Abstract
This study aimed to determine the optimal supplementation level of sodium humate (SH) for improving rumen fermentation efficiency in vitro. Using rumen fluid from four donor ewes with three experimental replicates per treatment, we evaluated a basal diet supplemented with SH at 0 (control), 0.5 (SH0.5), 1 (SH1), and 2 (SH2) g/kg dry matter. The results of this study revealed that after 12 h of incubation, compared to the control group, the SH0.5 group significantly decreased gas production (GP) by −11.66% (p < 0.01). There were no significant differences in pH values, bacterial crude protein (BCP) content, and ammonia nitrogen (NH₃-N) concentration among the groups (p > 0.05). After 24 h of incubation, no significant differences in pH values were observed among the groups (p > 0.05). The SH1 group exhibited significantly higher BCP content compared to other treatments (p < 0.05), concomitant with a marked reduction in NH₃-N concentration (p < 0.01). Compared to the control group, GP in the SH1 group increased significantly by 7.16%, and a significant increase of 5.43% (p < 0.05), while it decreased significantly by −9.96% in the SH0.5 group (p < 0.01). However, no significant differences in volatile fatty acids were observed among the groups after either 12 or 24 h of fermentation. The addition of 1 g/kg SH altered the composition of the rumen bacterial community, which was indicated by the increased relative abundances of Prevotella, Anaerovibrio, and Saccharofermentans and the decreased relative abundances of Actinobacteriota, Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group, and [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group (p < 0.05). Furthermore, Anaerovibrio was negatively correlated with NH₃-N and positively correlated with gas production, while [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group was negatively correlated with gas production. The study indicates that the addition of 1 g/kg SH optimizes rumen fermentation efficiency and improves nutrient utilization by modulating the structure and composition of the bacterial community, thus serving as an effective additive for enhancing rumen fermentation and feed utilization in ruminants.
1. Introduction
In recent years, in pursuit of enhanced production efficiency, sheep were often provided with high-concentrate diets. However, long-term feeding of such diets may adversely affect rumen function, including disruptions to bacterial balance and fermentation patterns []. To address these challenges, supplementation of ruminant diets with additives has emerged as a promising strategy to modulate rumen fermentation and microbiota structure, thereby improving rumen health [,].
Among these additives, humic substances (HSs), including humic acids (HAs) and fulvic acids (FAs), are organic macromolecules derived from decomposed plant and natural residues, widely distributed in soils, aquatic systems, and sediments []. Due to their anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties, HSs have been utilized in traditional medicine for millennia [,]. Notably, HSs form a protective film on the mucous epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract against infections and toxins; their large colloidal structure ensures good shielding of the gastrointestinal mucosa, peripheral capillaries, and damaged mucous cells. As a result of this process, the re-absorption of toxic metabolites is reduced or completely prevented, especially after infections or in the presence of harmful substances in animal feed []. For instance, Murbach et al. (2020) [] demonstrated that dietary supplementation with 0.5 g/kg HAs significantly improved the health status of monogastric animals by mitigating inflammation, a mechanism particularly beneficial in the presence of feed-borne toxins or post-infection recovery. Beyond their protective role, HSs have been shown to improve feed efficiency and growth performance. In poultry, the addition of HSs at a dose of 0.2 g/kg in the diet increased egg production and quality []. In pigs, HSs at a dose of 0.3 g/kg improved growth rates and feed conversion efficiency [].
Sodium humate (SH), a salt of HAs, has been used as a therapeutic agent for dyspepsia, diarrhea, and acute intoxication in animals, with potential antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antidiarrheal, and antirheumatic properties []. As a result, it may enhance immunity, promote growth, improve the feed conversion rate, and reduce nitrogen losses, making it a useful feed additive in livestock production [,]. Research shows that adding 1 g/kg SH can reduce diarrhea incidence []. SH has also been shown to enhance feed conversion efficiency by 15% in dairy cows at a dose of 1.5 g/kg []. However, despite these benefits in monogastric animals, the effects of SH on rumen function remain unclear. Therefore, this study used an in vitro fermentation system to evaluate the effects of SH on ruminal ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration, bacterial crude protein (BCP) content, gas production, volatile fatty acid (VFA) production, and bacterial community composition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates and Treatments
SH was purchased from the market in Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province, China. SH is dark black in color. The effective component content is 28% fulvic acid and 29% free humic acid. The substrate was a high-concentrate diet; the ingredients and chemical composition of the basal diet are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Ingredient and chemical composition of the basal diet (%, air-dry basis).
