Abstract
Malaria, which is caused by Plasmodium parasites through Anopheles mosquito transmission, remains one of the most life-threatening diseases affecting hundreds of millions of people worldwide every year. Plasmodium vivax, which accounts for the majority of cases of recurring malaria caused by the Plasmodium (non-Laverania) subgenus, is an ancient and continuing zoonosis originating from monkey hosts probably outside Africa. The emergence of other zoonotic malarias (P. knowlesi, P. cynomolgi, and P. simium) further highlights the seriousness of the disease. The severity of this epidemic disease is dependent on many factors, including the parasite characteristics, host-parasite interactions, and the pathology of the infection. Successful infection depends on the ability of the parasite to invade the host; however, little is known about the parasite invasion biology and mechanisms. The lack of this information adds to the challenges to malaria control and elimination, hence enhancing the potential for continuation of this zoonosis. Here, we review the literature describing the characteristics, distribution, and genome details of the parasites, as well as host specificity, host-parasite interactions, and parasite pathology. This information will provide the basis of a greater understanding of the epidemiology and pathogenesis of malaria to support future development of strategies for the control and prevention of this zoonotic infection.
1. Introduction
Malaria is a life-threatening infectious disease, with approximately 200 million cases and 400,000 deaths annually worldwide [1]. This major public health burden is caused by infection with Plasmodium species transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito.
The life cycle of Plasmodium species involves three phases: the sexual sporogonic phase in the Anopheles mosquito vector, followed by the asexual pre-erythrocytic and asexual and sexual erythrocytic phases in a vertebrate intermediate host, such as humans and monkeys. Sporozoites are the infectious agents introduced into the intermediate hosts from the salivary glands of the female Anopheles mosquito during their blood meal. Once injected, the sporozoites migrate to the liver to infect hepatocytes and develop into liver schizonts (liver stage). When the hepatic schizont bursts, multiple merozoites are released and enter the bloodstream (blood stage) (Figure 1). During the erythrocytic stage, the merozoites invade erythrocytes via coupled receptor-ligand interactions. Several changes occur on the merozoite surface to facilitate the invasion process [2]. The infected erythrocyte is effectively hijacked to supply nutrients for parasite growth and to evade host immune responses [3]. After invasion, a parasitophorous vacuole is formed around the parasite. This process is followed by parasite development of ring stage trophozoites and replication to form mature schizonts. The number of merozoites released from the burst schizonts to invade new erythrocytes depends on the Plasmodium species. The clinical symptoms of malaria, especially fever, chills, and nausea, are linked with each round of merozoite release and erythrocyte destruction, and the blood cycle duration differs among Plasmodium species. During each blood stage replication, a small portion of the asexual parasites develop into sexual stage micro- or macro-gametocytes, with accelerated development under microenvironmental stress conditions such as high parasitemia, anemia, host immune responses, or drug treatment [4]. These gametocytes are responsible for the transmission of the disease following their uptake by the Anopheles mosquito during feeding, which will then undergo sexual reproduction and then multiple rounds of division to generate sporozoites (mosquito stage).
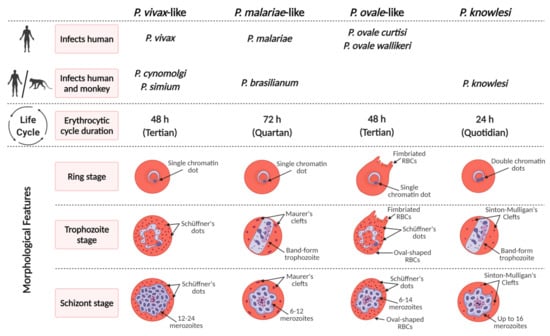
Figure 1.
Characteristics of non-Laverania Plasmodium species in the erythrocytic cycle.
Plasmodium species are known to cause malaria in vertebrate hosts, which include humans, non-human primates, reptiles, birds, and rodents [5]. Plasmodium species are categorized into 14 subgenera based on their morphology and host range. Plasmodium species that infect humans and African apes are classified under the subgenus Laverania (P. falciparum is the species in humans). Of the non-Laverania species, four are specifically found in humans: P. vivax, P. ovale wallikeri, P. ovale curtisi, and P. malariae. Of the other species, P. knowlesi, P. simium [6], P. brasilianum [7], and recently P. cynomolgi [8] which have non-human primates as natural hosts, have also been found to infect humans naturally zoonotically. A list of non-Laverania primate-infecting Plasmodium species and their potential for zoonosis is provided in Table 1. The emergence of zoonotic malaria depends on several possible factors, including changes in human habitation patterns and ecology, the presence of susceptible Anopheles mosquitoes and human hosts in the same region, frequency of human-primate-mosquito contacts, vector adaptation (anthropophagic or zoophagic behavior), and potential genetic recombination between the human-infecting Plasmodium species and closely related non-human primate-infecting Plasmodium species resulting in increased virulence [9].

Table 1.
Geographical distribution, human infectivity, and natural host(s) of non-Laverania Plasmodium species. ● = Species infecting humans naturally; ● = species infecting humans experimentally; ● = species that fail to infect humans; ● = unknown human infectivity.
The emergence of zoonotic malaria represents a challenge to malaria control and elimination and further magnifies the seriousness of malaria as a global health concern. The severity of this epidemic disease is determined by the parasitic characteristics, host-parasite interactions, and pathology of each of these human-infecting species. Little is currently known about the biology and invasion mechanism of these parasites, which might enhance the potential of zoonosis continuation. In this review, we provide an overview of the literature describing the characteristics, distribution, and genomes of the parasites as well as their host specificity, host-parasite interactions, and pathology of infection by zoonotic malaria species in the non-Laverania clade. A better understanding of the epidemiology and pathogenesis of malaria will help to support the future development of strategies for the control and prevention of these zoonotic infections.
2. Geographical Distribution and Vertebrate Hosts of Zoonotic Plasmodium Species
The establishment of zoonotic malaria requires that the Anopheles vector has access to both monkey hosts and humans in the same area. The absence of any of these factors will impede the occurrence of zoonotic malaria. Recent progress in industrialization and extension of agricultural areas has led to extensive deforestation, leading to the loss of wildlife habitats and a displacement in animal populations, with monkeys’ groups living closer to human habitation. These conditions increase the risk of zoonotic malaria. Understanding the geographical distribution of the human-infecting Plasmodium species is important for the development of targeted strategies that increase the efficiency of measures for malaria control and elimination.
Non-Laverania Plasmodium species are widely distributed throughout the world, and are particularly prevalent in tropical and sub-tropical regions of Southeast Asia. Infections also occur in sub-Saharan Africa, and Central and South America (Figure 2 and Table 1).
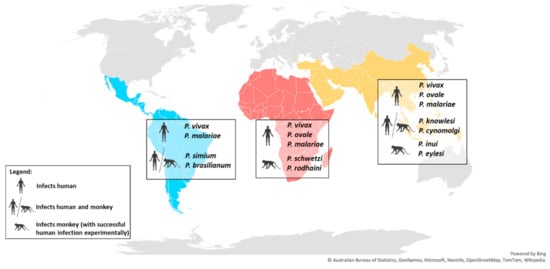
Figure 2.
World map showing the distribution of the main non-Laverania human-infecting Plasmodium species.
Among the non-Laverania subgenus, P. vivax is the most widespread human-infecting species and is prevalent in Southeast Asia, Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East. In 2018, 85% of the P. vivax infections were reported in only six countries: India (47%), Afghanistan (11%), Pakistan (8%), Ethiopia (8%), Papua New Guinea (6%), and Indonesia (5%) [1]. On the other hand, the cases of human infections by P. ovale and P. malariae are less frequent than the dominant P. vivax. P. ovale is predominantly distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, and occurs less frequently in Southeast Asia and the Middle East [10,11,12], while P. malariae is distributed widely across the tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa, Central and South America, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East [6,10]. However, due to its characteristically low parasitemia [6], the prevalence of P. malariae infections is likely to be underreported.
In Southeast Asia, long-tailed and pig-tailed macaques are the most common hosts for the zoonotic P. knowlesi and P. cynomolgi [13,14] (Table 1). A study in Singapore, one of the two major cities with Rio de Janeiro with a tropical rainforest, has detected the presence of simian malaria in the wild macaques, which included mono- or co-infection of P. coatneyi (28.5%), P. fieldi (32.5%), P. inui (42.0%), P. knowlesi (47.5%), and the dominant P. cynomolgi (71.5%) [25]. On the other hand, the peridomestic macaques in Singapore are malaria-free, suggesting a low zoonotic transmission risk to the human population [25]. However, P. knowlesi and P. cynomolgi that are found only in Southeast Asia in their macaque natural hosts, were shown to infect humans zoonotically in the same region in 2004 and 2014, respectively [8,26,27,28,29,30,31]. The outbreak of P. knowlesi in Malaysia infers the high zoonotic malaria transmission risk in the areas where the natural macaque and human hosts and the Anopheles vectors co-exist. The similarities in the morphology of P. malariae and P. knowlesi in the erythrocytic stage resulted in misdiagnosis of this species in humans [29]. The morphology of P. cynomolgi is indistinguishable from that of P. vivax [13] and the species share 98% homology in the 18S RNA gene sequence [32]. These similarities increase the risk of misdiagnosis of P. cynomolgi as P. vivax. Asymptomatic human infection by P. knowlesi and P. cynomolgi have also been reported, raising difficulties in the evaluation of the distribution and prevalence of these parasites in humans [32]. Two other primate malarias that are found in Southeast Asia have been shown to be capable of infecting humans experimentally: P. inui naturally infects various species of the genus Macaca and Presbytis [13,14,17], while P. eylesi is found in Hylobates lar [13]. The ability of these parasites to infect humans may drive their zoonotic risk to the same region due to the sharing of natural hosts, and perhaps the Anopheles vectors with other human-infecting Plasmodium species.
