Abstract
Background. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is responsible for tropical spastic paraparesis and HTLV-1-associated leukemia/lymphoma. The infection is endemic in some areas of Peru, but its prevalence in the Peruvian Amazon is not well established. We aimed to assess the seroprevalence of HTLV-1 infection in pregnant women in the Peruvian Amazon. Moreover, we performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of the seroprevalence of HTLV infection in Peru. (2) Methods. This is a prospective cross-sectional study involving pregnant women attending health centers in the city of Iquitos, Peru, in May and June 2019. The presence of antibodies against HTLV-1 was assessed using ELISA (HTLV I + II ELISA recombinant v.4.0, Wiener lab, Rosario, Argentina). Positive cases were confirmed by Western Blot and HTLV-1 proviral load. (3) Results. The study included 300 pregnant women with a mean age of 26 years (standard deviation [SD] 6.4). Five patients were diagnosed with HTLV-1 infection (prevalence 1.7%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.7% to 3.8%). Pregnant women with HTLV-1 infection were discretely younger (mean age 22.6 [SD 22.6] vs. 26.8 [SD 6.3]; p = 0.128). None of the five women had been transfused, and all were asymptomatic. Two (40%) also had a positive serology for Strongyloides, but larvae were not detected in any of the parasitological stool studies. The systematic review component identified 40 studies, which showed that the prevalence of HTLV infection in the general population was 2.9% (95% CI 1.2% to 5.3%) and in women of childbearing age, 2.5% (95% CI 1.2% to 4.0%). (4) Conclusion. The prevalence of HTLV-1 in the Peruvian Amazon basin is about 1.7%, indicating an endemic presence. Screening for HTLV-1 in prenatal care is warranted.
1. Introduction
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) was the first human retrovirus identified. It is mostly sexually transmitted [1] but it can also be shed perinatally by breastfeeding [2] and parenterally through contaminated blood, either following transfusions or by needle sharing among injection drug users [3]. Acute infection with HTLV-1 is followed by long-lasting persistence of the virus in all carriers, although clinical manifestations develop only in about 10%. Typically, it presents as a subacute myelopathy known as tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-1-associated myelopathy [4] or a lymphoproliferative disorder named adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) [5].
HTLV can spread through mother-to-child transmission (MTCT), mainly through breastfeeding. As this is one of the main mechanisms of transmission in endemic areas, systematic HTLV antenatal screening is carried out in some countries, such as Japan and a few Latin American countries like Brazil [6,7]. Mothers found to be HTLV positive are advised to substitute breastfeeding with formula feeding for their infants [6].
Worldwide, approximately 5 to 10 million people are infected with the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) [8,9]. A large proportion of these people are in Central and South America, where the disease is endemic. In Peru, HTLV-1 prevalence in candidate blood donors varies from 1.2% to 1.7% across regions, with higher figures for some Andean areas [10]. Most studies have taken place in Lima or the Andes [11,12,13], whereas there are scant data from the Amazon [11,14,15,16].
Knowledge on the prevalence of HTLV-1 is vital for understanding whether antenatal screening is justified in the Amazon Basin, so that infected mothers can avoid breastfeeding to effectively prevent vertical HTLV transmission. Thus, this study aimed to assess the seroprevalence of HTLV-1 infection in pregnant women in the Peruvian Amazon. In addition, we undertook a systematic literature review and comprehensive review of the incidence of HTLV-1 in Peruvian cohorts and meta-analyzed the seroprevalence of HTLV infection in Peru.
2. Results
2.1. HTLV Infection in Pregnant Women
We included 300 pregnant women with an average age of 26 years (standard deviation [SD] 6.4 years). The mean number of deliveries was 2.9 (SD 1.7), and the mean gestation period, 172 days (SD 59). Just under half (44.7%) lived in peri-urban areas, while the rest lived in the city.
Five patients were diagnosed with HTLV-1 infection by serology (prevalence 1.7%, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.7% to 3.8%). Pregnant women with HTLV-1 infection were slightly younger (mean age 22.6 [SD 22.6] years vs. 26.8 [SD: 6.3] years; p = 0.13). None of the five women with HTLV-1 had been transfused, had a tattoo, or had a history of leukemia or neoplasm. All of them with other children had breastfed in the past. Strongyloides serology was positive in 2 of the 5 pregnant women (40%); however, the parasitological study in stool was negative for Strongyloides larvae in all of them. All HTLV-infected women were asymptomatic.
