Abstract
Parasitic diseases caused by ticks constitute a barrier on global animal production, mainly in tropical and subtropical regions. As a country with a temperate and subtropical climate, Turkey has topography, climate, and pasture resources, and these resources are suitable for animal breeding and parasite–host–vector relationships throughout the country. This geography restricts the regulations on animal movements in the southeastern and eastern Anatolia because of the close contact with the neighboring states. The livestock resources in Turkey are regulated by strong foundations. Almost 30% of the agriculture-based gross domestic product is provided by the livestock industry. Parasitic diseases arising from ticks are endemic in Turkey, and they have a significant impact on the economy and animal health, particularly for ruminants. The main and economically-important tick-borne diseases (TBDs) suffered by animals include theileriosis, babesiosis, hepatozoonosis, and cytauxzoonosis caused by protozoa, and anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis caused by rickettsiae. The most common hemoprotozoan and rickettsial agents are Anaplasma marginale, Anaplasma ovis, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Anaplasma platys, Babesia bigemina, Babesia caballi, Babesia ovis, Cytauxzoon felis, Ehrlichia canis, Hepatozoon canis, Theileria annulata and Theileria equi. These diseases are basically controlled through treatment and measures for tick control. Vaccination can be performed for only tropical theileriosis caused in Turkey. We reviewed the studies published in domestic and international journals to gather epidemiological data regarding the major TBDs suffered by animals in Turkey.
1. Introduction
Located between 26°–45° eastern longitudes and 36°–42° northern latitudes, Turkey has a critically strategic location in the Mediterranean region, functioning as a bridge between the Europe and Asia. Turkey’s climate, topography, and forage resources make the country very suitable for animal agriculture. Additionally, Turkey’s temperate and subtropical climate characteristics ensure appropriate conditions for maintaining parasite–host–vector relationships. The regulation of animal movement is limited in the southeastern and eastern parts of Anatolia because of close geographical contact with neighboring countries. Generally, management systems are extensively and traditionally implemented for ruminants which typically graze in pastures during almost the whole year, usually from early days of spring to late periods of autumn. Conventional farms are mostly found in the eastern provinces while the modern farms have usually been constructed in the western provinces. Although the Turkish government grants subsidies to maintain the sector, traditional farming is on the decline because of high feed expenses and limitations regarding the access to pastures on common lands [1]. All factors associated with climate and geographic conditions and management systems leave the animals open to possible exposure to a variety of diseases [2,3].
The economy of Turkey is made of contemporary industry, commerce, and agriculture sectors. Thanks to the suitable climate, geographic conditions, rich soil sources and biological diversity, agriculture is one of the main sectors in the country. Though this sector tended to shrink following the 1980s, it is still a significant part of the current Turkish economy, accounting for 19.2% of the total employment in August 2020 [4]. Turkey has a remarkable foundation for livestock resources, and its share within the livestock sector of agricultural gross domestic product is approximately 30%. The main products of the Turkish livestock sector include poultry, beef, and veal. Poultry is the type of meat produced the most in the country. Most of the beef and veal is produced at traditional farms. Small ruminants represent the main livestock resource, with over 55 million in total animal numbers. Sheep constitute 57.98% of the total number of animals, while cattle represent 25.01%. Moreover, goats constitute 16.76%, and buffalo cover 0.25% of total livestock resource. Registered horses are solely present in state stud farms and jockey clubs. According to the report of the State Institute of Statistics, the number of horses was 131,497 in 2014 [1,4]. While the number of dogs and cats is unknown due to the absence of any compulsion regarding registration, these animals are believed to be plenty in Turkey.
Diseases arising from ticks cause significant medical and management issues in the farming sectors of Asian, African, and South American countries located in the tropical and subtropical regions of the globe. The geographic and climatic conditions and management systems in Turkey support the reproduction of ticks and emergence of TBDs. Relevant studies indicate that Turkey is an endemic location for TBDs, and various TBDs have been seen among domestic animals [2]. This study reviews epidemiological studies on frequent TBDs, including anaplasmosis, babesiosis, cytauxzoonosis, ehrlichiosis, hepatozoonosis, and theileriosis to emphasize the importance of these infections for animal health.
2. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases in Turkey
A total of 51 tick species, 43 from the Ixodidae family and 8 from the Argasidae family, have been identified in Turkey. The most important species are involved in nine genera including Dermacentor, Haemaphysalis, Hyalomma, Ixodes, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus), Amblyomma, Argas, Otobius, and Ornithodoros. The first five genera widely distributed throughout Turkey. The most prevalent species are Rhipicephalus bursa, Rhipicephalus annulatus, Rhipicephalus sanguineus, Rhipicephalus turanicus, Hyalomma anatolicum, Hyalomma excavatum, Hyalomma marginatum, Dermacentor marginatus, Dermacentor niveus, Haemaphysalis parva, Haemaphysalis punctata, and Haemaphysalis sulcata. The seasonal fluctuation of ticks depends on the genus, with Rhipicephalus and Hyalomma species found in spring, summer, and autumn, and Dermacentor, Hemaphysalis, Ixodes, and Ornithodoros species found in autumn, winter, and spring. The rate of tick-infested animals is usually > 20% of the herd [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Anaplasmosis, babesiosis, and theileriosis have been well-recognized TBDs of animals for many years, and remain as the most important diseases affecting livestock. Although the actual numbers of infections cannot be estimated from literature sources, the huge number of disease-specific drugs consumed during the tick activity seasons every year indicates the significance of these diseases on the economy and animal health.
3. Theileriosis
3.1. Bovine Theileriosis
Among several Theileria species, Theileria annulata and Theileria parva are the most pathogenic and financially critical species infecting cattle. The main TBD affecting cattle is tropical theileriosis resulting from T. annulata transmitted by Hyalomma in Turkey. Consequently, high morbidity and mortality occurs among the cattle in the entire country. Primary vectors of T. annulata are Hyalomma anatolicum and H. detritum but other Hyalomma species, including H. marginatum, H. excavatum, and H. dromedarii, can also transmit this hemoprotozoan agent. Benign Theileria species, Theileria mutans and Theileria sergenti/buffeli/orientalis, have been reported to be present in cattles from different locations of Turkey [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Discussions concerning the taxonomy of T. sergenti/buffeli/orientalis group has been continued for many years. These hemoparasites are classified as T. orientalis due to various biological characteristics [25,26]. As an emerging disease, oriental theileriosis, which is mainly characterized by hemolytic anemia, abortion, yield decrease, and pyrexia, can adversely affect cattle industry [27,28,29]. The molecular prevalence of T. orientalis has varied between 0.9% and 13.6% [14,18,23], and investigations conducted for determining the genotypes of T. orientalis revealed the presence of chitose (type 1) and buffeli (type 3) genotypes in Turkey [23,24].
Tropical theileriosis is more significant for pure breeds compared to the domestic and cross-breeds. Cattle that are brought from other countries and unvaccinated are most susceptible to T. annulata infection. The mortality rate is >70% among them, while the same rate is < 45% in cross-bred indigenous cattle [10,19]. The disease usually occurs in a seasonal form, from May to September, and with peaks in July. Acute theileriosis is accompanied by anemia, fever, petechial hemorrhages on mucosal membranes, enlarged lymph nodes, labored respiration, abortion, decreased milk production, and death (Figure 1) [30].
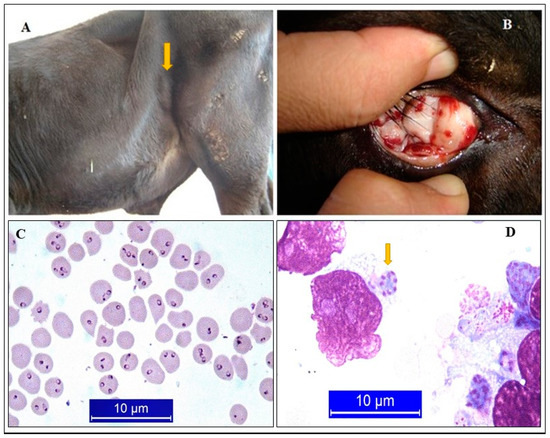
Figure 1.
Certain clinical symptoms of tropical theileriosis. Swollen sub-iliac lymph node (A), Petechial hemorrhages in the conjunctiva (B), Giemsa-stained pyroplasmic forms of T. annulata (C), Schizont of T. annulata in a lymphoid cell (D) [30].
A mixture of buparvaquone and oxytetracycline has been utilized to provide treatment to sick animals. Early diagnosis plays a key role in the effectiveness of the treatment. In cases with a parasitemia level > 20%, the treatment regime has also been supported with hematinic and anti-inflammatory agents. Blood transfusions have been necessary for severely anemic animals. A live-attenuated T. annulata schizont cell-culture-derived vaccine produced by the Ministry of Agriculture has been used to achieve disease control [8,10,20,31]; however, certain clinical reactions and deaths arising from the disease have been reported in vaccinated cattle [32,33].
Under field conditions, the significant factors affecting the severity of clinical infections are animal breed, management systems, and vaccination status. In an epidemiological study performed in the Cappadocia area that comprises a majority of the Central Anatolia Region, a total of 554 cattle, 62% of which were vaccinated against tropical theileriosis, were monitored for occurrences of clinical disease from April 1999 to November 2001, including three disease seasons. The findings indicated that the morbidity and mortality rate was higher among unvaccinated compared to vaccinated animals, in grazed compared to semi-grazed animals, and in pure breeds compared to cross or local breeds. The number of acute infections was 156 (27.61%), 86 of which died from tropical theileriosis. During the survey in the Cappadocia area, the total financial losses attributed to the infection were estimated to be 598,133 USD [19].
The diagnosis of theileriosis is mainly made through the microscopic examination of lymph and blood smears. In different parts of Turkey, the piroplasm forms of T. annulata in cattle have been detected upon the microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained blood smears at rates ranging from 2.3% to 60.5% [19,34,35]. Serological investigations performed by indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT) revealed the seroprevalence of T. annulata between 10% and 90%. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and reverse line blot assays showed that the molecular prevalence of T. annulata varied between 18.1% and 61.2% in cattle, and 12.6% and 46.9% in ticks [6,7,14,16,17,21,22,23,34,36,37,38]. Majority of the relevant studies are conducted in the Central and Eastern Anatolia Regions with high prevalence rates of tropical theileriosis. The results obtained from the Black Sea Region indicate the prevalence of hemoparasites to be lower than those of previously mentioned regions [17].
