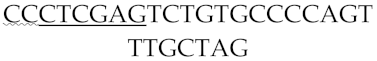Abstract
The Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas is one of the most important cultured marine species around the world. Production of Pacific oysters in China has depended primarily on hatchery produced seeds since 2016, with the successful introduction and development of triploid oysters. However, the seed supply of Pacific oysters is threatened by recurring mass mortality events in recent years. Vibriosis is the most commonly encountered disease associated with intensive oyster culture in hatcheries and nurseries. Vibrio alginolyticus and Bacillus hwajinpoensis were the two strains with pathogenic and probiotic effects, respectively, identified during the Pacific oyster larvae production. To monitor their colonization process in Pacific oyster larvae, green fluorescent protein (GFP) and red fluorescent protein (RFP) were labeled to the pathogenic V. alginolyticus and the probiotic B. hwajinpoensis stain, respectively. The pathogenic and probiotic effects of the two strains during the colonization process were then assessed. Stabile expression of GFP and RFP were observed in corresponding stains, and the capabilities of growth, biofilm formation and in vitro adhesion of GFP- and RFP- tagged stains were not significantly different from those of the wild-type strains. Usage of probiotics of 105 CFU/mL significantly inhibited the growth of pathogenic V. alginolyticus and reduced the mortality of D-sharped larvae. Both the pathogenic and probiotic strains employed a similar route to enter and colonize the oyster larvae, which indicates that competing with pathogens for binding and spreading sites were one of the mechanisms of B. hwajinpoensis to provide the probiotic effects to oyster larvae. In summary, employment of fluorescence-tagged pathogenic and probiotic strains simultaneously provides us with an excellent bioassay model to investigate the potential mechanisms of probiotics.
1. Introduction
The Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas, also referred to as Magallana gigas, is a bivalve mollusk originally distributed in Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, and Sakhalin Island [1]. As the potential for rapid growth and tolerance of a wide range of environmental conditions, the species has been introduced for cultivation in many coastal areas of North and South America, Europe, Australia and East Asia [2]. The production of Pacific oysters has increased rapidly in recent years in China, and reached 1.46 million tons in 2018 [3]. The Pacific oyster aquaculture relied on diploid seeds before 2016 in China, which were primarily collected from local waters where oyster aquaculture is practiced [4]. In recent years, the triploid oysters were successfully developed in China, and widely embraced by farmers [4]. It is estimated that the production of triploid oysters has accounted for over 70 percent of the production in China [5]. Because the triploid pacific oyster is generally sterile, the seed supply depends completely on hatchery production. To meet the huge demands for triploid oyster seeds, the bivalve hatcheries have expanded rapidly, which has brought new threats to the industry [6]. This is due to, as all researchers and practitioners have noted, more frequent occurrences of production failure of oyster seeds [4]. Mass hatchery crashes have caused shortages in seed oysters for commercial shellfish producers. Epidemiological investigation of hatchery epidemics indicated that Ostreid herpesvirus 1 (OsHV-1), Vibrio algniolyticus, Vibrio mediterranei, and Pseudoalteromonas spp. were the potential pathogenic microorganisms [6,7,8,9]. The poor facilities to eliminate pathogens from seawater, poor biosecurity concepts during the operation, and management were assumed to be responsible for the insufficiency of disease prevention [6,10].
Hatchery production of bivalves constitutes several activities that are highly susceptible to bacterial contamination, which includes introduction of broodstocks, phytoplankton, and seawater to the cultivation system [11]. This is because microorganisms, including pathogenic Vibrio spp., were natural component of coastal waters, which makes them difficult to avoid [12]. Vibriosis disease, caused by various Vibrio species, is reported as the most common disease in association with mass mortality in bivalve hatcheries [13]. Bacillary necrosis associated with Vibrio tubiashii infection (reclassified as Vibrio coralliilyticus latterly [14]) has been responsible for major hatchery crashes of oysters since 1965 [15,16,17]. According to the summary of Dubert et al. (2017), 12 Vibrio species of 6 clades have been identified as the etiological agent responsible for the larval and spat mortalities of different hatchery cultured bivalve species worldwide. The antibiotics have been applied to kill or inhibit pathogenic Vibrio growth [13,15]. While the overall effect of antibiotics varies considerably among cases, antibiotic usage is discouraged because of bacteria’s potential development of resistance and negative impacts on healthy microbiota [18,19].
Probiotics are live microorganisms that are intended to have health benefits to the host when consumed or applied in adequate amounts [20]. The beneficial effects of probiotics have not only been linked to human health, but also widely recognized by livestock and aquaculture production [21]. Candidate probiotics from over 17 genera have been developed for use during the early stages of bivalve development in hatchery and nursery [22,23,24]. Several studies investigated certain mechanisms behind the beneficial effects, such as pathogen inhibition, secretion of antimicrobials, immunomodulation, host growth promotion, competition for nutrients with pathogens, and improvement of water quality [22,23,25]. For example, Phaeobacter inhibens S4 (S4) and Bacillus pumilus RI06–95 (RI) protect larval Eastern oysters (Crassostrea virginica) from Vibrio coralliilyticus RE22 infection through different mechanisms [19,26]. The health benefits of S4 were derived from biofilm formation, secretion of the antibiotic tropodithietic acid, quorum quenching, and host immune modulation [25,27,28]. Mechanisms of RI include stimulating the immunity and promoting enhanced digestion in oysters [26,28]. Vibrio strain OY15 improved the survival of Eastern larval oysters by immuno-stimulation of oyster hemocytes [29,30].
The pathognomonic signs and infection process of Vibriosis in bivalve larvae were firstly investigated by means of histological observation [15]. Subsequently, immunohistochemical staining was employed to detected the colonization sites in great scallop (Pecten maximus) larvae [31]. But histological and immunohistochemical staining approaches could not trace the colonization process of specific bacteria [31]. Itis difficult to estimate the distribution and loads of pathogens at different time-points post infection. Fluorescent proteins allow direct observation of molecular processes in living systems and are therefore widely used in biochemistry, cell biology, and microbiology [32]. The main fluorescent protein currently used is green fluorescent protein (GFP), and the labelling method is well established and widely used [33]. GFP was firstly used to trace the colonization process of bacteria in bivalve larvae of Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) [34], then Chilean scallop (Argopecten purpuratus) [35], and blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) [36]. The results demonstrated that the microvilli and cilia of the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract were the first to be destroyed by Vibrio and these sites were the most sensitive to Vibriosis [36]. The colonization routes of bacteria in these larvae could be defined to three stages [34,36]. At the first stage, the bacteria were filtrated through the vellum, and entered the stomach through the esophagus. Then, the bacteria diffused to the surrounding organs localized in the dorsal and ventral regions, and finally, the whole visceral mass [34]. Pathological signs characterized by necrosis of digestive organs and disorganized cilia were correspondingly observed along the colonization process [13]. However, the processes of bacterial colonization and infection in oyster larvae have not been investigated using the labeling method according to our knowledge.
