Abstract
In the northern South China Sea, pockmarks are widely distributed on the seabed offshore on the southwestern Xisha Uplift. The mineralogy and geochemistry of the clay minerals and surface sediments from the pockmark field were identified using X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis to trace the provenance, weathering, and sediment transportation system in the area. The clay minerals are primarily comprised of illite, smectite, kaolinite, and chlorite, showing a distribution of average weight percentages of 35%, 35%, 18%, and 13%, respectively. Based on the surrounding fluvial drainage basins and various transport mechanisms (current or monsoon), illite and chlorite primarily originate from rivers in Taiwan and the Mekong and Red Rivers. Kaolinite primarily originates from the Pearl River, and smectite derived from the Luzon arc system is primarily transported by surface currents with significant influence from the Kuroshio intrusion.
1. Introduction
Understanding processes involved in modern sedimentary environments is a prerequisite in paleo-oceanographic reconstruction [1,2,3]. Climatic conditions and lithology of the source rock are the key factors generally controlling the geo-chemical and the mineralogical fingerprints of the surface sediments. Clay minerals, which are widely distributed in the marine sediments, are vital contents, as well as the content assemblages and concentration of chemical elements, which provide useful tools for deciphering provenance, weathering intensity, transport patterns, and paleo-climatic changes (e.g., [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]).
Clay minerals, such as illite and chlorite, are common weathering products of igneous and metamorphic rocks. These minerals are typically found in high-latitude marine sediments after mobilization by physical weathering. Kaolinite forms under warm and humid conditions by the intensive chemical weathering of feldspar in tropical soils and is often denoted as a low-latitude mineral [15,16]. The alteration of volcanic rock-derived smectite can be a good indicator of volcanic sediment sources.
Terrigenous sediment loads are received into the northern South China Sea (SCS) annually, from the Red River (130 metric tons (Mt)) into the northwest, Pearl River (69 Mt) into the north, rivers in Taiwan (187.5Mt) into the northeast, and some rivers on Luzon Island (>8.2 Mt) into the east [5,17]. However, the detrital sediments in the region have an unknown provenance due to this complexity in the source of the detrital sediments and circulation patterns in the northern SCS. In previous studies, especially in the northeastern region of the SCS, the Pearl River and volcanoes were considered as the primary sedimentary sources [18,19,20,21]. Nevertheless, recent investigations on elemental geochemistry and clay mineralogy have focused on three major origins: Taiwan, the Pearl River, and Luzon, where the contribution to the northern slope of the SCS was semi-quantitatively assessed [22,23].
A number of sedimentological and geochemical approaches have been used to analyze of the source of SCS sediments, such as measurements of grain size distribution [24,25,26], the occurrence of clay and heavy minerals (e.g., [5,22,23,27]) strontium and neodymium isotopes (e.g., [10,28,29]), and major and trace element geochemistry [5].
The SCS is a semi-enclosed basin and known as one of the largest marginal seas in the world, and is located between the Pacific Ocean and the Asian continent. Previous studies mainly focused on the northeastern region of the SCS, due to the complexity of the origin of detrital sediment in the SCS, the interaction and patterns of sea surface currents in combination with the East Asian monsoon winds, and the subsurface intrusion of Kuroshio and deep waters through the Luzon Strait from the western Pacific [22,30,31,32]. There is a lack of studies on the provenance and geochemistry of sediments on the Xisha Uplift. The aim of this study is to adequatelycorrelate the distribution characteristics of the clay minerals, major elements, and element geochemistry of surface sediment with the relationships between provenance and the sediment transportation in the Xisha Uplift, southwestern SCS.
2. Geological Setting
The study area is located in the southwestern Xisha Uplift between the Guangle Uplift and Zhongjian Island, northern SCS (Figure 1), where the water depth ranges from 800–1300m. The evolution of the sedimentary filling can be categorized into the Eocene–Oligocene rift and a Neocene–Quaternary post-rift subsidence. The deposition of the total thickness of the sedimentary layers occurred during the Eocene–Oligocene rift stage, which could be the major high-quality source rocks in this study area. The Neocene–Quaternary post-rift subsidence stage can be further categorized into thermal subsidence and accelerated subsidence sub-stages. The study is characterized by high sedimentation rates (up to 1.2 mm/yr) and high geothermal gradients (39–41 °C/km) [33,34,35]. A high percentage of the pockmarks within the study area are classified as mega pockmarks (1000–2500 min diameter and 60–140 min depth). The distribution of these pockmarks is linked with the underlying fluid migration structures, such as gas chimneys, polygonal faults, faults, unconformities, and paleo-channels [36] Moreover, the phase boundaries between free gas and solid gas hydrate for this area have been described with the distinct bottom-simulating reflectors (BSRs) [37]. Furthermore, compelling evidence on gas hydrate dissociation, such as decreased chlorinity and increased pore water δ18O, has been reported (in core C14) in the pockmark field [38,39]. Meanwhile, high geothermal gradients in the region accelerated the maturity of the source rock, and drifted towards the seabed, which refers to the composition change of the sediments.
