Simple Summary
The recent emergence of SARS-CoV-2 has highlighted the recent increase in Emerging Infectious Diseases since the 1940s. This has made evident the need for wildlife studies investigating pathogen dynamics in wildlife species. Rodents have proved excellent models, in both laboratory and natural settings for studying disease dynamics. Due to the single introduction point, continuous spread and presence of baseline data, we propose that the recent invasion of Myodes glareolus in Ireland can be used as a model system to understand the changes in helminth species during a biological invasion. Through long-term studies using this invasive species as a model, we will be able to fill large knowledge gaps surrounding the area of pathogen dynamics in wild populations.
Abstract
The primary driver of the observed increase in emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) has been identified as human interaction with wildlife and this increase has emphasized knowledge gaps in wildlife pathogens dynamics. Wild rodent models have proven excellent for studying changes in parasite communities and have been a particular focus of eco-immunological research. Helminth species have been shown to be one of the factors regulating rodent abundance and indirectly affect disease burden through trade-offs between immune pathways. The Myodes glareolus invasion in Ireland is a unique model system to explore the invasion dynamics of helminth species. Studies of the invasive population of M. glareolus in Ireland have revealed a verifiable introduction point and its steady spread. Helminths studies of this invasion have identified enemy release, spillover, spillback and dilution taking place. Longitudinal studies have the potential to demonstrate the interplay between helminth parasite dynamics and both immune adaptation and coinfecting microparasites as M. glareolus become established across Ireland. Using the M. glareolus invasion as a model system and other similar wildlife systems, we can begin to fill the large gap in our knowledge surrounding the area of wildlife pathogen dynamics.
1. Emerging Infectious Diseases and the Need for Wildlife Models
In 2020, a global public health emergency was declared by the World Health Organisation (WHO) following the detection of a new zoonotic disease, similar to the SARS-CoV virus [1]. This disease, called COVID-19, has caused an ongoing global pandemic resulting in over 3.8 million deaths worldwide [2]. The COVID-19 disease sparked an unprecedented scientific effort including the rapid identification and genome sequencing of the virus, and the swift development of efficacious vaccines [3,4,5]. Despite this, relatively little is known about the wildlife origins of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Although evidence supports an origin from a bat species, it is not known exactly from what species of bat is associated or if there was an intermediate host involved between bats and humans [6]. This prevents the investigation of any sylvatic epidemiological or host factors that may have led to the spillover to humans. This pandemic is not an isolated event, the incidence of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) has increased since the 1940s [7]. A review by Jones et al. [7] demonstrated that 60% of EIDs originate from wildlife. These EID events further spotlight the need for investigation into wildlife pathogens. EID events not only pose a risk to humans, but also can be detrimental to indigenous wildlife and livestock [8,9,10]. The increased frequency of EIDs has been primarily attributed to the increasing rate of environmental change, caused by processes such as human development, habitat destruction, lowering habitat diversity and biological invasions [11,12,13]. Invasive species can also harbour zoonotic parasites [14], such as the golden apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata), a freshwater mollusc which harbours Echinostoma revolutum, Angiostrongylus cantonensis and Gonathstoma spinigerum, helminths known to impair human health [15]. Similarly, it has been suggested that the bioinvasion of the grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis), has caused the spillover of Squirrelpox (Parapoxvirus) to indigenous wildlife, such as the native red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris) [16,17,18]. The introduction of pathogens can occur through co-invasion with non-native host species, these pathogens can then infect native species, a process known as pathogen spillover (Figure 1B) [19]. The emergence of these new pathogens from invasive species, once established, can cause increased disease risk for both humans and animals [20]. The introduction of exotic pathogens to immunologically naïve indigenous wildlife has been largely ignored by conservation biologists, possibly due to their cryptic nature [8]. Another process, known as spillback, can occur when an invasive species is a more competent host for native parasite species than a native host, resulting in an amplification of infection in native hosts (Figure 1C) [21,22]. Aside from pathogen spillover and spillback, during a biological invasion, non-native species can benefit from a reduction in parasitism, known as enemy release (Figure 1A), this can happen through various mechanisms, such as absence from the founder population, or unsuitable environmental conditions [14,23,24,25,26]. For example, the invasive rodent, Mus musculus domesticus, in Senegal has been shown to exhibit enemy release by demonstrating a low prevalence and abundance of gastrointestinal helminths in general and specifically, enemy release along its invasion route, with the helminth, Aspiculuris tetraptera, absent from populations at the invasion front [27]. This reduction in parasites has been postulated to enhance invasiveness by allowing a reallocation of resources from immune functions to dispersal and reproduction, known as the evolution of increased competitive ability theory (EICA) [23,24].
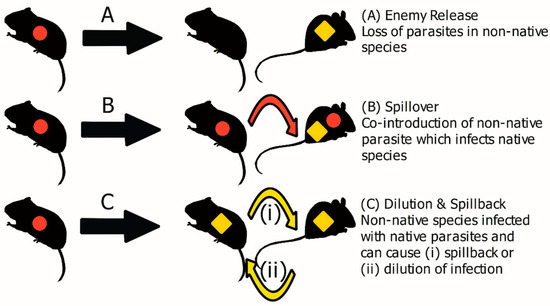
Figure 1.
Disease dynamics of a biological invasion. Parasites introduced with the non-native species are indicated by red circles, while parasites from the native host are indicated by yellow diamonds. Adapted from Loxton [26] and Hatcher and Dunn [28].