The characteristics of the five positive cases are summarized in Table 1. The numbers of HTLV-1 pro-viral copies were evaluated in four patients, who presented 3324 copies/10,000 cells, 950 copies/10,000 cells, and <10 copies/10,000 cells; in one, the proviral load was undetectable. No data were available for the remaining patient.

Table 1.
Characteristics of five cases of human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV) infection in pregnant women in greater Iquitos, Peru, diagnosed with ELISA serology.
2.2. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of HTLV Infection in Peru
The electronic search in PubMed and SciELO yielded 135 records, while a further 6 studies were identified from other sources. After screening the abstracts, we examined the full text of 61 potentially relevant papers, excluding 21 that did not report data on HTLV-1 prevalence. Therefore, the total number of included papers was 40 studies, plus the present study (Figure 1). Figure 1 shows the flow chart for study selection.
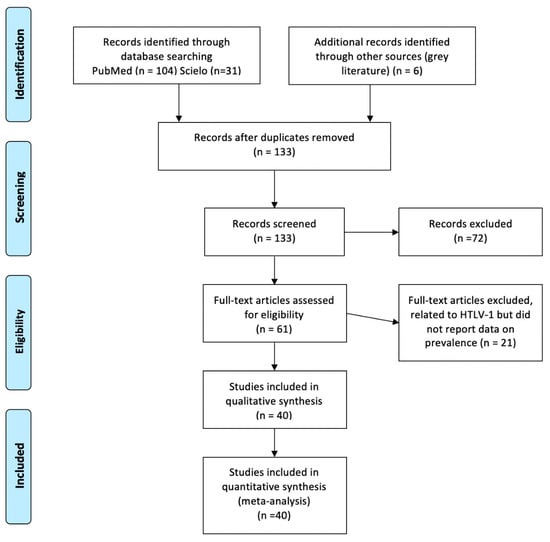
Figure 1.
Flow chart for study selection.
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of the studies from our literature review of HTLV prevalence in Peru [10,11,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Some studies were performed in the general population cohorts (including prisoners or hospital inpatients), as well as specific populations, like pregnant women or women of childbearing age, sex workers, people with HIV infections, men who have sex with men (MSM), relatives or descendants of people infected with HTLV, people with Strongyloides infections, people infected with tuberculosis, and blood donors.

Table 2.
Peruvian studies of HTLV prevalence.
The pooled proportion of HTLV in the general population was 2.34% (95% CI 1.96% to 2.75%; I2 95.51%). Table 3 summarizes the results of pooled prevalence in different groups, assuming a random-effects model. As expected, we found high heterogeneity with the exception of studies related to tuberculosis-infected patients. Figure 2 and Figure 3 summarize the forest plot prevalence in different groups.

Table 3.
Pooled prevalence of HTLV infection in different population groups.
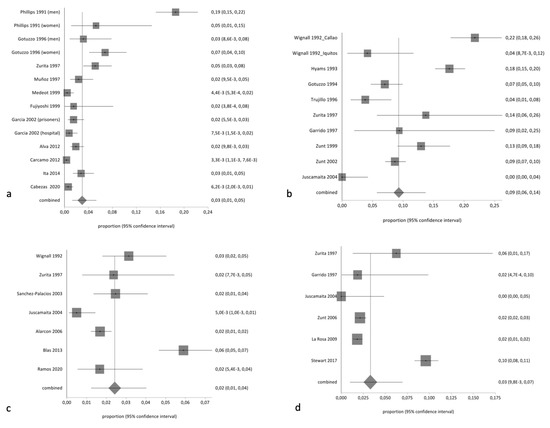
Figure 2.
Forest plot of pooled prevalence of HTLV (random effects) in (a) the general population, (b) sex workers, (c) pregnant women or women of childbearing age, and (d) men who have sex with men.
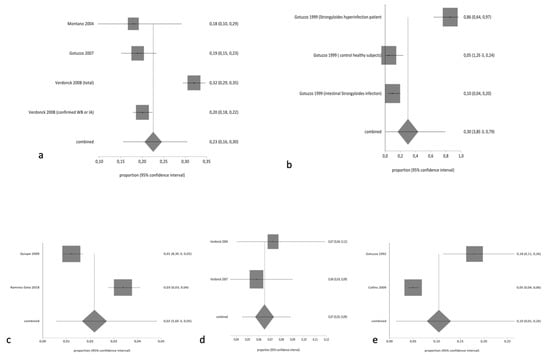
Figure 3.
