Optimizing Mycophenolate Therapy in Renal Transplant Patients Using Machine Learning and Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Population Pharmacokinetics Modeling
- Pi is the PK parameter value for the ith subject;
- Ppop is the population mean estimate of the parameter;
- betaC is the effect of the continuous covariate Ci for the ith subject on the PK parameter;
- betaG is the effect size of the categorical covariate Gi for the ith subject on the PK parameter;
- Cmean is the mean value of the covariate for normalization;
- n~N(0, ω2) represents the interindividual variability (IIV). Thus, for the ith subject, the IIV is ni;
- k~N(0, γ2) represents the interoccasion variability (IOV). Thus, for the ith subject at the jth visit the IOV is kij.
- Cobs represents the observed concentration;
- Cpred represents the model-predicted concentration;
- a is the additive component reflecting a constant deviation independent of concentration;
- b is the proportional component reflecting variability that increases with concentration;
- ε1 and ε2 ~N(0, 1) are the random variables that represent the unexplained deviation between Cpred and Cobs.
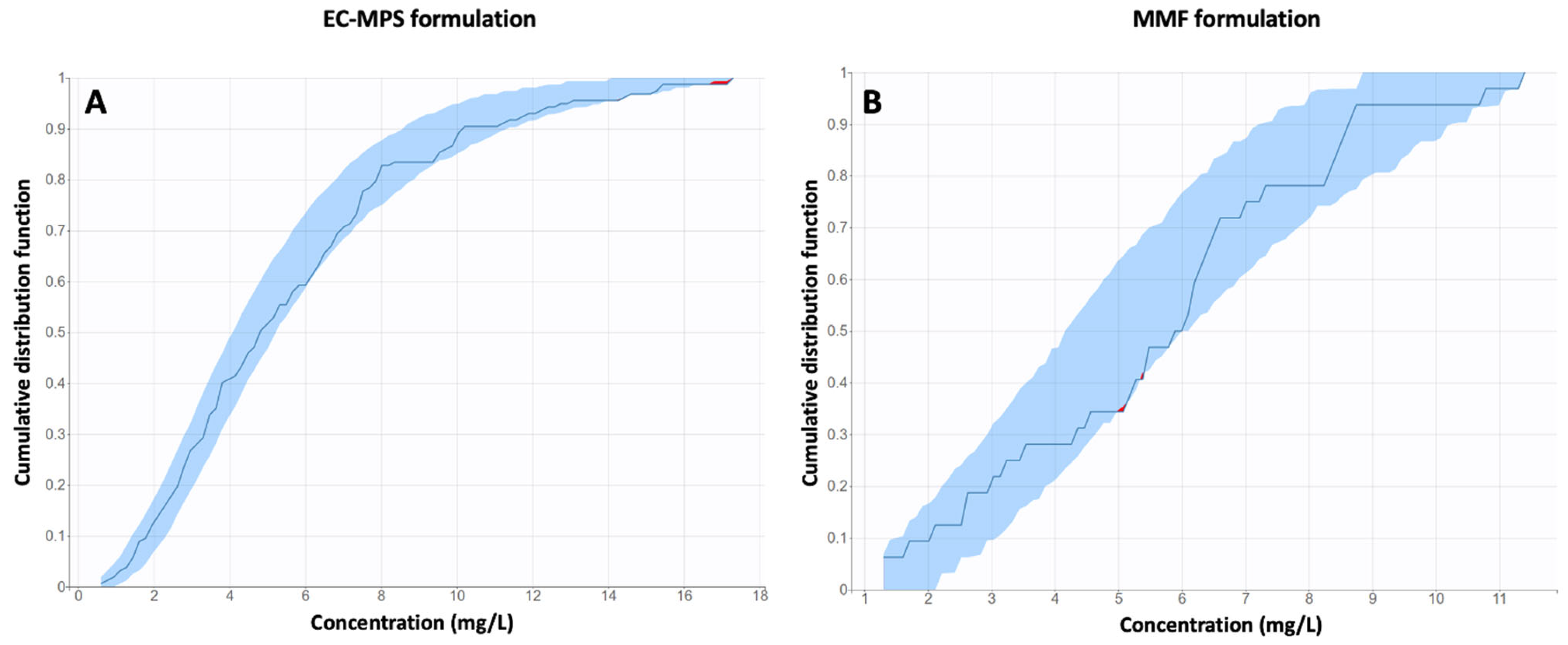
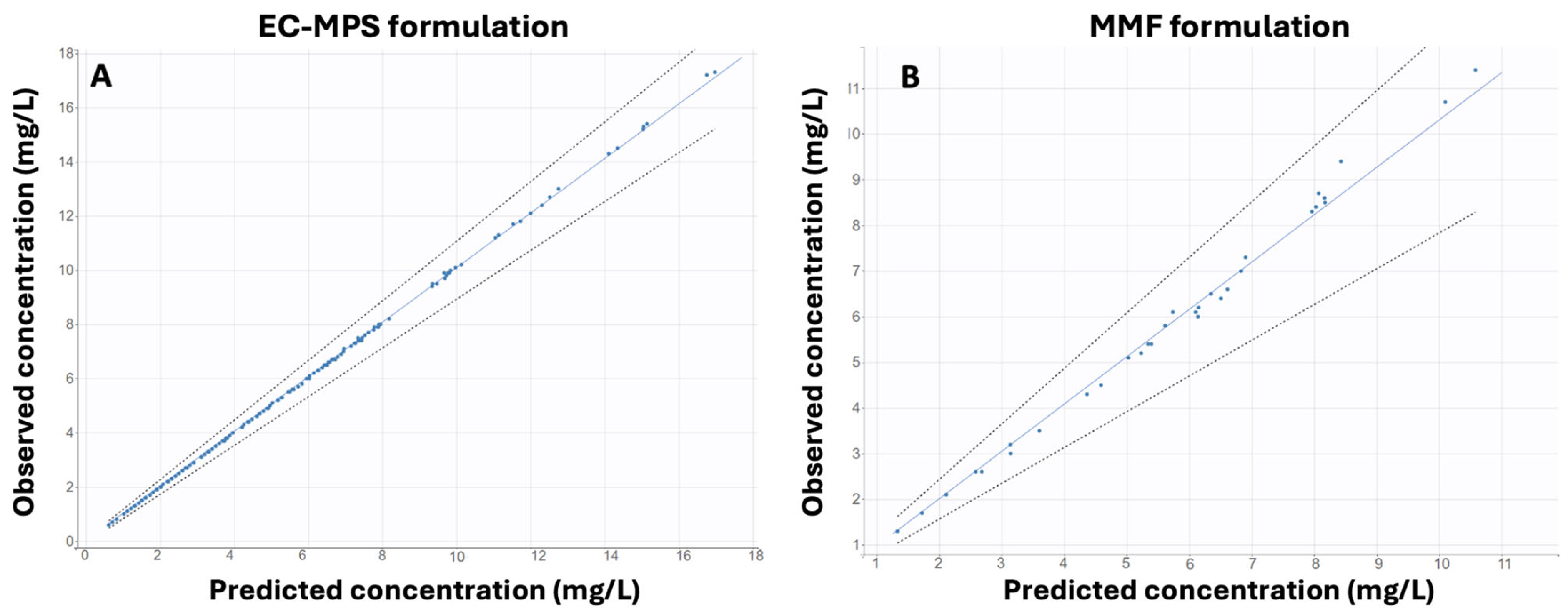
Model Validation
2.4. Machine Learning Techniques
2.4.1. Unsupervised Machine Learning: Principal Component Analysis
2.4.2. Ensemble Methods
2.4.3. Model Implementation and Software
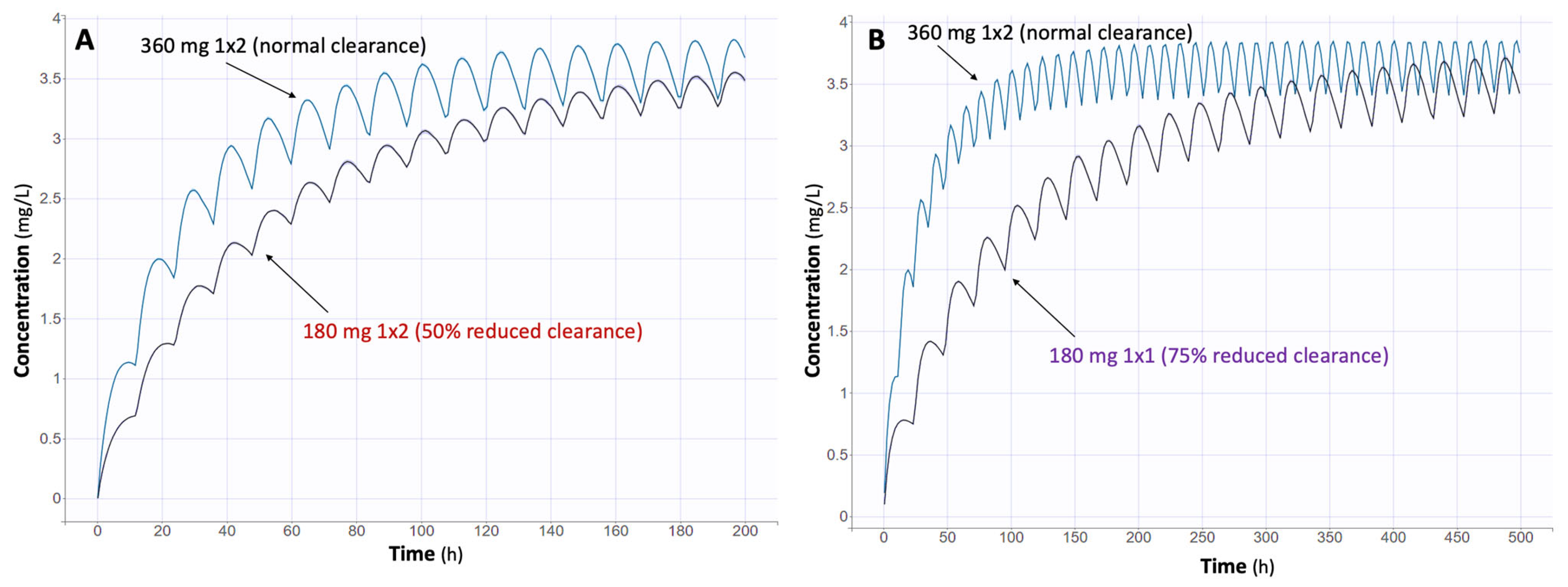
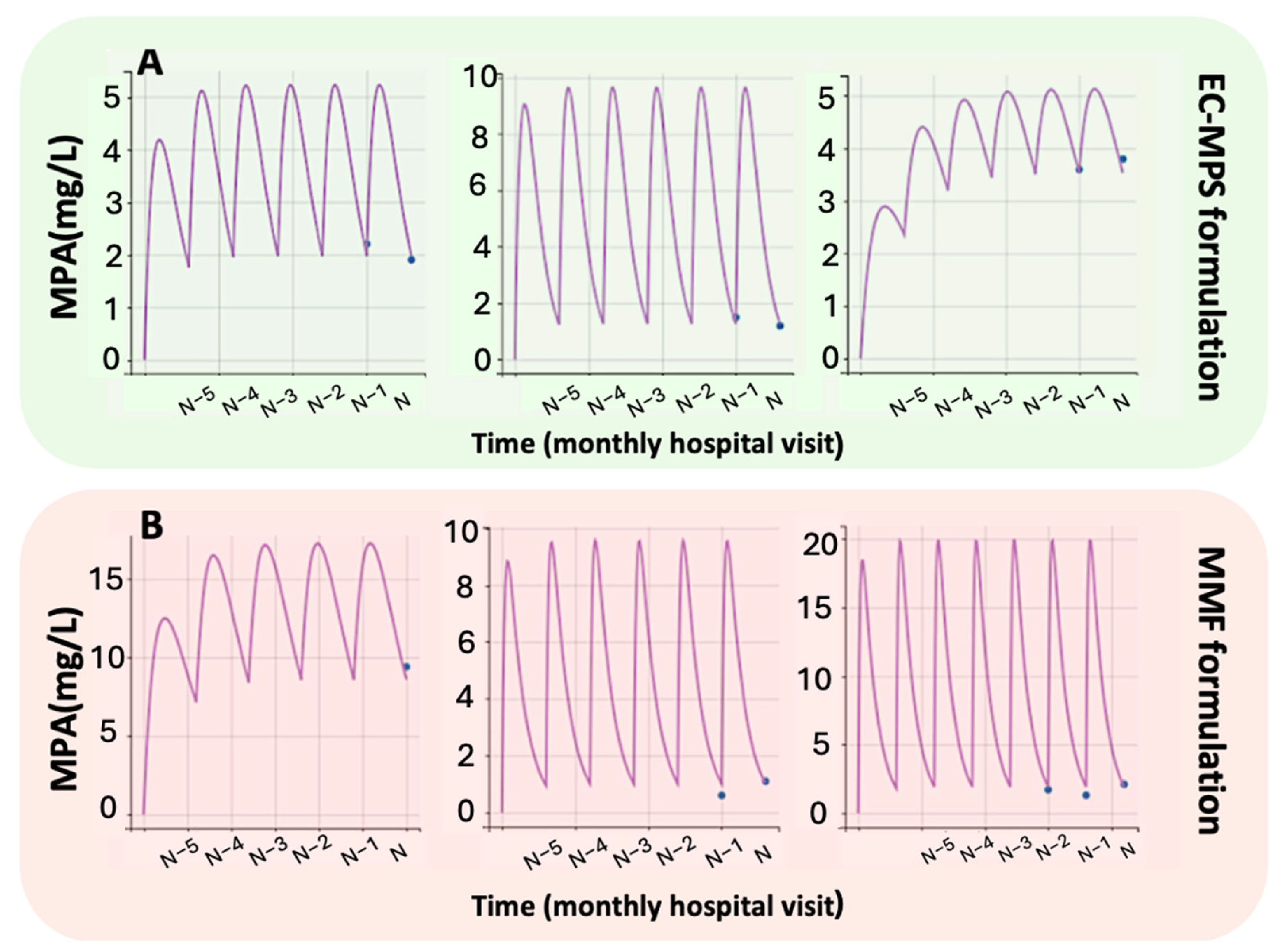
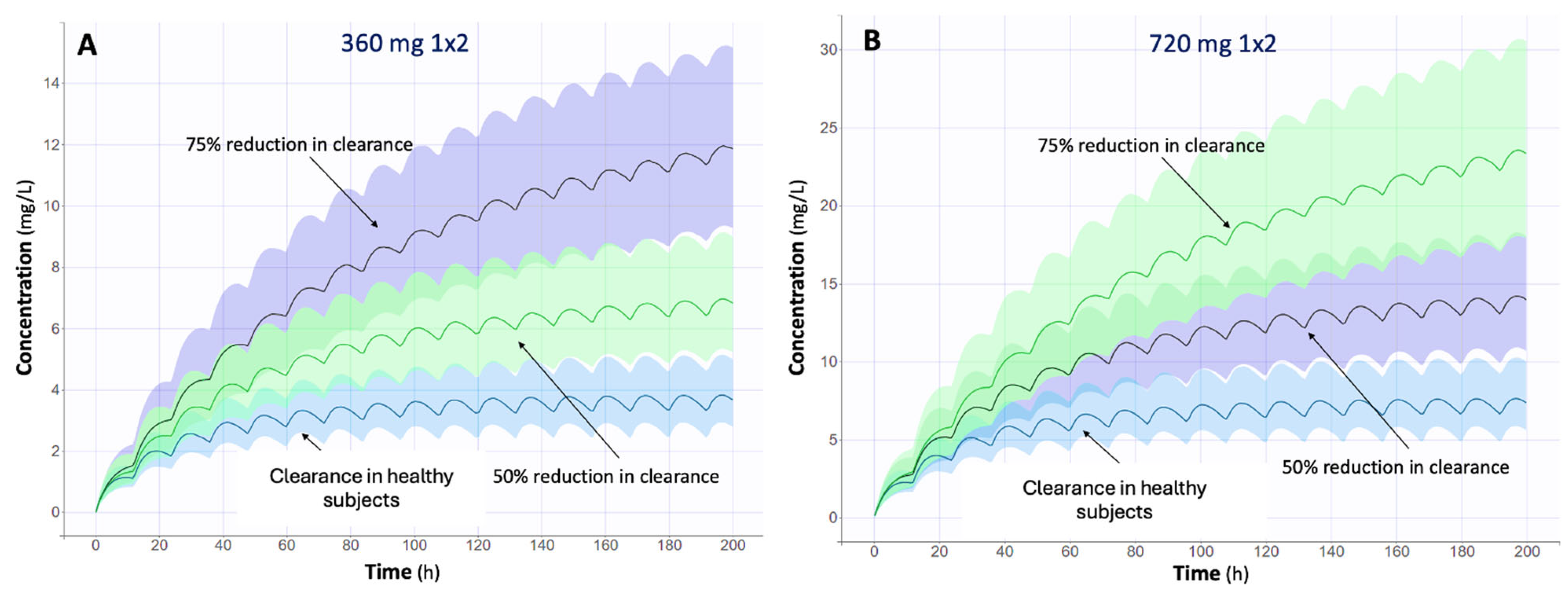
2.5. Monte Carlo Simulations
3. Results
3.1. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling
3.1.1. EC-MPS Model (Model 1)
3.1.2. MMF Model (Model 2)
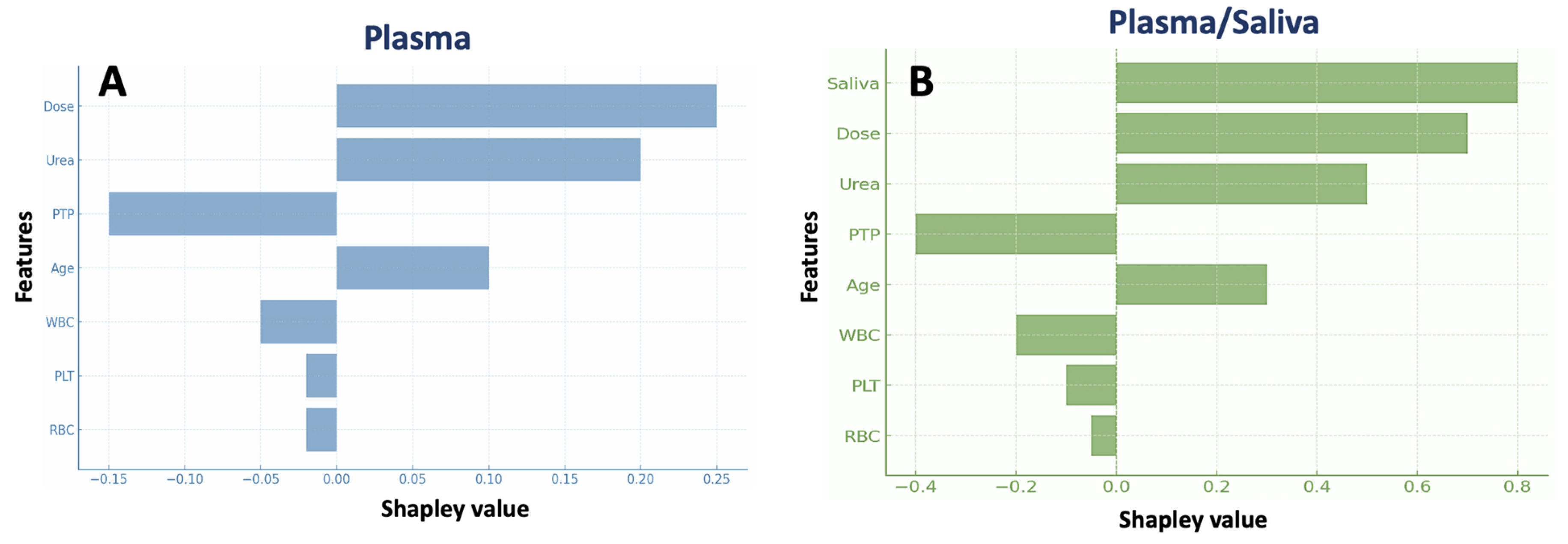
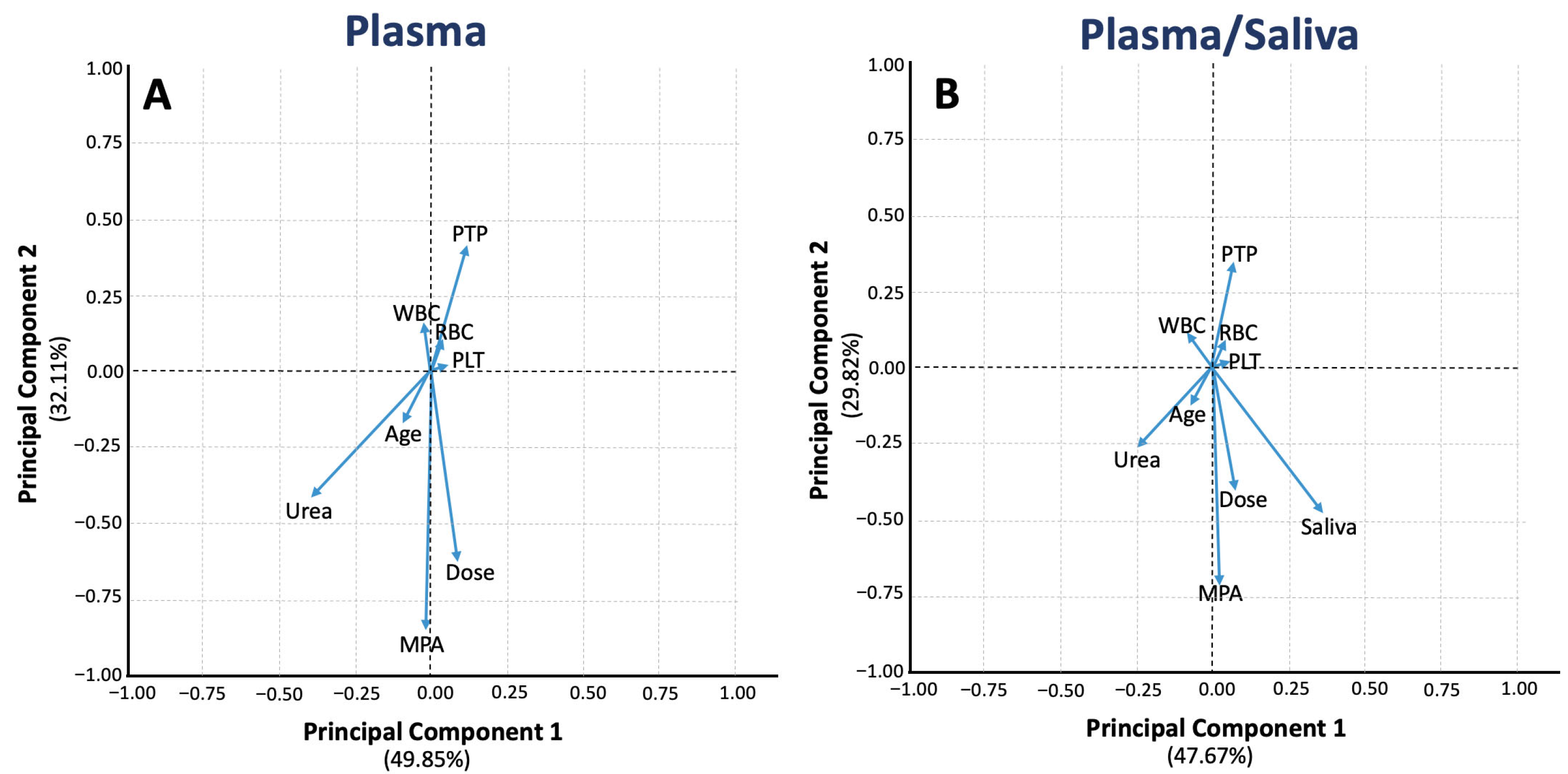
3.2. Machine Learning Analysis
3.2.1. Boosted Trees
3.2.2. Principal Component Analysis
3.3. Impact of Renal Function on MPA Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| −2LL | −2 log likelihood |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks |
| AUC0–12 | Area Under the Concentration curve from zero to 12 h |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| CL | Clearance |
| CNIs | Calcineurin Inhibitors |
| CrCl | Creatinine Clearance |
| EC-MPS | Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium |
| EHR | Enterohepatic Recirculation |
| GFR | Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| Hb | Hemoglobulin |
| Ht | Hematocrit |
| IIV | Inter-individual variability |
| IMPDH | Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase |
| IOV | Inter-occasion variability |
| ka | Absorption rate constant |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MMF | Mycophenolate Mofetil |
| MPA | Mycophenolic Acid |
| MPAG | Mycophenolic Acid Glucuronide |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| NLME | Nonlinear mixed-effects |
