Abstract
A total of 131 contemporary and 33 reference isolates representing a number of multi-locus genotypes of Magnaporthe oryzae were subjected to a PCR test to detect the presence/absence of avirulence (Avr) genes. Results revealed that the more frequently occurring genes were Avr-Pik (81.50%), Avr-Pita (64.16%) and Avr-Pii (47.98%), whereas the less frequently occurring genes were Avr-Pizt (19.08%) and Avr-Pia (5.20%). It was also laid out that the presence of Avr genes in M. oryzae is strongly associated with agroecosystems where the complementary resistant (R) genes exist. No significant association, however, was noted on the functional Avr genes and the major geographic locations. Furthermore, it was identified that the upland varieties locally known as “Milagrosa” and “Waray” contained all the R genes complementary to the Avr genes tested.
1. Introduction
The interaction between rice and the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae, is a well-documented plant pathosystem. Valent [1] reported rice blast as a model system to further one’s understanding on the concept of host species specificity and cultivar specificity, including the mechanisms of plant pathogenesis. The rice-blast pathogen interaction fits the gene-for-gene system, and resistance in rice cultivars are due to specific interactions between R genes in a host and Avr genes of M. oryzae strains under favorable conditions [2,3]. Magnaporthe oryzae can easily mutate to overcome such specific interactions, thereby challenging plant pathologists and plant breeders for its effective management.
Avirulence gene in plant pathogens is simply defined as a gene encoding for a specific protein which is recognized by a host plant bearing the matching R gene [4]. The interaction between the Avr gene and its corresponding R gene follows the classic gene-for-gene concept as illustrated by reference [5]. The primary or secondary products of Avr genes, termed as “elicitors” induces the host receptor to mount various defense responses which oftentimes involve a hypersensitive response [6]. Fungal Avr genes have been successfully isolated by reverse genetics and positional cloning [6]. To date, several Avr genes had been recognized in plant pathogens [7,8]. The cloned avirulence genes identified in M. oryzae include the four genes of PWL [9,10], AVR-Pita [11], ACE1 [12], AvrPiz-t [13], Avr-Pia [14,15], Avr-Pii [15], Avr-Pik/km/kp [15], Avr1-CO39 [16] and AvrPi9 [17]. Among these, Avr-Pita and Avr-Pii were linked to a subtelomeric location, suggesting that loss of chromosome tips could result in gain of virulence of M. oryzae [11,18]. On the other hand, Sone et al. [19] reported homologous recombination, which causes DNA rearrangements, deletions, translocations and even horizontal transfers between strains, as a mechanism for the loss of Avr-Pia and adaptation of M. oryzae against resistant rice cultivars. In addition, the presence of transposable elements such as MAGGY and Pot3 adjacent to the gene regions of Avrs- Pita, Pii, Pia and Pizt aid the pathogen in overcoming host R genes, making the Avr genes gained or lost during the evolution of the pathogen [15,20]. Moreover, nucleotide substitutions were noted in Avr-Pik polymorphisms [21]. It was further cited that, in order for M. oryzae to adapt to rice R genes, it must have to lose or recover its Avr genes [15,19,21,22]. These scenarios constitute an arms race between the R gene and the pathogen Avr gene. Selection pressure on the host plant population favors direct or indirect recognition of the pathogen avirulence genes through its R gene to mount defense responses, whereas selection pressure on the pathogen population favors escape of host recognition [23]. Recently, host jumps were observed in the case of M. oryzae isolated from ryegrass, which cannot infect wheat due to recognition of the avirulence gene PWT3 in the ryegrass pathogen by the resistance gene Rwt3 in wheat. The loss of the avirulence gene resulted in wheat infection of the ryegrass pathogen, when PWT3 was disrupted [24]. In our previous study, we tested the presence of ACE1 genotypes among 53 Philippine isolates of M. oryzae where 13% were avirulent genotype Guy11 and 83% were virulent genotypes PH14 and CM28 [25].
