Abstract
Klebsiella (K.) pneumoniae is a One Health pathogen that has been isolated from humans, animals, and environmental sources and is responsible for a diverse range of potentially life-threatening infections. In the present study, we analyzed the genomes of 64 presumptive K. pneumoniae strains isolated in 2023 from different companion and farm animals in Germany. Using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data, 59 isolates (92.2%) were identified as K. pneumoniae and five (7.8%) as K. quasipneumoniae. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) assigned 53 isolates to 46 distinct sequence types (STs). Eleven isolates could not be assigned to existing STs of the Pasteur classification scheme because they contained novel alleles not previously documented. Thus, these were considered novel and designated as ST7681-ST7689 and ST7697-ST7698. Almost all isolates in this study were assigned unique STs, and only five STs were shared among multiple isolates. This research highlights the genetic diversity among K. pneumoniae strains isolated from different companion and farm animals in Germany, provides information to help in surveillance strategies to mitigate zoonotic transmission risks, and demonstrates the value of WGS and MLST in identifying novel STs of K. pneumoniae.
1. Introduction
Klebsiella (K.) pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, and facultatively anaerobic bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae [1]. It is ubiquitous in nature and can be found in animals, water, and soil [2]. K. pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen recognized globally as one of the most critical multidrug-resistant (MDR) microorganisms [3]. It is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections worldwide [4]. It can cause serious diseases, including pneumonia and urinary tract and bloodstream infections, as well as liver abscesses [2], with high mortality rates due to its resistance to multiple antibiotics [1]. K. pneumoniae is characterized by various virulence factors that contribute to its pathogenicity. These include a polysaccharide capsule, surface lipopolysaccharides, fimbriae, and siderophores, which facilitate adhesion to host tissues, evasion of the immune response, and acquisition of essential nutrients [5]. Additionally, it possesses the ability to form biofilms and harbors a diverse array of resistance genes, enhancing its resilience against aminoglycosides, quinolones, polymyxins, and β-lactams [6]. In animals, K. pneumoniae is highly pathogenic and can affect the urogenital, respiratory, and digestive systems [7]. Its ability to infect nearly every organ or tissue makes K. pneumoniae a significant concern in animal health [8]. In Germany, multiple outbreaks of K. pneumoniae have been reported in humans [9,10], and it has been isolated from various animals such as dogs, cats, horses, pigs, and cattle [11,12,13,14] as well as from milk powder [15]. However, the knowledge on STs of K. pneumoniae is limited in Germany, due to a lack of isolated strains. This study aimed to perform molecular characterization of 64 presumptive K. pneumoniae isolates from companion and farm animals across various federal states in Germany, and to identify novel STs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates and Identification
Sixty-four presumptive K. pneumoniae isolates from the strain collection of IDEXX Laboratories, Kornwestheim, Germany, were used in the current study. The isolates were isolated from various companion and farm animals in Germany in 2023. The majority of isolates (75%, 48/64) were obtained from dogs, followed by horses (17.2%, 11/64), cats (4.7%, 3/64), and 1.6% (1/64) each from cattle and chickens, as shown in Table 1. All isolates were identified at the species level using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Sample preparation, protein extraction, and species identification using MALDI-TOF were conducted as previously described [16] using a Microflex LT instrument (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany).

Table 1.
Host, source, and MLST diversity of 53 K. pneumoniae/quasipneumoniae strains with 46 distinct STs obtained from various companion and farm animals in Germany in 2023.
2.2. DNA Extraction, WGS, and In Silico Detection of Sequence Types
Genomic DNA extraction was performed from a single colony grown overnight on Columbia blood agar at 37 °C using the High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit was used to prepare sequencing libraries, and paired-end sequencing was carried out on an Illumina MiSeq sequencer (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Raw sequencing data analysis and quality checks of the assembled genomes were performed as previously described [17,18]. The multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was determined in silico using the in-house pipeline WGSBAC (https://gitlab.com/FLI_Bioinfo/WGSBAC, accessed on 2 December 2024) and the software mlst v2.16.1 (https://github.com/tseemann/mlst, accessed on 2 December 2024) that uses the PubMLST website [19] and the scheme proposed by Diancourt and colleagues [20], known as the Pasteur typing scheme. Neighbor-Joining (NJ) analysis was performed using GrapeTree software for constructing a phylogenetic tree [21]. Microreact was employed to visualize both epidemiological data and phylogenetic trees [22].