Few cases of human infection by P. vivax have been reported in sub-Saharan Africa due to the Duffy-negative genotype that is predominantly found in African populations [33]. Studies have shown the importance of the interaction between the Duffy receptor for chemokine (DARC) and Duffy binding protein (DBP) in P. vivax and P. knowlesi invasion during the erythrocytic stage [34,35]. However, the ability of P. vivax to invade Duffy-negative erythrocytes was uncovered by the recent detection of P. vivax infection of Duffy-negative populations in African countries, such as Angola [36], Benin [37], Botswana [38], Cameroon [39], Ethiopia [40], Equatorial Guinea [36], Kenya [41], Madagascar [42], Mali [43], Mauritania [44], Senegal [45], Sudan [46], Uganda [47], and Namibia [48]. This might be due to a genotypic adaptation of this parasite that enhances its transmission. The receptor-ligand interactions involved in P. vivax and P. knowlesi invasion have not been fully elucidated; however, it is possible that the parasites utilize another route or receptor-ligand interaction, such as reticulocyte specific receptors [49,50], for successful invasion during the erythrocytic stage. The primate malaria P. schwetzi and P. rodhaini are found in sub-Saharan Africa where they infect African chimpanzees and gorillas [13,24]. The tertian malaria, P. schwetzi, has similar morphology to P. vivax and P. ovale [51,52], while P. rodhaini is closely related to P. malariae [13,51,52]. Both species can infect humans experimentally and because of their similarities with the human-infecting Plasmodium species, they have the potential for zoonotic transmission [13,24,53].
P. simium was reported to naturally infect New World monkeys including howler, woolly spider, and capuchin monkeys [6]. These monkeys are distributed in South and Central America, which is consistent with the reports of human P. simium infections that are restricted to the Atlantic Forest of the Southeast region of Brazil [6]. By contrast, P. brasilianum was shown to infect a large diversity of New World monkey species, covering the five families of these primates across regions of South America [20,54]. In terms of morphology, genetics, and immunological responses, the similarities between P. simium and P. vivax, and between P. brasilianum and P. malariae, have been confirmed [55,56,57,58]. The evolutionary and phylogenetic relationships between P. vivax and P. simium, and between P. malariae and P. brasilianum, have been evaluated on the basis of the genetic sequences of cytochrome b, merozoite surface protein-1, and SSU rRNA [59]. The similarities between these species have led to cases of misdiagnosis [6], which is further discussed in the next section.
3. Genome Characteristics of Zoonotic Plasmodium Species
Genomic research on Plasmodium species has undergone tremendous progress with the advances in technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) that have overcome the challenges associated with obtaining sufficient gDNA of acceptable quality for whole genome shotgun sequencing (WGSS). The advent of NGS has facilitated the analysis of very small amounts of genetic material (5 Plasmodium genomes/μL) [60] without compromising the quality of the sequencing. This has led to a reduction in costs, making sequencing analyses more readily available. Consequently, the amount of information deposited in databases has increased over the years and several reference genomes of various Plasmodium species are now available. Public databases provide not only the sequences of human-infecting species of Plasmodium, but also genome information for zoonotic parasites such as P. cynomolgi and P. knowlesi. This knowledge has shed light on their evolutionary relationships. This, in turn, has provided important information that has clarified the genome diversity, host invasion strategies, and drug resistance mechanisms. Advances in single-cell sequencing techniques have facilitated the constant updating of reference genomes for each species with more accurate annotations. Comparative genomics, which provide an invaluable insight into the biology of the parasite and host-parasite interactions, will be covered in this review.
The genomes of the different Plasmodium species range from 20 to 35 megabases (Mb), with the nuclear genome distributed among 14 chromosomes (Table 2). Genomic comparisons of the different species showed variation in the arrangement of homologous genes on different chromosomes [61,62], which indicates a lack of synteny. However, it is important to note that P. knowlesi, P. vivax, and P. cynomolgi have highly conserved gene synteny along all 14 chromosomes despite several microsyntenic breaks [63]. This is expected as these species are from the same monkey malaria clade. While several comparative genomics have been conducted, these synteny maps tend to focus on human and rodent malaria. Hence, there is lack of synteny maps on zoonotic malaria which makes studying the zoonotic parasite traits and populations challenging. There are also marked variations in the guanine–cytosine (GC) content for the Plasmodium species. The GC-rich genes are also known to evolve faster than adenine–thymine (AT)-rich subtelomeric genes [64]. For the P. knowlesi chromosomes, the GC-rich repeat regions containing intrachromosomal telomeric sequences are found at multiple internal sites, arrayed tandemly or as components of larger repeat units [65]. This is unusual for Plasmodium species and these sequences appear infrequently in P. vivax, for example, while rodent malaria parasites have a relatively higher AT content of approximately 60%. Protein-coding exons have lower AT content than introns and intergenic noncoding regions. The rich AT content in the genomes of Plasmodium species often contributes to the technical hurdles in genomic sequencing [66]. A high AT content often reflects the existence of many low-complexity regions, microsatellites, and simple sequence repeats [67].

Table 2.
Comparison of genome features of zoonotic Plasmodium species.
P. vivax has a unique evolutionary path that is closely related to that of P. cynomolgi, P. knowlesi, and P. simium (Figure 3). A recent study which characterized 447 human P. vivax strains and 19 ape P. vivax-like strains has shown phylogenetic evidence that P. vivax is a sister clade of P. vivax-like instead of a lineage within the radiation of P. vivax-like [72]. Furthermore, the 19 P. vivax-like strains were categorized in two distinct clades which form a sister monophyletic lineage to the human P. vivax. These findings challenge previous studies which suggested that P. vivax is included inside P. vivax-like diversity [73,74]. Although P. knowlesi is closely related to P. vivax phylogenetically, there are distinct phenotypic differences such as the lack of hypnozoites (the latent hepatic form) in P. knowlesi. The first P. knowlesi to be sequenced was that of the H strain, Ok1 (A1) clone [65]. The nuclear genome of P. knowlesi, with a size of 24.4 Mb, contains genes that are approximately 80% orthologous to those of P. vivax [65]. A large proportion of the P. vivax genes were also found to be orthologous to P. cynomolgi genes. The orthologues identified had highly conserved genome positions [64] throughout all 14 chromosomes. Mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (mtCOI) gene amplicons were analyzed to detect P. knowlesi cases in Indonesian patients as it possesses a greater range of phylogenetic signal than any other mitochondrial and nuclear gene [75,76]. Phylogenetic analyses based on WGS of P. simium isolates indicated that P. simium is monophyletic within the broader diversity of P. vivax [68]. This suggested that P. simium first infected non-human primates as a result of a host-switch from humans carrying P. vivax. Large deletions within the coding region of reticulocyte-binding protein 2a (RBP2a) were observed in P. simium compared with P. vivax [68]. This is corroborated by another study conducted recently in which the authors observed host switching from humans to sylvatic monkeys in P. simium, indicating reverse zoonosis [77]. The study suggested the cause of the adaptation of P. simium to non-human primate hosts could be due to the >40% deletion of the coding sequence of PvRBP2a in the P. simium genome. Hence, the lack of PvRBP2a-mediated erythrocyte binding in P. simium may lead to a facilitation of alternative ligands for a more efficient monkey host cell infection [77]. While information about the genetic basis of P. simium zoonosis is scarce, the deletions suggest the existence of a possible facilitator of zoonotic transfer. As P. simium is almost indistinguishable from P. vivax, it is also possible that zoonotic transmission of P. simium has always existed, but the cases were misdiagnosed as P. vivax.
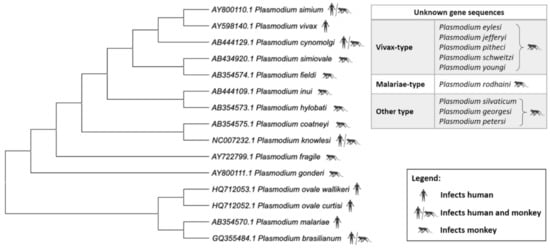
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of the Plasmodium species. Relationship of non-Laverania Plasmodium species based on mitochondrial cox3, cox1, and cytb sequences. Created using MegaX (Table S1).
Due to low prevalence and parasite densities, P. malariae and P. ovale infections have not been widely discussed until recently. The improved sensitivity of the current molecular techniques has revealed an increasing number of mixed infections that include P. malariae and/or P. ovale. The nuclear genome of P. malariae was first sequenced from the CDC Uganda I strain [71]. The nuclear genome of P. malariae has a size of 33.6 Mb, with a GC content of approximately 24%. Interestingly, in this species almost all of its Plasmodium interspersed repeats (pir) genes, which may be important for antigenic variation, are pseudogenes. Phylogenetic analyses show that P. ovale is grouped together with P. malariae.
Approximately 40% of the total genes of P. malariae and P. ovale are subtelomeric [69]; however, the gene content of these subtelomeres differs greatly. The ancient divergence of the two P. ovale sub-species is corroborated by their discernible pir repertoires [69]. While the nuclear genomes of both P. ovale wallikeri isolates are approximately 35 Mb in size, a marked difference in the genome sizes of the P. ovale curtisi isolates was observed. The significant variation in the genome sizes of P. ovale curtisi 1 and P. ovale curtisi 2 was found to be due to differences in the magnitude of the pir gene family repertoires represented within the genome [71]. Both P. ovale species have a significantly larger genome size than the zoonotic Plasmodium species which are highlighted in this review (Table 1). This could be due to the expansion of variant gene families. In both P. ovale species, the surfin gene family contains more genes. The roles of surfin gene products are predicted to be erythrocyte surface receptors as they are exported to host erythrocyte cytoplasm and then exposed on the erythrocyte surface [78]. The SURFIN genes in P. malariae and both P. ovale species contain schizont-infected cell agglutination (SICA) domain. Since SICAvar proteins are known to have an evolutionary link with SURFIN proteins in P. vivax [79], the differential expansion of surfin genes in both P. ovale species (125 genes in P. ovale wallikeri and 50 genes in P. ovale curtisi) could be useful for discerning the species at the molecular level.
The simian parasite P. brasilianum was first reported in New World monkeys. Investigations in the 1960s demonstrated that humans could be experimentally infected with P. brasilianum from monkeys and vice versa [13]. However, it was only recently reported that naturally acquired infections of P. brasilianum occur in humans [7]. P. brasilianum is morphologically indistinguishable from P. malariae and their genomes are very similar [69,80], with 99% similarity when aligned [80]. Hence, this could pose a problem in the use of molecular diagnostic techniques to distinguish between these two species with confidence and it is possible the recent unexpected detection of P. malariae in Costa Rica could be due to a misdiagnosis of P. brasilianum. The close genetic relationship of P. brasilianum and P. malariae subtypes suggests that both species constitute a complex group that has diverged as a result of allopatric speciation.
