Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a versatile Gram-negative pathogen that causes various infections in humans. The bacterium possesses a type III secretion system (T3SS) to deliver cytotoxic effector proteins into host cells, which plays an important role in bacterial pathogenesis. The T3SS is regulated by the master regulator ExsA, whose expression is controlled by multiple pathways. Here, we demonstrate that the catabolite repression control protein Crc controls T3SS activity by modulating exsA expression. We find that mutation of crc reduces the intracellular cAMP level by 1.76-fold under T3SS-inducing conditions, leading to approximately 2-fold reduction of the exsA expression. Further investigation reveals that Crc affects the mRNA stability of cyaB, which encodes an adenylate cyclase involved in cAMP synthesis. The cyaB 5′-UTR is identified as a key region through which Crc affects its mRNA stability. Our study elucidates a novel regulatory mechanism by which Crc controls the T3SS through modulating cyaB mRNA stability and subsequent cAMP synthesis under T3SS-inducing conditions.
1. Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic Gram-negative pathogen that causes a variety of nosocomial infections in immunocompromised individuals [1,2]. The bacterium utilizes multiple virulence factors to establish chronic and acute infections [2,3]. The type III secretion system (T3SS) plays a critical role during acute infections [4,5]. It is a syringe-like apparatus that directly injects cytotoxic effector proteins into host cells to counteract immune responses and cause tissue damage [6,7,8].
The activation of T3SS is energetically costly, thus it is subject to tight regulation in response to environmental signals, such as low calcium and host cell contact [9]. ExsA is the master regulator that regulates all the T3SS genes. The exsA gene is localized in the exsCEBA operon [10,11]. Its transcription is driven by its own adjacent promoter and the exsC promoter, which are directly regulated by Vfr in combination with cAMP and ExsA, respectively [12,13]. In P. aeruginosa, intracellular cAMP is synthesized by adenylate cyclases CyaA/CyaB and degraded by the phosphodiesterase CpdA [14,15,16]. It has been demonstrated that CyaB plays a major role in the biosynthesis of cAMP [14]. Additionally, the exsA promoter is directly regulated by the transcription factors PsrA, Fis, and MvaT [17,18,19].
In P. aeruginosa, the Crc protein plays a crucial role in carbon catabolite repression (CCR), ensuring the hierarchical utilization of carbon sources [20]. In the presence of a preferred carbon source, Crc inhibits the use of less-preferred carbon sources by repressing the expression of corresponding enzymes at the posttranscriptional level [21,22]. Crc and the RNA chaperone Hfq form a complex that binds to target mRNAs and represses their translation [23]. The small RNA CrcZ binds to Hfq, alleviating CCR [24]. The expression of CrcZ is controlled by the two-component system CbrA/B [25]. Besides CCR, Crc also influences multiple pathways related to bacterial pathogenesis, such as motility [26], quorum sensing [27,28], biofilm formation [29,30], and the T3SS [22].
Yeung et al. demonstrated that a mutation of crc reduced bacterial cytotoxicity [31]. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses revealed that Crc is required for the expression of the T3SS genes in P. aeruginosa [22,32]. Gil-Gil et al. demonstrated that a mutation of crc reduced the expression of exsA and the bacterial proton motive force (PMF) [33]. However, the mechanism of Crc-mediated regulation of the T3SS remains elusive. The objective of the present research was to determine the mechanism of Crc-mediated regulation on the T3SS and to provide insight on the interconnection between bacterial virulence and metabolism. In this work, we constructed a crc deletion mutant in the wild type reference P. aeruginosa strain PAK [34,35]. Our results revealed that Crc modulates the mRNA stability of cyaB, which then regulates the T3SS through the cAMP-Vfr pathway under T3SS-inducing conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
The bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers utilized in this study are listed in Tables S1 and S2. P. aeruginosa and E. coli strains were grown in the Lysogeny broth (LB) medium with shaking at 200 rpm at 37 °C. Antibiotics were used at the following concentrations: for P. aeruginosa, tetracycline 50 μg/mL, carbenicillin 150 μg/mL, and gentamicin 50 μg/mL; for E. coli, tetracycline 10 μg/mL, kanamycin 25 µg/mL, gentamicin 10 μg/mL, and ampicillin 100 μg/mL.
2.2. Western Blot Assay
Overnight bacteria cultures were diluted into 3 mL fresh LB medium with or without 5 mM EGTA, and cultured to OD600 of 1.0. Bacterial cells and supernatants were collected following centrifugation at 12,000× g for 3 min. The samples were run in a 12% SDS-PAGE gel and then transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. The protein levels were determined using antibodies against ExoS, FLAG (Sigma, Livonia, MI, USA), His (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) or RpoA (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), and HRP-conjugated anti-Rabbit IgG (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) or anti-Mouse IgG (Promega, USA). The signals were detected with an Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP Substrate (Millipore, USA) and a Bio-Rad molecular imager (ChemiDocXRS+, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxicity assay was carried out as previously described with minor modification [36]. A549 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in a 24-well plate at 37 °C in 5% CO2. Log growth phase bacteria (OD600 = 1.0) were resuspended in PBS and used to infect A549 cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 50. Two hours post infection, the dead cells were removed by washing with PBS and the remaining cells were stained with 0.25% crystal violet. After washed twice with PBS, the crystal violet that reflected the number of live cells was dissolved by a destaining buffer (40% methanol, 10% acetic acid) and measured at a wavelength of 595 nm using a Varioskan Flash microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. cAMP Assay
Intracellular cAMP concentration was measured as previously described [37]. Bacteria were grown in LB to an OD600 of 1.0. Then, 1.5 mL of the bacteria were centrifuged at 13,000× g for 2 min at 4 °C, then washed twice with cold 0.9 M NaCl. The pellets were resuspended in 100 μL of 0.1 M HCl, and incubated on ice for 10 min with a vortex. After centrifugation at 13,000× g for 5 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was used to measure cAMP concentration with an ELISA kit (Cayman, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The bacterial protein concentration was measured by a BCA assay (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). The cAMP levels were normalized by protein concentrations.
