Abstract
A novel Borrelia species, Candidatus Borrelia javanense, was found in ectoparasite ticks, Amblyomma javanense, from Manis javanica pangolins seized in anti-smuggling operations in southern China. Overall, 12 tick samples in 227 (overall prevalence 5.3%) were positive for Candidatus B. javanense, 9 (5.1%) in 176 males, and 3 (5.9%) in 51 females. The phylogenetic analysis, based on the 16S rRNA gene and the flagellin gene sequences of the Borrelia sp., exhibited strong evidence that Candidatus B. javanense did not belong to the Lyme disease Borrelia group and the relapsing fever Borrelia group but another lineage of Borrelia. The discovery of the novel Borrelia species suggests that A. javanense may be the transmit vector, and the M. javanica pangolins should be considered a possible origin reservoir in the natural circulation of these new pathogens. To our knowledge, this is the first identification of a novel Borrelia species agent in A. javanense from pangolins. Whether the novel agent is pathogenic to humans is unknown and needs further research.
1. Introduction
Borrelia, a bacteria genus of the spirochete phylum, are the causative agents of major vector-borne diseases, including Lyme disease (LD) and relapsing fevers (RFs), which are transmitted by ticks and lice worldwide [1]. The LD and RF Borrelia species from two separate sister groups are considered two sister genera [2,3,4,5]. However, recent surveys have uncovered new Borrelia species and strains that do not belong to the LD or RF group. They form the third group, encompassing only two designated species, B. turcica and “Candidatus Borrelia tachyglossi”, and a few strains not taxonomically described [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. The third Borrelia group has been detected in Amblyomma, Hyalomma, Bothriocroton, and Ixodes genera hard ticks, mainly associated with reptiles and echidna. However, only two genomes sequenced confirmed that these Borrelia are substantially different from the LD and RF Borrelia groups [15].
Here, we report a novel Borrelia species in Amblyomma javanense ticks collected from 25 M. javanica pangolins from uncertain countries in Southeast Asia, seized in anti-smuggling operations by Guangxi Customs officers in Fang Cheng Gang and Nan Ning cities, southern China, during the period October 2016–January 2018. We obtained the complete 16S rRNA gene (rrs) and the partial flagellin gene (flaB) by PCR and sequencing. All positive samples have 100% similar nucleotide sequences to each other. Both the rrs and the flaB gene sequences did not fall into either the Lyme disease Borrelia group or the relapsing fever Borrelia group but into another Borrelia group lineage in phylogenetic analysis.
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Borrelia sp. in Ticks
During the study period, we screened a total of 227 adult ticks captured from 25 M. javanica pangolins seized in anti-smuggling operations in southern China (Figure 1). The animals were brought to the wildlife medical-aid center during the veterinary examination, and the ticks were removed and preserved. All ticks were not engorged or not fully engorged and identified as A. javanense by morphologic features to the species level and the developmental stage by two entomologists (Y. Sun and R.-M. Xu). Twelve tick samples (overall prevalence 5.3%) were screened positive for Borrelia, 9 (5.1%) in 176 males and 3 (5.9%) in 51 females, with no significant gender difference. All nucleotide sequences of the 353-bp amplicons were sequenced and identical to one another. The nucleotide sequences of nearly entire rrs (1532 bp) were obtained by nested PCR for segmented amplification, sequencing, and splice according to the overlap area from 5 tick samples; all of them were identical to one another (GenBank accession no. MW889882) and similar to Borrelia crocidurae (GenBank accession no. CP004267), with 25 base-pair differences (1507/1532, homologous 98%). We also amplified and sequenced the partial flagellin gene (flaB) (GenBank accession no. MW916611) by nested PCR from 3 tick samples; these sequences were 100% homologous to one another and shown to be 92% (424/460) homologous with the corresponding sequence of the Borrelia johnsonii strain from bat tick Carios kelleyi from the US [18]. Both the rrs and flaB showed relatively large differences with the Borrelia sp. in GenBank and cannot be clustered into their Borrelia group. Therefore, they should be considered a separate branch or another Borrelia group.

