Bacteriophage Therapy in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaculture Species
Abstract
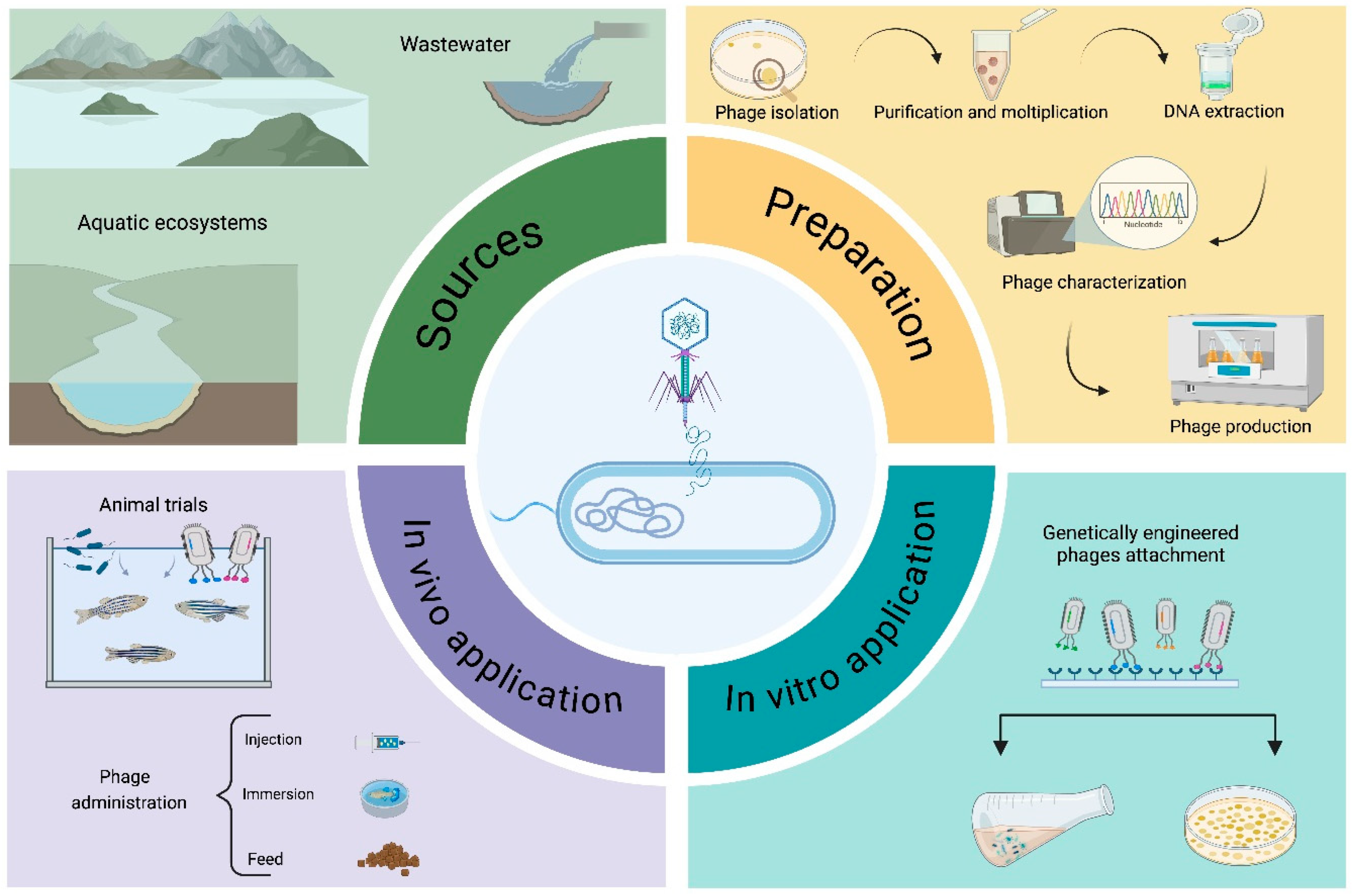
1. Introduction
2. Antibiotic Resistance and Bacteriophages
3. Phage Therapy in Aquaculture
3.1. Phage Therapy in Fish Culture
3.1.1. Aeromonas
| Bacterium (Aeromonas) Strain/ Administration Route/Dosage (CFU) | Phage Acronym/Administration Route/Dosage (PFU) | Fish | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. hydrophila isolated from diseased fish or environmental/intraperitoneal injection/2.6–26 × 106/fish | pAh-1-C or pAh6-C/intraperitoneal injection–oral/1.7–3 × 107/fish | Cyprinid loach | [20] |
| A. hydrophila 4.4T isolated from diseased fish/immersion/103–107/mL of water | PVN02/oral/104–106/g of pellet | Striped catfish | [21] |
| A. hydrophila BT14 isolated from diseased fish/immersion/2 × 107/mL of water | pAh6.2TG/immersion/2–20 × 106/mL of water | Nile tilapia | [22] |
| A. hydrophila UR1 isolated from diseased fish/intraperitoneal injection/3.16 × 105/fish | PAh4/oral/105–108/g of diet | Tilapia | [23] |
| A. hydrophila KCTC2358 from Korean Collection/immersion/106–108/mL of water | Akh-2/immersion/108/mL of water | Loach | [24] |
| A. hydrophila 152 multidrug-resistant/intraperitoneal injection/2 × 108/fish | PZL-Ah152/intraperitoneal injection/2 × 109/fish | Crucian carp | [25] |
| A. hydrophila A18 isolated from market aquatic produce/intraperitoneal injection/107/fish | Ahy-Yong1/intraperitoneal injection/106/fish | Brocade carp | [26] |
| A. hydrophila KCTC12487 from Korean Collection/intraperitoneal injection/2 × 106/fish | pAh-1/intraperitoneal injection/2 × 107/fish | Zebrafish | [27] |
| A. hydrophila GW3-10 isolated from diseased trout/immersion–immersion following dermal abrasion–intraperitoneal injection/105–107/mL of water—107/mL of water after dermal abrasion—102–107/fish | AhMtk13a/immersion/108/mL of water | Zebrafish | [28] |
| A. salmonicida AS01 isolated from diseased turbot/intraperitoneal injection/8 × 104/fish | vB_AsM_ZHF/intraperitoneal injection/8 × 102–106/fish | Turbot | [30] |
| A. salmonicida CECT894 from Collection/immersion/108/mL of water | AS-A/immersion/1010/mL of water | Sole Senegalese juvenile | [31] |
| A. schubertii GC1 islated from diseased snakehead/intraperitoneal injection–immersion/1.5 × 102/fish-105/mL of water | SD04/intraperitoneal injection–immersion/1.5 × 104/fish-107/mL of water | Snakehead | [32] |
| A. hydrophila Ah-138//intraperitoneal injection/2 × 106/fish | vB_ AhaP_PZL-Ah8 and vB_ AhaP_PZL-Ah1(cocktail)/intraperitoneal/104/fish | Crucian carp | [34] |
| A. hydrophila MTCC1739 from Collection/intraperitoneal injection/106–107/fish | D6 and CF7 (cocktail)/oral/106–108/g of feed | Carp | [35] |
| A. hydrophila N17/intraperitoneal injection/3.2 × 106/fish | Φ2 and Φ5 (cocktail)/injection/105–107/fish | Striped catfish | [36] |
| A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens/intraperitoneal injection/0.2 mL of the [1.5] mL/fish | BAFADOR® cocktail (7 phages)/immersion/105/mL of water | Rainbow trout | [37] |
| A. hydrophila 10098 from Philippine National Collection/intramuscular injection/2 × 106/fish | vB_AehM_DM8, vB_AehM_DM12, vB_AehM_DM14 and vB_AehP_DM11 (cocktail)/injection–immersion–oral/4 × 109/fish-6.1 × 106/mL of water-1.2 × 1010/g of pellet | Nile tilapia | [40] |
3.1.2. Vibrio
| Bacterium (Vibrio spp.) Strain/Administration Route/Dosage (CFU) | Phage Name or Acronym/Administration Route/Dosage (PFU) | Fish | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| V. harveyi VH2 from Hellenic Center for Marine Research Collection/immersion/106–107/mL of water | Virtus/immersion/108/mL of water repeated twice | Gilthead seabream larvae | [46] |
| V. harveyi MM46 from Hellenic Center for Marine Research Collection/immersion/106–107/mL of water | vB_VhaS_MAG7/immersion/108/mL of water | Gilthead seabream larvae | [43] |
| V. anguillarum PF4 isolated from diseased fish/immersion/5 × 105/mL of water | CHOED/immersion/5 × 106–108/mL of water | Salmon | [47] |
| V. anguillarum isolated from aquaculture environment/immersion/106/mL of water | VP-2/immersion/108/mL of water | Zebrafish larvae | [9] |
| - | vB_Pd_PDCC-1/immersion/1.41 × 1010/mL of water | Longfin yellowtail larvae | [54] |
| V. anguillarum isolated from aquaculture environment/immersion/0.5–1 × 106/mL of water | KVP40//immersion/0.5–12 × 108/mL of water | Cod and turbot larvae | [55] |
3.1.3. Edwardsiella
3.1.4. Streptococcus
3.1.5. Flavobacterium
| Bacterium (Flavobacterium spp.) Strain/ Administration Route/Dosage (CFU) | Phage Name or Acronym/Administration Route/Dosage (PFU) | Fish | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| F. columnare B185 from diseased fish/immersion/3 × 106/mL of water | FCL2/immersion/3 × 108–107/mL of water | Zebrafish and rainbow trout | [70] |
| F. columnare FC7/immersion/107/mL of water | FCL2/107/immersion/107/mL of water | Atlantic salmon | [71] |
| F. columnare FCO-S1, FCO-S2, and B185 isolated from diseased fish/immersion/5 × 103–1.5 × 106/mL of water | FCOV-S1, FCOV-F27, and FCL-2/immersion-oral/5 × 102–104/mL of water-12.5–6 × 106/g of feed | Rainbow trout fry | [69] |
| F. psychrophilum 950106-1/1 isolated from diseased fish/immersion/106/mL of water | FPV-9/immersion-oral/108/mL of water-108/fish via intubation-2.5 × 107/fish via feed | Rainbow trout | [79] |