The example of cross-species transmission, increase in frequency of EIDs and ongoing human-wildlife interactions outlined above demonstrate a pressing need to increase our understanding of the role wildlife, ecology and inter-species interactions play in pathogen transmission and spillover [12,29,30]. Host diversity has been shown to have a positive effect on reducing the presence of pathogens in the environment, providing a dilution effect [22,31]. This dilution effect occurs through the presence of hosts with a lower competency for a specific pathogen, reducing the overall prevalence of that pathogen in competent hosts (Figure 1C) [32,33]. As the dilution effect has been frequently observed in studied bio-invasion they present an ideal system to study the dilution effect, in particular through longitudinal studies [22]. For example, a study by Tierney et al. [34] found that the invasive populations of the freshwater cyprinid dace (Leuciscus leuciscus) in Ireland caused a dilution effect in the native brown trout (Salmo trutta), reducing the abundance of the native helminth Pomphorhynchus tereticollis in S. trutta at sites where L. leuciscus was established longest. Consequently, studying wildlife and biological invasions can provide a unique insight into improving our understanding of pathogen dynamics and in-turn our comprehension of EIDs [12,29,31,35,36].
2. Cycling Rodent Populations as Wildlife Disease Models
In the past, experimental approaches have used laboratory rodents to study zoonotic-borne pathogens and describe stages of infection and transmission [37,38]. In comparison to the wild, laboratory settings can be highly regulated, with constant food and water supplies, reduced genetic diversity, controlled infection and known immune markers [38]. While these laboratory-based studies have their strengths for determining cellular-level responses and the structure of molecular pathways [39], relative to natural systems they fall short in identifying the influence of natural genetic variation and habitat diversity on disease spread and vaccination success [38,40]. For example, Voutilainen et al. [41] found that wild populations of the bank vole Myodes glareolus infected with Puumala Orthohantavirus manifested life-long periods of virus shedding compared to laboratory studies. Other disadvantages of laboratory studies include the lower genetic diversity of laboratory-reared inbred mice compared to wild populations [40]. Pedersen and Babayan [38], identified that the majority of knowledge on immune responses come from laboratory studies, showing an increasing need for ecological studies to expand our knowledge of immunology in wild populations, known as wild immunology or ecoimmunology. Rodents make up the largest group of mammals, consisting of ~1500 species, with large populations and wide distributions, short generation times and considerable laboratory-based knowledge [38,39]. This makes studying rodent pathogens and their natural ecology, an ideal model system for studying pathogens in wildlife populations and parasite communities in a natural setting, potentially identifying possible reservoirs of zoonotic diseases and pathogen dynamics during biological invasions [38,42].
As a group, rodent population dynamics have been thoroughly studied, with some populations having been shown to display population multi-annual fluctuations, known as population cycles, while others show less-extreme fluctuations seasonally and are considered non-cyclic [43,44,45]. These population dynamics have been shown to be a response to extrinsic factors, such as local environmental conditions, number of generalist or specialist predators and food availability [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. It has been shown that parasites can affect fecundity and mortality rates of rodents [44,51,52]. In a laboratory setting, Scott [53] infected outbred CD1 mice with the nematode, Heligmosomoides polygyrus, and observed a reduction in host abundance. This was due to a high initial host mortality following infection, which Scott postulates could be what happens when a new parasite is introduced to a naïve host [53]. Following this, anthelmintic treatment was provided to the mice and the populations then recovered to original densities [53]. Scott [53] also acknowledged the need for their study to be extrapolated into wild rodent populations, to test if these findings hold true in natural systems. Likewise, wild populations of white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) and deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus) were treated with food supplementation and an anthelmintic drug, ivermectin, showed significantly reduced population crashes compared to control groups not receiving the treatment [54].
Studying cycling populations of rodents has also extended our knowledge of parasite dynamics. The changing population of rodents during each phase makes rodent cycles an informative wildlife model to study parasite epidemiology, with the sequential density fluctuations and corresponding resource availability and trophic interactions, allowing for the rigorous testing of hypotheses. For example Haukisalmi, Henttonen and Tenora [55] recorded that the peak Heligmosomum mixtum infection in bank voles and red voles (Myodes rutilus), occurred in winter, followed by a subsequent decline in spring, coinciding with vole maturation, followed by a new increase in old overwintered voles in summer. It was also found that Heligmosomum sp. and Catenotaenia sp. showed interspecific synchrony, despite their different life cycles, direct in Heligmosomum or via intermediate hosts [55]. Furthermore, Haukisalmi and Henttonen [56,57] found H. mixtum and Heligmosomum glareoli had a positive co-occurrence pattern, despite occupying the same microhabitat. These authors also noted that a negative interaction would be expected, however, the different feeding nodes and radial distribution of these two helminth species may account for their positive co-occurance [57]. Likewise, Mastophorus muris was shown to have a positive association with Capillaria sp., however these species occupy different microhabitats, with M. muris present in the stomach and Capillaria in the small intestine [56]. Stien et al. [58] linked arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) parasite abundance to the patchy local presence of the intermediate host, sibling vole (Microtus levis), showing that increasing distance from vole sites resulted in reduction in the prevalence of vole-transmitted cestodes, Echinococcus multilocularis, Taenia crassiceps and Taenia polyacantha, in arctic foxes. In years of lower sibling vole abundance, it was shown that there was a lower presence in the fox diet [58]. Similarly, increases in abundances of Toxascaris leonina and Toxocara canis in red fox (Vulpes vulpes) have proven to be proportionate to increases in rodent density [59].
