Abstract
Staphylococcus is a major bacterial species that contaminates retail meat products. The objective of this study was to clarify the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and genetic determinants of Staphylococcus/Mammaliicoccus species in retail ground meat in Japan. From a total of 146 retail ground meat samples (chicken, pork, mixed beef/pork) purchased during a 5-month period, 10 S. aureus and 112 isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CoNS)/Mammaliicoccus comprising 20 species were recovered. S. aureus isolates were classified into five genetic types, i.e., coa-IIa/ST5, coa-VIc/ST352 (CC97), coa-VIIb/ST398, coa-Xa/ST15, and coa-XIc/ST9, which were all related to those of livestock-associated clones. All the staphylococcal isolates were mecA-negative and mostly susceptible to all the antimicrobials tested, except for ampicillin among S. aureus (resistance proportion; 50%). Among CoNS, the fosfomycin resistance gene fosB was prevalent (30/112; 26.8%), primarily in S. capitis, S. warneri, and S. saprophyticus. Phylogenetic analysis of fosB revealed the presence of seven clusters, showing broad diversity with 65–81% identity among different clusters. In the CoNS isolates from ground meat samples, fosB was assigned into three clusters, and S. saprophyticus harbored the most divergent fosB with three genetic groups. These findings suggested the circulation of multiple fosB-carrying plasmids among some CoNS species.
1. Introduction
Staphylococcus is a common commensal bacteria that inhabits skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body in humans and animals [1]. This genus is recognized as a major pathogenic microorganism and causes a wide spectrum of diseases. The genus Staphylococcus consists of at least 62 species (https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/staphylococcus; accessed on 1 March 2022) as of March 2022, which have been classified into coagulase-positive and -negative staphylococcus (CoPS and CoNS, respectively), and coagulase-positive/variable staphylococcus [2]. CoPS includes major pathogenic species, i.e., Staphylococcus aureus, and three other species (S. argenteus, S. schweitzeri, and S. singaporensis) that form S. aureus complex [3,4], with S. argenteus being increasingly reported as a human pathogen worldwide [5]. Coagulase-positive/variable staphylococcus consists of several species represented by S. hyicus and S. intermedius [2]. Although CoNS colonizes healthy individuals more rigidly than S. aureus and is thus considered less virulent, some species/strains of CoNS are recognized as causes of specific infections (e.g., device-related infections), associated with increased drug resistance and biofilm formation [2,6]. Recently, five former CoNS species (S. sciuri group) were reclassified into the genus Mammaliicoccus (e.g., M. sciuri) [7].
Staphylococci originating from animals harbor a wide variety of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes [8]. Part of the AMR genes shared by humans and animals (e.g., tet(L), cfr, fexA, and dfrK) have already been identified and more commonly in animal-related staphylococci, suggesting an animal origin. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), one of the most important antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, carries a composite SCCmec element containing mecA, a determinant of methicillin-resistance. The origin of mecA was also presumed to be an animal-related species, Staphylococcus fleurettii (Mammaliicoccus fleurettii) [9], which is distributed to pigs, cows and other animal products [10]. Meat products, as well as dairy products are commonly contaminated with S. aureus and CoNS [11,12]. A mecA homologue, mecC is also distributed to humans and animals at low prevalence [8]. Those foods are considered a potential vehicle for the transmission of staphylococcus, mediating the introduction of AMR genes and/or virulence factor genes to the human population.
To date, numerous published reports have described the prevalence of S. aureus/MRSA isolated from retail meat products in many countries around the world, revealing their AMR traits and genotypes [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Though much less information is available, increased AMR rates in various CoNS species from meat have also been shown in some studies [10,11,23]. In Japan, information on S. aureus in retail meat is limited to some studies for older isolates [24,25,26], while there is no data on CoNS. Therefore, we conducted this study to reveal the prevalence of Staphylococcus and Mammaliicoccus in retail ground meat in Japan, their AMR and its responsible genetic determinants.
Fosfomycin is a broad-spectrum bactericidal antibiotic that interferes with cell wall biosynthesis, via inhibition of the MurA enzyme catalizing peptidoglycan precursor, which is a different mechanism from that of beta-lactams [27]. Resistance to fosfomycin through the fosfomycin-inactivating enzyme (FosB) has been occurring in S. aureus/MRSA clinical isolates, posing concern for treatment [28,29,30]. Though prevalence of fosfomycin resistance in staphylococci from meat has been scarcely studied, we revealed relatively high prevalence of fosfomycin resistance gene fosB in CoNS. Through the phylogenetic analysis of the broad genetic diversity of fosB, we proposed a reclassification scheme of fosB genetic groups of staphylococcal species.