Most rice farmers in developing nations are financially constrained to purchase chemical inputs to manage rice blast or lack the technical know-how to use such inputs effectively [26]. The use of resistant varieties reduces the environmental risk associated with the dependence on heavy applications of chemical inputs. Genetic resistance is considered the ideal way to control rice blast. However, with a very high genetic variability of the pathogen, each cultivar is useful only for a few years, after which it becomes susceptible to infection as new races of M. oryzae develop [27].
This study aimed at assessing the Avr genes possessed by the rice blast isolates collected in Philippine rice fields during the 2012 cropping season from various geographic locations and distinct agroecosystems.
2. Materials and Mathods
2.1. Magnaporthe oryzae Isolates and DNA Extraction
Rice blast isolates used in this study were previously known to represent a distinct genotype, based on Simple Sequence Repeat (microsatellite) analysis made in The French Agricultural Research Centre for International Development (CIRAD), France. These isolates were collected during the 2012 cropping season from various rice-growing areas in the three major islands of the Philippines (Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao) (Figure 1) under different agroecosystems: irrigated lowland, rainfed lowland and rainfed upland. Samplings were made from farmers’ fields as well as from the various experimental stations of the Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) and those from the blast nursery of the University of the Philippines Los Baños (UPLB).
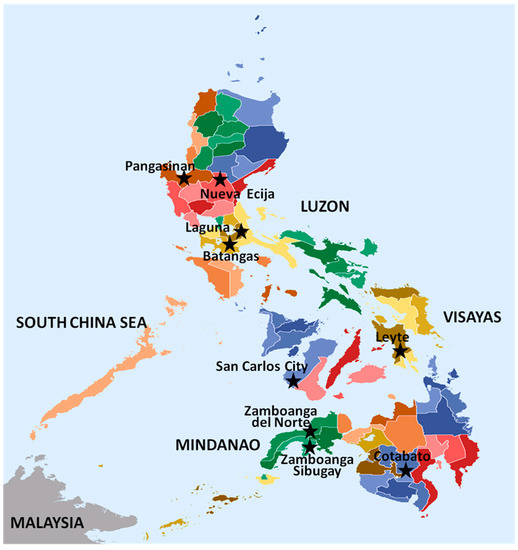
Figure 1.
A map of the Philippines showing sampling locations of Magnaporthe oryzae isolates from various rice growing areas. Actual locations are named and indicated with a 5-point star shape.
Monoconidial cultures were maintained in rice flour agar (20 g rice flour, 2 g yeast extract, 15 g agar and 1 L water) combined with 500,000 IU of penicillin G after autoclaving for 20 min. at 120 °C. Total genomic DNA was extracted following the cell-wall digestion procedure as described by Sweigard et al. [28]. Reference strains considered as representative of the diversity were observed in the reference study of Chen et al. [29].
2.2. PCR Assay for the Presence of Avirulence Genes
Total genomic DNA was amplified using the primer sets as shown in Table 1. Extracted DNA (10 ng) was used as a template in the PCR reaction containing 10X optimized DyNAzyme Buffer [1X buffer contains: 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.8 at 25°C), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 0.1% Triton], 10 µM each of the forward and reverse primers, 10 mM dNTP mix, 0.5 U DyNAzyme II DNA Polymerase (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and sterile distilled water to a volume of 25 µL. A total of 164 isolates, from 131 newly collected and 33 old and reference isolates also collected from Philippine rice fields but maintained in Didier Tharreau’s laboratory in CIRAD, Montpellier, France was considered.

Table 1.
Specific sequences, avirulence gene amplified and PCR product size of primers tested against M. oryzae isolates.
The PCR program was set at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 53–64 °C for 45 s, depending on the primer set, and 72 °C for 1 min with a final extension of 72 °C for 7 min in a PTC100 (MJ Research, Waltham, MA, USA) thermocycler. Polymerase chain reaction products were analyzed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis in TAE buffer for 30 min at 100 V. Gels were stained in ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light.