In a completely randomized design, treatments involved supplementing 1 g (air-dry matter basis) substrates with different levels of SH (0 g/kg, 0.5 g/kg, 1 g/kg, and 2 g/kg). Moreover, a blank/control group was established, which contained neither the substrate nor SH. This blank group was utilized to account for the variations in rumen fluid used for in vitro fermentation and to determine the net gas production. Each experimental run consisted of four parallel experiments, and the entire experiment was replicated three times.
2.2. In Vitro Batch Culture
All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Protocol No. 2020069).
Four healthy female small-tailed Han sheep with similar body conditions, weighing 35.20 ± 1.45 kg and aged 6 months, were selected as rumen fluid donors. The experimental donor ewes were housed individually and fed a basic diet (with the same composition as shown in Table 1) at 08:00 and 18:00 daily, with free access to feed and water. Rumen fluid was collected using an oral stomach tube sampler connected to a vacuum pump (VP30, Beijing LabTech, Beijing, China) two hours prior to morning feeding. The initial saliva was discarded, and the receiving bottle was rinsed with a small amount of the original rumen fluid. The initial pH value of the rumen fluid was 7.13. The collected rumen fluid was filtered through four layers of gauze into an insulated bottle that was preheated to 39 °C and contained carbon dioxide. After collection, the insulated bottle was quickly transported to the laboratory and placed in a 39 °C water bath for insulation, with continuous introduction of carbon dioxide. According to Menke and Steingass [], the rumen inoculum was mixed with a buffer solution in a ratio of 1:2 (v/v) with continuous flushing with CO₂. The mixed artificial rumen culture medium (~60 mL) was added to a culture bottle (100 mL) containing 1 g of substrate and incubated in a 39 °C incubator. After the bottle was sealed tightly, it was placed on a water bath shaker and incubated for 12 and 24 h.
2.3. Sample Collection and Chemical Analyses
After 12 and 24 h of fermentation, the bottles were placed in an ice bath at −10 °C to stop fermentation, and final pH was measured with a pH meter (FiveEasy Plus, Shanghai Mettler Toledo Co., Shanghai, China). The culture solution was placed in a 10 mL centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 4500 r min−1 for 15 min. The supernatant was separated and stored at −20 °C to determine the concentrations of BCP and NH3-N; the remainder was stored at −80 °C for analysis of VFAs.
2.4. Ruminal 16S rDNA Amplification, Sequencing, and Analysis
The DNA of the rumen microbiome in rumen fluid was extracted using an Omega Biotek kit (Norcross, GA, USA) and subsequently analyzed via 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis. The V3-V4 regions of the 16S rRNA gene were amplified by PCR using universal primers 338F and 806R to characterize the rumen bacterial community. The PCR procedure was as follows: Each reaction mixture contained 15 µL of Phusion High Fidelity PCR Master Mix (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), 0.2 µM primers, and 10 ng of genomic DNA template. The amplification protocol consisted of an initial denaturation at 98 °C for 1 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 98 °C for 10 s, annealing at 50 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s. A final extension was performed at 72 °C for 5 min. The PCR products were detected using 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Qualified PCR products were purified using magnetic beads, quantified by enzyme labeling, and pooled in equimolar amounts based on their concentrations. The pooled PCR products were then re-evaluated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The target bands were excised, and the DNA was recovered using a universal DNA purification and recovery kit (TianGen, Beijing, China). The purified products were then subjected to high-throughput sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform (Version QIIME2-202202).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA using SPSS 26.0 software. Duncan’s multiple range test was used for multiple comparisons. Orthogonal polynomial analysis was conducted to assess the linear and quadratic effects of increasing SH levels on the respective indicators. A probability value of p < 0.05 (two-tailed) was considered statistically significant. Furthermore, intergroup differences in microbial composition were statistically analyzed using nonparametric t-tests. Significant differences were expressed as p < 0.05. When the synergistic effect was more pronounced, it resulted in more favorable outcomes for rumen fermentation and nutrient utilization. The multiple combination index (MFAEI) for different combinations is the sum of the single combination effect index (SFAEI) for different combinations (treatments) and can be used to determine the fermentation status of the rumen []. The calculation is as follows:
m: Time of each fermentation point.
n: Total number of fermentation time points.
A: The values of each individual indicator in the experimental group at different cultivation time points.