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Staphylococcus/Mammaliicoccus Isolates
A total of 146 packages of retail ground meat products were purchased from several grocery stores located in Sapporo and its neighboring towns in the Hokkaido prefecture, in the northern main island of Japan, during a 5-month period (from May to September 2021). These meat products were collected by convenience sampling, and comprised chicken (n = 93), pork (n = 22), and a mixture of beef and pork (n = 31). All the samples were non-frozen raw meat and were kept at a low temperature (<10 ℃) in the retail outlet. Purchased samples were placed in a portable cold insulation bag and transported to the laboratory.
From the 146 ground meat specimens, 10 S aureus isolates (6.8%) and 112 isolates of CoNS/Mammaliicoccus were recovered (Table 1). The proportion of S. aureus from the mixed ground meat (beef and pork) (16%) was higher than that from chicken and pork. CoNS/Mammaliicoccus consisted of 20 species (16 Staphylococcus and 4 Mammaliicoccus species), with S. saprophyticus being the most common, followed by M. sciuri, S. warneri, S. pasteuri, S. capitis, and S. chromogenes. From the three types of ground meat, S. saprophyticus was commonly isolated with a similar prevalence rate (15–18%), as well as S. pasteuri (5–9%).

Table 1.
Isolation of S. aureus, CoNS/Mammaliicoccus species from different types of ground meat specimens.
2.2. AMR and Genetic Characterization of S. aureus
The 10 S. aureus isolates were all mecA-negative (methicillin-susceptible) and genetically classified into five genetic groups (coagulase genotype/sequence type (clonal complex)), i.e., coa-IIa/ST5, coa-VIc/ST352 (CC97), coa-VIIb/ST398, coa-Xa/ST15, and coa-XIc/ST9 (CC1) (Table 2). ST15 and ST352 S. aureus were susceptible to all the antimicrobials tested, and other isolates showed resistance to a few antimicrobials (ampicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, and levofloxacin), harboring blaZ or erm(C). Resistance proportion (percentage) to ampicillin of S. aureus (50%) was significantly higher than CoNS/Mammaliicoccus (19.6%) (Table 3). None of the isolates had PVL genes and ACME-arcA. An enterotoxin gene seb was detected in ST15 isolates, while the enterotoxin gene cluster (egc) (seg-sei-sem-sen-seo) was detected in ST5 and ST9 isolates. A leukocidin gene lukM was identified only in an isolate of ST352.

Table 2.
Genotypes, antimicrobial resistance profile, resistance genes and virulence factors in 10 S. aureus isolates from retail ground meat specimens.

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance profile of S. aureus and CoNS/Mammaliicoccus species isolated from ground meat specimens.
2.3. AMR and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in CoNS/Mammaliicoccus
Resistance proportions to individual antimicrobials and prevalence of resistance genes in each CoNS/Mammaliicoccus species are shown in Table 3. Distribution of MIC to eight antimicrobials was illustrated in Figure S1. CoNS/Mammaliicoccus derived from meat samples were susceptible to most of the antimicrobials, while 8–20% of the isolates showed resistance to ampicillin, gentamicin, clindamycin, and tetracycline. For antimicrobial susceptibility testing, we employed a commercial kit (Dry Plate Eiken DP32, Eiken Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) based on the broth microdilution method to test 18 antimicrobials, including fosfomycin. However, the agar dilution method is recommended for susceptibility testing of fosfomycin [31]. Accordingly, results of fosfomycin are not shown in Table 1, but mentioned here as reference information; 51 CoNS/Mammaliicoccus isolates (45.5%) showed an MIC of ≥64 μg/mL (46 isolates, ≥128 μg/mL), representing presumptive resistance to fosfomycin, while all the S. aureus isolates were susceptible to fosfomycin.
Among the CoNS species with multiple isolates, S. warneri showed the highest resistance proportions to ampicillin and gentamicin, harboring blaZ and aminoglycoside modifying enzyme (AME) genes (aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2”)-Ia, ant(4′)-Ia). Resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin was the most common in S. chromogenes, associated with erm(C) and lnu(B), despite the low number of isolates (n = 6). Tetracycline resistance was found in 10 species, with tet(K) being the most common, followed by tet(M). The fosfomycin resistance gene, fosB was found to be prevalent among CoNS/Mammaliicoccus (30 isolates; 26.8%). High prevalence of fosB was noted in S. capitis (63%, 5/8), S. warneri (62%, 9/14), and S. saprophyticus (57%, 13/23), while S. lugdunensis and S. pasteuri also harbored this gene. All the isolates were negative for optrA, fexA, and cfr, showing susceptibility to linezolid (MIC, 0–2 μg/mL).
