Abstract
Cryptosporidium spp. are protozoan pathogens that are widespread within mammals. In recent years, extensive molecular epidemiology studies on Cryptosporidium in dairy cattle have been conducted in Yunnan and worldwide. However, the infection status of these pathogens in beef cattle in Yunnan remains unclear. To examined the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle in Yunnan Province, China, we collected 735 fecal samples from six breeds of beef cattle in five regions of Yunnan. Nested PCR and DNA sequencing revealed the infection, species, and genotypes of Cryptosporidium spp. in these animals. The occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in Simmental cattle, Brahman cattle, Aberdeen Angus cattle, Yunnan Yellow cattle, Dulong cattle, and Hereford cattle was 32.9% (137/416), 3.8% (4/106), 24.4% (20/82), 3.8% (3/79), 3.2% (1/31), and 0% (0/21), respectively, with an overall rate of 22.4% (165/735). Regarding the regions, the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in Boshan City, Kunming City, Lincang City, Dehong City and Xishuangbanna City was 41.8%, 28.6%, 19.4%, 6.7%, and 3.8%, respectively. In terms of age, the infection rates of Cryptosporidium spp. in pre-weaned, post-weaned, juvenile, and adult cattle were 62.1%, 52.6%, 42.7%, and 7.7%, respectively. According to sex, male cattle were more susceptible to Cryptosporidium infection (28.0%) than females (15.7%). Four Cryptosporidium species were identified in beef cattle: C. andersoni (n = 146), C. bovis (n = 11), C. ryanae (n = 7), and C. occultus (n = 1). Multilocus sequence typing analysis at the MS1, MS2, MS3, and MS16 gene loci revealed four subtype families of C. andersoni (A4A4A4A1, A5A4A4A1, A4A4A2A1, A1A4A4A1). Additionally, sequencing analysis of the 60-kDa glycoprotein gene identified three subtype families of C. bovis (XXVIc, XXVId, XXVIe) and one subtype family of C. ryanae (XXIb). These findings document the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle in Yunnan Province for the first time, providing reference data on the distribution, infection rate, species diversity, and genetic structure of these pathogens in China. To effectively reduce the prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle in Yunnan, the implementation of proper sanitation management, rigorous rodent control, and farmer education programs is crucial. These integrated measures are critical for maintaining herd health, reducing economic losses, and ensuring meat safety across the province.
1. Introduction
Cryptosporidium spp. are important zoonotic protozoa that infect a wide range of vertebrates worldwide, including humans and domestic and wild animals [1,2]. Cryptosporidium oocysts are widely distributed in the environment, and can be ingested by susceptible humans and animals, resulting in cryptosporidiosis [3]. The main clinical feature of cryptosporidiosis is persistent diarrhea, and the disease has been reported in over 40 countries worldwide [4]. Bovine species are common hosts of these pathogens [5]. In beef cattle, cryptosporidiosis often results in high neonatal mortality rates and increased pharmaceutical costs, leading to significant economic losses in the livestock industry [6].
To date, approximately 44 valid species and 120 genotypes of Cryptosporidium spp. have been reported, with C. andersoni, C. bovis, C. ryanae, and C. parvum being the four major species found in cattle [7]. The prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. in cattle varies globally, ranging from 6.25% to 39.6% [8]. Several factors influence the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in cattle, including geographical location, climate, host age, herd management, food and water sources, sanitation, and rodent control [9].
Several subtyping tools for Cryptosporidium spp. play important roles in epidemiological studies [10,11]. The 60-kDa glycoprotein (gp60) gene-targeted subtyping method and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) have been reported as the most widely used tools for subtype identification of these pathogens [12,13]. Thus far, at least twenty, eight, and six different gp60 subtypes have been identified in C. parvum, C. ryanae, and C. bovis, respectively [14,15,16]. In addition, more than 10 MLST subtypes of C. andersoni have been reported in cattle in China [17]. These diagnostic tools have been widely applied to study the transmission and diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. [18].