Multilocus genotypes (MLGs) are a unique combination of alleles across two or more loci and are useful for identifying the spread of the pathogen. Multilocus genotypes were determined through analyzing the result of the DNA sequencing from PCR products amplified utilizing the 12 microsatellite markers. Those belonging to the same MLG have the same sizes of amplified products in all of the 12 microsatellite markers using the software GeneMapper version 4.1 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The MLG:isolate ratio means the proportion of unique MLG which can be expressed as percentage from the number of isolates collected.
The determination of the R genes present in the rice genotype was mainly attributed to the presence of Avr genes. This is based on the gene-for-gene concept of Flor [5] which states that “for each gene that conditions reaction in the host there is a corresponding gene in the parasite that conditions pathogenicity”. Each gene in either member of a host-parasite system may be identified only by its counterpart in the other member of the system. If there are Avr genes in the pathogen, the corresponding R genes in the host are also assumed to be present.
2.3. Data Analysis
Data from plus/minus PCR test to assess for the presence or absence of six AVR genes in each isolate were subjected to contingency chi-square (χ2) analysis against geographic locations and types of agroecosystem utilizing the JMP-N SAS software v 10 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). χ2 values computed for each cell used the formula (O − E)2 / E where O and E represent observed and expected frequencies, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Avirulence Genes in the Isolates
Avr-Pik was present in the majority of the isolates (81.50%). The relative frequencies of the other Avr genes were 64.2% (Avr-Pita), 48.0 % (Avr-Pii), 19.1% (Avr-Pizt), 8.67% (Avr-PWL3) and 5.2% (Avr-Pia). Gel electrophoresis showing the migration pattern of the different Avr genes is presented in Figure 2. As expected, isolates belonging to the same MLGs possessed similar Avr genes except for isolates PH 217 and 358, which differ in Avr-Pita. This could not be a potential error as the amplification was done three times. A comparative frequency of Avr genes found in isolates collected from each type of agroecosystem and those in the reference strains is shown in Figure 3. The upland agroecosystem was noted to contain all the six classes of avirulence genes, whereas the irrigated lowland areas were devoid of Avr-Pia and Avr-PWL3, and a very small percentage of isolates from irrigated lowland contain Avr-Pizt (Figure 3).
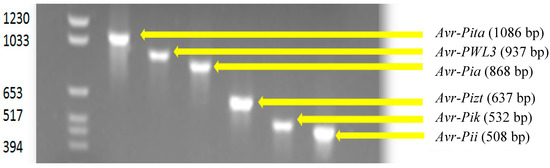
Figure 2.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products from M. oryzae isolates tested for a specific avirulence gene.
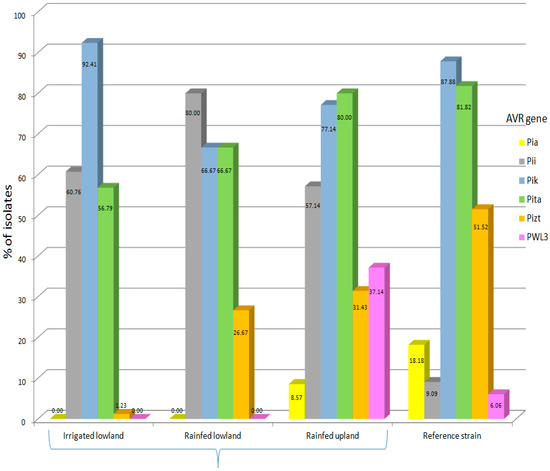
Figure 3.
Comparative frequency of avirulence genes in the contemporary M. oryzae genotypes collected across the various agroecosystems and in the reference strains. Sample sizes for irrigated lowland (90), rainfed lowland (15), rainfed upland (35) and reference strains (33).
Contingency analysis of the type of agroecosystem and the presence of Avr genes in the isolates indicated that there was no significant association between geographic locations (islands) and the presence of Avr genes, except for Avr-PWL3, which shows to highly prevail in the Visayas (Table 2), but this gene is known to be non-functional in rice [9]. In contrast, Avr-Pia, Avr-Pizt and Avr-PWL3 were significantly associated with the upland condition. This seems to show that a specific Avr gene would prevail on a certain type of agroecosystem but not on others; however, the distribution of Avr gene is affected by the distribution of rice cultivars possessing the corresponding R genes. Hence, data on R genes present on rice genotypes grown in the various agroecosystems are shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
Expected frequency (E) and computed chi-square (χ2) values for the presence (1) and absence (0) of a specific avirulence gene in M. oryzae isolates against geographic location and type of agroecosystem.