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of fosB
The nucleotide sequence of fosB was determined for most of the fosB-positive isolates (n = 29) and was phylogenetically analyzed with representative fosB sequences available in the GenBank database, which were grouped as a Staphylococcus cluster (FosB-S) by Song et al. [32]. The constructed phylogenetic tree of fosB (Figure 1) revealed the presence of at least seven clusters discriminated by high bootstrap values at the nodes of branches (>85). Because the dominant staphylococcus species were evident in individual clusters, these species names were assigned to the designation of clusters. Nevertheless, two distinct clusters were revealed for S. aureus (I and II), and subclusters (SC) were differentiated for four clusters. The fosB genes identified in the present study were assigned to three clusters: a S. saprophyticus cluster, S. warneri cluster, and S. capitis cluster. fosB of S. saprophyticus in this study was classified into three distinct groups within a cluster (S. saprophyticus cluster SC-1, SC-2, and divergent group). fosB of S. lugdunensis and S. pasteuri were grouped into the S. warneri cluster.
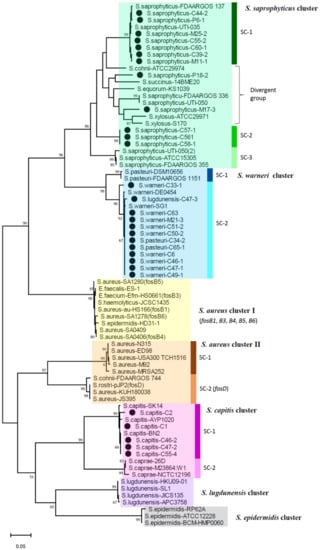
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic dendrogram of fosB belonging to FosB-S clade constructed by maximum-likelihood method with MEGA.11 program. Trees were statistically supported by bootstrapping with 1000 replicates, and genetic distances were calculated by the Kimura two-parameter model. Variation scale is described at the bottom. Percent bootstrap support is indicated by the values at each node (the values <80 are omitted). Filled circles indicate staphylococcal isolates analyzed in the present study, and sequences of other strains were retrieved from the GenBank database. Seven clusters are shown on the right. Strains included in these clusters are drawn with different colors. Subclusters (SC) are also indicated on the right with vertical bars.
As reported for FosB-S [29,32], fosB of S. saprophyticus and S. warneri clusters in the present isolates comprised 420 nucleotides encoding a 139-amino acid protein. However, FosB of all the isolates of S. capitis cluster in the present study was one-amino acid longer (i.e., 140 amino acids), which was also found in the reference sequence of S. capitis in GenBank (Figure S2). The nucleotide sequence identity of fosB among the different clusters were analyzed for those of the present isolates together with those available in the GenBank database (Table S1). fosB was revealed to be highly divergent, showing a 65–81% identity among different clusters, with a 79–100% identity within the same cluster. In particular, clusters of S. saprophyticus, S. aureus-II, and S. capitis exhibited more diversity than other clusters. While fosB sequences of S. saprophyticus exhibited 86–99% identity within the cluster, fosB of two isolates M17-3 and P18-2 showed 87–92% identity to those of other S. saprophyticus isolates in the present study, as well as any fosB sequences in the GenBank database. In contrast, within the S. warneri cluster (SC-2) and the S. capitis cluster (SC-1), the nucleotide sequence identity of fosB was more than 97% (Table S1, Figure S2).
2.5. Prevalence of 6-TG Synthesis Genes among CoNS/Mammaliicoccus
Recently, some CoNS species were reported to produce 6-thioguanine (6-TG), which suppresses the growth of S. aureus [33]. To examine the possible association of 6-TG synthesis in CoNS and the isolation of S. aureus, the presence of three genes (tgsB, tgsC, tgsD) included in the 6-TG biosynthetic gene cluster was analyzed by PCR using newly designed primers (Table S2). The 6-TG synthesis genes were detected in only S. capitis (3 isolates) and S. chromogenes (2 isolates) among all the CoNS/Mammaliicoccus isolates (Table 4). Nevertheless, only two genes (tgsC and tgsD) were found in S. chromogenes. From the meat samples with tgs-positive S. capitis or S. chromogenes, S. aureus was not isolated, while other staphylococcal species were recovered. Among the 10 S. aureus isolates, six isolates with ST9, ST15, and ST398 were isolated with other staphylococcal species from the same meat specimens, including S. chromogenes, S. warneri, M. sciuri (Table 5). Two S. chromogenes isolates co-isolated with S. aureus were negative for the tgs genes.

Table 4.
S. capitis and S. chromogenes isolates with and without tgsB, C, D.

Table 5.
Co-isolation of S. aureus and CoNS/Mammaliicoccus.