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolate Identification and MLST Analysis
MALDI-TOF MS initially identified all 64 K. pneumoniae isolates as K. pneumoniae. However, subsequent WGS-based analysis only identified 59 strains (92.2%) as K. pneumoniae and 5 (7.8%) as K. quasipneumoniae. MLST analysis revealed that the majority of the strains (53/64, 82.8%) belonged to 46 distinct STs, as shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
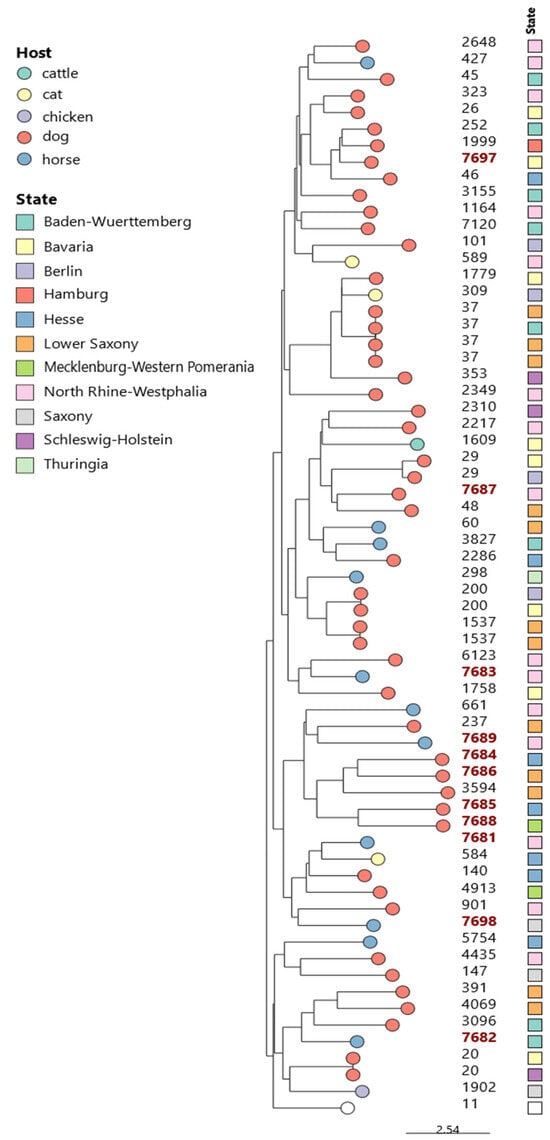
Figure 1.
The phylogenetic tree of 64 K. pneumoniae/quasipneumoniae isolates from companion and farm animals in Germany was constructed using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method based on MLST data. The tree includes STs and corresponding geographical locations. Novel STs are indicated in red.
3.2. Novel STs, Their Hosts, and Geographical Distribution
Of the 64 studied strains, 17.2% (n = 11) could not be assigned to any known ST and were therefore classified as novel STs according to the institute Pasteur database (https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/, accessed on 29 October 2024). Seven of them were identified as K. pneumoniae and four as K. quasipneumoniae. The newly identified STs included ST7681 to ST7689 and ST7697 to ST7698. These novel STs were detected in isolates from dogs (n = 6) and horses (n = 5), originating from various sample materials, including the feces, uterus, cervix, and urine. The isolates were distributed across seven different federal states, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 2.

Table 2.
MLST characteristics of the eleven K. pneumoniae/quasipneumoniae isolates with novel STs obtained from companion and farm animals in Germany in 2023.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we characterized 64 presumptive K. pneumoniae strains isolated from different companion and farm animal species in Germany in 2023. These isolates were initially identified as K. pneumoniae using MALDI-TOF MS. However, subsequent confirmation via whole-genome sequencing (WGS) revealed that 59 isolates were K. pneumoniae and 5 were K. quasipneumoniae. The five K. quasipneumoniae strains were found in fecal and urine samples from dogs. K. quasipneumoniae was described for the first time in 2014 and identified in human infections [23]. K. quasipneumoniae has been isolated from humans, animals, and various environmental sources in Germany [24,25,26], as well as in other European countries, including France [23], Sweden [27], Portugal [28], and Italy [29]. Our study also shows a genetic diversity, with 57 sequence types (STs) among 64 K. pneumoniae/quasipneumoniae strains. Altogether, 52 STs were represented by a single isolate each, including eleven novel STs. These novel STs originated from seven different German federal states, highlighting their geographical spread. Detecting novel alleles is essential for advancing future surveillance and diagnostic strategies. Some identified STs in this study, such as ST45, ST29, ST101, and ST147, have been previously reported in human infections in Germany [30,31,32,33], highlighting the potential for zoonotic transmission of K. pneumoniae.