Figure 1.
Illustrations of the host M. javanica pangolin, the attached ticks, A. javanense, below the scales, the removed female and male adult ticks, the nymph ticks (A–E), the electrophoretogram of Borrelia sp. screening for the 353-bp rrs (F), the 790-bp front half segment of full-length rrs (G), the 743-bp back half segment of full-length rrs (H), and the 506-bp flaB (I). The size of the DNA marker was 2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, and 100 bp from top to bottom, respectively.
2.2. Genetic Characteristics of Borrelia sp.
The rrs and flaB phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method based on the trimmed rrs and flaB sequences generated in this study, together with 36 rrs sequences and 31 flaB sequences from other Borrelia spp. retrieved from GenBank. The phylogenetic trees based on nearly complete rrs (1401 bp; Figure 2) and partial flaB (466 bp; Figure 3) demonstrated that the Borrelia sp. identified from the A. javanense ticks in this study were clustered in a separate clade that was distinct from both LD Borrelia and RF Borrelia groups.
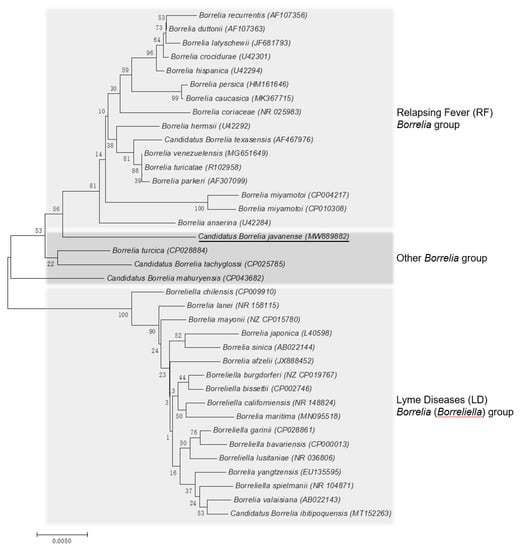
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on nucleotide sequences of the 16S rRNA (1401-bp) genes of Candidatus Borrelia javanense in ectoparasite ticks, A. javanense, from M. javanica pangolins and the comparison sequences. Underline indicates the Candidatus B. javanense identified in this study; GenBank accession numbers are provided for all isolates. The neighbor-joining method was used to construct the evolutionary tree. The percentage of replicate evolutionary trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site (MEGA7, 2015).
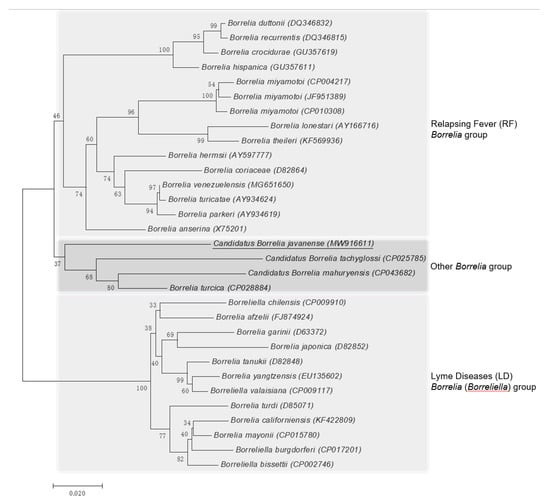
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree based on nucleotide sequences of the flagellin gene (466-bp) of Candidatus Borrelia javanense in ectoparasite ticks, A. javanense, from M. javanica pangolins and the comparison sequences. Underline indicates the Candidatus B. javanense identified in this study; GenBank accession numbers are provided for all isolates. The neighbor-joining method was used to construct the evolutionary tree. The percentage of replicate evolutionary trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site (MEGA7, 2015).
