Importance of Spring Habitats for Amphibians: The Case of Estavelle Ecotones in the Classical Karst Region
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
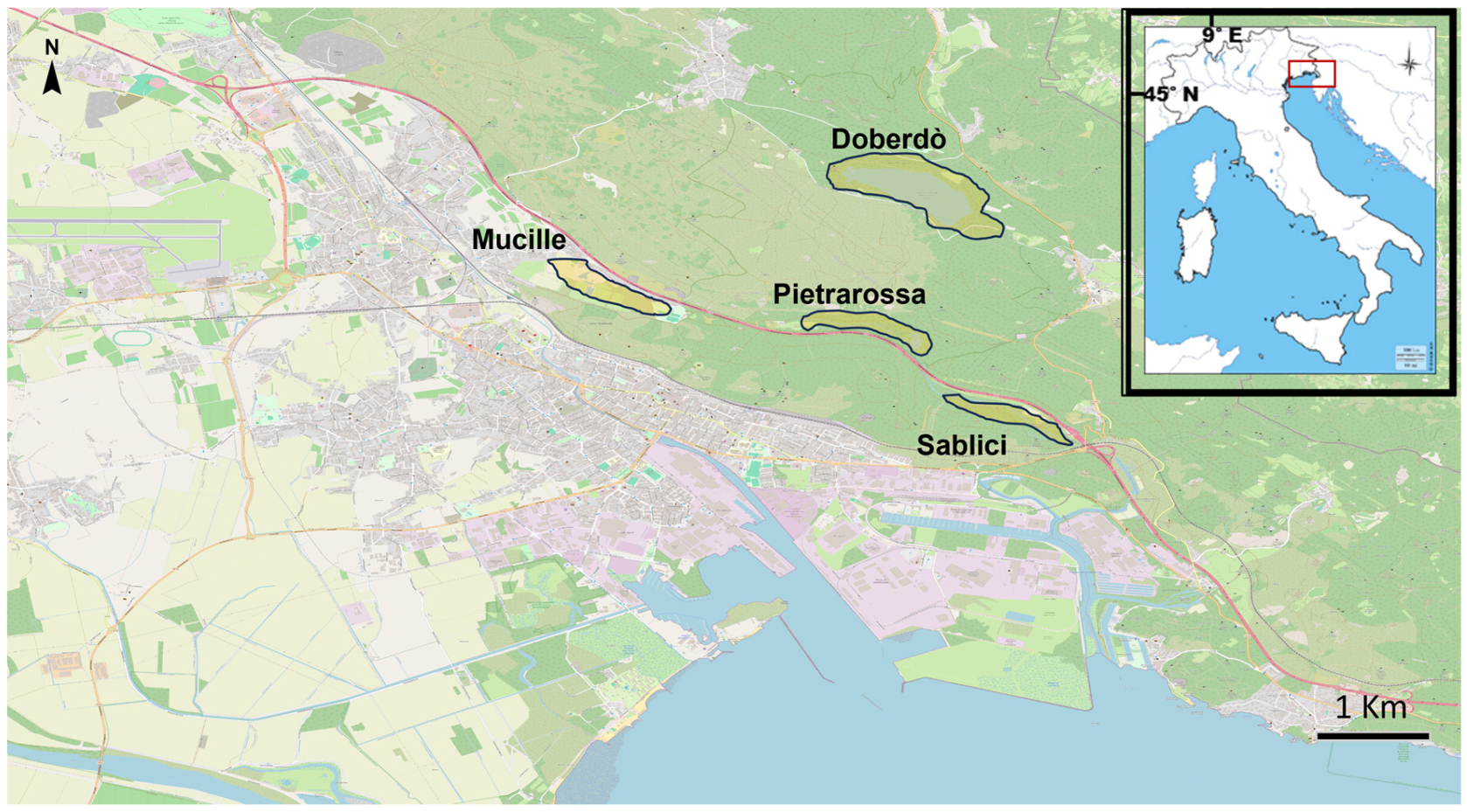
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Surveys
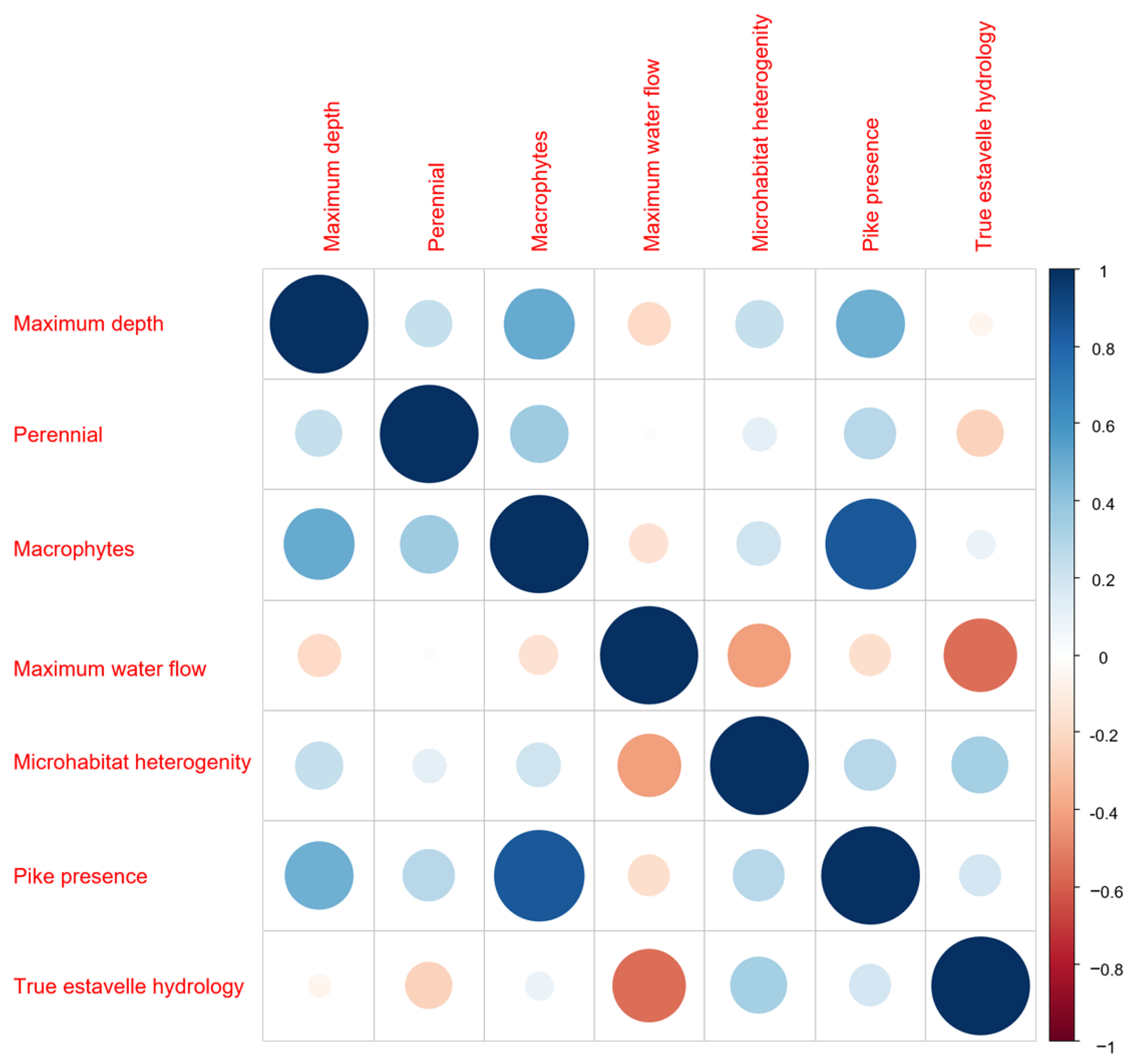
2.3. Statistical Analyses
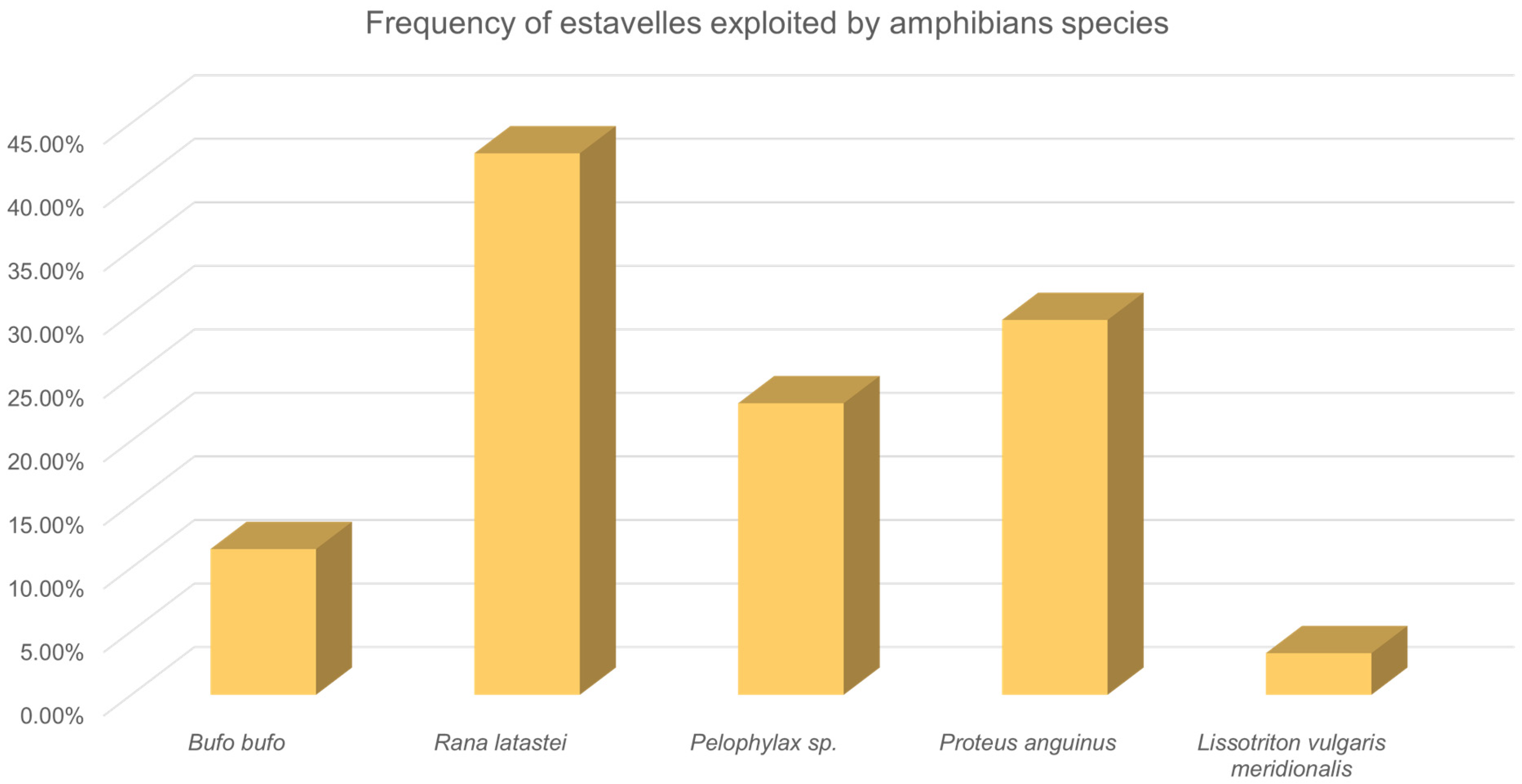
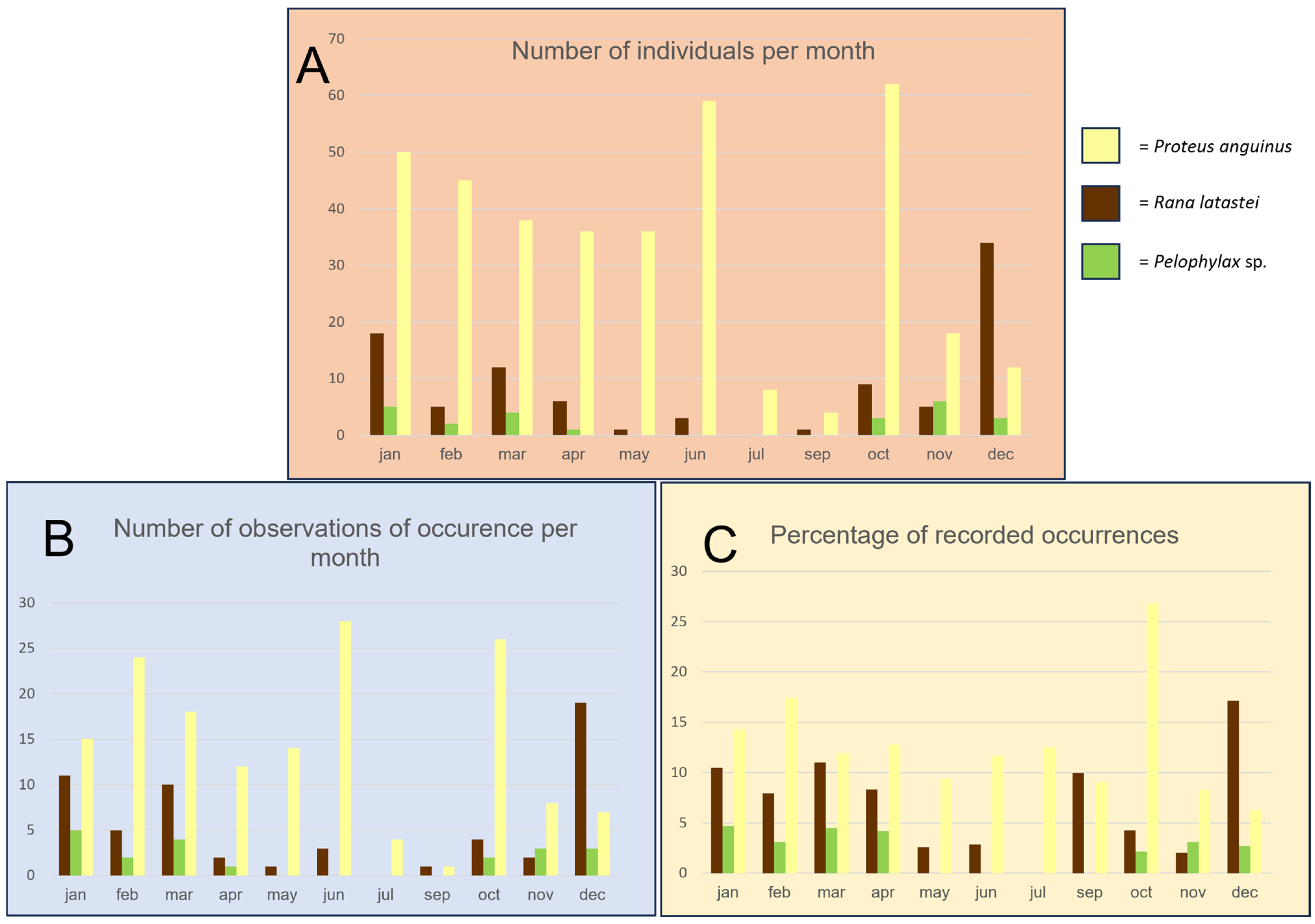
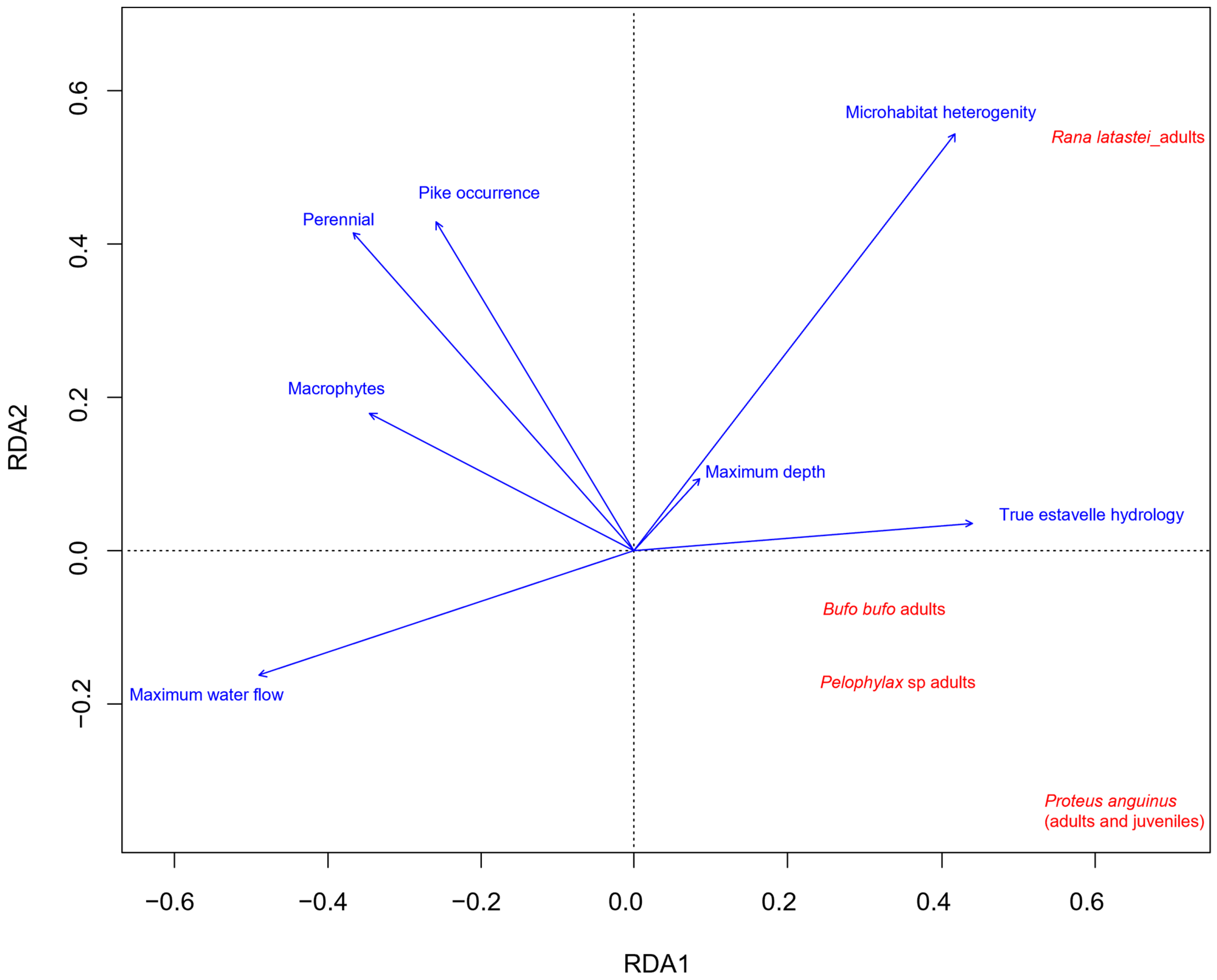
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grover, M.C.; Wilbur, H.M. Ecology of ecotones: Interactions between salamanders on a complex environmental gradient. Ecology 2002, 83, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, U.; Bersier, L.F.; Borcard, D. Ecotones and gradient as determinants of herpetofaunal community structure in the primary forest of Mount Kupe, Cameroon. J. Trop. Ecol. 2000, 16, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Langhans, S.D.; Tockner, K. Edge Effects Are Important in Supporting Beetle Biodiversity in a Gravel-Bed River Floodplain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarero, J.J.; Gutierrez, E. Structure and recent recruitment at alpine forest-pasture ecotones in the Spanish central Pyrenees. Ecoscience 1999, 6, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Colin, P.; Hulshof, C.M. Ecotones as Windows into Organismal-to-Biome Scale Responses across Neotropical Forests. Plants 2024, 13, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilthuizen, M. Ecotone: Speciation-prone. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantonati, M.; Lichtenwöhrer, K.; Leonhardt, G.; Seifert, L.; Mustoni, A.; Hotzy, R.; Schubert, E.; Blattner, L.; Bilous, O.; Lotz, A.; et al. Using Springs as Sentinels of Climate Change in Nature Parks North and South of the Alps: A Critical Evaluation of Methodological Aspects and Recommendations for Long-Term Monitoring. Water 2022, 14, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, T.; Cipriani, D.; Bono, P.; Rossini, L.; De Laurentiis, P.; Fiasca, B.; Pantani, C.; Galassi, D.M.P. Dynamics of groundwater copepod assemblages from the Mazzoccolo karstic spring (central Italy). Meiofauna Mar. 2005, 14, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.R.; Harden, S.J.; Fries, J.N. Survey and distribution of invertebrates from selected springs of the Edwards Aquifer in Comal and Hays counties, Texas. Southwest Nat. 2008, 53, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, F.; Boutin, C.; Camacho, A.I.; Ferreira, D.; Michel, G.; Sket, B.; Stoch, F. Diversity patterns of stygobiotic crustaceans across multiple spatial scales in Europe. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 756–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Pezzoli, E. Think of what lies below, not only of what is visible above, or: A comprehensive zoological study of invertebrate communities of spring habitats. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dole-Olivier, M.J.; Castellarini, F.; Coineau, N.; Galassi, D.M.P.; Martin, P.; Mori, N.; Valdecasas, A.; Gibert, J. Towards an optimal sampling strategy to assess groundwater biodiversity: Comparison across six European regions. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtimova, V.V.; Pandourski, I.S.; Benderev, A.D. Stygofauna of Karstic Ecosystem in Ponor Mountains, Western Bulgaria: Present Knowledge and Research Challenges. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2009, 61, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins, B.T.; Gibson, J.R.; Diaz, P.H.; Schwartz, B.F. Stygobiont diversity in the San Marcos artesian well and Edwards aquifer groundwater ecosystem, Texas, USA. Diversity 2021, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Forlani, M.; Lapadula, S.; Galbiati, M.; Barzaghi, B.; Ficetola, G.F.; Melotto, A. Landscape of fear in freshwater ecotones: How predation risk and light conditions affect mesopredator activity and foraging in springs. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 68, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Siesa, M.E.; Ficetola, G.F. Odonata occurrence in caves: Active or accidentals? A new case study. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2013, 75, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T. Shallow Subterranean Habitats: Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A. Cave Biology: Life in Darkness; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adcock, Z.C.; MacLaren, A.R.; Jones, R.M.; Villamizar-Gomez, A.; Wall, A.E.; White Iv, K.; Forstner, M.R.J. Predicting surface abundance of federally threatened Jollyville Plateau Salamanders (Eurycea tonkawae) to inform management activities at a highly modified urban spring. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, B.T. The conservation status of Texas groundwater invertebrates. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 475–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, F.; Machado, E.G.; Casane, D.; Cooper, S.; Fišer, C.; Eme, D. Dispersal and geographic range size in groundwater. In Groundwater Ecology and Evolution; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, N.A. Adaptation and constraint in the complex life cycles of animals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1994, 25, 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.M.; Norris, D.R.; Crossin, G.T.; Cooke, S.J. Biological carryover effects: Linking common concepts and mechanisms in ecology and evolution. Ecosphere 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, H.K.; Richardson, J.S. Predation risk and competition effects on the life-history characteristics of larval Oregon spotted frog and larval red-legged frog. Oecologia 2002, 132, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capellan, E.; Nicieza, A.G. Trade-offs across life stages: Does predator-induced hatching plasticity reduce anuran post-metamorphic performance? Evol. Ecol. 2007, 21, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoël, M.; Poncin, P. The effect of food on growth and metamorphosis of paedomorphs in Triturus alpestris apuanus. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2001, 152, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, E.T.; Steinfartz, S.; Caspers, B.A. Poor nutritional conditions during the early larval stage reduce risk-taking activities of fire salamander larvae (Salamandra salamandra). Ethology 2011, 117, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, C.A.; Snaas, H.; Shaffer, H.B. Determinants of size at metamorphosis in an endangered amphibian and their projected effects on population stability. Oikos 2015, 124, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwegg, R.; Reyer, H.U. Patterns of natural selection on size at metamorphosis in water frogs. Evolution 2003, 57, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoel, M.; Drapeau, L.; Oromi, N.; Winandy, L. The role of predation risk in metamorphosis versus behavioural avoidance: A sex-specific study in a facultative paedomorphic amphibian. Oecologia 2019, 189, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capps, K.A.; Berven, K.A.; Tiegs, S.D. Modelling nutrient transport and transformation by pool-breeding amphibians in forested landscapes using a 21-year dataset. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, J.E.; Semlitsch, R.D. Reciprocal subsidies in ponds: Does leaf input increase frog biomass export? Oecologia 2012, 170, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regester, K.J.; Lips, K.R.; Whiles, M.R. Energy flow and subsidies associated with the complex life cycle of ambystomatid salamanders in ponds and adjacent forest in southern Illinois. Oecologia 2006, 147, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.E.; Skelly, D.K.; Relyea, R.A.; Yurewicz, K.L. Amphibian species richness across environmental gradients. Oikos 2007, 116, 1697–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, F.E.; Rawlings, M.B.; Semlitsch, R.D. Joint effects of resources and amphibians on pond ecosystems. Oecologia 2017, 183, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behangana, M.; Kasoma, P.M.B.; Luiselli, L. Ecological correlates of species richness and population abundance patterns in the amphibian communities from the Albertine Rift, East Africa. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 2855–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasumi, M.; Hongorzul, T.; Terbish, K. Animal species diversity at a land-water ecotone in Mongolia. Limnology 2011, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.H. Application of stable isotope analysis to study temporal changes in foraging ecology in a highly endangered amphibian. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, D.C.; Gibson, J.R.; Ostrand, K.G.; Norris, C.W.; Diaz, P.H. Monitoring and marking techniques for the endangered comal springs riffle beetle, Heterelmis comalensis Bosse, Tuff, and Brown, 1988 (Coleoptera: Elmidae). Coleopt. Bull. 2015, 69, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, Z.C.; MacLaren, A.R.; Adcock, M.E.; Forstner, M.R.J. Spatial Variation in Abundance Parameters of a Federally Threatened Groundwater Salamander Within and Among Central Texas Headwater Creeks. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O. Poljes, Ponors and Their Catchments. In Treatise on Geomorphology: Volume 1–14; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 1–14, pp. 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Florea, L.J.; Noe-Stinson, C.L.; Brewer, J.; Fowler, R.; Kearns, J.B.; Greco, A.M. Iron oxide and calcite associated with Leptothrix sp. biofilms within an estavelle in the upper Floridan aquifer. Int. J. Speleol. 