B: The values of each individual indicator in the control group at different cultivation time points.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of SH Supplementation on NH3-N Concentration, BCP Content, and Gas Production
As shown in Table 2, after 12 h of incubation, the addition of different concentrations of SH had no significant effect on rumen pH, NH3-N concentration, and BCP content (p > 0.05). However, compared with the control group, 0.5 g/kg SH decreased GP by 11.66%, while 1 g/kg increased GP by 5.3% (p < 0.01).

Table 2.
Effects of different fermentation times and SH additions on the pH value, NH3-N concentration, BCP content, and gas production of fermentation liquor.
After 24 h of incubation, the quadratic effect of SH supplementation decreased NH3-N concentration (p < 0.01) and increased BCP content (p < 0.05), while the linear effect increased gas production (p < 0.01). Compared with the control group, the SH1 group significantly decreased NH3-N concentration, while the SH2 group significantly increased NH3-N concentration (p < 0.01). The SH1 group had higher BCP content than the other groups (p < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the SH1 and SH2 groups significantly increased GP, while the SH0.5 group significantly decreased GP (p < 0.01). No significant differences in pH were observed among the groups.
3.2. Effect of SH Supplementation on Volatile Fatty Acids
The results from Table 3 illustrate that after 24 h of fermentation, SH supplementation linearly decreased (p < 0.05) the proportion of acetate compared with the control group.

Table 3.
Composition and production of VFAs under different levels of SH supplementation.
3.3. Effect of SH Supplementation on SFAEI and MEAEI
As shown in Table 4, the MFAEI value of SH1 is the absolute maximum in this experiment, indicating that the appropriate concentration of SH for regulating rumen fermentation is SH1.

Table 4.
SFAEI and MFAEI values under different SH concentrations.
3.4. Effect of SH Supplementation on Rumen Bacterial Diversity
Taken together, we found that the addition of SH to the ration had a positive effect on rumen fermentation parameters, and the effect was optimal when SH was added at 1 g/kg. Therefore, we selected the CON and SH1 groups for bacteria analysis to reveal the effect of SH on rumen health and its mechanism.
A total of 543,013 original tags were produced, averaging 90,502 tags per sample. After size filtering, quality control, and removal of chimeras, 394,996 valid tags were retained, producing an average of 65,832 valid tags per sample, with a ratio of valid to raw data of 71.40% to 74.32%. The alpha diversity indices of the bacterial community, as depicted in Figure 1, demonstrated no significant variations (p > 0.05) across the Chao1, Dominance, Goods_coverage, Observed_otus, Shannon, and Simpson metrics. This suggests that the sequencing depth was adequate for the current investigation and that dietary supplementation with SH1 had no discernible impact on the richness or diversity of the rumen bacteria in the experimental subjects. The bacterial community composition was compared between the two treatment groups and analyzed using beta diversity analysis. As shown in the principal coordinate analysis (Figure 2a), the treatment and control groups were not clustered separately, indicating similar structures of the rumen bacteria. A Venn diagram (Figure 2b) depicted the overlap and unique ASVs between the two groups, with a total of 2218 ASVs identified.
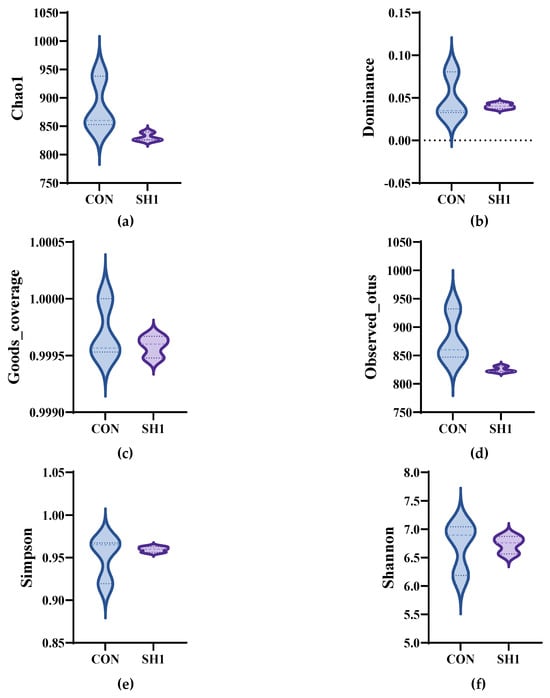
Figure 1.
Effects of SH supplementation on the alpha diversity of the bacterial community in the rumen fluid of sheep. (a) Chao index; (b) Dominance index; (c) Goods_coverage; (d) Observed_otus; (e) Simpson index; (f) Shannon index. CON = without supplementation, SH1 = supplementation with 1 g/kg SH based on dry matter weight.