Previously, we isolated a strain of Bacillus hwajinpoensis from healthy Pacific oyster larvae, which showed typical features of potential probiotic candidates. It exhibited anti-Vibrio activity and increased oyster larvae survival when challenged with V. algniolyticus. However, the mechanisms by which the probiotic B. hwajinpoensis enters the oyster, spreads among individuals, or interacts with the pathogenic V. algniolyticus remain thus far almost unknown. In this study, we tagged the probiotic B. hwajinpoensis with red fluorescent protein (RFP) and the pathogen V. algniolyticus with green fluorescent protein (GFP). Subsequently, we investigated the colonization process of these strains in Pacific oyster larvae. Finally, we assessed the bacterial inhibition effects and probiotic effects of B. hwajinpoensis on the larvae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
The pathogen, V. alginolyticus CD, was isolated from the diseased C. gigas larvae, and its pathogenicity had already been verified in a previous study [6]. The probiotics, B. hwajinpoensis RC, were selected from healthy C. gigas larvae, exhibiting anti-Vibrio activity and beneficial effects on the survival of oyster larvae [6]. Both strains used in this study were cryopreserved isolates stored at −80 °C. To facilitate recovery, the strains were inoculated in 2216E medium containing 5 g/L tryptone, 1 g/L yeast extract, and 0.01 g/L FePO4. The inoculation process took place at 28 °C.
2.2. Construction of Plasmids, GFP/RFP-Tagged Strains
The plasmid preparation, extraction of DNA fragments from agarose gels, and purification of PCR products were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions of the relevant kits (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China).
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) and the Turbo red fluorescent protein (RFP) with gene lengths of 720 bp and 696 bp, respectively, were employed as reporter proteins. To reach higher GFP and TurboRFP expression efficiency, a double promoter Ptrc-T7 plasmid was constructed using the plasmids pET28a and pTrcHis A [37]. Briefly, the promoter Ptrc was amplified from the template pTrcHis A using the primer pair PTrc-F and PTrc-R (Table 1), and then ligated to the plasmid pET28a. For the generation of the recombinant plasmid pET28a-PTrc-T7-GFP and pET28a-PTrc-T7-RFP, the complete sequences of the GFP and TurboRFP genes were amplified from the plasmids pEGFP and pRFP-C-RS (Clontech, Fitchburg, WI, USA) using the primer pairs GFP-F/GFP-R and RFP-F/RFP-R respectively (Table 1). The amplified complete genes were then ligated to pET28a-Ptrc-T7 vector using T4 DNA ligase, which had been digested by NcoI and XhoI. Subsequently, the recombinant plasmids were transformed into Escherichia coli S17-1λpir (AngYu Bio, Shanghai, China) to obtain S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP and S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-RFP.

Table 1.
All primer sequences and reaction conditions used in this study.
2.3. Bacterial Conjugation and Selection
To obtain the antibiotics required for strain fusion and screening, drug sensitivity tests were carried out on the pathogenic V. alginolyticus CD and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC using 6 antibiotics. Bacterial conjugation was performed followed the procedure described in a previous study [33]. Briefly, the donor strains S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP and S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-RFP were grown overnight in LB medium containing 50 μg/mL kanamycin at 37 °C. The recipient strains (V. alginolyticus CD and B. hwajinpoensis RC) were grown overnight in 2216E medium containing 200 μg/mL of the screening antibiotic at 28 °C. Each liquid culture was then collected and washed with PBS, both strains were resuspended in 2216E medium at a concentration of 1 × 108 colony forming units (CFU)/mL. Two sets of donor and recipient strains, including S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP × V. alginolyticus CD and S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-RFP × B. hwajinpoensis RC, were mixed at a ratio of 3:1 (v/v) in a total volume of 2 mL. The mixtures were then centrifuged 100 revolutions per minute (RPM) to promote coupling, then the centrifuging sediments were resuspended and cultured for 6 h at 28 °C. Subsequently, the mixtures were diluted in 103, 104, and 105 folds, and 100 μL of each dilution, and spotted onto a fresh 2216E agar plate supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin and 200 μg/mL of the screening antibiotics. After being incubated at 28 °C for 48 h, DNA was extracted from colonies of each mixture. For the validation of successful conjugation, PCR amplification was performed with the primer pairs GFP-F/GFP-R and RFP-HF/RFP-HR, respectively. Then, the colonies grown on double antibiotics were observed using fluorescent microscope (Olympus CK40, Tokyo, Japan). Finally, the strains were further identified by sequencing of the 16S rRNA amplification with the primers 27F and 1492R.
2.4. Measurement of Bacterial Growth
To assess the impact of the presence of GFP and RFP genes on V. alginolyticus and B. hwajinpoensis, the growth of the GFP/RFP-tagged and wild-type strains were measured and compared as described in a previous study [38]. Briefly, a single colony of each strain was selected and cultured continuously in 200 µL of 2216E medium without antibiotics at 28 °C for 20 h. The cell density of 3 independent samples were characterized in 2 h intervals by monitoring the absorbance at 600 nm using microbial high-throughput growth curve detector (Bioscreen C, Oulu, Finland). One-way ANOVA in GraphPad Prism software (Version 9.0) was used to determine the significant differences between the control and treatment groups, with a significance level set at 5%.
2.5. Measurement of Bacterial Fluorescence Stability
To assess the stability of fluorescence expression in GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus and RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis, the fluorescence intensity in both strains was measured over a period of 12 days, with measurements taken at one-day intervals [38]. Briefly, the GFP/RFP-tagged strains were cultured overnight at 28 °C in 2216E medium supplemented with antibiotics to ensure 100% plasmid preservation and prevent contamination. A 100 µL solution was then serially diluted in a 105 folds and spread onto fresh 2216E plates without antibiotics, followed by 3 independent samples that were incubated at 28 °C for 48 h. The number of fluorescent colonies and non-fluorescent colonies were determined by examining them under a fluorescence microscope and calculating their percentage relative to the total bacterial count. Then, each day, a new culture was initiated using a fluorescent colony from the previous day, and this process was continued for 12 days.