2011, 40, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvanec, B. Popovo polje, a different view. Acta Carsologica 2016, 45, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. An assessment of groundwater resource vulnerability to pollution in the Jiangjia spring basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Goldscheider, N. Modeling spatially and temporally varied hydraulic behavior of a folded karst system with dominant conduit drainage at catchment scale, Hochifen-Gottesacker, Alps. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, M.; Slabe, T. Lithostratigraphic characteristics of the intermittent Pivka lakes region and Matijeva jama cave estavelle. Acta Carsologica 2005, 34, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačič, G. The Šembije intermittent lake. Geogr. Obz. 2014, 61, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lučić, I. Shafts of life and shafts of death in Dinaric karst, Popovo Polje case (Bosnia & Herzegovina). Acta Carsologica 2007, 36, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- López-Chicano, M.; Calvache, M.L.; Martín-Rosales, W.; Gisbert, J. Conditioning factors in flooding of karstic poljes—The case of the Zafarraya polje (South Spain). Catena 2002, 49, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzić, J.; Reberski, J.L.; Rubinić, J. Groundwater Protection and Climate Change Predictions of a Complex Dinaric Karst Catchment. A Case Study of the Bokanjac-PoličNik Area, Croatia. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory—Volume 1: Climate Change and Engineering Geology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Balestrini, R.; Delconte, C.A.; Sacchi, E.; Buffagni, A. Groundwater-dependent ecosystems as transfer vectors of nitrogen from the aquifer to surface waters in agricultural basins: The fontanili of the Po Plain (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, D.A.; Dell’Orto, V.; Destefanis, E.; Forno, M.G.; Lasagna, M.; Masciocco, L. Hydrogeological structure of the “fontanili” in Turin plain. Rend. Online Soc. Geol. Ital. 2009, 5, 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, M. Spatial modeling of the water table and its historical variations in Northeastern Italy via a geostatistical approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Di Nicola, M.R.; Zampieri, V.; Grassi, G.; Creanza, T.; Mauri, E.; Ficetola, G.F.; Barzaghi, B. Wandering outside of the Styx: Surface activity of an iconic subterranean vertebrate, the olm (Proteus anguinus). Ecology 2024, 105, e4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljančič, G. History of research on Proteus anguinus Laurenti 1768 in Slovenia. Folia Biol. Geol. 2019, 60, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Zampieri, V.; Pacinotti, G.; Cassarino, F.; Galbiati, M.; Lapadula, S.; Gajdošová, M.; Messina, V.; Balestra, V.; Falaschi, M.; et al. Back from the underworld: The exploitation of spring habitats by stygobiont species. Hydrobiologia 2025, 852, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoch, F. Il Lacus Timavi: La fauna acquatica sotterranea, con particolare riguardo alle risorgive del Fiume Timavo. Atti E Mem. Della Comm. Grotte “E. Boegan” 2017, 47, 173–203. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorenza, T. Anfibi del Friuli Venezia Giulia; Editrice CO.EL.: Udine, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabo, I.; Brunelli, E. Comparative morphological analysis during larval development of three syntopic newt species (Urodela: Salamandridae). Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquegranelli, A.; Salvi, D.; Vignoli, L. The amphibians of the Circeo National Park, central Italy: Distribution and aquatic habitat use. Herpetozoa 2015, 28, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ficetola, G.F.; De Bernardi, F. Amphibians in a human-dominated landscape: The community structure is related to habitat features and isolation. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 119, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Garner, T.W.J.; Wang, J.L.; De Bernardi, F. Rapid selection against inbreeding in a wild population of a rare frog. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Abbona, I.; Papi, F. Storia delle ricerche del Proteo in Italia e attuali conoscenze a 250 anni dalla sua prima descrizione da parte di Laurenti. In Atti del Convegno SPELEO2018; Regione Autonoma Friuli Venezia Giulia: Trieste, Italy, 2018; pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zini, L.; Calligaris, C.; Cucchi, F. Along the hidden Timavo. Geol. Field Trips Maps 2022, 14, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradisi, S.; Miotti, E.; Miotti, L. Pesci D’acqua Dolce del Friuli Venezia Giulia; Editrice CO.EL.: Udine, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.R.; Blanchet, R.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Henry, M.; Stevens, H.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Department of Statistics and Mathematics, Vienna University of Economics and Business Administration, Vienna. Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- von Fumetti, S.; Nagel, P.; Baltes, B. Where a springhead becomes a springbrook—A regional zonation of springs. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 169, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesic, V.; Gligorovic, B.; Savic, A.; Buczynski, P. Ecological patterns of Odonata assemblages in karst springs in central Montenegro. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premate, E.; Fišer, Ž.; Kuralt, Ž.; Pekolj, A.; Trajbarič, T.; Milavc, E.; Hanc, Ž.; Kostanjšek, R. Behavioral observations of the olm (Proteus anguinus) in a karst spring via direct observations and camera trapping. Subterr. Biol. 2022, 44, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, R.S. On the Eyes and Reactions to Light of Proteus anguinus. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 1945, 86, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, M.; Bulog, B.; Szél, Á.; Röhlich, P. Immunocytochemical demonstration of visual pigments in the degenerate retinal and pineal photoreceptors of the blind cave salamander (Proteus anguinus). Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 303, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balázs, G.; Lewarne, B.; Herczeg, G. Extreme site fidelity of the olm (Proteus anguinus) revealed by a long-term capture–mark–recapture study. J. Zool. 2020, 311, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulog, B. Surface Ultrastructure of Lateral Line Sensory Receptors in Proteus anguinus Laur (Urodela, Amphibia). Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1988, 93, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume, O. Role of chemical communication and behavioural interactions among conspecifics in the choice of shelters by the cave-dwelling salamander Proteus anguinus (Caudata, Proteidae). Can. J. Zool. 2000, 78, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, P.A. Magnetic and other non-visual orientation mechanisms in some cave and surface urodeles. J. Ethol. 2008, 26, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, P.A.; Roth, A. Tuning of electroreceptors in the blind cave salamander, Proteus anguinus L. Brain Behav. Evol. 1997, 49, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, P.A.; Steinfartz, S.; Bulog, B. Non-visual sensory physiology and magnetic orientation in the Blind Cave Salamander, Proteus anguinus (and some other cave-dwelling urodele species). Review and new results on light-sensitivity and non-visual orientation in subterranean urodeles (Amphibia). Anim. Biol. 2009, 59, 351–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laundre, J.W.; Hernandez, L.; Altendorf, K.B. Wolves, elk, and bison: Reestablishing the “landscape of fear” in Yellowstone National Park, USA. Can. J. Zool. 2001, 79, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyly, M.S.; Villers, A.; Koivisto, E.; Helle, P.; Ollila, T.; Korpimäki, E. Avian top predator and the landscape of fear: Responses of mammalian mesopredators to risk imposed by the golden eagle. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matassa, C.M.; Trussell, G.C. Landscape of fear influences the relative importance of consumptive and nonconsumptive predator effects. Ecology 2011, 92, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikenros, C.; Aronsson, M.; Liberg, O.; Jarnemo, A.; Hansson, J.; Wallgren, M.; Sand, H.; Bergström, R. Fear or food—Abundance of red fox in relation to occurrence of lynx and Wolf. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaguri, M.; Hawlena, D. Bearding the scorpion in his den: Desert isopods take risks to validate their ‘landscape of fear’ assessment. Oikos 2019, 128, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, W.J. Searching Behaviour: The Behavioural Ecology of Finding Resources; Chapman and Hall: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes, E.E.; Daly, R.; Leos-Barajas, V.; Langrock, R.; Gleiss, A.C. Evaluating the constraints governing activity patterns of a coastal marine top predator. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroa, N.; Fernandez-Saez, M.J.; Zoroa, P. A foraging problem Sit-and-wait versus active predation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 208, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, F.; Bernini, F. Distribution and status of Rana latastei in Italy (Amphibia, Ranidae). Ital. J. Zool. 2004, 71, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, R.; Cigognini, R.; Gazzola, A.; Bernini, F.; Razzetti, E. Male calling activity in syntopic populations of Rana latastei and Rana dalmatina (Amphibia: Anura). Ital. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, F.; Mazzotti, S. Rana latastei. In Atlante Degli Anfibi e Dei Rettili D’italia/Atlas of Italian Amphibians and Reptiles; Sindaco, R., Doria, G., Razzetti, E., Bernini, F., Eds.; Societas Herpetologica. Italica, Edizioni Polistampa: Firenze, Italy, 2006; pp. 