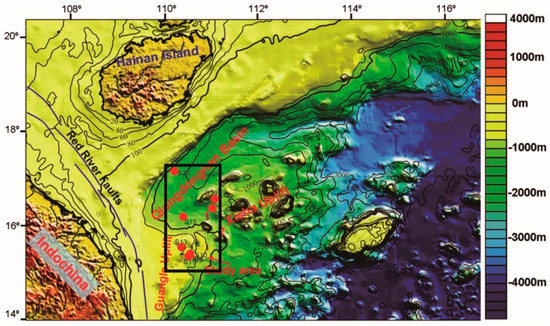
Figure 1.
Map of the study area and sampling sites (modified from Sun et al., 2011).
3. Materials and Methods
A total number of 8 surface sediment samples were collected using a box sampler from the southwestern region of the Xisha Uplift, northern region of SCS, cruised by the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, CAS on the Shiyan-1 in May 2012. The samples were collected either from or near the giant pockmarks in the southern region of the Qiongdongnan (QDN) basin (details are shown in Figure 1). The characterization of the sediments was done by grayish-green foraminiferous silty clay.
The X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) method was used for the measurement of the mineralogical composition in the bulk sediments. For each sample, 5 g of sediment sample were taken and oven-dried for 24 h at 45 °C, and ground to ≤200 mesh size in an agate mortar. For the XRD analysis, approximately 1 g of powder was used. The results were semi-quantitatively elucidated using Jade 6.0 software, based on the relationships between the mineral diffraction peak heights and integral area.
Precisely weighed 4g of powder were subsequently added into the center of a poly-oxyethylene abrasive apparatus and made into circular samples (4 cm diameter and 8 mm thickness) with the apparatus pressurized for 20 s at 30 tm−2 pressure. Major oxides and a few trace elements were determined by a Philips Panalytical Magix PW2403 X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer (Holland) at standard room temperature and pressure (approximately 20 °C, 85 kPa).
Carbonate and organic matter were removed using 10% H2O2 and 0.5N HCl, respectively. Then clay minerals (<2 µm) were separated into 1000 mL glassware, according to Stoke’s settling velocity principle [40]. XRD runs were performed three times, followed by air-drying, ethylene glycol (55 °C for 9 h), and heating at 550 °C for 2 h. Based on Liu et al. [5], clay mineral abundances were semi-quantitatively calculated.
The Axios X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) was used for measuring of the percentages of the major elements, including Al2O3, SiO2, Fe2O3, MgO, CaO, K2O, MnO, Na2O, P2O5, and TiO2. Loss on ignition (LOI) was determined by referring to a method proposed by Heiri et al. [41].
Normalization of the concentration of selected elements was done by considering the standard concentration of elements in the upper continental crust (UCC; [42,43]). The chemical index of alteration (CIA) was used for the estimation of the intensity of chemical weathering [44]:
where CaO∗ is only found in silicates.
CIA = Al2O3/ (Al2O3 + Na2O + K2O + CaO∗) × 100
In this study, there were two correction methods used, because precise correction of CaO bound in carbonate and phosphate minerals is difficult [45]. The CIA index was calculated from chemical analyses following acid treatment to remove carbonates and phosphates.
4. Results
4.1. Principal Mineral Composition in Surface Sediments/Mineralogy
The studied samples were mostly silt, with abundant foraminifera. XRD analysis of bulk sediment revealed that minerals, including clay minerals (34.8–42.9%), calcite (20.2–24.1%), quartz (15.9–18.4%), minor plagioclase, dolomite, siderite and pyroxene, pyrite, gypsum, anhydrite, k-feldspar, and amphiboles were also detected in the samples (Figure 2, Table 1).
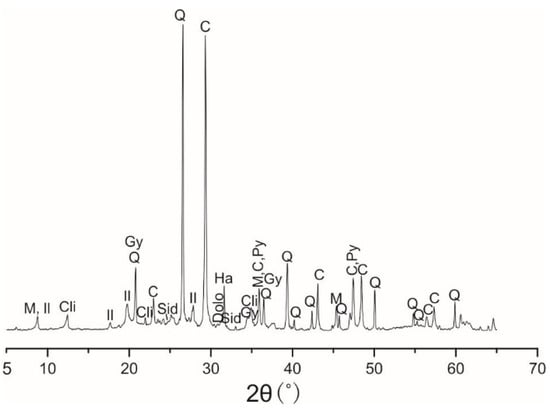
Figure 2.