| F. psychrophilum FPS-S6, 160401-1/5N, FPS-R9, and 950106-1/1 isolated from diseased fish/intraperitoneal injection/8 × 107/fish | FPSV-D22 and FpV-4/intraperitoneal injection/1.2–2.2 × 104–108/fish | Rainbow trout | [81] |
| F. psychrophilum 950106-1/1 isolated from diseased fish/intraperitoneal injection/0.5–5 × 103–1.7 × 106/fish | FPSV-D22 and FpV-4/oral sprayed–oral immobilized–immersion–intraperitoneal injection/4.8–16 × 107/g of feed—2.5–8.3 × 107/g of feed—0.3–6 × 105/mL of water twice—1.7 × 107/fish | Rainbow trout fry | [82] |
| F. psychrophilum 950106-1/1 isolated from diseased fish/intraperitoneal injection/104/fish | FpV-9/intraperitoneal injection/107/fish | Rainbow trout | [83] |
| - | FCL-2/immersion/107/mL of water | Rainbow trout | [14] |
3.1.6. Citrobacter
3.1.7. Pseudomonas
3.1.8. Yersinia
3.1.9. Plesiomonas
3.1.10. Photobacterium
3.2. Phage Therapy in Mollusk Culture
3.3. Phage Therapy in Crustacean Culture
3.4. Phage Therapy in Echinoderm Culture
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, S.K.; Hwang, S.R.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchessi, L.; De Bernardi, G.; Vigorelli, M.; Dall’Ara, P.; Turin, L. Bacteriophage therapy in companion and farm animals. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.R.; Kutter, E. Bacteriophage: Therapeutic uses. In The Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, B.K.; Abedon, S.T.; Loc-Carrillo, C. Phage cocktails and the future of phage therapy. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasikumar, R.; Saranya, S.; Lourdu Lincy, L.; Thamanna, L.; Chellapandi, P. Genomic insights into fish pathogenic bacteria: A systems biology perspective for sustainable aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, S.; Turin, L.; Zanella, A.; Ponti, W.; Poli, G. What’s going on in vaccine technology? Med. Res. Rev. 1997, 17, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.J.; Costa, L.; Pereira, C.; Mateus, C.; Cunha, A.; Calado, R.; Gomes, N.C.; Pardo, M.A.; Hernandez, I.; Almeida, A. Phage therapy as an approach to prevent Vibrio anguillarum infections in fish larvae production. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnay, J.P.; De Vos, D.; Verbeken, G.; Merabishvili, M.; Chanishvili, N.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Zizi, M.; Laire, G.; Lavigne, R.; Huys, I.; et al. The phage therapy paradigm: Prêt-à-porter or sur-mesure? Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Salvador, S.; Arrojado, C.; Silva, Y.; Santos, A.L.; Cunha, A.; Gomes, N.C.; Almeida, A. Evaluating seasonal dynamics of bacterial communities in marine fish aquaculture: A preliminary study before applying phage therapy. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.J.; Costa, L.; Pereira, C.; Cunha, Â.; Calado, R.; Gomes, N.C.; Almeida, A. Influence of environmental variables in the efficiency of phage therapy in aquaculture. Microb. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Silva, Y.J.; Santos, A.L.; Cunha, Â.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Almeida, A. Bacteriophages with potential for inactivation of fish pathogenic bacteria: Survival, host specificity and effect on bacterial community structure. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2236–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, G.M.F.; Mäkelä, K.; Laanto, E.; Pulkkinen, J.; Vielma, J.; Sundberg, L.R. The fate of bacteriophages in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS)—Towards developing phage therapy for RAS. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çağatay, I.T. Bacteriophage applications in aquaculture. Isr. J. Aquac—Bamidgeh 2023, 75, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Gao, S.; Dong, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages against virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Lu, T.; Mou, Z. Genomic characterization of a novel virulent phage infecting the Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Virus Res. 2019, 273, 197764. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U.; Nikapitiya, C.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Heo, G.J.; De Zoysa, M.; Lee, J. Isolation and characterization of phage AHP-1 and its combined effect with chloramphenicol to control Aeromonas hydrophila. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, S.P.; Han, J.E.; Chai, J.Y.; Park, S.C. Protective effects of the Aeromonas phages pAh1-C and pAh6-C against mass mortality of the cyprinid loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) caused by Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2013, 416–417, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.H.O.; Xuan, T.T.T.; Duyen, L.T.M.; Le, N.P.; Hoang, H.A. Protective efficacy of phage PVN02 against hemorrhagic septicaemia in striped catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus via oral administration. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Dien, L.T.; Ky, L.B.; Huy, B.T.; Mursalim, M.F.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Senapin, S.; Rodkhum, C.; Dong, H.T. Characterization and protective effects of lytic bacteriophage pAh6.2TG against a pathogenic multidrug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e435–e450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phumkhacho, P.; Rattanacha, P. Use of bacteriophage to control experimental Aeromonas hydrophila infection in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 23, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Akmal, M.; Rahimi-Midani, A.; Hafeez-ur-Rehman, M.; Hussain, A.; Choi, T.J. Isolation, characterization, and application of a bacteriophage infecting the fish pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila. Pathogens 2020, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Jia, K.; Chi, T.