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Pozzi, A. Ecologia di Rana latastei Boul. (Amphibia Anura). Atti Soc. Ital. Sci. Nat. Museo Civ. Stor. Nat. Milano. 1980, 121, 221–274. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, D.; Pobolisaj, K. New data on the distribution of the Italian agile frog Rana latastei Boulenger, 1879 in Slovenian Istra. Nat. Slov. 2013, 15, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ildos, A.; Ancona, N. Analysis of amphibian habitat preferences in a farmland area (Po Plain, northern Italy). Amphib. Reptil. 1994, 15, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; De Bernardi, F. Interspecific social interactions and breeding success of the frog Rana latastei: A field study. Ethology 2005, 111, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melotto, A.; Melotto, A.S.; Ficetola, G.F.; Manenti, R.; Falaschi, M. First report of overwintering tadpoles in the endemic Italian agile frog Rana latastei. Acta Herpetol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, R.; Diaz-Paniagua, C.; Gomez-Mestre, I. Ecological consequences of amphibian larvae and their native and alien predators on the community structure of temporary ponds. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1996–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, F.; Renai, B.; Corti, C. Crayfish predation on tadpoles: A comparison between a native (Austropotamobius pallipes) and an alien species (Procambarus clarkii). Bull. Fr. Peche Piscic. 2001, 361, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, F.; Tricarico, E.; Ilheu, M. Movement patterns of an invasive crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, in a temporary stream of southern Portugal. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2002, 14, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R. Ecological interest of draining galleries. Rev. Ecol—Terre Vie 2014, 69, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, S.; Mazzotti, S. Ecologia di popolazione e ritmi riproduttivi della rana di Lataste (Rana latastei) nel biotopo “Valle Brusà” (VR). Quad. Della Stn. Di. Ecolologia E Del. Civ. Mus. Di. Stor. Nat. Di. Ferrara 2005, 15, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bissattini, A.M.; Buono, V.; Vignoli, L. Disentangling the trophic interactions between American bullfrogs and native anurans: Complications resulting from post-metamorphic ontogenetic niche shifts. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenda, K.; Kaczmarski, M.; Żurawska, J.; Ogielska, M. Decline of Pelophylax lessonae in mixed populations of water frogs over the last 50 years. Eur. Zool. J. 2024, 91, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentino, D.; Scillitani, G.; Marra, M.; Mastrodonato, M. Seasonal changes in the liver of a non-hibernating population of water frogs, Pelophylax kl. esculentus (Anura: Ranidae). Eur. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, B.; Andreone, F.; Bologna, M.A.; Corti, C.; Razzetti, E.; Bologna, P.C. Fauna d’Italia, Vol. XLII, Amphibia; Calderini: Bologna, Italy, 2007; Volume XLII. [Google Scholar]