Yunnan Province, located in southwestern China, provides a high-quality production environment for beef cattle, due to its suitable geographical and climatic conditions [19]. As the largest beef cattle production province in China, it maintained over 9 million head of cattle in 2023, and is home to at least 15 different cattle breeds [19]. In previous studies, an indigenous breed of cattle (i.e., Yunling cattle) in Yunnan Province was found to be infected with C. andersoni and C. ryanae in a small-scale survey of animals [20]. However, the occurrence of these parasites in other beef cattle in Yunnan Province remains unknown. The “One Health” framework emphasizes integrated approaches to reduce disease risks at the human–animal–environment interface. A better understanding of Cryptosporidium species in beef cattle and their transmission potential can lead to better control strategies. These measures would improve animal health and production efficiency, thus supporting the growing demand for sustainable food production. Therefore, the aim of our study was to investigate the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in six breeds of cattle from five regions in Yunnan, and to determine their species and subtypes in order to assess the transmission risks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Sampling Area
A total of 735 fecal samples from six breeds of beef cattle (i.e., Simmental cattle, Brahman cattle, Aberdeen Angus cattle, Yunnan Yellow cattle, Dulong cattle, Hereford cattle) from five regions in Yunnan Province, China, were used for sampling (Table 1 and Figure 1). Sampling in Baoshan, Dehong, and Xishuangbannna took place in June, while sampling in Lincang took place in September, and sampling in Kunming occurred in October 2024. All sampling periods coincided with the rainy season in Yunnan Province. Six representative breeds of beef cattle were selected for this study. Among them, Simmental and Aberdeen Angus are extensively raised in Yunnan, and serve as the main source of income for local farms. Yunnan Yellow, Hereford cattle, and Dulong cattle, known for their excellent meat quality, are primarily raised in small-scale farms in Yunnan. Additionally, Brahman cattle, imported from Laos due to their low cost, are temporarily raised in farms in Yunnan before being sold.

Table 1.
Geographical distribution and sample collection details of six species of beef cattle at five locations in Yunnan Province, China, for Cryptosporidium spp. investigations.
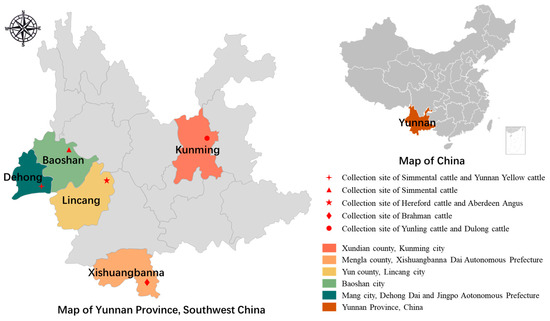
Figure 1.
Map of beef cattle sampling sites in Yunnan Province, China.
In the study regions, Simmental cattle and Aberdeen Angus cattle are managed in intensive farms with herd sizes of more than 1000 head. Yunnan Yellow, Hereford cattle, and Dulong cattle are managed in small-scale farms with herd sizes of less than 400 head. These animals are kept in confined places, and are fed a diet consisting of self-produced silage and commercially purchased concentrated feed. Brahman cattle are grazed in a special area of Xishuangbanna. In the Dehong and Kunming regions, cattle of two different breeds were sampled from two separate farms. The average annual rainfall in these five regions ranged from 720 mm to 1441 mm in 2024 (Table 1). Except for Xishuangbanna, which has a tropical climate, the other regions have a subtropical climate (Table 1).
Rectal sampling was performed separately for each beef cattle breed to avoid contamination. Each sample was placed in a separate self-sealing bag with clear information, such as the distribution, breed of cattle, date of birth, and gender. Collected samples were transported to a laboratory at 2 °C to 8 °C for no more than 72 h and stored in 2.5% potassium dichromate at 4 °C until DNA extraction.
2.2. DNA Extraction
Prior to the extraction of genomic DNA, 200 mg of fecal sample was placed in a centrifuge tube and centrifuged (2000× g, 10 min), washed with distilled water, and the supernatant was discarded to remove potassium dichromate. DNA was extracted from the pellet using a FastDNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH, USA), as previously described [21]. The extracted DNA from the collected fecal samples was stored at −20 °C until analysis by PCR.
2.3. PCR Amplification
Nested PCR based on the small ribosomal subunit RNA (SSU rRNA) gene was used to detect and identify Cryptosporidium species in all DNA samples, with a target product size of approximately 830 bp [22]. Nested PCR was also employed for subtype identification of C. bovis and C. ryanae based on the gp60 gene, with product sizes of approximately 1300 bp and 1000 bp [15,16]. C. andersoni was subtyped by analyzing four minisatellite/microsatellite targets (MS1, MS2, MS3, MS16) according to previous studies [17].