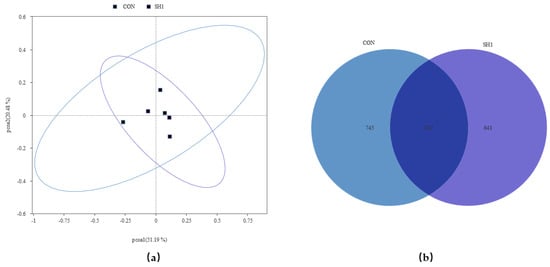
Figure 2.
Effects of SH supplementation on the beta diversity of the bacterial community in the rumen fluid of sheep. (a) Bray–Curtis distance matrix PCoA of the bacterial community. (b) Venn Graph. CON = without supplementation, SH1 = supplementation with 1 g/kg SH based on dry matter weight.
3.5. Alteration in Rumen Microbial Composition Caused by SH
A total of 23 phyla and 205 genera were isolated and taxonomically classified in the current study. At the phylum level, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria were the dominant phyla, with a relative abundance greater than 1%; moreover, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes have the highest relative abundance among all taxa, accounting for over 70% of the total abundance (Figure 3a). As shown in Figure 3b, the relative abundance of the phylum Actinobacteriota was higher in the CON group than in the SH1 treatment (p < 0.05). At the genus level (Figure 3c), 15 genera had a relative abundance greater than 0.1%, and Prevotella_7, Succiniclasticum, Succinivibrio, Escherichia-Shigella, and Dialister were the dominant genera. The two groups of genus-level t-test samples showed (Figure 3d) that in the SH1 group, the relative abundances of Prevotella, Anaerovibrio, and Saccharofermentans were significantly elevated (p < 0.05), while the relative abundances of Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group and [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group were significantly reduced (p < 0.05) compared to the control group.
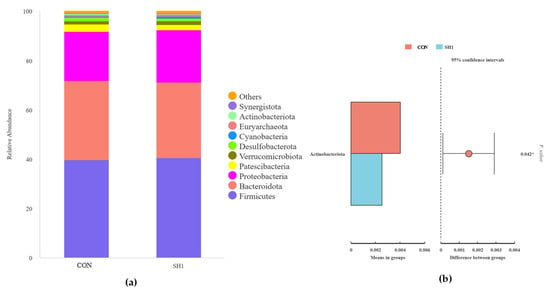
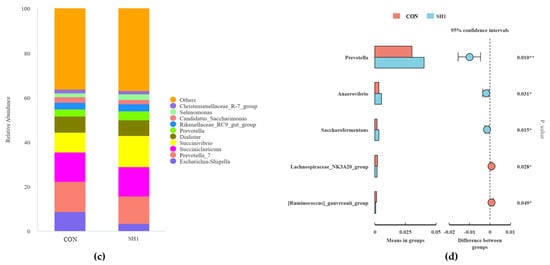
Figure 3.
Effects of SH supplementation on ruminal bacteria at phylum and genus levels. The relative abundances (%) of bacterial phyla (a) and genera (b) in the in vitro rumen fermentation of CON and SH1. The t-test analysis of differential phyla (c) and genera (d). CON = without supplementation, SH1 = supplementation with 1 g/kg SH based on dry matter weight. (a) Relative abundance of phyla in fermentation broth after 24 h of fermentation and t-test analysis of differential bacteria (b). Relative abundance of genera in fermentation broth after 24 h of fermentation (c) and t-test analysis of differential bacteria (d). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
3.6. Correlation Analysis
The correlation between rumen fermentation parameters and bacterial abundance differences during in vitro fermentation is shown in Figure 4. Anaerovibrio is positively correlated with NH3-N and negatively correlated with gas production. [Ruminococcus] _gauvreauii_group is negatively correlated with gas production.
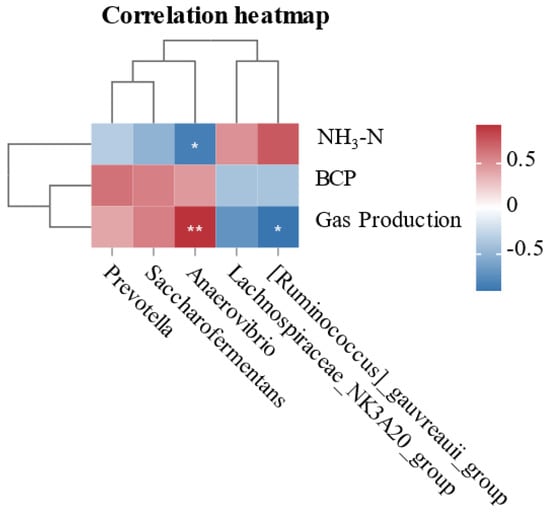
Figure 4.