3. Discussion
Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae), which are obligate blood-feeding arthropods, are distributed worldwide from tropic to subarctic regions, capable of transmitting the broadest spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, protozoa, fungi, nematodes, and viruses, to humans, livestock, and wildlife. Here, we report a non-described Borrelia species in A. javanense ticks attached below the scales of M. javanica pangolins distributed in south Asia, southeast Asia, and southern China. This novel Borrelia species is prevalent in this tick species, abundantly attached to the Malayan pangolins. The novel Borrelia species is divergent not only from the LD species and the RF species but also from a third Borrelia group, B. turcica and B. tachyglossi, the reptile- and echidna-associated Borrelia group that was recently described [19]. Sequence analysis showed that this novel Borrelia sp. perhaps has a unique genome and indicates that this novel Borrelia is an intermediate taxon between the LD and RF species. The designation “Candidatus Borrelia javanense” is proposed for this species.
We reported for the first time the identification of novel Borrelia agents in A. javanense from pangolins. A. javanense is an important ectoparasite of M. javanica pangolin. A. javanense has been found in almost all the pangolin species and could be the coendangered tick species on pangolins in Asia [20]. It is reported that the tick also infests various wild animals such as wild boar, lizards, python, skink, hill turtle, bat, hyena, bear, and sambar deer [21,22]. A previous study also reported that A. javanense could infect humans [23]. The geographical distribution of the tick is also very extensive. Voltzit and Keirans have reported A. javanense from Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines, and China [24,25]. Among the 227 ticks tested in this study, 12 (overall prevalence 5.3%) were infected with the new agents, indicating that A. javanense may be acting as the tick vector of the newly identified Borrelia sp. There is a low probability of transmission to people, but whether it is pathogenic to humans is unknown and needs further exploration.
In conclusion, we have identified a novel Borrelia species, Candidatus Borrelia javanense, in ectoparasite ticks, Amblyomma javanense, from M. javanica pangolin. This is the first report of Borrelia agents in A. javanense from pangolins. Further studies should be conducted to isolate this bacterium and investigate its epidemiologic, genetic, and pathogenic features.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
The Malayan pangolins studied here were rescued and treated by the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Terrestrial Wildlife Medical-Aid and Monitoring Epidemic Diseases Research Center under ethics approval (Wild Animal Treatment Regulation No. [2011] 85). The tick samples were collected following the procedure guideline (Pangolins Rescue Procedure, November 2016).
4.2. Tick Sample Collection and Identification
Ticks were collected from under the scales of the M. javanica pangolins seized by Guangxi Customs officers in anti-smuggling operations in Fang Cheng Gang city (108.35342° S, 21.76913° E) and Nan Ning city (108.33639° S, 22.87786° E). All the pangolins were from southeast Asian countries. Briefly, smugglers in the Sino-Vietnamese border collected the pangolins from Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand and illegally introduced them into China. In the process of smuggling, the pangolins were intercepted and seized. During the rescue of the pangolins, all ticks, including engorged and not-engorged adults and nymphs, were removed from the body surface, preserved in a moist breathable bottle at 4 degrees, and sent to the Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology for species identification and molecular analyses. All ticks were identified by entomologists Yi Sun and Rong-Man Xu. All identified ticks corresponded to Amblyomma javanense. For this study, a total of 227 adult ticks, including 176 males and 51 females, were collected, and 156 ticks that were not fully engorged were used for DNA isolation and molecular detection. Nymphs were not processed.
4.3. DNA Extraction, Borrelia-Specific PCR, and Sequencing
Ticks were surface-sterilized with 10% sodium hypochlorite and washed with sterile and DNA-free water and 70% ethanol. The ticks were grounded individually in 200 μL phosphate-buffered saline buffer, and total DNA was extracted with the DNeasy Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA). The ticks were subjected to two Borrelia genus-specific PCR assays (ABI9700, ). The Borrelia-specific nested-PCR assays were conducted by targeting the 16S rRNA gene (rrs) and the flagellin gene (flaB) (Table 1). Each 25 μL PCR reaction contained 1× PerfectTaq buffer, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dNTPs, 400 nM of each primer, 1.25 U PerfectTaq polymerase, and 2 μL undiluted DNA. Both the primary and nested Borrelia 16S PCR assays were performed with the following thermal conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 1.5 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. The flaB PCR assays were performed with an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C (primary and nested) for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. Amplified PCR products were electrophoresed through 1.5% agarose gels, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized under UV light. To avoid the risk of contamination, the DNA extraction, PCR reagent setup, amplification, and agarose gel electrophoresis were performed in separate rooms, and a negative control (distilled water) was concurrently included in each amplification. All the PCR products were purified with the QIAmp Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA) and then directly sequenced on an automated DNA sequencer (3730 DNA Sequencer; Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). We compared the sequences obtained with previously published sequences deposited in GenBank by using BLAST (http://blast.ncbi.nim.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 15 June 2020).