X-ray diffraction diagram of surface sediments in the Xisha Uplift (s9). M: muscovite, Il: illite, Cli: clinopyroxenite, Gy: gypsum, Q: quartz, C: calcite, Sid: siderite, Dolo: dolomite, Ha: halite, Py: pyrite.

Table 1.
Mineralogical assemblages in bulk sediments of the southwestern Xisha Uplift, South China Sea (SCS).
Clay minerals in sediments carried by rivers and small mountainous rivers comprised ~80% of total SCS surface sediments [46,47]. Biogenic carbonates with negligible biogenic silicates and volcanic materials are primarily observed as other components of the sediments. In this study, the clay mineral components of eight samples are characterized by moderate smectite (24–44%, average 35%) and illite (29–40%, average 35%), with a lesser abundance of chlorite (16–22%, average 18%) and kaolinite (8–16%, average 13%) (Table 1; Figure 3).
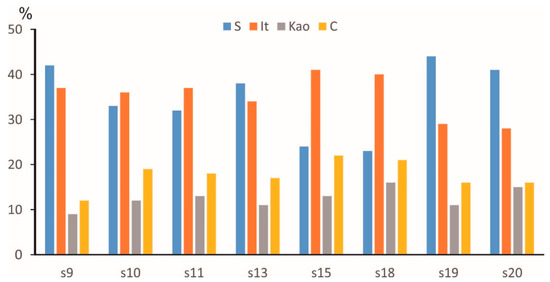
Figure 3.
Clay mineral composition of Xisha Uplift surface sediments (<2 microns). S: smectite, It: illite, Kao: kaolinite, C: chlorite.
4.2. Geochemistry
The composition of the major elements in the bulk sediments are characterized by high SiO2, CaO, and Al2O3 (total average content is 66%) and low K2O, Fe2O3, Na2O, MgO, P2O5, TiO2, and MnO (total average content is 11%) (Table 2). Major elements increase when SiO2 increases, however, Ca decreases with SiO2, except for Na and Mn (Figure 3). Xisha sediments enriched in CaO and depleted in Si, Na, Al, Fe, Mg, and K correspond to the UCC standard.

Table 2.
Major element composition (%) and chemical index of alteration (CIA) of surface sediment samples in the southwestern Xisha Uplift, SCS.
5. Discussion
5.1. Sediment Provenance
Previous studies have indicated that different sediment sources may originate different clay minerals in the SCS. Terrigenous sediments transported to the northern SCS, through by fluvial input from southern China, and loaded by the large Pearl River and Taiwan and Luzon Islands via small mountainous rivers [5,21,23,24,48]. Smectite in marine sediments, related to volcanic materials, volcanic activity, or the alteration of volcanic materials by hydrothermal, weathering, or halmyrotic processes [21,49,50]. There are three areas with high smectite content, considered as significant sources in the SCS. The first is around the Philippines (west of Luzon Island), where 15–50% account for volcanic materials in the silt fraction of sediments [4]. The second area is the east of the Indochina Peninsula, where smectite originates from the Mekong Basin [51] and/or the Red River [52]. The third area is adjacent to the Wan’an Shoal, enriched with volcanic glass [53]. In the surface sediments of the studied area, smectite is the dominant clay minerals, with the average contents of 34%, which means the three high-smectite sources are possible.
Illite and chlorite in marine sediments are some major components which are derived from the continent [48].The six predominant areas of high illite content in the SCS may be the possible sources for the Xisha Uplift: rivers in Taiwan (48–66%, average 56%), Pearl River (21–51%, average 35%), Red River (31–58%, average 44%), Mekong River (33–42%, average 37%), north Borneo (44–75%, 56%) and north Palawan (38–52%, average 42%) [27].
The formation of kaolinite is mainly considered in tropical conditions from well-developed ferrallitic soils in a plain environment with active hydrolysis processes [54,55]. The Pearl River, Hainan Island, and the southern Sunda Shelf are the kaolinite-rich areas. Liu [1] analyzed the drainage basin surface sediments of the Pearl River, the results indicated that kaolinite is common in clay mineral assemblages, while chlorite and illite are less abundant, and smectite is scarce. Possible sources for kaolinite and smectite on the Indonesian and Malaysian islands are abundant andesitic volcanic rocks and older granitic intrusives [48,56,57,58]. Sediments from the Taiwanese rivers primarily consist of illite and cholorite, with scarce smectite and kaolinite [5]. According to previous studies, the Taiwan-sourced sediments can be transported westward via the Kuroshio Current along the northern slope [58].