Epidemiological data regarding the vectors of bovine theileriosis were collected from surveys conducted under laboratory and field conditions. Inci et al. [35] found T. annulata infection to be at a rate of 17.49% in H. anatolicum’ salivary glands by microscopy. Sayin et al. [39] examined the developmental stages of T. annulata in four Hyalomma spp. which fed on experimentally infected calves. They investigated the impacts of tick sex and species on the intensity of T. annulata infection in the tick salivary glands. The infection rates were almost equally high in all ticks, but the mean intensity of the infection was higher in female ticks. Aktas et al. [37] examined the intensity and prevalence of Theileria infections in Hyalomma ticks collected from shelters and cattle reared using the traditional management system in the eastern provinces. According to their results, 44% of cattle were infested with four Hyalomma species. Hyalomma anatolicum was the predominant tick with a rate of 63.1%, and the other species were H. excavatum, H. detritum, and H. marginatum with rates of 23.8%, 11.7%, and 0.6%, respectively. Hyalomma anatolicum displayed the highest infection rate. The ticks collected from shelters and cattles displayed the infection rates of 46.9% and 12.6%, respectively. Female ticks collected from cattle had a higher prevalence rate compared to male ticks, but the difference between the infection rates of female and male ticks collected from shelters was not significant. The mean intensity of infection was higher in female ticks collected from both shelters and cattle. In another research performed in the Central Anatolia region [7], 39% of cattle were infested with Rhipicephalus annulatus, R. turanicus, and H. marginatum, and 27.9% of 42 tick pools were found to be positive for hemoparasites including Babesia bigemina, T. annulate, and Babesia sp. The most common tick species was R. annulatus, and the most common hemoparasite was B. bigemina, followed by T. annulata.
3.2. Ovine Theileriosis
Many Theileria species (T. ovis, Theileria lestoquardi, T. luwenshuni, T. recondita, T. uilenbergi, T. separata, Theileria sp. OT1, and Theileria sp. OT3) are found in small ruminants. Among these, T. ovis, T. separata, and T. recondita are non-pathogenic species. The most pathogenic Theileria species are T. lestoquardi, T. luwenshuni, and T. uilenbergi. These species cause malignant theileriosis, while the others cause non-pathogenic theileriosis in goats and sheep [40,41,42,43,44]. Malignant ovine theileriosis causes death in sheep in the Middle East, South East Asia, the Mediterranean region, and the Indian subcontinent [45]. Theileria ovis is the most prevalent species for small ruminants in Turkey. While T. recondita and T. lestoquardi have been found, no associated clinical infections have been documented [31,46]. Among Theileria species, most of which are transmitted by Hyalomma spp. and Haemaphysalis spp. [47], T. luwenshuni, T. ovis, T. uilenbergi, [48,49] and some isolates such as Theileria sp. OT1, Theileria sp. OT3, and Theileria sp. MK [15,48,50,51,52] have been detected in goats and sheep in Turkey. Moreover, the DNA of T. annulata, a bovine Theileria species, has been described in goats and sheep in the country [52]. The results of epidemiological investigations indicated that the prevalence of T. ovis ranged from 9.2% to 67.96% in sheep, and 0% to 17.1% in goats in Turkey [15,49,50,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. Rhipicephalus bursa plays a key role as a natural tick vector of T. ovis [53,59]. When compared to bovine theileriosis, small ruminant theileriosis has a minor impact on animal health in the country.
3.3. Cytauxzoonosis
As an emerging tick-borne hemoprotozoan infection of wild and domestic felids, cytauxzoonosis has been increasing in significance. The etiological agents of cytauxzoonosis are Cytauxzoon species which are apicomplexan parasites belonging to the order Piroplasmorida and the family Theileriidae. The disease in cats is characterized by anemia, dyspnea, inappetence, icterus, pyrexia, listlessness, and death [60,61,62]. Cytauxzoon felis, Cytauxzoon manul, and undetermined Cytauxzoon species which have minor genetic differences in 18S rRNA genes cause infections in domestic cats and wild felids [62]. These agents are transmitted to felid intermediate hosts by blood-feeding ticks harboring infective sporozoites of parasites [63,64]. Among these species, C. felis has a wide distribution and was detected in Turkey where the number of studies on feline hemoprotozoan and rickettsial diseases is restricted. Cytauxzoon felis infection in the cats of Van has been reported in only one study conducted in Van province of Turkey [65]. More detailed and comprehensive epidemiological surveys should be conducted to obtain data on feline cytauxzoonosis in Turkey.
4. Babesiosis
Babesiosis is a hemoprotozoan infection caused by Babesia species among humans and various domestic and wild animals. This disease is endemic, particularly in ruminants in tropical and subtropical zone countries. In regard to the number of clinical infections and deaths, ovine babesiosis has considerable economic and health significance for the Turkish livestock industry.
4.1. Bovine Babesiosis
Bovine Babesia species are B. bigemina, B. bovis, B. divergens, B. major and B. occultans. These species are transmitted by the ticks belonging to the Ixodes and Rhipicephalus genera [3]. Most of the bovine babesioses cases occur owing to B. bigemina in Turkey [3,6,23,33,66,67] and are usually transmitted by R. annulatus. During an acute infection, the host becomes severely ill, generally suffering from severe anemia, high fever, hemoglobinuria, inappetence, and lethargy. In B. bigemina infections, parasitemia may reach a rate of 50% to 100%. Parasitemia of B. bovis is not as high as that of B. bigemina, but can be as high as 90% in impression smears prepared from brain tissue [68]. Death occurs following hypothermia accompanied by uremia with icterus in severe cases. The mortality rate is high in most acute babesiosis cases. Main post-mortem findings include an enlarged bladder with hemoglobinuric urine, icterus on mucosal membranes, and connective tissues, and jaundice of the liver (Figure 2) [30].
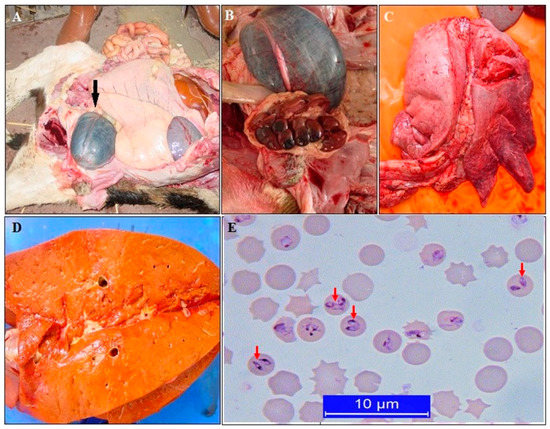
Figure 2.
Post-mortem findings of bovine babesiosis caused by Babesia bigemina. Enlarged urinary bladder containing dark-colored urine (A), kidney degeneration (B), lung edema (C), jaundice of the liver (D), intra-erythrocytic merozoites on a Giemsa-stained blood smear (E) [30].
Imidocarb dipropionate has been administered as an anti-babesial drug to treat animals [69]. Live-attenuated vaccines have been used to control bovine babesiosis in many global locations; a single dose of vaccine ensures long-lasting protective immunity in cattle [70,71,72,73,74]. Nevertheless, there is no available vaccine against bovine babesiosis in Turkey [46,67] where B. bigemina, B. bovis, and B. divergens were detected through microscopy and serology while B. major was detected with PCR [75]. The prevalence of B. bigemina reportedly ranges from 0.6% to 53.07% depending on the geographic region [3,6,23,33,38,66,76]. Molecular studies have recently revealed the presence of B. occultans in Turkey. Aktas and Ozubek [77] determined the molecular prevalence of B. occultans as 3% in the Black Sea Region of the country. Moreover, the DNA of B. occultans were detected in H. marginatum and R. turanicus [78,79]. However, the role of these ticks in the effective transmission of B. occultans remains to be proved in Turkey [3]. Within the hemoparasites detected in ticks, B. bigemina has been reported as the predominant species in the central Turkey. The most prevalent tick species was R. annulatus at 26.37% followed by H. marginatum at 21.12% and R. turanicus at 18.7% [7]. While records on bovine babesiosis have been received regularly by veterinary practitioners throughout the disease seasons, the data is yet to be adequate to evaluate the number of cases and predict the economic impact on the livestock industry due to the absence of a case recording system.
4.2. Ovine Babesiosis
Babesia species causing ovine babesiosis are Babesia ovis, Babesia crassa, Babesia foliata, Babesia motasi, Babesia taylori, Babesia spp. Xinjiang, and Babesia spp. from China [80,81,82]. In a recent study, a new Babesia sp., which differs from the ovine Babesia species and genotypes registered in GenBank, was reported in goats in Turkey [83]. Babesia ovis is the most significant species infecting small ruminants in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Far East. The geographic distribution of Babesia species shows parallelism that of their vectors, which are mostly Haemaphysalis and Rhipicephalus spp. in tropical and subtropical regions [42,81,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91]. Babesiosis is the main TBD affecting small ruminants considered as the major livestock species of Turkey. Ovine babesiosis is an acute disease characterized by hemolytic anemia, fever, icterus, and hemoglobinuria in small ruminants (Figure 3) [30]. The disease emerges mostly as outbreaks in Turkey [92].
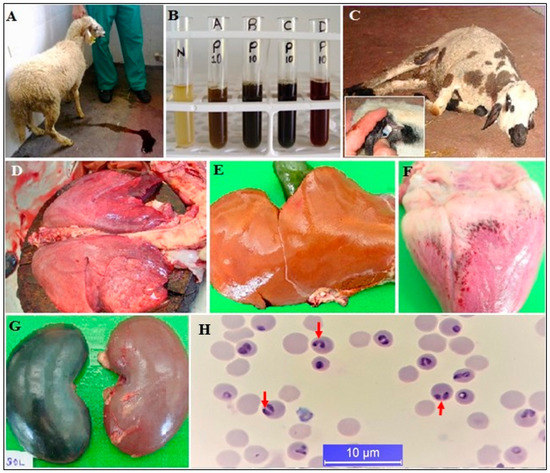
Figure 3.
Post-mortem and clinical signs of ovine babesiosis. Hemoglobinuria, which is the most prominent clinical symptom of acute infection and anemia (A–C), lung edema (D), jaundice of the liver (E), petechial hemorrhages in the heart (F), kidney degeneration (G), and intra-erythrocytic merozoites on Giemsa-stained blood smears (H), ref. [30].