The heatmap of correlations between altered ruminal bacteria (genus level) and in vitro fermentation parameters. Positive and negative correlations are shown in red and blue, respectively. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
4.1. Rumen Fermentation
The pH value in ruminal pH varies from 5.5 to 7.5, which reflects the fermentation level of feed and the activity of microorganisms in rumen []. A low ruminal pH can impair ruminal fermentation function and affect the proliferation of fibrolytic bacteria []. The pH values of fermentation fluids showed no significant differences across various incubation periods and SH supplementation levels, demonstrating that SH administration did not markedly disrupt the ruminal pH homeostasis. This stability likely reflects the remarkable pH-buffering capacity inherent to rumen microbial ecosystems. It should be noted that the observed minor pH fluctuations might still exert biologically relevant effects on specific microbial populations, though these effects were not statistically significant under our experimental conditions. The lack of change in rumen pH in vitro or in vivo is also supported by previously reported results [,]. However, El-Zaiat et al. [] found that the direct introduction of humate compounds into the rumen increased rumen pH in dairy goats. Differences between the current study and others can be attributed to species differences and the use of different experimental methods.
In the present study, supplementation with 1 g/kg SH significantly reduced the NH3-N concentration while increasing the BCP content in 24 h fermentation cultures compared to the control group. Notably, quadratic responses were observed for both parameters, with the NH3-N concentration showing a dose-dependent decrease and the BCP content demonstrating a corresponding increase at 24 h of fermentation. At the same time, the NH₃-N concentration decreased with the increase in bacterial populations, which suggests that NH₃-N was assimilated to support microbial growth. This reduction is driven by the nitrogen-binding activity of SH, which prolongs ruminal retention of NH₃-N [], while concurrent bacterial uptake converts the retained NH₃-N into BCP through intracellular assimilation [,,]. These dynamics align with fundamental rumen nitrogen metabolism, which begins when microbes degrade food protein or non-protein nitrogen into NH3-N, which is then transformed into BCP []. Microbial protein generated in the rumen provides an essential supply of amino acids for ruminants [,]. At the same time, BCP levels in the rumen usually reflect the growth rate and number of rumen microorganisms []. This phenomenon may be attributed to SH creating a more favorable microbial environment for utilizing nitrogen sources that enhances microbial NH3-N assimilation and conversion efficiency, consequently modulating both NH3-N dynamics and BCP synthesis parameters.
Gas production in the rumen is primarily the outcome of the fermentation of carbohydrates into VFA, and significant variations in carbohydrate fractions are reflected in the overall gas generated [,,]. The cumulative gas production increased gradually with the increase in fermentation time and the gas production with the addition of 1 g/kg SH was the highest among all the groups. In this study, adding different doses of SH at different fermentation times had no effect on rumen total VFA, as well as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, and A:P. The results of other researchers are consistent with this fact [,]. This observation suggests that while SH supplementation modulates certain microbial activities during fermentation, it does not significantly alter the primary metabolic pathways or stoichiometric ratios of carbohydrate-derived VFA production. The microbial degradation and utilization of carbohydrates constitute a complex metabolic network, and although SH may induce subtle structural and functional adaptations in the microbial community, these modifications appear insufficient to disrupt the overall VFA production profile.
4.2. Rumen Bacteria
Following comprehensive evaluation of fermentation parameters, the experimental group supplemented with 1 g/kg SH and the basal diet group (control) were selected for 16S rRNA sequencing to investigate bacterial community dynamics. The rumen bacteria’s composition and activity have been demonstrated to have a dramatic impact on the host’s performance, health, and immune system [,]. The results revealed no significant difference in alpha diversity; this indicates that the sequencing depth was appropriate for the analysis and that SH supplementation had no effect on the bacterial community’s richness and diversity. Beta diversity resulted in identical clusters in the treatment and control groups, indicating similar compositions of bacteria in the rumen.