Luzon sediments, which are combined with weathering of volcanic materials, are generally characterized by a high percent value (average 46%) of smectite, which generally transports to the northwest of the island via the Kuroshio Current. Taiwan-sourced sediments are characterized by high percentages of illite (69%) and chlorite (30%) due to a relatively higher rate of physical weathering and relatively moderate chemical weathering processes [59] and, moreover, sediments which are characterized by a high percentage value of kaolinite in the Pearl River [1].
We carried out a cluster analysis and developed a ternary diagram of smectite–(illite+chlorite)–kaolinite in the studied area and the adjacent regions, to better constrain the provenance of clay minerals sampled from the Xisha Uplift. The distributions of the clay mineral assemblages in the surface sediments of the Xisha Uplift are shown in Figure 4. Clay minerals in the sediments plotted and fell between the data from the Luzon River and the Mekong River. Further, the clay mineral assemblages showed higher smectite and illite values. Results of the data show that the clay mineral components acquired greater contributions from the Red River and rivers in Taiwan than from the Pearl River. Therefore, illite is primarily supplied to this region by the Red River and rivers in Taiwan, however, the study should extend towards a further analysis in the future.
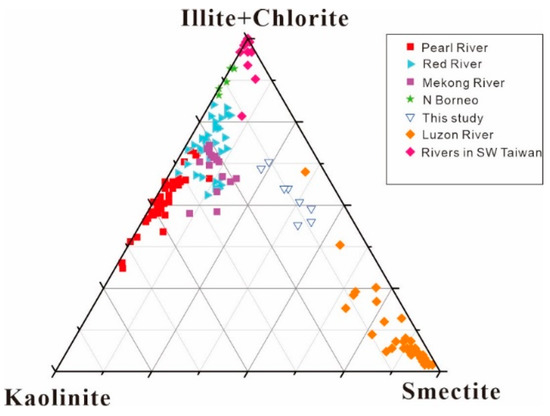
Figure 4.
Ternary diagram of clay minerals of surface sediments from the study area compared with those from the adjacent regions.
Data of Taiwan rivers [22] and Pearl, Red, and Mekong Rivers [1], Luzon rivers [52], north Borneo rivers [58], and Hainan rivers [27] are plotted for comparison.
Recent studies indicated that weathered materials of both the Mekong and Red Rivers are directly involved in forming illite in the southwestern Xisha Uplift sediments, and smectite is primarily derived from the Luzon River [22]. Similar trends of the variation can be seen in analogous minerals like illite and chlorite and these are depleted in correlation with smectite composition (Figure 5), suggesting that the Red River and Mekong River are not the principal source of illite and chlorite. We concluded that the illite originates primarily from Taiwan.
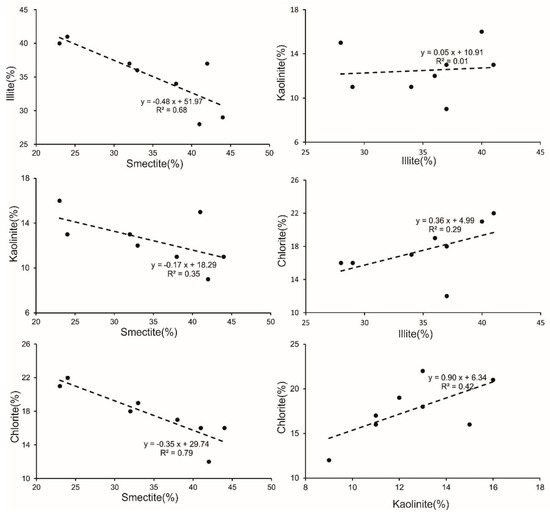
Figure 5.
Variation diagrams of clay minerals of surface sediments in the Xisha Uplift.