An essential part of studying the epidemiology of EIDs in humans is through the understanding of disease cycles in wild host populations [60]. This topic has been extensively studied in rodents. Laakkonen et al. [61], showed that Eimeria infections cycle seasonally in three vole populations, Microtus agrestis, Microtus oeconomus and M. glareolus, with the highest peak being in autumn, corresponding to the high number of immunologically naïve juveniles, and the lowest in spring when most of the vole population had increased its immunity over winter. Similarly, Puumala orthohantavirus (PUUV) prevalence in M. glareolus populations cycles seasonally, however in contrast to the study outlined above by Laakkonen et al. [61], it was found that prevalence was highest in spring and lowest in late summer–early autumn [62]. The Spring peak is believed to be result of age-related accumulation of the virus over winter, while in Autumn, prevalence is diluted by the presence of juveniles at the end of the breeding season [62]. The ecology of PUUV in Europe is biome specific [63] in the boreal zone it is top down (specialist predation on hosts), while in the temperate zone, bank vole dynamics are driven by mast years (years of heavy seed crops), which were also accompanied by high human hantavirus incidence [64].
Rodents also prove to be excellent models for studying immunological variation in wild populations. A review by Ezenwa and Jolles, [65] highlights the impact of coinfection on disease dynamics, with helminths inducing T-helper cell type 2 (Th2) responses, which down-regulate T-helper cell type 1 (Th1) responses. Similarly, these authors note that some helminth species exploit regulatory T cells to suppress immune responses [65]. In addition, the presence of helminths has also been found to be a factor influencing Puumala hantavirus prevalence in rodents, with PUUV infection being positively associated with the presence of H. mixtum [66]. Guivier et al. [67] also found a negative correlation between proinflammatory responses TNF-α and MX2 genes with PUUV load. These authors also demonstrated that PUUV-infected voles demonstrated higher TNF-α expression compared to uninfected voles or voles co-infected with H. mixtum [67,68]. Similarly, during a study in Kielder Forest, Jackson et al. [69], showed two potential trade-offs in the field vole (Microtus agrestis), the first being a potential trade-off with immune expression between Th1 and Th2 immune responses in the field vole-Th2 transcription factor Gata-3 was significantly negatively associated with IFN-γ and IL-2 (Th1 mediators). The second potential trade-off was between breeding condition and the immune response, due to an increased allocation of resources to reproduction [69]. Trade-offs in immune responses have the potential to influence parasite communities and the infection risk and severity of viral diseases of human importance [66]. A recent study by Charbonnel et al. [70] found a bias in immune gene expression towards the upregulation of serpins, alipoproteins and proinflammatory cascades at sites recently invaded by the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus), suggesting that phenotypic differentiation in immune response between conspecific hosts along invasion routes could be mediated by changes in parasite infections. The knowledge from these studies combined prove that rodents provide the potential to be used as model systems to understand pathogen dynamics, and the complex relationship between parasites and host immune responses in wild populations.
3. Factors Present in the Irish Invasion System Making It an Ideal Study System for Parasite Dynamics
Ireland has a relatively depauperate community of small mammals in contrast to mainland Europe, with some debate regarding what species are truly native as opposed to those species that have been introduced by humans and hence been naturalised [71]. However, it is widely accepted that the wood mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) is native and M. glareolus is non-native [72,73]. Evidence supports the introduction of M. glareolus into Ireland around the 1920s during construction of the Shannon Hydroelectric Plant when equipment was imported from Germany [74]. Evidence for the vole introduction was demonstrated by the close relationship of mtDNA sequences of Irish and German populations of M. glareolus [74]. M. glareolus in Ireland is a particularly informative model because the vole population has an identified core population, expansion front and area beyond the expansion front where M. glareolus is absent [22,75]. The vole population has also been shown to have a constant rate of spread ranging from 2.23–2.63 km per year in unconstrained areas, creating an invasion gradient from core established sites to more recently invaded frontier sites [22,76,77]. Most invasive species are under current eradication plans, however, there has never been an attempt to eradicate M. glareolus from Ireland [22,76].
White et al. [75] studied the allele frequency of M. glareolus during its expansion in Ireland, and found that there was an overall loss of vole genetic diversity along the transects (relevant to the core) due the strong selection pressures present during an expansion. These authors also found that the eastern expansion had lost the least diversity, possibly because of a lack of barriers to dispersal, and that the northern and north-eastern groups had lost the most, possibly due to the numerous barriers to dispersal such as the River Shannon and presence of unsuitable bog habitat [75]. However, pooling all three transects together, the genetic diversity was nearly as high as that described for the founder population, showing that each transect had different selection pressures, causing selection for different genes [75]. White et al. [75] also identified the selection for genes of immunological function in M. glareolus in sites furthest from the identified point of introduction. Stuart et al. [22] suggested that the immunogenetic changes observed during the White et al. study [75] may be related to the variation in helminth infection witnessed in M. glareolus across the invasion gradient.
Early studies on the helminths of M. glareolus and A. sylvaticus, respectively, on Ross Island in Ireland, identified the species of helminth parasites present and included cestodes, nematodes and trematodes (Table 1) [78]. Similar studies in the north of Ireland, documented nine helminth species in the alimentary canal of A. sylvaticus, sampled during the period of November 1978 to October 1981, with additional parasite surveys conducted in 1980 and 1985 (Table 1), with Capillaria murissylvatici, Heligosomoides polygyrus, Syphacia stroma and Corrigia vitta showing cyclic seasonal patterns [79,80,81]. Likewise, due to these seasonal patterns, the authors demonstrated that samples collected during similar seasons between years showed more similarities than samples collected within the same year [81].

