Yeast Ecology in White Brined Cheeses: Correlations with Physicochemical Parameters in Artisanal and Industrial Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cheese Samples
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Detection and Count of Yeasts
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Milk and Milk Product Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Milk_and_milk_product_statistics#Milk_products (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Zheng, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. A review on the general cheese processing technology, flavor biochemical pathways and the influence of yeasts in cheese. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 703284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I. Statistics of Dairy and Milk Flows for Bulgaria. 2025. Available online: https://www.mzh.government.bg/media/filer_public/2024/09/12/situatsiia_na_pazara_na_mliako_i_mlechni_produkti_-_septemvri_2024_pHKk9k1.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Bintsis, T. Yeasts in different types of cheese. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montel, M.C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional cheeses: Rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G. Worldwide traditional cheeses: Banned for business? Dairy Sci. Technol. 2010, 90, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindstedt, P.S. The history of cheese. In Global Cheesemaking Technology: Cheese Quality and Characteristics, 1st ed.; Papademas, P., Bintsis, T., Eds.; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Banjara, N.; Suhr, M.J.; Hallen-Adams, H.E. Diversity of yeast and mold species from a variety of cheese types. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.P.; Melo, C.N.; Genisheva, Z.; Schwan, R.F.; Duarte, W.F. Yeasts from Canastra cheese production process: Isolation and evaluation of their potential for cheese whey fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2017, 91, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swearingen, P.A.; O’Sullivan, D.J.; Warthesen, J.J. Isolation, characterization, and influence of native, nonstarter lactic acid bacteria on cheddar cheese quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, J.; Goerges, S.; Gelsomino, R.; Vancanneyt, M.; Vandemeulebroecke, K.; Hoste, B.; Brennan, N.; Scherer, S.; Swings, J.; Fitzgerald, G.; et al. Sources of the adventitious microflora of a smear-ripened cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, K.; Sørensen, L.M.; Petersen, M.A.; Jespersen, L.; Arneborg, N. Debaryomyces hansenii strains differ in their production of flavor compounds in a cheese-surface model. Microbiologyopen 2012, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Wyder, M.T.; Arias-Roth, E.; Jakob, E. Cheese yeasts. Yeast 2019, 36, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H. (Eds.) Microbiology of cheese ripening. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 206–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lopandic, K.; Zelger, S.; Banszky, L.K.; Eliskases-Lechner, F.; Prillinger, H. Identification of yeasts associated with milk products using traditional and molecular techniques. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagiotti, C.; Ciani, M.; Canonico, L.; Comitini, F. Occurrence and involvement of yeast biota in ripening of Italian Fossa cheese. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, P.; Ricciardi, A.; Salzano, G.; Suzzi, G. Yeasts from Water Mozzarella, a traditional cheese of the Mediterranean area. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 69, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, K.; Touchette, M.; St-Gelais, D.; Labrie, S. Characterization of the fungal microflora in raw milk and specialty cheeses of the province of Quebec. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Kandasamy, S.; Bruntha Devi, P.; Shetty, P.H. Recent developments on encapsulation of lactic acid bacteria as potential starter culture in fermented foods—A review. Food Biosci. 2018, 21, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.C.; Andrade, R.P.; Oliveira, D.R.; Quintanilha, M.F.; Martins, F.S.; Duarte, W.F. Kluyveromyces lactis and Torulaspora delbrueckii: Probiotic characterization, anti-Salmonella effect, and impact on cheese quality. LWT 2021, 151, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkar, K.G.; Teger, S.G. The presence of some pathogen microorganisms, yeasts and moulds in cheese samples produced at small dairy-processing plants. Acta Agric. Slov. 2006, 88, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Geronikou, A.; Srimahaeak, T.; Rantsiou, K.; Triantafillidis, G.; Larsen, N.; Jespersen, L. Occurrence of yeasts in white-brined cheeses: Methodologies for identification, spoilage potential and good manufacturing practices. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavenne, E.; Mounier, J.; Asmani, K.; Jany, J.-L.; Barbier, G.; Le Blay, G. Fungal diversity in cow, goat and ewe milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D. Microbiota of raw milk and raw milk cheeses. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P., Fox, P., Cotter, P., Everett, D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 301–316. [Google Scholar]