5.2. Quantifying Weathering Intensity in the Xisha Uplift
Clay minerals appeared as the weathered products of parent rocks on the Earth’s surface. The composition of the clay minerals provide important information regarding weathering types and intensity, which are primarily determined by various climatic conditions (rainfall, temperature), rock composition, and tectonic activities [54,57,60,61,62,63,64]. Chemical weathering through the hydrolysis of minerals alters the parent rock composition. This process involves the production of typical weathering products like kaolinite and smectite. Generally, kaolinite is found in monosialitic soils, which are characterized by the complete removal of mobile cations and an extreme hydrolysis process. Furthermore, this is primarily controlled by the continental hydrolysis of the parent aluminosilicate rocks in warm and humid climatic conditions [60]. Kaolinite is abundant around the Pearl River, the Malay Peninsula, and Hainan [27,58,63], which suggested a warm and humid climate. Smectite is conventionally related to the chemical weathering of volcanic rocks under hot and humid climatic conditions [65,66]. A rapid rate of volcanic rock weathering is often associated with a high abundance of smectite, which easily forms on basic materials, such as Fe-Mg species [60]. For instance, volcanic rocks are predominant in Luzon and in the Mekong River areas with abundant smectite. Both illite and chlorite are primary minerals, which are strongly correlated with the physical erosion of bedrocks, with relatively dry and cold climatic conditions. To identify and evaluate the weathering intensity, we use the CIA and the elemental ratios calculated with respect to the least mobile element Al, which according to the mobile elements (e.g., K, Na, and Ca), was depleted in the parent rocks, but the least mobile elements (e.g., Al, Fe, and Ti) were enriched in the weathering products during chemical weathering [44].
The sediments are derived from heterogeneous sources, and the state of chemical weathering of the rocks is quantified by the CIA values with reference to the loss of mobile elements, such as Na, Ca, and K. The results demonstrate that CIA values for bulk sediments are 48–57, which indicates low chemical weathering intensity, compared with the terrestrial materials from the South China coast. Comparing previously published CIA values with this study showed that chemical weathering occurred at the same intensity.
Here, the elemental ratios were calculated with respect to Al, and used to identify and assess the mobility of major elements. The content ratio of element X and Al2O3 in river samples divided by the ratio of the elemental content of UCC provides the following elemental ratio [67]: elemental ratio (X) = (X/Al2O3)rivers/(X/Al2O3)UCC. Hence, the elemental ratio indicates the relative enrichment or depletion of the element, i.e., >1 indicates enrichment, <1 indicates depletion, and 1 indicates no change in the relative abundance of the element. The elemental ratios calculated from average major element concentrations normalized to UCC are shown in Figure 6.
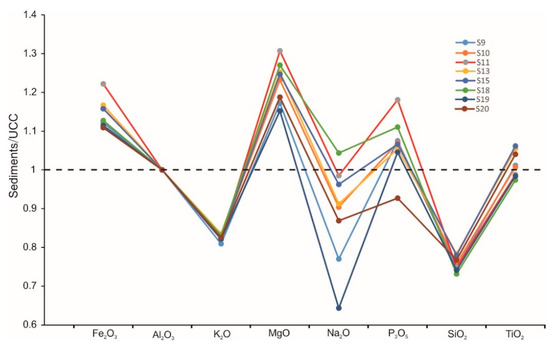
Figure 6.
Elemental ratios of surface sediments in the Xisha Uplift normalized to the upper continental crust (UCC) (Taylor and McLennan, 1985) with respect to Al2O3.
With the predominance of smectite clay minerals are formed by chemical weathering, which is carried out by the leaching of Na and K and later of Fe and Mn. The combination of both results of the CIA and elemental ratios showed a low–moderate degree of chemical weathering of surface sediments in all analyzed sections of the Xisha Uplift.
5.3. Transport Mechanism of Clay Minerals in the Northern SCS
Recent research works focused on the clay minerals of surface sediments and core sediments to discover the sources, transport pathways, and paleo-environmental conditions (e.g., [4,20,21,22,23,26,55,68,69,70,71,72,73]). The dispersal and transport mechanisms of the clay minerals were deduced from the provenance supply and ocean circulation patterns. Most ocean circulation studies indicated that sediment transport in the SCS is controlled by both the surface and deep water currents (DWC) [27,48]. For this study, the distribution of clay minerals is closely related with the current patterns. The relatively high smectite contents prevail in the Xisha Uplift, highly correlated with the flow shift from the westward SCS Kuroshio branch to the northeastward SCS warm current [27], which generates numerous mesoscale westward propagating eddies to transport the smectite from the Luzon Strait westward to the Xisha Uplift, before the deposition on the slope and outer shelf [63].Therefore, the surface currents may be primarily involved in the transportation of smectite. The high illite and chlorite content in the Xisha Uplift indicates the provenance from the Red River, the Mekong River, and rivers in Taiwan. The illite content in both Red and Mekong Rivers is higher or equal to that in the Xisha Uplift [1]. Moreover, in the Red and Mekong River basins, humid and cold climatic conditions increase the physical erosion and decrease the hydrolytic weathering processes of metamorphic and granitic parent rocks. This weathering process is associated with the production of a high illite content [1]. The high physical weathering rate in Taiwan is consistent with the present illite chemistry index and illite crystallinity data with complete Fe–Mg-rich illite.