Table 3.
Resistance genes identified through PCR assay of M. oryzae isolates taken from each of the host genotypes in distinct agroecosystems.
3.2. Resistance Genes Present in Rice Genotypes
Based on the data generated after testing for the presence of Avr genes in the isolates, the complementary R genes, contained in a rice genotype where a specific M. oryzae isolate originated, were thus determined. It was known that the irrigated lowland rice genotypes contained the lowest number of R genes (mostly Pik, Pita and Pii), whereas the rainfed upland rice genotypes contained the highest number of R genes. Furthermore, the upland rice genotypes locally known as “Milagrosa” and “Waray” from Cavinte, Laguna possessed all of the six complementary R genes (Table 3).
Knowledge of the geographic distribution and frequency of avirulence genes present in the collection of isolates will lead to the development of strategies for proper deployment of resistant varieties. Studies dealing with spatial and temporal changes in population diversity of the invading plant pathogen illustrated that Avr genes appeared to have a significant degree of diversity at both small and large sampling scales, suggesting that pathogen evolution varies among local conditions [30].
In this study, the ratio of samples amplified is similar for Avr-Pik, Avr-Pita and Avr-Pia to the worldwide samples [31]. Avr-Pii was more frequently amplified in our sample but compared to the ratio of the Philippine subsamples (reference strains), it was similar. Avr-Pizt was exceptional because it was said to be amplified in 90% of worldwide strains and 67% of the Philippines strains (reference strains), so it seemed that our collected samples were very different. Jia et al. [32] examined the Avr genes present on isolates collected in southern US from 1970 to 2009 and reported that the majority of their collections contained Avr-Pita (65.7%). The other Avr genes and their relative frequencies noted in their collections were Avr-Pizt (57.1%), Avr-Pik (11.4%), Avr-Pia (2.9%) and Avr-Pii (0.3%). In Yunnan, China, the presence of AvR-Pii was 82 out of 454 field isolates of M. oryzae [33], whereas in Eastern India, Avr-Pizt and Avr-Pik had the highest frequency (100%) and Avr1-CO39 had the lowest (2%) [34]. In Thailand, PWL-2, Avr-Pii and Avr-Pizt gene-specific primer amplification had the highest frequency of 100%, 60% and 54%, respectively [35]. From this, it can be inferred that there is a different avirulence gene composition of our new isolates, especially for Avr-Pizt. Avr-PWL3 is rarely present in M. oryzae isolates from rice [9], but it is even more frequent than Avr-Pia in our samples.
Significant correlations were noted on the type of agroecosystem as well as the classes of avirulence genes present. All of the cloned avirulence genes tested were present in fair proportions in the upland agroecosystem. This result reinforces the fact that rice blast is most favorable in the upland [36], and that rainfed still is more favorable than the irrigated lowland. In spite of this, examining the data further had made known that Avr-Pik and Avr-Pii occur in highest frequency in the irrigated lowland and rainfed lowland, respectively. This implies that the rice varieties planted can have significant impact on the existence of avirulence genes in the area. This result corroborates with those of Li et al. [37] who studied the geographic distribution of avirulence genes in rice blast fungus in Yunnan province in China. Their study illustrated that the composition and distribution of rice genetic diversity are more important than climate and environmental conditions in the prevalence of avirulence genes in populations of M. oryzae. Considering the weak geographic structure of M. oryzae populations in the Philippines, where gene flow occurs among the major islands, usually through the transport of infected seeds [38], the spread of avirulence genes as well could impact the stability of resistance genes in the agricultural fields. Some avirulence genes tested in this study are functional, such as Avr-Pizt and AvrPii, based on our results of pathogenicity test [38]. However, the polymorphisms of the avirulence genes were not tested, and the pathotypes of all the 131 isolates were not completely investigated. Therefore, it is advisable to conduct these experiments for future outlook of the project. Such strategy of assessing the avirulence genes currently present in an area would be useful for efficient deployment of resistant genes in order to better manage rice blast.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.J.C.; Formal analysis, A.L.L.; Funding acquisition, C.J.C.; Investigation, T.Y-M.; Methodology, A.L.L.; Project administration, C.J.C.; Resources, T.Y-M.; Supervision, C.J.C. and T.Y-M.; Writing—original draft, A.L.L.; Writing—review and editing, C.J.C.