3. Discussion
Prevalence of S. aureus/MRSA contaminating retail meat has been reported worldwide, while their isolation proportions vary by individual studies. In several recent studies in Asia and the Middle East, the isolation frequency of S. aureus from raw meat ranged from about 10 to 21% [11,17,18,22,34], while the higher prevalence of S. aureus (>28%) with the detection of MRSA (generally ~8% of S. aureus) was described in the US, Africa, and China [14,16,21,35,36,37]. Although information in Japan is available in only a few old studies (2002–2006), the isolation frequency of S. aureus was 66% in raw chicken meat [24], and 33% in retail raw meat (3% of MRSA), with a higher prevalence in chicken than pork/beef [25]. In contrast, in the present study, S. aureus was isolated at a lower level (6.8%) compared with those in the above-mentioned reports, without the detection of MRSA, showing a higher proportion of S. aureus in mixed beef/pork than in chicken. Such difference in the prevalence of S. aureus/MRSA may be caused by the study design, including the sample number and period, culture method, and environmental conditions at the study site.
Genotypes of S. aureus isolates in the present study were coa-IIa/ST5, coa-XIc/ST9, coa-VIc/ST352 (CC97), coa-VIIb/ST398, and coa-Xa/ST15, among which ST398 (CC398) has been the most frequently reported for S. aureus/MRSA from retail meat, particularly pork [15,19,20,35,38,39], and is known as that of livestock-associated S. aureus [40]. Other STs, i.e., ST5, ST9, ST15, and CC97, were also reported for animal-associated types [41,42] and isolates from meat samples, with ST5 and ST9 being more common than ST398 occasionally [14,19,20,35,39,43]. The gene of a leukocidin lukM, which is involved in bovine mastitis [44] and is scarcely detected in human clinical isolates, was identified in an ST352 (CC97) isolate in the present study, which may also suggest its relation to animals.
While CoNS/Mammaliicoccus isolates in the present study were susceptible to most of the antimicrobials, a higher resistance proportion to some drugs (ampicillin, gentamicin, clindamycin, tetracycline, fosfomycin) were noted for S. chromogenes, S. pasteuri, S. saprophyticus, and S. warneri, associated with resistance genes blaZ, erm(C), aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, tet(K), tet(M), and fosB. In particular, S. warneri showed multiple drug resistance. Although much less work has been done on the drug resistance of CoNS from meat products, S. chromogenes, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, and S. xylosus were described as common species showing resistance to tetracycline harboring tet(K), tet(L), or tet(M) [23,45,46].
In the present CoNS study, fosB was identified in 60% of the presumptive fosfomycin-resistant isolates (30/51). This incidence of fosB may be comparable to that reported for S. aureus from milk samples (67% of fosfomycin-resistant isolates) [47]. Except for fosB, mutations in murA, uhpT, and glpT were revealed as the mechanism of fosfomycin resistance in Staphylococus [30], which are suggested to be responsible for the fosfomycin resistance in fosB-negative isolates. Nevertheless, these mutations were commonly identified in hospital-associated, fosfomycin-resistant S. aureus, despite low prevalence of fosB [48]. Thus, fosB-associated resistance appears to be more related to CoNS distributed to animals. Although fosB in Staphylococci from calves and dogs was detected in a few reports [49,50], its prevalence in individual animal species has been scarcely understood. Thus, fosB-carrying bacteria in animals will be of significance to be studied in the future. Furthermore, because a high proportion of fosfomycin resistance was described for S. saprophyticus from urogenital infections [51], this resistance in CoNS should be carefully monitored for clinical isolates.
FosB is Mg2+ dependent thioltransferase encoded by fosB located in plasmid, one of the four clades (fosA, fosB, fosC, and fosX) [28]. fosB is distributed to Gram-positive bacteria and is phylogenetically differentiated into three groups, fosB-B1 and fosB-B2 in Bacillus, and fosB-S in Staphylococcus [32]. In the present study, we revealed broad genetic diversity among fosB-S genes, including those identified in the isolates from meat, and the presence of distinct clusters related to staphylococcal species. Remarkably, fosB in S. saprophyticus was the most divergent, including at least three genetic groups in our isolates, suggesting the circulation of plasmids harboring different fosB genes in this species. Through the phylogenetic analysis, the previously described designation of staphylococcal fosB could be reassigned to the clusters revealed in the present study: “fosB1, fosB3–fosB6” described for MRSA [29] were classified into the S. aureus cluster I, fosD into S. aureus, S. rostri, and S. arlettae [52,53,54] was grouped into the S. aureus cluster II-SC2 (Figure 1).
Production of 6-TG is a newly identified anti-S. aureus mechanism of some CoNS species [33], unlike the already known antimicrobial peptide, i.e., bacteriocin [55]. In our present study, the presence of the 6-TG biosynthetic gene (tgs) cluster was detected in S. capitis and S. chromogenes isolates, which supported the finding through the survey of tgs operon among genomic data [33]. Although S. aureus was not co-isolated from the samples with tgs-positive CoNS in our study, the inhibition effect of 6-TG in the natural environment is still not clear, because of low numbers of S. aureus and tgs-positive isolates. Further epidemiological study is necessary to evaluate the effect of 6-TG from CoNS to the prevalence of S. aureus in nature.
