Straw-Enhanced Soil Bacterial Robustness via Resource-Driven Niche Dynamics in Tea Plantations, South Henan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sites and Sampling
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Property Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Illumina Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
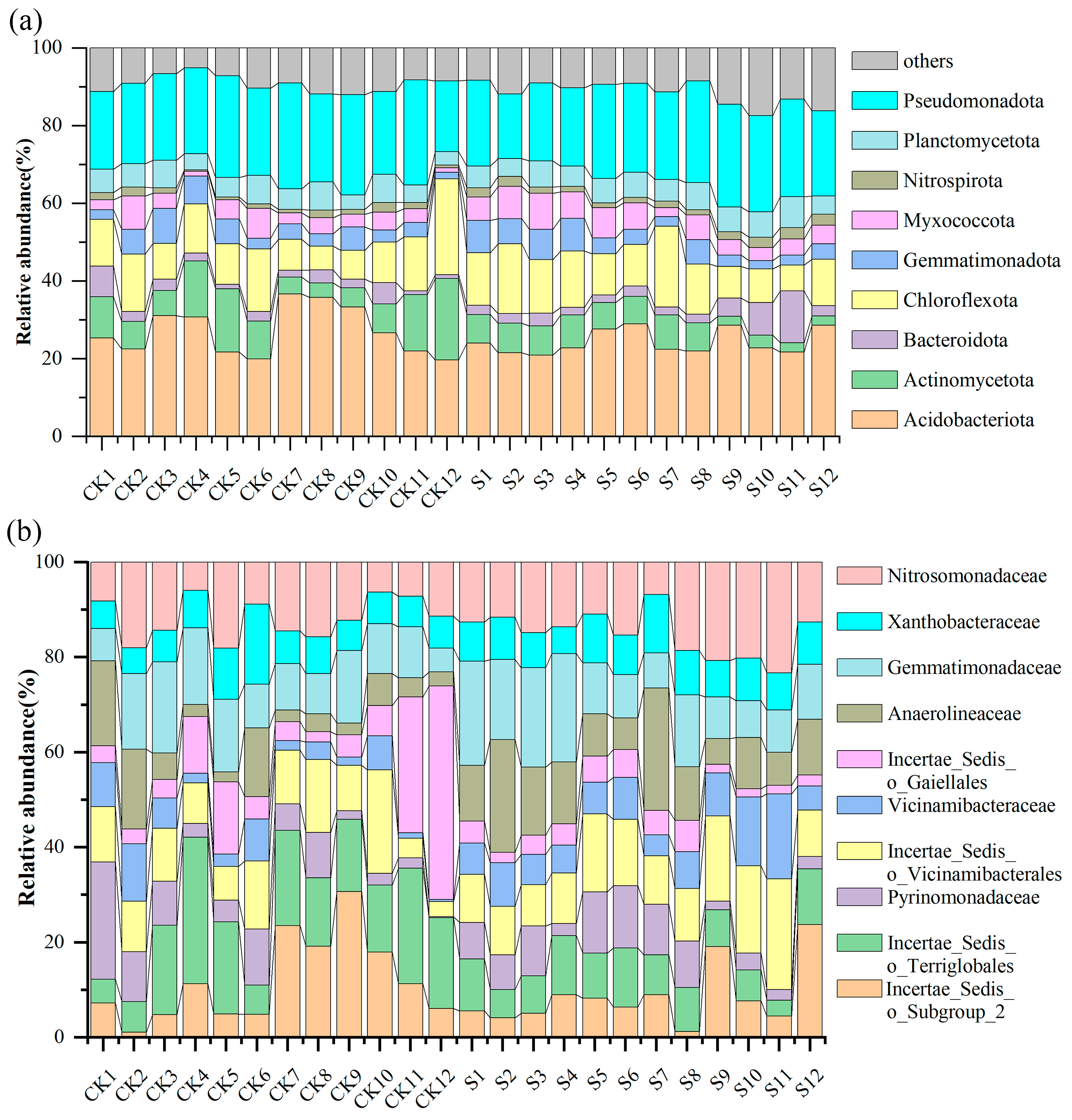
3.1. Community Composition of Dominant Bacteria
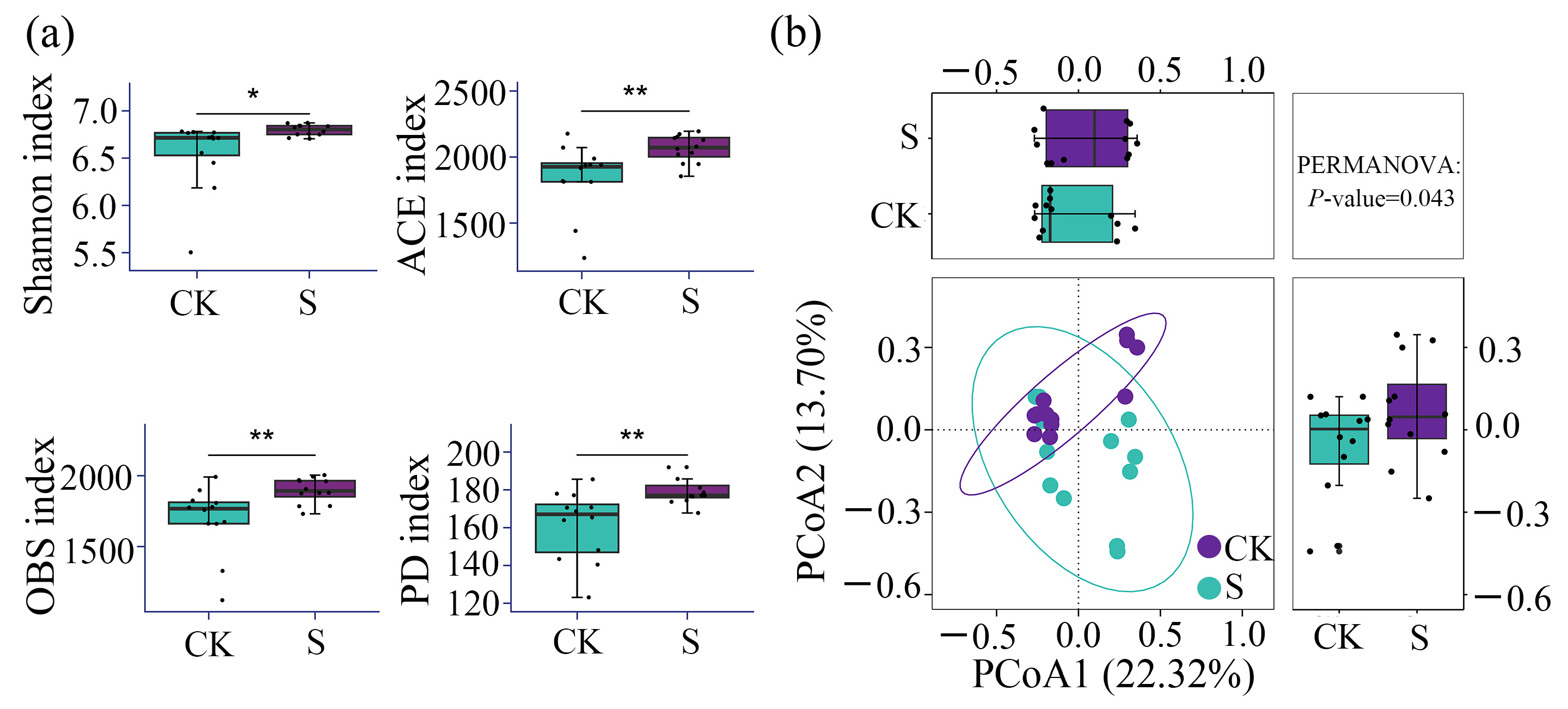
3.2. α- and β-Diversity of Bacterial Communities
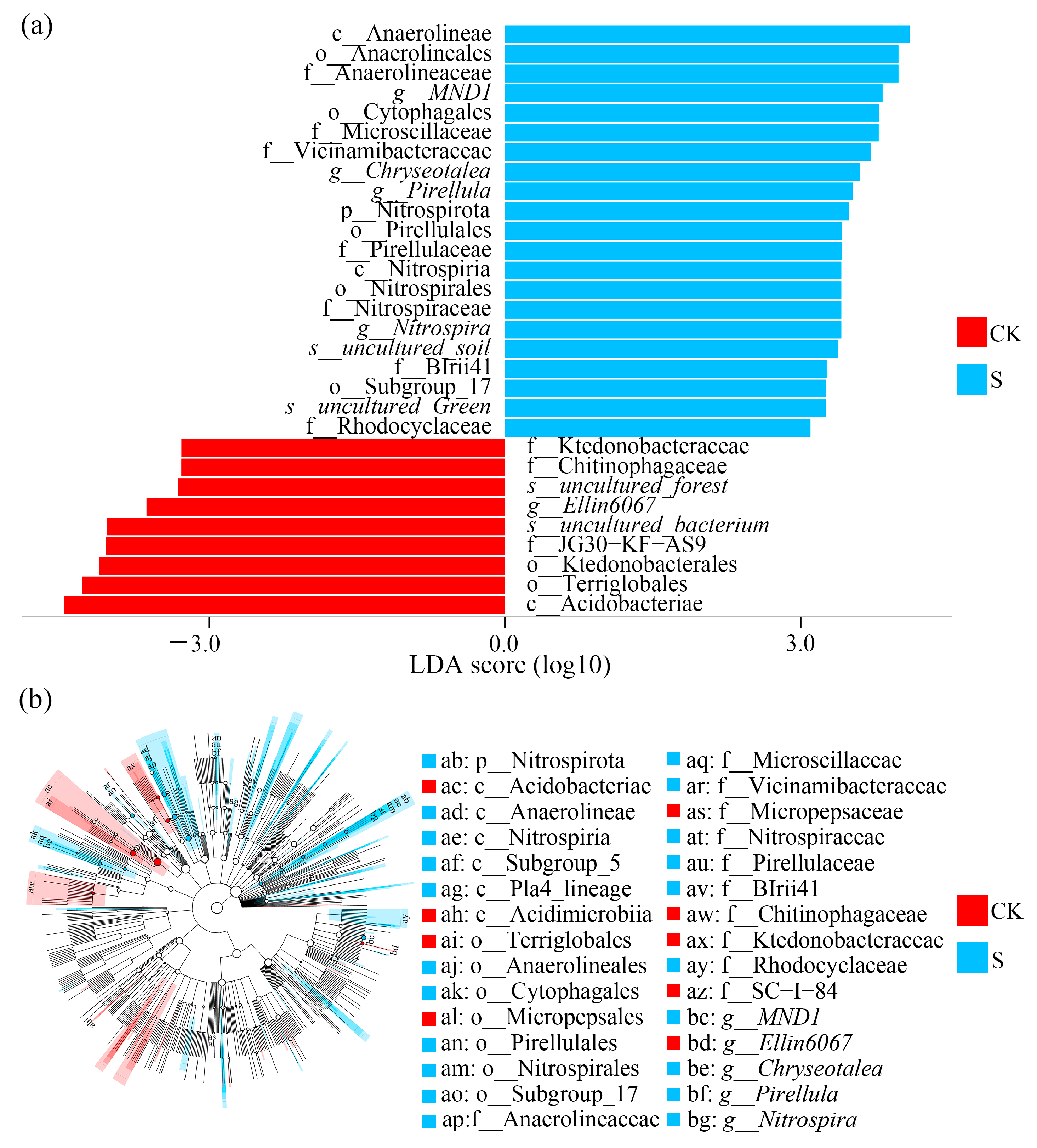
3.3. Biomarker Analysis
3.4. Soil Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
3.5. Soil Factors Influencing Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Abundance-based coverage estimator |
| AP | Available phosphorus content |
| ASVs | Amplicon sequence variants |
| C | Clustering coefficient |
| CK | A soil sample from the tea plantations without straw application |
| dbRDA | Distance-based redundancy analysis |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| HP | Hierarchical partitioning |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| OBS | Observed OTUs |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| PD | Phylogenetic diversity |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| Pi | Among-module connectivity |
| Q | Modularity index |
| QIIME2 | Quantitative insights into microbial ecology 2 |
| S | A soil sample from the tea plantations with straw application |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| SP | Straw application |
| WC | Water content |
| Zi | Within-module connectivity |
References
- Cheng, J.; Lin, B.J.; Chen, J.S.; Duan, H.X.; Sun, Y.F.; Zhao, X.; Dang, Y.P.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.L. Strategies for crop straw management in China’s major grain regions: Yield-driven conditions and factors influencing the effectiveness of straw return. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X.J. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, H.C.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Gao, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.C.; Li, Z.X.; Zamanian, K. Microbial community and functions depending on tillage and straw returning management: Consequences for soil health and ecosystem services. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5357–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Dang, P.F.; Haegeman, B.; Han, X.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Pu, X.; Qin, X.L.; Siddique, K.H. The effects of straw return on soil bacterial diversity and functional profiles: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 195, 109484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, K.S.; Suleiman, A.K.A.; Pijl, A.; Veen, A.V.; Cantarella, H.; Kuramae, E.E. Resilience of the resident soil microbiome to organic and inorganic amendment disturbances and to temporary bacterial invasion. Microbiome 2018, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.T.; Tu, B.