Abstract
This paper summarizes the results of one of the first comprehensive laboratory studies that was conducted to evaluate the effects of adding different contents of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPETE) as a modifier to an asphalt binder on the rheological and mechanical properties of the modified binder as well as on the agglomeration behavior between the rPETE and asphalt binder at a multiscale level. The high-temperature and low-temperature performances of the modified binder were investigated at the macro-scale and compared with those of the unmodified binder using dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) and bending-beam rheometer (BBR) rheological tests, as well as asphalt binder cracking device (ABCD) testing. The nano-scale evaluation of the binder properties, including the surface roughness, bonding energy, and reduced modulus, was accomplished using atomic force microscopy (AFM). The results indicated that the addition of rPETE enhanced the high- and intermediate-temperature rheological properties of the modified PG 64-22 binder. The low-temperature rheological properties and resistance to cracking decreased slightly with increasing rPETE content in the asphalt binder. However, this reduction was not remarkable when adding 4%, 8%, and 10% rPETE contents. The asphalt binder modified with 4% rPETE had a low-temperature grade of −22, similar to that of the unmodified binder, indicating that 4% rPETE can be added to the binder to improve its high- and intermediate-temperature properties without reducing its resistance to low-temperature damage. The AFM tapping-mode results indicated that the inclusion of rPETE in the asphalt binder improved the stiffness properties of the modified binder as compared with those of the control asphalt binder. In addition, the rPETE-modified binders showed rougher surfaces than the control binder. The addition of rPETE to the binder increased the values of the reduced modulus and bonding energy compared with those of the control binder.
1. Introduction
In the last two decades, the need for using plastics in industry or recycling waste plastics has become very important owing to the harmful effects of these materials on the environment and the pollution they produce. The pollution risk of waste plastics comes from the fact that they are, unlike some other waste materials, non-biodegradable for a relatively long time that can be more than 100 years. There are three methods for disposing of plastic materials, including using landfills, using incinerators to burn them, which also represents a very severe environmental concern because of very large numbers and amounts of volatiles that are generated from using this method [1], or recycling. The interest in recycling plastics is at a high level, and many methods for recycling plastics have been developed to mitigate the environmental risks for not using the right procedures to dispose of these materials. One of the alternatives to recycling plastic materials is to try to mix them or reuse them in industry and the production of other construction, medical, agricultural, or chemical industrial materials. Enhancing the rheological properties of the asphalt binder that is used in highway construction is a suitable alternative that can mediate the mentioned problems by enhancing the binder’s rheological and mechanical properties and adding some additives or modifiers, such as polymers, to the binder. These modifiers can add more stiffness to the binder or improve its flexibility. To evaluate the performance of the asphalt binder and understand the interactions between the modified binder and its additives, the evaluation of the rheological properties of the modified binder and the intermolecular forces between the binder and the additives is essential to determine the potential benefits for adding any modifier to the asphalt binder. In the past two decades, several additives, such as fibers, polymers, and plastics, have been used in previous studies to enhance the binder’s performance [2,3,4,5,6,7]. The use of polymers is a common practice in the pavement industry, as polymers improve the high- and intermediate-temperature properties of the asphalt binder without reducing its resistance to low-temperature cracking; the most used types of polymers for modifying asphalt binders include rubber, styrene–butadiene–styrene (SBS), styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR), Elvaloy®, and polyethylene [8,9]. Fibers and Sasobit® are also being used currently in the pavement industry to improve the rheology of the asphalt binder at high temperatures [5,10].