Table 1.
Helminth species recorded in A. sylvaticus and M. glareolus from selected studies published between 1982–2020. Names in brackets are previous species names.
More recent studies on the Irish population of M. glareolus revealed a depauperate helminth community compared to their native range, with only three species of helminth recovered, a phenomenon known as enemy release (Figure 1A), possibly aiding the spread of voles across Ireland (Table 1) [22,82,83]. Most noticeable was the absence of H. mixtum in Irish populations, a helminth often found in European M. glareolus [82,84]. Loxton et al. [82] proposed that the enemy release resulted from the loss of helminth species from the indigenous range in the founder population of M. glareolus during translocation and establishment in Ireland, and the lack of native helminth species obtained following establishment. Furthermore, Loxton et al. [82], found that M. glareolus carried a relatively low number of helminth species in comparison to the sympatric native A. sylvaticus. Furthermore, M. glareolus at the expansion front were found to be less parasitised than M. glareolus in longer established areas, with the abundance of Aspiculuris tianjinensis being highest at the core [22]. An increased prevalence of Aonchotheca murissylvatici was observed at core and invaded sites, which is believed to be amplified by the increased competence of M. glareolus as a host [22,83]. Loxton et al. [83] also detected Taenia martis in A. sylvaticus for the first time, at sites invaded by M. glareolus suggesting the possibility of co-invasion. In addition, more recent studies revealed T. polyacantha infection in M. glareolus and A. sylvaticus at invaded sites [22]. However, M. glareolus is the intermediate host and it is suggested these helminths may have been overlooked previously in studies due to their presence outside the digestive tract, residing in the thoracic and abdominal cavities [22]. A comparable study by Perkins et al. [77] found M. glareolus from the invasion front to have lower parasite abundances compared to conspecifics at core sites.
There is evidence to suggest that, overall, the presence of M. glareolus in Ireland has a dilution effect on the helminth community in A. sylvaticus, with a lower Brillouin’s Index of Diversity at the core invaded sites [22]. M. glareolus has also resulted in the dilution of Bartonella in A. sylvaticus with a lower prevalence observed in sites with high M. glareolus density, as M. glareolus appears to be resistant to native strains [85]. Previously, studies had shown M. glareolus to have a strong dilution effect on Syphacia stroma in A. sylvaticus [83]. However, more recently, S. stroma was found to show higher abundances in A. sylvaticus at core sites, suggesting it could be taking advantage of the lower helminth species diversity [22]. These observations also indicate that helminth communities show a lag effect during a biological invasion, changing as the invasive host becomes more established [22]. Both studies found the abundance of Skrjabinotaenia lobata to be higher in A. sylvaticus at core sites [22,83]. Both species, S. stroma and S. lobata, are known to compete for resources and are postulated to be benefitting from the lower species diversity [22]. Seasonal patterns were also detected for S. stroma, showing the lowest prevalence in autumn [22]. Kronfeld-Schor et al. [86] highlights the need for more wildlife studies, focusing on the seasonality of infectious diseases, and host immune responses.
The addition of a second invasive mammal, the greater white-toothed shrew (Crocidura russula), has had a positive, synergistic effect on M. glareolus abundance, with a negative effect on A. sylvaticus numbers and the complete perturbation of the native pygmy shrew (Sorex minutus), a process known as invasional meltdown [87]. This more recent introduction, discovered in 2007, was estimated to have happened around 2001 [88], and C. russula has been shown to displace other shrew species in central Europe [89]. The factors outlined here, including dilution, spillover, spillback, enemy release and the recent discovery of invasional meltdown, demonstrate that the Irish M. glareolus population is an informative model system to study the dynamics of an invasive species, including disease, and their effects on native fauna through longitudinal and spatiotemporal studies.
4. Opportunities Presented by the Bank Vole Invasion Model
Studies on Irish populations of M. glareolus have managed to pinpoint the possible origin of the invasion in Ireland, probable source population and the expansion rate throughout the island [74]. While our knowledge of helminth communities in M. glareolus has increased over the past century [84], we still have the opportunity to explore new avenues with the Irish population, as a model system for studying disease during a species invasion [22]. Previous studies have used spatiotemporal studies to examine parasite dynamics during a biological invasion [22,82,83]. However, longitudinal studies are required to fully understand the dynamic nature of parasite infections [22,60,90]. As seen in Figure 2a, M. glareolus currently occupies about 40% of the island of Ireland, mainly found in the Munster and Connacht regions and is actively spreading from its proposed point of entry near the River Shannon in Foynes, Co. Limerick [73,74]. Building on the recent rodent studies in Ireland [22,79,81,82,83,91] this constant rate of expansion and the presence of uninvaded sites presents the opportunity for long term studies that investigate the establishment and change in parasite communities during a biological invasion and provides natural perturbation experiments for exploring the effects of host diversity.
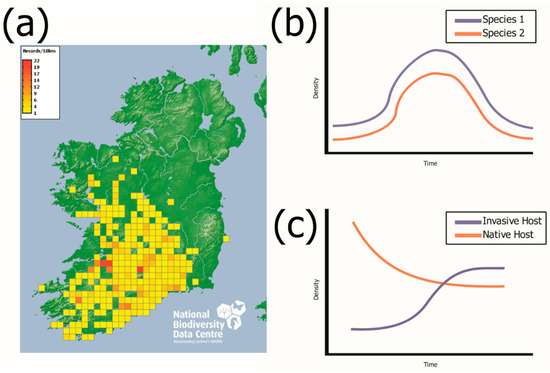
Figure 2.