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Haidar Abbas Raza, S.; Alshammari, A.M.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Lytic bacteriophage PZL-Ah152 as biocontrol measures against lethal Aeromonas hydrophila without distorting gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 898961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, D.; Lin, W.; Liu, W.; Qu, C.; Qian, M.; Cai, R.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, F.; Tong, Y. Novel Aeromonas phage Ahy-Yong1 and its protective effects against Aeromonas hydrophila in brocade carp (Cyprinus aka Koi). Viruses 2022, 14, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easwaran, M.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Park, S.C.; Lee, J.; Shin, H.; de Zoysa, M. Characterization of bacteriophage pAh-1 and its protective effects on experimental infection of Aeromonas hydrophila in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, N.; Jaiani, E.; Didebulidze, E.; Kusradze, I.; Kotorashvili, A.; Chalidze, K.; Porchkhidze, K.; Khukhunashvili, T.; Tsertsvadze, G.; Jgenti, D.; et al. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila phage AhMtk13a and evaluation of its therapeutic potential on simulated Aeromonas infection in Danio rerio. Viruses 2022, 14, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Tong, G.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Huang, L.; Jiang, X.; Wei, X.; Lin, M. The characterization and genome analysis of a novel phage phiA034 targeting multiple species of Aeromonas. Virus Res. 2023, 336, 199193. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Jin, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Shao, S.; Liu, Q. Isolation of a Virulent Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. masoucida Bacteriophage and Its Application in Phage Therapy in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0146821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.J.; Moreirinha, C.; Pereira, C.; Costa, L.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Cunha, A.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R.; Almeida, A. Biological control of Aeromonas salmonicida infection in juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) with Phage AS-A. Aquaculture 2016, 450, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liao, G.; Fu, X.; Liang, H.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liu, L.; Ma, B.; Li, N. A novel and effective therapeutic method for treating Aeromonas schubertii infection in Channa maculata. Animals 2024, 14, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.H.; Tran, T.T.X.; Le, P.N.; Dang, T.H.O. Selection of chages to Control Aeromonas hydrophila—An infectious agent in striped catfish. Biocontrol. Sci. 2019, 24, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Feng, C.; Chi, T.; Qi, Y.; Abbas Raza, S.H.; Gao, N.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, R.; et al. A phage cocktail in controlling phage resistance development in multidrug resistant Aeromonas hydrophila with great therapeutic potential. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.; Tyagi, A.; Naveen Kumar, B.T. Oral feed-based administration of phage cocktail protects rohu fish (Labeo rohita) against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Vo, H.P.; Doan, V.C.; Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, M.T.; Tran, T.T.; Southgate, P.C.; Kurtböke, D.İ. Protective effects of bacteriophages against Aeromonas hydrophila causing motile Aeromonas septicemia (MAS) in striped catfish. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, P.; Pajdak-Czaus, J.; Robak, S.; Dastych, J.; Siwicki, A.K. Bacteriophage-based cocktail modulates selected immunological parameters and post-challenge survival of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, N.; Paquet, V.E.; Chehreghani, M.; Moineau, S.; Charette, S.J. Phage cocktail development against Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strains is compromised by a prophage. Viruses 2021, 13, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.; Paquet, V.E.; Marcoux, P.É.; Alain, C.A.; Paquet, M.F.; Moineau, S.; Charette, S.J. MQM1, a bacteriophage infecting strains of Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida carrying Prophage 3. Virus Res. 2023, 334, 199165. [Google Scholar]
