mitochondria; scale bar, 0.2 μm.
During the initial stage of activation, platelets showed pseudopodia formation and release of components from the granules (Figure 2B). Granules released their contents either directly onto the surface or into the OCS. We observed that granule contents were being released from the surface of activated platelets (asterisk in Figure 2B). In addition, a relatively central electron-dense core was usually separated from the membrane in α-granules of activated platelets (arrowheads in Figure 2B). Dense granules were smaller than α- granules, and had a high-density core surrounded by a stain-free rim (as shown in Figure 2B).
3.3. Negative Staining Images of Platelet Granules with the K-kit Microchip
Isolated platelet granules in aqueous solution were mixed with uranyl acetate to carry out negative staining, then directly examined using the K-kit microchip under an electron microscope. The micrograph shows that there were several types of granules in the chambers of the microchip (Figure 3A). Round or ovoid pale-staining membrane-bound granules might be α-granules with an average diameter of about 200 nm in the long axis and 100 nm in the short axis (Figure 3B). The other small granules or vesicles might be lysosomes, vacuoles, or fragments of the OCS. However, the number of dense granules was few, so we did not find and identify the electron-dense core with membrane-bound granules in negative staining samples.
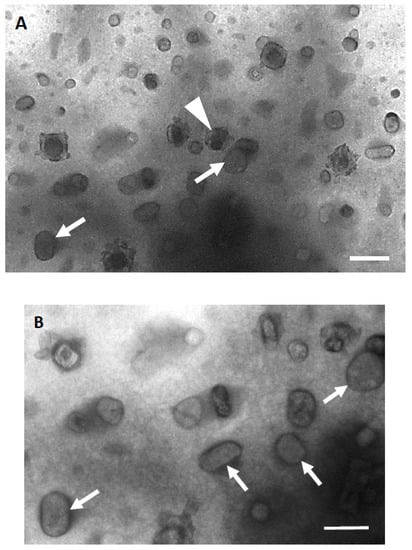
Figure 3.
Negative staining electron micrographs of isolated platelet granules in the microchip. (A) There are many types of isolated platelet granules with different sizes in the micrograph. The boundary of isolated platelet granules was black after negative staining. Among them, α-granules are large and round or oval in shape, with homogeneous gray content (indicated by white arrows). A dense granule with a high-density core surrounded by a stain-free rim was also identified (indicated by a white arrowhead). The small circular vesicles with low electron density and whitish-gray in color are lysosomes or exosomes. Some broken granules could also be observed. (B) The negative stained granules was shown in higher magnification. The α-granules (indicated by white arrows) could be identified with a long axis length of about 200 nm. Scale bar, 0.2 μm.
3.4. Identification of α-Granules by Immunogold Labeling Using the K-Kit Microchip
We used the K-kit microchip to perform immunoelectron microscopy to identify the α-granules of platelets using the anti-P-selectin antibody. There were several different size granules in the chamber of K-kit microchip. The boundary of granules was not very clear because we did not execute negative staining to avoid masking the label of gold particles. Use the immunogold labeling technique by the anti-P-selectin antibody demonstrated that a heavy decoration of gold particles was located on the surface of granules (Figure 4A). Several small vesicles not labeled by abundant gold particles might be lysosomes or exosomes. The average diameter of granules, which were decorated by abundant gold particles, was about 200 nm and they should be the α-granules (Figure 4B). These results suggested that we could successfully perform the immunogold labeling technique to identify specific nanogranules using this K-kit microchip.
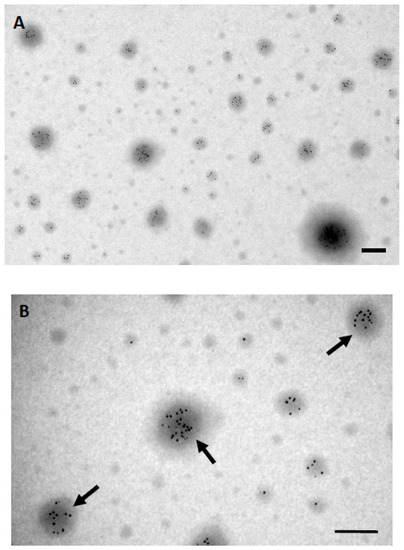
Figure 4.
Immunoelectron micrographs of isolated platelet granules in the microchip. (A) This picture shows that the 6-nm gold particle-labeled granules are α-granules, because P-selectin is located on the surface of these granules. The other vesicles not significantly labeled by gold particles might be lysosomes or exosomes. (B) The gold particles labeled granules were shown in higher magnification. There are abundant gold particles located on the surface of α-granules (indicated by arrows). Scale bar, 0.2 μm.
4. Discussion
In this study, a newly developed novel microchip was used to quickly examine nanogranules of human platelets in an aqueous solution. We could identify α-granules of platelets by negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy using this microchip. Due to the required sample volume being very small and the steps being simple, this microchip and technology are believed to have more applications for observing nanogranules in the biomedical field in the future.