2.5. RNA Purification and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
RNA purification and quantitative real-time PCR were carried out following the manufacturer’s instructions with minor modifications as described below. Bacteria were grown in LB with or without 5 mM EGTA to OD600 of 1.0. Total RNA was isolated with a Bacteria Total RNA Kit (Zomanbio, Beijing, China). The DNA removal and cDNA synthesis were carried out using HiScript III RT SuperMix (+gDNA wiper) (Vazym, Nanjing, China). RT-qPCR was performed using PerfectStart® Green qPCR SuperMix (Transgen, Beijing, China). The primers used in this study are listed in Table S2. The housekeeping ribosomal gene rpsL was used as the reference gene for normalization. The data are presented as the relative transcript abundance of the indicated genes compared to the internal control transcript for rpsL using the comparative Ct method (2−∆∆CT).
To test the mRNA stability, the bacteria were grown in LB with 5 mM EGTA to the OD600 of 1.0, followed by treatment with 200 μg/mL rifampicin. At each indicated time point after rifampicin treatment, qual numbers of bacterial cells were harvested and mixed with equal numbers of gfp-expressing E. coli cells. Then, the corresponding RNA was extracted for RT-qPCR with gfp as an internal control.
2.6. 5′ Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (5′ RACE) Assay
The 5′ RACE assay was carried out as previously described [38]. Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were carried out as previously mentioned. PolyG was added to the 3′ end of the cDNA using a Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Kit (Takara, Beijing, China). The product was used as a template to amplify the cyaB sequence using primers 5-AP and RACE-cyaB-R (Table S2). The product was purified and used as a template for a second round of amplification using the primers 5-NP and RACE-cyaB-R2 (Table S2). The product was then purified and sequenced to determine the transcription start site.
2.7. β-Galactosidase Assay
The β-galactosidase assay was carried out as described previously with minor modifications [39]. Bacteria from 1 mL of culture were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in 1.5 mL Z-buffer (60 mM Na2HPO4, 40 mM NaH2PO4, 50 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 10 mM KCl, 1 mM MgSO4). Then, 1 mL of the resuspension was used to measure OD600. To the remaining 500 μL resuspension, 10 μL chloroform and 10 μL 0.1% SDS were added. After vortexing for 10 s, 100 μL ONPG (4 mg/mL) was added. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C, and 500 μL 1 M Na2CO3 was added to stop the reaction. The reaction time was recorded. After centrifugation at 16,000× g for 5 min, OD420 was measured. The β-galactosidase activity (Miller units) was calculated as 1000 × OD420/Tmin/VmL/OD600.
2.8. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA). Student’s t-test was used for comparisons in real-time qPCR, cytotoxicity, and β-galactosidase assays. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Crc Regulates the Transcription of exsA
By using a Δcrc mutant in wild type PAK, we verified that Crc is required for the bacterial cytotoxicity and expression of the T3SS effector protein ExoS (Figure S1). Since ExsA functions as a master regulator of the T3SS, we investigated the expression of ExsA. The exsA mRNA level was reduced by the mutation of crc (Figure 1A). Given that the transcription of exsA is driven by both its own promoter and the ExsA-activated exsC promoter, we firstly assessed the ExsA expression by using a 6 × His-tagged exsA driven by the exsA promoter (PexsA-exsA-His). Mutation of crc decreased the ExsA levels in the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure 1B). In addition, a β-galactosidase assay with a PexsA-lacZ transcriptional fusion demonstrated reduced exsA promoter activity in the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure 1C). Meanwhile, overexpression of ExsA increased the expression of ExoS (Figure 1D). Collectively, these results demonstrate that Crc controls the T3SS by regulating the exsA promoter activity.
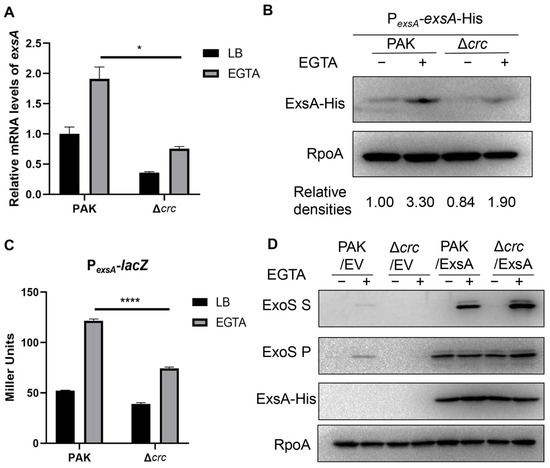
Figure 1.
Crc regulates the transcription of exsA. (A) exsA mRNA levels in PAK and the Δcrc with or without EGTA were determined by RT-qPCR. The fold changes were calculated relative to the expression level in wild type PAK grown in LB. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. *, p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (B) Western blot analysis of the ExsA-His levels in samples prepared from PAK/PexsA-exsA-His and Δcrc/PexsA-exsA-His strains with or without EGTA. RNA Polymerase α subunit (RpoA) served as a loading control. The density of each band was determined with Image J 1.51J8. Relative densities were determined by using RpoA as the internal control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. (C) Promoter activities of exsA were determined by a β-galactosidase activity assay after the bacteria containing PexsA-lacZ transcriptional fusion were grown with or without EGTA. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. ****, p < 0.0001 by Student’s t-test. (D) Western blot analysis of ExsA-His and ExoS in the supernatants and bacterial pellets from indicated strains grown with or without EGTA. RpoA served as a loading control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. S, supernatant; P, pellet; EV, empty vector.