Forest plot of pooled prevalence of HTLV (random effects) in (a) descendants and relatives of HTLV patients, (b) people with Strongyloides infection, (c) people living with HIV, (d) people infected with tuberculosis, and (e) blood donors.
3. Discussion
Few studies on the prevalence of HTLV have been carried out in pregnant women in Peru. In our study, the prevalence was 1.7%, which is lower than that reported by Wignall et al. [11] and Zurita et al. [22], higher than in the study by Juscamaita et al. [33], and similar to Alarcon et al. [36] a study involving 2492 pregnant women in Lima (the largest sample size in the literature), which also reported a prevalence of 1.7%. The prevalence in pregnant Peruvian women is higher than reported in other South American countries like Argentina (0.19% to 2.25%) [51,52] or Brazil (0.10% to 1.70%) [53,54], and lower than that in studies from French Guyana (4%) [55,56].
HTLV is effectively transmitted from mother to child, mainly through breastfeeding, which is one of the main transmission routes in endemic areas. In fact, pooled prevalence among descendants of HTLV-infected women has been estimated as high as 22.5% in the Peruvian population. However, HTLV screening in women attending antenatal clinics in endemic areas appears cost-effective [57], as preventing MTCT contributes to reducing both the incidence of HTLV and the burden of HTLV-associated diseases [2].
In Peru, HTLV-1 infections are reported in 1.2% to 3.4% of potential blood donors [10,50]. Blood products have been screened for HTLV-1 since 1997 in this country, but there is no specific program in pregnant women or neonates. The prevalence we observed in pregnant women supports the need to implement measures to prevent MTCT. However, to better understand the public health importance of HTLV infections, additional, adequately powered studies examining HTLV seroprevalence across Peru are a priority [2].
The main risk factors for HTLV-1 infection, as described in the literature, are age of more than 30 years, first sexual intercourse before the age of 20 years, and history of abortion or transfusion [30,36,47]. In our study, most infected women had been sexually active before the age of 20 years, but the rest of the factors did not seem to play a role.
Two studies have examined the prevalence of HTLV-1 in the Peruvian Amazon: one in remote indigenous communities, where the prevalence was 1.9% [14], and another in sex workers in Iquitos, who showed a seropositivity of 4.2% [11]. Despite the geographical proximity, the study populations were not comparable. The prevalence in our study was lower than in either of these studies. Nevertheless, in a cross-sectional, population-based study in 14 indigenous communities of the Matsés ethnic group in Requena province (Loreto region), the prevalence was 0.6% lower than that in our study [15].
Incidence of Strongyloides infection in patients with HTLV is higher than that in non-infected patients [58]. HTLV infection is considered a risk factor for S. stercoralis dissemination, which can be fatal. S. stercoralis infection is related to HTLV-1 clonal expansion in asymptomatic individuals [59]. Moreover, in Peru, Gotuzzo et al. reported HTLV infection in 85.7% of Strongyloides hyperinfection patients and 9.7% of patients with intestinal Strongyloides infection [27]. In our study, Strongyloides serology was positive in 40% of pregnant women; however, the parasitological study in stool was negative. Testing for antibodies against S. stercoralis is one strategy to identify a Strongyloides infection in patients with a negative parasitological study (direct stool smears, the Baermann technique, the Harada-Mori filter paper culture, charcoal cultures, and nutrient agar plate cultures) [60,61]. There is no clear explanation for the high seroprevalence of Strongyloides in HTLV-infected women in our study. The Peruvian Amazon may be an endemic region for Strongyloides, signaling high prevalence in the general population, including pregnant women [60]. Future studies are needed to evaluate clinical and subclinical Strongyloides infection in pregnant, HTLV-infected women.
The main strength of this study is its evaluation of HTLV-1 prevalence in pregnant women in greater Iquitos, providing information that is relevant for monitoring the risk of perinatal transmission through breastfeeding. This study has several limitations, Firstly, it screened a small sample for a prevalence study, so differences in patient characteristics between positive and negative cases could not be detected. Secondly, the proviral load was determined retrospectively, and data could not be collected from one patient who was not followed up. Thirdly, it was not possible to follow up the pregnant women and recommend avoiding breastfeeding for preventing transmission.
We consider necessary a large study in the Peruvian Amazon to understand the relevance of asymptomatic HTLV infections in pregnant women and the coinfection with Strongyloides, to provide definitive evidence supporting implementation of screening in pregnant women, as already in place for HIV and other viral infections.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Type of Study and Study Period
We performed a cross-sectional survey of HTLV-1 and strongyloidiasis in May and June 2019.