- Gordola, K.M.C.; Boctuanon, F.A.U.; Diolata, R.A.A.; Pedro, M.B.D.; Gutierrez, T.A.D.; Papa, R.D.S.; Papa, D.M.D. Evaluation of phage delivery systems on induced motile Aeromonas septicemia in Oreochromis niloticus. Phage (New Rochelle) 2020, 1, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yaşa, İ.; Evran, S.; Eren Eroğlu, A.E.; Önder, C.; Allahyari, M.; Menderes, G.; Kullay, M. Partial characterization of three bacteriophages isolated from aquaculture hatchery water and their potential in the biocontrol of Vibrio spp. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yun, H.; Chen, R.; Jiao, N.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R. Characterization of a Vibriophage Infecting Pathogenic Vibrio harveyi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droubogiannis, S.; Pavlidi, L.; Skliros, D.; Flemetakis, E.; Katharios, P. Comprehensive characterization of a novel bacteriophage, vB_VhaS_MAG7 against a fish pathogenic strain of Vibrio harveyi and its in vivo efficacy in phage therapy trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, T.M.; Sano, M.; Ransangan, J. Isolation and characterization of large marine bacteriophage (Myoviridae), VhKM4 infecting Vibrio harveyi. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2017, 29, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misol, G.N.; Kokkari, C.; Katharios, P. Biological and genomic characterization of a novel jumbo bacteriophage, vB_VhaM_pir03 with broad host lytic activity against Vibrio harveyi. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droubogiannis, S.; Katharios, P. Genomic and biological profile of a novel bacteriophage, Vibrio phage Virtus, which improves survival of Sparus aurata larvae challenged with Vibrio harveyi. Pathogens 2022, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera, G.; Bastías, R.; Tsertsvadze, G.; Romero, J.; Espejo, R.T. Recently discovered Vibrio anguillarum phages can protect against experimentally induced vibriosis in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquaculture 2013, 392–395, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Higuera, G.; Gajardo, F.; Castillo, D.; Middleboe, M.; García, K.; Ramírez, C.; Espejo, R.T. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio anguillarum phage CHOED successfully used for phage therapy in aquaculture. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00091-14. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, D.; Rørbo, N.; Jørgensen, J.; Lange, J.; Tan, D.; Kalatzis, P.G.; Svenningsen, S.L.; Middelboe, M. Phage defense mechanisms and their genomic and phenotypic implications in the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz004. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, T.M.; Sano, M.; Ransangan, J. Genome characterization of a novel vibriophage VpKK5 (Siphoviridae) specific to fish pathogenic strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 872–888. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ai, C.; Zhang, R. A broad-host-range lytic phage vB_VhaS-R18L as a candidate against vibriosis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1191157. [Google Scholar]
- Kalatzis, P.G.; Bastías, R.; Kokkari, C.; Katharios, P. Isolation and characterization of two lytic bacteriophages, φSt2 and φGrn1; phage therapy application for biological control of Vibrio alginolyticus in aquaculture live feeds. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. A novel method to create efficient phage cocktails via use of phage-resistant bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0232321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrand-Quirós, B.; Guzmán-Villanueva, L.T.; Reyes, A.G.; Rodríguez-Jaramillo, C.; Salas-Leiva, J.S.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Balcázar, J.L.; Quiroz-Guzman, E. Assessment of bacteriophage vB_Pd_PDCC-1 on bacterial dynamics during ontogenetic development of the longfin yellowtail (Seriola rivoliana). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rørbo, N.; Rønneseth, A.; Kalatzis, P.G.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Engell-Sørensen, K.; Kleppen, H.P.; Wergeland, H.I.; Gram, L.; Middelboe, M. Exploring the effect of phage therapy in preventing Vibrio anguillarum infections in cod and turbot larvae. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jun, J.W.; Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, J.W.; Han, S.J.; Jeong, D.; Park, S.C. Isolation and characterisation of pVa-21, a giant bacteriophage with anti-biofilm potential against Vibrio alginolyticus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, L.; Wu, Q.; et al. Characterization of the novel phage vB_VpaP_FE11 and its potential role in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilms. Viruses 2022, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikapitiya, C.; Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; de Zoysa, M.; Lee, J. Isolation and characterization of phage (ETP-1) specific to multidrug resistant pathogenic Edwardsiella tarda and its in vivo biocontrol efficacy in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Biologicals 2020, 63, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikapitiya, C.; Dananjaya, S.H.S.; Edirisinghe, S.L.; Chandrarathna, H.P.S.U.; Lee, J.; de Zoysa, M. Development of phage delivery by bioencapsulation of artemia nauplii with Edwardsiella tarda phage (ETP-1). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Cong, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Control of Edwardsiella tarda infection in turbot Scophthalmus maximus (L.) using phage vB_EtaM_ET-ABTNL-9. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3010–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Huang, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, R. Bacteriophage EPP-1, a potential antibiotic alternative for controlling edwardsiellosis caused by Edwardsiella piscicida while mitigating drug-resistant gene dissemination. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.; Yen, M.; Ngoan, V.; Nga, L.; Oanh, D. Virulent bacteriophage of Edwardsiella ictaluri isolated from kidney and liver of striped catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus in Vietnam. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 132, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Xuan, T.T.T.; Ngoc, T.H.; Duyen, L.T.M.; Vinh, T.Q.; My, P.D.T.; Hoang, H.A.; Nga, L.P. Diverse bacteriophages infecting the bacterial striped catfish pathogen Edwardsiella ictaluri. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shao, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Therapeutic efficacies of two newly isolated Edwardsiella phages against Edwardsiella piscicida infection. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 263, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liao, G.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Lin, M.; Zhao, C.; Tao, J.; Huang, Z. Characterization of bacteriophage HN48 and its protective effects in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus agalactiae infections. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preenanka, R.; Safeena, M.P. Morphological, biological and genomic characterization of lytic phages against Streptococcus agalactiae causing streptococcosis in tilapia. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshotel, M.B.; Dave, U.M.; Farmer, B.; Kemboi, D.; Nelson, D.C. Bacteriophage endolysin treatment for systemic infection of Streptococcus iniae in hybrid striped bass. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 145, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.; Norcross, N.L.; Kahn, D.E. Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophage. J. Gen. Virol. 1969, 5, 315–317. [Google Scholar]
- Kunttu, H.M.T.; Runtuvuori-Salmela, A.; Middelboe, M.; Clark, J.; Sundberg, L.R. Comparison of delivery methods in phage therapy against Flavobacterium columnare infections in rainbow trout. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laanto, E.; Bamford, J.K.H.; Ravantti, J.J.; Sundberg, L.R. The use of phage FCL-2 as an alternative to chemotherapy against columnaris disease in aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 829. [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler, A.W.; Gundersen, M.S.; Vo, T.P.; Almaas, E.; Vadstein, O.; Bakke, I. Phage therapy minimally affects the water microbiota in an Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) rearing system while still preventing infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19145. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, D.; Højsting, A.R.; Roosvall, A.; Smyrlis, G.; Jørgensen, J.; Middelboe, M. In vitro evolution of specific phages infecting the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Phage (New Rochelle) 2022, 3, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Gomez, D.K.; Nakai, T.; Park, S.C. Isolation and identification of bacteriophages infecting ayu Plecoglossus altivelis altivelis specific Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.; Middelboe, M. Genomic diversity of bacteriophages infecting the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jørgensen, J.; Sundell, K.; Castillo, D.; Dramshøj, L.S.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Madsen, S.B.; Landor, L.; Wiklund, T.; Donati, V.L.; Madsen, L.; et al. Reversible mutations in gliding motility and virulence genes: A flexible and efficient phage defence mechanism in Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 4915–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laanto, E.; Sundberg, L.R.; Bamford, J.K. Phage specificity of the freshwater fish pathogen Flavobacterium columnare. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7868–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runtuvuori-Salmela, A.; Kunttu, H.M.T.; Laanto, E.; Almeida, G.M.F.; Mäkelä, K.; Middelboe, M.; Sundberg, L.R. Prevalence of genetically similar Flavobacterium columnare phages across aquaculture environments reveals a strong potential for pathogen control. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2404–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laanto, E.; Mäkelä, K.; Hoikkala, V.; Ravantti, J.J.; Sundberg, L.R. Adapting a phage to combat phage resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, R.H.; Dalsgaard, I.; Middelboe, M.; Lauritsen, A.H.; Madsen, L. Detection and quantification of Flavobacterium psychrophilum-specific bacteriophages in vivo in rainbow trout upon oral administration: Implications for disease control in aquaculture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7683–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, V.L.; Madsen, L.; Middelboe, M.; Strube, M.L.; Dalsgaard, I. The gut microbiota of healthy and Flavobacterium psychrophilum-infected rainbow trout fry is shaped by antibiotics and phage therapies. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 771296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundell, K.; Landor, L.; Castillo, D.; Middelboe, M.; Wiklund, T. Bacteriophages as biocontrol agents for Flavobacterium psychrophilum biofilms and rainbow trout infections. Phage (New Rochelle) 2020, 1, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, V.L.; Dalsgaard, I.; Sundell, K.; Castillo, D.; Er-Rafik, M.; Clark, J.; Wiklund, T.; Middelboe, M.; Madsen, L. Phage-mediated control of Flavobacterium psychrophilum in aquaculture: In vivo experiments to compare delivery methods. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 628309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.; Bertelsen, S.K.; Dalsgaard, I.; Middelboe, M. Dispersal and survival of Flavobacterium psychrophilum phages in vivo in rainbow trout and in vitro under laboratory conditions: Implications for their use in phage therapy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4853–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madurantakam Royam, M.; Nachimuthu, R. Isolation, characterization, and efficacy of bacteriophages isolated against Citrobacter spp. An in vivo approach in a zebrafish model (Danio rerio). Res. Microbiol. 2020, 171, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.; Yang, N.; Zhang, X.; Cai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Raza, S.H.A.; Kang, Y.; Qian, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Genomic, morphological and functional characterization of virulent bacteriophage IME-JL8 targeting Citrobacter freundii. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 585261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Shimamura, I.; Fukunaga, M.; Mori, K.I.; Nakai, T. Isolation of bacteriophages specific to a fish pathogen, Pseudomonas plecoglossicida, as a candidate for disease control. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Nakai, T. Bacteriophage control of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida infection in ayu, Plectoglossis altivelis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairnar, K.; Raut, M.P.; Chandekar, R.H.; Sanmukh, S.G.; Paunikar, W.N. Novel bacteriophage therapy for controlling metallo-beta-lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in Catfish. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, T.J. Characterization of a novel Yersinia ruckeri serotype O1-specific bacteriophage with virulence-neutralizing activity. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; Hu, S.; Yan, F.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y. Screening of a Plesiomonas shigelloides phage and study of the activity of its lysis system. Virus Res. 2021, 306, 198581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrand-Quirós, B.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Lomeli-Ortega, C.O.; Escobedo-Fregoso, C.; Millard, A.D.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Balcázar, J.L.; Quiroz-Guzmán, E. Use of bacteriophage vB_Pd_PDCC-1 as biological control agent of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae during hatching of longfin yellowtail (Seriola rivoliana) eggs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, S.K.; Chai, J.Y.; Park, S.C. Eating oysters without risk of vibriosis: Application of a bacteriophage against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 188, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, H.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Pang, M.; Sun, L.; Zhou, X. Application of a phage in decontaminating Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 275, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.S.; Southgate, P.C.; O’Connor, W.; Abramov, T.; Shelley, D.; Vu, S.; Kurtböke, D.İ. Use of bacteriophages to control Vibrio contamination of microalgae used as a food source for oyster larvae during hatchery culture. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, R.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Khan, M.N.; Li, M. Reductions of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters after bacteriophage application during depuration. Aquaculture 2014, 418–419, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Shaila, S.; Park, H.J.; Sul, J.D.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D. Isolation, characterization, and application of bacteriophage on Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm to control seafood contamination. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Madison, D.; Soffer, N.; Needleman, D.S.; Soroka, D.S.; Uknalis, J.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Church, K.M.; Polson, S.W.; et al. Bacteriophages against Vibrio coralliilyticus and Vibrio tubiashii: Isolation, characterization, and remediation of larval oyster mortalities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00008-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, A.; Lu, L.; Dang, H. Isolation and characterization of a novel Vibrio natriegens-infecting phage and its potential therapeutic application in abalone aquaculture. Biology 2022, 11, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, C.S.; Wight, N.; Crosson, L.M.; VanBlaricom, G.R.; Lafferty, K.D. Reduced disease in black abalone following mass mortality: Phage therapy and natural selection. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.S.; Southgate, P.C.; O’Connor, W.; Poole, S.; Kurtböke, D.I. Bacteriophages as biological control agents of enteric bacteria contaminating edible oysters. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Moreirinha, C.; Teles, L.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Calado, R.; Romalde, J.; Nunes, M.L.; Almeida, A. Application of phage therapy during bivalve depuration improves Escherichia coli decontamination. Food Microbiol. 