| NPC | Numerical predictive check |
| OATP | Organic anion transport polypeptide |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PK | Pharmacokinetic |
| PKPD | Pharmacokinetic–Pharmacodynamic |
| MRP2 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 |
| PLT | Platelets |
| PopPK | Population Pharmacokinetic |
| PTP | Post-Transplant Time |
| RBC | Red Blood Cells |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RSE | Relative standard error |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive Explanations |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| TDD | Total Daily Dose |
| UGT | Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase |
| Vd | Volume of distribution |
| VPC | Visual predictive check |
| WBC | White Blood Cells |
Appendix A

References
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Myfortic® (Mycophenolic Acid) Delayed-Release Tablets Prescribing Information; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: East Hanover, NJ, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/050791s007lbl.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Myfortic (Mycophenolic Acid) Delayed-Release Tablets—Prescribing Information. 2022. Available online: https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/myfortic.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. CellCept (Mycophenolate Mofetil)—Summary of Product Characteristics; Roche: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cellcept (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. CellCept (Mycophenolate Mofetil) Prescribing Information. 2023. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/050722s049s051,050723s049s051,050758s047s049lbl.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- UpToDate. Up-To-Date. Available online: https://www.Uptodate.Com/Contents/Mycophenolate-Mofetil-Cellcept-Myhibbin-and-Mycophenolate-Sodium-Myfortic-Drug-Information?Source=history_widget (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Honarbakhsh, N.; Rouini, M.R.; Lesan-Pezeshki, M.; Javadi, M.R.; Karimzadeh, I.; Mohebbi, N.; Gholami, K. Mycophenolic Acid Pharmacokinetics Early After Kidney Transplant. Exp. Clin. Transpl. 2013, 11, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, C. Impact of Renal Impairment on Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolate Mofetil in Chinese Adult Renal Transplant Recipients Early after Kidney Transplantation. Chin. J. Organ. Transplant. 2017, 12, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, E.; Tett, S.E.; Isbel, N.M.; McWhinney, B.; Staatz, C.E. Investigation of the Association Between Total and Free Plasma and Saliva Mycophenolic Acid Concentrations Following Administration of Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. Drug Investig. 