Sheep are the primary livestock resource, constituting 57.98% of the total livestock in Turkey [4]. Small ruminants are raised mostly under traditional systems. Grazing on pastures from spring to late autumn, the sheep are usually exposed to tick infestations. Rhipicephalus species is the common vectors of the disease in the country. As a seasonal disease, babesiosis is observed from April to October every year, most commonly in June and July [5,8,9,51,92]. Babesia ovis is highly pathogenic to sheep, and clinical cases are usually severe. In acute cases, pancytopenia characterized by anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia occurs in sick animals [81,84,85,86,87,92]. Untreated cases frequently result in death for some animals with severe infection despite treatment. Many recurrences may also take place after the treatment of animals with an anti-babesial drug. Even when acutely infected cases are treated with a specific drug, compensation for the abnormalities in the hematologic picture still takes a long time [92]. Serologic surveys indicate that serum samples collected from randomly-selected sheep have B. ovis-specific antibodies with a percentage ranging from 32% to 80% [8,75,93,94,95,96,97,98]. In a recent country-wide seroepidemiological study, the seroprevalence of B. ovis was determined as 49.16% by IFA test and 29.89% by rBoSA1-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Ovine babesiosis has been observed to be particularly common in the Central, Southeastern, and Eastern Anatolia regions [99]. The molecular prevalence of B. ovis was determined to be between 0% and 21.42% in randomly selected sheep in Turkey [48,54,100,101,102,103]. However, Sevinc et al. [49] detected 70.81% molecular positivity in sheep showing clinical symptoms. Benedicto et al. [58] also detected high molecular positivity in tick-infested sheep (64.8%) and goats (53.6%) from Turkey. Making predictions regarding the current actual intensity of clinical cases is challenging considering the lack of a case recording system. Nevertheless, the results of a follow-up study performed in Konya located in the central part of Turkey reflect the importance of ovine babesiosis. A total of 122 acute infections (14.35%) were detected in only two sheep flocks between June and July in 2011, and 15 sheep died despite intensive treatment [92].
The control of ovine babesiosis is solely provided by chemotherapy and limited tick-control precautions. Imidocarb dipropionate has prophylactic efficiency as well as a therapeutic effect on the disease [69], therefore significant amounts of the agent are used every year. An immunoprophylactic control method against ovine babesiosis has not been developed. According to the relevant authorities, despite certain disadvantages, the attenuated parasites should be used to immunize the animals against TBDs as long as non-living parasite vaccines are absent [70,104,105]. The rapid passage of the virulent strain via susceptible splenectomized calves is one of the most extensively used methods for reducing the virulence of B. bovis. The literature displays limited attention to the immunoprophylaxis of B. ovis infection and no information regarding how many passages are required to attenuate a virulent B. ovis strain is available. Yeruham et al. [106] were unable to conduct more than three successive passages of B. ovis in splenectomized lambs since the third passage lamb had a very low level of parasitemia with no reduction in virulence. In a preliminary study [107], rapid blood passages were performed to reduce the virulence of B. ovis in 13 susceptible splenectomized lambs. The obtained results indicated the virulence of B. ovis was not eliminated after 12 successive passages. Therefore, alternative methods or further passages may be required to attenuate B. ovis.
Acute babesiosis is diagnosed depending on clinical signs of disease and the demonstration of the Giemsa-stained parasites in the erythrocytes by microscopy. Microscopical and clinical examinations are not sufficient for the diagnosis of subclinical infections. Immunological and molecular techniques have been employed to determine the subclinically infected animals [72,108,109]. A synthetically derived bovine B. bovis antigen has been utilized in an ELISA to detect anti-B. ovis antibodies for the immunodiagnosis of B. ovis [93,94,96,97]. IFAT is also being utilized in a small number of laboratories [69,98,99,110]. The IFA test has some disadvantages in that it is subjective, arduous, time-consuming, and requires well-experienced personnel. As diagnostic antigens, the immunoreactive proteins of certain Babesia species have widely been used in the immunodiagnosis of bovine, canine, and equine babesiosis [111,112,113,114]. In a recent study, the presence of five immunoreactive proteins of B. ovis was documented; however, further studies are still needed in terms of the purification of these proteins and their possible usage as diagnostic antigens [115]. Recombinant immunoreactive proteins have been utilized as antigen sources in quantitative diagnostic techniques and as vaccine candidates for the control of diseases. The results of a new research indicate that secreted antigen 1 of B. ovis (rBoSA1) is a promising diagnostic antigen that can be used for the development of serological assays for the diagnosis of ovine babesiosis [116]. Apart from rBoSA1, various immunoreactive proteins of B. ovis such as rBoSA2, BoSPD, and ovipain-2 have been produced [116,117,118,119]. These proteins are the strongest candidates to be used in future diagnostic kits and vaccine development. Recombinant BoSA1-based indirect ELISA was successfully used in a seroepidemiological study to determine the endemic status of B. ovis in Turkey [99].
Urgent measures should be taken to control ovine babesiosis. For the implementation of effective control strategies, diagnostic methods that are sensitive, specific, cost-effective, and suitable for use in the field should be developed. Furthermore, the presence of a vaccine would reduce the losses from outbreaks of the disease; thus, the development of vaccines is critical in this regard.
4.3. Equine Babesiosis
Equine babesiosis poses risks for horse breeding and racing industries in Turkey where international horse races are still held with growing interest. Most of the epidemiological surveys regarding this infection have been conducted to determine the prevalence of infection. The results of relevant researches indicate that Theileria equi is more prevalent compared to Babesia caballi. According to microscopical investigations, the prevalence of equine babesiosis varies from 0% to 58.18% [120,121,122,123,124]. Serologic studies indicated that the occurrence of T. equi varied from 12.8% to 64.5% and B. caballi from 0% to 34.6% [121,122,123,125,126,127,128,129]. Molecular prevalence was detected as 1.97% to 3% for B. caballi and 2.96% to 20.2% for T. equi [130,131,132,133]. However, Derinbay Ekici et al. [124] currently reported a high molecular prevalence for B. caballi (38.8%) and T. equi (50%) in tick-infested wild horses (Equus ferus caballus) from Central Anatolia in Turkey. Results from a comparative research revealed that equine piroplasm infections were more frequent in racehorses compared to stud-horses [127]. Theileria equi genotype A, D, E, and B. caballi genotype A have been detected in equids in Turkey [131,133].
Certain studies report that the occurrence of equine babesiosis differs according to the geographic region. Akkan et al. [121] detected that equine babesiosis was more prevalent in the eastern Turkey compared to other regions, with high positivity rates of 58.18% and 69.9% by microscopy and IFAT, respectively, which was attributed to the deficiency of regulations on animal movement across the border.
The information concerning the vectors of equine babesiosis is limited in Turkey. According to a few number of researches, H. detritum, H. marginatum, R. bursa, and R. turanicus were detected on horses with babesiosis [120,121,126]. Dik et al. [134] detected tick infestations caused by Hae. parva, H. excavatum, and D. marginatus in feral horses in Turkey. From an epidemiological point of view, most of these reports are not sufficient to elucidate the vector of the disease.
4.4. Canine Babesiosis
The epidemiology of canine Babesia species transmitted by Dermacentor, Haemaphysalis, and Rhipicephalus [81], is poorly studied in Turkey, but there has been an increase in the number of studies on this subject in recent years. Although tick-borne pathogens of pets are of economic importance in many developed countries [135], there are limited case reports indicating the occurrence of Babesia infections in dogs in Turkey [136,137,138]. Molecular studies investigating Babesia species showed the presence of Babesia canis, Babesia gibsoni, and Babesia vogeli in dogs in the country. The molecular prevalence of canine babesiosis was determined to be between 0% and 12% in these studies [139,140,141,142,143,144]. An unnamed novel Babesia spp. isolate has recently also been detected in dogs in Turkey [145].
5. Anaplasmosis
Anaplasma genus includes Anaplasma bovis, A. centrale, A. marginale, and A. ovis that are pathogens for ruminants, A. platys for canines, and A. phagocytophilum for domestic animals and humans. The main vectors of the Anaplasma species are ticks, particularly the genera Ixodes, Amblyomma, Dermacentor, and Rhipicephalus [146]. The direct transfer of A. marginale-infected erythrocytes from carrier animals to susceptible animals by biting arthropods or iatrogenically can result in the transmission of the disease. In Turkey, A. marginale infection is endemic with most animals being reservoirs.
5.1. Bovine Anaplasmosis
Bovine anaplasmosis is the most prevalent TBD of cattle initiated by A. marginale that causes a hemolytic disease. The disease can be fatal in susceptible cattle, and as such, partially responsible for the high mortality rate seen in affected herds. The clinical symptoms of the disease are anemia, fever, icterus, lethargy, abortion, weight loss, and often death in animals that are older than two years. Calves of immune mothers take temporary protection through the colostrum which prevents anaplasmosis. This protection lasts almost 3 months, and is mostly followed by an age resistance lasting until the animals are about 9 to 12 months. Animals recovered from acute infections become carriers of disease for life. Therefore, they significantly contribute to the spread of bovine anaplasmosis [147,148,149].
Acute anaplasmosis is diagnosed using microscopy and identifying the infected erythrocytes on stained blood smears (Figure 4). During the acute infection, anemia occurs in a couple of days, and a sharp decline in the hematocrit indicates the severity of infection. During the persistent infection, the infected erythrocytes cannot always be detected in stained blood smears, and therefore, different serologic tests to detect specific antibodies are used for diagnosis. Competitive ELISA (cELISA) is generally preferred for this aim. It was reported that cELISA was positive in calves acutely infected with A. marginale before or along with the development of rickettsemia and that the antibodies were detectable in sera from persistently infected cattle vaccinated as long ago as six years previously [150].
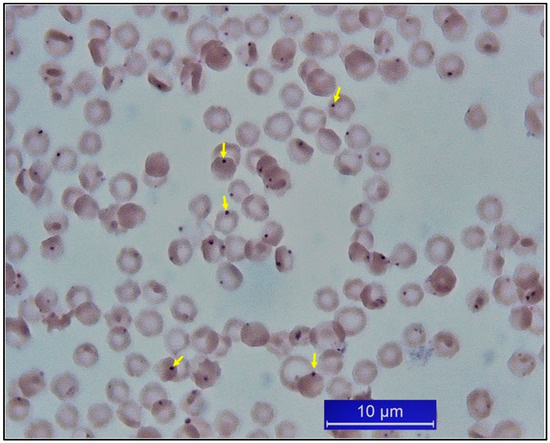
Figure 4.
Anaplasma marginale-infected erythrocytes from a cattle (original).
Bovine anaplasmosis caused by A. marginale, A. bovis, A. centrale, and A. phagocytophilum has been reported in almost all regions of Turkey [23,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161]. Most cattle represent the carrier state. In carrier animals, clinical infections may be developed as a result of immunosuppression usually related to pregnancy, transportation, and high milk yield. Deaths arising from acute infections have been recorded from both private [160] and governmental dairy cattle farms (unpublished data) in the country. Birdane et al. [155] reported fatal A. marginale infections in a dairy cattle herd from the central Aegean Region. In the herd, 34.11% and 55.35% of 645 animals were found positive with microscopy and cELISA, respectively, and fifteen cows died because of per-acute infection. Clinical cases were considerably associated with the age of the animals, as understood from the results. General microscopic and serologic surveillance in the herd showed cattle of all ages, except those aged 9 to 12 months and infected with A. marginale. Disease severity and the number of deaths increased with age. Seropositive calves aged younger than nine months did not exhibit any clinical symptoms of acute infection. Clinical bovine anaplasmosis cases caused by A. phagocytophilum were first reported by Aktas and Özübek [157] in 2015.