Previous studies have evaluated the effects of using recycled PETE as a modifier of the asphalt binder on the rheological properties of the modified binder [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Polyethylene terephthalate, commonly abbreviated as PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P, is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibers for clothing (>60%) and containers for liquids and foods (30%). PETE is a clear, strong, and lightweight plastic that is widely used for packaging foods and beverages. PETE consists of polymerized units of the monomer ethylene terephthalate, with repeating (C10H8O4) units [20]. PETE is commonly recycled and has the number “1” as its resin identification code (RIC) [21]. It is worth noting that the procedure for extracting PETE from recycled plastics is complex and requires processing the recycled plastics at high temperatures and high pressures [22,23]. It was indicated that the optimal processing of the waste polyethylene (WPE)-modified binder can be conducted at a shear rate of 3750 rpm for 1.5 h at 150 °C to obtain the improved storage stability of the binder. It was also indicated that the thermal stability of modified bitumen was higher than that of the unmodified binder. However, it was generally independent of the processing procedure [24]. PETE-modified asphalt binder showed improved penetration, softening points, and temperature susceptibility values, which would result in better performance at high temperatures [25]. The rotational viscosity, G*, and rutting parameter (G*/sin δ) of the asphalt binder were improved by increasing the content of PE in the binder, while no improvement in the phase angle results was indicated when increasing the PE content [26]. Almeida e Silva et al. indicated that PETE-modified binder exhibited an improved consistency, an elastic response, and lower oxidation levels, which indicates an improved resistance to aging [27]. Lower penetration values and higher softening point values contribute to the PETE-modified asphalt binder as compared with the unmodified one. It was also found that although the rutting parameter for the binder was improved by the addition of PETE, it could not be considered as being storage stable at high temperatures [28].
In addition, measuring the interaction between the modified asphalt binder and its additives can provide a better understanding of its performance and its interaction with different materials. Nazzal and coworkers indicated from atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging results that the width of the “bee-like” structures (revealing dispersed black and white successions of elongated structures within a relatively flat matrix) within the binder was reduced by adding Sasobit, whereas no significant effect on these structures was found for the other warm-mix asphalts (WMAs) used in the study [29]. In another study by Abu Qtaish and coworkers [30], it was indicated based on AFM-testing results that although the aging of the binders increased their reduced modulus values, it also reduced their bonding energies. It was also indicated from AFM, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) testing results that less or equal aging will occur in WMA binders over pavement’s service life as compared to HMA binders. The effects of the reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) source’s content on the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures containing high RAP contents was also evaluated using micro-scale and macro-scale tests [31]. Based on AFM testing results, it was indicated that the microstructures obtained for RAP binders were different from those of virgin asphalt binders, and significantly lower adhesions were obtained for the two RAP binders from different sources as compared with those of the virgin asphalt binders. Using polymer additives was the most significant factor that affected the binder’s AFM adhesive forces. In addition, the adhesive bonds between the aggregates and binder inside the mixture had more a pronounced effect on the indirect tensile strength than the cohesive bonds inside the binder, as stress concentrates at the aggregate–binder interface, which leads to an increased tendency for cracking to occur in that area [32].
In summary, there is increasing interest currently in using recycled PETE as a modifier of the asphalt binder to enhance its physical and rheological properties, especially the rutting performance of the modified binder [11,13,17], and improving the properties of asphalt mixtures and their resistances to rutting and fatigue cracking [12,19]. Also, there is increased potential in the current state-of-the-art uses of recycled PETE in the asphalt binder and asphalt mixtures from an environmental perspective to help in recycling waste plastic materials and reduce the environmental concerns related to the increasing quantities of these waste materials and the conventional ways for disposing of them [14,15,18]. This leads to introducing the use of rPETE in the asphalt pavement industry as an effective modifier that helps to improve the properties of asphalt pavement materials for sustainable and clean asphalt production [15].
Despite several research efforts that have been made to characterize and simulate the performance of the asphalt binder and understand the interaction of the binder with its additives or with mineral aggregates using AFM testing, to date, no research has investigated the interaction between rPETE as an additive of the asphalt binder and the binder itself using AFM. Therefore, very limited information is available in the literature regarding the interaction between these two materials at the micro-scale and the effects of the rPETE addition on the mechanical properties of the modified binder. Thus, research is needed to evaluate these properties and compare them with the results of macro-scale tests. This paper presents one of the first research studies to discuss the addition of rPETE as a modifier for the asphalt binder and the simulation of the interaction between rPETE and the binder at the micro-scale using AFM. This study also evaluates the rheological and mechanical properties of the rPETE-modified asphalt binder at the macro-scale using Superpave® rheological tests, which allow for the understanding of the properties of the rPETE-modified binder and its interaction with the rPETE modifier at both the micro-scale and macro-scale. It is worth noting that the rPETE material was extracted in the laboratory by performing complex reactions at high temperatures and high pressures because recycled plastics cannot be directly used as a modifier for the asphalt binder and, therefore, processing for extraction is required for having a rPETE material without any impurities.