3.2. Crc Regulates ExsA Through the cAMP-Vfr Pathway
The exsA promoter is regulated by multiple transcription factors, including PsrA, MvaT, Fis, and Vfr/cAMP [12,17,18,19]. By using 6 × His-tagged fusions driven by each of their own promoters, we found that the expression of these regulators was not affected by the mutation of crc (Figure S2). We then examined the cAMP levels with a gfp gene driven by the lacP1 promoter, which is regulated by the intracellular cAMP level [37]. The GFP level in the Δcrc mutant was lower than that in the wild type PAK under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure 2A). We then determined the intracellular cAMP levels. In P. aeruginosa, cAMP is synthesized by CyaA, CyaB, and degraded by CpdA [14,15,16,40]. The cAMP synthesis enzyme CyaB was used as a control. ELISA results demonstrated that the cAMP level was reduced in the ΔcyaB mutant and increased in the cyaB-overexpressing strain (PAK/cyaB) (Figure 2B). In the Δcrc mutant, the intracellular cAMP level was reduced under the T3SS-inducing condition (Figure 2B). In addition, supplementation of cAMP increased the expression levels of ExsA and ExoS as well as the cytotoxicity of the Δcrc mutant (Figure 2C,D). Collectively, these results suggest that Crc regulates the expression of exsA by influencing the intracellular cAMP level.
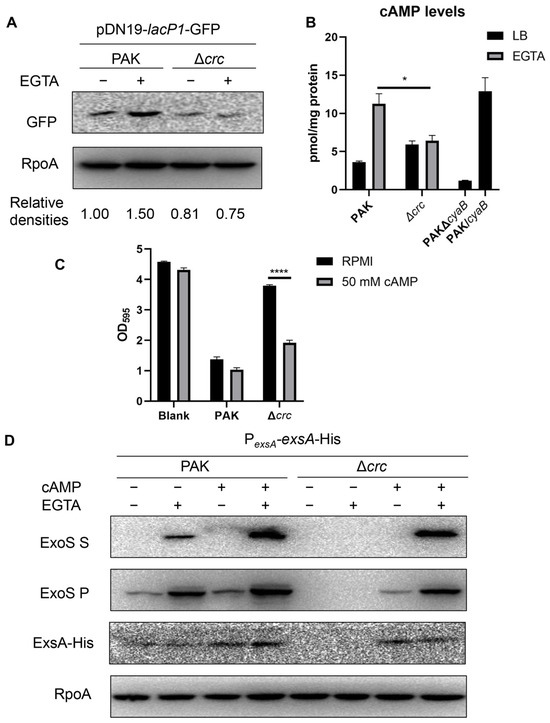
Figure 2.
Crc regulates ExsA through the cAMP-Vfr pathway. (A) Western blot analysis of GFP driven by lacP1 promoter from equivalent bacterial cells. RpoA served as a loading control. The density of each band was determined with Image J. Relative densities were determined by using RpoA as the internal control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. (B) Intracellular cAMP levels of indicated strains. The cAMP levels of indicated strains were measured by an ELISA Kit. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from two samples. *, p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (C) Bacterial cytotoxicity. A549 cells were infected with wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 50 with or without exogenous supplement of 50 mM cAMP. The live cells levels were quantified by crystal violet staining. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. ****, p < 0.0001 by Student’s t-test. (D) Expression of ExoS and ExsA-His in indicated strains with or without 5 mM EGTA and 50 mM cAMP. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. S, supernatant; P, pellet.
3.3. Crc Regulates the cyaB mRNA Stability
To understand the mechanism of the reduced cAMP level, we constructed Flag-tagged CyaA, CpdA, and 6 × His-tagged CyaB driven by their native promoters. Under T3SS-inducing conditions, the expression level of CyaA was similar in wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant (Figure 3A), while the expression level of CyaB was lower in the Δcrc mutant (Figure 3B). Meanwhile, the CpdA level was reduced in the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions, presumably due to the lower cAMP level (Figure 3C), as the expression of cpdA is positively regulated by cAMP [16]. We then overexpressed cyaB in the bacteria, which resulted in similar levels of ExsA (expressed from the PexsA-exsA-His) and ExoS in the Δcrc mutant and wild type PAK (Figure 3D).
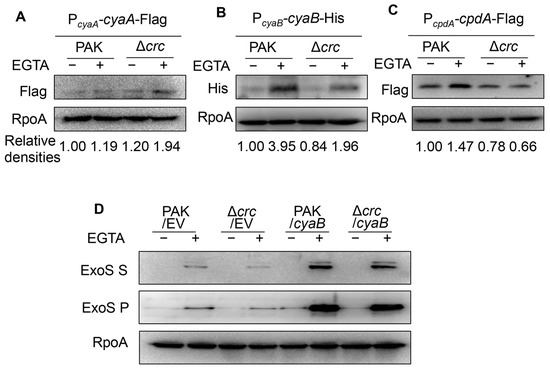
Figure 3.
Crc regulates CyaB. (A–C) Western blot analysis of CyaA (A), CpdA (B), and CyaB (C) in indicated strains grown with or without EGTA. RpoA served as a loading control. The density of each band was determined with Image J. Relative densities were determined by using RpoA as the internal control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analysis of ExoS in indicated strains grown with or without EGTA. RpoA served as a loading control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. S, supernatant; P, pellet; EV, empty vector.
To understand the mechanism of CyaB downregulation, we examined the relative mRNA levels of cyaB by RT-qPCR. The mRNA level of cyaB was lower in the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure 4A). We thus examined the cyaB promoter activity by using a lacZ transcriptional fusion (PcyaB-lacZ) and a 6 × His tagged GST driven by PcyaB (PcyaB-gst-His). The expression levels of both LacZ and GST-His were similar in the wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant (Figure 4B,C), demonstrating similar cyaB promoter activities. These results indicated a posttranscriptional regulation of cyaB by Crc. Thus, we examined the cyaB mRNA stability by RT-qPCR. Under T3SS-inducing conditions, mutation of crc resulted in a faster degradation of the cyaB mRNA (Figure 4D,E), suggesting that Crc affects cyaB mRNA stability.