2.6. Determination of Bacterial Biofilm Formation Capability
The biofilm assay was performed using the microtiter dish method described in a previous study with minor modifications [39,40]. Briefly, a single colony of GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus and RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis were individually selected and grown in 2216E medium without antibiotics for 12 h at 28 °C. The GFP/RFP-tagged strains were then washed 3 times with PBS and diluted in 200 µL of PBS. The bacterial suspension was added to 96-well plates and allowed to adhere for 6 h. After washing 3 times with PBS, 200 μL of 0.1% crystal violet dye was added to each well for 30 min. Next, 200 µL of 95% ethanol was added to each well and incubated on a shaker for 1 h to fully dissolve the attached crystal violet. Finally, the extent of biofilm formation was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 570 nm using Varioskan® Flash enzyme markers (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.7. Determination of Bacterial In Vitro Adhesion Capability
The adhesion efficiency of bacteria to slides was evaluated by bacterial cell counts [40,41]. Briefly, the fluorescent strain and wild-type were separately incubated until reaching an OD600 of approximately 0.5. The bacterial cultures were centrifuged and washed with PBS 3 times. Then 100 mL of each strain was placed onto sterile slides, and incubated for 6 h to achieve full adherence. The excess liquid was removed, and washed with PBS for 10 min to remove non-adhered cells. Adhered cells were eluted using an elution solution and diluted 103-fold, plated on 2216E plates and incubated at 28 °C for 48 h. The adhesion capability was determined by counting the number of colonies appearing on the plates.
2.8. Colonization Process and Probiotic Effects
The colonization and infection process of GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp and RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp was assessed using the challenge method described in a previous study with minor modifications [42]. Briefly, a size of 60–80 μm C. gigas D-shaped larvae were placed on 12-well plates of containing sterile seawater at a density of 15–20 larvae per well. RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp were inoculated in 12-well plates at a final concentration of 1 × 105 CFU/mL. 6 h later, GFP-tagged and wild-type strains of V. alginolyticus were inoculated at a final concentration of 1 × 103 CFU/mL. D-shaped larvae inoculated only with wild-type V. alginolyticus were used as the positive control, while uninoculated D-shaped larvae served as the negative control. The D-shaped larvae were incubated at 25 °C for 48 h. The larvae morbidity and integrity were examined using an inverted microscope (Olympus CK40, Shinjuku, Japan). Bacterial infection of the D-shaped larvae was observed and photographed using epifluorescence microscopy (40×) every 6 h, and larvae were considered dead if there was no movement. Fluorescence images showing the coexistence of GFP and RFP were acquired using the Image J software (https://imagej.nih.gov/). The enumeration of Vibrios in the seawater was performed using TCBS (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salts Sucrose) agar culture plates.
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Fluorescent Strains
To construct the GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp and RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp, an antibiotic marker of both strains was selected. The sensitivity of both strains to six antibiotics is presented in Table 2. The V. alginolyticus CD and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC exhibited resistance to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin, respectively, while both were sensitive to kanamycin. Therefore, ampicillin and ciprofloxacin were selected as the screening antibiotics. Then an exogenous DNA fragment containing Ptrc-GFP and Ptrc-RFP was successfully introduced to S17-1λpir, respectively, using the plasmid pET28a with kanamycin resistance as a carrier vector. Finally, the GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp and RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp were successfully constructed by the conjugation of S17-1λpir containing GFP and RFP genes and respective recipient strains.

Table 2.
Results of drug sensitivity test of recipient strain and donor strain.
Strong fluorescence was observed under fluorescence microscopy in the GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp, RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp, and S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP/RFP (Figure 1). Furthermore, the colony PCR products displayed discernible bands on the gel electrophoresis. Nevertheless, the intensities of these gel electrophoresis bands of the recipient cells were comparatively lower than those of the donor cells (Figure 2). Through the amplification of the colonies using 16s rRNA primers, it was confirmed that both strains were the target strains, and no contamination was detected.
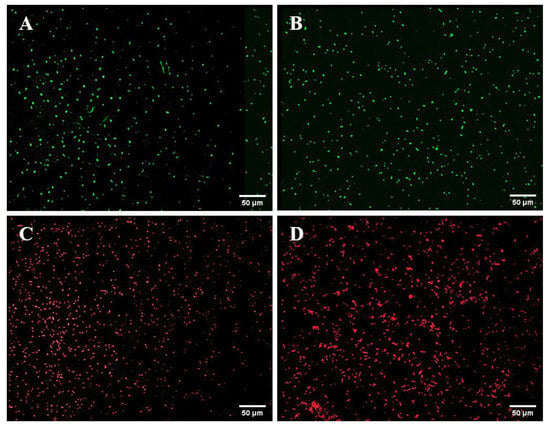
Figure 1.
Observation of GFP-tagged and RFP-tagged strains using the fluorescence microscope: (A) S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP; (B) GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp; (C) S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-RFP; (D) RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp.

Figure 2.
Gel electrophoresis bands of the fluorescent bacteria: (A) GFP-tagged strains. 1: S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-GFP; 2~5: GFP-tagged V. alginolyticus CDgfp; (B) RFP-tagged strains. 1–3: S17-1λpir/pET28a-Ptrc-T7-RFP; 4~5: RFP-tagged B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp.
3.2. Growth Capability and Fluorescence Stability of the Fluorescent Strains
The growth curves of the fluorescent V. alginolyticus CDgfp, B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp, and their respective wild-types were measured under the same culture conditions. Both the tagged strains and wild-types reached the exponential growth period at about 4 h post cultivation. The GFP- and RFP-tagged strains showed a relative low OD600 compared to their counterparts. After 20 h of growth, all cultures eventually reached the same biomass (Figure 3A). Although the OD600 values of FP-tagged strains were slightly lower than those of the wild-type at some time points, no significant differences were detected by ANOVA analysis. The results indicated that there was no significant difference in the growth capability of the GFP/RFP-tagged strains and respective wild-types at 28 °C.