In the present study, we revealed the low prevalence of S. aureus and the species diversity of CoNS/Mammaliicoccus in ground meat products in Japan, along with the prevalence of CoNS with divergent fosB. These observations indicated the need for periodic surveillance of staphylococci in raw meat products to reveal change in the ecological nature of bacteria, which may be potentially affected by the practice of the livestock industry.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus/Mammaliicoccus Species
A 10-g portion of ground meat sample was aseptically taken and transferred into a sterile plastic tube containing 5 mL of Mueller Hinton broth (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Sparks, MD, USA), followed by stirring with a vortex mixer and subsequent enrichment culture at 37 °C for 5 h. Thereafter, a loopful of the culture was streaked on CHROMagar™ Staph aureus (Kanto Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) agar plates, followed by incubation at 37 °C for 48 h aerobically. Staphylococcus-like colonies grown on the agar plates were picked up and subcultured on blood agar plates by incubation at 37 °C overnight. Bacterial species in the isolates were identified genetically by a determination of the partial sequence of the 16S rRNA gene (approx. 1500-bp) as reported previously [56]. For species identification, >99% identity of the 16S rRNA sequence revealed by BLASTR search (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 1 December 2021) was employed. The presence of nuc, mecA, Panton–Valentine leucocidin (PVL) and arginine catabolic element (ACME)-arcA genes was examined for all the isolates by multiplex PCR as described by Zhang et al. [57]. For all the isolates assigned to S. aurues, a PCR targeting non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (nrps) gene was performed to discriminate from S. argenteus [58]. From a single meat sample, multiple isolates showing different colonial morphology on CHROMagar plates were picked up and analyzed. However, only one isolate representing a single Staphylococccus/Mammaliicoccus species was selected for further characterization.
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
For all the isolates, antimicrobial susceptibility was measured by broth microdilution test using a Dry Plate Eiken DP32 (Eiken Chemical, Tokyo, Japan). Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) within limited ranges were measured for 18 antimicrobial agents: beta-lactam (oxacillin(OXA), cefoxitin (FOX), ampicillin (AMP), cefazoline (CFZ), cefmetazole (CMZ), flomoxef (FMX), imipenem (IPM)), aminoglycoside (gentamicin(GEN), arbekacin (ABK)), macrolide (erythromycin (ERY)), lincosamide (clindamycin (CLI)), glycopeptide (vancomycin (VAN), teicoplanin (TEC)), fluoroquuinolone (levofloxacin (LVX)), tetracycline (minocycline (MIN)), and others (linezolid (LZD), fosfomycin (FOF), and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT)), and resistance was judged according to breakpoints mentioned in the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) standards (2018) [59] except for FOF, ABK and FMX. We referred to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) breakpoint for FOF (Resistance, MIC of >32 µg/mL, Staphylococcus spp.) measured in agar dilution method [60], and employed a unique breakpoint for ABK (4 µg/mL, which is higher than the 2 µg/mL defined by the Japanese Society of Chemotherapy for a respiratory infection), and a breakpoint of FMX (16 µg/mL) defined by the Japanese Society of Chemotherapy for a urinary tract infection [61]. MIC of Tetracycline (TET) was measured manually using a broth microdilution test for all the isolates
4.3. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes, Genetic Analysis of fosB
Presence of genes conferring resistance to penicillin (blaZ), macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramins (erm(A), erm(B), erm(C), msrA, lnuA, lnuB), aminoglycosides (aac(6′)-Im, aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, ant(3″)-Ia, ant(4′)-Ia, ant(6)-Ia, ant(9)-Ia, ant(9)-Ib, aph(2″)-Ib, aph(2″)-Ic, aph(2″)-Id and aph(3′)-IIIa), oxazolidinone, phenicols, lincosamide, and pleuromutilins (optrA, cfr) were examined by a uniplex or multiplex PCR using the primers previously reported [62,63]. For the detection of fosB, primers for PCR detection were newly designed in this study depending on each staphylococcal species (Table S3), based on sequence information in the GenBank database, because fosB is genetically divergent. All the primer pairs were attempted to detect fosB. The full-length fosB gene sequence was determined by Sanger sequencing for the PCR products with primers shown in Table S4, using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) on an automated DNA sequencer (ABI PRISM 3100, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). A phylogenetic dendrogram of fosB was constructed by the maximum likelihood method using the MEGA11 software, together with fosB sequence data of staphylococcal strains available in the GenBank database. Multiple alignments of fosB/FosB and calculation of sequence identity were performed using the Clustal Omega program (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/, accessed on 1 December 2021). Sequence data of fosB determined in the present study were deposited in the GenBank database under accession numbers shown in Table S5. PCR detection of tgsB, tgsC, tgsD genes in the 6-TG biosynthetic gene cluster was performed for all the CoNS/Mammaliicoccus using the primers listed in Table S2.