- Rantsiou, K.; Urso, R.; Dolci, P.; Comi, G.; Cocolin, L. Microflora of Feta cheese from four Greek manufacturers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.M.; Borelli, B.M.; Lara, C.A.; Soares, M.A.; Pataro, C.; Bodevan, E.C.; Rosa, C.A. The influence of seasons and ripening time on yeast communities of a traditional Brazilian cheese. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, K. Fungal diversity in different types of cheese and the effect of natamycin on their survival during Feta cheese manufacture and storage. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2016, 3, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togay, S.O.; Capece, A.; Siesto, G.; Aksu, H.; Altunatmaz, S.S.; Aksu, F.Y.; Romano, P.; Yuceer, Y.K. Molecular characterization of yeasts isolated from traditional Turkish cheeses. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geronikou, A.; Larsen, N.; Lillevang, S.K.; Jespersen, L. Diversity and succession of contaminating yeasts in white-brined cheese during cold storage. Food Microbiol. 2023, 113, 104266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macit, E.; Yücel, N.; Dertli, E. The characterization of the non-starter lactic acid bacteria and yeast microbiota and the chemical and aromatic properties of traditionally produced Turkish White Cheese. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2227–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šuranská, H.; Raspor, P.; Uroić, K.; Golić, N.; Kos, B.; Mihajlović, S.; Begović, J.; Šušković, J.; Topisirović, L.; Čadež, N. Characterisation of the yeast and mould biota in traditional white pickled cheeses by culture-dependent and independent molecular techniques. Folia Microbiol. 2016, 61, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.I.; Aldabbagh, S.Y.A.; Shareef, A.M. Isolation, identification and detection of some virulence factors in yeasts from local cheese in Mosul city. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 32, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, M.; Choiset, Y.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Chobert, J.; Dousset, X.; Ivanova, I.; Haertlé, T. Isolation and partial biochemical characterization of a proteinaceous anti-bacteria and anti-yeast compound produced by Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei strain M3. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 87, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, L.; Valence, F.; Mounier, J. Diversity and control of spoilage fungi in dairy products: An update. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, A.J.; Evanowski, R.L.; Martin, N.H.; Boor, K.; Wiedmann, M. Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequencing reveals considerable fungal diversity in dairy products. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8814–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, L.; Valence, F.; Pawtowski, A.; Auhustsinava-Galerne, L.; Frotté, N.; Baroncelli, R.; Deniel, F.; Coton, E.; Mounier, J. Diversity of spoilage fungi associated with French dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 241, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haastrup, M.K.; Johansen, P.; Malskær, A.H.; Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Kot, W.; Krych, L.; Arneborg, N.; Jespersen, L. Cheese brines from Danish dairies reveal a complex microbiota comprising several halotolerant bacteria and yeasts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 285, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, J.; Le Blay, G.; Vasseur, V.; Le Floch, G.; Jany, J.-L.; Barbier, G. Application of denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) for yeasts identification in red smear cheese surfaces. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Frisso, G.; Mauriello, G.; Salvatore, F.; Coppola, S. Microbial diversity in natural whey cultures used for the production of Caciocavallo Silano PDO cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kačániová, M.; Terentjeva, M.; Kunová, S.; Nagyová, L.; Horská, E.; Haščík, P.; Kluz, M.; Puchalski, C. Identification of the Slovak traditional cheese “Parenica” microflora. Acta Agrar. Debreceniensis 2018, 150, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://lex.bg/laws/ldoc/2135700088 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/55777.html (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Tkahcenko, N.A.; Nekrasov, P.O.; Vikul, S.I. Optimization of formulation composition of health whey-based beverage. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2016, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/35249.html (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Available online: https://cdn.standards.iteh.ai/samples/43922/41446e4ae977424a9f4b6453101325d3/ISO-5943-2006.