2.4. Sequence Analysis
Based on the gel electrophoresis results, all secondary positive PCR products were sent to Sangon Biotech (Kunming, China) for bidirectional sequencing on an ABI 3730 sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Each raw sequence was assembled using ChromasPro 2.1.5.0 (http://technelysium.com.au/ChromasPro.html/, accessed on 23 October 2024). Assembled sequences were compared with GenBank dates to select appropriate reference sequences. ClustalX software 2.1.5.0 (http://clustal.org/, accessed on 23 October 2024) was used for comparative analysis between the sample sequences and the reference sequences. Detailed corrections of the sequences were performed using BioEdit 7.1 software (http://thalljiscience.github.io, accessed on 23 October 2024) to accurately determine the species and subtype of Cryptosporidium spp. in the samples [23]. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0 software (http://www.megasoftware.net/, accessed on 24 December 2024) based on the maximum likelihood method. The genetic relationship and reliability of the phylogenetic tree were assessed using the general time-reversible model and by bootstrapping with 1000 replicates, with values greater than 50% marked at the nodes [24]. The representative sequences were deposited in GenBank under accession numbers OL912798-OL912805, OM066896-OM066904, ON890790, and ON890791.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The frequency of Cryptosporidium spp. occurrence among regions, breeds, ages, and genders were calculated using chi-squared tests implemented in SPSS20.0 (IMB SPSS Int, Chicago, IL, USA) and SAS9.1 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Statistical difference was considered significant at p < 0.05. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to assess whether the associated factors were risk factors.
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence of Cryptosporidium Species
Cryptosporidium spp. were found in 165 (22.4%) of the 735 beef cattle fecal samples from five cities in Yunnan Province (Table 2). Among them, the infection rate in Baoshan (41.8%) was significantly higher than in Kunming (28.6%, χ2 = 6.787, p = 0.01114), Lincang (19.4%, χ2 = 15.146, p = 0.00011), Dehong (6.7%, χ2 = 57.73, p < 0.00001), and Xishuangbanna (3.8%, χ2 = 49.054, p < 0.00001). The occurrence in the six beef cattle breeds ranged from 0% to 32.9%. The detection rate in Simmental cattle (32.9%) was significantly higher than in Aderdeen Angus cattle (24.4%, χ2 = 2.315, p = 0.1526), Yunnan Yellow cattle (3.8%, χ2 = 27.784, p < 0.00001), Brahman cattle (3.8%, χ2 = 36.431, p < 0.00001), Dulong cattle (3.2%, χ2 =11.930, p = 0.00017), and Hereford cattle (0%).

Table 2.
Occurrence and factors associated with Cryptosporidium spp. infection in beef cattle in Yunnan Province, China.
The occurrence in pre-weaned calves (62.1%, χ2 = 89.090, p < 0.00001), post-weaned calves (52.6%, χ2 = 92.789, p < 0.00001), and juvenile cattle (42.7%, χ2 = 112.391, p < 0.00001) was significantly higher than in adults (7.7%). In terms of gender, the infection rate in male cattle (28.0%, χ2 =15.709, p = 0.0008) was significantly higher than in female cattle (15.7%). Thus, all the studied factors (i.e., location, breed, age and sex) significantly influenced the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle in Yunnan.
3.2. Identification of Cryptosporidium Species
Small subunit rRNA (SSU rRNA) sequence analysis was conducted on Cryptosporidium-positive specimens. As shown in Table 3, C. andersoni was identified in 19.8%, (146/735) of the samples, while C. bovis accounted for 1.4% (11/735), C. ryanae for 0.9% (7/735), and C. occultus for 0.1% (1/735) in beef cattle fecal samples collected from the five regions in Yunnan Province. C. andersoni was detected in all areas; C. bovis and C. ryanae were found in Baoshan, Dehong, and Kunming; and C. occultus was exclusively identified in Baoshan. By breed, C. andersoni was the most prevalent species in four beef cattle breeds, whereas C. ryanae was found only in Simmental cattle and Yunnan yellow cattle. In contrast, C. bovis and C. occultus were exclusively found in Simmental cattle. Meanwhile, both C. andersoni and C. bovis were detected across all age groups, whereas C. ryanae was absent in juveniles, and C. occultus was found only in juveniles. Additionally, C. andersoni, C. bovis, and C. ryanae were detected in both male and female cattle, while C. occultus was exclusively found in male cattle. The nucleotide sequences obtained from C. andersoni, C. bovis, C. ryanae, and C. occultus were identical to GenBank sequences JN400881, MT950118, JN400880, and MK982467, respectively. As expected, these Cryptosporidium spp. sequences were placed in relation to their reference sequence in the phylogenetic analysis of the SSU rRNA gene (Figure 2).

Table 3.
Species and subtype identification of Cryptosporidium spp. from beef cattle in Yunnan Province, China.
