Antibiofilm Effects of N-Acetyl Cysteine on Staphylococcal Biofilm in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Tissue Collection
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Strains
2.4. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
2.5. Effects of NAC on Biofilm Formation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity of NAC
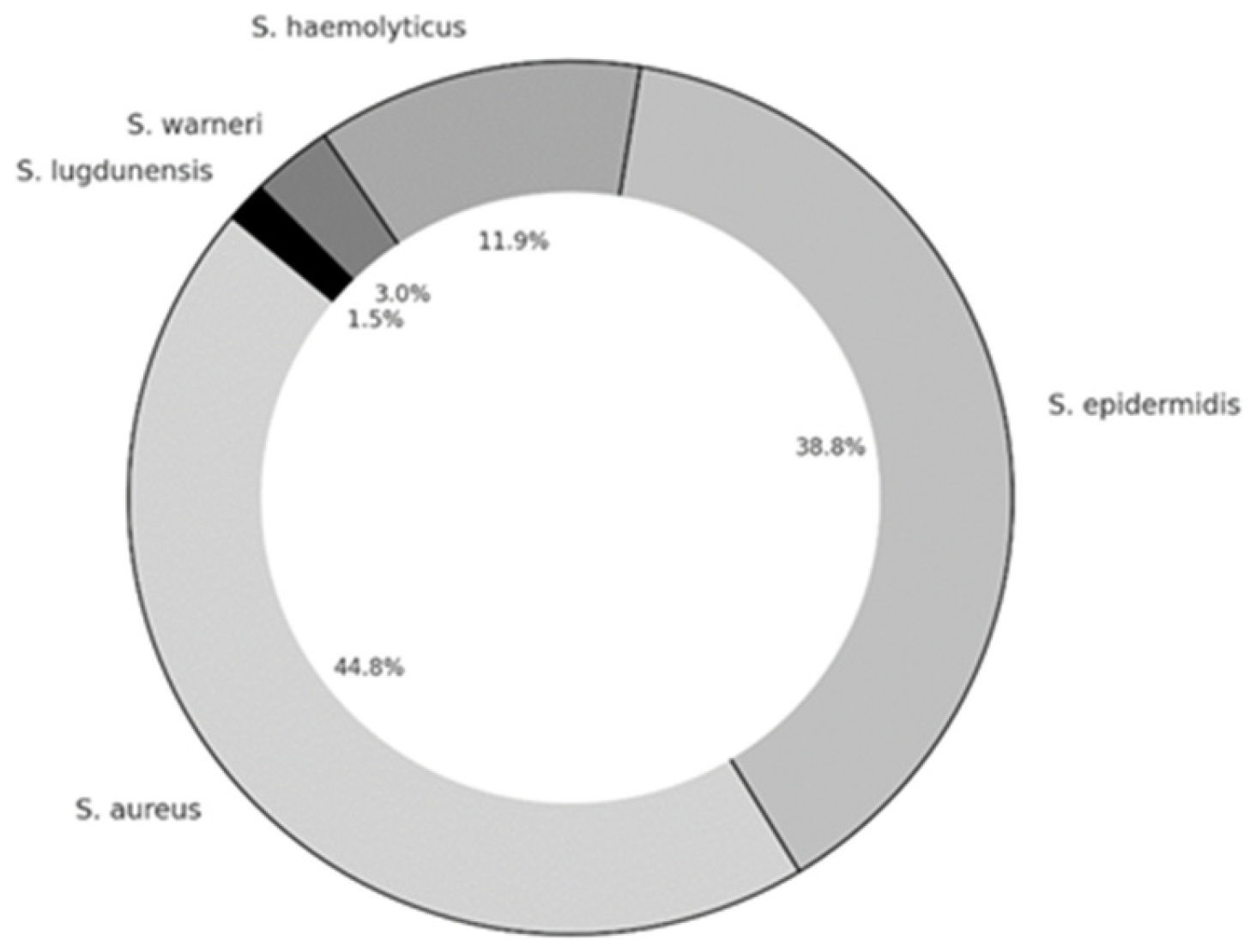
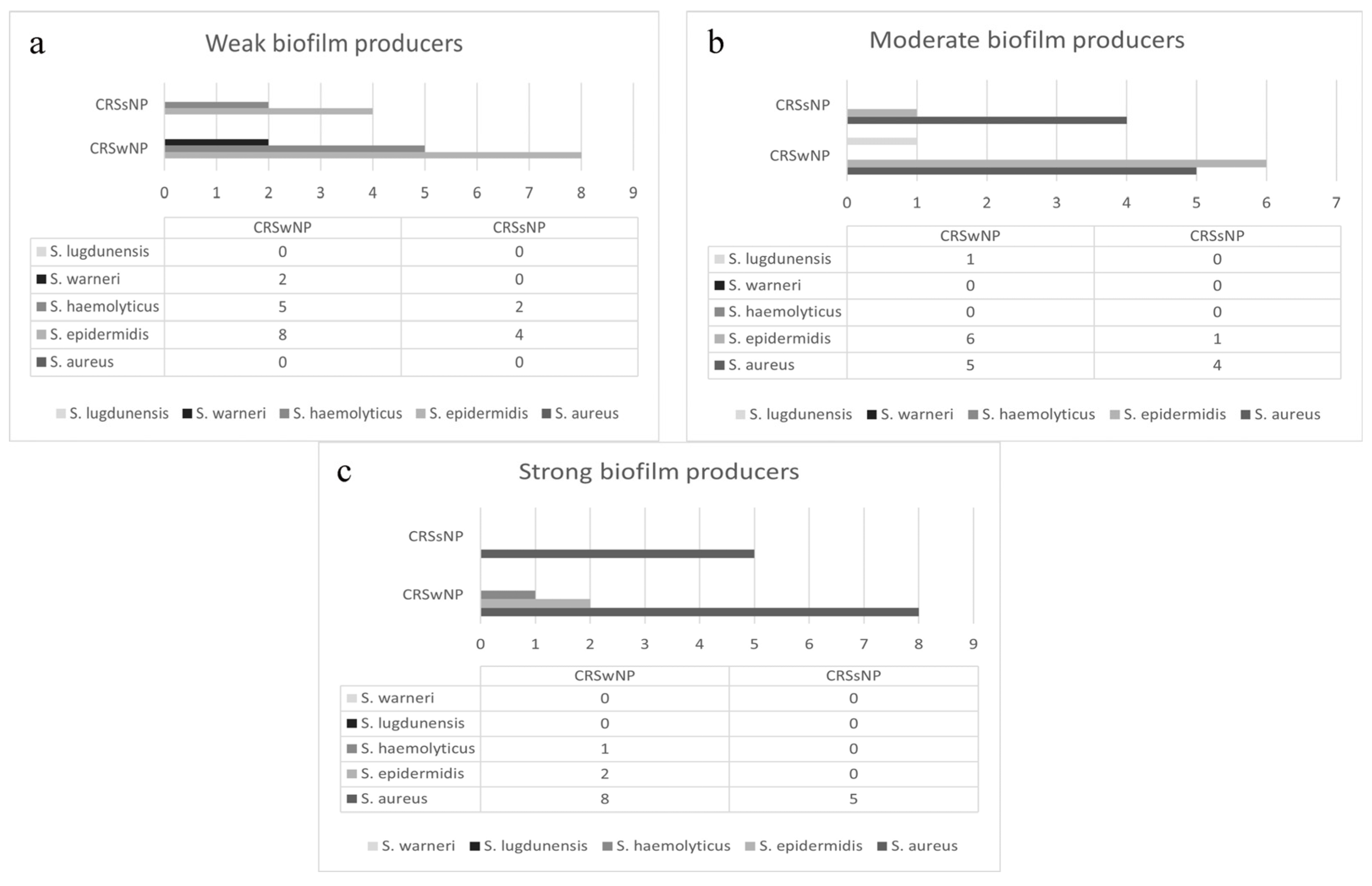
3.3. Biofilm Production
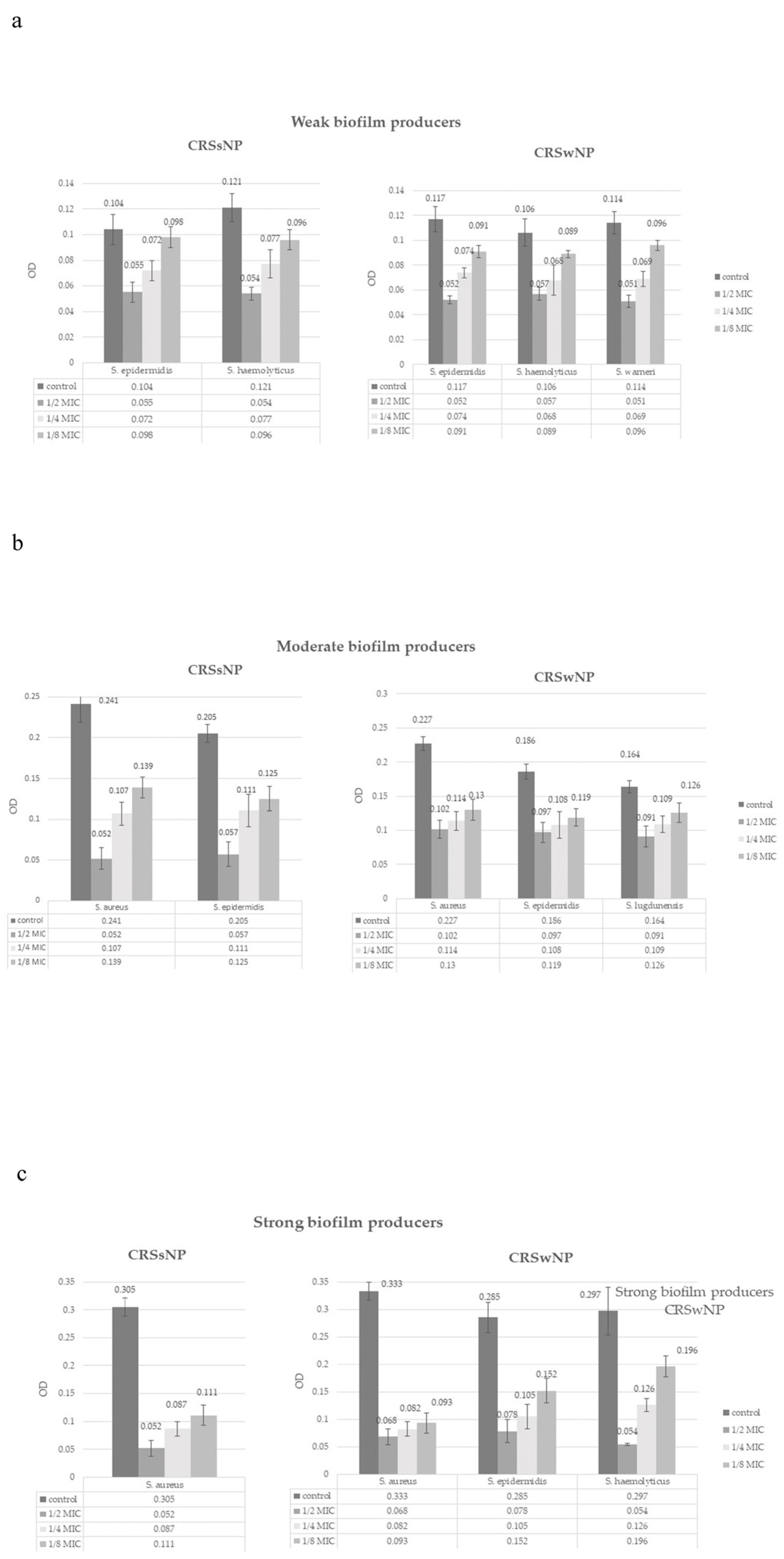
3.4. Effect of NAC on Biofilm Formation
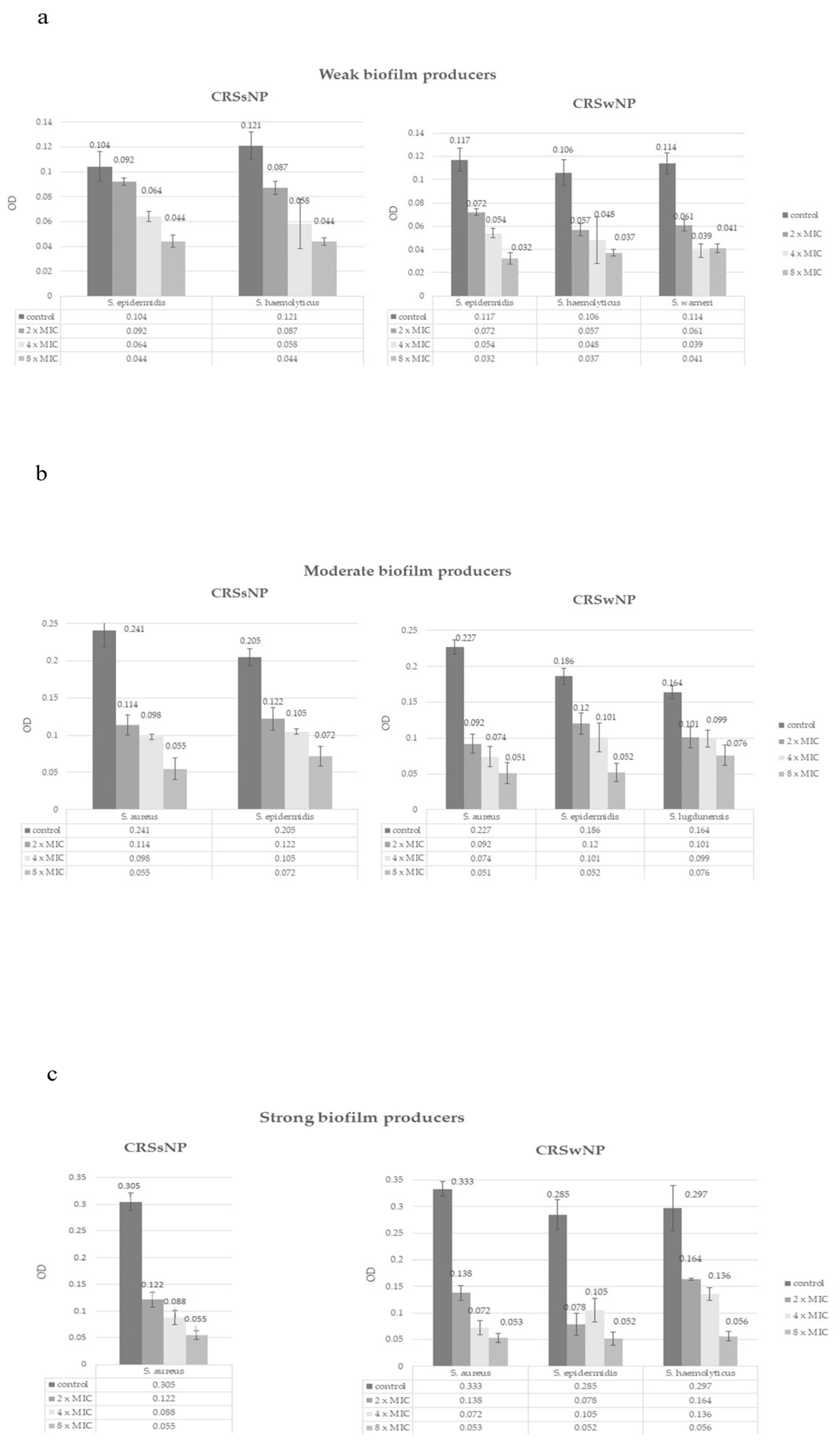
3.5. Effect of NAC on Biofilm Eradication
4. Discussion
4.1. Staphylococcal Bacterial Biofilms in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
4.2. The Effect of NAC on Staphylococcal Bacterial Biofilms in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAC | N-acetyl cysteine |
| CRSwNP | Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps |
| CRSsNP | Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps |
| CNS | Coagulase-negative Staphylococci |
| MIC | Minimal inhibitory concentration |
| MSSA | Methicillin-susceptible S. aureus |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant S. aureus |
| EPM | Extracellular polymeric matrix |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
References
- Manciula, L.G.; Jeican, I.I.; Tudoran, L.B.; Albu, S. Biofilms and inflammation in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutairi, D.; Kilty, S.J. Bacterial biofilms and the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilling, A.; Coombs, G.W.; Tan, H.L.; Pearson, J.C.; Boase, S.; Psaltis, A.; Speck, P.; Vreugde, S.; Wormald, P.J. Cousins, siblings, or copies: The genomics of recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infections in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugaszewska, J.; Leszczynska, M.; Lenkowski, M.; Tatarska, A.; Pastusiak, T.; Szyfter, W. The pathophysiological role of bacterial biofilms in chronic sinusitis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtak, G.; Bouras, G.; Nepal, R.; Shaghayegh, G.; Cooksley, C.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. The intra-host evolutionary landscape and pathoadaptation of persistent Staphylococcus aureus in chronic rhinosinusitis. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, T.W.; Ramakrishnan, V.R.; Suh, J.D. The Role of Staphylococcus aureus in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. In Emerging Modalities in Mitigation of Antimicrobial Resistance, 1st ed.; Akhtar, N., Singh, K.S., Goyal, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 291–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ciofu, O.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N. Tolerance and resistance of microbial biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiroudaki, S.; Sabbatini, S.; Pecoraro, C.; Cascioferro, S.; Diana, P.; Wauthoz, N.; Antognelli, C.; Monari, C.; Giovagnoli, S.; Schoubben, A. Development of a new indole derivative dry powder for inhalation for the treatment of biofilm-associated lung infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Löffler, B.; Proctor, R.A. Persistence of Staphylococcus aureus: Multiple metabolic pathways impact the expression of virulence factors in small-colony variants (SCVs). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vor, L.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; van Strijp, J.A.G. Staphylococci evade the innate immune response by disarming neutrophils and forming biofilms. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2556–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T.; Francois, P.; Liebeke, M.; Fraunholz, M.; Goerke, C.; Krismer, B.; Schrenzel, J.; Lalk, M.; Wolz, C. The stringent response of Staphylococcus aureus and its impact on survival after phagocytosis through the induction of intracellular PSMs expression. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, K.L.; Strange, E.; Parkhill, J.; Bamford, K.B.; Armstrong-James, D.; Edwards, A.M. Staphylococcus aureus adapts to oxidative stress by producing H2O2-resistant small-colony variants via the SOS response. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1830–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, V.J.; Chopra, I.; O’Neill, A.J. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms promote horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S.; Franklin, M.J. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Xiong, J.; Yang, G.X.; Hu, J.F.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm: Formulation, regulatory, and emerging natural products-derived therapeutics. Biofilm 2024, 7, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaghayegh, G.; Cooksley, C.; Ramezanpour, M.; Wormald, P.J.; Psaltis, A.J.; Vreugde, S. Chronic rhinosinusitis, S. aureus biofilm and secreted products, inflammatory responses, and disease severity. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, Z.; Didehdar, M.; Khoshbayan, A.; Karami, J.; Yousefimashouf, M.; Shariati, A. The role of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkiewicz, J.; Stręk, P.; Strus, M.; Głowacki, R.; Ciszek-Lenda, M.; Zagórska-Świeży, K.; Gawda, A.; Tomusiak, A. Staphylococcus epidermidis and biofilm-associated neutrophils in chronic rhinosinusitis: A pilot study. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 96, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghayegh, G.; Cooksley, C.; Bouras, G.; Nepal, R.; Houtak, G.; Panchatcharam, B.S.; Fenix, K.A.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm properties and chronic rhinosinusitis severity scores correlate positively with total CD4+ T-cell frequencies and inversely with its Th1, Th17 and regulatory cell frequencies. Immunology 2023, 170, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, M.; Navari, E.; Esin, S.; Menichini, M.; Barnini, S.; Trampuz, A.; Casani, A.; Batoni, G. Detection of biofilms in biopsies from chronic rhinosinusitis patients: In vitro biofilm forming ability and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm mode of growth of isolated bacteria. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1057, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A review of biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and its regulation mechanism. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Park, M.W.; Choi, Y.S.; Jung, H.J. Sinus irrigation with N-acetylcysteine after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A preliminary report of a single-blind randomized controlled trial. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grooters, K.E.; Ku, J.C.; Richter, D.M.; Krinock, M.J.; Minor, A.; Li, P.; Kim, A.; Sawyer, R.; Li, Y. Strategies for combating antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1352273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, F.; Page, C.; Rossolini, G.M.; Pallecchi, L.; Matera, M.G.; Rogliani, P.; Cazzola, M. The effect of N-acetylcysteine on biofilms: Implications for the treatment of respiratory tract infections. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, A.; Das, T.; Whiteley, G.S.; Glasbey, T.; Kriel, F.H.; Manos, J. The effect of N-acetylcysteine in a combined antibiofilm treatment against antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinicola, S.; De Grazia, S.; Carlomagno, G.; Pintucci, J.P. N-acetylcysteine as powerful molecule to destroy bacterial biofilms: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2942–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, B.; Gomes, F.; Melo, P.; Souza, C.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Pizzolitto, E. N-acetylcysteine and vancomycin alone and in combination against staphylococci biofilm. Rev. Bras. Eng. Bioméd. 2013, 29, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, M.C.D.S.; Graciliano, N.G.; Moura, F.A.; Oliveira, A.C.M.; Goulart, M.O.F. N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): Impacts on human health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Jiang, B.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; You, B.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. The interaction of N-acetylcysteine and serum transferrin promotes bacterial biofilm formation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Bonaventura, G.D.; Djukić, S.; Ćirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by Staphylococci. J. Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Desrosiers, M.; Khan, A.H. Burden of disease in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeConde, A.S.; Soler, Z.M. Chronic rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and burden of disease. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2016, 30, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.J.; Lund, V.J. Biofilms and chronic rhinosinusitis: Systematic review of evidence, current concepts and directions for research. Rhinology 2007, 45, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fastenberg, J.H.; Hsueh, W.D.; Mustafa, A.; Akbar, N.A.; Abuzeid, W.M. Biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis: Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 2, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, I.W.; Patel, N.N.; Cohen, N.A. Understanding the role of biofilms and superantigens in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2018, 6, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Meng, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis contributes to healthy maturation of the nasal microbiome by stimulating antimicrobial peptide production. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 68–78.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, E.M.; Lemos, M.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Giambiagi-deMarval, M. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaioli, S.; De Donno, A.; Bottau, G.; Campoccia, D.; Maso, A.; Dolzani, P.; Balaji, P.; Pegreffi, F.; Daglia, M.; Arciola, C.R. The opportunistic pathogen Staphylococcus warneri: Virulence and antibiotic resistance, clinical features, association with orthopedic implants and other medical devices, and a glance at industrial applications. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronner, S.; Foster, T.J. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: A skin commensal with invasive pathogenic potential. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, e00205-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Giraldo, C.; Rodríguez-Benito, A.; Morán, F.J.; Hurtado, C.; Blanco, M.T.; Gómez-García, A.C. Influence of N-acetylcysteine on the formation of biofilm by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landini, G.; Di Maggio, T.; Sergio, F.; Docquier, J.D.; Rossolini, G.M.; Pallecchi, L. Effect of high N-acetylcysteine concentrations on antibiotic activity against a large collection of respiratory pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7513–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyucuklu, G.; Kaynak Onurdağ, F.; Eryıldız, C. Stafilokok İzolatlarında antibiyotiklerin antibiyofilm etkinliği üzerine N-asetilsisteinin etkisi [Effect of N-acetylcystein on antibiofilm efficiency of antibiotics in Staphylococci isolates]. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2021, 55, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogliani, P.; Manzetti, G.M.; Gholamalishahi, S.; Cazzola, M.; Calzetta, L. Impact of N-acetylcysteine on mucus hypersecretion in the airways: A systematic review. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2024, 19, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedre, B.; Barayeu, U.; Ezeriņa, D.; Dick, T.P. The mechanism of action of N-acetylcysteine (NAC): The emerging role of H2S and sulfane sulfur species. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 228, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, L.C.; Finlinson, J.; Jones, B.; Berges, B.K. Beyond the double helix: The multifaceted landscape of extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1400648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, K.L.; Riquelme, S.A. Host-bacteria metabolic crosstalk drives S. aureus biofilm. Microb. Cell 2021, 8, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, A.C.; Hermansson, M.; Elwing, H. N-acetyl-L-cysteine affects growth, extracellular polysaccharide production, and bacterial biofilm formation on solid surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4814–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroshenko, D.; Polyudova, T.; Korobov, V. N-acetylcysteine inhibits growth, adhesion and biofilm formation of Gram-positive skin pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Sato, F.; Miyakawa, R.; Chiba, A.; Onodera, S.; Hori, S.; Mizunoe, Y. Broad impact of extracellular DNA on biofilm formation by clinically isolated methicillin-resistant and -sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lopez, A.; Marshall, C.W.; Scribner, M.R.; Snyder, D.J.; Cooper, V.S. Evolutionary pathways to antibiotic resistance are dependent upon environmental structure and bacterial lifestyle. Elife 2019, 8, e47612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, N.R.; Lazazzera, B.A. Defining the genetic differences between wild and domestic strains of Bacillus subtilis that affect poly-gamma-DL-glutamic acid production and biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.L.; Heard, K.J.; Reynolds, K.M.; Albert, D. Oral and intravenous acetylcysteine for treatment of acetaminophen toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 14, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffezzoni, E.; Notargiacomo, M.; Agostini, S.; Gelardi, M. Efficacy of a nasal spray containing N-acetylcysteine in hypertonic solution in the treatment of nonallergic chronic rhinitis with goblet cell metaplasia. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex | |
|---|---|
| Male Female | 48 (64%) 27 (36%) |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 45.5 ± 14.3 |
| Type of chronic rhinosinusitis n (%) | |
| Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps (CRSsNP) Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) | 33 (44%) 42 (64%) |
| Lund–MacKay score (maximum = 24) | 9 (4–23) |
| Microorganism | Highest MIC (mg/mL) | Lowest MIC (mg/mL) | Mean ± SD MIC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | 10 | 2.5 | 6.4 ± 2.8 |
| Coagulase-negative Staphylococci | 10 | 2.5 | 6.1 ± 2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jotic, A.; Cirkovic, I.; Bozic, D.; Savic Vujovic, K.; Milovanovic, J.; Folic, M.; Trivic, A.; Cvorovic, L.; Radivojevic, N. Antibiofilm Effects of N-Acetyl Cysteine on Staphylococcal Biofilm in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092050
Jotic A, Cirkovic I, Bozic D, Savic Vujovic K, Milovanovic J, Folic M, Trivic A, Cvorovic L, Radivojevic N. Antibiofilm Effects of N-Acetyl Cysteine on Staphylococcal Biofilm in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092050
Chicago/Turabian StyleJotic, Ana, Ivana Cirkovic, Dragana Bozic, Katarina Savic Vujovic, Jovica Milovanovic, Miljan Folic, Aleksandar Trivic, Ljiljana Cvorovic, and Nemanja Radivojevic. 2025. "Antibiofilm Effects of N-Acetyl Cysteine on Staphylococcal Biofilm in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092050
APA StyleJotic, A., Cirkovic, I., Bozic, D., Savic Vujovic, K., Milovanovic, J., Folic, M., Trivic, A., Cvorovic, L., & Radivojevic, N. (2025). Antibiofilm Effects of N-Acetyl Cysteine on Staphylococcal Biofilm in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092050