4. Characteristics and Pathology Associated with Individual Zoonotic Plasmodium Species
Among the non-Laverania subgenus that infect humans, P. vivax and P. ovale are similar morphologically and phenotypically. Like P. vivax, P. ovale infects reticulocytes preferentially whereas P. malariae invades senescent erythrocytes [81,82,83]. Many studies have shown that P. malariae exhibit normocyte cell tropism, although in vitro culture is still problematic [84]. P. malariae-infected cells are usually smaller than uninfected erythrocytes. It is possible that P. malariae causes acceleration of the maturation of the infected erythrocytes, leading to the mature erythrocyte phenotype of infected cells as demonstrated for reticulocytes with P. vivax [85]. This phenomenon may lead to the erroneous conclusion that P. malariae infects senescent normocytes preferentially.
The typical characteristic of P. ovale is the stippling or Schüffnerization [13], which appears in the early blood stages of P. ovale and intensifies as the parasite grows. Schüffnerization in P. ovale is also more marked than that in P. vivax [13]. Interestingly, caveola–vesicle complexes, which are similar to those of P. vivax, are also present in P. ovale-infected erythrocytes. These complexes consist of caveolae surrounded by vesicles in an alveolar fashion and form along the host cell plasmalemma. The fact that these complexes have not been reported in P. malariae suggests that a caveola–vesicle complex corresponds to a Schüffner’s dot. P. malariae induces the production of spikes, caveolae, electron-dense material, vesicles, clefts, and knobs in the erythrocyte [86,87]. The vesicles and caveolae, which may be involved in antigen trafficking, do not form the caveola–vesicle type complexes that are seen in P. vivax-infected erythrocytes [86].
Deformation of erythrocytes is required to allow their passage through the microvasculature and the sinusoids of the spleen. P. vivax increases the deformability of the infected erythrocytes, which facilitates their passage through the narrow inter-endothelial slits of the splenic sinusoids. Nonetheless, P. vivax-infected erythrocytes do sequester [88] and avoid splenic clearance [89]. Recently, it has been observed that intact P. vivax-infected erythrocytes accumulate in the spleen. Splenic tropism is the highest in P. vivax infections with more than 98% of asexual-stage parasites. This may suggest that chronic malaria could be due to the infection of the spleen, instead of blood infection solely [90,91]. Infected erythrocytes deformability can also be observed in P. ovale and P. cynomolgi infections [87].
As mentioned previously, it is highly implied that P. brasilianum and P. simium are a zoonotic transfer from P. malariae and P. vivax, respectively. It is therefore no surprise that some of the morphologies of the zoonotic Plasmodium species are similar to those of P. vivax, P. malariae, and P. ovale. The characteristics and pathology of P. knowlesi, P. cynomolgi, P. simium, and P. brasilianum are discussed below.
4.1. Plasmodium knowlesi
Naturally acquired human P. knowlesi infections were thought to be extremely rare until a large focus of human infections was reported in Malaysia Borneo in 2004 [29]. Before the advent of molecular detection methods, P. knowlesi infections were often misdiagnosed as P. malariae due to morphological similarities [92]. Double-chromatin dots in early trophozoites and no enlargement of infected erythrocytes are the morphological features of P. knowlesi [92]. The band-form trophozoites of P. knowlesi greatly resemble those of P. malariae; however, minor differences can be observed between P. knowlesi and P. malariae, mainly, in the double-chromatin dots in trophozoites and the number of merozoites produced. These minor differences are often overlooked during microscopic diagnosis especially when only thick blood films are examined because parasitemia are low. The median peak parasitemia observed in knowlesi malaria is ca. 2500/μL in humans, but can reach much higher levels in severe cases [93]. P. knowlesi-infected erythrocytes also show ‘Sinton and Mulligan’ stipplings [13]. Some of the ultrastructural features of P. knowlesi-infected erythrocytes include lack of knobs and the presence of caveolar pits without vesicles association in the infected erythrocytes during the trophozoite stage [94,95]. This is unlike P. vivax infection, in which caveola–vesicle complexes and clefts are formed in the erythrocytes [95]. These structures are involved in protein trafficking from the vivax parasite to the erythrocyte membrane [86,87]. Cleft-like structures and tubular vesicles features that wrap around regions of the host cell cytoplasm are also observed in knowlesi malaria. Electron tomography analysis revealed budding of small vesicles from the Sinton Mulligan’s clefts [94]. Generally, the prepatent period ranges from 9 to 12 days in humans and from 7 to 14 days in Macaca fascicularis [13,96].
P. knowlesi has the shortest asexual replication cycle of all Plasmodium species leading to rapidly increased parasite levels. Most human P. knowlesi cases are chronic and symptomatic with a potentially fatal outcome [97,98,99]. Thrombocytopenia is the most reported condition in the majority of these cases [92,98,100,101]. Furthermore, knowlesi malaria patients may be hyperparasitemic and develop hepatorenal/renal dysfunction, with jaundice, hypoglycemia, and lactic acidosis being the potentially devastating metabolic consequences [102]. Other clinical findings include respiratory distress with increased permeability of the pulmonary capillaries [102]. Similarly, vivax malaria is known to cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in which pulmonary vascular sequestration and post-treatment alveolar-capillary inflammation are observed [103].
The pathogenesis of severe P. knowlesi infection is not yet fully understood. In one study, a P. knowlesi-infected patient died within 2 h of admission to hospital and was found to have multiorgan failure [98]. An accumulation of infected erythrocytes was found in this patient, indicating possible sequestration of parasites and hemorrhagic complications in vital organs, though chronic inflammatory infiltrates were not present. The kidney showed signs of acute tubular necrosis and prominent endothelial cell infiltration was observed in heart sections [98]. Complicated knowlesi malaria cases often had higher levels of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-6, IL-8, IL-1ra, and IL-10 [104]. This is similar to vivax malaria in which high plasma levels TNF-α and IFN-γ are correlated with disease severity. However, plasma concentrations of IL-10 were shown to be inversely related to disease severity of vivax malaria [105]. While further investigations are needed to fully understand the pathology of severe P. knowlesi infection, studies have shown that the pathogenesis of complicated disease is different from that of P. vivax.
4.2. Plasmodium cynomolgi
P. cynomolgi was first discovered in 1907 in long-tailed macaques (Macaca fascicularis) imported into Germany from Java [13]. The first case of a naturally acquired human infection with P. cynomolgi was reported in the Malay Peninsular in 2014 [8]. More recently, asymptomatic human infections with both P. knowlesi and P. cynomolgi were discovered in western Cambodia [32]. As a zoonotic species, P. cynomolgi has a high degree of morphological and biological similarities with P. vivax, making it hard to distinguish the two species [8,32]. Therefore, it can be speculated that some P. cynomolgi infections have been misdiagnosed as P. vivax. Due to these similarities, P. cynomolgi has been used as a model for P. vivax [106]. In the early stages, enlargement of the infected erythrocytes becomes noticeable as the young parasite grows to a diameter of approximately half more than that of the original host cell. Eventually, Schüffner’s stippling and pigments become more prominent as the parasite progresses through the stages of development [13]. The late trophozoite stage of P. cynomolgi closely resembles that of P. vivax [13] with the presence of Schüffner’s dots in both trophozoites and schizonts as for P. vivax [107,108]. At maturity, the number of merozoites ranges from 14 to 20, with an average of 16 [13]. The duration of the erythrocytic stage cycle of P. cynomolgi is 48 h, with a prepatent period of 19 days observed in humans. In M. speciosa and M. mulatta, the prepatent period ranges from 7 to 16 days [13]. The two most studied strains of P. cynomolgi in its experimental host Macaca mulatta are the Mulligan or M strain and the subspecies P. c. bastianellii or the B strain. The mean parasitemia for the B strain is higher than that of the M strain [13].
During primary infections in rhesus macaques, mild to severe anemia is observed, with mild thrombocytopenia observed in all infected macaques [109]. Accidental laboratory-acquired human infections with P. cynomolgi resulted in clinical symptoms including anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperglobulinemia [110]. The patients with the naturally acquired human infection with P. cynomolgi experienced non-specific symptoms that mimicked a flu-like syndrome [8]. In a recent case of a naturally acquired human infection, the patient experienced muscle pain, fever, headache, and abdominal pain with low-grade parasitemia. The different parasitic stages observed in the patient’s blood smears resembled P. vivax with slight morphological differences [111]. It has long been established that P. cynomolgi is a relapsing malaria in macaques [13,112]. However, to date, no studies have been reported on any relapse cases in naturally acquired human infections.
4.3. Plasmodium simium
P. simium was first identified in 1951 in a monkey from the state of São Paolo in Brazil [113]. It is similar at the morphological, genetic, and immunological levels to P. vivax [6]. However, the trophozoites of P. simium are reported to be less amoeboid, with coarser, and more prominent Schüffner’s dots than P. vivax [6]. The Schüffner’s stippling is very distinct in all stages, except, in the young ring stage and can be seen filling up the entire host cell [13]. Young erythrocytes infected with late developmental forms of P. simium often display multiple surface clefts and cytoplasm-associated microvesicles (Schüffner’s dots) [13,58]. Dual infections are quite common in simium malaria. The mature schizonts of P. simium produce 12 to 18 merozoites. The asexual blood stage cycle is approximately 48 h [13]. In squirrel monkeys, the mean parasitemia can be greater than 10,000 per µL by day 8 and may remain at this level or higher for 25 days.
Patients with naturally acquired P. simium infection reported clinical symptoms that are consistent with those of P. vivax malaria. These patients responded successfully to chloroquine and primaquine, with no relapses or deaths [6]. The pyrogenic threshold of P. simium infection is extremely low [6], although the reason for this is still unknown. Further studies are required to establish whether P. simium is capable of producing hypnozoites and in turn, causing relapse.