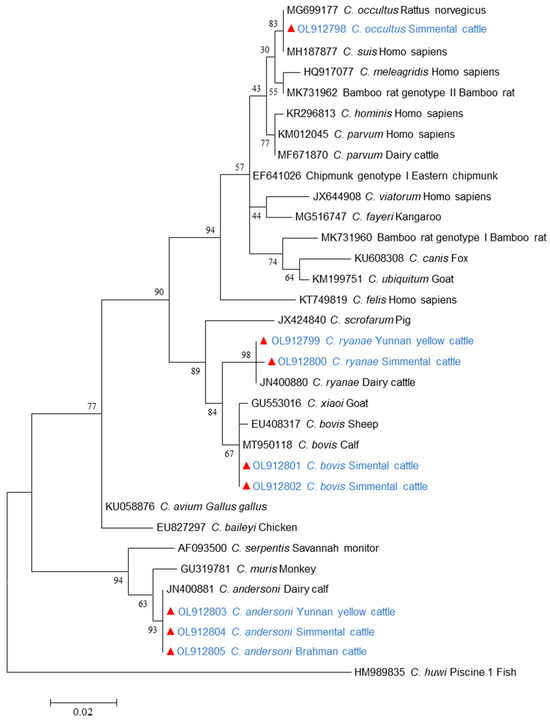
Figure 2.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of Cryptosporidium species based on 18S rRNA gene sequence. Sequences identified in this study are marked by filled red symbols.
3.3. Subtyping of Cryptosporidium spp.
A total of 146 C. andersoni positive samples were subtyped using MLST at four loci (i.e., MS1, MS2, MS3, and MS16). From these, 45 C. andersoni specimens were successfully classified into four distinct MLST subtypes. The most prevalent subtype identified was A4A4A4A1 (n = 23), which was predominantly found in Simmental cattle and Aderdeen Angus cattle. This was followed by the subtypes A5A4A4A1 (n = 11) and A4A4A2A1 (n = 9), and A1A4A4A2 (n = 2), in Simmental cattle and Brahman cattle (Table 2). The subtype A1A4A4A2 (n = 2) was detected in female cattle, while the other three subtypes were found in both male and female cattle. Moreover, samples positive for C. bovis and C. ryanae were analyzed using the gp60 locus for subtyping. Of the eleven C. bovis-positive samples collected in Simmental cattle from Kunming and Baoshan, six were successfully categorized into three genetic groups: XXVIc (n = 4), XXVId (n = 1), and XXVIe (n = 1). For C. ryanae, four out of seven positive samples were identified, with only one subtype, XXIb, detected in Simmental cattle from Kunming (Table 3).
4. Discussion
Our results suggest that Cryptosporidium spp. are prevalent in beef cattle in Yunnan Province. The occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in this study (22.4%) was higher than that reported in Bangladesh (5.0%) [25] and Egypt (10.2%) [26], but lower than that reported in Japan (77.5%) [27], Scotland (59.3%) [28], Italy (38.8%) [29], and Estonia (23.0%) [30], as well as being lower than the global prevalence of bovine cryptosporidiosis (29.1%) [31]. Within China, our findings were lower than those in Taiwan (37.6%) [32] and Henan (26.5%) [33], but higher than those in Shaanxi (20.2%) [34], Heilongjiang (17.5%) [35], Hubei (15.6%) [36], Jiangxi (12.8%) [37], Shanxi (11.1%) [38], and the two reports of pooled prevalence in China (14.5% and 8.0%) [24,39]. Cryptosporidium spp. infection rates demonstrated regional variability, influenced by factors such as geographical location, herd size, animal age, sampling time, total sample size, study design, climate, and sanitation conditions [40,41].
The occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in calves aged 0–18 months was significantly higher than that in adult cattle, with the highest positive rate observed in pre-weaned calves. This suggests that younger animals are more prone to infection, which is consistent with previous studies [42,43]. Furthermore, a significantly higher incidence of Cryptosporidium spp. was detected in Simmental cattle and Aberdeen Angus cattle than in other local beef breeds. This might be due to the fact that these two common beef breeds were reared in intensive farming systems, whereas other local beef breeds were reared mainly on small-scale farms or under free-range conditions. Several previous reviews have reported that concentrated animal feeding operations have been shown to be conducive to the transmission of pathogens, due to large numbers of susceptible animals in confined spaces, together with low genetic diversity of animals [44,45]. In recent years, Simmental cattle have been the dominant beef cattle breed and widely distributed in Yunnan Province [46]. This study collected a larger number of samples from this breed in three regions, which may be a contributing factor to the observed higher occurrence. In further studies, we need to balance sample sizes across breeds to better understand the role of breed-specific factors in Cryptosporidium spp. infection. Most studies have shown that the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. is highly sensitive to climatic conditions, such as temperature, rainfall, and humidity [47]. However, we did not observe a similar phenomenon in this study. In Xishuangbanna, a region with a tropical climate characterized by higher temperature and humidity, the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in cattle was the lowest. This may be because the factors influencing infection rates are multifaceted.