6. Conclusions
Surface sediments from the Xisha Uplift in the SCS were measured for clay minerals, primary elements and minerals for tracing sediment provenances, weathering intensity, and transport. Our results emphasize that the clay mineral assemblages of the study areas primarily consist of smectite (24–44%, average 35%) and illite (29–40%, average 35%), with a lesser abundance of chlorite (16–22%, average 18%) and scarce kaolinite (8–16%, average 13%). In conclusion, sediments in the study areas are derived primarily from large rivers in the northern SCS (the Mekong and Red Rivers and Luzon River). We suggest that the DWC and surface monsoon circulation are the primary transport dynamics for sediments in the Xisha Uplift by combining the clay mineral compositions of the surrounding basins and surface sediments in the northern SCS.
Author Contributions
H.Z., H.L., Q.C., C.L. and N.W. performed the expedition with fieldwork and sediment sampling and test; M.Z. wrote the paper. M.Z. and G.B. revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was partially supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (No. 201804010372), NSFC (No. 41306061), and the Open Research Fund Program of the Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals and Geological Environment Monitoring (Central South University), Ministry of Education (No. 2019YSJS19).
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the crew of the Shiyan-1 exploration ship and colleagues from the Key Laboratory of Marginal Sea Geology, CAS for collecting sediment cores. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their critical and constructive suggestions, which greatly helped to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Z.; Colin, C.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Trentesaux, A.; Chen, J. Clay minerals in surface sediments of the Pearl River drainage basin and their contribution to the South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, S.; Bai, F.; Zhang, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, L. Clay mineral distributions in surface sediments of the Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea and surrounding river sediments: Source and transport patterns. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 73, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, S.; Fang, X.; Qiao, S.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N. Distribution of clay minerals in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: Sources and transport patterns. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Trentesaux, A.; Clemens, S.C.; Colin, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, B.; Boulay, S. Clay mineral assemblages in the northern South China Sea: Implications for East Asian monsoon evolution over the past 2 million years. Mar. Geol. 2003, 201, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Colin, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tuo, S.; Chen, Z.; Siringan, F.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; You, C.; et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: Source and transport. Mar. Geol. 2010, 277, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, D.Z.; Ludington, S.; Duval, J.S.; Taylor, H.E. Geochemical of bed and suspend sediment in the Mississippi river system: Provenance versus weathering and winnowing. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.B.; Huh, Y.; Moon, S.; Noh, H. Provenance and weathering control on river bed sediments of the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Russian Far East. Chem. Geol. 2008, 254, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. Major, trace and REE geochemistry of the Ganga River sediments: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Chem. Geol. 2009, 266, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, F.; Critelli, S.; Mongelli, G.; Cullers, R.L. Sedimentary evolution of the Mesozoic continental redbeds using geochemical and mineralogical tools: The case of Upper Triassic to Lowermost Jurassic Monte di Gioiosa mudrocks (Sicily, southern Italy). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 100, 1569–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Cui, R.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Fang, X.; Ding, X.; Zou, L.; Bai, F. Clay mineralogy of the riverine sediments of Hainan Island, South China Sea: Implications for weathering and provenance. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Feng, X.; Fang, X.; Cao, P.; Sun, X.; Wenxing, Y.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N. Distributions of clay minerals in surface sediments of the middle Bay of Bengal: Source and transport pattern. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 145, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Pan, B.; Garzanti, E.; Gao, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, D. Mineralogy and geochemistry of modern Yellow River sediments: Implications for weathering and provenance. Chem. Geol. 2018, 488, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critelli, S. Provenance of Mesozoic to Cenozoic Circum-Mediterranean sandstones in relation to tectonic setting. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 624–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Hosseini-Barzi, M.; Sadeghi, A.; Critelli, S. Geochemistry of Asara Shale member of Karaj Formation, Central Alborz, Iran: Provenance, Source Weathering and Tectonic Setting. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 121, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarciglia, F.; Le Pera, E.; Critelli, S. The onset of sedimentary cycle in a mid-latitude upland environment: Weathering, pedogenesis and geomorphic processes on plutonic rocks (Sila Massif, Calabria). In Sedimentary Provenance: Petrographic and Geochemical Perspectives; Arribas, J., Critelli, S., Johnsson, M., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Paper: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007; Volume 420, pp. 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Scarciglia, F.; Critelli, S.; Borrelli, L.; Coniglio, S.; Muto, F.; Perri, F. Weathering profiles in granitoid rocks of the Sila Massif uplands, Calabria, southern Italy: New insights into their formation processes and rates. Sediment. Geol. 2016, 336, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K. River Discharge into the Coastal Ocean—AGlobal Synthesis, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sarnthein, M.; Erlenkeuser, H.; Grimalt, J.; Grootes, P.; Heilig, S.; Ivanova, E.; Kienast, M.; Pelejero, C.; Pflaumann, U. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene: High-resolution sediment records from the South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 1999, 156, 245–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, G.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Jian, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, P. Geochemical and Nd isotopic variations in sediments of the South China Sea: A response to Cenozoic tectonism in SE Asia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 211, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, S.; Colin, C.; Trentesaux, A.; Pluquet, F.; Bertaux, J.; Blamart, D.; Buehring, C.; Wang, P. Mineralogy and Sedimentology of Pleistocene Sediment in the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144). Prell, W., Wang, P., Blum, P., Rea, D., Clemens, S.C., Eds.; 2003. Available online: http://www-odp.tamu.edu/publications/184_SR/ (accessed on 18 February 2003).