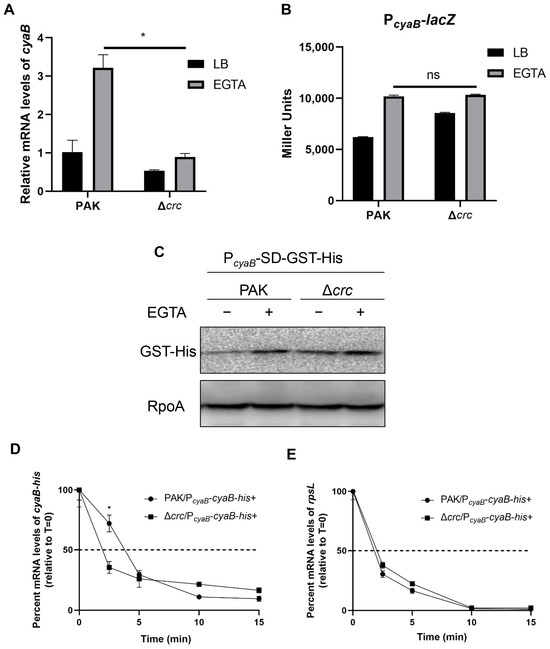
Figure 4.
Crc influences the expression of CyaB at the posttranscriptional level. (A) Relative quantification of cyaB expression in PAK and the Δcrc mutant grown with or without EGTA determined by RT-qPCR. The fold changes were calculated relative to the expression level in wild type PAK grown in LB. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. *, p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (B) Promoter activities of cyaB determined by the β-galactosidase activity assay. Wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant carrying the PcyaB-lacZ transcriptional fusion were grown with or without EGTA, followed by the β-galactosidase activity assay. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. ns, not significant. (C) Western blot analysis of the GST-His in samples prepared from PAK and the Δcrc mutant carrying PcyaB-SD-GST-His grown with or without EGTA. RpoA served as a loading control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. (D,E) Relative quantification of the cyaB-His or rpsL mRNAs by RT-qPCR in rifampicin-treated strains under EGTA-inducing conditions. Data represent the percentage of mRNA transcripts relative to the time point when rifampicin was added. The gfp mRNA level in each sample was used as the internal control for normalization. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. *, p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test.
3.4. Crc Affects cyaB mRNA Stability Through Its 5′-UTR
Since 5′-UTR has been shown to be involved in regulating its mRNA stability, we investigated the role of the cyaB 5′-UTR in the Crc-mediated regulation. A 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′ RACE) assay located the transcription start site (TSS) of cyaB at 85 bp upstream of its start codon (Figure S3). We replaced the 85 bp 5′-UTR sequence in the PcyaB-cyaB-His with a ribosome binding site from the vector pET28a, resulting in PcyaB-SD-cyaB-His. However, the CyaB-His level was diminished, making it difficult to directly compare the protein levels by western blotting. Thus we enriched the CyaB-His protein by Ni-chromatography. In contrast to the lower CyaB-His level from the PcyaB-cyaB-His in the Δcrc mutant, replacing the native 5′-UTR sequence with the exogenous sequence (PcyaB-SD-cyaB-His) resulted in similar levels of CyaB-His in wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure S4A), indicating a role of the native 85 bp 5′-UTR in regulating the cyaB mRNA stability.
To verify the result, we utilized a stronger promoter to drive the expression of the cyaB-His fusions. A previous study demonstrated that the expression of secA is not affected by crc mutation [41]. By using RT-qPCR and a C-terminal 6 × His tagged secA driven by its native promoter (PsecA-secA-His), we demonstrated that the expression of secA is similar between wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions (Figure S4B–D). Then we fused the secA promoter with the cyaB-His with the native and exogenous 5′-UTRs, resulting in PsecA-85-cyaB-His and PsecA-cyaB-His, respectively (Figure 5A,B). The expression of CyaB-His from PsecA-85-cyaB-His was lower in the Δcrc mutant under T3SS-inducing conditions, whereas the expression of CyaB-His from PsecA-cyaB-His was similar in wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant (Figure 5C,D). In addition, the presence of the native cyaB 5′-UTR sequence resulted in lower stability of the cyaB mRNA in the Δcrc mutant, whereas replacement with the exogenous 5′-UTR sequence resulted in similar mRNA stability in the two strains (Figure 5E–H). In combination, these results demonstrate that Crc regulates cyaB mRNA stability through the 5′-UTR region.
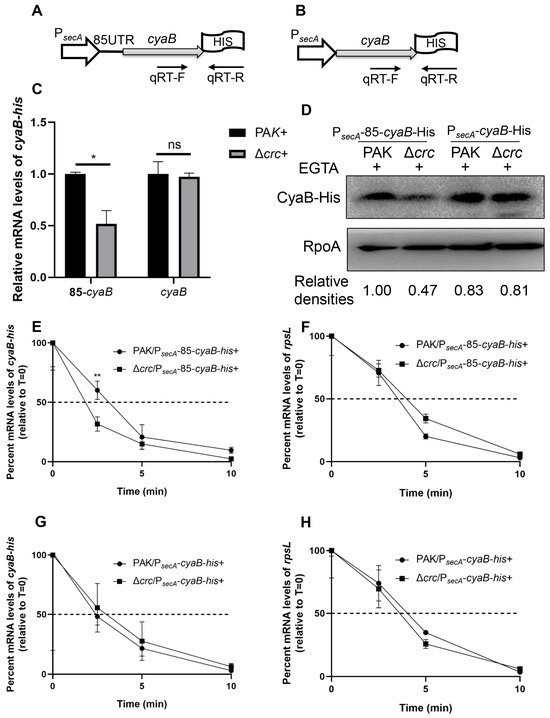
Figure 5.
Crc regulates the cyaB mRNA stability through its 5′-UTR. Schematic diagram of a cyaB-His gene driven by the secA promoter with the cyaB (A) or secA (B) 5′-UTR. The positions of qPCR primers are indicated by arrows. (C) Relative mRNA levels of the cyaB-His in PAK and the Δcrc mutant grown in the presence of EGTA were determined by RT-qPCR. The fold changes were calculated relative to the expression level in wild type PAK. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. *, p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test; ns, not significant. (D) Amounts of CyaB-His. The CyaB-His protein from indicated strains grown with 5 mM EGTA was detected by western blot assay. RpoA served as a loading control. The density of each band was determined with Image J. Relative densities were determined by using RpoA as the internal control. The data shown represent the results from three independent experiments. (E–H) Relative quantification of the cyaB-his or rpsL mRNA by RT-qPCR in rifampicin-treated strains under the EGTA inducing condition. Data represent the percentage of mRNA transcripts relative to the time point when rifampicin was added. The gfp mRNA level in each sample was used as the internal control for normalization. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of the results from three samples. **, p < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.