2019, 39, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossart, A.R.; Staatz, C.E.; Gorham, G.; Barraclough, K.A. Comparison of Free Plasma versus Saliva Mycophenolic Acid Exposure Following Mycophenolate Mofetil Administration in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 100, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiak, J.; Kamińska, J.; Głyda, M.; Duda, G.; Chrzanowska, M. Effect of Mycophenolate Mofetil on Hematological Side Effects Incidence in Renal Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, E407–E414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Fakhoury, M.; Deschênes, G.; Roussey, G.; Brochard, K.; Niaudet, P.; Tsimaratos, M.; André, J.L.; Cloarec, S.; Cochat, P.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacogenetics of Mycophenolic Acid Following Administration of Mycophenolate Mofetil in De Novo Pediatric Renal-Transplant Patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Jury, E.C.; Dönnes, P.; Ciurtin, C. Machine Learning Techniques for Personalised Medicine Approaches in Immune-Mediated Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Applications and Challenges. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 720694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Tang, B.; Wu, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Van Den Anker, J.; Hao, G.; Zhao, W. Machine Learning: A New Approach for Dose Individualization. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 115, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Nakamaru, Y.; Yamashita, F. Application of Machine Learning Techniques in Population Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics Modeling. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2024, 56, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Rey, I.; Bandín-Vilar, E.; Toja-Camba, F.J.; Cañizo-Outeiriño, A.; Cajade-Pascual, F.; Ortega-Hortas, M.; Mangas-Sanjuan, V.; González-Barcia, M.; Zarra-Ferro, I.; Mondelo-García, C.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications to Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Dose Prediction of Antibiotics: A Scoping Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevičiūtė, K.; Woillard, J.-B.; Peck, R.W.; Marquet, P.; Van Der Schaar, M. Bridging the Worlds of Pharmacometrics and Machine Learning. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2023, 62, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Françoise, B.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B. Population Pharmacokinetics and Bayesian Estimation of Mycophenolic Acid Concentrations in Chinese Adult Renal Transplant Recipients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardi, S.; Tran, J.L.; Clarkson, M.R. Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium. Ann. Pharmacother. 