- Boulay, S.; Colin, C.; Trentesaux, A.; Frank, N.; Liu, Z. Sediment sources and East Asian monsoon intensity over the last 450 ky. Mineralogical and geochem-ical investigations on South China Sea sediments. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 228, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Tuo, S.; Colin, C.; Liu, J.T.; Huang, C.-Y.; Selvaraj, K.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Zhao, Y.; Siringan, F.P.; Boulay, S.; et al. Detrital fine-grained sediment contribution from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea and its relation to regional ocean circulation. Mar. Geol. 2008, 255, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Yan, W. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South China Sea and its significance for sediment sources and transport. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, A.; Clift, P.; Stutt, J. Development of the East Asian monsoon: Mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 254, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, R.; Lu, J. Preservation of radiolarian diversity and abundance in surface sediments of the South China Sea and its environmental implication. J. Chin. Univ. Geosci. 2008, 19, 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, E.; Tian, J.; Steinke, S. Millennial-scale dynamics of the winter cold tongue in the southern South China Sea over the past 26ka and the East Asian winter monsoon. Quat. Res. 2011, 75, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jian, Z.; Shi, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Shi, F. A Holocene record of millennial-scale climate changes in the mud area on the inner shelf of the East China Sea. Quatern. Int. 2015, 384, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Qiao, P.J.; Pang, X.; Wei, G.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Miao, W.L.; Li, A. Nd isotopic variations and its implications in the recent sediments from the northern South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.L.; Xie, L.H.; Chen, J.F.; Deng, W.F.; Tang, S. Nd, Sr isotopes and elemental geochemistry of surface sediments from the South China Sea: Implications for provenance tracing. Mar. Geol. 2012, 319–322, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J. The role of hydrological processes in ocean-atmosphere interactions. Rev. Geophys. 1994, 32, 427–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Fang, W.; Fang, Y.; Wang, K. A survey of studies on the South China Sea upper ocean circulation. Acta Oceanogr. Taiwan. 1998, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, M.; Gawarkiewicz, G.; Beardsley, R.C. Interannual variability of the Kuroshio intrusion in the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 62, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, B.; Mi, L.; Wilkins, R.W.T.; Fu, N.; Xiao, X. Geochemistry, origin, and deep-water exploration potential of natural gases in the Pearl River Mouth and Qiongdongnan basins, South China Sea. Aapg Bull. 2009, 93, 741–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xiao, X.; Li, X. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, offshore South China Sea. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Wu, S.G.; Cartwright, J.; Lüdmann, T.; Yao, G.S. Focused fluid flow systems of the Zhongjiannan Basin and Guangle Uplift, South China Sea. Basin Res. 2013, 25, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.L.; Wu, S.G.; Hovland, M.; Luo, P.; Lu, Y.T.; Qu, T.L. The morphologies and genesis of mega-pockmarks near the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Yao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G. Geophysical signatures associated with fluid flow and gas hydrate occurrence in a tectonically quiescent sequence, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Geofluids 2010, 10, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, D. Pockmark activity inferred from pore water geochemistry in shallow sediments of the pockmark field in southwestern Xisha Uplift, northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 48, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Chen, L.; Tong, H.; Yan, W.; Chen, D. Gas hydrate occurrence inferred from dissolved Cl− concentrations and δ18O values of pore water and dissolved sulfate in the shallow sediments of the pockmark field in southwestern Xisha Uplift, northern South China Sea. Energies 2014, 7, 3886–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, A.; Clift, P.; Jiang, H. Development of the East Asian summer monsoon: Evidence from the sediment record in the South China Sea since 8.5 Ma. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 241, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell, Malden, Mass: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst 2001, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Resentini, A. Provenance control on chemical indices of weathering (Taiwan river sands). Sediment. Geol. 2016, 336, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. Sediment Distributional Patterns and Evolution in the South China Sea Since the Oligocene. Ph.D. Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2004; 113p. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Wang, P. Sediment mass and distribution in the South China Sea since the Oligocene. Sci. China D 2006, 49, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiang, R.; Chen, Z.; Chen, M.H.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Sources, transport and deposition of surface sediments from the South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. 