2. Objectives
The first objective of this paper is to evaluate the diffusion and agglomeration of the PETE material in the asphalt binder using AFM. The second objective is to evaluate the rheological and mechanical properties of the PETE-modified binder using laboratory rheological tests.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Asphalt Binder
The asphalt binder from Barrett Paving, which is frequently used in highway construction, was selected for evaluation in this study. It is the unmodified binder having a performance grade of PG 64-22. Table 1 presents the properties of the selected asphalt binder, as obtained from the results of laboratory rheological testing conducted in this study.

Table 1.
Properties of asphalt binder selected in this study.
3.1.2. Hydrothermal Recycling of PETE
End-of-life PETE bottles were hydrothermally recycled to evaluate them as asphalt binders. Commercial PETE bottles were first cut to a 2 cm × 2 cm size. A 1.5 gal Parr batch stirred reactor manufactured by Parr Instrument Company (Moline, IL, USA) was used to recycle the PETE. Details about the hydrothermal method can be found elsewhere [22,23]. In short, 200 g of PETE and 2 L of deionized (DI) water were poured into the reactor. The reactor was sealed and heated at 5 K/min from room temperature to 260 °C, and the isothermal condition was kept for 30 min. After the end of the reaction time, the reactor was cooled by passing cool water until the reactor temperature reached the ambient temperature. The recycled PETE (rPETE) was then filtered from the process liquid using vacuum filtration. The rPETE was dried in a drying oven overnight and stored in a Ziplock® bag until further characterization and application. The yield of the rPETE was 80.1 ± 0.5%. Table 2 presents the basic properties of the selected rPETE material, as obtained from laboratory testing conducted in this study.

Table 2.
Typical basic properties of rPETE material.
3.2. Mixing Procedure
Five different contents of rPETE by the weight of the asphalt binder were selected for modifying the binder in this study (0%, 4%, 8%, 10%, and 12%). Each content of rPETE was mixed with the asphalt binder by preheating the liquid binder at 165 °C for 10 min; rPETE was then gradually added to the binder while mixing at a slow velocity of 500 rpm for 5 min using a mechanical mixer. The binder–rPETE mix was then mixed at a rate of 2200 rpm for 60 min at 165 °C until the mix was visually homogeneous [24,25,28]. After mixing, the modified binder was re-stored in a metal can at room temperature and covered to prevent any contamination or loss of properties.
3.3. Rheological Testing
The evaluation of the high-temperature, intermediate-temperature, and low-temperature rheological properties of the control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders was conducted using Superpave rheological tests. The rolling thin-film oven (RTFO), and pressure-aging vessel (PAV) were used to simulate the short-term and long-term aging of the binder, respectively. The RTFO device was used to apply the short-term aging of the asphalt binders in the laboratory according to the AASHTO T 240 standard [33]. In addition, the PAV device was used to apply the long-term aging of the asphalt binders in the laboratory to the RTFO short-term binder samples according to the AASHTO R 28 standard [34].
3.3.1. Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR) Testing
DSR equipment was used to test the rheological properties of the control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders before and after aging according to the AASHTO T 315 standard [35] to evaluate the resistances of these binders to rutting and fatigue at high and intermediate temperatures, as well as repeated load conditions. In addition, the DSR device was used to determine the high-temperature performance grades for these binders.
In the DSR test, binder samples with a diameter of 25 mm and a thickness of 1 mm were prepared from unaged and RTFO-aged asphalt binders and tested at the high temperature, starting from 46 °C and incrementing by 6 °C to the failure temperature, at which the rutting parameter is less than the standard value. Also, binder samples with a diameter of 8 mm and a PAV residue thickness of 2 mm were tested at temperatures ranging from 16 °C to 42 °C in increments of 6 °C for each test temperature.
During the test, the binder sample was sandwiched between top and bottom plates, and the test was performed in the strain-control mode. The top plate oscillated at 10 rad/s (1.59 Hz) in a sinusoidal waveform on top of the fixed bottom plate. The DSR measured the maximum applied stress, the resulting maximum strain, and the time lag between them. The values of the complex modulus (G*) and phase angle (δ) were then calculated automatically by the software.
3.3.2. Bending-Beam Rheometer (BBR) Testing
A BBR device was used to test the low-temperature rheological properties (stiffness and creep) of the control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders after PAV aging according to the AASHTO T 313 standard [36]. In addition, BBR was used to determine the low-temperature performance grades for these binders according to the AASHTO PP 42 standard [37].