Ruminants have a very diverse bacterial community []. Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes are the major phyla in rumen, as previous research has indicated [], and the results of our investigation corroborate this finding. Actinobacteriota usually have the ability to degrade complex organic matter and produce antimicrobial substances that help maintain the microbial balance in the rumen []. The genus Prevotella is thought to be the most prevalent group of ruminal bacteria [,], and representatives of this genus have been found to have a number of enzymes involved in the digestion of fiber [,]. Research on the genus Anaerovibrio in the rumen has focused primarily on its role in fat metabolism [,]. In particular, Anaerovibrio lipolyticus is considered one of the main lipolytic bacteria in the rumen and is capable of removing fat from the rumen for improved absorption and utilization, thereby enhancing the body’s efficiency in fat utilization []. Saccharofermentans can mainly promote cellulose decomposition [], [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group improves the digestive utilization of feeds []. Supplementation with 1 g/kg SH significantly reduced the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota at the phylum level, decreased Lachnospiraceae_NK3A20_group and [Ruminococcus]_gauvreauii_group at the genus level, and increased the relative abundance of Prevotella_7, Succiniclasticum, and Succinivibrio, compared with the control group. Correlation analysis showed that Anaerovibrio was negatively correlated with ammonia concentration and positively correlated with gas production. These findings suggest that Anaerovibrio may reduce NH3-N concentration while enhancing gas production during rumen fermentation through its metabolic activities. This phenomenon likely results from SH-induced modifications in microbial diversity and functional capacity, demonstrating that 1 g/kg SH supplementation can effectively modulate rumen bacterial community structure and consequently improve fermentation efficiency. In fact, microorganisms with a higher abundance proportion play an important role in the functioning of the rumen microbial ecosystem. However, a small portion of bacteria in the rumen community may have important ecological functions, but these functions have not been fully understood. One limitation of this study is the limited number of experimental replicates, which should be addressed in future experiments. In addition, bacterial diversity evaluated only at the 24 h time point may not be sufficient to reveal the potential relationship between bacteria and rumen fermentation parameters.
5. Conclusions
In summary, these findings demonstrate that dietary supplementation with SH at 1 g/kg improves rumen fermentation, enhances BCP synthesis, and modulates ruminal microbial composition. Therefore, the optimal inclusion rate for future animal studies appears to be 1 g of SH per kg of dietary dry matter in ruminant diets. However, further in vivo experiments should be conducted to determine the optimal SH dosage across different dietary types and growth stages in ruminants, evaluating its adaptive effects on rumen microbiota and animal production performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and J.Q.; methodology, N.Y.; software, L.G. and X.C.; validation, Y.W.; investigation, N.Y., Y.H., W.W., L.G. and X.C.; resources, Y.W. and J.Q.; data curation, N.Y. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.W.; supervision, Y.W. and J.Q.; project administration, J.Q.; funding acquisition, J.Q. and Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Project for Technological Innovating Talent of Hohhot (grant number: 2022RC-researchcenter-4), the Team Project from ‘Talent Revitalization of Inner Mongolia’ Program (grant number: 2025TYL10), and the Special Training Project for Young Talents from ‘Talent Revitalization of Inner Mongolia’ Program, Inner Mongolia Education Department Special Research Project for First Class Disciplines (grant number: YLXKZX-NND-007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures related to animal care and use for this study received approval from the Inner Mongolia Agricultural University’s Animal Care and Use Committee on 15 June 2022 with the ethical review application number [2020069].
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to all participants for their advice and support of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fan, S.; Zheng, M.; Ren, A.; Mao, H.; Long, D.; Yang, L. Effects of High-Concentrate-Induced SARA on Antioxidant Capacity, Immune Levels and Rumen Microbiota and Function in Goats. Animals 2024, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, V.; Petri, R.; Humer, E.; Kröger, I.; Mann, E.; Reisinger, N.; Wagner, M.; Zebeli, Q. High-Grain Diets Supplemented with Phytogenic Compounds or Autolyzed Yeast Modulate Ruminal Bacterial Community and Fermentation in Dry Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, B. Ruminal Degradation of Rumen-Protected Glucose Influences the Ruminal Microbiota and Metabolites in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01908-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabbour, E.A.; Davies, G. (Eds.) Humic Substances: Structures, Models and