2003, 37, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Cai, Q.; Xiong, N.; Qin, Y.; Lai, L.; Sun, X.; Hu, Y. Limited Sampling Strategy for Estimating Mycophenolic Acid Exposure on Day 7 Post-Transplant for Two Mycophenolate Mofetil Formulations Derived From 20 Chinese Renal Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Fukuda, T.; Cox, S.; De Vries, M.T.; Hooper, D.K.; Goebel, J.; Vinks, A.A. Population Pharmacokinetic−pharmacodynamic Modelling of Mycophenolic Acid in Paediatric Renal Transplant Recipients in the Early Post-transplant Period. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staatz, C.E.; Tett, S.E. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Mycophenolate in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 46, 13–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J.; Kang, J.; Feng, G.; Zhou, L.; Zuo, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolate Mofetil and Development of Limited Sampling Strategy in Early Kidney Transplant Recipients. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonate, P.L. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling and Simulation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- De Winter, B.C.M.; Monchaud, C.; Prémaud, A.; Pison, C.; Kessler, R.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Dromer, C.; Stern, M.; Guillemain, R.; Knoop, C.; et al. Bayesian Estimation of Mycophenolate Mofetil in Lung Transplantation, Using a Population Pharmacokinetic Model Developed in Kidney and Lung Transplant Recipients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damnjanović, I.; Tsyplakova, N.; Stefanović, N.; Tošić, T.; Catić-Đorđević, A.; Karalis, V. Joint Use of Population Pharmacokinetics and Machine Learning for Optimizing Antiepileptic Treatment in Pediatric Population. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2023, 14, 20420986231181337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sheng, C.; Liu, L.; Luo, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Deng, R.; Jiao, Z.; et al. Systematic External Evaluation of Published Population Pharmacokinetic Models of Mycophenolate Mofetil in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients Co-administered with Tacrolimus. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Machine Learning Methods; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; ISBN 978-981-99-3916-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Xu, Q.; Yang, G.; Ding, J.; Pei, Q. Machine Learning for Prediction of Drug Concentrations: Application and Challenges. Clin. Pharma. Ther. 2025, 117, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Probabilistic Machine Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Buchlak, Q.D.; Esmaili, N.; Leveque, J.