4.2. Study Population and Data Collection
We included pregnant adults (≥18 years) attending health centers in four districts of greater Iquitos, a city in the Peruvian Amazon. Participants were selected through convenience sampling (i.e., on days when the researcher was at the health center) when they visited the midwife for prenatal check-ups. Previous studies performed by our group have reported details of the study population and data collection [60,62].
The presence of antibodies against HTLV-1 was assessed by ELISA (HTLV I+II ELISA recombinant v.4.0, Wiener lab, Rosario, Argentina). Positive cases were confirmed by Western blot and SYBR Green–based real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay, developed in the Institute of Tropical Medicine ‘Alexander von Humboldt’, Peruvian University Cayetano Heredia, Lima [63]. Briefly, DNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was amplified by real-time PCR to detect and quantify HTLV-1 using the Light Cycler 480 II System (Roche Life Sciences). Genomic DNA was extracted from 5 × 106 PBMCs by a spin column using the QIAamp blood DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany).
Serology was processed for Strongyloides stercoralis with the Strongyloides IgG IVD-ELISA kit (DRG Instruments GmbH, Marburg, Germany), while Baermann’s method and charcoal culture were performed in stool specimens from HTLV-1 positive patients.
4.3. Data Analysis
Patient information was recorded in a Microsoft Excel database. The collected data were analyzed using SPSS statistical software (version 22.0, IBM). We used the chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test to analyze the presence of HTLV infection according to several demographic variables, considering results to be significant when the p value was less than 0.05.
4.4. Ethical Considerations
The Ethics Committee of the General University Hospital of Alicante (Spain) approved the project (PI2018/113), as did the Ethics Committee of Loreto Regional Hospital in Iquitos (Peru) (027-CIEI-HRL-2019). After receiving information on the study, individuals who volunteered to participate gave their written consent and were included. All results were kept strictly confidential, and participants with positive results were referred to their health centers for assistance or treatment.
4.5. Literature Review of the Prevalence of HTLV Infection in Peru
We performed an electronic search in PubMed and SciELO on 1 April 2020, using the following key words, grouped into three main concepts: “HTLV” AND “Peru”. Studies collected were published from 1 January 1991 to 1 April 2020. The search was limited to studies in humans and written in English, Spanish, Italian, or French. Additional records were identified by means of cited reference searching and electronic searches for gray literature (Google and Google Scholar).
We examined surveys, reports, reviews, and epidemiological studies on the prevalence of HTLV. Titles and abstracts were screened for relevant papers, and full texts were retrieved when appropriate. Data on the prevalence of HTLV were extracted, regardless of the type of population (children, adults, immunosuppressed patients, etc.).
We performed a proportion meta-analysis, using the Stuart-Ord (inverse double arcsine square root) method to calculate the 95% coefficient intervals and create the forest plots. Heterogeneity was analyzed using the I2 statistic (StatsDirect Statstical software v. 3.3.4) [64]. The prevalence meta-analysis was presented according to six population groups: (1) general population, (2) pregnant women or women of childbearing age, (3) sex workers, (4) people with HIV infections, (5) MSM, (6) relatives or descendants of people infected with HTLV, (7) people with Strongyloides infections, (8) people with tuberculosis, and (9) blood donors. We use a random-effects (inverse variance) method.
5. Conclusions
The prevalence of HTLV-1 in the Peruvian Amazon basin is about 1.7%. Since HTLV is endemic (prevalence > 1%) in this population of pregnant women, screening for HTLV in prenatal care is warranted.
Author Contributions
S.O.-M., formal analysis, investigation, project administration, software, supervision, writing—original draft, and writing—review & editing. J.-M.R.-R., conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, project administration, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, study design, clinical data analysis, and manuscript preparation and review. M.-E.V.-C., methodology, writing—review & editing. E.d.-M.-B., data curation, and writing—review &editing. O.-N.G.-P., data curation, Software, supervision, writing—review & editing. M.-J.T.-A., methodology, writing—review & editing. G.L.-C., methodology, and writing—review & editing, J.C.C.-S., methodology, writing—original draft, and writing—review & editing, L.P.-P.: formal analysis, writing—original draft, and writing—review & editing; M.G.-H., conceptualization; writing—original draft, and writing-review & editing. M.C.-M., conceptualization; project administration, writing—original draft, and writing—manuscript review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was co-funded by University Development Cooperation Program, Miguel Hernández University of Elche and Generalitat Valenciana. Grant number [SOLCIF/2017/0005].