4. Discussion
In this work, we demonstrated that mutation of crc reduces the cyaB mRNA stability under T3SS-inducing conditions, leading to reduced intracellular cAMP level and defective T3SS. We further demonstrated that the 5′-UTR of cyaB mRNA is involved in Crc-mediated regulation on the mRNA stability. Based on our results, we propose a regulatory model (Figure 6).
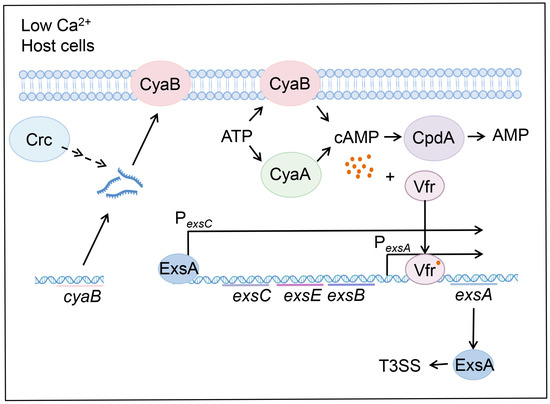
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the Crc-mediated regulation on the T3SS. In P. aeruginosa, CyaA and CyaB synthesize cAMP using ATP as the substrate, CpdA degrades cAMP to AMP. The transcription factor Vfr binds to cAMP and activates the promoter of exsA. exsA is located in the exsCEBA operon, and its transcription is driven by its own adjacent promoter and the exsC promoter. ExsA is the central regulator that controls the expression of all the T3SS genes. Under T3SS-inducing conditions, such as contact with host cells and EGTA-caused calcium depletion, Crc affects the expression of CyaB by influencing the mRNA stability, which subsequently affects cAMP levels, thereby impacting the expression of exsA and the T3SS genes.
Crc is a global regulator controlling CCR that prevents the utilization of less-preferred carbon sources [42]. In Escherichia coli, CCR depends on the phosphotransferase system (PTS) and cAMP-CRP complex [43]. The cAMP levels correspond to glucose availability. In the absence of glucose, the intracellular cAMP concentration is increased, leading to the formation of the cAMP-CRP complex, which activates the alternative catabolic pathways by activating transcription of corresponding genes [44]. Unlike glucose, the preferred carbon source of E. coli, certain organic acids and amino acids are preferred carbon sources of P. aeruginosa [45]. The hierarchy of carbon source preference in P. aeruginosa has been demonstrated. Succinate and malate are at the top of the preferred carbon sources, followed by glucose, citrate or histidine, and then mannitol, oxaloacetate or pyruvate [46,47,48]. Although the P. aeruginosa Vfr is 91% similar to the E. coli CRP and also binds cAMP, it is not required for CCR [49]. The intracellular cAMP level remains similar in response to different carbon sources, indicating that cAMP is not involved in CCR in P. aeruginosa [50]. The distinct CCR mechanisms in E. coli and P. aeruginosa might reflect their adaptation strategies to different ecological niches. For E. coli, the CRP-cAMP mechanism aligns with the feast–famine cycles of the gut, switching to alternative catabolic pathways upon glucose depletion to optimize resource capture [51,52,53]. Conversely, for P. aeruginosa in its nutrient-poor environmental niche, the Crc/Hfq system ensures metabolic efficiency by directly repressing the synthesis of enzymes for less favorable substrates when preferred carbon sources are present [54,55]. Meanwhile, the utilization of organic acids is not only an adaptation to nutrient availability but also a metabolically efficient strategy. These organic acids can be directly utilized in the TCA cycle for energy production or as biosynthetic precursors [45,54,56].
Crc usually functions together with the RNA chaperone Hfq, regulating gene expressions at the posttranscriptional level [20]. Initially, Crc is considered to directly bind to CA rich regions of mRNAs [57,58]. However, further studies have shown that Crc does not directly bind RNA. Instead, Hfq is the protein that binds target mRNAs [23,59]. For example, the aliphatic amidase gene amiE is a typical CCR-regulated gene, whose translation is inhibited by Hfq and Crc [23,24,58,60,61]. The Lon protease mRNA was bound by the complex which represses its translation [28]. Mutation of crc increases the amount of Lon protease, leading to excessive degradation of RhlI and subsequent attenuation of the quorum sensing system [28]. The sRNA CrcZ relieves CCR by binding to Hfq [58]. CrcZ is directly regulated by the two-component system CbrA/B in response to extracellular carbon sources [25]. Besides CrcZ, a CrcA protein interacts with Crc and prevents the formation of the Hfq-Crc complex on target mRNA [62].
Combined transcriptomic and proteomic analyses revealed around 200 Hfq-Crc targets [41,63]. Besides catabolite repression, Crc is involved in the regulation of iron uptake, c-di-GMP metabolism, oxidative stress response, etc. [41,60]. By using a ChIPPAR-seq assay, Kambara et al. identified the potential direct targets of Hfq/Crc, a set ranging from carbon metabolic functions to virulence regulators, which further supports the pleiotropic effects of Crc in coordinating the carbon source utilization and virulence factor expression [64].
Based on the function of Crc, we explored the regulatory mechanism of Crc on the T3SS. We found that in the absence of EGTA, mutation of crc slightly increased the cAMP level. However, the presence of EGTA increased the cAMP level in the wild type strain but not in the Δcrc mutant (Figure 2B). We speculated that, as a catabolite repression control protein, mutation of crc may affect bacterial metabolism, leading to increased cAMP in the LB medium. Meanwhile, Crc is involved in bacterial response to the T3SS inducing signal, such as EGTA-caused calcium depletion. Further research is needed to explore the role of Crc in gene regulation under T3SS-inducing conditions.