In the past, to observe the ultrastructure of biological specimens, investigators usually used TEM, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), or cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM). The specimen had to be fixed, dehydrated, infiltrated, and embedded in resin to obtain ultrathin sections, and then the ultrastructure of the sample was examined under an electron microscope [1]. Using SEM, specimens do not need to go through the steps of embedding and sectioning, but they must be dried and coated with metal particles, and only the surface structure of the sample can be observed [30]. Cryo-EM fixes specimens and obtains ultrathin sections by rapid freezing, without the need to administer many chemicals, which can maintain the native ultrastructure of a specimen. However, the operation process and experimental equipment of Cryo-EM have strict requirements to protect the specimen and prevent artifacts [31,32]. The specimen preparation for this novel microchip is relatively simple and rapid to observe the ultrastructure compared with that for TEM, SEM, or CryoEM. In addition, the specimen needs to be fixed with chemicals or liquid nitrogen in existing used technologies, but the specimen in this microchip can maintain its native state in the buffer or aqueous solution and can be directly observed under an electron microscope.
Currently, flow cytometry is a powerful technique used to detect and isolate specific cells or particles according to their physical and chemical characteristics [33]. Functional analyses of platelets or granules often use flow cytometry [34]. Flow cytometry uses light properties scattered from cells or granules for identification or quantitative measurements of physical properties. More properties of a cell or granule can be explored, and more labels, dyes, and antibodies can be used for multi-parametric analyses. Therefore, the use of flow cytometry for particle identification or separation requires a lot of time, and samples should be labeled with antibodies to obtain sufficient results. The novel K-kit microchip requires only a very small amount of sample to quickly identify different granules, and can be used to perform morphological observations and comparative quantitative analyses. We could achieve qualitative analysis by comparing the shape of granules. In addition, the size of the nanoparticles can be directly measured and quantitatively analyzed.
In addition, when using this novel K-kit microchip, the amount of biological samples required is less than 10 µL. Therefore, this novel microchip is very suitable for use if biological samples are very precious or difficult to obtain. In addition, the protocols from whole-blood collection, platelet-rich preparation, isolation of platelet granules, and then examination by electron microscope just took less than 6 h using the microchip in this study. This allows investigators engaged in platelet research to quickly confirm and analyze the types of granules in a preparation and then proceed with advanced research.
The disadvantage of this novel microchip is that it can only provide observation of the structure of tiny particles. Samples with a diameter of >2 μm cannot enter the chamber of this novel microchip. In addition, long-term observation can easily cause a specimen to be damaged by the irradiation of the electron beam, so the preparation must be observed and photographed as soon as possible after the preparation is completed.
In summary, this study used a newly developed novel K-kit microchip to successfully observe granules of human platelets in an aqueous solution. In addition, the type of granules was distinguished by immunoelectron microscopy, showing that this novel microchip can be used not only to directly observe tiny nanoscale biological specimens, but also to perform immunoelectron microscopy. Although this novel microchip has some disadvantages, compared to traditional TEM, SEM, Cryo-EM, and flow cytometry, it still has many advantages such as simple specimen preparation, no impact of chemical substances, and low technical requirements. We believe that these materials and technologies will have more applications for observing tiny granules or particles in the biomedical field in the future.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a novel K-kit microchip was used to successfully observe native nanogranules of human platelets in an aqueous solution. Compared to traditional TEM, SEM, Cryo-EM, and flow cytometry technologies, the microchip is simpler and easier to operate. In addition, this novel microchip can also be used for immunoelectron microscopy to successfully label and identify the isolated α-granules of platelets. We believe that such materials and technologies will enjoy additional development and future applications in biomedicine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.-H.F.; Funding acquisition, C.-C.C. (Chao-Chien Chang); Investigation, N.T.T.T.; Methodology, H.-M.C.; Project administration, J.C.; Resources, C.-C.C. (Chih-Chun Chen); Supervision, J.C.; Validation, W.-A.C.; Writing—original draft, N.T.T.T.; Writing—review and editing, C.-C.C. (Chao-Chien Chang) and T.-H.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST108-2314-B-281-006) and Cathay General Hospital (CGH-MR-A10901).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate J.R. Sheu provided human platelet suspensions for this experiment (TMU-JIRB-N201812024). We also thank Materials Analysis Technology Inc. (MA-tek, Hsinchu, Taiwan) for providing the K-kit microchips. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST108-2314-B-281-006) and Cathay General Hospital (CGH-MR-A10901).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russell, L.D. Specimen Preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy. In Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Boston, NV, USA, 1992; pp. 14–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini, D.D.; Bensch, K.; Barrnett, R.J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy: The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 19–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, Y.J.; Peng, H.L.; Chang, H.Y.; Chang, P.; Hsu, L.; Yew, T.R. Novel microchip for in situ TEM imaging of living organisms and bio-reactions in aqueous conditions. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.J.; Cheng, W.L.; Huang, S.C.; Chen, Y.P.; Chou, H.K.; Cheng, H.F. Characterizing titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreen spray. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.E.; Hong, Y.