-C.; Farrokhi, F.; Bennett, C.; Piccardi, M.; Sethi, R.K. Machine Learning Applications to Clinical Decision Support in Neurosurgery: An Artificial Intelligence Augmented Systematic Review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 1235–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L. Application of Machine Learning Combined with Population Pharmacokinetics to Improve Individual Prediction of Vancomycin Clearance in Simulated Adult Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1352113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ette, E.I.; Williams, P.J. Population Pharmacokinetics I: Background, Concepts, and Models. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Investigation on Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid in Chinese Adult Renal Transplant Patients. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, T.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Leng, P.; Sun, J. Published Population Pharmacokinetic Models of Mycophenolate Sodium: A Systematic Review and External Evaluation in a Chinese Sample of Renal Transplant Recipients. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1632568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexiti, K.; Jiang, X.; Kong, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Wei, X. Population Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid and Dose Optimisation in Adult Chinese Kidney Transplant Recipients. Xenobiotica 2023, 53, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sheng, C.; Liao, G.; Su, Y.; Feng, L.; Xia, Q.; Jiao, Z.; Xu, D. Genetic Polymorphisms in Metabolic Enzymes and Transporters Have No Impact on Mycophenolic Acid Pharmacokinetics in Adult Kidney Transplant Patients Co-treated with Tacrolimus: A Population Analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawinski, T.; Durlik, M.; Szlaska, I.; Urbanowicz, A.; Majchrnak, J.; Gralak, B. Comparison of Mycophenolic Acid Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Kidney Transplant Patients within the First 3 Months Post-Transplant. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2006, 31, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Nawrocki, A.; Korecka, M.; Solari, S.; Kang, J. Using Established Immunosuppressant Therapy Effectively: Lessons from the Measurement of Mycophenolic Acid Plasma Concentrations. Ther. Drug Monit. 2004, 26, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, O.; Karimzadeh, I.; Davani-Davari, D.; Shafiekhani, M.; Sagheb, M.M.; Raees-Jalali, G.A. Drug-Drug Interactions among Kidney Transplant Recipients in The Outpatient Setting. Int. J. Organ. Transplant. Med. 2020, 11, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Kagaya, H.; Miura, M.; Satoh, S.; Inoue, K.; Saito, M.; Inoue, T.; Habuchi, T.; Suzuki, T. No Pharmacokinetic Interactions between Mycophenolic Acid and Tacrolimus in Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2008, 33, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković-Radovanović, R.M.; Janković, S.M.; Milovanović, J.R.; Catić-Đorđević, A.K.; Spasić, A.A.; Stefanović, N.Z.; Džodić, P.L.; Šmelcerović, A.A.; Cvetković, T.P. Variability of Mycophenolic Acid Elimination in the Renal Transplant Recipients—Population Pharmacokinetic Approach. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, X.; Feng, Y.; Qin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shang, W.; Feng, G.; Zhang, X. Population Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolic Acid in Renal Transplant Patients: A Comparison of the Early and Stable Posttransplant Stages. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 859351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woillard, J.; Labriffe, M.; Debord, J.; Marquet, P. Mycophenolic Acid Exposure Prediction Using Machine Learning. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, K.; Jia, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, D.; An, H.; Zhou, Q.; Rong, R.; Zhu, T.; et al. Estimation of Mycophenolic Acid Exposure in Chinese Renal Transplant Patients by a Joint Deep Learning Model. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Shao, K.; Lu, J.; An, H.; Shi, H.; Zhou, P.; Chen, B. Influence of Calcineurin Inhibitors and Genetic Polymorphism of Transporters on Enterohepatic Circulation and Exposure of Mycophenolic Acid in Chinese Adult Renal Allograft Recipients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 63, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hest, R.M.; Van Gelder, T.; Bouw, R.; Goggin, T.; Gordon, R.; Mamelok, R.D.; Mathot, R.A. Time-dependent Clearance of Mycophenolic Acid in Renal Transplant Recipients. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 63, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostaing, L.; Jouve, T.; Terrec, F.; Malvezzi, P.; Noble, J. Adverse Drug Events after Kidney Transplantation. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiak, J.; Głyda, M.; Malec, M.; Chrzanowska, M. Pharmacokinetics of Mycophenolate Mofetil Metabolites in Older Patients on the Seventh Day After Renal Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, T.; Meur, Y.L.; Shaw, L.M.; Oellerich, M.; DeNofrio, D.; Holt, C.; Holt, D.W.; Kaplan, B.; Kuypers, D.; Meiser, B.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Mycophenolate Mofetil in Transplantation. Ther. Drug Monit. 