CyaB is a member of the class III adenylyl cyclase that produces the secondary messenger molecule cAMP [14,65]. In P. aeruginosa, CyaB rather than CyaA produces the majority of cAMP [14,66]. At the transcriptional level, cyaB is upregulated under T3SS-inducing conditions (EGTA treatment) [14]. However, the signaling mechanism and regulatory genes remain to be elucidated. At the posttranslational level, FimL modulates the CyaB activity [37,67]. It has been demonstrated that c-di-GMP negatively regulates cAMP level [68]. Further studies have demonstrated that c-di-GMP does not affect the expression of CyaA, CyaB or their activities [68]. Here in this work, we demonstrated that the cyaB mRNA stability is regulated by Crc under T3SS-inducing conditions. We further demonstrated that the 5′-UTR region of cyaB is involved in the regulation. Collectively, the expression of CyaB is regulated at multiple levels, which indicates a delicate regulation on the critical messenger molecule cAMP. It is worth noting that the 5′-UTR was also included in the experiments when we detected the promoter activity by using lacZ and gst transcriptional fusions, but no difference was observed between wild type PAK and the Δcrc mutant (Figure 4B,C). We suspect that the presence of exogenous ribosome binding site sequences in front of the reporter genes might affect the secondary structure of the cyaB 5′-UTR, thereby altering its stability. The mRNA stability is regulated by multiple mechanisms. Various nucleases are involved in mRNA degradation, such as endoribonucleases (RNase E and RNase III), exoribonucleases (PNPase and RNase R), and oligoribonucleases (Orn) [69]. The mRNA sequence and/or structure affects its stability by influencing the accessibility of nucleases [70]. sRNAs are involved in regulating mRNA stabilities in response to environmental cues. For instance, the sRNA PhrS stimulates synthesis of the quinolone signal through activating the translation of PqsR in response to oxygen availability [71]. Another sRNA PqsS binds to the pqsL mRNA and destabilizes it through recruiting RNase E [72]. Considering that Crc is a posttranscriptional regulator, it is likely that Crc regulates the expression of CyaB through another protein or sRNA. Further research is needed to investigate the mechanism of Crc-mediated regulation on the cyaB mRNA stability.
On the other hand, while observing a decrease in CyaB and cAMP, we also observed a decrease in CpdA, which confirms that the expression of cpdA is positively regulated by cAMP in couple with Vfr [16]. This feedback mechanism contributes to the homeostasis of cAMP in P. aeruginosa [16]. Our results demonstrated reduction of the CyaB protein level under T3SS-inducing conditions, which might be the major cause that results in the defective T3SS gene expression. However, it is possible that Crc regulates the expression of cpdA through a cAMP independent pathway. Further studies are warranted to examine the possibility.
Disturbances in carbon metabolism affect bacterial virulence through various pathways. For example, mutation of the isocitrate lyase gene aceA results in defective T3SS gene expression [73]. The glucose transport regulator GltR is involved in the regulation of the T3SS genes [74]. How P. aeruginosa balances metabolism and virulence remains unclear. One possible reason is that metabolic changes alter bacterial energy levels. In response, bacteria might coordinate the expression of the energy-costly virulence determinants and survival. The regulation of Crc on the T3SS further verify the interrelationship between bacterial carbon metabolism and virulence. These results indicate that the carbon metabolism pathway can be targeted to inhibit bacterial virulence gene expression. Inhibitors targeting Crc-mediated regulatory pathways or metabolism genes could decrease bacterial virulence without exerting the selection pressure as antibiotics. Such strategy presents a promising approach to delay the development of resistance. In addition, these inhibitors may achieve synergistic effect with antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial infections.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we demonstrated the role of Crc in regulating the cyaB mRNA stability under inducing conditions, which affects cAMP production and subsequent expression of T3SS genes. Our results shed light on the complex regulatory network of the T3SS in response to environmental signals. Further research is needed to elucidate the mechanisms by which Crc regulates mRNA stability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13112587/s1, Figure S1: Crc influences the T3SS; Figure S2: Expression levels of the transcription factors; Figure S3: Identification of the transcription start site of cyaB; Figure S4: The CyaB expression level; Table S1: Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study; Table S2: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.W. and L.Y.; methodology, W.W. and L.Y.; software, J.Q.; validation, L.Y., Y.Z. and Y.L.; formal analysis, L.Y. and X.G.; investigation, L.Y.; data curation, Y.J. and S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.W.; visualization, L.Y.; supervision, W.W.; project administration, W.W.; funding acquisition, W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32170177, 32170199), and the Science and Technology Committee of Tianjin (22JCYBJC00790, 22JCYBJC00560), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Nankai University (2122021405, 63231048, 63241535). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EV | Empty vector |
| UTR | Untranslated Regions |
| T3SS | Type III Secretion System |
References
- Sousa, A.M.; Pereira, M.O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review. Pathogens 2014, 3, 680–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, A.; Coraux, C.; Guillard, T. Current concepts on Pseudomonas aeruginosa interaction with human airway epithelium. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouault, A.; Saliba, A.M.; Touqui, L. Modulation of the immune response by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type-III secretion system. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1064010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.G.; Nieto, V.; Kroken, A.R.; Jedel, E.; Grosser, M.R.; Hallsten, M.E.; Mettrucio, M.M.E.; Yahr, T.L.; Evans, D.J.; Fleiszig, S.M.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Can Diversify after Host Cell Invasion to Establish Multiple Intracellular Niches. mBio 2022, 13, e0274222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horna, G.; Ruiz, J. Type 3 secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, K.S.; Tessmer, M.H.; Frank, D.W.; Audia, J.P. Perspectives on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Effector ExoU and Its Subversion of the Host Innate Immune Response to Infection. Toxins 2021, 13, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Balachandran, P. Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III effectors in disease. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams McMackin, E.A.; Djapgne, L.; Corley, J.M.; Yahr, T.L. Fitting Pieces into the Puzzle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Gene Expression. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.W.; Iglewski, B.H. Cloning and sequence analysis of a trans-regulatory locus required for exoenzyme S synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 6460–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yahr, T.L.; Frank, D.W. Transcriptional organization of the trans-regulatory locus which controls exoenzyme S synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 3832–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, K.H.; Corley, J.M.; Djapgne, L.; Cribbs, J.T.; Voelker, D.; Slusher, Z.; Nordell, R.; Regulski, E.E.; Kazmierczak, B.I.; McMackin, E.W.; et al. Hfq and sRNA 179 Inhibit Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cAMP-Vfr and Type III Secretion Regulons. mBio 2020, 11, e00363-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, A.E.; Intile, P.J.; Schulmeyer, K.H.; Simmons-Patterson, E.R.; Urbanowski, M.L.