Four Cryptosporidium species were identified, including C. andersoni, C. bovis, C. ryanae, and C. occultus. Among these, C. andersoni was the dominant species in beef cattle, which is consistent with previous findings from many regions of China, India, and Spain [48,49,50]. In contrast, C. bovis has been identified as the predominant species in beef cattle in other countries [51,52,53]. Compared to calves, C. andersoni was more prevalent in adult cattle [54]. Infections caused by this species could lead to gastritis, poor weight gain, and adverse effects on production efficiency [55]. However, the present study showed that C. andersoni was the dominant species in all age groups of beef cattle, a phenomenon that may be attributed to the mixed housing of adult cattle with calves. In addition, C. occultus has been reported in humans, dairy cattle, water buffalo, yaks, and rats [56,57,58,59,60]. Among these, rodents might serve as the primary host for C. occultus [61]. Some studies have found that the presence of C. occultus in cattle is attributed to their consumption of food contaminated with rodent feces [62]. Therefore, despite the low detection rate of C. occultus in this study, it is indicative of inadequate rodent control measures on farms. Although C. parvum was one of the top four species infecting cattle worldwide, no cases of C. parvum were detected in our study. Previous research has suggested that C. parvum is more prevalent in certain dairy farms, because of the relatively short history of intensive livestock production in China [63].
A common diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. was detected in this study, with four MLST subtypes of C. andersoni identified. One MLST subtype (A4,A4,A4,A1) was the dominant subtype in beef cattle, which was also prevalent in dairy cattle in this province [64]. This confirms previous findings that the (A4,A4,A4,A1) subtype was the most prevalent in China, including in the Guangdong [65], Heilongjiang [36], and Shaanxi Provinces [66]. The three MLST subtypes (A5A4A4A1, A4A4A2A1, and A1A4A4A1) detected in the present study have also been reported in dairy cattle from Xinjiang Province [67] and Yunnan Province [68]. The present study also reported three C. bovis subtype families (XXVId, XXVIc, and XXVIe) that are similar to those reported in Henan Province [16]. This finding corroborates other observations of a lack of geographical segregation and host adaptation in C. bovis [16]. The C. bovis subtype XXVIc was prevalent in both pre-weaned and post-weaned calves in the present study, aligning with previous longitudinal studies conducted in Guangzhou [68]. This indicates that the distribution of C. bovis subtypes is influenced by host age and subtype-specific immunity [43]. To date, only two subtypes of C. ryanae (XXIa, XXIf) have been reported in beef cattle in Shijiazhuang [15], with XXIa identified for the first time in this study. Compared to dairy cattle in Yunnan, a low diversity of C. bovis and C. ryanae has been detected in beef cattle in this province [69].
To meet the growing demand for meat products, Yunnan Province has significantly expanded the beef cattle industry. However, large numbers of animals in confined spaces could promote the transmission of Cryptosporidium spp. Both farmers and consumers should be aware of cattle-associated Cryptosporidium species, as these pathogens can spread through fecal contamination of water, soil, and food, potentially exposing humans to infectious oocysts. This poses a particular risk to immunocompromised individuals, as there is no effective treatment against cryptosporidiosis. Our study identified key risk factors, including overcrowding, poor sanitation, and insufficient rodent control, all of which contribute to the transmission of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle. Only through implementing the “One Health” approach, which emphasizes human–animal–environment interactions, can Cryptosporidium infections be effectively mitigated [70].
5. Conclusions
The results of this study reveal a higher prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. in Yunnan beef cattle, with C. andersoni as the dominant species. Infection rates were significantly higher in Simmental cattle, pre-weaned calves, and male cattle, highlighting breed, age, and sex as key risk factors. The four C. andersoni subtypes (A4,A4,A4,A1, A5,A4,A4,A1, A4,A4,A2,A1, and A1,A4,A4,A1), three C. bovis subtypes (XXVId, XXVIc, and XXVIe) and one C. ryanae subtype (XXIa) were identified in this province. The precise differentiation of these subtypes facilitates a more profound comprehension of the transmission mechanisms and pathogenic characteristics of pathogens. These results improve our understanding of the occurrence of Cryptosporidium spp. in beef cattle in Yunnan, providing a fundamental dataset for the control of the transmission of these pathogens in the province.