Table 1.
Primers used for Borrelia-specific 16S rRNA and flaB gene amplification in this study, including primer sequences, annealing temperature, and expected product size.
4.4. Sequence Analysis
Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene (rrs) and the flagellin gene (flaB) was conducted using MEGA7 software. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method based on the trimmed sequences generated in this study, together with sequences from other Borrelia spp. retrieved from GenBank. The stability of the tree was evaluated by bootstrap analysis with 1000 replications. The 16S rRNA and flagellin nucleotide sequences determined in this study have been submitted to Genbank under accession numbers MW889882 and MW916611.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.-C.Q. and J.-F.J.; methodology and data curation, B.-G.J., A.-Q.W. and T.-T.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, B.-G.J.; validation, formal analysis, and review, Q.X., C.-L.L., J.-J.C. and Y.S.; supervision, L.-Q.F.; project administration, X.-D.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the China Mega-Project on Infectious Disease Prevention (No. 2018ZX10101003-002), the National Major Science and Technology Projects for Infectious Diseases (2018ZX10712001-018-001), and the State Key Research Development Program of China (2019YFC1200501).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines (Pangolins Rescue Procedure, November 2016), and approved by the Ethics Committee (Wild Animal Treatment Regulation No. [2011] 85).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in MDPI.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Rong-Man Xu for Morphological identification of ticks in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Boyer, P.H.; Bergstrom, S.; Vial, L.; Boulanger, N. Relapsing Fevers: Neglected Tick-Borne Diseases. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Marosevic, D.; Cutler, S.; Derdakova, M.; Diuk-Wasser, M.; Emler, S.; Fish, D.; Gray, J.; Hunfeldt, K.-P.; Jaulhac, B.; et al. There is inadequate evidence to support the division of the genus Borrelia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ras, N.M.; Lascola, B.; Postic, D.; Cutler, S.J.; Rodhain, F.; Baranton, G.; Raoult, D. Phylogenesis of relapsing fever Borrelia spp. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, A.; Nakao, M.; Masuzawa, T.; Takada, N.; Yano, Y.; Ishiguro, F.; Fujita, H.; Ito, T.; Ma, X.; Oikawa, Y.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing implicates rodents as the main reservoir host of human-pathogenic Borrelia garinii in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adeolu, M.; Gupta, R.S. A phylogenomic and molecular marker based proposal for the division of the genus Borrelia into two genera: The emended genus Borrelia containing only the members of the relapsing fever Borrelia, and the genus Borreliella gen. nov. containing the members of the Lyme disease Borrelia (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex). Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2014, 105, 1049–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guner, E.S.; Watanabe, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Kadosaka, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Ezaki, T.; Kawabata, H.; Imai, Y.; Kaneda, K.; Masuzawa, T. Borrelia turcica sp. nov., isolated from the hard tick Hyalomma aegyptium in Turkey. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, S.-M.; Gofton, A.W.; Lo, N.; Gillett, A.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J.; Oskam, C.L. Novel Borrelia species detected in echidna ticks, Bothriocroton concolor, in Australia. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, S.M.; Gillett, A.; Ryan, U.; Irwin, P.; Oskam, C. Molecular characterization of ‘Candidatus Borrelia tachyglossi’ (family Spirochaetaceae) in echidna ticks, Bothriocroton concolor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, J.L.; Sima, R.; Calvani, N.E.D.; Hajdusek, O.; Chandra, S.; Panuccio, J.; Slapeta, J. Reptile-associated Borrelia species in the goanna tick (Bothriocroton undatum) from Sydney, Australia. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, A.; Goka, K.; Une, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Fujita, H.; Shiino, T.