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, J.X.; Liang, Y.T. Mechanisms of rhizosphere microorganisms in regulating plant root system architecture in acidic soils. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 570–578. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Ning, S.Y.; Han, Y.Y.; Qi, N.; Zhang, Y. Research advances on the impact of soil disturbance on soil microorganisms. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2024, 44, 43–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.L.; Shao, S.B.; Li, D.L.; Liu, H.; Xie, W.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Nie, C.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Hong, Y.C.; et al. Exploring the impact of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Ktze.)/Trachelospermum jasminoides (Lindl.) Lem. inter-cropping on soil health and microbial communities. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, G.W.; Zheng, Z.S.; Chen, Y.; Li, O.; Peng, Y.L.; Hu, X.F. Acidification induce chemical and microbial variation in tea plantation soils and bacterial degradation of the key acidifying phenolic acids. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Chen, W.L.; Dong, L.Z.; Wang, W. Grassland degradation amplifies the negative effect of nitrogen enrichment on soil microbial community stability. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.P.; Yang, T.J.; Bao, Y.Z.; He, P.P.; Yang, K.M.; Mei, X.L.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Banerjee, S. Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.J.; Yang, S.Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Xue, Y. Microbial composition change and heavy metal accumulation in response to organic fertilization reduction in greenhouse soil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.L.; Duan, L.L.; Zhou, R.; Wu, F.F.; Xiong, M.Q.; Zhang, B.Y.; Geng, S.B.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, F.M. Effect of streptomyces costaricanus strain a-m1 as a bioinoculant on tea garden soil and tea quality. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A. Life and death in the soil microbiome: How ecological processes influence biogeochemistry. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.B.; Liu, Y.P.; Li, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, N.; Miao, Y.Z.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Specialized metabolic functions of keystone taxa sustain soil microbiome stability. Microbiome 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Zheng, Y.T.; Li, P.F.; Cui, J.X.