Acknowledgments
We want to thank all members of the Spanish-Peruvian Chagas, HTLV and Strongyloides Network for their active contribution to the study. We also express our thanks to Meggan Harris for her assistance in editing this paper. Members of the Spanish-Peruvian Chagas, HTLV and Strongyloides Network: J.M. Ramos-Rincón & A. Gimeno (Hospital General Universitario Alicante & Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain), J. Llenas-García (Hospital Vega Baja Alicante & Universidad Miguel Hernández, Alicante, Spain), M. Górgolas-Hernández-Mora, R. Pérez-Tanoira & L. Prieto-Pérez (Hospital Universitario Fundación Jiménez-Díaz & Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain), S. Ortiz-Martínez (Consultorio El Ballestero, Albacete, Spain) M.E. Vásquez-Chasnamote (Centro de Investigación de Recursos Naturales, Universidad Nacional de la Amazonia Peruana. Iquitos, Peru), O.N. Gamboa-Paredes, J. Parraguez-de-la-Cruz J.J. Alarcón-Baldeón., P. Schillyk-Guerra, J. Bardales-Vásquez, G. Pérez-Bardales, A. Hernández-Vargas T. Zumaeta Silva, & R.P Pezo-Flores (Asociación Civil Selva Amazónica, Iquitos, Perú), L.A. Espinoza-Venegas, Juan-Carlos Celis & C. Ramal-Asayag (Hospital Regional de Loreto, Iquitos, Perú), V.V. Pinedo Cancino. (Laboratorio de Biología Molecular e Inmunología de la Unidad Especializada, Universidad Nacional de la Amazonia Peruana & Asociación Civil Selva Amazónica, Iquitos, Perú), M.J. Talledo-Albujar, G. López-Campana (Instituto de Medicina Tropical ‘Alexander von Humboldt’, universidad Cayetano Heredia, Lima, Peru) & Martín Casapía Morales (Hospital Regional de Loreto, & Asociación Civil Selva Amazónica, Universidad Nacional de la Amazonia Peruana, Iquitos, Perú).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paiva, A.; Smid, J.; Haziot, M.; Assone, T.; Pinheiro, S.; Fonseca, L.; Al, E. High risk of heterosexual transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection in Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosadas, C.; Taylor, G.P. Mother-to-Child HTLV-1 Transmission: Unmet Research Needs. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.L. Infection with human T-lymphotropic virus types-1 and -2 (HTLV-1 and -2): Implications for blood transfusion safety. Transfus Clin. Biol. 2016, 23, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.; Araujo, A.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.A.; Harewood, J.C.K. Adult T Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma (ATL): State of the Art. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, S.; Katamine, S.; Miyata, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Yamabe, T.; Miyamoto, T. Primary Prevention of HTLV-I in Japan. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1996, 13, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Fabbro, M.M.F.J.; Da Cunha, R.V.; Bóia, M.N.; Portela, P.; Botelho, C.A.; De Freitas, G.M.B.; Soares, J.; Ferri, J.; Lupion, J. Infecção pelo HTLV 1/2: Atuação no pré-natal como estratégia de controle da doença no Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2008, 41, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological Aspects and World Distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagaya, Y.; Matsuoka, M.; Gallo, R. 40 years of the human T-cell leukemia virus: Past, present, and future. F1000Res 2019, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, N.C.; Feria, E.B.; De Santos-Fortuna, E.L.; Caterino-De-Araujo, A. Confirming the presence of HTLV-1 infection and the absence of HTLV-2 in blood donors from Arequipa, Peru. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2009, 51, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignall, F.S.; Hyams, K.C.; Phillips, I.A.; Escamilla, E.; Tejada, A.; Li, O.; Al, E. Sexual transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus type I in Peruvian prostitutes. J. Med. Virol. 1992, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalb, A.; Pérez-Muto, V.; Cachay, R.; Tipismana, M.; Álvarez, C.; Mejía, F.; González-Lagos, E.; Gotuzzo, E. Early-Onset HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotuzzo, E.; Escamilla, J.; Phillips, I.A.; Sanchez, J.; Wignall, F.S.; Antigoni, J. The Impact of Human T-Lymphotrophic Virus Type I/II Infection on the Prognosis of Sexually Acquired Cases of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, I.E.; Orellana, E.R.; Blas, M.M.; Bernabe-Ortiz, A.; Cotrina, A.; Chiappe, M.; Kochel, T.J.; Carcamo, C.P.; García, P.J.; Zunt, J.R.; et al. HTLV-1 and -2 infections among 10 indigenous groups in the Peruvian Amazon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, C.; Trujillo, O.; Balbuena, J.; Marin, L.; Suárez, M.; Themme, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Valencia, P.; Crispin-Huamani, L. Prevalencia de infección por los virus de la hepatitis B, D y por retrovirus en la etnia Matsés (Loreto, Peru). Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2020, 37, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeot, S.; Nates, S.; Recalde, A.; Gallego, S.; Maturano, E.; Giordano, M.; Serra, H.; Reategui, J.; Cabezas, C. Prevalence of antibody to human T cell lymphotropic virus types 1/2 among aboriginal groups inhabiting northern Argentina and the Amazon region of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, I.A.; Hyams, K.C.; Wignall, F.S.; Moran, A.; Gotuzzo, E.; Sanchez, J.; Roberts, C. HTLV-I Coinfection in a HIV-1-Infected Peruvian Population. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1991, 4, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyams, K.C.; Phillips, I.A.; Tejada, A.; Wignall, F.S.; Roberts, C.R.; Escamilla, J. Three-year incidence study of retroviral and viral hepatitis transmission in a Peruvian prostitute population. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1993, 6, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gotuzzo, E.; Sánchez, J.; Escamilla, J.; Carrillo, C.; Phillips, I.A.; Moreyra, L.; Stamm, W.; Ashley, R.; Roggen, E.L.; Kreiss, J.; et al. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I infection among female sex workers in Peru. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 169, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, L.; Muñoz, D.; Gotuzzo, E.; Yi, A.; Watts, D. Prácticas sexuales y seroprevalencia de infección por VIH, HTLV-1 sífilis en meretrices clandestinas de Lima. Rev. Med. Hered 1996, 7, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotuzzo, E.; Yamamoto, V.; Kanna, M.; Chauca, G.; Watts, D.M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I infection among Japanese immigrants in Peru. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 1, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zurita, S.; Costa, C.; Waits, D.; Indacochea, S.; Campos, P.; Sanchez, J.; Gotuzzo, E. Prevalence of human retroviral infection in Quillabamba and Cuzco, Peru: A new endemic area for human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, P.; Anicama, R.; Gotuzzo, E.; Chauca, G.; Watts, D. HTLV-I en población de alto riesgo sexual de Pisco, Ica, Perú. Rev. Med. Hered 2013, 8, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.; Trujillo, L.; Gotuzzo, E.; Nizama, M.; Watts, D. Prácticas sexuales de riesgo y seroprevalencia de infección por VIH-1. HTLV-1, sífilis y hepatitis B en varones drogadictos no endovenosos de Lima. Rev. Med. Hered 1997, 8, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyoshi, T.; Li, H.C.; Lou, H.; Yashiki, S.; Karino, S.; Zaninovic, V.; Oneegllo, S.G.; Camacho, M.; Andrade, R.; Hurtado, L.V.; et al. Characteristic distribution of HTLV type I and HTLV type II carriers among native ethnic groups in South America. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1999, 15, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunt, J.R.; Alarcón, J.; Montano, S.; Longstreth, W.J.; Price, R.; Holmes, K. Quantitative assessment of subclinical spasticity in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I infection. Neurology 1999, 53, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotuzzo, E.; Terashima, A.; Alvarez, H.; Tello, R.; Infante, R.; Watts, D.M.; Freedman, D.O. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection associated with human T cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection in Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García Pinto, J.; Jiménez Luna, G. Estudio Comparativo Sobre la Seroprevalencia de HTLV-1 en Una Población de Adultos en Régimen Privado de Libertad y una Población Urbano Marginal de Lima. 2002. Available online: https://cybertesis.unmsm.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.12672/2076/Garcia_pj.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Zunt, J.R.; Dezzutti, C.S.; Montano, S.M.; Thomas, K.K.; Alarcón, J.O.V.; Quijano, E.; Courtois, B.N.; Sánchez, J.L.; Campos, P.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Cervical shedding of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I is associated with cervicitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanchez-Palacios, C.; Gotuzzo, E.; Vandamme, A.M.; Maldonado, Y. Seroprevalence and risk factors for human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV-I) infection among ethnically and geographically diverse Peruvian women. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, K.; Henriquez, C.; Echevarria, J.; Huayanay, L.; Agapito, J.; Cairampona, R.; Ramos, C.; Gotuzzo, E. Asociación entre infección por el virus linfotrópico humano de células T tipo I (HTLV-I) y mortalidad en pacientes hospitalizados con tuberculosis. Rev. Médica Hered. 2004, 15, 197–202. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.pe/pdf/rmh/v15n4/v15n4ao3.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2021). [CrossRef]