Imidocarb dipropionate and tetracyclines are commonly used drugs for the treatment of acute anaplasmosis. According to the reduction value in packed cell volume, the treatment regimen may be strengthened with blood transfusion and supportive therapy; however, death occurs in some per-acute cases despite all the treatment approaches [69].
5.2. Ovine Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis caused by Anaplasma ovis in goats and sheep is generally asymptomatic, but severe anemia may occasionally occur. The symptoms similar to those found in bovine anaplasmosis usually develop in the case of immunosuppression in small ruminants. Anaplasma ovis infection is transmitted by various ticks, particular Dermacentor and Rhipicephalus species, in Turkey mainly by R. bursa [44]. Clinical and subclinical infections in small ruminants were reported in a few studies by microscopic and serologic examination [8,99,151,162]. As a result of recently conducted molecular surveys, the prevalence of A. ovis was determined as 18% to 67.06% in Turkey [48,49,58,101,163,164,165,166].
Up to 2005, the occurrence of A. phagocytophilum in sheep was not reported in Turkey. In parallel to the development of TBDs in humans in recent years, A. phagocytophilum, which is thought to be zoonotic, was found in domestic animals and ticks [156,167,168,169,170]. The molecular prevalence of A. phagocytophilum in randomly selected sheep has varied between 0% and 18.90% in Turkey [48,49,101,164,165,168]. Benedicto et al. [58] detected the highest prevalence of A. phagocytophilum (66.7%) in tick-infested sheep and goats with clinical symptoms in Turkey. Further researches are required to obtain more epidemiological data concerning ovine anaplasmosis.
5.3. Canine Granulocytic Anaplasmosis and Cyclic Thrombocytopenia
Anaplasma species causing infections in dogs are A. phagocytophilum and A. platys. The diseases caused by these species are called canine granulocytic anaplasmosis and canine cyclic thrombocytopenia, respectively [171]. The main clinical symptoms of canine granulocytic anaplasmosis in dogs are fever, lethargy, lymphadenomegaly, anorexia, arthritis, splenomegaly, weight loss, and vomiting. Anaplasma platys frequently causes asymptomatic infections in dogs. Canine cyclic thrombocytopenia shows symptoms similar to canine granulocytic anaplasmosis, with the most prominent symptom being thrombocytopenia associated with anemia and leukopenia [172]. These diseases have a large distribution worldwide, including in Turkey. The serologic prevalence of A. platys/A. phagocytophilum was reported to range from 0% to 30.1% [173,174,175,176,177,178,179]. Several molecular studies have investigated the presence of these rickettsial organisms of dogs in Turkey [141,180,181,182]. The main tick vector of A. phagocytophilum is I. ricinus. However, apart from this tick species, A. phagocytophilum has been detected in R. bursa and Hae. parva in Turkey [170,181,183]. Anaplasma platys’ DNA has frequently been detected in R. sanguineus. For this reason, this tick species is considered the vector of A. platys in dogs [171]. Anaplasma platys was detected in R. sanguineus and R. turanicus in Turkey [181].
6. Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is caused by obligately tick-transmitted rickettsial microorganisms belonging to the family Anaplasmatacea. Ehrlichia canis, Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Ehrlichia ewingii, Ehrlichia muris, Ehrlichia mineirensis, and Ehrlichia ruminantium are the main causative agents of the disease. However, the number of new species or genotypes of this genus is increasing as a result of developing molecular techniques [184,185]. Ehrlichia canis, E. chaffeensis, and E. ewingii are the most important species threatening human and animal health, especially in dogs. Severe canine infections are principally associated with E. canis, and the disease caused by this microorganism is called canine monocytic ehrlichiosis (CME) [186]. CME is mainly characterized by fever, anorexia, mucosal pallor, generalized lymphadenomegaly, depression, lethargy, and splenomegaly. Hypothermia may even occur in severely pancytopenic dogs [187].
The geographic distribution of E. canis shows parallelism with the presence of the primary vector tick, R. sanguineus [188]. This tick species transmits E. canis transstadially under field conditions [189] and intrastadially under experimental conditions [190] and distributed worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical zone countries, including Turkey [5,188].
Ehrlichiosis is one of the most common TBDs in Turkey. Clinical infections have commonly been encountered in dogs, but the disease is rarely found in different hosts [181,191]. Mylonakis et al. [187] stated that CME may be one of the main causes of life-threatening pancytopenia in dogs in E. canis-endemic countries as well as places such as Turkey and South East Asia. The presence of R. sanguineus throughout Turkey supports this view [5].
Studies conducted in Turkey have shown that E. canis is the only species detected in dogs [140,141,181,192,193,194,195,196]. CME is common in Turkey, and the prevalence of the disease has been detected by serologic and molecular investigations [140,197,198]. Serologic tests such as ELISA and IFAT used to detect anti-E. canis specific antibodies, show the seroprevalence of E. canis to be between 0% and 74% [174,176,177,179,181,198,199,200,201,202,203,204]; however, the molecular prevalence was determined to be between 0% and 39.3% [140,141,142,144,181,193,194,196]. The genetic diversity of E. canis was poorly studied in Turkey. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the Tandem Repeat Protein 36 (TRP36) revealed five Tandem Repeat sequences (TRs) indicating genetic diversity. By far, three different genotypes including Brazilian genotype, US genotype and a novel genotype similar to a previously detected genotype in humans from Costa-Rica were reported in Turkey [195].
Apart from E. canis, Ehrlichia risticii (Neorickttsia risticii), the causative agent of equine monocytic ehrlichiosis, specific antibodies have been detected in thoroughbred horses in Turkey [205]. Ehrlichia spp. Omatjenne strain was also detected in cattle [156]. Further, a clinical infection case caused by E. canis was reported in a cat in Turkey [191]. The first human ehrlichiosis case has been reported in Konya province of Turkey [206]. In addition, E. canis DNA was detected in R. sanguineus, R. bursa, D. marginatus, and Hae. sulcata ticks in Turkey [181,183]. Although the number of studies concerning CME has increased in recent years in Turkey, it is thought that more comprehensive and detailed studies are required. A human ehrlichiosis case recently reported from the central part of Turkey [206] reveals the importance of these zoonotic rickettsial microorganisms.
7. Hepatozoonosis
Hepatozoon species, apicomplexan protozoan parasites (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae), cause infections characterized by moderate to severe symptoms including fever, lethargy, cachexia, anemia, hyperglobulinemia, weight loss, and anorexia in a broad spectrum of animals, particularly mammals and reptiles, but also birds and amphibians [207]. Hepatozoonosis is caused by more than 340 species, and the species of veterinary importance among these parasitize domestic and wild carnivores [208]. While Hepatozoon canis and Hepatozoon americanum are the main etiological agents of canine hepatozoonosis, feline hepatozoonosis is primarily associated with Hepatozoon felis [209,210]. Transmission occurs when a host animal orally ingests an infected tick harboring mature oocysts of Hepatozoon species [208]. Amblyomma maculatum and R. sanguineus sensu lato are the primary vectors of H. americanum and H. canis, respectively [211]. However, the oocysts of H. canis have also been described in different ixodid ticks infesting dogs, including Haemaphysalis flava, Hae. longicornis, Amblyomma ovale, R. microplus, and R. turanicus [212,213,214,215]. Transplacental transmission of H. canis has also been reported [216].
Hepatozoonosis was firstly reported in Turkey in 1933 [217]. Thereafter, the majority of conducted studies have been related to the clinical course, treatment, and epidemiology of canine hepatozoonosis [140,218,219,220]. Microscopic, serologic, and molecular studies show that the prevalence of canine hepatozoonosis varies between 0.5% and 54.3% in Turkey [140,141,142,143,145,193,221,222,223,224]. Considering that dogs from many different parts of the country were included in these studies, it is concluded that canine hepatozoonosis is endemic throughout Turkey.
Feline hepatozoonosis, which is mainly caused by H. felis, is not as prevalent as canine hepatozoonosis, and clinical infection was reported in a cat in only one study [225]. The agent causing infection in that study was molecularly confirmed as Hepatozoon spp. at the genus level; therefore, there is no study reporting feline hepatozoonosis caused by H. felis in Turkey.
Hepatozoon canis, H. felis, H. ursi, and Hepatozoon sp. MF genotypes have been detected in ticks and carnivores, including dogs, red foxes, and bears in Turkey [183,223,226,227,228,229] Hepatozoon sp. MF was detected in dogs in the central part of Turkey [143,223]. The presence of H. canis DNA was detected in red foxes by Orkun and Nalbantoglu [226]. Akyuz et al. [227] recently reported the infection of H. ursi in Ursus arctos (Turkish brown bears) from the eastern part of Turkey.
In studies investigating the pathogens carried by ticks, H. canis was detected in R. sanguineus, R. turanicus, D. marginatus, Hae. parva, Hae. sulcata, and I. ricinus in Turkey [183,222,226,228]. Hepatozoon felis was also detected in R. sanguineus [183]. Orkun and Emir [228] detected H. felis DNA in Hae. parva collected from Eurasian lynx. In addition, H. ursi was recently reported in H. marginatum, R. turanicus, and I. ricinus collected from brown bears in Turkey [228]. The detection of Hepatozoon species in different ticks does not mean that those tick species are vectors of this protozoa. To confirm this idea, further experimental studies are required [230].
8. Conclusions
In Turkey, the primary TBDs of veterinary relevance are theileriosis, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis in cattle, babesiosis in sheep and goats, equine piroplasmosis in horses, cytauxzoonosis in cats, and babesiosis and anaplasmosis in dogs. These infections have been well-known by veterinarians and farmers. The principal tick-borne pathogens are A. marginale, B. bigemina and T. annulata in cattles, B. ovis in sheep and goats, and B. caballi and T. equi in donkeys and horses in Turkey. These infectious agents may cause acute clinical infections and deaths in animals. The infections can emerge as co-infections, and frequently become complicated with the presence of other diseases, so struggling with infections get challenging. Effective drugs are available and used in the treatment of all these infections. Early diagnosis of the infections increases the rates of recovery, and in addition to the primary treatment regimen, supportive treatment is most essential. Acute infections can be diagnosed via microscopic examination, but carrier animals are still tough to determine by microscopy. IFA test has been commonly used to determine the carrier animals of Anaplasma, Babesia, Ehrlichia, and Theileria species for many years. A recombinant antigens termed rMSP5- and MSP5-specific monoclonal antibodies based cELISA is currently used to detect Anaplasma infections in animals. Veterinary practitioners usually treat animals according to their clinical diagnostic experiences under field conditions. PCR-based molecular techniques have also been utilized to detect TBDs. These diagnostic techniques are valuable investigation tools for certain studies. However, they are of little value for the practitioners, and laborious for the examination of large numbers of samples. It is necessary to develop diagnostic methods which are sensitive, specific, and practical for use even under field conditions.