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Isolation and characterization of a novel Borrelia group of tick-borne borreliae from imported reptiles and their associated ticks. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, E.A.; Williamson, P.C.; Billingsley, P.M.; Seals, J.P.; Ferguson, E.E.; Allen, M.S. Frequency and Distribution of Rickettsiae, Borreliae, and Ehrlichiae Detected in Human-Parasitizing Ticks, Texas, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, A.; Cordeiro, M.D.; Cepeda, M.B.; Luz, H.R.; Cardozo, S.V.; Berto, B.P.; Guterres, A.; Fonseca, A.H. Hemoparasites in ticks of wild birds of Serra dos Orgaos National Park, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2019, 28, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuttin, G.L.; De Salvo, M.N.; Venzal, J.M.; Nava, S. Borrelia spp. in ticks and birds from a protected urban area in Buenos Aires city, Argentina. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Smith, W.C.; McIntosh, C.; Ferrari, F.G.; Moore-Henderson, B.; Varela-Stokes, A. Detection of a Borrelia species in questing Gulf Coast ticks, Amblyomma maculatum. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofton, A.W.; Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Hepner, S.; Loh, S.M.; Ryan, U.; Irwin, P.; Oskam, C.L. Genome-wide analysis of Borrelia turcica and ‘Candidatus Borrelia tachyglossi’ shows relapsing fever-like genomes with unique genomic links to Lyme disease Borrelia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 66, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaenkan, W.; Nooma, W.; Chelong, I.A.; Baimai, V.; Trinachartvanit, W.; Ahantarig, A. Reptile-associated Borrelia spp. In Amblyomma ticks, Thailand. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinachartvanit, W.; Hirunkanokpun, S.; Sudsangiem, R.; Lijuan, W.; Boonkusol, D.; Baimai, V.; Ahantarig, A. Borrelia sp. phylogenetically different from Lyme disease- and relapsing fever-related Borrelia spp. in Amblyomma varanense from Python reticulatus. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingry, L.C.; Anacker, M.; Pritt, B.; Bjork, J.; Respicio-Kingry, L.; Liu, G.; Sheldon, S.; Boxrud, D.; Strain, A.; Oatman, S.; et al. Surveillance for and Discovery of Borrelia Species in US Patients Suspected of Tickborne Illness. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetruy, F.; Garnier, S.; Boulanger, N.; Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Loire, E.; Faivre, B.; Noel, V.; Buysse, M.; Duron, O. A novel Borrelia. species, intermediate between Lyme disease and relapsing fever groups, in neotropical passerine-associated ticks. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Gherman, C.M.; Cozma, V. Coendangered hard-ticks: Threatened or threatening? Parasit Vectors 2011, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollars, T.M., Jr.; Sithiprasasna, R. New host, and distribution record of Amblyomma javanense (Acari: Ixodidae) in Thailand. J. Med. Entomol. 2000, 37, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Names for Ixodidae (Acari: Ixodoidea): Valid, synonyms, incertae sedis, nomina dubia, nomina nuda, lapsus, incorrect and suppressed names--with notes on confusions and misidentifications. Zootaxa 2014, 3767, 1–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Sulaiman, M.H.; Lian, C.J. The prevalence and intensity of Amblyomma javanense infestation on Malayan pangolins (Manis javanica Desmarest) from Peninsular Malaysia. Acta Trop. 2013, 126, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voltzit, O.V.; Keirans, J.E. A review of Asian Amblyomma species (Acari, Ixodida, Ixodidae). Acarina 2002, 10, 95–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, M.L.; Hsu, C.D.; Douay, G.; Ahmad, A.A. The first authenticated record of the pangolin tick Amblyomma javanense (Acari: Ixodidae) in Singapore, with notes on its biology and conservation. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 76, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platonov, A.E.; Karan, L.S.; Kolyasnikova, N.M.; Makhneva, N.A.; Toporkova, M.G.; Maleev, V.V.; Fish, D.; Krause, P.J. Humans infected with relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi, Russia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).