- Bonardi, A.; Manenti, R.; Corbetta, A.; Ferri, V.; Fiacchini, D.; Giovine, G.; Macchi, S.; Romanazzi, E.; Soccini, C.; Bottoni, L.; et al. Usefulness of volunteer data to measure the large scale decline of “common” toad populations. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Klaus, I.; Baumgartner, C.; Ward, J.V. Amphibian diversity and nestedness in a dynamic floodplain river (Tagliamento, NE-Italy). Hydrobiologia 2006, 565, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Babik, W.; Rafinski, J. Amphibian breeding site characteristics in the Western Carpathians, Poland. Herpetol. J. 2001, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kloskowski, J. Size-structured effects of common carp on reproduction of pond-breeding amphibians. Hydrobiologia 2009, 635, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, K.M.; Springer, A.E.; Tobin, B.W.; Parnell, R.A. Karst Spring Processes and Storage Implications in High Elevation, Semiarid Southwestern United States; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanelly, T.J. Sinkholes and a disappearing lake: Victory lake case study. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2014, 76, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesper, D.J.; Herman, E.K. Common Spring Types in the Valley and Ridge Province: There Is More than Karst. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2020, 26, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, K.M.; Brown, J.S.; Middleton, A.D.; Power, M.E.; Brashares, J.S. Landscapes of Fear: Spatial Patterns of Risk Perception and Response. Trend Ecol. Evol. 2019, 34, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, H.; Manenti, R.; Melotto, A. The Role of Experience in the Visual and Non-Visual Prey Recognition of Fire Salamander Populations from Caves and Streams. Diversity 2024, 16, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, K. Foraging activity patterns in the goosander (Mergus merganser) and the red-breasted merganser (M. serrator) in relation to patterns of activity in their major prey species. Oecologia 1985, 67, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brognoli, D.; Lo Parrino, E.; Terraneo, G.; Grassi, G.; Zampieri, V.; Galbiati, M.; Balestra, V.; Messina, V.; Barzaghi, B.; Lapadula, S.; et al. Importance of Spring Habitats for Amphibians: The Case of Estavelle Ecotones in the Classical Karst Region. Animals 2025, 15, 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223228
Brognoli D, Lo Parrino E, Terraneo G, Grassi G, Zampieri V, Galbiati M, Balestra V, Messina V, Barzaghi B, Lapadula S, et al. Importance of Spring Habitats for Amphibians: The Case of Estavelle Ecotones in the Classical Karst Region. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223228
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrognoli, Damiano, Elia Lo Parrino, Giorgia Terraneo, Giorgio Grassi, Veronica Zampieri, Matteo Galbiati, Valentina Balestra, Valeria Messina, Benedetta Barzaghi, Stefano Lapadula, and et al. 2025. "Importance of Spring Habitats for Amphibians: The Case of Estavelle Ecotones in the Classical Karst Region" Animals 15, no. 22: 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223228
APA StyleBrognoli, D., Lo Parrino, E., Terraneo, G., Grassi, G., Zampieri, V., Galbiati, M., Balestra, V., Messina, V., Barzaghi, B., Lapadula, S., & Manenti, R. (2025). Importance of Spring Habitats for Amphibians: The Case of Estavelle Ecotones in the Classical Karst Region. Animals, 15(22), 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223228