Relevant studies have been mostly performed to determine the prevalence of infections in Turkey. Detailed studies are required in terms of risk factors and host–parasite–vector interactions. Additionally, the studies have mostly been undertaken in the provinces of Central and Eastern Anatolia Regions, and since Turkey is a wide country, it is still necessary to perform studies representing the entire country.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S., X.X. and O.C.; formal analysis, F.S. and O.C.; investigation, O.C. and F.S.; resources, F.S. and O.C.; data curation, O.C. and F.S.; writing—original draft preparation, O.C. and F.S.; writing—review and editing, F.S., X.X. and O.C.; visualization, O.C.; supervision, F.S. and X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Turkish Statistical Institute. Available online: http://www.turkstat.gov.tr/ (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Inci, A.; Yildirim, A.; Duzlu, O.; Doganay, M.; Aksoy, S. Tick-borne diseases in Turkey: A review based on one health perspective. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozubek, S.; Bastos, R.G.; Alzan, H.F.; Inci, A.; Aktas, M.; Suarez, C.E. Bovine babesiosis in Turkey: Impact, current gaps, and opportunities for intervention. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkish Agriculture Industry Report. Available online: http://www.invest.gov.tr/en-US/infocenter/publications/Documents/AGRICULTURE.INDUSTRY.PDF(2010) (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- Aydin, L.; Bakirci, S. Geographical distribution of ticks in Turkey. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ica, A.; Inci, A.; Yildirim, A. Parasitological and molecular prevalence of bovine Theileria and Babesia species in the vicinity of Kayseri. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2007, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ica, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Yildirim, A.; Duzlu, O.; Inci, A. Detection of Theileria and Babesia species in ticks collected from cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Dyncer, S.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Yukary, B.A.; Eren, H.; Deger, S.; Nalbantoglu, S. Status of the tick-borne diseases in sheep and goats in Turkey. Parassitologia 1997, 39, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sayin, F.; Dyncer, S.; Karaer, Z.; Dumanly, N.; Cakmak, A.; Incy, A.; Yukary, B.A.; Vatansever, Z. Status of tick infestation of sheep and goats in Turkey. Parassitologia 1997, 39, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Sayin, F.; Dincer, S.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Inci, A.; Yukari, B.A.; Eren, H.; Vatansever, Z.; Nalbantoglu, S. Studies on the epidemiology of tropical theileriosis (Theileria annulata infection) in cattle in Central Anatolia, Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2003, 35, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursalı, A.; Keskin, A.; Tekin, Ş. A review of the ticks (Acari: Ixodida) of Turkey: Species diversity, hosts and geographical distribution. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, A.; Erciyas-Yavuz, K. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitizing Passerine birds in Turkey with new records and new tick-host associations. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursalı, A.; Tekin, Ş.; Keskin, A. A contribution to the tick (Acari: Ixodidae) fauna of Turkey: The first record of Ixodes inopinatus Estrada-Pena, Nava & Petney. Acarol. Stud. 2020, 2, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanli, N. A molecular survey of bovine Theileria parasites among apparently healthy cattle and with a note on the distribution of ticks in eastern Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, K.; Dumanli, N.; Aktas, M. Molecular identification, genetic diversity and distribution of Theileria and Babesia species infecting small ruminants. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, K.; Aktas, M.; Dumanli, N. Erzincan yöresinde sığırlarda Theileria annulata ve Theileria buffeli/orientalis’in reverse line blotting yöntemi ile araştırılması. Türkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2007, 31, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Altay, K.; Aydin, M.F.; Dumanli, N.; Aktas, M. Molecular detection of Theileria and Babesia infections in cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, H.; Cicek, H.; Eser, M.; Tandogan, M. Current status of ruminant theileriosis and its economic impact in Turkey. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2009, 33, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Inci, A.; Ica, A.; Yildirim, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Albasan, H.; Cam, Y.; Atasever, A.; Sariozkan, S.; Duzlu, O. Economical impact of tropical theileriosis in the Cappadocia region of Turkey. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Dincer, S.; Vatansever, Z.; Uncu, A.; Yukari, B.A.; Eren, H.; Nay, M.G.; et al. Studies on tropical theileriosis in Turkey 5. Studies on various numbers of attenuated vaccine cells used in cattle against tropical theileriosis. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2004, 28, 963–971. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, A.; Öncel, T.; Içen, H.; Şimşek, A. Detection of Theileria annulata and T. buffeli in cattle by multiplex PCR in Diyarbakir area. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2012, 18, A111–A114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokpinar, S.; Aydenizoz, M. Investigation of Theileria annulata and Theileria buffeli/orientalis in cattle from Kirikkale-Turkey by revers line blotting analyses. Isr. J. Vet. Med. 2016, 71, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Cao, S.; Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Iguchi, A.; et al. Molecular detection and genetic identification of Babesia bigemina, Theileria annulata, Theileria orientalis and Anaplasma marginale in Turkey. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Genetic diversity of Theileria orientalis from cattle in Turkey. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 65, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, M.J.; Yin, H.; Bai, Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Nijman, I.J.; Jongejan, F. The phylogenetic position of the Theileria buffeli group in relation to other Theileria species. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, T.; Hayashida, K.; Sugimoto, C.; Yokoyama, N. Evolution and genetic diversity of Theileria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Jabbar, A.; Campbell, B.E.; Cantacessi, C.; Gasser, R.B. Bovine theileriosis—An emerging problem in south-eastern Australia? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 2095–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, A.M.J.; Rawdon, T.G.; Meyer, J.; Makin, J.; Morley, C.M.; Clough, R.R.; Tham, K.; Mullner, P.; Geysen, D. An outbreak of hemolytic anaemia associated with infection of Theileria orientalis in naïve cattle. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 59, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.G.; Playford, M.C.; Hickey, K.L. Theileria orientalis: A review. N. Z. Vet. J. 2016, 64, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, F.; Xuan, X. Major tick-borne parasitic diseases of animals: A frame of references in Turkey. Eurasian J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 31, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Dincer, S.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Inci, A.; Eren, H.; Yukari, B.A.; Kirvar, E. Studies on tropical theileriosis in Turkey. In Recent Developments in the Research and Control of Theileria annulata, Proceedings of the Workshop Held at ILRAD, Nairobi, Kenya, 17–19 September 1990; Dolan, T.T., Ed.; English Press: Nairobi, Kenya, 1990; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Aysul, N.; Karagenc, T.; Eren, H.; Aypak, S.; Bakirci, S. Prevalence of tropical theileriosis in cattle in the Aydin region and determination of efficacy of attenuated Theileria annulata vaccine. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2008, 32, 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Inci, A.; Cakmak, A.; Karaer, Z.; Dincer, S.; Sayin, F. Seroprevalence of bovine babesiosis around Kayseri. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2002, 26, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Dumanli, N.; Aktas, M.; Cetinkaya, B.; Cakmak, A.; Koroglu, E.; Saki, C.E.; Erdogmus, Z.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Ongor, H.; Simsek, S.; et al. Prevalence and distribution of tropical theileriosis in eastern Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 127, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inci, A.; Ica, A.; Yildirim, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Albasan, H.; Cam, Y.; Atasever, A.; Duzlu, O. Epidemiology of tropical theileriosis in the Cappadocia region. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2008, 32, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vatansever, Z.; Nalbantoglu, S. Detection of cattle infected with Theileria annulata in fields by nested PCR, IFAT and microscopic examination of blood smears. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2002, 26, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, M.; Dumanli, N.; Angin, M. Cattle infestation by Hyalomma ticks and prevalence of Theileria in Hyalomma species in the east of Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevgili, M.; Cakmak, A.; Gokcen, A.; Altas, M.G.; Ergun, G. Prevalence of Theileria annulata and Babesia bigemina in cattle in the vicinity of Sanliurfa. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 9, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sayin, F.; Karaer, Z.; Dincer, S.; Cakmak, A.; Inci, A.; Yukari, B.A.; Eren, H.; Vatansever, Z.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Melrose, T.R. A comparison of susceptibilities to infection of four species of Hyalomma ticks with Theileria annulata. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 113, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedhoff, K.T. Tick-borne diseases of sheep and goats caused by Babesia, Theileria or Anaplasma spp. Parasitologia 1997, 39, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Darghouth, M.A. Piroplasmids of livestock in Tunisia. Archs. Inst. Pasteur Tunis 2004, 81, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, J.S.; Luo, J.; Schnittger, L.; Seitzer, U.; Jongejan, F.; Yin, H. Phylogenetic position of small ruminant infecting piroplasms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1081, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Imam, A.H.; Hassan, S.M.; Gameel, A.A.; El Hussein, A.M.; Taha, K.M.; Oosthuizen, C. Molecular identification of diffrent Theileria and Babesia species infecting sheep in Sudan. Ann. Parasitol. 2016, 62, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuen, S. Haemoparasites in small ruminants in European countries: Challenges and clinical relevance. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 142, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandra, T.; Santo, C. Tick-borne diseases in sheep and goats: Clinical and diagnostic aspects. Small Rumin. Res. 2012, 106S, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Dincer, S.; Cakmak, A.; Inci, A.; Yukari, B.A.; Vatansever, Z.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Deniz, A. Tick-borne diseases in Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1997, 29, 53S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Yin, H.; Bakheit, M.; Liu, Z.; Mehlhorn, H.; Seitzer, U. Small ruminant theileriosis. In Progress in Parasitology; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgic, H.B.; Bakirci, S.; Kose, O.; Unlu, A.H.; Hacilarlioglu, S.; Eren, H.; Weir, W.; Karagenc, T. Prevalence of tick-borne haemoparasites in small ruminants in Turkey and diagnostic sensitivity of single-PCR and RLB. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, F.; Zhou, M.; Cao, S.; Ceylan, O.; Aydin, M.F.; Sevinc, M.; Xuan, X. Haemoparasitic agents associated with ovine babesiosis: A possible negative interaction between Babesia ovis and Theileria ovis. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 252, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, K.; Aktas, M.; Dumanlı, N. Theileria infections in small ruminants in the East and Southeast Anatolia. Türkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2007, 31, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Altay, K.; Aktas, M.; Dumanli, N.; Aydin, M.F. Evaluation of a PCR and comparison with RLB for detection and differentiation of Theileria sp. MK and other Theileria and Babesia species of small ruminants. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular and parasitological survey of ovine piroplasmosis, including the first report of Theileria annulata (Apicomplexa: Theileridae) in sheep and goats from Turkey. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, A.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Cam, Y.; Atasever, A.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Sayin, F.; Yukari, B.A.; Ica, A.; Deniz, A. Theileriosis and tick infestations in sheep and goats around Kayseri. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2003, 27, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanli, N. Survey of Theileria parasites of sheep in eastern Turkey using polymerase chain reaction. Small Rum. Res. 2005, 60, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, K.; Dumanli, N.; Holman, P.J.; Aktas, M. Detection of Theileria ovis in naturally infected sheep by nested PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 127, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Nalbantoglu, S.; Yukari, B.A.; Cakmak, A.; Karaer, Z. Epidemiological studies on sheep and goat Theileria infection. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2009, 56, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, A.; Ica, A.; Yıldırım, A.; Duzlu, O. Identification of Babesia and Theileria species in small ruminants in Central Anatolia (Turkey) via reverse line blotting. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2010, 34, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, B.; Ceylan, O.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Lee, S.; Li, J.; Galon, E.M.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Ji, S.; Tumwebaze, M.A.; et al. Molecular detection and assessment of risk factors for tick-borne diseases in sheep and goats from Turkey. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanli, N. PCR-based detection of Theileria ovis in Rhipicephalus bursa adult ticks. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 140, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinkoth, J.H.; Kocan, A.A. Feline cytauxzoonosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 35, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoolman, P.J.; Snowden, K.F. Canine hepatozoonosis and babesiosis, and feline cytauxzoonosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Liu, G.H.; Zhu, W.Q.; Yao, C. Two tales of Cytauxzoon felis infections in domestic cats. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 30, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, M.V.; Meinkoth, J.H.; Edwards, A.C.; Snider, T.A.; Kocan, K.M.; Blouin, E.F.; Litte, S.E. Transmission of Cytauxzoon felis to a domestic cat by Amblyomma americanum. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.E.; Thomas, J.E.; Wohltjen, M.L.; Reichard, M.V. Transmission of Cytauxzoon felis to domestic cats by Amblyomma americanum nymphs. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, M.; Akkan, H.A.; Tütüncü, M.; Özdal, N.; Değer, S.; Ağaoğlu, Z.T. Cytauxzoonosis in van cats. YYÜ Vet. Fak. Derg. 2007, 18, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Birdane, F.M.; Altınöz, F. Prevalence of Babesia bigemina in cattle. Rev. Méd. Vét 2001, 152, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Sevinc, F.; Ozdemir, O.; Coskun, A. Acute babesiosis in an eleven days of age calf. Erciyes Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2005, 2, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Rojas, C.; Figueroa, J.V. Diagnostic tools for the identification of Babesia sp. in persistently infected cattle. Pathogens 2019, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, F.; Turgut, K.; Sevinc, M.; Ekici, O.D.; Coskun, A.; Koc, Y.; Erol, M.; Ica, A. Therapeutic and prophylactic efficacy of imidocarb dipropionate on experimental Babesia ovis infection of lambs. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waal, D.T.; Combrink, M.P. Live vaccines against bovine babesiosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Ramos, J.A.; Rojas, E.E.; Mosqueda, J.J.; Vega, C.A.; Olvera, A.M.; Figueroa, J.V.; Cantó, G.J. Field challenge of cattle vaccinated with a combined Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina frozen immunogen. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1026, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; De Vos, A.J.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, A.J.; Bock, R.E. Vaccination against bovine babesiosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 916, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipano, E. Live vaccines against hemoparasitic diseases in livestock. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Dumanlı, N.; Karaer, Z.; Cakmak, A.; Sevgili, M. Seroprevalences of Babesia species in cattle in Elazığ, Malatya and Tunceli provinces. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2001, 25, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Ekici, O.D.; Sevinc, F. Seroepidemiology of Babesia bigemina in cattle in the Konya province, Turkey: Endemic status. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2009, 53, 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S. Molecular and parasitological survey of bovine piroplasms in the Black Sea Region, including the first report of babesiosis associated with Babesia divergens in Turkey. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, M.; Vatansever, Z.; Ozubek, S. Molecular evidence for trans-stadial and transovarial transmission of Babesia occultans in Hyalomma marginatum and Rhipicephalus turanicus in Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 204, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkun, Ö.; Çakmak, A.; Nalbantoğlu, S.; Karaer, Z. Turkey tick news: A molecular investigation into the presence of tick-borne pathogens in host-seeking ticks in Anatolia; initial evidence of putative vectors and pathogens, and footsteps of a secretly rising vector tick, Haemaphysalis parva. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Liu, G.; Liu, D.; Ren, J.; Li, X. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a large Babesia sp. from sheep and goats in the eastern part of Gansu Province, China. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uilenberg, G. Babesia—A historical overview. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Yin, H.; Guan, G.Q.; Schnittger, L.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, M.L.; Dang, Z.S.; Liu, J.L.; Ren, Q.Y.; Bai, Q.; et al. At least two genetically distinct large Babesia species infective to sheep and goats in China. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular evidence of a new Babesia sp. in goats. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, I.; Hadani, A.; Galker, F.; Mauer, E.; Rubina, M.; Rosen, S. The geographical distribution and animal hosts of Rhipicephalus bursa (Canestrini and Fanzago, 1877) in Israel. Rev. Elev. Med. Vet. Pays. Trop. 1985, 38, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Yeruham, I.; Hadani, A.; Galker, F. Some epizootiological and clinical aspects of ovine babesiosis caused by Babesia ovis—A review. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 74, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, I.; Hadani, A.; Galker, F.; Avidar, Y.; Bogin, E. Clinical, clinico-pathological and serological studies of Babesia ovis in experimentally infected sheep. J. Vet. Med. 1998, 45, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttler, K.L. World-wide impact of babesiosis. In Babesiosis of Domestic Animals and Man; Ristic, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Razmi, G.R.; Naghibi, A.; Aslani, M.R.; Dastjerdi, K.; Hossieni, H. An epidemiological study on Babesia infection in small ruminants in Mashhad suburb, Khorasan province, Iran. Small Rum. Res. 2003, 50, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, P.; Hooshmand, E.; Rahbari, S.; Nabian, S. Determination of Rhipicephalus spp. as vectors for Babesia ovis in Iran. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Bahadori, S.; Eckert, B.; Omidian, Z.; Shirazi, N.S.; Shayan, P. Babesia ovis as the main causative agent of sheep babesiosis in Iran. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhar, M.; Hajihasani, A.; Maroufi, S.; Alizadeh, H.; Shirzad, H.; Piri, F.; Pagheh, A.S. An epidemiological survey on bovine and ovine babesiosis in Kurdistan Province, western Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Ekici, O.D.; Yildiz, R.; Isik, N.; Aydogdu, U. Babesia ovis infections: Detailed clinical and laboratory observations in the pre- and post-treatment periods of 97 field cases. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgun, A.; Wright, I.G.; Waltisbuhl, D.J.; Gale, K.R.; Goodger, B.V.; Dargie, J.D.; Alabay, M.; Cerci, H. An ELISA for the diagnosis of Babesia ovis infection utilizing a synthetic, Babesia bovis-derived antigen. Vet. Parasitol. 1991, 39, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, F.; Dik, B. The diagnosis of Babesia ovis in sheep in Konya around by ELISA. Vet. Bilim. Derg. 1996, 12, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Dumanli, N.; Köroğlu, E.; Düzgün, A.; Angın, M.; Küçükerden, N. Seroprevalance of Babesia ovis in Sheep in Elazig. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 1997, 21, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Emre, Z.; Düzgün, A.; İriadam, M.; Sert, H. Seroprevalence of Babesia ovis in Awassi sheep in Urfa, Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2001, 25, 759–762. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, H.; Düzgün, A.; Emre, Z.; Karaer, Z. Seroprevalence of Babesia ovis in sheep around Afyon. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2004, 28, 683–686. [Google Scholar]
- Ekici, O.D.; Sevinc, F.; Isik, N. Instability of ovine babesiosis in an endemic area in Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, O.; Sevinc, F. Endemic instability of ovine babesiosis in Turkey: A country-wide sero-epidemiological study. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 278, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, K.; Dumanli, N.; Aktas, M. A study on ovine tick-borne hemoprotozoan parasites (Theileria and Babesia) in the East Black Sea Region of Turkey. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Cao, S.; Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O.; Ekici, S.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; et al. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Babesia, Theileria and Anaplasma amongst apparently healthy sheep and goats in the central region of Turkey. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.F.; Dumanli, N. Tick-borne pathogens in small ruminants in Turkey: A systematic review. Turk. Vet. J. 2019, 1, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Karatepe, B.; Ozubek, S.; Karatepe, M.; Aktas, M. Detection of Theileria and Babesia species in sheep and goats by microscopy and molecular methods in Nigde province, Turkey. Revue Med. Vet. 2019, 170, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Seitzer, U.; Ahmed, J. Attenuated vaccines for animal diseases. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Yin, H.; Schnittger, L.; Jongejan, F. Ticks and tick-borne diseases in Asia with special emphasis on China. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeruham, I.; Hadani, A.; Galker, F. Attenuation of Babesia ovis by rapid successive passages in splenectomized lambs. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1998, 30, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M.; Koc, Y.; Alkan, F.; Ekici, O.D.; Yildiz, R.; Isik, N.; Aydogdu, U. The effect of 12 successive blood passages on the virulence of Babesia ovis in splenectomized lambs: A preliminary study. Small Rum. Res. 2014, 116, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.; Jorgensen, W.K.; Dalgliesh, R.J.; Friedhoff, K.T.; De Vos, A.J. Current state and future trends in the diagnosis of babesiosis. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, K.; Loria, G.R.; Riili, S.; Greco, A.; Caracappa, S.; Jongejan, F.; Sparagano, O. Detection of haemoparasites in cattle by reverse line blot hybridisation with a note on the distribution of ticks in Sicily. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.G. Immunodiagnosis of and immunoprophylaxis against the haemoparasites Babesia sp. and Anaplasma sp. in domestic animals. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1990, 9, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikadai, H.; Osorio, C.R.; Xuan, X.; Igarashi, I.; Kanemaru, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Fujisaki, K.; Suzuki, N.; Mikami, T. Detection of Babesia caballi infection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant 48-kDa merozoite rhoptry protein. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 633–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchit, S.; Xuan, X.; Yokoyama, N.; Goff, W.L.; Wagner, G.; Igarashi, I. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with recombinant rhoptry-associated protein 1 antigen against Babesia bovis for the detection of specific antibodies in cattle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3771–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xuan, X.; Yokoyama, N.; Xu, L.; Suzuki, H.; Sugimoto, C.; Nagasawa, H.; Fujisaki, K.; Igarashi, I. High-level expression and purification of a truncated merozoite antigen-2 of Babesia equi in Escherichia coli and its potential for immunodiagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Fujisaki, K.; Xuan, X. Babesia gibsoni rhoptry-associated protein 1 and its potential use as a diagnostic antigen. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, F.; Güler, L.; Sevinc, M.; Ekici, O.D.; Isik, N. Determination of immunoreactive proteins of Babesia ovis. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, F.; Cao, S.; Xuan, X.