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/46336.html (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/38275.html (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Bintsis, T.; Papademas, P. Microbiological quality of white-brined cheeses: A review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2002, 55, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu-Yalcin, S.; Senses-Ergul, S.; Ozbas, Z.Y. Enzymatic characterization of yeast strains originated from traditional Mihalic cheese. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2017, 6, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaloglu, A.A. Cheese varieties ripened under brine. In Cheese Varieties Ripened Under Brine, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: London, UK, 2017; pp. 997–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westall, S.; Filtenborg, O. Yeast occurrence in Danish Feta cheese. Food Microbiol. 1998, 15, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, O.G.; Meyers, S.P.; Nichols, R.A. Extracellular proteinases of yeasts and yeast-like fungi. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 16, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Nafisa, A.E.; Seham, I.F.; Orsi, F. Effect of pasteurization and storage condition on the microbial, chemical and organoleptic quality of soft cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 94, 177–190. [Google Scholar]
- Shabatai, Y. Isolation and characterization of a lipolytic bacterium capable of growing in a low-water content oil–water emulsion in cheese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 57, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.G.; Turkoglu, H.; Dayisoylu, K.S. The microbiological and chemical quality of Sikma cheese produced in Turkey. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharoud, W.; Belloch, C.; Peris, D.; Querol, A. Molecular identification of yeasts associated with traditional Egyptian dairy products. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobnicka-Kupiec, A.; Gołofit-Szymczak, M.; Górny, R. Microbial contamination level and microbial diversity of occupational environment in commercial and traditional dairy plants. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borelli, B.M.; Ferreira, E.G.; Lacerda, I.C.A.; Franco, G.R.; Rosa, C.A. Yeast populations associated with the artisanal cheese produced in the region of Serra da Canastra, Brazil. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarbati, A.; Marini, E.; Galli, E.; Canonico, L.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Characterization of wild yeasts isolated from artisan dairies in the Marche region, Italy, for selection of promising functional starters. LWT 2021, 139, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, C.; Martirosyan, D.M. The bioactive compounds of probiotic foods/supplements and their application in managing mental disorders. Bioact. Compd. Health Dis. 2019, 2, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Sahoo, D. Biotechnological potential of yeasts in functional food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, M.; Čadež, N.; Uroić, K.; Miljkovic, M.; Tolinacki, M.; Dousova, P.; Kos, B.; Suskovic, J.; Raspor, P.; Topisirovic, L. Evaluation of probiotic potential of yeasts isolated from traditional cheeses manufactured in Serbia and Croatia. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, N.M.Z.; de Souza, A.C.; de Souza Costa Sobrinho, P.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F.; Ramos, C.L. Novel yeasts with potential probiotic characteristics isolated from the endogenous ferment of artisanal Minas cheese. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanak, E.K.; Öztürk Yılmaz, S. Determination of the probiotic and functional properties of yeasts isolated from different dairy products. Fermentation 2025, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.P.; Oliveira, D.R.; Lopes, A.C.A.; de Abreu, L.R.; Duarte, W.F. Survival of Kluyveromyces lactis and Torulaspora delbrueckii to simulated gastrointestinal conditions and their use as single and mixed inoculum for cheese production. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarbati, A.; Canonico, L.; Marini, E.; Zannini, E.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Potential probiotic yeasts sourced from natural environmental and spontaneous processed foods. Foods 2020, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Dai, C.; Tong, L.; Lv, H.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of the probiotic potential of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. indicus WDS-7 isolated from Chinese traditional fermented buffalo milk in vitro. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisseire, P.; Bonnet, M.; Saraoui, T.; Poupet, C.; Camarès, O.; Gachinat, M.; Callon, C.; Febvre, G.; Chassard, C.; Bornes, S. Investigation into in vitro and in vivo Caenorhabditis elegans models to select cheese yeasts as probiotic candidates for their preventive effects against Salmonella Typhimurium. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, K.; Nath, L.S. Studies on the air quality in a dairy processing plant. Indian J. Vet. Anim. Sci. Res. 2014, 43, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Kyosev, H. Commodity Microbiology; University Publishing House of the University of Economics: Varna, Bulgaria, 1999; Volume 350, p. 272. ISBN 954-21-0052-8. [Google Scholar]
- Massouras, T.; Zoidou, E.; Baradaki, Z.; Karela, M. Physicochemical, microbiological and sensory characteristics of white brined cheese ripened and preserved in large-capacity stainless steel tanks. Foods 2023, 12, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.S.; Ma, Y.; Maubois, J.L.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, Q.H.; Guo, J.P. Identification of yeasts from raw milk and selection for some specific antioxidant properties. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Aa Kühle, A.; Jespersen, L. The taxonomic position of Saccharomyces boulardii as evaluated by sequence analysis of the D1/D2 domain of 26S rDNA, the ITS1-5.8 S rDNA-ITS2 region and the mitochondrial cytochrome-c oxidase II gene. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 26, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, J.C.; Jiménez-Estrada, M.; Peña, A. Comparative analysis of trehalose production by Debaryomyces hansenii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae under saline stress. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
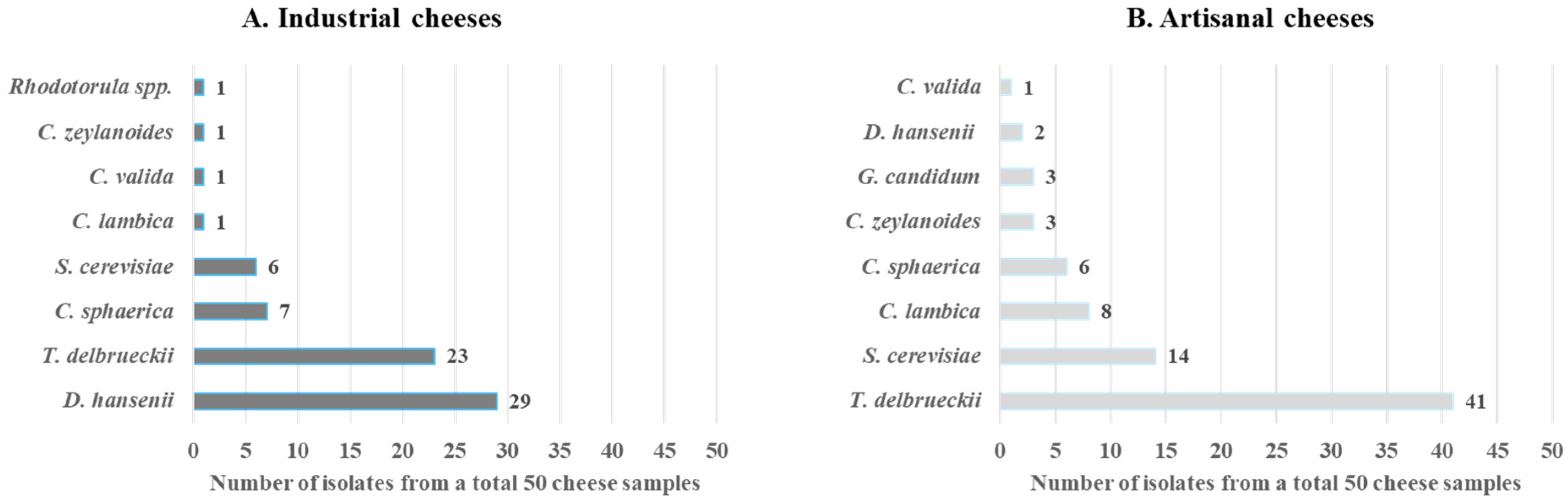
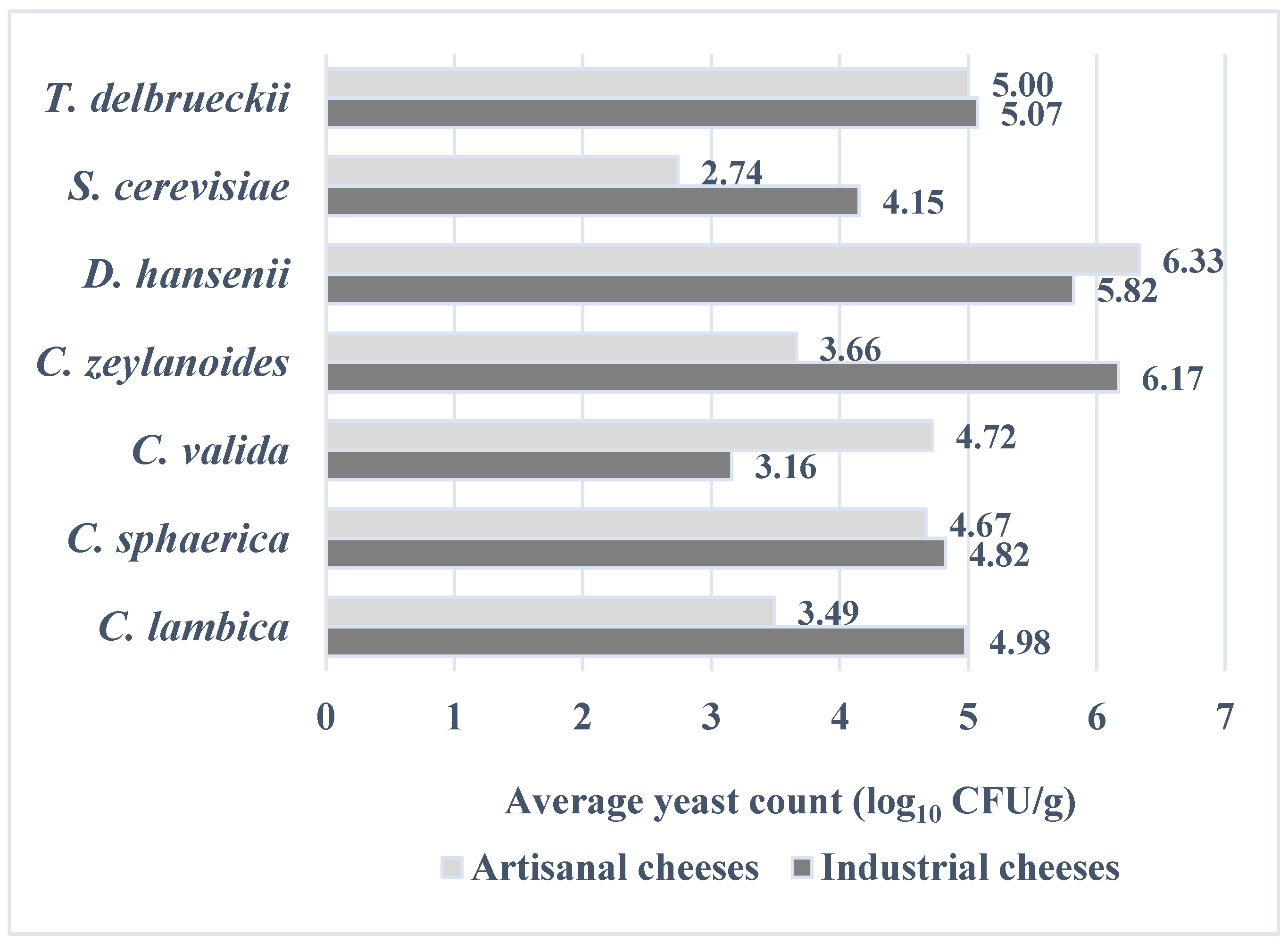
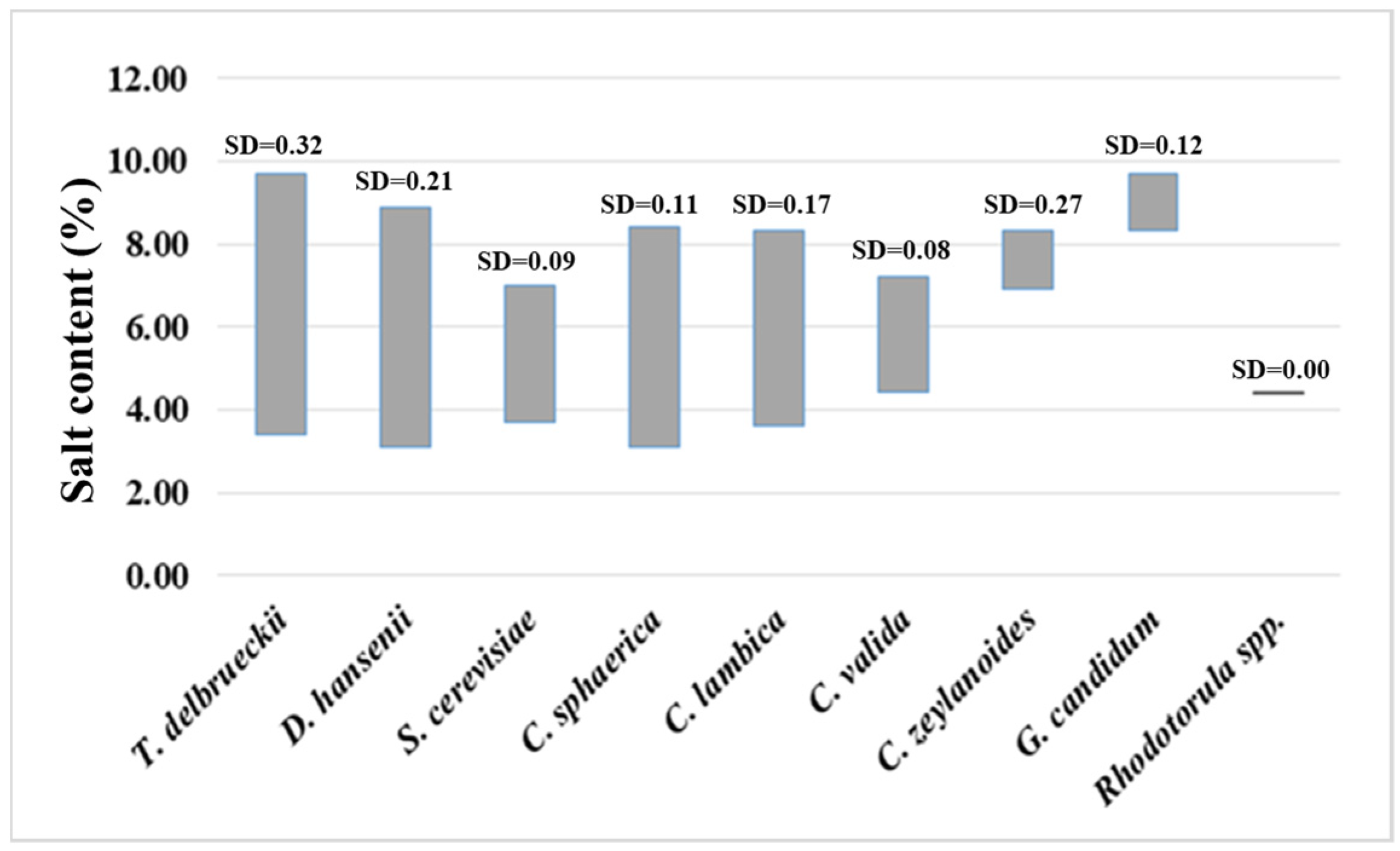
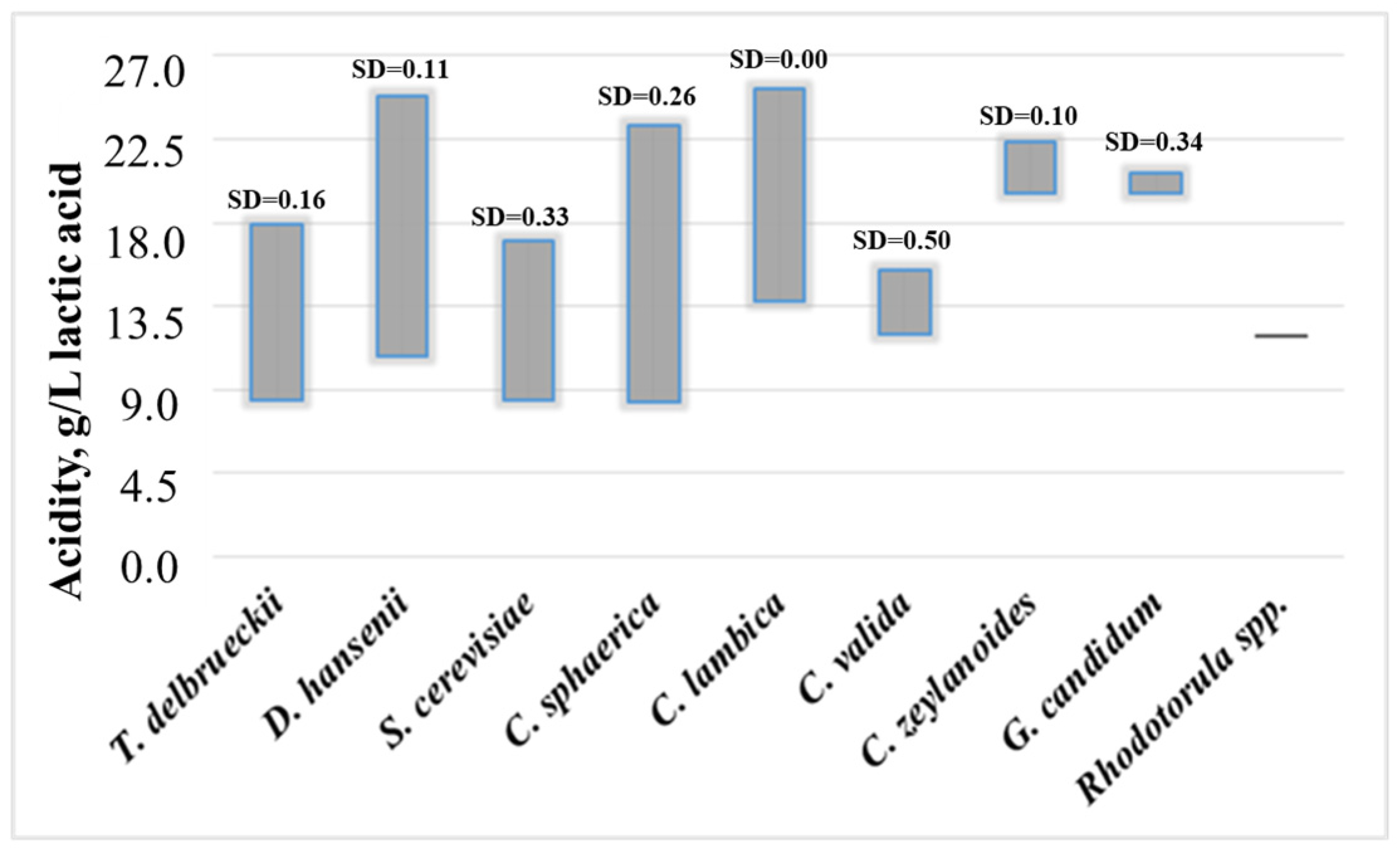
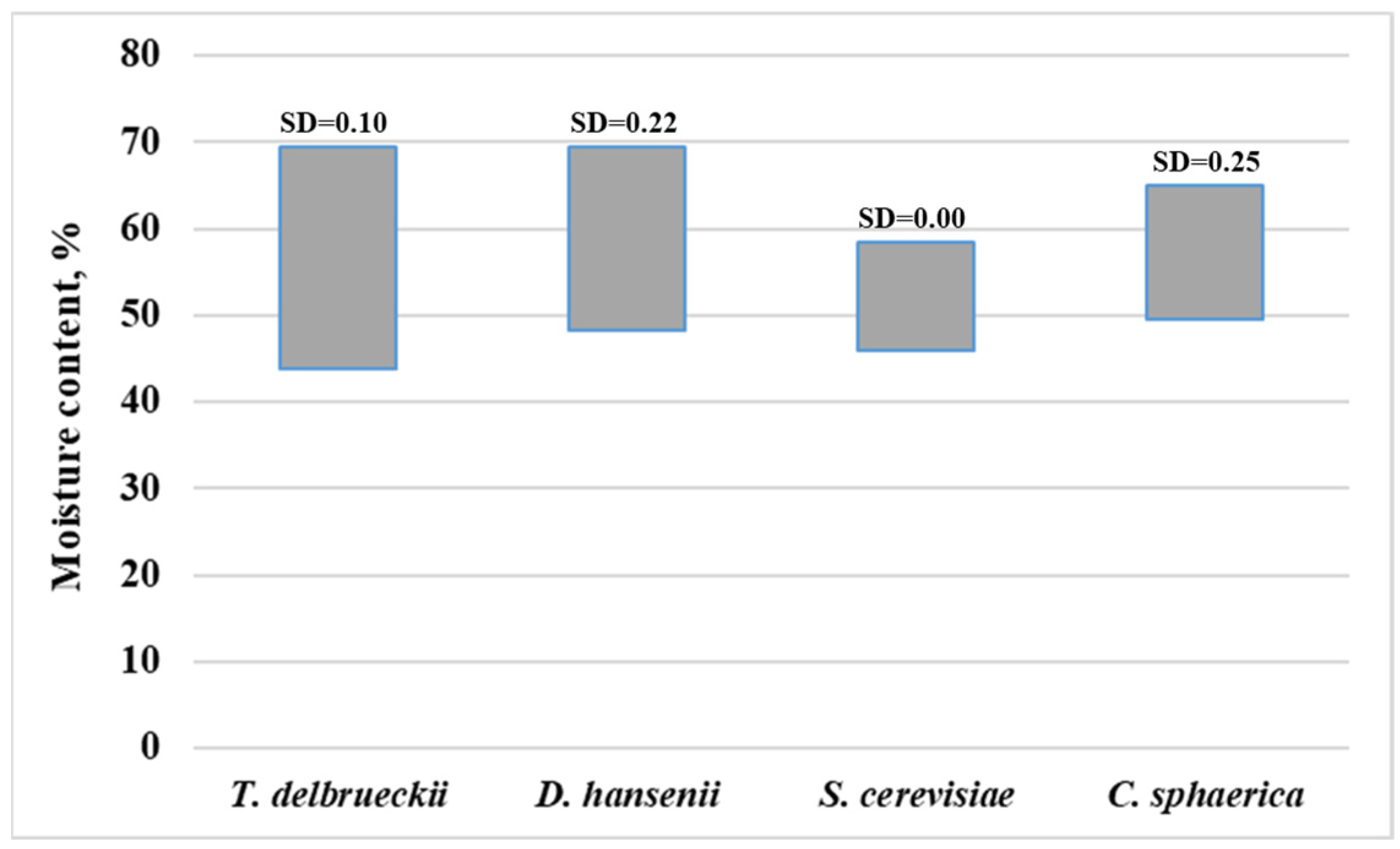

| Correlation Analysis of Differences in Physicochemical Parameters Between Artisanal and Industrial Cheeses (Mann–Whitney U Test/t-Test) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cheese samples | salt content p = 0.700 | acidity p = 0.381 | fat content p = 0.101 | moisture content p = 0.048 | degree of maturity p = 0.155 |
| Correlation between physicochemical parameters and the species composition of isolated yeasts (ANOVA test) | |||||
| Total cheese samples | * salt content p = 0.0074 | * acidity p = 0.0028 | fat content p = 0.351 | moisture content p = 0.585 | degree of maturity p = 0.634 |