4.4. Plasmodium brasilianum
P. brasilianum was first described in monkeys in the early 20th century. To date, no consistent morphological, immunological, or genetic differences between P. brasilianum and P. malariae have been identified [7,56,114]. P. brasilianum causes quartan malaria as it has a 72 h erythrocytic cycle [13]. In malaria-endemic regions, co-infections of P. brasilianum with other Plasmodium species are common. In areas of South America where both humans and monkeys co-exist, differentiating P. malariae and P. brasilianum infections is impossible due to their high degree of morphological similarity [115]. Since parasitemia in the human host is low and parasite counts rarely exceed 50 per µL [13], co-infections are often under-detected by microscopy. Ziemann’s stippling can be observed during the late ring stage [13]. Once mature, the schizonts release between 8 and 12 merozoites. Similarly, P. malariae has a production of relatively low number of merozoites (6 to 14, with an average of 8) per erythrocytic cycle [13,115]. P. brasilianum infection induces the formation of knobs, short and long clefts, and electron-dense material—all of which can also be observed in P. malariae-infected erythrocytes. Spikes, which are superficially similar to knobs, are also present in great quantity on RBCs infected with P. brasilianum and P. malariae. While these spikes are also present in P. ovale-infected RBCs, they are usually lesser and bigger in size [116]. These structures appear to contain different P. brasilianum antigens, indicating that each structure functions independently in trafficking P. brasilianum protein to the erythrocyte surface [86].
During the course of an infection in Ateles monkeys, the parasitemia may rise and fall following a predetermined pattern. An initial rise in parasite numbers is followed by a significant reduction, a low-grade blood infection and finally, short periods of sub-patent parasitemia interspersed with spontaneous recrudescence [13]. Recrudescence can occur when the host is subjected to stressful conditions or becomes immunocompromised [117]. While the infection in Ateles and Saimiri monkeys can continue for at least 249 days, the parasitemia in humans infected with P. brasilianum did not exceed 27 days. On the other hand, there is a wide range of prepatent period in naturally transmitted P. malariae, ranging from 18 to 59 days in humans [13]. The clinical manifestations were generally milder than observed in infections with P. cynomolgi or P. knowlesi [13]. P. brasilianum can induce renal pathology when it persists as a chronic infection in humans [117].
5. Role of Plasmodium Ligands in Erythrocytic Invasion
Successful infection of vertebrate hosts by Plasmodium species depends on several factors, one of the main determinants being the presence of appropriate erythrocyte surface receptors. The two types of infected erythrocytes are reticulocytes and normocytes. There is variation in the levels of surface receptors expressed by erythrocytes at different stages of differentiation, which lead to the differences in the cell tropism for Plasmodium parasites invasion. P. vivax [118], P. ovale wallikeri [82], P. ovale curtisi [82], P. cynomolgi [119], and P. simium [120] have strict reticulocyte-restriction in humans. By contrast, P. malariae [83] and P. brasilianum [120] invades only senescent normocytes, while P. knowlesi [121] invades normocytes with a preference for reticulocytes.
To date, P. knowlesi is the only zoonotic form of malaria for which continuous in vitro culture in human erythrocytes has been established [122]. In the human blood circulation, reticulocytes account for only 1 to 2% of the adult peripheral blood and mature to form normocytes over a 72 h period. This poses a challenge to maintaining an in vitro cultivation of parasites that invade only reticulocytes. Conversely, P. malariae that invades normocytes has difficulties in establishing its long-term culture with adult peripheral blood, which has made its cell tropism a controversy. The difficulties in establishing continuous parasite culture hinder the identification of the receptor-ligand interactions involved in the merozoite invasion mechanism.
The basic structure of merozoites is similar across the different Plasmodium species; hence, all may utilize the same invasion mechanism during their erythrocytic stage despite having different cell tropism patterns and receptor-ligand interaction preferences [123] (Figure 4). As merozoites are released from schizonts, invasion of erythrocytes through a series of events is required to initiate a new cycle of erythrocytic development. This process is initiated by reversible attachment of the merozoite to an erythrocyte, which is thought to be mediated by glycosylphosphatidyl inositol (GPI)-anchored merozoite surface proteins (MSPs), although the specific receptor-ligand interaction has not yet been fully elucidated [123]. The merozoite then undergoes apical reorientation, which has been shown to trigger different interactions involving the reticulocyte-binding-like (RBPs) and erythrocyte-binding-like (EBPs) proteins. These interactions initiate the formation of a tight and irreversible attachment between the merozoite and the erythrocyte. The formation of the tight junction has been shown to involve members of the rhoptry neck proteins (RON) family, specifically RON2, and apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1) [124]. After tight junction formation, the merozoites penetrate the erythrocyte via glideosome activity and finally seal themselves within the parasitophorous vacuole.
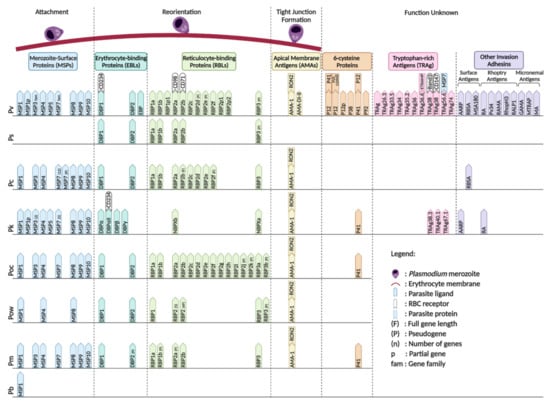
Figure 4.
Non-Laverania Plasmodium species ligands with their respective erythrocyte receptors during invasion in erythrocytic stage. (F) = full gene length; (P) = pseudogene; (n) = number of genes; p = partial genes; fam = gene family. Created with BioRender.com.
The recognition and initial attachment of merozoites to the erythrocyte surface is governed by the MSPs on the merozoite surface. Several MSPs have been identified, with MSP1, MSP3, MSP4, MSP5, MSP6, MSP7, MSP8, MSP9, and MSP10 being commonly found in all the non-Laverania human-infecting Plasmodium species, except P. simium, which is less well characterized. PvMSP1 has been proved to have highly specific binding affinity towards reticulocytes, and has similar cleavage sites to those of PfMSP1 [125]. Cleavage at these sites generates 42- and 19-kDa carboxy-terminal fragments that are believed to be involved in initial attachment to the erythrocyte and the invasion process [125]. P. vivax merozoite surface protein 1 paralog (PvMSP1P) has been reported and hypothesized to play an important role in parasite adhesion based on its ability to bind erythrocytes via its 19-kDa C-terminal region [126]. MSP3 gene family members confer the antigenic properties on the parasite and contribute to the immune response induced in non-human primates against erythrocytic stage Plasmodium parasites [64]. It has been demonstrated that MSP7 in P. falciparum binds to MSP1 on the merozoite surface and the invasion efficiency has been shown to be reduced by MSP1 knockout [64,127]. The significant expansion of the MSP3 and MSP7 gene families in P. vivax compared with P. falciparum might account for its improved immune evasion and adhesion properties [64]. The other MSP gene families do not have any known function in the invasion mechanism.
RBPs and EBPs are the two major ligand families that account for the cell tropism of the parasites. A total of 11 PvRBP family members have been identified through homology analysis of P. vivax RBP and P. yoelli Py235 member gene sequences [128]. The 11 Pv-RBPs contain five full-length genes, three partial genes and three pseudogenes [128]. PvRBP2a has been shown to bind CD98 on reticulocytes with high affinity [129]. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), immunoprecipitation, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based assays further confirmed the specific binding of PvRBP2b to CD71 [130,131]. Gruszczyk et al. showed that the PvRBP2b binding ability is directly proportional to the level of CD71 expression on the erythrocyte surface [131]. The interaction of PvRBP2a and PvRBP2b with CD98 and CD71, respectively, on reticulocytes is the basis of the strict reticulocyte cell tropism of P. vivax. The RBP-encoding genes of P. ovale curtisi and P. ovale wallikeri have expanded to 15 and 12 copies, respectively, with several identified as pseudogenes [71,132]. P. cynomolgi is known to infect reticulocytes and also has seven full-length RBPs (PcRBP1a, PcRBP1b, PcRBP2a, PcRBP2c, PcRBP2d, PcRBP2e, and PcRBP3) and two fragmented RBPs (PcRBP2b and PcRBP2f) [132]. On the other hand, five PsRBPs, comprising four full-length RBPs and one pseudogene have been reported in P. simium [68]. The Plasmodium species that invade normocytes have been shown to possess fewer copies of RBPs compared with the reticulocyte-invading Plasmodium species, which highlights the importance of the RBPs in determining Plasmodium cell tropism. The senescent normocyte-invading P. malariae appears to have three full-length RBPs (PmRBP1a, PmRBP2b, and PmRBP-3) and two pseudo RBPs (PmRBP1b and PmRBP2a) [132]. P. knowlesi, which invades both normocytes and reticulocytes, possesses only two full-length RBPs, PkNBPXa [133] and PkNBPXb [132]. The limited number of RBPs in these normocyte-invading parasites indicates the presence of alternative receptor-ligand interactions that facilitate the invasion process.
EBPs are released to the merozoites surface from the microneme during apical reorientation of the merozoite [127]. The EBPs that have been discovered in the non-Laverania Plasmodium species are members of the Duffy binding protein (DBP) family, with DBP1 and DBP2 being the most commonly identified forms [68,69,132,134,135]. However, P. knowlesi has three DBP copies (DBPα, DBPβ, and DBPγ) [132]. CD234, which is also known as the Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC), is utilized by P. vivax and P. knowlesi for their invasion into erythrocytes via interaction with DBP1 and DBPα, respectively [136]. Following CD234 knockout, the invasion ability of P. vivax was reportedly reduced [137]. However, it has recently been reported that the Duffy-null population in Africa is infected with P. vivax [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. DBP1 has been shown to expand from three to eight copies in Duffy-null-infected cells [134], leading to the hypothesis that the expansion of DBP1 facilitates binding to other erythrocyte receptors with low affinity to achieve successful invasion [134]. Moreover, the failure of Pv-DBP1 to bind to Duffy-null erythrocytes, and the binding of PvDBP2 to Duffy-positive and Duffy-null erythrocytes at low frequency suggests that PvDBP2 may have a role in the invasion mechanism when PvDBP1 is non-functional [134].
During tight junction formation, AMA1 is secreted to the merozoite surface while RON complexes are injected to the erythrocyte surface via the rhoptry neck. AMA1 is known to bind to RON2 and both are found in all the species discussed in this review, with the exception of P. simium and P. brasilianum, for which there is no evidence to date. P. vivax AMA1 domains I and II (Pv-AMA1_DI-II) are responsible for the specific targeting of CD71+ reticulocytes [138].