2017, 61, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Ortega, C.O.; Martínez-Díaz, S.F. Phage therapy against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in the whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Stalin, N.; Srinivasan, P. Characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its specific phage from shrimp pond in Palk Strait, South East coast of India. Biologicals 2016, 44, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.W.; Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.J.; Lightner, D.V.; Kim, J.; Seo, S.W.; Park, S.C. Potential application of bacteriophage pVp-1: Agent combating Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, J.W.; Han, J.E.; Giri, S.S.; Tang, K.F.J.; Zhou, X.; Aranguren, L.F.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, S.; Chi, C.; Kim, S.G.; et al. Phage application for the protection from acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Penaeus vannamei. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Sun, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, H. Isolation and characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophage vB_VpaS_PG07. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198080. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Bao, Z.; Wang, M. Characterization and preliminary application of a novel lytic Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophage vB_VpaP_SJSY21. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammatinna, K.; Sinprasertporn, A.; Naknaen, A.; Samernate, T.; Nuanpirom, J.; Chanwong, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Pogliano, J.; Sathapondecha, P.; Thawonsuwan, J.; et al. Nucleus-forming vibriophage cocktail reduces shrimp mortality in the presence of pathogenic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17844. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B.T.N.; Singh, N.K.; Tyagi, A. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages from inland saline aquaculture environments to control Vibrio parahaemolyticus contamination in shrimp. Indian J. Microbiol. 2021, 61, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Lomelí-Ortega, C.O.; Martínez-Sández, A.J.; Barajas-Sandoval, D.R.; Reyes, A.G.; Magallón-Barajas, F.; Veyrand-Quíros, B.; Gannon, L.; Harrison, C.; Michniewski, S.; Millard, A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of vibriophage vB_Vc_SrVc9: An effective agent in preventing Vibrio campbellii infections in brine shrimp nauplii (Artemia franciscana). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Ortega, C.O.; Martínez-Sández, A.J.; Barajas-Sandoval, D.; Magallón-Barajas, F.J.; Millard, A.; Martínez-Villalobos, J.M.; Arechiga-Carvajal, E.T.; Quiroz-Guzman, E. Characterization and complete genome sequence of bacteriophage vB_Vc_SrVc2, a marine phage that infects Vibrio campbellii. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisangthong, I.; Sangseedum, C.; Chaichanit, N.; Surachat, K.; Suanyuk, N.; Mittraparp-arthorn, P. Characterization and Genome Analysis of Vibrio campbellii Lytic Bacteriophage OPA17. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01623-22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raghu Patil, J.; Desai, S.; Roy, P.; Durgaiah, M.; Saravanan, R.; Vipra, A. Simulated hatchery system to assess bacteriophage efficacy against Vibrio harveyi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 112, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalin, N.; Srinivasan, P. Efficacy of potential phage cocktails against Vibrio harveyi and closely related Vibrio species isolated from shrimp aquaculture environment in the south east coast of India. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Benala, M.; Vaiyapuri, M.; Sivam, V.; Raveendran, K.; Mothadaka, M.P.; Badireddy, M.R. Genome characterization and infectivity potential of Vibriophage-ϕLV6 with lytic activity against luminescent vibrios of Penaeus vannamei shrimp aquaculture. Viruses 2023, 15, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, T.G.; Maiti, B.; Venugopal, M.N.; Karunasagar, I. Influence of some environmental variables and addition of r-lysozyme on efficacy of Vibrio harveyi phage for therapy. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, C.; He, Z. Characterization and genomic analysis of a bacteriophage with potential in lysing Vibrio alginolyticus. Viruses 2022, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, C.; He, Z. Characterization of vB_ValM_PVA8, a broad-host-range bacteriophage infecting Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1105924. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, C.; Venail, P.; Holguin, A.V.; Vives, M.J. Co-evolutionary dynamics of the bacteria Vibrio sp. CV1 and phages V1G, V1P1, and V1P2: Implications for phage therapy. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 897–905. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Fan, J.; Yan, T.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Deng, D.; Huang, S.; Ma, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Specific Phages to Prepare a Cocktail Preventing Vibrio sp. Va-F3 Infections in Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2337. [Google Scholar]