| Industrial cheese samples | * salt content p = 0.016 | acidity p = 0.721 | fat content p = 0.296 | * moisture content p = 0.0057 | degree of maturity p = 0.647 |
| Artisanal cheese samples | * salt content p = 0.022 | * acidity p = 0.0055 | fat content p = 0.748 | moisture content p = 0.0788 | degree of maturity p = 0.320 |
| Correlation between physicochemical parameters and yeast count (log10 CFU/g) (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient) | |||||
| Total cheese samples | salt content p = 0.414 | acidity p = 0.427 | fat content p = 0.561 | moisture content p = 0.910 | degree of maturity p = 0.086 |
| Industrial cheese samples | * salt content p = 0.029 | acidity p = 0.52 | fat content p = 0.71 | moisture content p = 0.51 | degree of maturity p = 0.78 |
| Artisanal cheese samples | salt content p = 0.91 | acidity p = 0.81 | fat content p = 0.727 | moisture content p = 0.80 | degree of maturity p = 0.909 |
| Yeast Species | Salt Content | Acidity | Fat Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| T. delbrueckii | r = −0.1687 | - | r = −0.2410 |
| D. hansenii | r = 0.2239 | r = 0.1761 | r = 0.2714 |
| S. cerevisiae | r = −0.1484 | r = −0.1844 | - |
| Candida spp. | r = 0.1078 | r = −0.0724 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ermenlieva, N.; Stamova, S.; Ivanova, N.; Atanasova, P.; Marinova, V.; Ibryamova, S.; Ivanov, I.; Georgieva, E. Yeast Ecology in White Brined Cheeses: Correlations with Physicochemical Parameters in Artisanal and Industrial Products. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091965
Ermenlieva N, Stamova S, Ivanova N, Atanasova P, Marinova V, Ibryamova S, Ivanov I, Georgieva E. Yeast Ecology in White Brined Cheeses: Correlations with Physicochemical Parameters in Artisanal and Industrial Products. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091965
Chicago/Turabian StyleErmenlieva, Neli, Sylvia Stamova, Nadezhda Ivanova, Petya Atanasova, Velichka Marinova, Sevginar Ibryamova, Ivan Ivanov, and Emilia Georgieva. 2025. "Yeast Ecology in White Brined Cheeses: Correlations with Physicochemical Parameters in Artisanal and Industrial Products" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091965
APA StyleErmenlieva, N., Stamova, S., Ivanova, N., Atanasova, P., Marinova, V., Ibryamova, S., Ivanov, I., & Georgieva, E. (2025). Yeast Ecology in White Brined Cheeses: Correlations with Physicochemical Parameters in Artisanal and Industrial Products. Microorganisms, 13(9), 1965. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13091965