Current range of the bank vole (M. glareolus) and hypothetical population dynamics at core and expansion front sites. Part (a) shows the current distribution of the M. glareolus in Ireland. Part (b) provides an illustration of the multi-annual population cycle of two host species. Part (c) provides an illustration of the population dynamics of two host species when the population of the native host species declines as the population of the invasive host species increases. Part (a) taken with permission from the National Biodiversity Data Centre, Ireland [92].
When studying changes in parasite dynamics during a biological invasion, baseline data are usually absent [20,22]. In the case of Ireland, data collected previously on M. glareolus, by Stuart et al. [22] and Loxton et al. [82,83]., can be used as a baseline for future studies investigating changes in parasite communities. Work by Stuart et al. [22] included uninvaded sites as control groups, which will be colonised given the constant expansion rate of M. glareolus, demonstrated by White et al. [76], giving clear insight to the changes in parasite communities during the early stages of invasion. Similarly, data collected on core sites can show how parasite dynamics fluctuate with time and previously collected data in expansion front sites showing changes as the population of M. glareolus becomes fully established (Table 2).

Table 2.
Summary of current knowledge, main research question and how this can be addressed using M. glareolus as a model system in Ireland.
It has also been shown that the analysis of helminth dynamics (infection parameters such as prevalence and incidence) is sensitive to the host population structure in collected samples, as parasite species and infection parameters can be dependent on age and functional group [93]. These vary seasonally and in density and phase-dependent ways. To allow us to fully understand the helminth dynamics of this system, this would need to be incorporated into future invasive model studies [22].
Further work on immune responses is needed [23], previous studies on rodents have demonstrated that the presence of certain helminth species can influence the presence and intensity of microparasite infections through trade-offs in the Th1 and Th2 immune pathways [66,69]. A review by White and Perkins [90], identified the need for empirical studies analysing immune gene expression during a biological invasion. These authors proposed that the enemy release observed in invasive populations could result in a relaxation of parasite-mediated selection, resulting in changes to the immune phenotype [90]. As mentioned previously, the Irish M. glareolus population demonstrates enemy release compared to its native range, but also between the core and invasion front [22,77]. Consequently, the Irish system also presents the opportunity to further investigate trade-offs in M. glareolus immune expression and potential associated changes in microparasite communities as their parasite communities change during establishment.
A. sylvaticus population numbers have also been shown to be negatively impacted by the presence of M. glareolus in both perturbation studies and in natural settings [87,94]. Figure 2b presents a multi-annual rodent population cycle, similar to the cycling present in the vole population in northern latitudes [44], while the presence of multi-annual cycles has not been thoroughly studied in Ireland, Figure 2c shows the changing population dynamics during a biological invasion, with an increase in one host species, while the other decreases, as A. sylvaticus has been shown to be negatively affected by the presence of M. glareolus [87]. We propose that just as cycling vole populations have proved a valuable model in the understanding of wildlife parasitology due to their changing host populations, the Irish invasion model also presents unique opportunities to answer novel questions through population changes resulting from the introduction of non-native species. For instance, the recent invasion of C. russula has added a potentially novel element to the model system, that is, when a second invader enters the system and causes invasional meltdown [87]. This provides an opportunity to sample C. russula in a similar way to how M. glareolus has been investigated in the Irish context. Invasive shrews can be sampled from sites where C. russula has been introduced the longest, recently invaded and absent. Furthermore, sampling sites where C. russula is present with M. glareolus and sites where M. glareolus is absent could be investigated.
The recent increase in EIDs has emphasised the need for a pre-emptive approach requiring empirical data on pathogen dynamics [35]. As demonstrated in this review, wild rodent models, globally, have added to our knowledge of parasite communities and ecoimmunology. However, significant gaps remain and the Irish invasion of M. glareolus presents a unique opportunity to study these relationships during a biological invasion. Furthermore, the availability of baseline data and the presence of an invasion gradient-consisting of core established sites, recently invaded and uninvaded sites provide a unique opportunity to perform longitudinal and spatiotemporal studies. The Irish model system has the potential to complement current knowledge and allow for further generalities to be identified, which can be adapted to other invasion systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M., P.S. and C.V.H.; writing—original draft prepara-tion, A.M.; writing—review and editing A.M., P.S., C.V.H. and H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded through the 2018–2019 BiodivERsA joint call for research proposals, under the BiodivErsA3 ERA-Net COFUND programme, and with the funding organisations EPA Research Programme, Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR), Research Foundation–Flanders (FWO), National Science Centre, Poland (NCN) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). This project is funded under the EPA Research Programme 2021–2030 and cofunded by Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR), Research Foundation–Flanders (FWO), National Science Centre, Poland (NCN) and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). The EPA Research Programme is a Government of Ireland initiative funded by the Department of the Environment, Climate and Communications.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would also like to thank Niamh Reilly for assisting in proofreading the literature review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, D.W. COVID-19: A novel zoonotic disease caused by a coronavirus from China: What we know and what we don’t. Microbiol. Aust. 2020, 41, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 24 June 2021).