2013, 71, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petschick, R.; Kuhn, G.; Gingele, F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic: Sources, transport, and relation to oceano- graphy. Mar. Geol. 1996, 130, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettke, T.; Halliday, A.N.; Hall, C.M.; Rea, D.K. Dust production and deposition in Asia and the north Pacific Ocean over the past 12 Myr. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 178, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Milliman, J.; Gao, S.; Cheng, P. Holocene development of the Yellow River’s subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 2004, 209, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Colin, C.; Siringan, F.; Wu, Q. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Tracing tropical and intermediate waters from the South China Sea to the Okinawa Trough and beyond. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, C05012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, M. Palaeoclimatic interpretation of clay minerals in marine deposits: An outlook from the continental origin. Earth Sci. Rev. 2000, 49, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Colin, C.; Trentesaux, A.; Siani, G.; Frank, N.; Blamart, D.; Farid, S. Late Quaternary climatic control on erosion and weathering in the eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Mekong Basin. Quat. Res. 2005, 63, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. Minerals in bottom sediments of the South China Sea. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1978, 89, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Sathiamurthy, E.; Colin, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Chemical weathering in Malay Peninsula and North Borneo: Clay mineralogy and element geo-chemistry of river surface sediments. Sci. Ser. 2011, D54, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiang, R.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Yan, W.; Liu, F. Influence of the Kuroshio current intrusion on depositional environment in the northern South China Sea: Evidence from surface sediment records. Mar. Geol. 2012, 285, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Chen, C.-T.A. Moderate chemical weathering of subtropical Taiwan: Constraints from solid-phase geochemistry of sediments and sedimentary rocks. J. Geol. 2006, 114, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamley, H. Clay Sedimentology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1989; 623p. [Google Scholar]
- Scarciglia, F.; Le Pera, E.; Critelli, S. The interplay of geomorphic processes and soil development in un upland environment, Calabria, South Italy. Geomorphology 2005, 64, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Fagel, N. Chapter four clay minerals, deep circulation and climate. In Developments in Marine Geology; Claude, H.M., De Anne, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 139–184. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Colin, C.; Huang, W.; Le, K.; Tong, S.; Chen, Z.; Trentesaux, A. Climatic and tectonic controls on weathering in South China and the Indochina Peninsula: Clay mineralogical and geochemical investigations from the Pearl, Red, and Mekong drainage basins. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2007, 8, Q05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Padoan, M.; Setti, M.; López-Galindo, A.; Villa, I.M. Provenance versus weathering control on the composition of tropical river mud (Southern Africa). Chem. Geol. 2014, 366, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluth, G.J.S.; Kump, L.R. Lithologic and climatic controls of river chemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 2341–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessert, C.; Dupré, B.; Francois, L.M.; Schott, J.; Gaillardet, J.; Chakrapani, G.J.; Bajpai, S. Erosion of Deccan Traps determined by river geochemistry: Impact on the global climate and the 87Sr/86Sr ratio of seawater. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 188, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, M.; Tobschall, H.L. Weathering of the Ganga alluvial plain, northern India: Implications from fluvial geochemistry of the Gomati River. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Böning, P.; Köhler, C.M.; Hillier, S.; Pressling, N.; Wan, S.; Brumsack, H.J.; Clift, P.D. Deep sea records of the continental weathering and erosion response to East Asian monsoon intensification since 14 ka in the South China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2012, 326–327, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, S.; Hanebuth, T.J.; Vogt, C.; Stattegger, K. Sea level induced variations in clay mineral composition in the southwestern South China Sea over the past 17,000 yr. Mar. Geol. 2008, 250, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, A.; Clift, P.D.; Wu, S.; Xu, K.; Li, T. Increased contribution of terrigenous supply from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea since 3 Ma. Mar. Geol. 2010, 278, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, A.; Xu, K.; Yin, X. Characteristics of clay minerals in the Northern South China Sea and its implications for evolution of East Asian Monsoon since Miocene. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2008, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.; Tian, J.; Steinke, S.; Li, A.; Li, T. Evolution and variability of the East Asian summer monsoon during the Pliocene: Evidence from clay mineral records of the South China Sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 293, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, X.; Kao, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Lü, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, S.; Qiao, S. Clay mineral composition and their sources for the fluvial sediments of Taiwanese rivers. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).