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Kang, Y.T.; Chang, P.; Yew, T.R. Direct-writing of Cu nano-patterns with an electron beam. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, L.A.; Kang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Liu, K.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Ko, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Quantitative characterization of nanoparticles in blood by transmission electron microscopy with a window-type microchip nanopipet. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6312–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.J. Platelet physiology and abnormalities of platelet function. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 293, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattil, S.J.; Bennett, J.S. Platelets and their membranes in hemostasis: Physiology and pathophysiology. Ann. Intern. Med. 1981, 94, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.G. Interaction of vascular endothelial cells with leukocytes, platelets and cancer cells in inflammation, thrombosis and cancer growth and metastasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Mezouar, S.; Mege, D.; Darbousset, R.; Farge, D.; Debourdeau, P.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Involvement of platelet-derived microparticles in tumor progression and thrombosis. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varon, D.; Shai, E. Platelets and their microparticles as key players in pathophysiological responses. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, C.G.; Michelson, A.D.; Flaumenhaft, R. Granule exocytosis is required for platelet spreading: Differential sorting of α-granules expressing VAMP-7. Blood 2012, 120, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirlashari, M.R.; Ryningen, A.; Mikkelsen, H.M.; Fukami, M.H. Differential secretion of blood platelet storage granules. Platelets 1996, 7, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.M.; Reed, G.L. Development of platelet secretory granules. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg, P.E.; McEver, R.P.; Schuman, M.A.; Jacques, Y.V.; Bainton, D.F. A platelet alpha-granule membrane protein (GMP140) is expressed on the plasma membrane after activation. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.; Cramer, E.M. Platelet alpha-granules. Blood Rev. 1993, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, J.C.; Escolar, G.; Sanz, C.; Cases, A.; Villamor, N.; Nieuwenhuis, H.K.; López, J.; Ordinas, A. Platelet activation during hemodialysis measured through exposure of p-selectin: Analysis by flow cytometric and ultrastructural techniques. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1994, 124, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pokrovskaya, I.D.; Yadav, S.; Rao, A.; McBride, E.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Zhang, G.; Aronova, M.A.; Leapman, R.D.; Storrie, B. 3D ultrastructural analysis of α-granule, dense granule, mitochondria, and canalicular system arrangement in resting human platelets. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 4, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamykowski, J.; Carlton, P.; Sehgal, S.; Storrie, B. Quantitative immunofluorescence mapping reveals little functional coclustering of proteins within platelet α-granules. Blood 2011, 118, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Storrie, B. The cellular basis of platelet secretion: Emerging structure/function relationships. Platelets 2017, 28, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lo, R.W.; Urban, D.; Pluthero, F.G.; Kahr, W.H. α-Granule biogenesis: From disease to discovery. Platelets 2017, 28, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cheng, L.H.; Cui, X.; Lei, X.X.; Tang, J.B.; Cheng, B. Investigating the effect of age on platelet ultrastructure using transmission electron microscopy. Int. Wound J. 2019, 16, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, M.H.; Salganicoff, L. Human platelet storage organelles. A review. Thromb. Haemost. 1977, 38, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicol, A.; Israels, S.J. Platelet dense granules: Structure, function and implications for haemostasis. Thromb. Res. 1999, 95, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israels, S.J.; McMillan, E.M.; Robertson, C.; Singhory, S.; McNicol, A. The lysosomal granule membrane protein, LAMP-2, is also present in platelet dense granule membranes. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 75, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedlitschky, G.; Tirschmann, K.; Lubenow, L.E.; Nieuwenhuis, H.K.; Akkerman, J.W.; Greinacher, A.; Kroemer, H.K. The nucleotide transporter MRP4 (ABCC4) is highly expressed in human platelets and present in dense granules, indicating a role in mediator storage. Blood 2004, 104, 3603–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, J.; Jedlitschky, G.; Greinacher, A.; Kroemer, H.K. Isolation of platelet granules. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2010, 46, 3.35.1–3.35.14. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, G.; Lee, J.J.; Lin, K.H.; Shen, C.H.; Fong, T.H.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. Characterization of a novel and potent collagen antagonist, caffeic acid phenethyl ester, in human platelets: In vitro and in vivo studies. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 75, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, B.P.; Stemmer, P.M.; Wang, S.; Mao, G.; Lewis, K.T.; Walz, D.A. Human platelet vesicles exhibit distinct size and proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russell, L.D. Specimen Preparation for Scanning Electron Microscopy. In Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Boston, NV, USA, 1992; pp. 40–62. [Google Scholar]
- Nogales, E.; Scheres, S.H. Cryo-EM: A unique tool for the visualization of macromolecular complexity. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, E. Cryo-EM. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R1127–R1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, J.; Guerin, C.L.; Kim, C.L.V.; Boulanger, C.M. Flow cytometry: Retrospective, fundamentals and recent instrumentation. Cytotechnology 2012, 64, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasalic, L.; Pennings, G.J.; Connor, D.; Campbell, H.; Kritharides, L.; Chen, V.M. Flow cytometry protocols for assessment of platelet function in whole blood. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1646, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).