- Daszak, P.; Olival, K.J.; Li, H. A strategy to prevent future epidemics similar to the 2019-nCoV outbreak. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Andreadakis, Z.; Kumar, A.; Román, R.G.; Tollefsen, S.; Saville, M.; Mayhew, S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382(8), 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO-Convened Global Study of Origins of SARS-CoV-2: China Part; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikelski, M.; Foufopoulos, J.; Vargas, H.; Snell, H. Galápagos birds and diseases: Invasive pathogens as threats for island species. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.J.; Albery, G.F.; Kessler, M.K.; Lunn, T.J.; Falvo, C.A.; Czirják, G.Á.; Martin, L.B.; Plowright, R.K. Macroimmunology: The drivers and consequences of spatial patterns in wildlife immune defence. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 972–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, C.L.; Nuismer, S.L.; Basinski, A.J. When to vaccinate a fluctuating wildlife population: Is timing everything? J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daszak, P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hyatt, A.D. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife--threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.A.; Gubler, D.J. Disease ecology and the global emergence of zoonotic pathogens. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2005, 10, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, M.J.; Dick, J.T.; Dunn, A.M. Disease emergence and invasions. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkowski, K.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Zohdy, S. Parasite ecology of invasive species: Conceptual framework and new hypotheses. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-L.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Limpanont, Y.; Wu, Z.-D.; Li, J.; Lv, Z.-Y. Zoonotic parasites carried by invasive alien species in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainsbury, A.W.; Nettleton, P.; Gilray, J.; Gurnell, J. Grey squirrels have high seroprevalence to a parapoxvirus associated with deaths in red squirrels. Anim. Conserv. 2000, 3, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, D.M.; Sainsbury, A.W.; Nettleton, P.; Buxton, D.; Gurnell, J. Parapoxvirus causes a deleterious disease in red squirrels associated with UK population declines. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strauss, A.; White, A.; Boots, M. Invading with biological weapons: The importance of disease-mediated invasions. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.M.; Hatcher, M.J. Parasites and biological invasions: Parallels, interactions, and control. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchio, E.; Crotta, M.; Romeo, C.; Drewe, J.A.; Guitian, J.; Ferrari, N. Invasive alien species and disease risk: An open challenge in public and animal health. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.; Paterson, R.; Townsend, C.; Poulin, R.; Tompkins, D. Parasite spillback: A neglected concept in invasion ecology? Ecology 2009, 90, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, P.; Paredis, L.; Henttonen, H.; Lawton, C.; Torres, C.A.O.; Holland, C.V. The hidden faces of a biological invasion: Parasite dynamics of invaders and natives. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, S.; Brouat, C.; Diagne, C.; Charbonnel, N. Eco-immunology and bioinvasion: Revisiting the evolution of increased competitive ability hypotheses. Evol. Appl. 2016, 9, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.A.; Klasing, K.C. A role for immunology in invasion biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, C.; Galan, M.; Tamisier, L.; d’Ambrosio, J.; Dalecky, A.; Bâ, K.; Kane, M.; Niang, Y.; Diallo, M.; Sow, A. Ecological and sanitary impacts of bacterial communities associated to biological invasions in African commensal rodent communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loxton, K. Parasites in a Host Species’ Invasion: A Unique Small Mammal Model System. Ph.D. Thesis, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 2015; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Diagne, C.; Granjon, L.; Gueye, M.S.; Kane, M.; Niang, Y.; Tatard, C.; Brouat, C. Association between temporal patterns in helminth assemblages and successful range expansion of exotic Mus musculus domesticus in Senegal. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3003–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, M.J.; Dunn, A.M. Parasites in Ecological Communities: From Interactions to Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, C.R.; Heau, J.G.; González, C.; Ibarra-Cerdeña, C.N.; Sánchez-Cordero, V.; González-Salazar, C. Using biotic interaction networks for prediction in biodiversity and emerging diseases. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, B.; Garchitorena, A.; Guégan, J.F.; Arnal, A.; Roiz, D.; Morand, S.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Suzán, G.; Daszak, P. Was the COVID-19 pandemic avoidable? A call for a “solution-oriented” approach in pathogen evolutionary ecology to prevent future outbreaks. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S. Emerging diseases, livestock expansion and biodiversity loss are positively related at global scale. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.; Bowers, R.; Begon, M.; Hudson, P.J. Persistence of tick-borne virus in the presence of multiple host species: Tick reservoirs and parasite mediated competition. J. Theor. Biol. 1999, 200, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, K.A.; Ostfeld, R.S. Biodiversity and the dilution effect in disease ecology. Ecology 2001, 82, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, P.A.; Caffrey, J.M.; Vogel, S.; Matthews, S.M.; Costantini, E.; Holland, C.V. Invasive freshwater fish (Leuciscus leuciscus) acts as a sink for a parasite of native brown trout Salmo trutta. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.A.; Schmidt, J.P.; Bowden, S.E.; Drake, J.M. Rodent reservoirs of future zoonotic diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7039–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzybek, M.; Tołkacz, K.; Sironen, T.; Mäki, S.; Alsarraf, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Biernat, B.; Nowicka, J.; Vaheri, A.; Henttonen, H.; et al. Zoonotic Viruses in Three Species of Voles from Poland. Animals 2020, 10, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, A.N.; Rollin, P.E.; Milazzo, M.L.; Molina, C.P.; Eyzaguirre, E.J.; Livingstone, W.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Fulhorst, C.F. Pathology of Black Creek Canal virus infection in juvenile hispid cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Babayan, S.A. Wild immunology. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J. Immunology in wild nonmodel rodents: An ecological context for studies of health and disease. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, K.M. Ecoimmunology at spatial scales. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2210–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutilainen, L.; Sironen, T.; Tonteri, E.; Bäck, A.T.; Razzauti, M.; Karlsson, M.; Wahlström, M.; Niemimaa, J.; Henttonen, H.; Lundkvist, Å. Life-long shedding of Puumala hantavirus in wild bank voles (Myodes glareolus). J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.K.; Beldomenico, P.M.; Bown, K.; Burthe, S.; Jackson, J.; Lambin, X.; Begon, M. Host–parasite biology in the real world: The field voles of Kielder. Parasitology 2014, 141, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.; Henttonen, H. Gradients in density variations of small rodents: The importance of latitude and snow cover. Oecologia 1985, 67, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J. Population Fluctuations in Rodents; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013; pp. 1–22, 162–174, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Andreassen, H.P.; Sundell, J.; Ecke, F.; Halle, S.; Haapakoski, M.; Henttonen, H.; Huitu, O.; Jacob, J.; Johnsen, K.; Koskela, E. Population cycles and outbreaks of small rodents: Ten essential questions we still need to solve. Oecologia 2021, 195, 601–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanski, I.; Hansson, L.; Henttonen, H. Specialist predators, generalist predators, and the microtine rodent cycle. J. Anim. Ecol. 1991, 60, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpimäki, E.; Norrdahl, K.; Klemola, T.; Pettersen, T.; Stenseth, N.C. Dynamic effects of predators on cyclic voles: Field experimentation and model extrapolation. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambin, X.; Bretagnolle, V.; Yoccoz, N.G. Vole population cycles in northern and southern Europe: Is there a need for different explanations for single pattern? J. Anim. Ecol. 2006, 75, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ims, R.A.; Henden, J.-A.; Killengreen, S.T. Collapsing population cycles. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korpela, K.; Helle, P.; Henttonen, H.; Korpimäki, E.; Koskela, E.; Ovaskainen, O.; Pietiäinen, H.; Sundell, J.; Valkama, J.; Huitu, O. Predator–vole interactions in northern Europe: The role of small mustelids revised. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20142119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, M.; Lewis, J. Population dynamics of helminth parasites in wild and laboratory rodents. Mammal. Rev. 1987, 17, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, D.; Begon, M. Parasites can regulate wildlife populations. Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.E. Regulation of mouse colony abundance by Heligmosomoides polygyrus. Parasitology 1987, 95, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.B.; Greives, T.J. The interaction of parasites and resources cause crashes in a wild mouse population. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukisalmi, V.; Henttonen, H.; Tenora, F. Population dynamics of common and rare helminths in cyclic vole populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 1988, 57, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukisalmi, V.; Henttonen, H. Coexistence in helminths of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus. I. Patterns of co-occurrence. J. Anim. Ecol. 1993, 62, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukisalmi, V.; Henttonen, H. Coexistence in helminths of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus. II. Intestinal distribution and interspecific interactions. J. Anim. Ecol. 1993, 62, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, A.; Voutilainen, L.; Haukisalmi, V.; Fuglei, E.; Mørk, T.; Yoccoz, N.; Ims, R.; Henttonen, H. Intestinal parasites of the Arctic fox in relation to the abundance and distribution of intermediate hosts. Parasitology 2010, 137, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørk, T.; Ims, R.A.; Killengreen, S.T. Rodent population cycle as a determinant of gastrointestinal nematode abundance in a low-arctic population of the red fox. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazel, S.; Bennett, M.; Chantrey, J.; Bown, K.; Cavanagh, R.; Jones, T.; Baxby, D.; Begon, M. A longitudinal study of an endemic disease in its wildlife reservoir: Cowpox and wild rodents. Epidemiol. Infect. 2000, 124, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakkonen, J.; Oksanen, A.; Soveri, T.; Henttonen, H. Dynamics of intestinal coccidia in peak density Microtus agrestis, Microtus oeconomus and Clethrionomus glareolus populations in Finland. Ecography 1998, 21, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voutilainen, L.; Kallio, E.R.; Niemimaa, J.; Vapalahti, O.; Henttonen, H. Temporal dynamics of Puumala hantavirus infection in cyclic populations of bank voles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H. Many faces of rodent-borne infections in Europe. In The Impact of A Decade (2004-2015) of Research on Vector-Borne Diseases in Europe; Lancelot, R., Laurens, S., Lewer, A., Eds.; CIRAD: Montpellier, France, 2015; pp. 10–16. ISBN 978-2-87614-707-2. [Google Scholar]
- Reil, D.; Imholt, C.; Eccard, J.A.; Jacob, J. Beech fructification and bank vole population dynamics-combined analyses of promoters of human Puumala virus infections in Germany. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezenwa, V.O.; Jolles, A.E. From host immunity to pathogen invasion: The effects of helminth coinfection on the dynamics of microparasites. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2011, 51, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.R.; Guivier, E.; Xuéreb, A.; Chaval, Y.; Cadet, P.; Poulle, M.-L.; Sironen, T.; Voutilainen, L.; Henttonen, H.; Cosson, J.-F. Concomitant influence of helminth infection and landscape on the distribution of Puumala hantavirus in its reservoir, Myodes glareolus. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guivier, E.; Galan, M.; Henttonen, H.; Cosson, J.-F.; Charbonnel, N. Landscape features and helminth co-infection shape bank vole immunoheterogeneity, with consequences for Puumala virus epidemiology. Heredity 2014, 112, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charbonnel, N.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Mustonen, J.; Vaheri, A. Immunogenetic factors affecting susceptibility of humans and rodents to hantaviruses and the clinical course of hantaviral disease in humans. Viruses 2014, 6, 2214–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.A.; Begon, M.; Birtles, R.; Paterson, S.; Friberg, I.M.; Hall, A.; Lowe, A.; Ralli, C.; Turner, A.; Zawadzka, M. The analysis of immunological profiles in wild animals: A case study on immunodynamics in the field vole, Microtus agrestis. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnel, N.; Galan, M.; Tatard, C.; Loiseau, A.; Diagne, C.; Dalecky, A.; Parrinello, H.; Rialle, S.; Severac, D.; Brouat, C. Differential immune gene expression associated with contemporary range expansion in two invasive rodents in Senegal. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, A.; Vega, R.; Rambau, R.V.; Yannic, G.; Herman, J.S.; Hayden, T.; Searle, J.B. Colonization of Ireland: Revisiting ‘the pygmy shrew syndrome’using mitochondrial, Y chromosomal and microsatellite markers. Heredity 2011, 107, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marnell, F.; Kingston, N.; Looney, D. Ireland Red List No. 3: Terrestrial Mammals; National Parks and Wildlife Service, Department of the Environment, Heritage and Local Government: Dublin, Ireland, 2009.