The 6-cysteine protein family comprises a group of conserved surface proteins expressed throughout the life cycle of the Plasmodium parasites in Anopheles mosquito and vertebrate hosts. Five of these proteins have been discovered in P. vivax: PvP12 [139], PvP12p [140], PvP38 [141], PvP41 [142], and PvP92 [140]. PvP12 is co-localized with PvRON2 in the rhoptry of P. vivax merozoites [139]. The immunogenicity of PvP12 discovered in a P. vivax-infected patient indicates that it plays a role in P. vivax invasion [139]. PvP41 is usually released from the merozoite surface in the schizont stage of the erythrocytic cycle [142]. PvP38 is found on the schizont during the erythrocytic cycle [141]. PvP12 and PvP41 form a complex on the merozoite surface and interact with PVX_110945, which is an uncharacterized protein [140]. PvP92 has been suggested to be responsible for preventing complement-dependent lysis of merozoites as its P. falciparum orthologue (PfP92) is known for this function [143]. P41 has also been identified in P. knowlesi, P. ovale curtisi, and P. malariae [144].
Tryptophan-rich antigens (TRAgs) have been recommended as malaria vaccine subunit candidates based on the ability of some members to bind to erythrocytes [145,146,147]. TRAgs have been identified in two Plasmodium species, P. vivax, and P. knowlesi. In P. vivax, 10 TRAgs were found to have the ability to bind to human erythrocytes (PvTRAg, PvTRAg26.3, PvTRAg33.5, PvTRAg34, PvTRAg35.2, PvTRAg36, PvTRAg36.6, PvTRAg38, PvTRAg69.4, and PvTRAg74) [147]. PvTRAg36.6 and early transcribed membrane protein (ETRAMP) were found to be co-localized in the apical region of the P. vivax merozoite in the early erythrocytic stage, indicating a functional role for their interaction in the development or maintenance of the parasitophorous vacuole membrane [148]. The interaction of PvTRAg38 with host erythrocytes is known to facilitate parasite growth. PvTRAg38 interacts with basigin and band 3 via the P2 and P4 regions (amino acid positions 167–178 and 197–208), respectively [149,150]. On the other hand, PvTRAg56.2 has been found to interact with PvMSP7 and co-localize with PvMSP1 on the merozoite surface, indicating that it might be involved in surface protein stabilization [148]. In contrast to P. vivax, P. knowlesi has been found to possess PkTRAg38.3, PkTRAg40.1, and PkTRAg67.1 that bind to human erythrocytes [151].
Other malarial proteins that remain poorly characterized have been proposed as potential malaria vaccine candidates. In P. vivax, these include the surface antigens AARP [152], RBSA [153], and MSA180 [154]; the rhoptry antigens P34 [140], RAMA [155], RhopH3 [156], RALP1 [157], and RA [158]; and the micronemal antigens GAMA [159,160], MTRAP [140], and MA [140]. Furthermore, the surface antigens RBSA [153] and AARP [152] were also identified in P. cynomolgi and P. knowlesi, respectively, and the rhoptry antigen RA [158] was identified in P. knowlesi. Most of these antigens are found on P. vivax, the most prevalent non-Laverania Plasmodium species. This suggests their possible role in the host-parasite interactions, pathology, and immunology in better adaptation to the human host. Plasmodium antigens can be identified based on their orthologs in other human infected Plasmodium species, such as P. falciparum [64]. By targeting these conserved regions, it is possible to generate a vaccine candidate for pan-malaria therapies, or species-specific therapies due to the multiple and diverse antigens across different families in all the Plasmodium species.
6. Conclusions
Eliminating malaria remains a challenge that is heightened with the rise in zoonotic infections. In recent years, more non-Laverania Plasmodium species, which were previously thought to infect only non-human primates, have been shown to be also capable to infect humans naturally (P. knowlesi, P. cynomolgi, P. simium, and P. brasilianum) and experimentally (P. eylesi, P. inui, P. schwetzi, and P. rodhaini). The emergence of host-switching relies on the presence of human hosts, monkey natural hosts, and the Anopheles vectors in the same region. The Anopheles vectors play a role in transmitting the parasites to either host, resulting in a change in the pattern of parasite infection. However, this review focuses only the Plasmodium species in human hosts. While the characteristics of these zoonotic species are similar, the development of molecular tools have greatly reduced the risk of zoonotic misdiagnosis, especially in developing countries where malaria is endemic. Thus, anti-malarial drug discovery should also concern all Plasmodium species and not only be focused on P. falciparum, in order to maximize the likelihood of achieving malaria elimination/eradication [161]. A comprehensive understanding of the genetic variability, molecular evolution, invasion mechanisms, and pathogenesis of these zoonotic species may provide insights that can be used to reduce the zoonotic risk and develop strategies for the control and elimination of existing zoonoses.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens10070889/s1, Table S1: title. Non-Laverania Plasmodium species mitochondrial gene sequences.
Author Contributions
Writing, review and editing of the manuscript were performed by J.W.H., F.T., E.Q.H.L., S.R.A., Y.A. and B.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by NUHS start-up funding (NUHSRO/2018/006/SU/01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available in the review.
Acknowledgments
We thank Georges Snounou for his valuable comments and critical reading of the review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2019; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 232. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, M.; Baum, J. The mechanics of malaria parasite invasion of the human erythrocyte-towards a reassessment of the host cell contribution. Cell Microbiol. 2016, 18, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddey, J.A.; Cowman, A.F. Plasmodium nesting: Remaking the erythrocyte from the inside out. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, C.J.; Rosa, T.F.D.A.; Pradel, G. The Biology of Malaria Gametocytes; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.L.; Styczynski, M.P. Systems biology-based investigation of host-Plasmodium interactions. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, P.; Zalis, M.G.; de Pina-Costa, A.; Siqueira, A.M.; Junior, C.B.; Silva, S.; Areas, A.L.L.; Pelajo-Machado, M.; de Alvarenga, D.A.M.; da Silva Santelli, A.C.F.; et al. Outbreak of human malaria caused by Plasmodium simium in the Atlantic Forest in Rio de Janeiro: A molecular epidemiological investigation. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1038–e1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalremruata, A.; Magris, M.; Vivas-Martinez, S.; Koehler, M.; Esen, M.; Kempaiah, P.; Jeyaraj, S.; Perkins, D.J.; Mordmuller, B.; Metzger, W.G. Natural infection of Plasmodium brasilianum in humans: Man and monkey share quartan malaria parasites in the Venezuelan Amazon. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, T.H.; Hisam, S.; Lanza, M.; Jiram, A.I.; Ismail, N.; Rubio, J.M. First case of a naturally acquired human infection with Plasmodium cynomolgi. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, R. Zoonotic malaria-global overview and research and policy needs. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, F.; Liu, Q.; Ferreira, M.U.; Tantular, I.S. How prevalent are Plasmodium ovale and P. malariae in East Asia? Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maktari, M.T.; Bassiouny, H.K.; Al-Hamd, Z.S.; Assabri, A.M.; El-Massry, A.G.; Shatat, H.Z. Malaria status in Al-Hodeidah Governorate, Yemen: Malariometric parasitic survey & chloroquine resistance P. falciparum local strain. J. Egypt Soc. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Autino, B.; Noris, A.; Russo, R.; Castelli, F. Epidemiology of malaria in endemic areas. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 4, e2012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coatney, G.R.; Collins, W.E.; Warren, M.; Contacos, P.G. The Primate Malarias; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2003. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/6538 (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Eyles, D.E. The species of simian malaria: Taxonomy, morphology, life cycle, and geographical distribution of the monkey species. J. Parasitol. 1963, 49, 866–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, W.; Moss, D.; Collins, W.E. The continuous cultivation of Plasmodium fragile by the method of Trager-Jensen. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handunnetti, S.M.; Mendis, K.N.; David, P.H. Antigenic variation of cloned Plasmodium fragile in its natural host Macaca sinica. Sequential appearance of successive variant antigenic types. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 1269–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coatney, G.R.; Chin, W.; Contacos, P.G.; King, H.K. Plasmodium inui, a quartan-type malaria parasite of Old World monkeys transmissible to man. J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, W. Malaria of the orang-utan (Pongo pygmaeus) in Borneo. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1976, 275, 439–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyles, D.E.; Fong, Y.L.; Dunn, F.L.; Guinn, E.; Warren, M.; Sandosham, A.A. Plasmodium youngi N. sp., a malaria parasite of the Malayan Gibbon. Hylobates Lar Lar. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, D.A.; Pina-Costa, A.; Bianco, C., Jr.; Moreira, S.B.; Brasil, P.; Pissinatti, A.; Daniel-Ribeiro, C.T.; Brito, C.F. New potential Plasmodium brasilianum hosts: Tamarin and marmoset monkeys (family Callitrichidae). Malar. J. 2017, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alvarenga, D.A.; de Pina-Costa, A.; de Sousa, T.N.; Pissinatti, A.; Zalis, M.G.; Suarez-Mutis, M.C.; Lourenco-de-Oliveira, R.; Brasil, P.; Daniel-Ribeiro, C.T.; de Brito, C.F. Simian malaria in the Brazilian Atlantic forest: First description of natural infection of capuchin monkeys (Cebinae subfamily) by Plasmodium simium. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirriez, J.; Dei-Cas, E.; Dujardin, L.; Landau, I. The blood-stages of Plasmodium georgesi, P. gonderi and P. petersi: Course of untreated infection in their natural hosts and additional morphological distinctive features. Parasitology 1995, 111, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirriez, J.; Dei-Cas, E.; Landau, I. Further description of blood stages of Plasmodium petersi from Cercocebus albigena monkey. Folia Parasitol. 1994, 41, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Contacos, P.G.; Coatney, G.R.; Orihel, T.C.; Collins, W.E.; Chin, W.; Jeter, M.H. Transmission of Plasmodium schwetzi from the chimpanzee to man by mosquito bite. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.I.; Mailepessov, D.; Vythilingam, I.; Lee, V.; Lam, P.; Ng, L.C.; Tan, C.H. Prevalence of simian malaria parasites in macaques of Singapore. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagami, M.; Nakatsu, M.; Khattignavong, P.; Soundala, P.; Lorphachan, L.; Keomalaphet, S.; Xangsayalath, P.; Kawai, S.; Hongvanthong, B.; Brey, P.T.; et al. First case of human infection with Plasmodium knowlesi in Laos. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongwutiwes, S.; Putaporntip, C.; Iwasaki, T.; Sata, T.; Kanbara, H. Naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in human, Thailand. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2211–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchavez, J.; Espino, F.; Curameng, P.; Espina, R.; Bell, D.; Chiodini, P.; Nolder, D.; Sutherland, C.; Lee, K.S.; Singh, B. Human Infections with Plasmodium knowlesi, the Philippines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kim Sung, L.; Matusop, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Shamsul, S.S.; Cox-Singh, J.; Thomas, A.; Conway, D.J. A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings. Lancet 2004, 363, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizaki, R.; Ujiie, M.; Kato, Y.; Iwagami, M.; Hashimoto, A.; Kutsuna, S.; Takeshita, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Kanagawa, S.; Kano, S.; et al. First case of Plasmodium knowlesi infection in a Japanese traveller returning from Malaysia. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kadir, K.A.; Quintanilla-Zarinan, L.F.; Villano, J.; Houghton, P.; Du, H.; Singh, B.; Smith, D.G. Distribution and prevalence of malaria parasites among long-tailed macaques (Macaca fascicularis) in regional populations across Southeast Asia. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imwong, M.; Madmanee, W.; Suwannasin, K.; Kunasol, C.; Peto, T.J.; Tripura, R.; von Seidlein, L.; Nguon, C.; Davoeung, C.; Day, N.P.J.; et al. Asymptomatic natural human infections with the simian malaria parasites Plasmodium cynomolgi and Plasmodium knowlesi. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, K.F.; Taravella, A.M.; Henn, B.M.; Bustamante, C.D.; Sikora, M.; Cornejo, O.E. Population genetic analysis of the DARC locus (Duffy) reveals adaptation from standing variation associated with malaria resistance in humans. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.D.; Dalton, J.P.; Klotz, F.W.; McGinniss, M.H.; Hadley, T.J.; Hudson, D.E.; Miller, L.H. Receptor-like specificity of a Plasmodium knowlesi malarial protein that binds to Duffy antigen ligands on erythrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheimer, S.P.; Barnwell, J.W. Plasmodium vivax interaction with the human Duffy blood group glycoprotein: Identification of a parasite receptor-like protein. Exp. Parasitol. 1989, 69, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.; Dias, F.; Figueiredo, J.; Mora, V.G.; Cano, J.; de Sousa, B.; do Rosario, V.E.; Benito, A.; Berzosa, P.; Arez, A.P. Duffy negative antigen is no longer a barrier to Plasmodium vivax—Molecular evidences from the African West Coast (Angola and Equatorial Guinea). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, P.; Doderer-Lang, C.; Atchade, P.S.; Lemoine, J.P.; de l‘Isle, M.C.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Pfaff, A.W.; Brunet, J.; Arnoux, L.; Haar, E.; et al. The hide and seek of Plasmodium vivax in West Africa: Report from a large-scale study in Beninese asymptomatic subjects. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motshoge, T.; Ababio, G.K.; Aleksenko, L.; Read, J.; Peloewetse, E.; Loeto, M.; Mosweunyane, T.; Moakofhi, K.; Ntebele, D.S.; Chihanga, S.; et al. Molecular evidence of high rates of asymptomatic P. vivax infection and very low P. falciparum malaria in Botswana. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fru-Cho, J.; Bumah, V.V.; Safeukui, I.; Nkuo-Akenji, T.; Titanji, V.P.; Haldar, K. Molecular typing reveals substantial Plasmodium vivax infection in asymptomatic adults in a rural area of Cameroon. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.; Yewhalaw, D.; Zhong, D.; Zemene, E.; Degefa, T.; Tushune, K.; Ha, M.; Lee, M.C.; James, A.A.; Yan, G. Molecular epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum malaria among Duffy-positive and Duffy-negative populations in Ethiopia. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.R.; Stoute, J.A.; Amon, J.; Dunton, R.F.; Mtalib, R.; Koros, J.; Owour, B.; Luckhart, S.; Wirtz, R.A.; Barnwell, J.W.; et al. Evidence for transmission of Plasmodium vivax among a duffy antigen negative population in Western Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, D.; Barnadas, C.; Bouchier, C.; Henry-Halldin, C.; Gray, L.R.; Ratsimbasoa, A.; Thonier, V.; Carod, J.F.; Domarle, O.; Colin, Y.; et al. Plasmodium vivax clinical malaria is commonly observed in Duffy-negative Malagasy people. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5967–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niangaly, A.; Karthigayan, G.; Amed, O.; Coulibaly, D.; Sa, J.M.; Adams, M.; Travassos, M.A.; Ferrero, J.; Laurens, M.B.; Kone, A.K.; et al. Plasmodium vivax infections over 3 years in Duffy blood group negative Malians in Bandiagara, Mali. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, N.; Mint Lekweiry, K.; Bogreau, H.; Pradines, B.; Rogier, C.; Ould Mohamed Salem Boukhary, A.; Hafid, J.E.; Ould Ahmedou Salem, M.S.; Trape, J.F.; Basco, L.K.; et al. Vivax malaria in Mauritania includes infection of a Duffy-negative individual. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niang, M.; Thiam, L.G.; Sow, A.; Loucoubar, C.; Bob, N.S.; Diop, F.; Diouf, B.; Niass, O.; Mansourou, A.; Varela, M.L.; et al. A molecular survey of acute febrile illnesses reveals Plasmodium vivax infections in Kedougou, southeastern Senegal. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraheem, M.H.; Albsheer, M.M.; Mohamed, H.S.; Amin, M.; Mahdi Abdel Hamid, M. Transmission of Plasmodium vivax in Duffy-negative individuals in central Sudan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asua, V.; Tukwasibwe, S.; Conrad, M.; Walakira, A.; Nankabirwa, J.I.; Mugenyi, L.; Kamya, M.R.; Nsobya, S.L.; Rosenthal, P.J. Plasmodium species infecting children presenting with malaria in Uganda. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haiyambo, D.H.; Uusiku, P.; Mumbengegwi, D.; Pernica, J.M.; Bock, R.; Malleret, B.; Renia, L.; Greco, B.; Quaye, I.K. Molecular detection of P. vivax and P. ovale foci of infection in asymptomatic and symptomatic children in Northern Namibia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleret, B.; Renia, L.; Russell, B. The unhealthy attraction of Plasmodium vivax to reticulocytes expressing transferrin receptor 1 (CD71). Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovici, J.; Roesch, C.; Rougeron, V. The enigmatic mechanisms by which Plasmodium vivax infects Duffy-negative individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.S. Studies on malaria in chimpanzees. V. The sporogonous cycle and mosquito transmission of Plasmodium vivax schwetzi. J. Parasitol. 1958, 44, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coatney, G.R. Simian malarias in man: Facts, implications, and predictions. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabert, A.; Otto, T.D.; Rutledge, G.G.; Franzon, B.; Ollomo, B.; Arnathau, C.; Durand, P.; Moukodoum, N.D.; Okouga, A.P.; Ngoubangoye, B.; et al. Plasmodium vivax-like genome sequences shed new insights into Plasmodium vivax biology and evolution. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco-de-Oliveira, R.; Deane, L.M. Simian malaria at two sites in the Brazilian Amazon. I--The infection rates of Plasmodium brasilianum in non-human primates. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1995, 90, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnwell, J.W. Antigens of Plasmodium vivax blood stage parasites identified by monoclonal antibodies. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1986, 81, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, A.H.; Barnwell, J.W.; Collins, W.E.; Nussenzweig, R.S. Monoclonal antibodies produced against sporozoites of the human parasite Plasmodium malariae abolish infectivity of sporozoites of the simian parasite Plasmodium brasilianum. Infect. Immun. 1985, 50, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandeur, T.; Volney, B.; Peneau, C.; de Thoisy, B. Monkeys of the rainforest in French Guiana are natural reservoirs for P. brasilianum/P. malariae malaria. Parasitology 2000, 120, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, T.M. Plasmodium simium:ultrastructure of erythrocytic phase. Exp. Parasitol. 1976, 39, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, I.F.; Qari, S.H.; Millet, P.G.; Collins, W.E.; Lal, A.A. Circumsporozoite protein gene of Plasmodium simium, a Plasmodium vivax-like monkey malaria parasite. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 57, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, A.M.; Daniels, R.F.; Farrell, T.M.; Grimsby, J.; Volkman, S.K.; Wirth, D.F.; MacInnis, B.L.; Neafsey, D.E. Detection of low-density Plasmodium falciparum infections using amplicon deep sequencing. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.; Silva, J.; Hall, N. The genome of model malaria parasites, and comparative genomics. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2005, 7, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kooij, T.W.; Carlton, J.M.; Bidwell, S.L.; Hall, N.; Ramesar, J.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P. A Plasmodium whole-genome synteny map: Indels and synteny breakpoints as foci for species-specific genes. PLoS Pathog. 2005, 1, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Sullivan, S.A.; Carlton, J.M. The biology of Plasmodium vivax explored through genomics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1342, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.M.; Adams, J.H.; Silva, J.C.; Bidwell, S.L.; Lorenzi, H.; Caler, E.; Crabtree, J.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Merino, E.F.; Amedeo, P.; et al. Comparative genomics of the neglected human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Nature 2008, 455, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, A.; Bohme, U.; Berry, A.E.; Mungall, K.; Finn, R.D.; Jackson, A.P.; Mourier, T.; Mistry, J.; Pasini, E.M.; Aslett, M.A.; et al. The genome of the simian and human malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature 2008, 455, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.L. Analysis of sequences from the extremely A + T-rich genome of Plasmodium falciparum. Gene 1987, 52, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Iyer, L.M.; Wellems, T.E.; Miller, L.H. Plasmodium biology: Genomic gleanings. Cell 2003, 115, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourier, T.; Alvarenga, D.A.M.d.; Kaushik, A.; Pina-Costa, A.d.; Guzmán-Vega, F.J.; Douvropoulou, O.; Guan, Q.; Forrester, S.; Abreu, F.V.S.d.; Júnior, C.B.; et al. The genome of the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium simium reveals adaptions to host-switching. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, G.G.; Bohme, U.; Sanders, M.; Reid, A.J.; Cotton, J.A.; Maiga-Ascofare, O.; Djimde, A.A.; Apinjoh, T.O.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Manske, M.; et al. Plasmodium malariae and P. ovale genomes provide insights into malaria parasite evolution. Nature 2017, 542, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, E.M.; Bohme, U.; Rutledge, G.G.; Voorberg-Van der Wel, A.; Sanders, M.; Berriman, M.; Kocken, C.H.; Otto, T.D. An improved Plasmodium cynomolgi genome assembly reveals an unexpected methyltransferase gene expansion. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.R.; Templeton, T.J.; Subudhi, A.K.; Ramaprasad, A.; Tang, J.; Lu, F.; Naeem, R.; Hashish, Y.; Oguike, M.C.; Benavente, E.D.; et al. Genome-scale comparison of expanded gene families in Plasmodium ovale wallikeri and Plasmodium ovale curtisi with Plasmodium malariae and with other Plasmodium species. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daron, J.; Boissiere, A.; Boundenga, L.; Ngoubangoye, B.; Houze, S.; Arnathau, C.; Sidobre, C.; Trape, J.F.; Durand, P.; Renaud, F.; et al. Population genomic evidence of Plasmodium vivax Southeast Asian origin. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Shaw, K.S.; Learn, G.H.; Plenderleith, L.J.; Malenke, J.A.; Sundararaman, S.A.; Ramirez, M.A.; Crystal, P.A.; Smith, A.G.; et al. African origin of the malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.E.; Plenderleith, L.J.; Sundararaman, S.A.; Liu, W.; Gruszczyk, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Trimboli, S.; Learn, G.H.; MacLean, O.A.; Morgan, A.L.K.; et al. Evolutionary history of human Plasmodium vivax revealed by genome-wide analyses of related ape parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8450–E8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.L. Evolutionary rates, divergence dates, and the performance of mitochondrial genes in Bayesian phylogenetic analysis. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiadi, W.; Sudoyo, H.; Trimarsanto, H.; Sihite, B.A.; Saragih, R.J.; Juliawaty, R.; Wangsamuda, S.; Asih, P.B.; Syafruddin, D. A zoonotic human infection with simian malaria, Plasmodium knowlesi, in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.C.; Rodrigues, P.T.; Early, A.M.; Duarte, A.; Buery, J.C.; Bueno, M.G.; Catao-Dias, J.L.; Cerutti, C., Jr.; Rona, L.D.P.; Neafsey, D.E.; et al. Plasmodium simium: Population genomics reveals the origin of a reverse zoonosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, G.; Kawai, S.; Haeggstrom, M.; Kaneko, O.; von Euler, A.; Kawazu, S.; Palm, D.; Fernandez, V.; Wahlgren, M. SURFIN is a polymorphic antigen expressed on Plasmodium falciparum merozoites and infected erythrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frech, C.; Chen, N. Variant surface antigens of malaria parasites: Functional and evolutionary insights from comparative gene family classification and analysis. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talundzic, E.; Ravishankar, S.; Nayak, V.; Patel, D.S.; Olsen, C.; Sheth, M.; Batra, D.; Loparev, V.; Vannberg, F.O.; Udhayakumar, V.; et al. First full draft genome sequence of Plasmodium brasilianum. Genome Announc. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegner, R. Relative frequency of ring-stage plasmodia in reticulocytes and mature erythrocytes in man and monkey. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 690–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerlin, D.H.; Gatton, M.L. Preferential invasion by Plasmodium merozoites and the self-regulation of parasite burden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, S.F. The infection of mature and immature erythrocytes by Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium malariae. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1939, s1-19, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingnau, A.; Doehring-Schwerdtfeger, E.; Maier, W.A. Evidence for 6-day cultivation of human Plasmodium malariae. Parasitol. Res. 1994, 80, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleret, B.; Li, A.; Zhang, R.; Tan, K.S.; Suwanarusk, R.; Claser, C.; Cho, J.S.; Koh, E.G.; Chu, C.S.; Pukrittayakamee, S.; et al. Plasmodium vivax: Restricted tropism and rapid remodeling of CD71-positive reticulocytes. Blood 2015, 125, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikawa, M. Morphological changes in erythrocytes induced by malarial parasites. Biol. Cell. 1988, 64, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.M.; Cooke, B.M. The rheopathobiology of Plasmodium vivax and other important primate malaria parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.T.; Lopes, S.C.; Ferrer, M.; Leite, J.A.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Bernabeu, M.; Nogueira, P.A.; Mourao, M.P.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Lacerda, M.V.; et al. On cytoadhesion of Plasmodium vivax: Raison d’etre? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106 (Suppl. S1), 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanarusk, R.; Cooke, B.M.; Dondorp, A.M.; Silamut, K.; Sattabongkot, J.; White, N.J.; Udomsangpetch, R. The deformability of red blood cells parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, S.; Qotrunnada, L.; Leonardo, L.; Andries, B.; Wardani, P.A.I.; Fricot, A.; Henry, B.; Hardy, D.; Margyaningsih, N.I.; Apriyanti, D.; et al. Evaluation of splenic accumulation and colocalization of immature reticulocytes and Plasmodium vivax in asymptomatic malaria: A prospective human splenectomy study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, S.; Qotrunnada, L.; Leonardo, L.; Andries, B.; Wardani, P.A.I.; Fricot, A.; Henry, B.; Hardy, D.; Margyaningsih, N.I.; Apriyanti, D.; et al. Hidden biomass of intact malaria parasites in the human spleen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2067–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Daneshvar, C. Human infections and detection of Plasmodium knowlesi. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, M.J.; William, T.; Barber, B.E.; Rajahram, G.S.; Menon, J.; Schimann, E.; Piera, K.; Wilkes, C.S.; Patel, K.; Chandna, A.; et al. Age-related clinical spectrum of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria and predictors of severity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Blanch, A.J.; Namvar, A.; Carmo, O.; Tiash, S.; Andrew, D.; Hanssen, E.; Rajagopal, V.; Dixon, M.W.A.; Tilley, L. Multimodal analysis of Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes reveals large invaginations, swelling of the host cell, and rheological defects. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, K.K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Lucky, A.B.; Asada, M.; Miyazaki, S.; Katakai, Y.; Kawai, S.; Song, C.; Murata, K.; Yahata, K.; et al. The Plasmodium knowlesi MAHRP2 ortholog localizes to structures connecting Sinton Mulligan‘s clefts in the infected erythrocyte. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderios, F.; Noorrain, A.; Vythilingam, I. In vivo study of human Plasmodium knowlesi in Macaca fascicularis. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, B.E.; William, T.; Grigg, M.J.; Menon, J.; Auburn, S.; Marfurt, J.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W. A prospective comparative study of knowlesi, falciparum, and vivax malaria in Sabah, Malaysia: High proportion with severe disease from Plasmodium knowlesi and Plasmodium vivax but no mortality with early referral and artesunate therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox-Singh, J.; Davis, T.M.; Lee, K.S.; Shamsul, S.S.; Matusop, A.; Ratnam, S.; Rahman, H.A.; Conway, D.J.; Singh, B. Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in humans is widely distributed and potentially life threatening. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajahram, G.S.; Barber, B.E.; William, T.; Menon, J.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W. Deaths due to Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in Sabah, Malaysia: Association with reporting as Plasmodium malariae and delayed parenteral artesunate. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figtree, M.; Lee, R.; Bain, L.; Kennedy, T.; Mackertich, S.; Urban, M.; Cheng, Q.; Hudson, B.J. Plasmodium knowlesi in human, Indonesian Borneo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, M.; Ahmed, A.; Siner, A.; Wong, I.T.; Woon, L.C.; Singh, B.; Krishna, S.; Cox-Singh, J. Laboratory markers of disease severity in Plasmodium knowlesi infection: A case control study. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, C.; Davis, T.M.; Cox-Singh, J.; Rafa’ee, M.Z.; Zakaria, S.K.; Divis, P.C.; Singh, B. Clinical and laboratory features of human Plasmodium knowlesi infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstey, N.M.; Handojo, T.; Pain, M.C.; Kenangalem, E.; Tjitra, E.; Price, R.N.; Maguire, G.P. Lung injury in vivax malaria: Pathophysiological evidence for pulmonary vascular sequestration and posttreatment alveolar-capillary inflammation. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox-Singh, J.; Singh, B.; Daneshvar, C.; Planche, T.; Parker-Williams, J.; Krishna, S. Anti-inflammatory cytokines predominate in acute human Plasmodium knowlesi infections. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, B.B.; Reis-Filho, A.; Souza-Neto, S.M.; Clarencio, J.; Camargo, L.M.; Barral, A.; Barral-Netto, M. Severe Plasmodium vivax malaria exhibits marked inflammatory imbalance. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, A.C.Y.; Ong, J.J.Y.; Malleret, B.; Suwanarusk, R.; Kosaisavee, V.; Zeeman, A.M.; Cooper, C.A.; Tan, K.S.W.; Zhang, R.; Tan, B.H.; et al. Robust continuous in vitro culture of the Plasmodium cynomolgi erythrocytic stages. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.K. Evidence and implications of mortality associated with acute Plasmodium vivax malaria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, C.J.; Holst, F.G.; Kern, P.; Chiwakata, C.B.; Dietrich, M.; Reisinger, E.C. Stronger host response per parasitized erythrocyte in Plasmodium vivax or ovale than in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyner, C.; Moreno, A.; Meyer, E.V.; Cabrera-Mora, M.; Ma, H.C.; Kissinger, J.C.; Barnwell, J.W.; Galinski, M.R. Plasmodium cynomolgi infections in rhesus macaques display clinical and parasitological features pertinent to modelling vivax malaria pathology and relapse infections. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuvin, S.F.; Beye, H.K.; Stohlman, F., Jr.; Contacos, P.G.; Coatney, G.R. Clinical and physiological responses in sporozoite-induced B strain Plasmodium cynomolgi and Plasmodium vivax infections in normal volunteers. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1962, 56, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmeyer, G.N.; Stensvold, C.R.; Fabricius, T.; Marmolin, E.S.; Hoegh, S.V.; Nielsen, H.V.; Kemp, M.; Vestergaard, L.S. Plasmodium cynomolgi as cause of malaria in tourist to Southeast Asia, 2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.H. Compatibility of relapse patterns of Plasmodium cynomolgi infections in rhesus monkeys with continuous cyclical development and hypnozoite concepts of relapse. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 1077–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, L.M. Simian malaria in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1992, 87 (Suppl. S3), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.A.; de la Cruz, V.F.; Campbell, G.H.; Procell, P.M.; Collins, W.E.; McCutchan, T.F. Structure of the circumsporozoite gene of Plasmodium malariae. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1988, 30, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.E.; Jeffery, G.M. Plasmodium malariae: Parasite and disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Russell, B.; Renia, L.; Lek-Uthai, U.; Nosten, F.; Lim, C.T. High density of ‘spiky‘ excrescences covering the surface of an erythrocyte infected with Plasmodium malariae. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 151, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkenswick, G.A.; Watsa, M.; Pacheco, M.A.; Escalante, A.A.; Parker, P.G. Chronic Plasmodium brasilianum infections in wild Peruvian tamarins. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, S.F. The infection of reticulocytes by Plasmodium vivax. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1938, s1-18, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaisavee, V.; Suwanarusk, R.; Chua, A.C.Y.; Kyle, D.E.; Malleret, B.; Zhang, R.; Imwong, M.; Imerbsin, R.; Ubalee, R.; Samano-Sanchez, H.; et al. Strict tropism for CD71(+)/CD234(+) human reticulocytes limits the zoonotic potential of Plasmodium cynomolgi. Blood 2017, 130, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazi, L.; Ayala, F.J. Unresolved direction of host transfer of Plasmodium vivax v. P. simium and P. malariae v. P. brasilianum. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Hansen, E.; DeSimone, T.M.; Moreno, Y.; Junker, K.; Bei, A.; Brugnara, C.; Buckee, C.O.; Duraisingh, M.T. Expansion of host cellular niche can drive adaptation of a zoonotic malaria parasite to humans. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, R.W.; Hall, J.; Rangkuti, F.; Ho, Y.S.; Almond, N.; Mitchell, G.H.; Pain, A.; Holder, A.A.; Blackman, M.J. Adaptation of the genetically tractable malaria pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi to continuous culture in human erythrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinski, M.R.; Barnwell, J.W. Plasmodium vivax: Merozoites, invasion of reticulocytes and considerations for malaria vaccine development. Parasitol. Today 1996, 12, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.R.; Sanders, P.R.; Weiss, G.; Gilson, P.R.; Crabb, B.S.; Beeson, J.G. Functional conservation of the AMA1 host-cell invasion ligand between P. falciparum and P. vivax: A novel platform to accelerate vaccine and drug development. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L.E.; Urquiza, M.; Ocampo, M.; Curtidor, H.; Suárez, J.; García, J.; Vera, R.; Puentes, Á.; López, R.; Pinto, M.; et al. Plasmodium vivax MSP-1 peptides have high specific binding activity to human reticulocytes. Vaccine 2002, 20, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ito, D.; Kong, D.H.; Ha, K.S.; Chen, J.H.; Lu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Takashima, E.; et al. The Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 paralog is a novel erythrocyte-binding ligand of P. vivax. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeson, J.G.; Drew, D.R.; Boyle, M.J.; Feng, G.; Fowkes, F.J.; Richards, J.S. Merozoite surface proteins in red blood cell invasion, immunity and vaccines against malaria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.J.; Dietrich, M.H.; Nguitragool, W.; Tham, W.H. Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte binding proteins for invasion into reticulocytes. Cell Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleret, B.; Sahili, A.E.; Tay, M.Z.; Carissimo, G.; Ong, A.S.M.; Novera, W.; Lin, J.; Suwanarusk, R.; Kosaisavee, V.; Chu, T.T.T.; et al. Plasmodium vivax binds host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to enter immature red blood cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Huang, R.K.; Chan, L.J.; Menant, S.; Hong, C.; Murphy, J.M.; Mok, Y.F.; Griffin, M.D.W.; Pearson, R.D.; Wong, W.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of an essential Plasmodium vivax invasion complex. Nature 2018, 559, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Kanjee, U.; Chan, L.J.; Menant, S.; Malleret, B.; Lim, N.T.Y.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Mok, Y.F.; Lin, K.M.; Pearson, R.D.; et al. Transferrin receptor 1 is a reticulocyte-specific receptor for Plasmodium vivax. Science 2018, 359, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, E.J.; Kanjee, U.; Duraisingh, M.T. Molecular interactions governing host-specificity of blood stage malaria parasites. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.L.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Fong, M.Y. The Duffy binding protein (PkDBPalphaII) of Plasmodium knowlesi from Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo show different binding activity level to human erythrocytes. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, K.; Lo, E.; Hostetler, J.B.; Yewhalaw, D.; Mu, J.; Neafsey, D.E.; Yan, G.; Miller, L.H. Role of Plasmodium vivax Duffy-binding protein 1 in invasion of Duffy-null Africans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6271–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, J.; Chan, E.R.; Menard, D.; Mercereau-Puijalon, O.; Barnwell, J.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Serre, D. De novo assembly of a field isolate genome reveals novel Plasmodium vivax erythrocyte invasion genes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.H.; Mason, S.J.; Dvorak, J.A.; McGinniss, M.H.; Rothman, I.K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science 1975, 189, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golassa, L.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Lo, E.; Amambua-Ngwa, A. The biology of unconventional invasion of Duffy-negative reticulocytes by Plasmodium vivax and its implication in malaria epidemiology and public health. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo-Pinzón, G.; Bermúdez, M.; Hernández, D.; Curtidor, H.; Patarroyocorresponding, M.A. Plasmodium vivax ligand-receptor interaction: PvAMA-1 domain I contains the minimal regions for specific interaction with CD71+ reticulocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ito, D.; Chen, J.H.; Lu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Ha, K.S.; Cao, J.; Torii, M.; Sattabongkot, J.; et al. Pv12, a 6-Cys antigen of Plasmodium vivax, is localized to the merozoite rhoptry. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, J.B.; Sharma, S.; Bartholdson, S.J.; Wright, G.J.; Fairhurst, R.M.; Rayner, J.C. A library of Plasmodium vivax recombinant merozoite proteins reveals new vaccine candidates and protein-protein interactions. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongui, A.; Angel, D.I.; Guzman, C.; Vanegas, M.; Patarroyo, M.A. Characterisation of the Plasmodium vivax Pv38 antigen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, D.I.; Mongui, A.; Ardila, J.; Vanegas, M.; Patarroyo, M.A. The Plasmodium vivax Pv41 surface protein: Identification and characterization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, S.A.; Kappe, S.H.I. The s48/45 six-cysteine proteins: Mediators of interaction throughout the Plasmodium life cycle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Chu, K.B.; Quan, F.S. The Plasmodium knowlesi Pk41 surface protein diversity, natural selection, sub population and geographical clustering: A 6-cysteine protein family member. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.H.; Jeon, H.Y.; Ha, K.S.; Cao, J.; Nyunt, M.H.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Immunoprofiling of the tryptophan-rich antigen family in Plasmodium vivax. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3083–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Bora, H.; Sharma, Y.D. Presence of memory T cells and naturally acquired antibodies in Plasmodium vivax malaria-exposed individuals against a group of tryptophan-rich antigens with conserved sequences. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Tyagi, K.; Sharma, Y.D. CD4+ T cell response correlates with naturally acquired antibodies against Plasmodium vivax tryptophan-rich antigens. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Hossain, M.E.; Thakur, V.; Aggarwal, P.; Malhotra, P.; Mohmmed, A.; Sharma, Y.D. Plasmodium vivax tryptophan rich antigen PvTRAg36.6 interacts with PvETRAMP and PvTRAg56.6 interacts with PvMSP7 during erythrocytic stages of the parasite. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Choudhary, V.; Zeeshan, M.; Tyagi, R.K.; Rathore, S.; Sharma, Y.D. Interaction of Plasmodium vivax tryptophan-rich antigen PvTRAg38 with Band 3 on human erythrocyte surface facilitates parasite growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20257–20272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Dass, S.; Kandari, D.; Kaur, I.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, Y.D. Basigin interacts with Plasmodium vivax tryptophan-rich antigen PvTRAg38 as a second erythrocyte receptor to promote parasite growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Gupta, D.; Saini, E.; Choudhary, S.; Jamwal, A.; Alam, M.S.; Zeeshan, M.; Tyagi, R.K.; Sharma, Y.D. Recognition of human erythrocyte receptors by the tryptophan-rich antigens of monkey malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muh, F.; Ahmed, M.A.; Han, J.H.; Nyunt, M.H.; Lee, S.K.; Lau, Y.L.; Kaneko, O.; Han, E.T. Cross-species analysis of apical asparagine-rich protein of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Perez, D.A.; Baquero, L.A.; Chitiva-Ardila, D.M.; Patarroyo, M.A. Characterising PvRBSA: An exclusive protein from Plasmodium species infecting reticulocytes. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muh, F.; Han, J.H.; Nyunt, M.H.; Lee, S.K.; Jeon, H.Y.; Ha, K.S.; Park, W.S.; Hong, S.H.; Ahmed, M.A.; Na, S.; et al. Identification of a novel merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium vivax, PvMSA180. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changrob, S.; Wang, B.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Nyunt, M.H.; Lim, C.S.; Tsuboi, T.; Chootong, P.; Han, E.T. Correction: Naturally-acquired immune response against Plasmodium vivax rhoptry-associated membrane antigen. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongui, A.; Perez-Leal, O.; Rojas-Caraballo, J.; Angel, D.I.; Cortes, J.; Patarroyo, M.A. Identifying and characterising the Plasmodium falciparum RhopH3 Plasmodium vivax homologue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Ito, D.; Kong, D.H.; Ha, K.S.; Lu, F.; Wang, B.; Sattabongkot, J.; Lim, C.S.; Tsuboi, T.; et al. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of PvRALP1, a novel Plasmodium vivax rhoptry neck protein. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, G.; Reddy, K.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Mian, S.Y.; Singh, H.; Mittal, S.A.; Amlabu, E.; Bassat, Q.; Mayor, A.; Chauhan, V.S.; et al. A novel Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry associated adhesin mediates erythrocyte invasion through the sialic-acid dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, L.A.; Moreno-Perez, D.A.; Garzon-Ospina, D.; Forero-Rodriguez, J.; Ortiz-Suarez, H.D.; Patarroyo, M.A. PvGAMA reticulocyte binding activity: Predicting conserved functional regions by natural selection analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Han, J.H.; Ito, D.; Kong, D.H.; Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Ha, K.S.; et al. Plasmodium vivax GPI-anchored micronemal antigen (PvGAMA) binds human erythrocytes independent of Duffy antigen status. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleret, B. Plasmodium kinase disruption: New hopes for anti-malarial drug discovery. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).