- Lomelí-Ortega, C.O.; Barajas-Sandoval, D.R.; Martínez-Villalobos, J.M.; Jaramillo, C.R.; Chávez, E.M.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Balcázar, J.L.; Quiroz-Guzmán, E. A broad-host-range phage cocktail selectively and effectively eliminates Vibrio species from shrimp aquaculture environment. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Kar, P.; Chakrabarti, S.; Pradhan, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Ghosh, K. Whole genome sequence analysis of Aeromonas-infecting bacteriophage AHPMCC7, a new species of genus Ahphunavirus and its application in Litopenaeus vannamei culture. Virology 2023, 588, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, F.; Jin, L.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Effect of Bacteriophages on Vibrio alginolyticus Infection in the Sea Cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). J. World Aquac. Society 2015, 46, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Efficiency of a bacteriophage in controlling vibrio infection in the juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 2016, 451, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Cao, Z.; Xu, Y. Use of phages to control Vibrio splendidus infection in the juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Pastorelli, G.; Tedesco, D.E.A.; Turin, L.; Guerrini, A. Alternative protein sources in aquafeed: Current scenario and future perspectives. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2024, 25, 100381. [Google Scholar]
| Bacterium | Disease | Common Target |
|---|---|---|
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Ulcerations | Various fish |
| Acinetobacter pittii | Ulcerations | Various fish |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Hemorrhagic Septicemia | Various fish |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | Furunculosis | Salmonids |
| Aeromonas veronii | Hemorrhagic Septicemia | Various fish |
| Chryseobacterium balustinum | Columnaris Disease | Various fish |
| Citrobacter freundii | Inflammation, Necrosis | Various fish |
| Cytophaga columnaris | Columnaris Disease | Various fish |
| Edwardsiella ictaluri | Enteric Septicemia | Catfish |
| Edwardsiella piscicida | Edwardsiellosis | Various fish |
| Edwardsiella tarda | Edwardsiellosis | Various fish |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Ulcers, Enteric Inflammation | Flatfish |
| Flavobacterium columnare | Columnaris disease | Various fish |
| Flavobacterium psychrophilum | Bacterial Cold Water Disease | Salmonids |
| Francisella noatunensis | Francisellosis | Atlantic cod |
| Lactococcus garvieae | Lactococcosis | Various fish |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Listeriosis | Various fish |
| Moritella viscosa | Winter Ulcer Disease | Salmonids |
| Mycobacterium fortuitum | Mycobacteriosis | Various fish |
| Mycobacterium marinum | Mycobacteriosis | Various fish |
| Mycobacterium salmoniphilum | Mycobacteriosis | Salmonids |
| Nocardia asteroids | Nocardiosis | Various fish |
| Nocardia seriolqe | Nocardiosis | Yellowtail, Seabass |
| Photobacterium damselae | Photobacteriosis | Various fish |
| Piscirickettsia salmonis | Piscirickettsiosis | Salmonids |
| Plesiomonas shigelloides | Hemorrhagic Ulcers | Various fish |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Ulcers, Hemorrhagic Septicemia | Various fish |
| Pseudomonas anguilliseptica | Red Spot Disease | Eels, various fish |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | Hemorrhagic Septicemia | Various fish |
| Renibacterium salmoninarum | Bacterial Kidney Disease | Salmonids |
| Streptococcus agalatiae | Streptococcosis | Tilapia, various fish |
| Streptococcus iniae | Streptococcosis | Various fish |
| Streptococcus parauberis | Streptococcosis | Various fish |
| Streptococcus phocae | Streptococcosis | Various fish |
| Tenacibaculum maritimum | Tenacibaculosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio anguillarum | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio harveyi | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio kanaloae | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio vulnificus | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Vibrio splendidus | Vibriosis | Various fish |
| Yersinia ruckeri | Enteric Redmouth Disease | Salmonids |
| First Pathogenic Bacterium | Second Pathogenic Bacterium | Common Target |
|---|---|---|
| Aliivibrio wodanis | Moritella viscosa | Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar |
| Edwardsiella ictaluri | Aeromonas hydrophila | Vietnamese catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus |
| Edwardsiella ictaluri | Flavobacterium columnare | Thailand striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus |
| Renibacterium salmonarum | Aeromonas hydrophila | Chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albarella, D.; Dall’Ara, P.; Rossi, L.; Turin, L. Bacteriophage Therapy in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaculture Species. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040831
Albarella D, Dall’Ara P, Rossi L, Turin L. Bacteriophage Therapy in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaculture Species. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040831
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbarella, Deborah, Paola Dall’Ara, Luciana Rossi, and Lauretta Turin. 2025. "Bacteriophage Therapy in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaculture Species" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040831
APA StyleAlbarella, D., Dall’Ara, P., Rossi, L., & Turin, L. (2025). Bacteriophage Therapy in Freshwater and Saltwater Aquaculture Species. Microorganisms, 13(4), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040831