2006, 28, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyplakova, N.; Ismailos, G.; Karalis, V.D. Optimising Pirfenidone Dosage Regimens in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Towards a Guide for Personalised Treatment. Xenobiotica 2025, 55, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsmadi, M.M.; Alfarah, M.Q.; Albderat, J.; Alsalaita, G.; AlMardini, R.; Hamadi, S.; Al-Ghazawi, A.; Abu-Duhair, O.; Idkaidek, N. The Development of a Population Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Mycophenolic Mofetil and Mycophenolic Acid in Humans Using Data from Plasma, Saliva, and Kidney Tissue. Biopharm. Drug Disp. 2019, 40, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catić-Đorđević, A.; Stefanović, N.; Pavlović, I.; Pavlović, D.; Živanović, S.; Kundalić, A.; Veličković-Radovanović, R.; Mitić, B. Utility of Salivary Mycophenolic Acid Concentration Monitoring: Modeling and Monte Carlo Validation Approach. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, e01034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.C.L.; Thiesen, F.V.; De Araujo, T.T.; D’Ávila, D.O.; Gadonski, G.; De Oliveira, C.S.A.; Zimmer, A.R.; Fröehlich, P.E. Comparison of Plasma and Oral Fluid Concentrations of Mycophenolic Acid and Its Glucuronide Metabolite by LC-MS in Kidney Transplant Patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wang, Z.-J.; Yang, H.-W.; Meng, L.; Tan, R.-Y.; Gu, M.; Wei, J.-F. Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on Mycophenolic Acid Pharmacokinetics and Patient Outcomes in Renal Transplantation. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Goebel, J.; Thøgersen, H.; Maseck, D.; Cox, S.; Logan, B.; Sherbotie, J.; Seikaly, M.; Vinks, A.A. Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase (IMPDH) Activity as a Pharmacodynamic Biomarker of Mycophenolic Acid Effects in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Rawson, T.M.; Ahmad, R.; Buchard, A.; Georgiou, P.; Lescure, F.-X.; Birgand, G.; Holmes, A.H. Machine Learning for Clinical Decision Support in Infectious Diseases: A Narrative Review of Current Applications. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 584–595, Correction in Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, R.S.; Kaplan, B.; Shah, T.; Cibrik, D.; Shaw, L.M.; Angelis, M.; Mulgaonkar, S.; Meier-Kriesche, H.-U.; Patel, D.; Bloom, R.D. Fixed- or Controlled-Dose Mycophenolate Mofetil with Standard- or Reduced-Dose Calcineurin Inhibitors: The Opticept Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.; Polkinghorne, K.R.; Leong, K.G.; Kanellis, J.; Mulley, W.R. Initial Mycophenolate Dose in Tacrolimus Treated Renal Transplant Recipients, a Cohort Study Comparing Leukopaenia, Rejection and Long-Term Graft Function. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | n (%) or Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Number of patients (n) | 76 |
| MPA plasma samples (n) | 209 |
| MPA saliva samples (n) | 65 |
| Age (years) | 51 (14) |
| Gender (Men, Women) | 50 (65.8%), 26 (34.2%) |
| Clinical Characteristics | |
| Post-Transplantation Time (months) | 70 (84.3) |
| Live Donor Transplant | 54 (71%) |
| Deceased Donor Transplant | 18 (24%) |
| Administered Formulation | |
| EC-MPS | 63 (82.9%) |