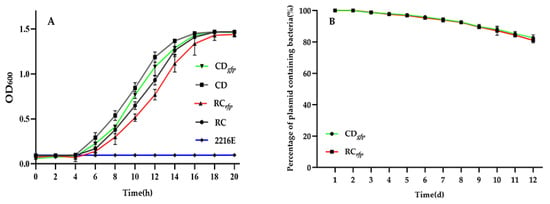
Figure 3.
Evaluation of the biological functions of the fluorescent bacteria: (A) Growth curve of the wild-type strain and fluorescent strain at 28 °C in 2216E medium; (B) Plasmid retention in bacterial strains over time in 2216E medium. Data are the means of three independent experiments and are presented as the means ± SD.
Our GFP/RFP-tagged strains will be utilized to track the bacteria within the oyster larvae. In order to visualize them throughout the infection process, it is essential for the GFP and RFP encoding plasmids to retain stable under nonselective growth conditions. As depicted in Figure 3B, the GFP and RFP genes demonstrated efficient expression in V. alginolyticus CDgfp and B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp over a continuous period of 12 days. Furthermore, 82% of the fluorescent bacteria maintained a high fluorescence level at day 12. These findings indicate that the exogenous GFP and RFP genes were able to persist through multiple passages in a medium without antibiotics. These results showed that the constructed GFP/RFP-tagged strains could meet the requirement for observing bacterial colonization in the larvae over a 7-day period.
3.3. Biofilm Formation and In Vitro Adhesion of the Fluorescent Strains
Crystalline violet staining was conducted to assess biofilm formation in both fluorescent bacteria and wild-type strains. OD570 values of the blank group (PBS) and wild-type strains (CD and RC) were 0.1379 ± 0.0122, 0.3395 ± 0.0132, and 0.4932 ± 0.0192, respectively, which indicated that both of the wild-type strains were capable of forming biofilms. For V. alginolyticus CDgfp and B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp, the OD570 values were determined to be 0.2924 ± 0.0268 and 0.5112 ± 0.0145, respectively. The number of biofilms formed by the fluorescent strains did not significantly differ from those formed by the wild-type strains (Figure 4A). These results suggested that the introduction of GFP and RFP genes did not have a substantial impact on biofilm formation.
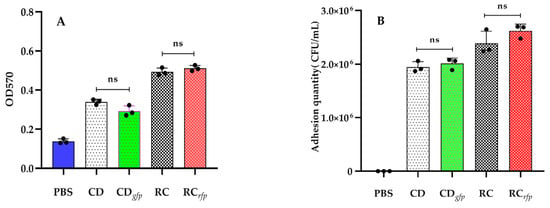
Figure 4.
Indicators of colonization capability of the fluorescent bacteria: (A) Biofilm formation of blank control (PBS), wild-type (CD, RC) and fluorescent strains (CDgfp, RCrfp); (B) The adhesion of blank control (PBS), wild-type (CD, RC) and fluorescent strains (CDgfp, RCrfp) to slide demonstrated by fluorescence colony counting. Data are the means of three independent experiments (•) and are presented as the means ± SD. ns: no significant difference (p > 0.05).
To evaluate the adhesion efficiency of the fluorescent strains to slides, plate colony counting and fluorescence microscopy were employed in this study. The wild-type strains (CD and RC) achieved adhesion levels of 1.95 ± 0.10 × 106 CFU/mL and 2.39 ± 0.23 × 106 CFU/mL, whereas the fluorescent strains (CDgfp and RCrfp) achieved levels of 2.01 ± 0.10 × 105 CFU/mL and 2.62 ± 0.12 × 105 CFU/mL, respectively. The results indicated that the B. hwajinpoensis exhibited relatively higher adhesion to the slides compared to the V. alginolyticus. The fluorescent strains (CDgfp and RCrfp) and corresponding wild-type strains (CD and RC) showed no significant difference in the adhesion ability (Figure 4B).
3.4. Colonisation Process and Effect on Survival of Fluorescently Tagged Strains in C. gigas D-Sharped Larvae
The colonization process of V. alginolyticus CDgfp and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp in C. gigas D-sharped larvae at 25 °C was observed. The larvae were healthy at the start of infection (0 h). By 4 h of infection, fluorescent bacteria start to adhere and accumulate around the larvae (Figure 5 Stage I). Between 6–8 h of infection, the bacteria entered the digestive organs of the larvae, such as the stomach and intestine, through the esophagus and established colonization in these areas (Figure 5 Stage II). From 12–18 h of infection, the bacteria spread from the dorsal to the abdomen (Figure 5 Stage III). By 22–24 h of infection, the fluorescence intensity in the larval abdomen increased significantly and some bacteria fully colonized the larval (Figure 5 Stage IV). The peak of bacterial colonization was reached at 30–36 h of infection (Figure 5 Stage V).

Figure 5.
Colonization process of fluorescently tagged bacterial in D-shaped larvae under a fluorescence microscope. bs: bacterial swarming; dg: digestive gland; i, intestine; u: umbo; vr: ventral region.
After administration of V. alginolyticus CDgfp, the larvae did not display any noticeable signs of illness until the early stage II (6 h) (Figure 6). The concentration of bacteria around the larvae increased steadily during the late stage II and early stage III (8–10 h). At this point, the initial symptoms became apparent, characterized by reduced mobility. By 18–24 h post-infection (late stage III and stage IV), the structure changes were evident in organs such as villi, cilia, and the stomach interior. Larvae mortalities were also initiated at 8 h post-infection, and reached 92.48% and 100% at about 24 h and 36 h post-infection, respectively (Figure 7A). Bacterial colonization, disrupted, and disintegrated larval soft tissues could be observed frequently in and around dying and dead larvae in this period (Figure 6). The larvae treated by both B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp and V. alginolyticus CDgfp displayed mortality rates of 45.71%, 56.39% and 65.76% at 24 h, 36 h and 48 h, respectively. These mortality rates were significantly lower than those observed in the V. alginolyticus CDgfp treatment group (Figure 7A). The negative control group exhibited no significant symptoms, with average mortality rates of 6.89%, 7.81% and 10.71% at 24 h, 36 h and 48 h, respectively.

Figure 6.
Main symptoms of pathogenic activity of V. alginolyticus CDgfp on experimentally infected C. gigas D-sharped larvae.

Figure 7.