- Montano, S.M.; Zunt, J.R.; Rodriguez, L.; Quispe, I.; Rodriguez, C.; Altamirano, J.; Bautista, C.T.; Alarcón, J.O.V.; Longstreth, W.T.; Holmes, K.K. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection and early neurologic development: A pilot study of 48 children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juscamaita, P.Z.; Torrealva, C.M.; Cairampoma, M.R.; Gotuzzo, H.E. Seroprevalencia del virus linfotropo T humano tipo 1 (HTLV-1) en gestantes y grupos de elevada prevalencia para enfermedades de transmisión sexual de Ayacucho, Perú. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2004, 21, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Blas, M.; Bravo, F.; Castillo, W.; Castillo, W.J.; Ballona, R.; Navarro, P.; Catacora, J.; Cairampoma, R.; Gotuzzo, E. Norwegian scabies in Peru: The impact of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna-Torres, V.A.; Pérez-Bao, J.; Chauca, G.; Sovero, M.; Blichtein, D.; Chunga, A.; Flores, W.; Retamal, A.; Mendoza, S.; Cruz, M.; et al. Epidemiology of transfusion-transmitted infections among multi-transfused patients in seven hospitals in Peru. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, J.O.; Friedman, H.B.; Montano, S.M.; Zunt, J.R.; Holmes, K.K.; Quinnan, G.V.J. High endemicity of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 among pregnant women in Peru. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 42, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunt, J.R.; La Rosa, A.M.; Peinado, J.; Lama, J.R.; Suarez, L.; Pun, M.; Cabezas, C.; Sanchez, J. Risk factors for HTLV-II infection in Peruvian men who have sex with men. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zunt, J.R.; Montano, S.M.; Beck, I.; Alarcón, J.O.V.; Frenkel, L.M.; Bautista, C.T.; Price, R.; Longstreth, W.T. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Viral load and muscle tone are correlated. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotuzzo, E.; Moody, J.; Verdonck, K.; Cabada, M.M.; González, E.; Van Dooren, S.; Vandamme, A.M.; Terashima, A.; Vermund, S.H. Frequent HTLV-1 infection in the offspring of Peruvian women with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis or strongyloidiasis. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2007, 22, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, K.; González, E.; Henostroza, G.; Nabeta, P.; Llanos, F.; Cornejo, H.; Vanham, G.; Seas, C.; Gotuzzo, E. HTLV-1 infection is frequent among out-patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in northern Lima, Peru. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2007, 11, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Verdonck, K.; González, E.; Schrooten, W.; Vanham, G.; Gotuzzo, E. HTLV-1 infection is associated with a history of active tuberculosis among family members of HTLV-1-infected patients in Peru. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, A.M.; Zunt, J.R.; Peinado, J.; Lama, J.R.; Ton, T.G.N.; Suarez, L.; Pun, M.; Cabezas, C.; Sanchez, J. Retroviral Infection in Peruvian Men Who Have Sex with Men. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Collins, J.A.; Hernández, A.V.; Hidalgo, J.A.; Salazar, R.; Rodríguez, L.; Castillo, R.; Vega, J.; Illescas, R.; Villena, J.; Sotelo, C.; et al. HTLV-I infection is not associated with a higher risk of death in Peruvian HIV-infected patients. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2009, 51, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; González, E.; Bravo, F.; Gotuzzo, E. Infección por HTLV-1 y HIV en pacientes con herpes zoster en Perú. Rev. Medica Hered. 2011, 22, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo, C.P.; Campos, P.E.; García, P.J.; Hughes, J.P.; Garnett, G.P.; Holmes, K.K. Prevalences of sexually transmitted infections in young adults and female sex workers in Peru: A national population-based survey. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.F.; Ita, F.; Gonzalez, E.; Verdonck, K.; Bravo, F.; Clark, D.; Gotuzzo, E. Association between onychodystrophy and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e312–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blas, M.M.; Alva, I.E.; García, P.J.; Cárcamo, C.; Montano, S.; Mori, N.; Al, E. High prevalence of human T-lymphotropic virus infection in indigenous women from the peruvian Amazon. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, F.; Mayer, E.F.; Verdonck, K.; Gonzalez, E.; Clark, D.; Gotuzzo, E. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection is frequent in rural communities of the southern Andes of Peru. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 19, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.; Heitzinger, K.; Pollett, S.; Calderón, M.; Alarcón, J.; Ton, T.G.N.; Zunt, J.R. The changing epidemiology of human t-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection in peruvian female sex workers, 1993-2010. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Soto, M.C.; Huichi-Atamari, M. Prevalence of hepatitis B and human T-lymphotropic virus infection among blood donors at a hospital in the south-central highlands of Peru. Transfus. Med. 2018, 28, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berini, C.A.; Delfino, C.; Torres, O.; García, G.; Espejo, R.; Pianciola, L.; Juarez, M.; Arribere, G.; Nadal, M.; Eirin, M.E.; et al. HTLV-1 cosmopolitan and HTLV-2 subtype b among pregnant women of non-endemic areas of Argentina. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2013, 89, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenchi, A.; Gastaldelllo, R.; Balangero, M.; Irizar, M.; Cudolá, A.; Gallego, S. Retrospective Study of the Prevalence of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus-Type 1/2, HIV, and HBV in Pregnant Women in Argentina. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiró-Filho, E.A.; Senefonte, F.R.D.A.; Lopes, A.H.A.; De Morais, O.O.; Souza, V.G.; Maia, T.L.; Duarte, G. Frequency of HIV-1, rubella, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, simple herpes virus, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Chagas’ disease and HTLV I/II infection in pregnant women of State of Mato Grosso do Sul. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2007, 40, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lima, L.H.M.; Viana, M.C. Prevalence and risk factors for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HTLV-I/II infection in low-income postpartum and pregnant women in Greater Metropolitan Vitória, Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Cad. Saude Publica 2009, 25, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carles, G.; Tortevoye, P.; Tuppin, P.; Ureta-Vidal, A.; Peneau, C.; El Guindi, W.; Gessain, A. HTLV1 infection and pregnancy. J. Gynecol. Obs. Biol Reprod. 2004, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortevoye, P.; Tuppin, P.; Peneau, C.; Carles, G.; Gessain, A. Decrease of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I prevalence and low incidence among pregnant women from a high endemic ethnic group in French Guiana. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 87, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treviño, A.; Aguilera, A.; Caballero, E.; Toro, C.; Eiros, J.; Ortiz de Lejarazu, R.; Rodríguez-Calviño, J.; Tuset, C.; Gómez-Hernando, C.; Rodríguez-Iglesias, M.; et al. Seroprevalence of HTLV-1 y 2 Infection among Native and Immigrant Pregnant Women in Spain. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.M.; Da Fonseca Porto, A. Epidemiological and clinical interaction between HTLV-1 and Strongyloides stercoralis. Parasite Immunol. 2004, 26, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Eusebio, E.; Anguita, E.; Paulino-Ramirez, R.; Candel, F.J. HTLV-1 infection: An emerging risk. Pathogenesis, epidemiology, diagnosis and associated diseases. Rev Esp Quim. 2019, 32, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Martínez, S.; Ramos-Rincón, J.M.; Vásquez-Chasnamote, M.E.; Alarcón-Baldeón, J.J.; Parraguez-De-La-Cruz, J.; Gamboa-Paredes, O.N.; Schillyk-Guerra, P.; Espinoza-Venegas, L.A.; Pinedo-Cancino, V.V.; Perez-Tanoira, R.; et al. A cross-sectional study of seroprevalence of strongyloidiasis in pregnant women (Peruvian amazon basin). Pathogens 2020, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfrate, D.; Formenti, F.; Perandin, F.; Bisoffi, Z. Novel approaches to the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Rincón, J.-M.; Ortiz-Martínez, S.; Vásquez-Chasnamote, M.-E.; Gamboa-Paredes, O.-N.; Pinedo-Cancino, V.-V.; Ramal-Asayag, C.; Górgolas-Hernández-Mora, M.; Casapía-Morales, M. Chagas Disease in Pregnant Women in the Peruvian Amazon Basin. Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaui, V.; Verdonck, K.; Best, I.; González, E.; Tipismana, M.; Arávalo, J.; Vanham, G.; Campos, M.; Zimic, M.; Gotuzzo, E. SYBR Green-based quantitation of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 proviral load in Peruvian patients with neurological disease and asymptomatic carriers: Influence of clinical status, sex, and familial relatedness. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.-S.; Liu, X. Statistical methods in the meta-analysis of prevalence of human diseases. J. Biostat. Epidemiol. 2016, 2, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).