- National Biodiversity Data Centre, Ireland. Bank Vole (Myodes glareolus). Available online: https://maps.biodiversityireland.ie/Species/119785 (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- Stuart, P.; Mirimin, L.; Cross, T.; Sleeman, D.; Buckley, N.J.; Telfer, S.; Birtles, R.; Kotlik, P.; Searle, J. The origin of Irish bank voles Clethrionomys glareolus assessed by mitochondrial DNA analysis. Ir. Nat. J. 2007, 28, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.A.; Perkins, S.E.; Heckel, G.; Searle, J.B. Adaptive evolution during an ongoing range expansion: The invasive bank vole (M yodes glareolus) in Ireland. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 2971–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.A.; Lundy, M.G.; Montgomery, W.I.; Montgomery, S.; Perkins, S.E.; Lawton, C.; Meehan, J.M.; Hayden, T.J.; Heckel, G.; Reid, N. Range expansion in an invasive small mammal: Influence of life-history and habitat quality. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.E.; White, T.A.; Pascoe, E.L.; Gillingham, E.L. Parasite community dynamics in an invasive vole–From focal introduction to wave front. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, H.M.; Smal, C.M.; Fairley, J.S. A Study of Parasite Infestations in Populations of Small Rodents (Apodemus Sylvaticus and Clethrionomys Glareolus) on Ross Island, Killarney. J. Life Sci R. Dubl. Soc. 1984, 5, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, S.; Montgomery, W. Cyclic and non-cyclic dynamics in populations of the helminth parasites of wood mice, Apodemus sylvaticus. J. Helminthol. 1988, 62, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, S.; Montgomery, W. Spatial and temporal variation in the infracommunity structure of helminths of Apodemus sylvaticus (Rodentia: Muridae). Parasitology 1989, 98, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.; Montgomery, W. Structure, stability and species interactions in helminth communities of wood mice, Apodemus sylvaticus. Int. J. Parasitol. 1990, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxton, K.C.; Lawton, C.; Stafford, P.; Holland, C.V. Reduced helminth parasitism in the introduced bank vole (Myodes glareolus): More parasites lost than gained. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loxton, K.C.; Lawton, C.; Stafford, P.; Holland, C.V. Parasite dynamics in an invaded ecosystem: Helminth communities of native wood mice are impacted by the invasive bank vole. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1476–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukisalmi, V.; Henttonen, H. Variability of helminth assemblages and populations in the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus. Pol. J. Ecol. 2000, 48, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Telfer, S.; Bown, K.J.; Sekules, R.; Begon, M.; Hayden, T.; Birtles, R. Disruption of a host-parasite system following the introduction of an exotic host species. Parasitology 2005, 130, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kronfeld-Schor, N.; Stevenson, T.; Nickbakhsh, S.; Schernhammer, E.; Dopico, X.; Dayan, T.; Martinez, M.; Helm, B. Drivers of infectious disease seasonality: Potential implications for COVID-19. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2021, 36, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, W.I.; Lundy, M.G.; Reid, N. ‘Invasional meltdown’: Evidence for unexpected consequences and cumulative impacts of multispecies invasions. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, D.G.; Lusby, J.; Montgomery, W.I.; O’halloran, J. First record of greater white-toothed shrew Crocidura russula in Ireland. Mammal. Rev. 2008, 38, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornette, R.; Tresset, A.; Houssin, C.; Pascal, M.; Herrel, A. Does bite force provide a competitive advantage in shrews? The case of the greater white-toothed shrew. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 114, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, T.A.; Perkins, S.E. The ecoimmunology of invasive species. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, W.; Dowie, M. The distribution of the wood mouse Apodemus sylvaticus and the house mouse Mus domesticus on farmland in north-east Ireland. Ir. Nat. J. 1993, 24, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- National Biodiversity Data Centre, Ireland. Bank Vole (Myodes glareolus), Image. Available online: https://maps.biodiversityireland.ie/Species/TerrestrialDistributionMapPrintSize/119785 (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Haukisalmi, V.; Henttonen, H.; Batzli, G.O. Helminth parasitism in the voles Microtus oeconomus and M. miurus on the North Slope of Alaska: Host specificity and the effects of host sex, age and breeding status. Ann. Zool. Fenn. JSTOR 1995, 32, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Fasola, M.; Canova, L. Asymmetrical competition between the bank vole and the wood mouse, a removal experiment. Acta Theriol. 2000, 45, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).