Pathogenic and probiotic effects of B. hwajinpoensis RCrfp and V. alginolyticus CDgfp on D-sharped larvae: (A) Survival of C. gigas D-sharped larvae in the challenged and control groups; (B) Vibrio levels in seawater during larval challenge experiments. Data are the means of three independent experiments and are presented as the means ± SD.
Larvae inoculated with V. alginolyticus exhibited an increasing levels of V. alginolyticus over 48 h. At 48 h, the average concentration of V. alginolyticus in the water was recorded as 0.67 × 104 CFU/mL. The V. alginolyticus level at 48 h was 5.48 times higher than that of 0 h (Figure 7B). On the other hand, the levels of V. alginolyticus were relatively stable over 48 h, when B. hwajinpoensis RC was present along with V. alginolyticus. These results indicated that probiotics exhibited an inhibitory effect on the growth of V. alginolyticus in larvae (Figure 7B).
4. Discussion
The Pacific oyster is one of the most important cultured marine species, with a high value and strong market demand around the world. It is estimated that the production of triploid Pacific oyster seeds increased from about 2.3 billion in 2018 [43], to about 60 billion in 2022 in China (Zhang, personal communication). Hatchery production of the triploid oyster seed is crucial for ensuring a constant and sufficient supply of juveniles to support the oyster industry. Changes in environmental conditions and disease outbreaks caused by pathogenic Vibrio spp. have constituted the main threats to the hatchery production process [13]. In an effort to maintain a healthy cultivation system, bivalve hatcheries try their best to maintain optimum water quality by controlling larval culture density, the use of water treatment systems and renewing the waters at a suitable frequency, according to experience [44]. Filtration, combined with UV-sterilization or ozone, has been recommended as the preferred method to sterilize all or part of the seawater before use [45]. However, the traditional breeding facilities and technologies for bivalve hatcheries were still widely employed for production in China [46]. These breeding methods were developed in the 1980s, which were characterized by poor facilities and management practices [46]. Before being introduced to the hatchery, the seawater from the open sea nearby was always only treated by flowing through once or twice of sand filter tanks. Vibrios including the potential pathogenic V. alginolyticus and V. mediterranei, are ubiquitous in marine and estuarine aquatic systems [6,9,47]. It is impossible to eliminate the potential pathogenic microorganisms from the bivalve hatcheries [7,9,47]. Moreover, there are always no biosecurity protocols, hygiene plans, or risk-based surveillance schemes for these family-style bivalve hatcheries in China [46]. The diseased larvae and hatchery effluents are always discharged directly into drains connecting to the open sea. It is common to find dozens of bivalve hatcheries densely distributed along the coastline, which will definitely exacerbate the spread of infectious diseases. All these factors combined together make pathogenic bacteria a major problem for hatchery production, and cause severe diseases and high mortality, which seriously affect hatchery production and cause significant economic loss. Antimicrobial agents have been employed for the control and treatment of bacterial disease in mollusk hatcheries. However, the use of antibiotics may lead to the rapid development of resistant pathogen populations, the elimination of beneficial organisms and the emergence of other microbial pathogens [15,16].
For the distinct disadvantages and regulation limitations of antibiotic usage, probiotics were widely used in aquaculture and bivalve hatcheries as an alternative strategy to control infection and regulate water quality [22,24,48,49,50]. Most of these studies have shown that probiotics can significantly improve the growth and survival of bivalve larvae. Daily addition of a mixture of S4 and RI (104 CFU/mL) could result in a significant decrease in the levels of total Vibrios in water and tank surfaces [51]. Use of the probiotics Phaeobacter gallaeciensis, Alteromonas macleodii 0444 and Neptunomonas sp. 0536 (104–105 CFU/mL) could increase the survival of Pecten maximus larvae by 50.2% [52]. As reviewed previously, many studies have shown that probiotics could act as pathogen inhibitors, ecological modifiers, and host growth promoters in bivalve hatcheries, with no negative effect on larval growth and survival [22,24,48]. Previous studies also showed that the mechanism of action of probiotics is stage- and species-specific, with different responses in different hosts [53,54]. In this study, the probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC was derived from healthy adult oyster gut tissue, whose biological functions have been investigated in previous studies and does not possess relevant virulence gene [55]. Usage of probiotics of 105 CFU/mL significantly inhibited the growth of pathogenic V. alginolyticus and reduced the mortality of D-sharped larvae.
Initial studies on the colonization of pathogenic bacteria in larvae of different bivalves such as oysters, scallops and mussels were carried out mainly by microscopic histological observation [15,56,57]. However, this method does not allow the main pathogens to be distinguished from conventional microorganisms in larval tissues. The use of fluorescent labelling of bacteria can be used in pathological studies to visualize the distribution, content and progression of infection within an organism [37]. Dubert et al. (2016) resolved the occurrence and development of vibriosis in Ruditapes philippinarum larvae by GFP labelling of pathogenic Vibrios [34]. Wang et al. (2021) used GFP to label Vibrio splendens ME9 and Vibrio eelis NB10, combined with histopathological analysis and ultrastructural observation, to resolve the pathogenesis of Vibrios in blue mussel larvae within 24 h [36]. Cabello et al. (2005) reported that about 85% of GFP-labelled Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in seawater adhered to, entered, and colonized the oyster through the gills [58]. GFP was also proved to be an ideal visualization tool to clearly study the localization of bacteria in different organs, entry routes, and the extent of bacterial infection of different tissues (gill epithelial cells and hemolymph sinus) in dying abalone [59]. However, some studies have also suggested that the introduction of fluorescent proteins into bacteria may adversely affect the growth, virulence, or other physiological functions of certain pathogenic bacteria [38,60]. Therefore, it is recommended that differences between the physiological functions of wild-type and GFP-labelled strains should be compared firstly to confirm the reliability of results obtained from GFP-labelled strains [61]. Biofilm formation is crucial for both pathogenic and probiotic bacteria to complete the process of adhesion and colonization [39]. For pathogenic microorganisms, biofilm formation not only plays an important role during invasion, but also protects them from host immune system [62]. On the other hand, biofilm-forming probiotics have significant advantages in combating pathogens, resistance, and immunomodulation [25]. Moreover, biofilms generated by specific microbial species play an important role during the settlement of oyster larvae [63,64]. Larval settlement always increased with biofilm age and mass [63]. In the present study, GFP and RFP were employed to label the pathogenic V. alginolyticus CD and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC strain, respectively, with the aim to distinguishing the two strains when they attached and entered the oyster larvae. No significant differences were found in capabilities of growth, biofilm formation and in vitro adhesion between the fluorescence-labelled and wild strains in the present study. Additionally, previous studies in animal models (Drosophila) have demonstrated that oxygen levels in the host organism could impact the in vivo distribution of GFP and RFP [65]. While oysters have an open circulatory system consisting of the heart, arteries, and veins connected to blood sinuses throughout the connective tissues [66]. The blood is in direct contact with the cell membranes of oyster tissues and the hemocytes can massively infiltrate the tissues of the oyster visceral mass. According to our knowledge, there is no report about oxygen disequilibrium in oyster tissues. It is difficult to estimate the influence of oxygen levels on the fluorescence intensity due to the scant information available.