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Yahr, T.L. Vfr Directly Activates exsA Transcription To Regulate Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfgang, M.C.; Lee, V.T.; Gilmore, M.E.; Lory, S. Coordinate regulation of bacterial virulence genes by a novel adenylate cyclase-dependent signaling pathway. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Expression of the cpdA gene, encoding a 3′,5′-cyclic AMP (cAMP) phosphodiesterase, is positively regulated by the cAMP-cAMP receptor protein complex. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.L.; Brutinel, E.D.; Klem, E.R.; Fehr, A.R.; Yahr, T.L.; Wolfgang, M.C. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cyclic AMP (cAMP) phosphodiesterase CpdA, required for cAMP homeostasis and virulence factor regulation. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2779–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Filopon, D.; Kuhn, L.; Polack, B.; Toussaint, B. PsrA is a positive transcriptional regulator of the type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Li, M.; Pan, X.; Zheng, R.; Liu, C.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, S.; Wu, W. Fis Regulates Type III Secretion System by Influencing the Transcription of exsA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain PA14. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams McMackin, E.A.; Marsden, A.E.; Yahr, T.L. H-NS Family Members MvaT and MvaU Regulate the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Wulf, A.; Campagne, S.; Pei, X.Y.; Wolfinger, M.T.; Forlani, G.; Prindl, K.; Abdou, L.; Resch, A.; Allain, F.H.; et al. Interplay between the catabolite repression control protein Crc, Hfq and RNA in Hfq-dependent translational regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, K.L.; Lehman, J.; Najar, F.; Song, L.; Roe, B.A.; MacGregor, C.H.; Hager, P.W.; Phibbs, P.V., Jr.; Sokatch, J.R. Crc is involved in catabolite repression control of the bkd operons of Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.F.; Moreno, R.; Fajardo, A.; Martínez-Solano, L.; Escalante, R.; Rojo, F.; Martínez, J.L. The global regulator Crc modulates metabolism, susceptibility to antibiotics and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 3196–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecka, E.M.; Bassani, F.; Dendooven, T.; Sonnleitner, E.; Rozner, M.; Albanese, T.G.; Resch, A.; Luisi, B.; Woodson, S.; Bläsi, U. Stabilization of Hfq-mediated translational repression by the co-repressor Crc in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 7075–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Bläsi, U. Regulation of Hfq by the RNA CrcZ in Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbon catabolite repression. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, L.; Chou, H.T.; Haas, D.; Lu, C.D. Promoter recognition and activation by the global response regulator CbrB in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2784–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Gibbs, K.A.; Hager, P.W.; Phibbs, P.V., Jr.; Kolter, R. The global carbon metabolism regulator Crc is a component of a signal transduction pathway required for biofilm development by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Q.; Chen, W.; Qin, H.; Hengzhuang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G. Regulation of pqs quorum sensing via catabolite repression control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 2013, 159, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Ding, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Di, H.; Cao, Q.; Deng, X.; Wu, M.; Wong, C.C.; et al. The Crc protein participates in down-regulation of the Lon gene to promote rhamnolipid production and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 526–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, P.; Tata, M.; Wolfinger, M.T.; Sonnleitner, E.; Häussler, S.; Bläsi, U. Cross-regulation by CrcZ RNA controls anoxic biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.R.; Smiley, M.K.; Asahara Thio, S.; Wei, M.; Florek, L.C.; Dayton, H.; Price-Whelan, A.; Min, W.; Dietrich, L.E.P. Spatial heterogeneity in biofilm metabolism elicited by local control of phenazine methylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2313208120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.T.; Bains, M.; Hancock, R.E. The sensor kinase CbrA is a global regulator that modulates metabolism, virulence, and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, L.H. The global regulator Crc plays a multifaceted role in modulation of type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiologyopen 2013, 2, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gil, T.; Cuesta, T.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Corona, F.; Linares, J.F.; Martínez, J.L. Virulence and Metabolism Crosstalk: Impaired Activity of the Type Three Secretion System (T3SS) in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Crc-Defective Mutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.K.; Bangera, M.; Lory, S.; Ramphal, R. A genomic island in Pseudomonas aeruginosa carries the determinants of flagellin glycosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9342–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet, I.; Olson, J.W.; Lory, S.; Lazdunski, A.; Filloux, A. The chaperone/usher pathways of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification of fimbrial gene clusters (cup) and their involvement in biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6911–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Yin, L.; Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Xu, C.; Ma, Z.; Xia, Y.; Shi, J.; Gong, Y.; et al. RplI interacts with 5′ UTR of exsA to repress its translation and type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulcher, N.B.; Holliday, P.M.; Klem, E.; Cann, M.J.; Wolfgang, M.C. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Chp chemosensory system regulates intracellular cAMP levels by modulating adenylate cyclase activity. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yin, L.; Qin, S.; Sun, X.; Gong, X.; Li, S.; Pan, X.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, S.; et al. Identification of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa AgtR-CspC-RsaL pathway that controls Las quorum sensing in response to metabolic perturbation and Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1013054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Liu, Q.; Pan, X.; Lv, C.; Bai, Y.; Bai, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, W.; Ha, U.H.; Jin, Y. MvaT binds to the PexsC promoter to repress the type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1267748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, F.; Peng, Q.; Weng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Bai, F.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, S.; et al. NrtR Regulates the Type III Secretion System Through cAMP/Vfr Pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, F.; Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Gil, C.; Martínez, J.L. The development of a new parameter for tracking post-transcriptional regulation allows the detailed map of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Crc regulon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gil, T.; Valverde, J.R.; Martínez, J.L.; Corona, F. In vivo genetic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbon catabolic repression through the study of CrcZ pseudo-revertants shows that Crc-mediated metabolic robustness is needed for proficient bacterial virulence and antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0235023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutscher, J. The mechanisms of carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, D.M.; Stabb, E.V. Rethinking the roles of CRP, cAMP, and sugar-mediated global regulation in the Vibrionaceae. Curr. Genet. 