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O. Identification and expression of a secreted protein 1 of Babesia ovis and an evaluation of its diagnostic potential in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, F.; Cao, S.; Zhou, M.; Sevinc, M.; Ceylan, O.; Xuan, X. A new immunoreactive recombinant protein designated as rBoSA2 from: Its molecular characterization, subcellular localization and antibody recognition by infected sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erster, O.; Roth, A.; Wolkomirsky, R.; Leibovich, B.; Savitzky, I.; Zamir, S.; Molad, T.; Shkap, V. Molecular detection of Babesia ovis in sheep and ticks using the gene encoding B. ovis surface protein D (BoSPD). Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carletti, T.; Barreto, C.; Mesplet, M.; Mira, A.; Weir, W.; Shiels, B.; Oliva, A.G.; Schnittger, L.; Florin-Christensen, M. Characterization of a papain-like cystein protease essential for the survival of Babesia ovis merozoites. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, A. Detection of Babesia caballi (Nuttall, 1901) and Babesia equi (Laveran, 1901) in horses by microscopic examination in military farm in Gemlik. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 1997, 21, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Akkan, H.A.; Karaca, M.; Tutuncu, M.; Deger, S.; Keles, I.; Agaoglu, Z. Serologic and microscopic studies on babesiosis in horses in the Eastern border of Turkey. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2003, 23, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, C. Adana Yöresi Atlarında Babesia equi ve Babesia caballi’nin Yayılışının Mikroskobik ve Serolojik (ELISA) Yöntemlerle Araştırılması. Master’s Thesis, Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi, Hatay, Turkey, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Balkaya, I.; Erdogmus, Z. Elazığ ve Malatya illerinde atlarda Babesia equi (Laveran, 1901) ve Babesia caballi (Nuttall, 1910) türlerinin yayılışının serolojik yöntemlerle araştırılması. F Ü Sağlık Bil Derg. 2006, 20, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Derinbay Ekici, Ö.; Ceylan, O.; Sönmez, G.; Dik, B.; Ceylan, C.; Semassel, A. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of T. equi and B. caballi in wild horses in Konya province of Turkey. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncel, T.; Vural, G.; Gicik, Y.; Arslan, M.O. Detection of Babesia (Theileria) equi (Laveran, 1901) in horses in the Kars province of Turkey. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2007, 31, 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Acici, M.; Umur, S.; Guvenc, T.; Arslan, H.H.; Kurt, M. Seroprevalence of equine babesiosis in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinc, F.; Maden, M.; Kumas, C.; Sevinc, M.; Ekici, O.D. A comparative study on the prevalence of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi infections in horse sub-populations in Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatepe, B.; Karatepe, M.; Cakmak, A.; Karaer, Z.; Ergün, G. Investigation of seroprevalence of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi in horses in Nigde province, Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 2009, 41, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, B.; Kırmızıgül, A.H.; Deniz, A.; Tasci, G.T. Seroprevalance of Babesia caballi and Theileria equi in horses from Kars and Ardahan provinces during the winter season. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2010, 16, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, H.Z.; Karaer, K.Z. Ankara Yöresinde Sportif ve Gösteri Amaçlı Yetiştirilen Atlarda Babesia caballi (Nuttall, 1910) ve Theileria equi (Syn. Babesia equi, Laveran, 1901)’nin Yayılışının Polimeraz Zincir Reaksiyonu ile Araştırılması. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2007, 31, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kizilarslan, F.; Yildirim, A.; Duzlu, O.; Inci, A.; Onder, Z.; Ciloglu, A. Molecular detection and characterization of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi in horses (Equus ferus caballus) in Turkey. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, E.; Avcioglu, H.; Deniz, A.; Balkaya, I.; Abay, U.; Yavuz, S.; Akyuz, M. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi in jereed horses in Erzurum, Turkey. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozubek, S.; Aktas, M. Genetic diversity and prevalence of piroplasm species in equids from Turkey. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 59, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dik, B.; Ceylan, O.; Ceylan, C.; Tekindal, M.A.; Semassel, A.; Sönmez, G.; Derinbay Ekici, Ö. Ectoparasites of feral horse [Equus ferus caballus (Linnaeus., 1758)] on Karadağ Mountain, Karaman, Turkey. J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülanber, A.; Gorenflot, A.; Schetters, T.P.; Carcy, B. First molecular diagnosis of Babesia vogeli in domestic dogs from Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 139, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysul, N.; Ural, K.; Ulutas, B.; Eren, H.; Karagenc, T. First detection and molecular identification of Babesia gibsoni in two dogs from the Aydın Province of Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2013, 37, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, E.; Kırmızıgül, A.H.; Taşçı, G.T.; Uzlu, E.; Gündüz, N.; Vatansever, Z. First clinical and parasitological detection of Babesia canis canis in dogs from Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2013, 19, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysul, N. Comparison of Microscobic and PCR-RLB Findings in Detection of Babesia Species of Dogs in Istanbul. Ph.D. Thesis, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turky, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Düzlü, Ö.; Inci, A.; Yıldırım, A.; Önder, Z.; Çiloğlu, A. The investigation of some tick-borne protozoon and rickettsial infections in dogs by real time PCR and the molecular characterizations of the detected isolates. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2014, 61, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S.; Altay, K.; Sayin Ipek, N.D.; Balkaya, I.; Utuk, A.E.; Kırbas, A.; Şimsek, S.; Dumanlı, N. Molecular detection of tick-borne rickettsial and protozoan pathogens in domestic dogs from Turkey. Parasit Vectors 2015, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sevinc, F.; Ceylan, O.; Sevinc, M.; Ince, E.; Gao, Y.; Moumouni, P.F.A.; Liu, M.; Efstratiou, A.; Wang, G.; et al. A PCR survey of vector-borne pathogens in different dog populations from Turkey. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkun, Ö.; Koç, N.; Sürsal, N.; Çakmak, A.; Nalbantoğlu, S.; Karaer, Z. Molecular characterization of tickborne blood protozoa in stray dogs from central anatolia region of Turkey with a high-rate Hepatozoon infection. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2018, 24, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgic, H.B.; Pekel, G.K.; Hosgor, M.; Karagenc, T. A retrospective epidemiological study: The prevalence of Ehrlichia canis and Babesia vogeli in dogs in the Aegean region of Turkey. Acta Vet. 2019, 69, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S. A survey of canine haemoprotozoan parasites from Turkey, including molecular evidence of an unnamed Babesia. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 52, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumler, J.S.; Rikihisa, Y.; Dasch, G.A. Family II. Anaplasmataceae. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology the Proteobacteria, Part C, Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria, 2nd ed.; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Garrity, G.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, M. Bovine anaplasmosis. In Parasitic Protozoa; Kreier, J., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 235–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kocan, K.M.; Blouin, E.F.; Barbet, A.F. Anaplasmosis control: Past, present, and future. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 916, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, P.; Carelli, G.; Ceci, L. Tick-borne diseases (TBDs) of dairy cows in a Mediterranean environment: A clinical, serological, and hematological study. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 969, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, D.; Torioni de Echaide, S.; Palmer, G.H.; McGuire, T.C.; Stiller, D.; McElwain, T.F. Antibody against an Anaplasma marginale MSP5 epitope common to tick and erythrocytes stages identifies persistently infected cattle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, H.C. Occurrence of Piroplasmosis in Domestic Animals in Ankara and its Surrounding Provinces and the Research on the TREATMENT of the Infections; Ankara University Press: Ankara, Turkey, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Goksu, K. Piroplasmida infections (Piroplasmosis, Babesiosis, Theileriosis) in cattle in various regions of Turkey and prevalence of anaplasmosis. J. Turk. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1970, 40, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mimioglu, M.; Ulutas, M.; Guler, S. Theileriosis and Other Blood Parasites in Cattle in Turkey; Ajans Turk Press: Ankara, Turkey, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzer, E. The research on the infections due to the species of Babesia, Theileria and Anaplasma in cattle in Istanbul and its surrounding provinces. J. Fac. Vet. Med. Univ. Istanb. 1981, 8, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Birdane, F.M.; Sevinc, F.; Derinbay, O. Anaplasma marginale infections in dairy cattle: Clinical disease with high seroprevalence. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2006, 50, 467–470. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanli, N. Molecular detection and identification of Anaplasma and Ehrlichia species in cattle from Turkey. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2011, 2, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S. Bovine anaplasmosis in Turkey: First laboratory confirmed clinical cases caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoşgör, M.; Bilgiç, H.B.; Bakırcı, S.; Ünlü, A.H.; Karagenç, T.; Eren, H. Detection of Anaplasma/Ehrlichia species of cattle and ticks in Aydın region. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2015, 39, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataş, M.; Dumanlı, N.; Altay, K. Molecular survey of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in small ruminants from Şanlıurfa. Manas J. Agric. Vet. Life Sci. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S. Outbreak of anaplasmosis associated with novel genetic variants of Anaplasma marginale in a dairy cattle. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.F.; Özübek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular survey of Anaplasma and Ehrlichia species in cattle from Karaman of Turkey, including a novel tandem report of Anaplasma marginale msp1a gene. Ank. Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2019, 66, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göksu, K. The Investigation on the Epizootiology and Biology of Babesidae and Theileridae (Piroplasmidea Wenyon, 1926) in Native Sheep. Ph.D. Thesis, Ankara Üniv Vet Fak Yay, Ankara, Turkey, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Renneker, S.; Abdo, J.; Salih, D.E.A.; Karagenc, T.; Bilgic, H.; Torina, A.; Oliva, A.G.; Campos, J.; Kullmann, B.; Ahmed, J.; et al. Can Anaplasma ovis in small ruminants be neglected any longer? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altay, K.; Dumanli, N.; Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S. Survey of Anaplasma infections in small ruminants from east part of Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2014, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, K.; Cetinkaya, H.; Vurusaner, C.; Toparlak, M.; Ergunay, K. Molecular detection and typing of Anaplasma species in small ruminants in Thrace Region of Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2016, 22, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Ozubek, S. Anaplasma ovis genetic diversity detected by major surface protein 1a and its prevalence in small ruminants. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, A.; Sahin, M.; Erdoğan, H.M.; Celebi, O. Koyunlarda Anaplasma phagocytophilum’a karşı antikorların Western Blot yöntemiyle araştırılması. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg. 2005, 11, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Gokce, H.I.; Genc, O.; Akca, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Unver, A.; Erdogan, H.M. Molecular and serological evidence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection of farm animals in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. Acta Vet. Hung. 2008, 56, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Altay, K.; Dumanli, N.; Kalkan, A. Molecular detection and identification of Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species in ixodid ticks. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, M.; Vatansever, Z.; Altay, K.; Aydin, M.F.; Dumanli, N. Molecular evidence for Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Ixodes ricinus from Turkey. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 104, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E.; Foley, J.E. Anaplasmosis, Canine and Feline Infectious Diseases, 1st ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2014; pp. 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otrando, D. Anaplasmosis. In Arthropod Borne Diseases; Marcondes, C.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Güneş, T.; Poyraz, Ö.; Babacan, A. The seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in clinically healthy dogs from Sinop region of Turkey. Cumhur. Vet. J. 2011, 33, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ural, K.; Gultekin, M.; Atasoy, A.; Ulutas, B. Spatial distribution of vector borne disease agents in dogs in Aegean region, Turkey. Rev. MVZ Cordoba 2014, 19, 4086–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçüker, S.; Şahinduran, Ş. Antalya ilinde bulunan köpeklerde dirofilariazis, borrelioziz, ehrlichiazis ve anaplazmozis’in hızlı test kitleri ile teşhisi ve insidansı üzerine araştırmalar. Atatürk Üniv. Vet. Bilim. Derg. 2018, 13, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven Gökmen, T.; Günaydın, E.; Turut, N.; Akın, B.; Koç, Ö.; Ütük, A.E. A serosurvey on canine vector-borne zoonoses (Anaplasma spp., Ehrlichia spp., Borrelia burgdorferi, Dirofilaria immitis and Leishmania spp.) in Osmaniye. Atatürk Univ. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydardedoğlu, A.E.; Büyükleblebici, O.; Aksoy, N.H.; Karaşahin, T. Investigation of hematological findings by determining the spatial distribution of infections of Ehrlichia canis, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi, Dirofilaria immitis in Aksaray Malakli Dogs. Harran Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2019, 8, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, O. Seroprevalence of vector-borne rickettsial and parasitic agents in dogs in Kocaeli province of Turkey. In Proceedings of the IV. International Eurasian Agriculture and Natural Sciences Congress, Konya, Turkey, 30–31 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, A.; Aktaş, M.S. Investigation of seroprevalence of Dirofilaria immitis, Ehrlichia canis, Borrelia burgdorferi and Anaplasma spp in dogs in Erzurum province. F Ü Sağ. Bilim. Vet. Derg. 2020, 34, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ulutaş, B.; Bayramlı, G.; Karagenç, T. First case of Anaplasma (Ehrlichia) platys infection in a dog in Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2007, 31, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cetinkaya, H.; Matur, E.; Akyazi, I.; Ekiz, E.E.; Aydin, L.; Toparlak, M. Serological and molecular investigation of Ehrlichia spp. and Anaplasma spp. in ticks and blood of dogs, in the Thrace Region of Turkey. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, B.; Değer, S. PCR detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in stray dogs in Batman, Turkey. Van Vet. J. 2019, 30, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M. A survey of ixodid tick species and molecular identification of tick-borne pathogens. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.B.; Walker, D.H. Ehrlichioses: An important one health opportunity. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.E. Ehrlichiosis. In Arthropod Borne Diseases, 1st ed.; Marcondes, C.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Little, S.E. Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. 2010, 40, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonakis, M.E.; Harrus, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. An update on the treatment of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia canis). Vet. J. 2019, 246, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.E. Ehrlichiosis. In Canine and Feline Infectious Diseases, 1st ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2014; pp. 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sayin Ipek, N.D.; Özübek, S.; Aktas, M. Molecular evidence for transstadial transmission of Ehrlichia canis by Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato under field conditions. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, W.G.; Schaefer, J.J.; Wagner, E.R.; Ewing, S.A.; Rikihisa, Y.; Needham, G.R.; Jittapalapong, S.; Moore, D.L.; Stich, R.W. Transstadial and intrastadial experimental transmission of Ehrlichia canis by male Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 131, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albay, M.K.; Sevgisunar, N.S.; Şahinduran, S.; Özmen, Ö. The first report of ehrlichiosis in a cat in Turkey. Ank. Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2016, 63, 329–331. [Google Scholar]
- Unver, A.; Rikihisa, Y.; Borku, K.; Ozkanlar, Y.E.; Hanedan, B. Molecular detection and characterization of Ehrlichia canis from dogs in Turkey. Berliner Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift 2005, 118, 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, E.; Avcioglu, H.; Cengiz, S.; Hayirli, A. Vector-borne pathogens in stray dogs in northeastern Turkey. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozubek, S.; Sayin Ipek, D.N.; Aktas, M. A molecular survey of rickettsias in shelter dogs and distribution of Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae) sensu lato in Southeast Turkey. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S. Genetic diversity of Ehrlichia canis in dogs from Turkey inferred by TRP36 sequence analysis and phylogeny. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 64, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, A.; Orunc Kilinc, O.; Erdogan, S.; Akyildiz, G.; Bia, M.M.; Lee, D. High prevalence of Ehrlichia canis in dogs in Van, Turkey. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elitok, B.; Ungur, B. Prevalence of Ehrlichia canis infection in Uşak and investigation of clinical, hematological and biochemical signs in infected dogs. IBBJ 2016, 2, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Erdeğer, J.; Sancak, A.; Ataseven, L. Detection of Ehrlichia canis in dogs by IFA test and dot-ELISA. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2003, 27, 767–773. [Google Scholar]
- Sancak, A.A.; Erdeger, J.; Ataseven, L.; Kurt, A. Serological survey for Ehrlichia canis in dogs from the Mediterranean Coast of Turkey. In Proceedings of the WSAVA Congress, Granada, Spain, 3–5 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Emek Tuna, G.; Ulutas, B. Prevalence of Ehrlichia canis infection in thrombocytopenic dogs. Lucr. Stiintifice Med. Vet. Timis. 2009, XLII, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Icen, H.; Sekin, S.; Simsek, A.; Kochan, A.; Celik, O.Y.; Altas, M.G. Prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis, Ehrlichia canis, Borrelia burgdorferi infection in dogs from Diyarbakir in Turkey. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 6, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Güneş, T.; Poyraz, Ö.; Babacan, A. The seroepidemiologic survey of Ehrlichia canis and Rickettsia conorii in clinically healthy dogs from Sinop region. Cumhur. Med. J. 2012, 34, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, M.G.; Ipek, D.N.; Sevgili, M.; Icen, H. Prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis, Ehrlichia canis, Borrelia burgdorferi infection in stray dogs from Sanliurfa in Turkey. Vet. Res. 2013, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, B.; Taşçı, G.T.; Kılıç, Y. Seroprevalence of Dirofilaria immitis, Ehrlichia canis and Borrelia burgdorferi in dogs in Iğdır province, Turkey. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2013, 19, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, S.; Turan, N.; Minbay, A.; Dutta, S.K. Detection of antibodies to Ehrlichia risticii in horses. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 1998, 22, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Emiroğlu, M.; Çelebi, B. First report of human ehrlichiosis in Turkey. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2019, 61, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneth, G. Perspectives on canine and feline hepatozoonosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otrando, D. Hepatozoonosis. In Arthropod Borne Diseases; Marcondes, C.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Baneth, G.; Samish, M.; Shkap, V. Life cycle of Hepatozoon canis (Apikomplexa: Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) in the tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus and domestic dog (Canis familiaris). J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modry, D.; Beck, R.; Hrazdilova, K.; Baneth, G. A review of methods for detection of Hepatozoon infection in carnivores and arthropod vectors. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F. The Brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806) (Acari: Ixodidae): From taxonomy to control. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 152, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Inoue, M.; Taura, Y.; Nakama, S.; Abe, H.; Fujisaki, K. Detection of Hepatozoon canis oocyst from ticks collected from the infected dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1995, 57, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlano, M.; Scofield, A.; Elisei, C.; Fernandes, K.R.; Ewing, S.A.; Massard, C.L. Diagnosis of Hepatozoon spp. in Amblyomma ovale and its experimental transmission in domestic dogs in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.L.; Castro, J.R.; Olegario, M.M.; Beletti, M.E.; Mundim, A.V.; O’Dwyer, L.H.; Eyal, O.; Talmi-Frank, D.; Cury, M.C.; Baneth, G. Oocysts of Hepatozoon canis in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from a naturally infected dog. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Lia, R.P.; Annoscia, G.; Buonavoglia, C.; Lorusso, E.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Baneth, G.; Otranto, D. Rhipicephalus turanicus, a new vector of Hepatozoon canis. Parasitology 2017, 144, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Inoue, M.; Tateyama, S.; Taura, Y.; Nakama, S. Vertical transmission of Hepatozoon canis in dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüzdil, A.N. Bizde ilk defa görülen bir Hepatozoon canis vak’ası. Türk Baytarlar Cemiyeti Mecmuası 1933, 13, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Voyvoda, H.; Pasa, S.; Uner, A. Clinical Hepatozoon canis infection in a dog in Turkey. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paşa, S.; Kıral, F.; Karagenç, T.; Atasoy, A.; Seyrek, K. Description of dogs naturally infected with Hepatozoon canis in the Aegean region of Turkey. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2009, 33, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasa, S.; Voyvoda, H.; Karagenc, T.; Atasoy, A.; Gazyagci, S. Failure of combination theraphy with imidocarp dipropionate and toltrazuril to clear Hepatozoon canis infection in dogs. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagenc, T.I.; Pasa, S.; Kirli, G.; Hosgor, M.; Bilgic, H.B.; Ozon, Y.H.; Atasoy, A.; Eren, H. A parasitological, molecular and serological sur-vey of Hepatozoon canis infection in dogs around the Aegean coast of Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 135, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S.; Sayın Ipek, D.N. Molecular investigations of Hepatozoon species in dogs and developmental stages of Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2381–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.F.; Sevinc, F.; Sevinc, M. Molecular detection and characterization of Hepatozoon spp. in dogs from the central part of Turkey. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölükbaş, C.S.; Pekmezci, D.; Gürler, A.T.; Pekmezci, G.Z.; Güzel, M.; Açici, M.; Umur, Ş. Molecular survey of Hepatozoon canis in dogs from Samsun province of northern part of Turkey. Etlik Vet. Mikrobiyol. Derg. 2016, 27, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emek Tuna, G.; Bakırcı, S.; Dinler, C.; Battal, G.; Ulutaş, B. Molecular identification and clinicopathological findings of Hepatozoon sp. infection in a cat: First report from Turkey. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2018, 42, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkun, Ö.; Nalbantoğlu, S. Hepatozoon canis in Turkish red foxes and their ticks. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 13, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuz, M.; Kirman, R.; Guven, E. Morphological and molecular data of Hepatozoon ursi in two Brown bears (Ursus arctos) in Turkey. Folia Parasitol. 2020, 67, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orkun, Ö.; Emir, H. Identification of tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from wild animals in Turkey. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, M.; Özübek, S.; Altay, K.; Balkaya, I.; Utuk, A.E.; Kırbas, A.; Şimsek, S.; Dumanlı, N. A molecular and parasitological survey of Hepatozoon canis in domestic dogs in Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 209, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Ramos, R.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Mencke, N.; Baneth, G.; Otranto, D. Experimental evidence against transmission of Hepatozoon canis by Ixodes ricinus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).