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Gao, W.S. Organic management increases beneficial microorganisms and promotes the stability of microecological networks in tea plantation soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. Analysis of fungal diversity characteristics in rhizosphere soils of Wuyi rock tea gardens with different elevations. Biotic Resour. 2024, 46, 467–477. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Cao, X.L.; Yuan, Z.F.; Guo, G.Y. Untargeted metabolomics coupled with chemometrics approach for Xinyang Maojian green tea with cultivar, elevation and processing variations. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, L.Y.; Feng, J.C.; Zheng, X.B.; He, W.; Liu, J.J. Research progress of factors influencing the quality of Xinyangmaojian. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2013, 42, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Yuan, G.Q.; Dong, Y.Z. The ecological environment of tea cultivation in Xinyang tea production region. Areal Res. Dev. 1998, 17, 94–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.X.; Mao, L.X.; Mo, X.G.; Zhao, W.M.; Lin, Z.H. Analysis of spatial variability of soil moisture and its driving force factors in the Shaanxi-Henan region along the Yellow River. Clim. Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 645–657. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agricultural Chemistry, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 12–14, 86–89, 289–290. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebius, L.J. A rapid method for the determination of organic carbon in soil. Anal. Chim. Acta 1960, 22, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisinger, J.J.; Bandel, V.A.; Angle, J.S.; O’Keefe, B.E.; Reynolds, C.M. Pre-sidedress soil nitrate test evaluation in Maryland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Baccan, N.; Nóbrega, J.A. Analytical performance of an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry with dual view configuration. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzua, P.; Bovio-Winkler, P.; Etchebehere, C.; Suarez-Ojeda, M.E. Microbial communities in an anammox reactor treating municipal wastewater at mainstream conditions: Practical implications of different molecular approaches. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.M.; Li, X.Z.; Yao, M.J. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, Z.D.; Müller, C.L.; Miraldi, E.R.; Littman, D.R.; Blaser, M.J.; Bonneau, R.A. Sparse and compositionally robust inference of microbial ecological networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.M.; McMahon, K.D. Cohesion: A method for quantifying the connectivity of microbial communities. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.X.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R package for microbiome network analysis and modularity-based multiple network layouts. iMeta 2022, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Yao, H.Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Jin, S.Q.; Cao, H. Reducing application of nitrogen fertilizer increases soil bacterial diversity and drives co-occurrence networks. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.X.; Mo, Y.Y.; Xiao, P.; Rønn, R.G.; Xu, Z.J.; Xue, Y.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Rivera, W.L.; Rensing, C.; Yang, J. Microeukaryotic plankton evolutionary constraints in a subtropical river explained by environment and bacteria along differing taxonomic resolutions. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycae026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.S.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca. hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, S.H.; Niu, H.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, Y.L.; Xing, M.Z.; Chen, X.B. Analysis of bacterial community characteristics in maize root zones under maize-soybean compound planting mode. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4894–4903. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, T.; Goordial, J.; Lindsay, M.R.; McGonigle, J.; Booker, A.; Moser, D.; Stepanauskus, R.; Orcutt, B.N. Replicated life-history patterns and subsurface origins of the bacterial sister phyla Nitrospirota and Nitrospinota. ISME J. 2023, 17, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.Y.; Bai, Y.L.; Wang, L.F.; Xu, P.N. Effects of long-term straw return on crop yield and ammonia volatilization of winter wheat-summer maize rotation system in typical fluvo-aquic soil region. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2025, 31, 213–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Wang, L.Y.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Liu, J.F.; Yang, S.Z.; Gu, J.D.; Mu, B.Z. Anaerolineaceae and Methanosaeta turned to be the dominant microorganisms in alkanes-dependent methanogenic culture after long-term of incubation. AMB Express 2015, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.M.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into plant interactions and the biogeochemical role of the globally widespread Acidobacteriota phylum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, J.W.; Gu, C.K.; Chen, G.; Peng, Y.Z. Novel three-sludge municipal wastewater treatment process coupling denitrifying phosphorus removal with anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, J.G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.F.; Zeng, W.A.; Deng, X.H.; Hu, Q.L. Effects of tobacco plant residue return on rhizosphere soil microbial community. Ann. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.F.; Ma, Y.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Sheng, J.D.; Cheng, J.H. Pattern and drivers of phylogenetic diversity in Xinjiang grassland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2285–2299. Available online: https://www.ecologica.cn/stxb/article/pdf/stxb201901190154 (accessed on 3 March 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zhou, S.H.; Wang, M.Q.; Song, Y.; Niu, H.J.; Zhao, J.W.; Hou, R.N.; Chen, X.B.; Huang, Y.L. Legacy effects of long-term straw returning on straw degradation and microbial communities of the aftercrop. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 532–542. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Wang, N.; Yu, M.K.; Yu, J.G.; Xue, L.H. Rhizosphere and straw return interactively shape rhizosphere bacterial community composition and nitrogen cycling in paddy soil. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 945927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daims, H.; Lebedeva, E.V.; Pjevac, P.; Han, P.; Herbold, C.; Albertsen, M.; Jehmlich, N.; Palatinszky, M.; Vierheilig, J.; Bulaev, A. Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 2015, 528, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.J.; Su, W.Q.; Huang, L.B.; Parikh, S.J.; Tang, C.X.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J.M. Bacterial community structure and putative nitrogen-cycling functional traits along a charosphere gradient under waterlogged conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 108420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zuo, S.S.; Cao, X.H.; Xu, C.C. Carbon and nitrogen transformation mechanism and functional microorganisms of sheep manure composting on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under different moisture content. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, J.B.; Eisen, J.A.; Penn, K.; Allison, S.D.; Horner-Devine, M.C. Drivers of bacterial β-diversity depend on spatial scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7850–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Xue, K.; Xie, J.P.; Deng, Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Cheng, X.L.; Fei, S.F.; Deng, S.P.; He, Z.L.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; et al. Microbial mediation of carbon-cycle feedbacks to climate warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xia, Y.Q.; Ti, C.P.; Shan, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, C.L.; Yan, X.; Yan, X.Y. Partial organic fertilizer substitution promotes soil multifunctionality by increasing microbial community diversity and complexity. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, Z.P.; Bol, R.; Zhang, S.X. Metagenomics reveals the underestimated role of bacteria in the decomposition of downed logs in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 187, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragone, N.B.; Hoffert, M.; Strickland, M.S.; Fierer, N. Taxonomic and genomic attributes of oligotrophic soil bacteria. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycae081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Li, C.; Ma, W.D.; Wu, Z.X.; Liu, W.; Wu, W.X. Exploitation alters microbial community and its co-occurrence patterns in ionic rare earth mining sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Xu, L.; Montoya, L.L.; Madera, M.; Hollingsworth, J.; Chen, L.; Purdom, E.; Singan, V.; Vogel, J.; Hutmacher, R.B. Co-occurrence networks reveal more complexity than community composition in resistance and resilience of microbial communities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, P.F.; Li, C.F.; Lu, C.; Zhang, M.M.; Huang, T.T.; Wan, C.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Qin, X.L.; Liao, Y.C. Effect of fertilizer management on the soil bacterial community in agroecosystems across the globe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Breitbart, M.; Nulton, J.; Salamon, P.; Lozupone, C.; Jones, R.; Robeson, M.; Edwards, R.A.; Felts, B.; Rayhawk, S. Metagenomic and small-subunit rRNA analyses reveal the genetic diversity of bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7059–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Jones, S.E.; Prober, S.M.; Barberán, A.; Borer, E.T.; Firn, J.L.; Harpole, W.S.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Knops, J.M.H. Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1508382112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Nunan, N.; Hirsch, P.R.; Sun, B.; Zhou, J.Z.; Liang, Y.T. Theory of microbial coexistence in promoting soil–plant ecosystem health. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.S.; Bradford, M.A.; Lindner, D.L.; van Diepen, L.T.; Frey, S.D.; Glaeser, J.A.; Crowther, T.W. Diversity begets diversity in competition for space. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizaludin, M.S.; Garbeva, P.; Zwart, M.; Hu, J. Microbial volatiles mediate bacterial evolutionary dynamics. ISME J. 2023, 17, 2144–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.A.; Durán, P.; Hacquard, S. Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Martiny, J.B. Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11512–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


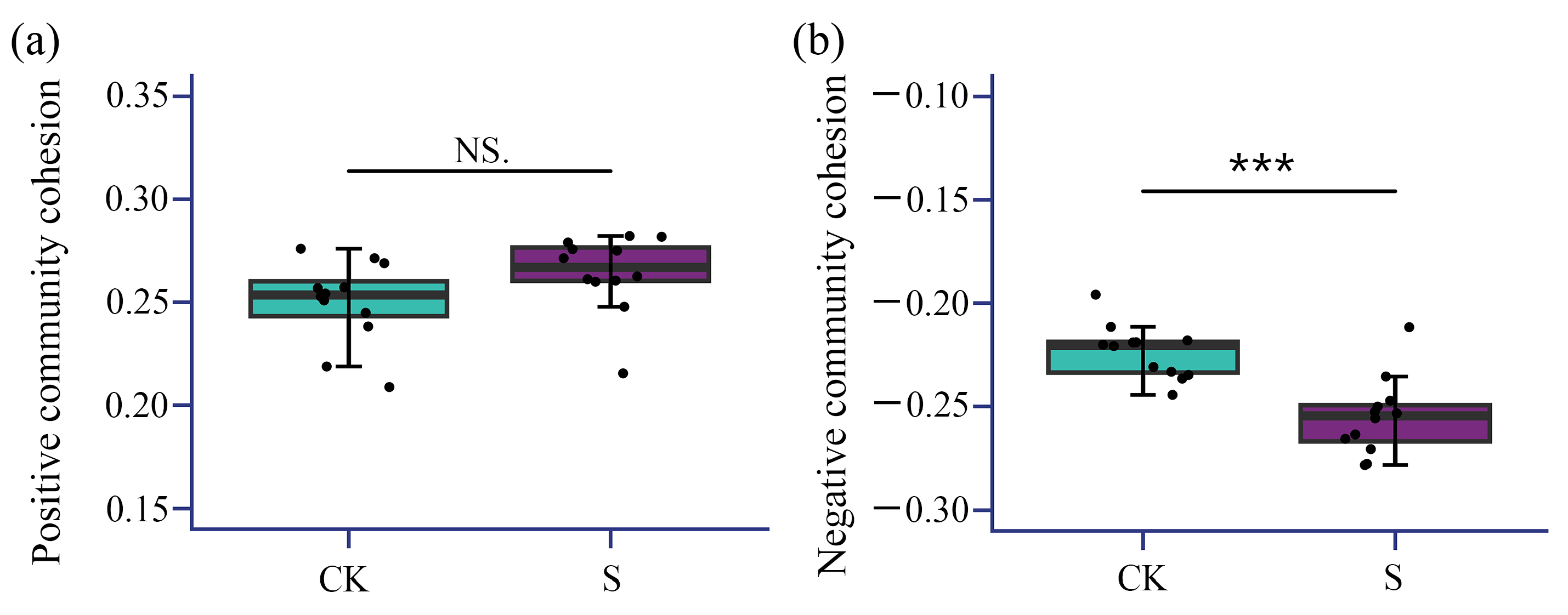

| Parameters | CK | S | S/CK Ratio Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| node | 1048 | 1020 | −2.67% |
| Edge | 9552 | 6036 | −36.8% |
| Average degree | 18.2 | 11.8 | −35.1% |