Since the formation of chromophores for both GFP and RFP depends on the presence of oxygen, hyper- and hypoxic- environments in the host organism have shown to reduce both fluorescence intensity and expression levels of these proteins. However, the findings of this study have not been documented in bivalve mollusks. Furthermore, none of the previous studies on GFP- and RFP-labeled bacteria colonization and distribution in aquatic animals have mentioned the potential detrimental impact of oxygen levels on GFP and RFP fluorescence. Therefore, the current study investigated the interactions between pathogenic and probiotic bacteria through an analysis of their distribution in oyster larvae, without taking the issue of oxygen content into account. Furthermore, we hypothesized that the maturation of GFP and RFP in bacteria relies on internal oxygen supply. In an oyster body, if certain areas lack sufficient oxygen to support bacteria growth, it is possible that bacterial distribution and colonization may be limited. In this study, clear visualization of the colonization process with fluorescence labelling showed that the pathogenic V. alginolyticus CD and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC strains adopted nearly the same routes during the entering and colonization in the oyster larvae. The distribution of bacteria in various sections of the oyster larvae was visible at different time intervals. Consequently, any fluorescent proteins affected by inadequate oxygen levels and hence, not fully matured whether in this study can be disregarded. In future studies, we will consider examining whether the expression of fluorescent proteins increases the aerobic burden on bacteria.
Studies have shown that ciliated bands on the membrane of bivalve larvae are capable of enriching bacteria and transferring them to the oral cavity [67]. The enriched bacteria subsequently pass through the esophagus to the digestive organs such as the stomach and intestine, where it subsequently proliferates rapidly and then spreads to the body cavity, and eventually colonizes the larvae completely [67]. In the present study, two fluorescently labelled bacteria were used for the first time to monitor their colonization process in C. gigas D-sharped larvae, and the results support the conclusions of Elston and Leibovitz (1980). Furthermore, clear visualization of the colonization process with fluorescence labelling showed that the pathogenic V. alginolyticus CD and probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC strains adopted nearly the same routes during the entering and colonization in the oyster larvae. These results indicated that B. hwajinpoensis RC could execute its’ probiotic effects by competing for adhering and colonization sites with V. alginolyticus. Studies have noted that probiotics repel pathogens when they are present before the pathogen, but not when both are added at the same time [68]. In this study, the pathogenic V. alginolyticus CD was added to the bioassay system 6 h later than the probiotic B. hwajinpoensis RC. The bacterial level of V. alginolyticus CD in the probiotic treated group were significantly higher than the control group (challenged with V. alginolyticus CD). The survival rate of oyster larvae in the treated group was significantly higher than that in the control group.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the GFP and RFP genes were for the first time used to label pathogenic V. alginolyticus and B. amyloliquefaciens, respectively. Our results demonstrated that the introduction of the exogenous genes did not significantly affect the physiological functions of the bacteria. Labelling the strains with different fluorescent proteins made it possible to visualize the colonization process of both pathogenic and probiotic bacteria in C. gigas larvae. It was observed that a similar route was employed to enter and colonize the oyster larvae by V. alginolyticus and B. amyloliquefaciens. It was concluded that competing with pathogens for binding and spreading sites were one of the mechanisms of B. hwajinpoensis to provide the probiotic effects to oyster larvae. The results indicated that the employment of fluorescence-tagged pathogenic and probiotic strains simultaneously provides us a tool to understand the potential mechanisms of the probiotics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-M.B. and Y.-D.Z.; methodology, Y.-D.Z., B.-W.H. and X.Z.; validation, L.-S.X. and C.-F.L.; formal analysis, B.-W.H. and Y.-D.Z.; resources, and C.-M.W.; data curation, C.-F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-M.B. and Y.-D.Z.; writing—review and editing, B.-W.H. and C.-M.B.; supervision, C.-M.W.; project administration, L.-S.X. and C.-M.B.; funding acquisition, C.-M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS, grant number 2023TD30, the earmarked fund for CARS, grant number CARS-49; and the Postdoctoral Innovation Project of Shandong Province, grant number SDCX-ZG-202303048.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Chao Sun for providing assistance during sample collection and transportation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bayne, B. Biology of Oysters; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.M. Use and exchange of genetic resources in molluscan aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2009, 1, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Agriculture Research System-Mollusk. Developemnt report of oyster industry in China. China Fish. 2021, 6, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.F.; Li, L.; Que, H.Y. An evolution of oyster mariculture industry in China: New knowledge, variety and product. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2020, 51, 740–749. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.H.; Mu, Y.T. Analysis of agglomeration characteristics of Chinese oyster breeding industry. Chin. Fish. Econ. 2021, 39, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, B.-W.; Zheng, Y.-D.; Xin, L.-S.; Chen, W.-B.; Yu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, C.-M.; Bai, C.-M. Identification and Characterization of Infectious Pathogens Associated with Mass Mortalities of Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) Cultured in Northern China. Biology 2023, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Xue, Q.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, M.; Lin, Z. Changes in Bacterial Communities of Kumamoto oyster Larvae During Their Early Development and Following Vibrio Infection Resulting in a Mass Mortality Event. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Chang, G.; Xu, H.; Lin, Z.; Xue, Q. Bacterial Community Dynamics in Kumamoto oyster Crassostrea sikamea Hatchery During Larval Development. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 933941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Liu, S.; Dai, W.; He, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Q. Characterization of Vibrio mediterranei Isolates as Causative Agents of Vibriosis in Marine Bivalves. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0492322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.-S. An early warning system for diseases during mollusc mariculture: Exploration and utilization. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2020, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sainz-Hernandez, J.C.; Maeda-Martinez, A.N. Sources of Vibrio bacteria in mollusc hatcheries and control methods: A case study. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, F.M.; Hatfield, R.; Powell, A.; Baker-Austin, C.; Lowther, J.; Turner, A.D. Methodological advances in the detection of biotoxins and pathogens affecting production and consumption of bivalve molluscs in a changing environment. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2023, 80, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubert, J.; Barja, J.L.; Romalde, J.L. New Insights into Pathogenic Vibrios Affecting Bivalves in Hatcheries: Present and Future Prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, G.P.; Watson, M.A.; Needleman, D.S.; Church, K.M.; Hase, C.C. Mortalities of Eastern and Pacific oyster Larvae caused by the pathogens Vibrio coralliilyticus and Vibrio tubiashii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubiash, H.S.; Chanley, P.E.; Leifson, E. Bacillary necrosis, a disease of larval and juvenile bivalve mollusks. I. Etiology and epizootiology. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumar, G.; Nakai, T.; Hirata, Y.; Matsubara, D.; Muroga, K. Vibrio splendidus biovar II as the causative agent of bacillary necrosis of Japanese oyster Crassostrea gigas larvae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1998, 33, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genard, B.; Miner, P.; Nicolas, J.L.; Moraga, D.; Boudry, P.; Pernet, F.; Tremblay, R. Integrative Study of Physiological Changes Associated with Bacterial Infection in Pacific Oyster Larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Giri, S.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.B.; Park, S.C. Isolation and Characterization of Two Bacteriophages and Their Preventive Effects against Pathogenic Vibrio coralliilyticus Causing Mortality of Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) Larvae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takyi, E.; LaPorte, J.; Sohn, S.; Stevick, R.J.; Witkop, E.M.; Gregg, L.S.; Chesler-Poole, A.; Small, J.; White, M.M.; Giray, C.; et al. Development and evaluation of a formulation of probiont Phaeobacter inhibens S4 for the management of vibriosis in bivalve hatcheries. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2023, 3, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Munoz-Quezada, S.; Gil, A. Sources, isolation, characterisation and evaluation of probiotics. Brit. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, S35–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhounde, S.; Adéoti, K.; Mounir, M.; Giusti, A.; Refinetti, P.; Otu, A.; Effa, E.; Ebenso, B.; Adetimirin, V.O.; Barceló, J.M.; et al. Applications of Probiotic-Based Multi-Components to Human, Animal and Ecosystem Health: Concepts, Methodologies, and Action Mechanisms. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Barja, J.L. Review of probiotics for use in bivalve hatcheries. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Kaspar, H.; Lategan, M.J.; Gibson, L. Probiotics in aquaculture: The need, principles and mechanisms of action and screening processes. Aquaculture 2008, 274, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E. Probiotic Strains for Shellfish Aquaculture. Aquac. Fish. 2020, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dao, C.; Karim, M.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Rowley, D.; Nelson, D.R. Contributions of tropodithietic acid and biofilm formation to the probiotic activity of Phaeobacter inhibens. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.; Zhao, W.J.; Rowley, D.; Nelson, D.; Gomez-Chiarri, M. Probiotic Strains for Shellfish Aquaculture: Protection of Eastern Oyster, Crassostrea Virginica, Larvae and Juveniles against Bacterial Challenge. J. Shellfish. Res. 2013, 32, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yuan, T.; Piva, C.; Spinard, E.J.; Schuttert, C.W.; Rowley, D.C.; Nelson, D.R. The Probiotic Bacterium Phaeobacter inhibens Downregulates Virulence Factor Transcription in the Shellfish Pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus by N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01545-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, T.H.; Gomez-Chiarri, M. Contrasting Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotic and Pathogenic Bacteria on Eastern Oyster, Crassostrea Virginica, Larvae. Vaccine 2020, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Kapareiko, D.; Schott, E.J.; Hanif, A.; Wikfors, G.H. Isolation and Evaluation of New Probiotic Bacteria for use in Shellfish Hatcheries: I. Isolation and Screening for Bioactivity. J. Shellfish. Res. 2011, 30, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapareiko, D.; Lim, H.J.; Schott, E.J.; Hanif, A.; Wikfors, G.H. Isolation and Evaluation of New Probiotic Bacteria for use in Shellfish Hatcheries: II. Effects of a Vibrio sp. Probiotic Candidate Upon Survival of Oyster Larvae (Crassostrea virginica) in Pilot-Scale Trials. J. Shellfish. Res. 2011, 30, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlund, N.; Torkildsen, L.; Magnesen, T.; Mortensen, S.; Bergh, Ø. Immunohistochemistry of great scallop Pecten maximus larvae experimentally challenged with pathogenic bacteria. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2006, 69, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudakov, D.M.; Matz, M.V.; Lukyanov, S.; Lukyanov, K.A. Fluorescent proteins and their applications in imaging living cells and tissues. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1103–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawabe, T.; Fukui, Y.; Stabb, E.V. Simple conjugation and outgrowth procedures for tagging vibrios with GFP, and factors affecting the stable expression of the gfp tag. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubert, J.; Nelson, D.R.; Spinard, E.J.; Kessner, L.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Costa, F.; Prado, S.; Barja, J.L. Following the infection process of vibriosis in Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) larvae through GFP-tagged pathogenic Vibrio species. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 133, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, R.; Miranda, C.D.; Romero, J.; Barja, J.L.; Dubert, J. Isolation and Pathogenic Characterization of Vibrio bivalvicida Associated with a Massive Larval Mortality Event in a Commercial Hatchery of Scallop Argopecten purpuratus in Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Mbewe, N.; De Bels, L.; Couck, L.; Van Stappen, G.; Van den Broeck, W.; Nevejan, N. Pathogenesis of experimental vibriosis in blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) larvae based on accurate positioning of GFP-tagged Vibrio strains and histopathological and ultrastructural changes of the host. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Guo, M.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, W. Green fluorescent protein-tagged Vibrio splendidus for monitoring bacterial infection in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubaker, M.H.; Sabrié, J.; Huet, M.; Koken, M. Establishment of stable GFP-tagged Vibrio aestuarianus strains for the analysis of bacterial infection-dynamics in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, e2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, W. FliC of Vibrio splendidus-related strain involved in adhesion to Apostichopus japonicus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizzi, S.Q.F.; Andrade, N.J.d.; Silva, C.A.d.S.; Soares, N.d.F.F.; Silva, E.A.M.d. Bacterial adherence to different inert surfaces evaluated by epifluorescence microscopy and plate count method. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2004, 47, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, S.; Dubert, J.; Barja, J.L. Characterization of pathogenic vibrios isolated from bivalve hatcheries in Galicia, NW Atlantic coast of Spain. Description of Vibrio tubiashii subsp. europaeus [corrected] subsp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 38, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Guo, X.; Scarpa, J. Induction and Establishment of Tetraploid Oyster Breeding Stocks for Triploid Oyster Production. In UF/IFAS Extension FA215; Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Colsoul, B.; Boudry, P.; Perez-Paralle, M.L.; Cetinic, A.B.; Hugh-Jones, T.; Arzul, I.; Merou, N.; Wegner, K.M.; Peter, C.; Merk, V.; et al. Sustainable large-scale production of European flat oyster (Ostrea edulis) seed for ecological restoration and aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1423–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, M.M.; Bourne, N. Hatchery Culture of Bivalves: A Practical Manual; FAO Fisheries Department: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, M.J. The Development of Oyster Breeding Industry in Shandong Province under the New Situation. J. Aquac. 2020, 41, 73–74+77. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, W.J.; Wang, H.X.; Liu, B.Z. Analysis of bacterial community and identification of pathogenic bacteria in the diseased clam larvae of Meretrix petechialis. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 069413. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R. Probiotics in aquaculture: A promising emerging alternative approach. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Kerkar, S. Bacterial probiotics over antibiotics: A boon to aquaculture. In Advances in Biological Science Research—A Practical Approach; Meena, S.N., Naik, M.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2019; pp. 215–232. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Austin, B. Probiotics for Disease Control in Aquaculture. In Diagnosis and Control of Diseases of Fish and Shellfish; Austin, B., Newaj-Fyzul, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 189–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.; Lundgren, K.M.; Tammi, K.; Karim, M.; Smolowitz, R.; Nelson, D.R.; Rowley, D.C.; Gómez-Chiarri, M. Probiotic Strains for Disease Management in Hatchery Larviculture of the Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica. J. Shellfish Res. 2016, 35, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Miner, P.; Nicolas, J.-L.; Asmani, K.; Robert, R. Pathogenic threats and probiotic use in larviculture of the scallop, Pecten maximus. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasolo-Pacheco, F.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Araya, R.; Saucedo, P.E. Enhancing growth and resistance to Vibrio alginolyticus disease in catarina scallop (Argopecten ventricosus) with Bacillus and Lactobacillus probiotic strains during early development. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 4597–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Miner, P.; Nicolas, J.-L.; Robert, R. Protective effect of four potential probiotics against pathogen-challenge of the larvae of three bivalves: Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas), flat oyster (Ostrea edulis) and scallop (Pecten maximus). Aquaculture 2012, 344–349, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.D. Screening of Probiotic bacteria in Shellfish and Their Effect on Bacterial Communities and Larval Survival; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kesarcodi-Watson, A.; Kaspar, H.; Lategan, M.J.; Gibson, L. Two pathogens of Greenshell™ mussel larvae, Perna canaliculus: Vibrio splendidus and a V. coralliilyticus/neptunius-like isolate. J. Fish. Dis. 2009, 32, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtubia, R.; Miranda, C.D.; Rodríguez, S.; Dubert, J.; Barja, J.L.; Rojas, R. First Report, Characterization and Pathogenicity of Vibrio chagasii Isolated from Diseased Reared Larvae of Chilean Scallop, Argopecten purpuratus (Lamarck, 1819). Pathogens 2023, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, A.E.; Espejo, R.T.; Romero, J. Tracing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters (Tiostrea chilensis) using a Green Fluorescent Protein tag. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 327, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, M.A.; Barbou, A.; Le Goïc, N.; Huchette, S.; Paillard, C.; Koken, M. Construction of a stable GFP-tagged Vibrio harveyi strain for bacterial dynamics analysis of abalone infection. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 289, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekecki, A.; Gunasekara, R.A.; Dierckens, K.; Laureau, S.; Boon, N.; Favoreel, H.; Cornelissen, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Ducatelle, R.; Bossier, P.; et al. Bacterial host interaction of GFP-labelled Vibrio anguillarum HI-610 with gnotobiotic sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.), larvae. J. Fish. Dis. 2012, 35, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.G.; Sattenstall, M.A. The influence of green fluorescent protein incorporation on bacterial physiology: A note of caution. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.S.; Zhang, S.; Eggermont, M.; Bruto, M.; Roux, F.L.; Defoirdt, T. The impact of the multichannel quorum sensing systems of Vibrio tasmaniensis and Vibrio crassostreae on virulence towards blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) larvae. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.H.; Meritt, D.W.; Franklin, R.B.; Boone, E.L.; Nicely, C.T.; Brown, B.L. Effects of age and composition of field-produced biofilms on oyster larval setting. Biofouling 2011, 27, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevick, R.J.; Sohn, S.; Modak, T.H.; Nelson, D.R.; Rowley, D.C.; Tammi, K.; Smolowitz, R.; Lundgren, K.M.; Post, A.F.; Gomez-Chiarri, M. Bacterial Community Dynamics in an Oyster Hatchery in Response to Probiotic Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidsky, P.V.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Misra, T.; Handke, B.; Mishin, A.S.; Lehner, C.F. A genetically encoded fluorescent probe for imaging of oxygenation gradients in living Drosophila. Development 2018, 145, dev156257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, P.; Duperthuy, M.; Montagnani, C.; Bachère, E.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. Immune responses in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas: An overview with focus on summer mortalities. In Oysters: Physiology, Ecological Distribution and Mortality; Qin, J., Ed.; Nova Science Pub Inc: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; p. 311. [Google Scholar]
- Elston, R.; Leibovitz, L. Pathogenesis of Experimental Vibriosis in Larval American Oysters, Crassostrea virginica. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrillón, M.; Rico, R.M.; Arijo, S.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A. Interactions of microorganisms isolated from gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L., on Vibrio harveyi, a pathogen of farmed Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup). J. Fish. Dis. 2005, 28, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).