| MMF | 13 (17.1%) |
| Laboratory Values | |
| White Blood Cells (109/L) | 7.9 (2.6) |
| Red Blood Cells (1012/L) | 4.7 (0.9) |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 138 (32) |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41.4 (8.9) |
| Platelets (109/L) | 225 (88) |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 7.8 (5.4) |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 136 (60) |
| Parameter | Value | Standard Error | Relative Standard Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Effects | |||
| kapop | 0.18 | 0.03 | 15.7 |
| Vpop | 192.42 | 36.18 | 18.8 |
| Clpop | 9.3 | 0.78 | 8.34 |
| β(PTP) | 0.16 | 0.04 | 24.7 |
| β(TDD) | 0.77 | 0.15 | 19.2 |
| Standard Deviation of the Random Effects | |||
| ω(ka) | 0.36 | 0.08 | 21.2 |
| ω(V) | 0.52 | 0.20 | 38.8 |
| ω(Cl) | 0.27 | 0.06 | 20.9 |
| γ(ka) | 0.28 | 0.14 | 48.3 |
| γ(V) | 0.52 | 0.15 | 29.2 |
| γ(Cl) | 0.31 | 0.04 | 11.2 |
| Residual Error Model | |||
| a | 0.04 | 0.01 | 26 |
| b | 0.06 | 0.02 | 24.6 |
| Parameter | Value | Standard Error | Relative Standard Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Effects | |||
| kapop | 0.23 | 0.052 | 22.6 |
| Vpop | 196.43 | 56.768 | 28.9 |
| Clpop | 9.3 | 1.042 | 11.2 |
| β(PTP) | 0.33 | 0.072 | 21.8 |
| β(TDD) | 1.27 | 0.293 | 23.1 |
| Standard Deviation of the Random Effects | |||
| ω(ka) | 0.27 | 0.072 | 26.5 |
| ω(V) | 0.09 | 0.029 | 32.4 |
| ω(Cl) | 0.32 | 0.061 | 19.2 |
| γ(ka) | 0.48 | 0.191 | 39.8 |
| γ(V) | 0.33 | 0.071 | 21.4 |
| γ(Cl) | 0.27 | 0.060 | 22.3 |
| Residual Error Model | |||
| b | 0.17 | 0.064 | 37.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsyplakova, A.; Catic-Djorđevic, A.; Stefanović, N.; Karalis, V.D. Optimizing Mycophenolate Therapy in Renal Transplant Patients Using Machine Learning and Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040235
Tsyplakova A, Catic-Djorđevic A, Stefanović N, Karalis VD. Optimizing Mycophenolate Therapy in Renal Transplant Patients Using Machine Learning and Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(4):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040235
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsyplakova, Anastasia, Aleksandra Catic-Djorđevic, Nikola Stefanović, and Vangelis D. Karalis. 2025. "Optimizing Mycophenolate Therapy in Renal Transplant Patients Using Machine Learning and Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling" Medical Sciences 13, no. 4: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040235
APA StyleTsyplakova, A., Catic-Djorđevic, A., Stefanović, N., & Karalis, V. D. (2025). Optimizing Mycophenolate Therapy in Renal Transplant Patients Using Machine Learning and Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Medical Sciences, 13(4), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040235