| Network diameter | 21 | 19 | −9.52% |
| Graph density | 0.017 | 0.012 | −29.4% |
| Modularity index (Q) | 0.663 | 0.687 | 3.62% |
| Clustering coefficient (C) | 0.573 | 0.530 | −7.50% |
| Positive edges | 0.987 | 0.978 | −0.86% |
| Negative edges | 0.013 | 0.022 | 69.2% |
| Phylum | CK Proportion | S Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Acidobacteriota | 26.24% | 22.25% |
| Pseudomonadota | 25.86% | 24.41% |
| Chloroflexota | 11.35% | 12.45% |
| others | 10.69% | 13.14% |
| Actinomycetota | 9.45% | 7.16% |
| Planctomycetota | 6.39% | 5.69% |
| Myxococcota | 3.72% | 5.78% |
| Gemmatimonadota | 2.96% | 4.61% |
| Bacteroidota | 2.77% | 3.33% |
| Nitrospirota | 0.57% | 1.18% |
| Group | Soil Physicochemical Properties | Unique | Average Share | Individual | Individual Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial β-diversity | WC | 0.1125 | 0.0264 | 0.1389 | 24.72 |
| pH | 0.0829 | 0.0326 | 0.1155 | 20.55 | |
| AP | 0.0395 | 0.0249 | 0.0644 | 11.46 | |
| OM | 0.0366 | 0.0165 | 0.0531 | 9.45 | |
| Ca | 0.028 | 0.0179 | 0.0459 | 8.17 | |
| NH4+-N | 0.0303 | 0.0122 | 0.0425 | 7.56 | |
| EC | 0.0343 | 0.004 | 0.0383 | 6.81 | |
| Al | 0.0249 | 0.0109 | 0.0358 | 6.37 | |
| NO3−-N | 0.0261 | 0.0019 | 0.028 | 4.98 | |
| Keystone taxa | WC | 0.1396 | 0.0549 | 0.1945 | 30.68 |
| pH | 0.0867 | 0.0466 | 0.1333 | 21.03 | |
| AP | 0.0613 | 0.0142 | 0.0755 | 11.91 | |
| NH4+-N | 0.0428 | 0.0144 | 0.0572 | 9.02 | |
| SOM | 0.0251 | 0.0256 | 0.0507 | 8 | |
| Ca | 0.0178 | 0.0268 | 0.0446 | 7.03 | |
| EC | 0.0253 | 0.0039 | 0.0292 | 4.61 | |
| Al | 0.0126 | 0.0149 | 0.0275 | 4.34 | |
| NO3−-N | 0.0151 | 0.0062 | 0.0213 | 3.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Wei, W.; Ma, G.; Li, M.; Yan, J. Straw-Enhanced Soil Bacterial Robustness via Resource-Driven Niche Dynamics in Tea Plantations, South Henan, China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040832
Cui X, Xu D, Zhang Y, Huang S, Wei W, Ma G, Li M, Yan J. Straw-Enhanced Soil Bacterial Robustness via Resource-Driven Niche Dynamics in Tea Plantations, South Henan, China. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040832
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xiangchao, Dongmeng Xu, Yu Zhang, Shuping Huang, Wei Wei, Ge Ma, Mengdi Li, and Junhui Yan. 2025. "Straw-Enhanced Soil Bacterial Robustness via Resource-Driven Niche Dynamics in Tea Plantations, South Henan, China" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040832
APA StyleCui, X., Xu, D., Zhang, Y., Huang, S., Wei, W., Ma, G., Li, M., & Yan, J. (2025). Straw-Enhanced Soil Bacterial Robustness via Resource-Driven Niche Dynamics in Tea Plantations, South Henan, China. Microorganisms, 13(4), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040832