In conclusion, collaborative efforts between veterinary and public health sectors are necessary to improve our understanding of transmission dynamics between companion and farm animals and humans. The findings of this study highlight the importance of molecular examination of Klebsiella strains isolated from animals, as it enables the identification of novel sequence types, reveals genetic diversity, and provides insights into their epidemiological significance. Further molecular studies on isolates from different one-health sectors are necessary to assess transmission pathways and the epidemiological impact of K. pneumoniae or K. quasipneumoniae.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B., H.N. and L.D.S.; methodology, M.B., H.B., P.A.K. and I.S.; validation and formal analysis, M.B., H.B. and L.D.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B.; writing—review and editing, H.N. and L.D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding and was funded internally by Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are provided in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the work of the Institute Pasteur for curating and maintaining the BIGSdb-Pasteur databases at http://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/ (accessed on 29 October 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Authors Ivonne Stamm and Peter A. Kopp are employed by IDEXX Laboratories, Kornwestheim, Germany. IDEXX Laboratories, Kornwestheim, Germany, provided isolates and had no role in the design of the study, or interpretation of data, or in the decision to publish the results. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| K. | Klebsiella |
| WGS | Whole genomic sequencing |
| MLST | Multilocus sequence typing |
| ST | Sequence type |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| NJ | Neighbor-Joining |
References
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, R.; Chakkour, M.; Zein El Dine, H.; Obaseki, E.F.; Obeid, S.T.; Jezzini, A.; Ghssein, G.; Ezzeddine, Z. General Overview of Klebsiella pneumonia: Epidemiology and the Role of Siderophores in Its Pathogenicity. Biology 2024, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerio, N.; Olimpieri, T.; Henrici De Angelis, L.; de Santis, F.; Thaller, M.C.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Fraziano, M. Fighting MDR-Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections by a Combined Host- and Pathogen-Directed Therapeutic Approach. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riwu, K.H.P.; Effendi, M.H.; Rantam, F.A.; Khairullah, A.R.; Widodo, A. A review: Virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumonia as emerging infection on the food chain. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The Characteristic of Virulence, Biofilm, and Antibiotic Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Menezes, J.; Belas, A.; Aboim, C.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Trigueiro, G.; Telo Gama, L.; Pomba, C. Klebsiella pneumoniae causing urinary tract infections in companion animals and humans: Population structure, antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.G.; de Morais, A.B.C.; Alves, A.C.; Bolaños, C.A.D.; de Paula, C.L.; Portilho, F.V.R.; de Nardi Júnior, G.; Lara, G.H.B.; de Souza Araújo Martins, L.; Moraes, L.S.; et al. Klebsiella-induced infections in domestic species: A case-series study in 697 animals (1997–2019). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, C.; Schütt, S.; Dalpke, A.H.; Konrad, M.; Mieth, M.; Trierweiler-Hauke, B.; Weigand, M.A.; Zimmermann, S.; Biehler, K.; Jonas, D. First outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae in Germany. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Kramer, R.; Becker, K.; Bohnert, J.A.; Eckmanns, T.; Hans, J.B.; Hecht, J.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Hübner, N.-O.; Kramer, A.; et al. Extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 outbreak, north-eastern Germany, June to October 2019. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1900734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierack, P.; Walk, N.; Reiter, K.; Weyrauch, K.D.; Wieler, L.H. Composition of intestinal Enterobacteriaceae populations of healthy domestic pigs. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3830–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; Stamm, I.; Pfeifer, Y.; Wieler, L.H.; Kopp, P.A.; Schønning, K.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Scheufen, S.; Stolle, I.; Günther, S.; et al. Clonal spread of highly successful ST15-CTX-M-15 Klebsiella pneumoniae in companion animals and horses. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2676–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, J.; Falgenhauer, L.; Domann, E.; Bauerfeind, R.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T. Multiresistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from humans, companion animals and horses in central Hesse, Germany. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waade, J.; Seibt, U.; Honscha, W.; Rachidi, F.; Starke, A.; Speck, S.; Truyen, U. Multidrug-resistant enterobacteria in newborn dairy calves in Germany. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Linde, J.; Hammer, P.; Pletz, M.W.; Neubauer, H.; Sprague, L.D. WGS-Based Phenotyping and Molecular Characterization of the Resistome, Virulome, and Plasmid Replicons in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Powdered Milk Produced in Germany. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, D.F.; Lela, R.A.; El-Diasty, M.; Moustafa, S.A.; Wareth, G. Detection of harmful foodborne pathogens in food samples at the points of sale by MALDT-TOF MS in Egypt. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, J.; Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Dangel, A.; Riehm, J.M.; Sundell, D.; Öhrman, C.; Forsman, M.; Tomaso, H. Genotyping of Francisella tularensis subsp. holarctica from Hares in Germany. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Linde, J.; Hammer, P.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, T.N.M.; Splettstoesser, W.D.; Makarewicz, O.; Neubauer, H.; Sprague, L.D.; Pletz, M.W. Phenotypic and WGS-derived antimicrobial resistance profiles of clinical and non-clinical Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Germany and Vietnam. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website, and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae Nosocomial Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argimón, S.; Abudahab, K.; Goater, R.J.E.; Fedosejev, A.; Bhai, J.; Glasner, C.; Feil, E.J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Yeats, C.A.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Microreact: Visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Grimont, P.A.D. Description of Klebsiella quasipneumoniae sp. nov., isolated from human infections, with two subspecies, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae subsp. nov. and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae subsp. nov., and demonstration that Klebsiella singaporensis is a junior heterotypic synonym of Klebsiella variicola. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3146–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, K.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Walker, S.V.; Behnke, M.; Dinkelacker, A.G.; Eisenbeis, S.; Gastmeier, P.; Gölz, H.; Käding, N.; Kern, W.V.; et al. Surveillance and Genomic Analysis of Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant and Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Complex in Germany. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, L.; Fuchs, S.; Pfeifer, Y.; Semmler, T.; Eckmanns, T.; Korr, G.; Sissolak, D.; Friedrichs, M.; Zill, E.; Tung, M.-L.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of CTX-M-15 Producing Klebsiella Isolates Allowed Dissecting a Polyclonal Outbreak Scenario. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaper, K.; Hammerl, J.A.; Rau, J.; Pfeifer, Y.; Werner, G. Genome-Based Analysis of Klebsiella spp. Isolates from Animals and Food Products in Germany, 2013–2017. Pathogens 2021, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatallah, M.; Vading, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Bakhrouf, A.; Kalin, M.; Nauclér, P.; Brisse, S.; Giske, C.G. Klebsiella variicola is a frequent cause of bloodstream infection in the stockholm area and associated with higher mortality compared to K. pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.; Tacão, M.; Henriques, I. Hidden threats in the plastisphere: Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales colonizing microplastics in river water. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, N.; Guarneri, F.; Bertasio, C.; Parisio, G.; Romeo, C.; Scali, F.; Birbes, L.; Boniotti, M.B.; Diegoli, G.; Candela, L.; et al. Wastewater-based surveillance in Italy leading to the first detection of mcr-10-positive Klebsiella quasipneumoniae. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, A.; Fischer, M.A.; Klaper, K.; Müller, A.; Borgmann, S.; Friesen, J.; Hunfeld, K.-P.; Ilmberger, A.; Kolbe-Busch, S.; Kresken, M.; et al. Presence of hypervirulence-associated determinants in Klebsiella pneumoniae from hospitalised patients in Germany. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 314, 151601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshana, S.E.; Fritzenwanker, M.; Falgenhauer, L.; Domann, E.; Hain, T.; Chakraborty, T.; Imirzalioglu, C. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of an outbreak causing Klebsiella pneumoniae clone carrying chromosomally located bla(CTX-M-15) at a German University-Hospital. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutin, S.; Welker, S.; Gerigk, M.; Miethke, T.; Heeg, K.; Nurjadi, D. Molecular surveillance of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in two nearby tertiary hospitals to identify regional spread of high-risk clones in Germany, 2019–2020. J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 149, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaase, M.; Schimanski, S.; Schiller, R.; Beyreiß, B.; Thürmer, A.; Steinmann, J.; Kempf, V.A.; Hess, C.; Sobottka, I.; Fenner, I.; et al. Multicentre investigation of carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in German hospitals. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).