Funding
This research was funded by the Experts II—ERASMUS Mundus Partnership in South and South East Asia, Göttingen International and Kirkhouse Trust, UK for the first author. The APC was funded by the University of Göttingen. The experimental work at the University of Turku was funded by Turku University Foundation, Olvi Foundation and the Academy of Finland.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yulin Jia (USDA-ARS) and Elizabeth Fournier (INRA, France) for providing the primer sets and Didier Tharreau (CIRAD, France) for comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Valent, B. Rice blast as a model system for plant pathology. Phytopathology 1990, 80, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.-M.; Xiao, Y.-I.; Yi, Y.J.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Zheng, K.I.; Lou, F. Relationship between blast resistance phenotypes and resistance gene analogue profiles in rice. Rice Sci. 2005, 2, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Silué, D.; Notteghem, J.L.; Tharreau, D. Evidence of a gene-for-gene relationship in the Oryza sativa Magnaporthe grisea pathosystem. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxel, T.; Balesdent, M.-H. Avirulence genes. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS); John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, H.H. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1971, 9, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauge, R.; De Wit, P.J.G.M. Fungal avirulence genes: Structure and possible functions. Fungal Genet. Biol. 1998, 24, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; He, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. The isolation of Pi1, an allele at the Pik locus which confers broad spectrum resistance to rice blast. Appl. Gen. 2012, 125, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; McAdams, S.A.; Bryan, G.T.; Hershey, H.P.; Valent, B. Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene. Products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4004–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Sweigard, J.A.; Valent, B. The PWL host specificity gene family in the blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1995, 8, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweigard, J.A.; Carroll, A.M.; Kang, S.; Farrall, L.; Chumley, F.G.; Valent, B. Identification, cloning, and characterization of PWL2, a gene for host species specificity in the rice blast fungus. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, M.J.; Farrall, L.; Sweigard, J.A.; Chumley, F.G.; Valent, B. A telomeric avirulence gene determines efficacy for the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, H.; Fudal, I.; Dioh, W.; Tharreau, D.; Notteghem, J.L.; Lebrun, M.H. A putative polyketide synthase/peptide synthetase from Magnaporthe grisea signals pathogen attack to resistant rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Lu, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AvrPiz-t encodes a predicted secreted protein that triggers the immunity in rice mediated by the blast resistance gene Piz-t. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, S.; Matsui, K.; Kito, H.; Otsuka, K.; Ashizawa, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the AVR-Pia locus from a Japanese field isolate of Magnaporthe Oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Saitoh, H.; Fujisawa, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; Yoshida, K.; Tosa, Y.; Chuma, I.; Takano, Y.; Win, J.; et al. Association genetics reveals three novel avirulence genes from the rice blast fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1573–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribot, C.; Césari, S.; Abidi, I.; Chalvon, V.; Bournaud, C.; Vallet, J.; Lebrun, M.-H.; Morel, J.-B.; Kroj, T. The Magnaporthe oryzae effector AVR1-CO39 is translocated into rice cells independently of a fungal-derived machinery. Plant J. 2013, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Kou, Y.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhu, X.; Ponaya, A.; Xiao, G.; Li, J.; Li, C.; et al. Comparative genomics identifies the Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence effector AvrPi9 that triggers Pi9-mediated blast resistance in rice. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, N.; Masako, T.; Noguchi, T.; Fujita, Y. Partial mapping of avirulence genes AVR-Pii and AVR-Pia in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 28, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Miki, Y.; Satoh, K.; Ohtsuka, A.; Abe, A.; Asano, K. Homologous recombination causes the spontaneous deletion of AVR-Pia in Magnaporthe oryzae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 339, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Bai, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, B. Genomic organization and sequence dynamics of the AvrPiz-t locus in Magnaporthe oryzae. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, H.; Yoshida, K.; Saitoh, H.; Fujisaka, K.; Hirabuchi, A.; Alaux, L.; Fournier, E.; Tharreau, D.; Terauchi, R. Arms race co-evolution of Magnaporthe oryzae AVR-Pik and rice Pik genes driven by their physical interactions. Plant J. 2012, 72, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuma, I.; Isobe, C.; Hotta, Y.; Ibaragi, K.; Futamata, N.; Kusaba, M.; Yoshida, K.; Terauchi, R.; Fujita, Y.; Nakayashiki, H.; et al. Multiple translocation of the AVR-Pita effector gene among chromosomes of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae and related species. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Does, H.C.; Rep, M. Virulence genes and the evolution of host specificity in plant-pathogenic fungi. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Vy, T.P.P.; Yoshida, K.; Asano, H.; Mitsuoka, C.; Asuke, S.; Anh, V.L.; Cumagun, C.J.R.; Chuma, I.; Terauchi, R.; et al. Evolution of the wheat blast fungus through functional losses in a host specificity determinant. Science 2017, 357, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.L.C.; Cumagun, C.J.R.; Didier, T. Diversity of ACE1 genotypes of the rice blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae B.C. Couch) in the Philippines. IAMURE Int. J. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 16, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonman, J.M.; Khush, G.S.; Nelson, R.J. Breeding rice for resistance to pests. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.H. Pathogen variability and host resistance in rice blast disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1980, 18, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweigard, J.A.; Orbach, M.J.; Valent, B.; Chumley, F.G. A miniprep procedure for isolating genomic DNA from Magnaporthe grisea. Fungal Genet. Rep. 1990, 37, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zeigler, R.S.; Leung, H.; Nelson, R.J. Population structure of Pyricularia grisea at two screening sites in the Philippines. Phytopathology 1995, 85, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukenbrock, E.H.; McDonald, B.A. Population genetics of fungal and oomycete effectors involved in gene-for-gene interactions. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharreau, D.; Fudal, I.; Andriantsimialona, D.; Kadrawi, S.; Utami, D.W.; Fournier, E.; Lebrun, M.-H.; Nottéghem, J.L. World Population Structure and Migration of the Rice Blast Fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae. In Advances in Genetics, Genomics and Control of Rice Blast Disease; Wang, G.L., Valent, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, J.; Wang, J.; Correll, J.C.; Cartwright, R. Natural Variation and Evolution of the Avirulence Genes in Magnaporthe oryzae. 2012. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=279490 (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- Lu, L.; Li, C.; Fan, H.; Jia, Y.; Li, J. Selection and mutation of the avirulence gene AVR-Pii of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Pathol. 2018, 68, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, J.; Alam, S.; Mandal, N.P.; Shukla, P.; Sharma, T.R.; Variar, M. Molecular identification and virulence analysis of AVR genes in rice blast pathogen, Magnaporthe oryzae from Eastern India. Euphytica 2015, 206, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisathaworn, T.; Srirat, T.; Longya, A.; Jantasuriyarat, C. Evaluation of mating type distribution and genetic diversity of three Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence genes, PWL-2, AVR-Pii and Avr-Piz-t, in Thailand rice blast isolates. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2017, 51, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.H.; Marchetti, M.A.; Petersen, H.D. Comparative slow-blasting in rice grown under upland and flooded blast nursery culture. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; He, H.; He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C. Geographic distribution of avirulence genes in rice blast fungus in Yunnan Province, China. J. Res. Ecol. 2011, 2, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.L.C.; Cumagun, C.J.R. Genetic structure of Magnaporthe oryzae populations in three island groups in the Philippines. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 153, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).