4.4. Genotyping and Detection of Virulence Factors
For S. aureus isolates, the genotype of the staphylocoagulase gene (coa) was determined through sequencing of the partial coa gene (D1, D2 and the central regions) as described previously [56]. The sequence type (ST) based on a multilocus sequencing typing (MLST) scheme [64] and spa type based on protein A gene X-region [65] were determined. The presence of gene encoding following virulence factors in S. aureus was analyzed by multiplex or uniplex PCRs as described previously [62,66]: staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) (-like) genes (sea-see, seg-seu, selw, selx, sey, selz, sel26, sel27), hemolysins (hla, hlb, hld, hlg), leukocidines (lukDE, lukM, LukS-PV-lukF-PV), toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1 (tst-1), adhesins (clfA, clfB, cna, ebpS, eno, fib, fnbA, fnbB, icaA, icaD, sdrC, sdrD, sdrE), immune evasion factors (chp, sak, scn).
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by IBM SPSS Statistics ver.26. The Chi-square test was used to analyze the differences in the isolation rate of S. aureus and the proportion of AMR/drug resistance genes depending on the staphylococccal species. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens11040469/s1, Figure S1: Distribution and frequency of MIC to eight antimicrobials of S. aureus and CoNS/Mammaliicoccus isolated from ground meat specimens; Figure S2: Alignment of FosB amino acid sequences analyzed in this study and their identities in clusters of S. saprophyticus, S. warneri, and S. capitis; Table S1: Nucleotide sequence identity (%) of fosB among different staphylococcal species/clusters/subclusters; Table S2: Primers to detect 6-TG biosynthesis cluster genes by PCR; Table S3: Primers used to detect fosB by PCR for different Staphylococcus and Enterococcus species; Table S4: Primers used to amplify whole fosB ORF to determine its nucleotide sequence; Table S5: Genbank accession numbers of fosB gene identified in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.O., M.S.A. and N.K.; methodology, M.O., M.S.A. and N.U.; investigation, M.O., M.S.A. and N.U.; resources, M.O., M.H., M.K., N.O. and N.K.; data curation, M.S.A. and N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.A.; writing—review and editing, M.S.A. and N.K.; supervision, M.S.A. and N.K.; project administration, N.K.; funding acquisition, M.S.A. and N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by JSPS (Japan Society for the Promotion of Science) KAKENHI, Grant No. JP20H03933 and JP21K10401.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Götz, F.; Bannerman, T.; Schleifer, K.H. The Genera Staphylococcus and Macrococcus. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 5–75. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Schaumburg, F.; Ellington, M.J.; Corander, J.; Pichon, B.; Leendertz, F.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Holt, D.C.; Peters, G.; et al. Novel staphylococcal species that form part of a Staphylococcus aureus-related complex: The non-pigmented Staphylococcus argenteus sp. nov. and the non-human primate-associated Staphylococcus schweitzeri sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.L.; Octavia, S.; Lai, D.; Lin, R.T.P.; Teo, J.W.P. Staphylococcus singaporensis sp. nov., a new member of the Staphylococcus aureus complex, isolated from human clinical specimens. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Schaumburg, F.; Kearns, A.; Larsen, A.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Skov, R.L.; Westh, H. Implications of identifying the recently defined members of the Staphylococcus aureus complex S. argenteus and S. schweitzeri: A position paper of members of the ESCMID Study Group for Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Diseases (ESGS). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C.; Ziebuhr, W.; Becker, K. Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Wirth, J.S.; Saravanan, V.S. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov., and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar]
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Meghraoui, A.; Dodémont, M.; Heinrichs, A.; Denis, O.; Nonhoff, C.; Roisin, S. Bacteria from Animals as a Pool of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubakishita, S.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Sasaki, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Origin and molecular evolution of the determinant of methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 54, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, H.; Ziegler, D.; Pflüger, V.; Vogel, G.; Zweifel, C.; Stephan, R. Prevalence and characteristics of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from livestock, chicken carcasses, bulk tank milk, minced meat, and contact persons. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, K.M.; Amer, A.M.; Badr, J.M.; Saad, A.S. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus species in chicken and beef raw meat in Egypt. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, H.Y.; Elmalı, M.; Karagöz, A. Molecular Typing and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Raw Milk, Cheese, Minced Meat, and Chicken Meat Samples. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour 2017, 37, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, A.; Pichon, B.; Wilkinson, H.; Doumith, M.; Hill, R.L.; McLauchlin, J.; Kearns, A.M. Detection and molecular characterization of Livestock-Associated MRSA in raw meat on retail sale in North West England. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Hsu, C.H.; Davis, J.A.; Tran, T.T.T.; Yang, Q.; Abbott, J.W.; Ayers, S.L.; Young, S.R.; Crarey, E.T.; et al. MRSA and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in U.S. retail meats, 2010–2011. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Larsen, J.; Kjeldgaard, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Skov, R.; Ingmer, H. Methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from retail meat in Denmark. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Retail Meat and Meat Products in China: Incidence, Antibiotic Resistance and Genetic Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Rahman, M.; Huq, M.; Nabi, A.; Khan, Z.U.M.; Ahmed, N.; Wagenaar, J.A. Occurrence and Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Processed Raw Foods and Ready-to-Eat Foods in an Urban Setting of a Developing Country. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Kwak, H.S. Prevalence and Characteristics of Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Retail Meat in Korea. Food Sci. Anim. Resour 2020, 40, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanomsridachchai, W.; Changkaew, K.; Changkwanyeun, R.; Prapasawat, W.; Intarapuk, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Yamasamit, N.; Flav Kapalamula, T.; Nakajima, C.; Suthienkul, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, H.A.; Koláčková, I.; Florianová, M.; Gelbíčová, T.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M.; Karpíšková, R. Detection and molecular characterisation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw meat in the retail market. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwala, T.; Madoroba, E.; Basson, A.; Butaye, P. Prevalence and Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Meat and Meat Products in African Countries: A Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şanlıbaba, P. Prevalence, antibiotic resistance, and enterotoxin production of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from retail raw beef, sheep, and lamb meat in Turkey. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 361, 109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.I.; Kim, S.D.; Park, J.H.; Yang, S.J. Species Distribution, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Enterotoxigenicity of Non-aureus Staphylococci in Retail Chicken Meat. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitai, S.; Shimizu, A.; Kawano, J.; Sato, E.; Nakano, C.; Kitagawa, H.; Fujio, K.; Matsumura, K.; Yasuda, R.; Inamoto, T. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in retail raw chicken meat throughout Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2005, 67, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiroi, M.; Kawamori, F.; Harada, T.; Sano, Y.; Miwa, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Masuda, T. Antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens from retail raw meats and food-producing animals in Japan. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Usui, M.; Konishi, N.; Kai, A.; Matsui, H.; Hanaki, H.; Tamura, Y. Closely related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from retail meat, cows with mastitis, and humans in Japan. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candel, F.J.; Matesanz David, M.; Barberán, J. New perspectives for reassessing fosfomycin: Applicability in current clinical practice. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2019, 32 (Suppl. S1), 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda-García, A.; Blázquez, J.; Rodríguez-Rojas, A. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Impact of Acquired and Intrinsic Fosfomycin Resistance. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, M. Characterization of Fosfomycin Resistance Gene, fosB, in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Chang, S.C. Prevalence of fosfomycin resistance and gene mutations in clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanile, F.; Wootton, M.; Davies, L.; Aprile, A.; Mirabile, A.; Pomponio, S.; Demetrio, F.; Bongiorno, D.; Walsh, T.R.; Stefani, S.; et al. Gold standard susceptibility testing of fosfomycin in Staphylococcus aureus and Enterobacterales using a new agar dilution panel®. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ahmad, O.; Qi, L.; Li, P.; Li, J. Taxonomic Distribution of FosB in Human-Microbiota and Activity Comparison of Fosfomycin Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, D.; Goncheva, M.I.; Flannagan, R.S.; Deecker, S.R.; Guariglia-Oropeza, V.; Ensminger, A.W.; Heinrichs, D.E. Coagulase-negative staphylococci release a purine analog that inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torki Baghbaderani, Z.; Shakerian, A.; Rahimi, E. Phenotypic and Genotypic Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteria Isolated from Retail Meat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukcangaz, E.; Velasco, V.; Sherwood, J.S.; Stepan, R.M.; Koslofsky, R.J.; Logue, C.M. Molecular typing of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) isolated from animals and retail meat in North Dakota, United States. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Davis, J.A.; Barrett, J.B. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from retail meat and humans in Georgia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thapaliya, D.; Forshey, B.M.; Kadariya, J.; Quick, M.K.; Farina, S.; O’ Brien, A.; Nair, R.; Nworie, A.; Hanson, B.; Kates, A.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in commercially available meat over a one-year period in Iowa, USA. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anjum, M.F.; Marco-Jimenez, F.; Duncan, D.; Marín, C.; Smith, R.P.; Evans, S.J. Livestock-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus From Animals and Animal Products in the UK. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Tang, T.; Stegger, M.; Dalsgaard, A.; Liu, T.; Leisner, J.J. Characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from retail foods in Beijing, China. Food Microbiol. 2021, 93, 103603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkade, E.; Kluytmans, J. Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus CC398: Animal reservoirs and human infections. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, E.; Katsuda, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Uchida, I.; Tanaka, K.; Eguchi, M. Genetic variation among Staphylococcus aureus strains from bovine milk and their relevance to methicillin-resistant isolates from humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastmalchi Saei, H.; Panahi, M. Genotyping and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy ruminants: Differences in the distribution of clonal types between cattle and small ruminants. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achek, R.; El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Hendam, A.; Tomaso, H.; Ehricht, R.; Neubauer, H.; Nabi, I.; Hamdi, T.M.; Monecke, S. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Human and Food Samples in Northern Algeria. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainard, P.; Corrales, J.C.; Barrio, M.B.; Cochard, T.; Poutrel, B. Leucotoxic activities of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from cows, ewes, and goats with mastitis: Importance of LukM/LukF’-PV leucotoxin. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Nalepa, B.; Sierpińska, M.; Łaniewska-Trokenheim, L. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) isolated from ready-to-eat food of animal origin—Phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guran, H.S.; Kahya, S. Species Diversity and Pheno- and Genotypic Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of Staphylococci Isolated from Retail Ground Meats. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M1291–M1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, C.; Merz, A.; Johler, S.; Younan, M.; Tanner, S.A.; Kaindi, D.W.M.; Wangoh, J.; Bonfoh, B.; Meile, L.; Tasara, T. East and West African milk products are reservoirs for human and livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Zeng, W.; Wu, Q.; Yu, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T. Molecular Mechanisms and Epidemiology of Fosfomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Patients at a Teaching Hospital in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCicco, M.; Weese, S.; Neethirajan, S.; Rousseau, J.; Singh, A. Fosfomycin susceptibility of canine methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 96, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.A.; Vanderhaeghen, W.; Butaye, P. Diversity of antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes in methicillin-resistant non-Staphylococcus aureus staphylococci from veal calves. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 99, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashide, M.; Kuroda, M.; Omura, C.T.; Kumano, M.; Ohkawa, S.; Ichimura, S.; Ohta, T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus saprophyticus isolates carrying staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec have emerged in urogenital tract infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakaminami, H.; Noguchi, N.; Nishijima, S.; Kurokawa, I.; Sasatsu, M. Characterization of the pTZ2162 encoding multidrug efflux gene qacB from Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid 2008, 60, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wang, Y.; Schwarz, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, J.; Wu, C. Genetic environment of the multi-resistance gene cfr in methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from chickens, ducks, and pigs in China. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Lei, C.W.; Zhang, A.Y.; Pan, Y.; Kong, L.H.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Y.X.; Wang, H.N. Colocation of the Multiresistance Gene cfr and the Fosfomycin Resistance Gene fosD on a Novel Plasmid in Staphylococcus arlettae from a Chicken Farm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01388-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Freire Bastos, M.D.C.; Miceli de Farias, F.; Carlin Fagundes, P.; Varella Coelho, M.L. Staphylococcins: An update on antimicrobial peptides produced by staphylococci and their diverse potential applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10339–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Aung, M.S.; Fukuda, A.; Yahata, S.; Fujita, Y.; Saitoh, M.; Hirose, Y.; Urushibara, N.; Kobayashi, N. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiological Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant and Susceptible Staphylococcal Isolates from Oral Cavity of Dental Patients and Staff in Northern Japan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; McClure, J.A.; Elsayed, S.; Louie, T.; Conly, J.M. Novel multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous identification of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains USA300 and USA400 and detection of mecA and Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes, with discrimination of Staphylococcus aureus from coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.F.; Xu, X.; Song, Q.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Identification of Staphylococcus argenteus in Eastern China based on a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; p. M100. Available online: http://iacld.ir/DL/public/CLSI-2018-M100-S28.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 11.0. 2021. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Watanabe, A.; Yanagihara, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kohno, S.; Aoki, N.; Oguri, T.; Sato, J.; Muratani, T.; Yagisawa, M.; Ogasawara, K.; et al. National surveillance of bacterial respiratory pathogens conducted by the Surveillance Committee of Japanese Society of Chemotherapy, Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2012, 18, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aung, M.S.; Urushibara, N.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Sumi, A.; Shinagawa, M.; Takahashi, S.; Kobayashi, N. Clonal Diversity and Genetic Characteristics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Japan. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Aung, M.S.; Paul, S.K.; Ahmed, S.; Haque, N.; Khan, E.R.; Barman, T.K.; Islam, A.; Abedin, S.; Sultana, C.; et al. Drug Resistance Determinants in Clinical Isolates of Enterococcus faecalis in Bangladesh: Identification of Oxazolidinone Resistance Gene optrA in ST59 and ST902 Lineages. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shopsin, B.; Gomez, M.; Montgomery, S.O.; Smith, D.H.; Waddington, M.; Dodge, D.E.; Bost, D.A.; Riehman, M.; Naidich, S.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3556–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aung, M.S.; Urushibara, N.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Ito, M.; Habadera, S.; Kobayashi, N. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin (-Like) Genes sey, selw, selx, selz, sel26 and sel27 in Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins 2020, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).