Functions; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-0-85404-811-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, P.; Ribeiro, G.O.; Wang, Y.; McAllister, T.A. Humic Substances Reduce Ruminal Methane Production and Increase the Efficiency of Microbial Protein Synthesis in Vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2152–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudák, M.; Semjon, B.; Marcinčáková, D.; Bujňák, L.; Naď, P.; Koréneková, B.; Nagy, J.; Bartkovský, M.; Marcinčák, S. Effect of Broilers Chicken Diet Supplementation with Natural and Acidified Humic Substances on Quality of Produced Breast Meat. Animals 2021, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, A. Humic Acid Substances in Animal Agriculture. Pak. J. Nutr. 2005, 4, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murbach, T.S.; Glávits, R.; Endres, J.R.; Clewell, A.E.; Hirka, G.; Vértesi, A.; Béres, E.; Pasics Szakonyiné, I. A Toxicological Evaluation of a Fulvic and Humic Acids Preparation. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Chang, Q.F.; Shi, B.M.; Shan, A.S. Effects of Fulvic Acid on Growth Performance and Meat Quality in Growing-Finishing Pigs. Livest. Sci. 2013, 158, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandts, I.; Balasch, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Martins, M.A.; Pereira, M.L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Teles, M.; Oliveira, M. Immuno-Modulatory Effects of Nanoplastics and Humic Acids in the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus Labrax). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöcking, R.; Helbig, B.; Schötz, G.; Schacke, M.; Wutzler, P. Anti-HSV-1 Activity of Synthetic Humic Acid-like Polymers Derived from p-Diphenolic Starting Compounds. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2002, 13, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, C.E.J.; Dekker, J.; Weis, R.; Smith, T.-L.; Janse van Rensburg, E.; Schneider, J. Investigation of the Anti-HIV Properties of Oxihumate. Chemotherapy 2002, 48, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zaiat, H.; Morsy, A.; El-Wakeel, E.A.; Anower, M.; Sallam, S. Impact of Humic Acid as an Organic Additive on Ruminal Fermentation Constituents, Blood Parameters and Milk Production in Goats and Their Kids Growth Rate. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2018, 27, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholif, A.E.; Matloup, O.H.; EL-Bltagy, E.A.; Olafadehan, O.A.; Sallam, S.M.A.; El-Zaiat, H.M. Humic Substances in the Diet of Lactating Cows Enhanced Feed Utilization, Altered Ruminal Fermentation, and Improved Milk Yield and Fatty Acid Profile. Livest. Sci. 2021, 253, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, K.H.; Steingass, H. Estimation of the Energetic Feed Value Obtained from Chemical Analysis and in Vitro Gas Production Using Rumen Fluid. Anim. Res. Dev. 1988, 28, 7–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Wan, X. Multiple-Factor Associative Effects of Peanut Shell Combined with Alfalfa and Concentrate Determined by in Vitro Gas Production Method. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 64, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsamiglia, S.; Ferret, A.; Devant, M. Effects of pH and pH Fluctuations on Microbial Fermentation and Nutrient Flow from a Dual-Flow Continuous Culture System. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.G.; Kobayashi, Y.; Chang, J.; Ha, A.; Hwang, I.H.; Ha, J.K. Low Ruminal pH Reduces Dietary Fiber Digestion via Reduced Microbial Attachment. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 20, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galip, N.; Polat, U.; Biricik, H. Effects of Supplemental Humic Acid on Ruminal Fermentation and Blood Variables in Rams. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 9, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurphy, C.P.; Duff, G.C.; Sanders, S.R.; Cuneo, S.P.; Chirase, N.K. Effects of Supplementing Humates on Rumen Fermentation in Holstein Steers. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 41, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurphy, C.P.; Duff, G.C.; Harris, M.A.; Sanders, S.R.; Chirase, N.K.; Bailey, C.R.; Ibrahim, R.M. Effect of Humic/Fulvic Acid in Beef Cattle Finishing Diets on Animal Performance, Ruminal Ammonia and Serum Urea Nitrogen Concentration. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2009, 35, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.; Calsamiglia, S.; Stern, M.D. Nitrogen Metabolism in the Rumen. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88 (Suppl. S1), E9–E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, F.N.; Lusby, K.S.; Mizwicki, K.; Forero, O. Slow Ammonia Release from Urea: Rumen and Metabolism Studies. J. Anim. Sci. 1980, 50, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, C.T.; Brandt, R.T.; Titgemeyer, E.C. Urea in Dry-Rolled Corn Diets: Finishing Steer Performance, Nutrient Digestion, and Microbial Protein Production. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, T.; Shem, M.N. Metabolism of Microbial Nitrogen in Ruminants with Special Reference to Nucleic Acids. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynal, S.M.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Liñeiro, M.; Brito, A.F.; Broderick, G.A.; Clark, J.H. Omasal Flow of Soluble Proteins, Peptides, and Free Amino Acids in Dairy Cows Fed Diets Supplemented with Proteins of Varying Ruminal Degradabilities1. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1887–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, J.L.; Cajarville, C.; D’Alessandro, J.; Curbelo, A.; Soto, C.; Garín, D. Effect of Wilting and Ensiling on Ruminal Degradability of Temperate Grass and Legume Mixtures. Anim. Res. 2005, 54, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, W.-K.; Wu, Q.-C.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Wang, W.; Cao, Z.-J.; Yang, H.-J. The Effect of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Addition on In Vitro Ruminal Fermentation Characteristics and Methane Production of Diets Differing in Forage-to-Concentrate Ratio. Fermentation 2023, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Xie, F.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, L.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Peng, K.; Yang, C. Fermentation Quality, Nutritive Value and in Vitro Ruminal Digestion of Napier Grass, Sugarcane Top and Their Mixed Silages Prepared Using Lactic Acid Bacteria and Formic Acid. Grassl. Sci. 2023, 69, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, G.; Robinson, P.H.; DePeters, E.J.; Taylor, S.J. Relationships between Chemical Composition, Dry Matter Degradation and in Vitro Gas Production of Several Ruminant Feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2004, 111, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesse, A.; Steingass, H.; Boguhn, J.; Rodehutscord, M. In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics and Effective Utilisable Crude Protein in Leaves and Green Pods of Moringa Stenopetala and Moringa Oleifera Cultivated at Low and Mid-Altitudes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 97, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmaz, Ö.; Köksal, B.H.; Yildiz, G. Rumen Fermentation Characteristics of Rams Fed Supplemental Boric Acid and Humic Acid Diets. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2022, 69, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, S.A.; Ribeiro, G.d.O.; Gruninger, R.J.; Hunerberg, M.; Ping, S.; Chaves, A.V.; Burlet, J.; Beauchemin, K.A.; McAllister, T.A. Effect of Humic Substances on Rumen Fermentation, Nutrient Digestibility, Methane Emissions, and Rumen Microbiota in Beef Heifers1. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 3863–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jami, E.; White, B.A.; Mizrahi, I. Potential Role of the Bovine Rumen Microbiome in Modulating Milk Composition and Feed Efficiency. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, M.P.; Diao, Q.Y.; Tu, Y. Saponin-Induced Shifts in the Rumen Microbiome and Metabolome of Young Cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. Status of the Phylogenetic Diversity Census of Ruminal Microbiomes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zened, A.; Combes, S.; Cauquil, L.; Mariette, J.; Klopp, C.; Bouchez, O.; Troegeler-Meynadier, A.; Enjalbert, F. Microbial Ecology of the Rumen Evaluated by 454 GS FLX Pyrosequencing Is Affected by Starch and Oil Supplementation of Diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, G.B.; Pandey, S.; Kim, E.S.; Doo, H.; Kwak, J.; Ryu, S.; Choi, Y.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.B. Understanding the Diversity and Roles of the Ruminal Microbiome. J. Microbiol. 2024, 62, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.M.; Weimer, P.J. Dominance of Prevotella and Low Abundance of Classical Ruminal Bacterial Species in the Bovine Rumen Revealed by Relative Quantification Real-Time PCR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D.O.; Denman, S.E.; Mackie, R.I.; Morrison, M.; Rae, A.L.; Attwood, G.T.; McSweeney, C.S. Opportunities to Improve Fiber Degradation in the Rumen: Microbiology, Ecology, and Genomics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 663–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercoe, P.E.; Gregg, K. DNA Sequence and Transcription of an Endoglucanase Gene fromPrevotella (Bacteroides) Ruminicola AR20. Molec. Gen. Genet. 1992, 233, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, R.A.; Lankhorst, A.; van der Meer, P.; Van Nevel, C.J. Some Characteristics of Anaerovibrio Lipolytica a Rumen Lipolytic Organism. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1975, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, C. The Lipases Produced by Anaerovibrio Lipolytica in Continuous Culture. Biochem. J. 1970, 119, 5P–6P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Z. Analysis of Differences in the Rumen Microbiome and Metabolic Function in Prepartum Dairy Cows with Different Body Condition Scores. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniel, A.; Amato, K.R.; Beehner, J.C.; Bergman, T.J.; Mercer, A.; Perlman, R.F.; Petrullo, L.; Reitsema, L.; Sams, S.; Lu, A.; et al. Seasonal Shifts in the Gut Microbiome Indicate Plastic Responses to Diet in Wild Geladas. Microbiome 2021, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Tang, G.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Lei, X.; Deng, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Multi-Omics Revealed the Long-Term Effect of Ruminal Keystone Bacteria and the Microbial Metabolome on Lactation Performance in Adult Dairy Goats. Microbiome 2023, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).