2016, 62, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, F. Carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas: Optimizing metabolic versatility and interactions with the environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 658–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwad, K.; Rajkumar, S. Rewiring the functional complexity between Crc, Hfq and sRNAs to regulate carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Paganin, C.; Gilardi, S.; Brignoli, T.; Bertoni, G.; Ferrara, S. Multifaceted Interplay between Hfq and the Small RNA GssA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2023, 14, e0241822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, M.; García-Mauriño, S.M.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Santero, E.; Canosa, I.; Lapouge, K. Hierarchical management of carbon sources is regulated similarly by the CbrA/B systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida. Microbiology 2014, 160, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.J.; Runyen-Janecky, L.J.; Maleniak, T.C.; Hager, P.; MacGregor, C.H.; Zielinski-Mozny, N.A.; Phibbs, P.V.; West, S.E.H. Effect of vfr mutation on global gene expression and catabolite repression control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, L.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Phibbs, P.V., Jr. Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate levels and activities of adenylate cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in Pseudomonas and Bacteroides. J. Bacteriol. 1977, 129, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, A.G.; Ihssen, J.; Egli, T. Effect of Global Regulators RpoS and Cyclic-AMP/CRP on the Catabolome and Transcriptome of Escherichia coli K12 during Carbon- and Energy-Limited Growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Notley-McRobb, L.; Death, A.; Ferenci, T. The relationship between external glucose concentration and cAMP levels inside Escherichia coli: Implications for models of phosphotransferase-mediated regulation of adenylate cyclase. Microbiology 1997, 143 Pt 6, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ihssen, J.; Egli, T. Global physiological analysis of carbon- and energy-limited growing Escherichia coli confirms a high degree of catabolic flexibility and preparedness for mixed substrate utilization. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1568–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, S.L.; Yung, Y.; Hunt, K.A.; Henson, M.A.; Hanley, L.; Carlson, R.P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa reverse diauxie is a multidimensional, optimized, resource utilization strategy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; McGill, S.L.; Arnold, A.D.; Carlson, R.P. Pseudomonad reverse carbon catabolite repression, interspecies metabolite exchange, and consortial division of labor. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görke, B.; Stülke, J. Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: Many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R.; Marzi, S.; Romby, P.; Rojo, F. The Crc global regulator binds to an unpaired A-rich motif at the Pseudomonas putida alkS mRNA coding sequence and inhibits translation initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 7678–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Abdou, L.; Haas, D. Small RNA as global regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21866–21871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojevic, T.; Grishkovskaya, I.; Sonnleitner, E.; Djinovic-Carugo, K.; Bläsi, U. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa catabolite repression control protein Crc is devoid of RNA binding activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, F.; Martínez, J.L.; Nikel, P.I. The global regulator Crc orchestrates the metabolic robustness underlying oxidative stress resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.Y.; Dendooven, T.; Sonnleitner, E.; Chen, S.; Bläsi, U.; Luisi, B.F. Architectural principles for Hfq/Crc-mediated regulation of gene expression. Elife 2019, 8, e43158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Bassani, F.; Cianciulli Sesso, A.; Brear, P.; Lilic, B.; Davidovski, L.; Resch, A.; Luisi, B.F.; Moll, I.; Bläsi, U. Catabolite repression control protein antagonist, a novel player in Pseudomonas aeruginosa carbon catabolite repression control. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1195558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Corona, F.; Monteoliva, L.; Gil, C.; Martínez, J.L. Quantitative proteomics unravels that the post-transcriptional regulator Crc modulates the generation of vesicles and secreted virulence determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Data Brief 2015, 4, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kambara, T.K.; Ramsey, K.M.; Dove, S.L. Pervasive Targeting of Nascent Transcripts by Hfq. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topal, H.; Fulcher, N.B.; Bitterman, J.; Salazar, E.; Buck, J.; Levin, L.R.; Cann, M.J.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Steegborn, C. Crystal structure and regulation mechanisms of the CyaB adenylyl cyclase from the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 416, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Lory, S. An adenylate cyclase-controlled signaling network regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence in a mouse model of acute pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inclan, Y.F.; Huseby, M.J.; Engel, J.N. FimL regulates cAMP synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almblad, H.; Harrison, J.J.; Rybtke, M.; Groizeleau, J.; Givskov, M.; Parsek, M.R.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. The Cyclic AMP-Vfr Signaling Pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Inhibited by Cyclic Di-GMP. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2190–2200, Erratum in J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, M.P.; Foley, P.L.; Belasco, J.G. Messenger RNA degradation in bacterial cells. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2014, 48, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Joshi, M.; Wang, A.; Myong, S. 5′UTR G-quadruplex structure enhances translation in size dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnleitner, E.; Gonzalez, N.; Sorger-Domenigg, T.; Heeb, S.; Richter, A.S.; Backofen, R.; Williams, P.; Hüttenhofer, A.; Haas, D.; Bläsi, U. The small RNA PhrS stimulates synthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Bi, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Ren, A.; Li, S.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Hfq-binding small RNA PqsS regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa pqs quorum sensing system and virulence. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.C.; Rzhepishevska, O.; Ramstedt, M.; Welch, M. Type III secretion system expression in oxygen-limited Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures is stimulated by isocitrate lyase activity. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 120131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, J.; Reen, F.J.; Adams, C.; Casey, P.G.; Gahan, C.G.M.; O’Gara, F. A novel host-responsive sensor mediates virulence and type III secretion during Pseudomonas aeruginosa-host cell interactions. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).