Author Contributions
F.Z. and F.S. conceived and designed the study. J.Y. collected fecal samples. D.L. performed the experiments. L.L. analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. F.Z. and J.H. critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Yunnan Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology (Grant No. 202449CE340019) and the International Science and Technology Commissioner Program (Grant No. 202403AK140046).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Yunnan Agricultural University Life Ethics Review Committee (protocol code: 202403094 and date of approval: 7 March 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Checkley, W.; White, A.C., Jr.; Jaganath, D.; Arrowood, M.J.; Chalmers, R.M.; Chen, X.M.; Fayer, R.; Griffiths, J.K.; Guerrant, R.L.; Hedstrom, L.; et al. A review of the global burden, novel diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccine targets for cryptosporidium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.M.; Feng, Y.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium and Giardia—A 50 year perspective (1971–2021). Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Qin, H.; Zhang, K.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, K.; Xiong, J.; Miao, W.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Cryptosporidium parvum by long-read sequencing of ten oocysts. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Ryan, U.M.; Xiao, L. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Cryptosporidium. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Björkman, C.; Lindström, L.; Oweson, C.; Ahola, H.; Troell, K.; Axén, C. Cryptosporidium infections in suckler herd beef calves. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, H.J.; Innes, E.A.; Morrison, L.J.; Katzer, F.; Wells, B. Long-term production effects of clinical cryptosporidiosis in neonatal calves. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidiosis in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1701. [Google Scholar]
- Gattan, H.S.; Alshammari, A.; Marzok, M.; Salem, M.; Al-Jabr, O.A.; Selim, A. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection and associated risk factors in calves in Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogendo, A.; Obonyo, M.; Wasswa, P.; Bitek, A.; Mbugua, A.; Thumbi, S.M. Cryptosporidium infection in calves and the environment in Asembo, Western Kenya: 2015. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2017, 28, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Rich, S.M.; Akiyoshi, D.; Tumwine, J.K.; Kekitiinwa, A.; Nabukeera, N.; Tzipori, S.; Widmer, G. Extensive polymorphism in Cryptosporidium parvum identified by multilocus microsatellite analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3344–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, A.R.; Abs El-Osta, Y.G.; Stevens, M.; Sinclair, M.I.; Gasser, R.B. Capillary electrophoretic analysis of fragment length polymorphism in ribosomal markers of Cryptosporidium from humans. Mol. Cell. Probes 2005, 19, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L. Molecular epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis: An update. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dărăbuș, G.; Lupu, M.A.; Mederle, N.; Dărăbuș, R.G.; Imre, K.; Mederle, O.; Imre, M.; Paduraru, A.A.; Morariu, S.; Olariu, T.R. Epidemiology of Cryptosporidium infection in Romania: A review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Feng, Y. Molecular epidemiologic tools for waterborne pathogens Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2017, 8–9, 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Huang, N.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Kváč, M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Subtyping Cryptosporidium ryanae: A common pathogen in bovine animals. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wan, M.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. Development and application of a gp60-based subtyping tool for Cryptosporidium bovis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Ryan, U.; Zhang, L.; Kvác, M.; Koudela, B.; Modry, D.; Li, N.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Development of a multilocus sequence tool for typing Cryptosporidium muris and Cryptosporidium andersoni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, U.; Hijjawi, N.; Xiao, L. Foodborne cryptosporidiosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chong, Y.; Li, M.; Hong, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Xi, D.; Deng, W. Beef cattle genome project: Advances in genome sequencing, assembly, and functional genes discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.X.; Zou, Y.; Li, T.S.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.S.; Cao, F.Q.; Yang, J.F.; Sun, X.L.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zou, F.C. First report of the prevalence and genetic characterization of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in Yunling cattle in Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105025. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Alderisio, K.A.; Singh, A.; Xiao, L. Development of procedures for direct extraction of Cryptosporidium DNA from water concentrates and for relief of PCR inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Escalante, L.; Yang, C.; Sulaiman, I.; Escalante, A.A.; Montali, R.J.; Fayer, R.; Lal, A.A. Phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the small-subunit rRNA gene locus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Yang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, L.; Guo, Y.; et al. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia spp. and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in eleven wild rodent species in China: Common distribution, extensive genetic diversity and high zoonotic potential. One Health 2024, 18, 100750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, L. Advances and perspectives on the epidemiology of bovine Cryptosporidium in China in the past 30 years. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1823. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, A.M.; Geurden, T.; Casaert, S.; Parvin, S.M.; Islam, T.M.; Ahmed, U.M.; Levecke, B.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E. Assessment of zoonotic transmission of Giardia and Cryptosporidium between cattle and humans in rural villages in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118239. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Abdel-Ghany, A.E.; Abdel-Latef, G.K.; Abdel-Aziz, S.A.; Aboelhadid, S.M. Epidemiology and public health significance of Cryptosporidium isolated from cattle, buffaloes, and humans in Egypt. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.H.B.; Itoh, M.; Shehata, A.A.; Bando, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Murakoshi, F.; Fujikura, A.; Okawa, H.; Endo, T.; Goto, A.; et al. Distribution of Cryptosporidium species isolated from diarrhoeic calves in Japan. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 78, 102153. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, H.J.; Armstrong, C.; Uttley, K.; Morrison, L.J.; Innes, E.A.; Katzer, F. Genetic diversity and shedding profiles for Cryptosporidium parvum in adult cattle and their calves. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2021, 1, 100027. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.; Varcasia, A.; Pipia, A.P.; Tamponi, C.; Sanna, G.; Prieto, A.; Ruiu, A.; Spissu, P.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P.; et al. Molecular characterisation and risk factor analysis of Cryptosporidium spp. in calves from Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, A.; Dorbek-Kolin, E.; Jeremejeva, J.; Tummeleht, L.; Orro, T.; Jokelainen, P.; Lassen, B. Molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium spp. in calves in Estonia: High prevalence of Cryptosporidium parvum shedding and 10 subtypes identified. Parasitology 2019, 146, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Ahmadpour, E.; Carmena, D.; Spotin, A.; Bangoura, B.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium infections in terrestrial ungulates with focus on livestock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yang, C.H.; Ooi, H.K. Cryptosporidium infection in livestock and first identification of Cryptosporidium parvum genotype in cattle feces in Taiwan. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 97, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in dairy cattle, beef cattle and water buffaloes in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.Z.; Fang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, R.J.; Du, S.Z.; Guo, Y.X.; Jia, Y.Q.; Yao, L.; Liu, Q.D.; et al. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in pre-weaned calves in Shaanxi Province, north-western China. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, A.; Cao, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L. MLST subtypes and population genetic structure of Cryptosporidium andersoni from dairy cattle and beef cattle in northeastern China’s Heilongjiang Province. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Hu, M.; Gasser, R.B. Molecular investigation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in pre- and post-weaned calves in Hubei Province, China. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, P.; Qu, M.R.; Zheng, W.B.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Prevalence and multilocus genotyping of Cryptosporidium spp. in cattle in Jiangxi Province, southeastern China. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, H.; Fan, W.; Yi, C.; Ding, Y.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in dairy and beef cattle in Shanxi, China. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 123, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Cao, X.F.; Deng, L.; Li, W.; Huang, X.M.; Lan, J.C.; Xiao, Q.C.; Zhong, Z.J.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of Cryptosporidium infection in cattle in China: A review. Parasite 2017, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, N.Z.; Gong, Q.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.X. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium in dairy cattle in China during 2008-2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb Pathog. 2019, 132, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.H.B.; Kato, K. Comprehensive molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium species in Japan. Parasitol. Int. 2024, 102, 102909. [Google Scholar]
- Cruvinel, L.B.; Ayres, H.; Zapa, D.M.B.; Nicaretta, J.E.; Couto, L.F.M.; Heller, L.M.; Bastos, T.S.A.; Cruz, B.C.; Soares, V.E.; Teixeira, W.F.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for agents causing diarrhea (Coronavirus, Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium spp., Eimeria spp., and nematodes helminthes) according to age in dairy calves from Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 777–791. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wen, L.; Wang, W.; Ryan, U.M.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. Longitudinal follow-up reveals occurrence of successive Cryptosporidium bovis and Cryptosporidium ryanae infections by different subtype families in dairy cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2023, 53, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.A.; Grace, D.; Kock, R.; Alonso, S.; Rushton, J.; Said, M.Y.; McKeever, D.; Mutua, F.; Young, J.; McDermott, J.; et al. Zoonosis emergence linked to agricultural intensification and environmental change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8399–8404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ryan, U.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Association of common zoonotic pathogens with concentrated animal feeding operations. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 810142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, H.; Jiang, H.; Mao, Y.; Qu, K.; Huang, B.; Gong, Y.; Yang, Z. Longissimus dorsi muscle transcriptomic analysis of Yunling and Chinese simmental cattle differing in intramuscular fat content and fatty acid composition. Genome 2018, 61, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikiroma, I.A.; Pollock, K.G. Influence of weather and climate on cryptosporidiosis—A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Chandra, D.; Tewari, A.K.; Banerjee, P.S.; Ray, D.D.; Raina, O.K.; Rao, J.R. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium andersoni: A molecular epidemiological survey among cattle in India. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ma, G.; Zhao, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Jian, F.; Ning, C.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium andersoni is the predominant species in post-weaned and adult dairy cattle in China. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.; Navarro, E.; Remesar, S.; García-Dios, D.; Martínez-Calabuig, N.; Prieto, A.; López-Lorenzo, G.; López, C.M.; Panadero, R.; Fernández, G.; et al. The age-related Cryptosporidium species distribution in asymptomatic cattle from north-western Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakoshi, F.; Xiao, L.; Matsubara, R.; Sato, R.; Kato, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Tada, C.; Nakai, Y. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in grazing beef cattle in Japan. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rieux, A.; Chartier, C.; Pors, I.; Paraud, C. Dynamics of excretion and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium isolates in pre-weaned French beef calves. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 195, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeywardena, H.; Jex, A.R.; Firestone, S.M.; McPhee, S.; Driessen, N.; Koehler, A.V.; Haydon, S.R.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Stevens, M.A.; Gasser, R.B. Assessing calves as carriers of Cryptosporidium and Giardia with zoonotic potential on dairy and beef farms within a water catchment area by mutation scanning. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.; Innes, E.A.; Jonsson, N.N.; Katzer, F. Shedding of Cryptosporidium in calves and dams: Evidence of re-infection and shedding of different gp60 subtypes. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Global prevalence of Cryptosporidium andersoni in dairy cattle: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2024, 260, 107427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Martí-Marco, A.; Moratal, S.; Lebbad, M.; Carmena, D. Cryptosporidium occultus in disguise. J. Microbiol. Methods 2024, 222, 106957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cai, J.; Cai, M.; Wu, W.; Li, C.; Lei, M.; Xu, H.; Feng, L.; Ma, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Distribution of Cryptosporidium species in Tibetan sheep and yaks in Qinghai, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Rao, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Cryptosporidium spp. in wild rats (Rattus spp.) from the Hainan Province, China: Molecular detection, species/genotype identification and implications for public health. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Kváč, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Common occurrence of divergent Cryptosporidium species and Cryptosporidium parvum subtypes in farmed bamboo rats (Rhizomys sinensis). Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Cao, J. First report of Cryptosporidium viatorum and Cryptosporidium occultus in humans in China, and of the unique novel C. viatorum subtype XVaA3h. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kváč, M.; Vlnatá, G.; Ježková, J.; Horčičková, M.; Konečný, R.; Hlásková, L.; McEvoy, J.; Sak, B. Cryptosporidium occultus sp. n. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in rats. Eur. J. Protistol. 2018, 63, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.; Quílez, J.; Chalmers, R.M.; Panadero, R.; López, C.; Sánchez-Acedo, C.; Morrondo, P.; Díez-Baños, P. Genotype and subtype analysis of Cryptosporidium isolates from calves and lambs in Galicia (NW Spain). Parasitology 2010, 137, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Ryan, U.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Emergence of zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum in China. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.W.; Shu, F.F.; Pu, L.H.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.F.; Zou, F.C.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, Z.; He, J.J. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in dairy cattle and dairy buffalo in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Animals 2022, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, N.; Wu, Y.; Sun, M.; Chang, Y.; Lin, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Cui, Z.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium spp. in dairy cattle in Guangdong Province, South China. Parasitology 2019, 146, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.H.; Ren, W.X.; Gao, M.; Bian, Q.Q.; Hu, B.; Cong, M.M.; Lin, Q.; Wang, R.J.; Qi, M.; Qi, M.Z.; et al. Genotyping Cryptosporidium andersoni in cattle in Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Wang, R.; Jing, B.; Jian, F.; Ning, C.; Zhang, L. Prevalence and multilocus genotyping of Cryptosporidium andersoni in dairy cattle and He cattle in Xinjiang, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 44, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Wan, M.; Huang, W.; Wang, W.; Liang, R.; Su, D.; Li, N.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. Age and episode-associated occurrence of Cryptosporidium species and subtypes in a birth-cohort of dairy calves. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1710–e1720. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.L.; Heng, Z.J.; Li, L.J.; Yang, J.F.; He, J.J.; Zou, F.C.; Shu, F.F. Cryptosporidium spp. infection and genotype identification in pre-weaned and post-weaned calves in Yunnan Province, China. Animals 2024, 14, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Zahedi, A.; Paparini, A. Cryptosporidium in humans and animals-a one health approach to prophylaxis. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