In the BBR test, a beam with a size of 6.25 × 12.5 × 127 mm was used as a mold for the binder sample. The binder sample was simply supported at two points at a distance of 102 mm in a controlled-temperature fluid bath. The samples were tested at two temperatures (−6 °C and −12 °C). The sample was then loaded at the midpoint with a 100 g load at a force of 0.98 N. The deflection of the loaded sample was measured at 8, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 240 s. Beam stiffness, often called “creep stiffness”, was calculated for these times. The BBR test was conducted on two beam samples.
3.3.3. Asphalt Binder Cracking Device (ABCD) Testing
ABCD testing was conducted on the control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders according to the AASHTO TP 92-14 standard [38] after PAV aging in the laboratory to evaluate their resistances to low-temperature thermally induced cracking. The cracking temperature is a parameter describing the lowest temperature that the binder can tolerate before thermally induced cracking develops.
3.4. AFM Nano-Scale Testing
AFM is a non-destructive effective imaging tool that was developed by Binning et al. [39] for imaging and characterizing a variety of surfaces at atomic or molecular levels [40]. AFM has several advantages over conventional microscopy techniques [41]. Different forces can be measured using AFM, such as, mechanical, friction, contact, van der Waals, capillary, chemical bonding, magnetic, and electrostatic [42]. In this study, an Agilent 5500 LS atomic force microscope manufactured by Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to test the adhesive/cohesive forces and agglomeration properties of the prepared control and rPETE-modified asphalt binder samples. PicoView 1.20 computer software was used in the AFM operation steps and data extraction, including controlling the AFM stage, setting the scanning parameters, displaying the force–distance (force spectroscopy) curves, and converting the scanning data to images.
3.4.1. Sample Preparation
The procedure of the AFM sample preparation was conducted by pouring the liquid asphalt binders on a glass microslide. The same binders used in the macro-scale rheological testing were used for preparing the AFM samples to ensure reliability in the macro- and micro-scale testing results. The method of the sample preparation used in this study is a modified version of the method in [43], as explained in [44]. This method was used in this study to evaluate the adhesive and cohesive forces as well as the healing properties of the control and rPETE-modified binders. In this procedure, a predetermined amount of asphalt binder (96 mg) was placed on a glass microscope slide at a specific desired thickness (0.4 ± 0.02 mm). Controlling the thickness of asphalt binder was achieved by placing the predetermined amount of the binder between four strips of a high-temperature-resistance tape; the liquid binder sample was then heated at 154 °C and allowed to spread in the predefined area (1.6 × 1.5 cm2). Figure 1 shows a typical asphalt binder sample used in AFM testing.
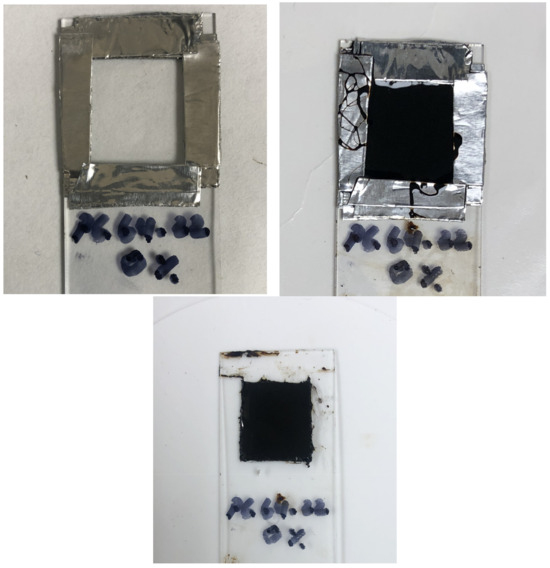
Figure 1.
AFM sample preparation steps.
3.4.2. AFM Techniques
The tapping mode was used in obtaining surface images of the samples. The tapping mode is a dynamic AFM mode that is referred to as an intermittent contact mode and an AC mode. In this mode, a piezoelectric element connected to the tip holder assembly allows the tip to oscillate at its resonance frequency. Surface topographical and phase images were obtained for the binder samples using the AFM tapping mode to evaluate the microstructure, viscoelastic properties, and mechanical properties of the binder. In addition, the surface roughness and flatness of the binder samples were evaluated by taking images in the tapping mode before measuring the cohesive and adhesive forces in the binder using the AFM contact mode.
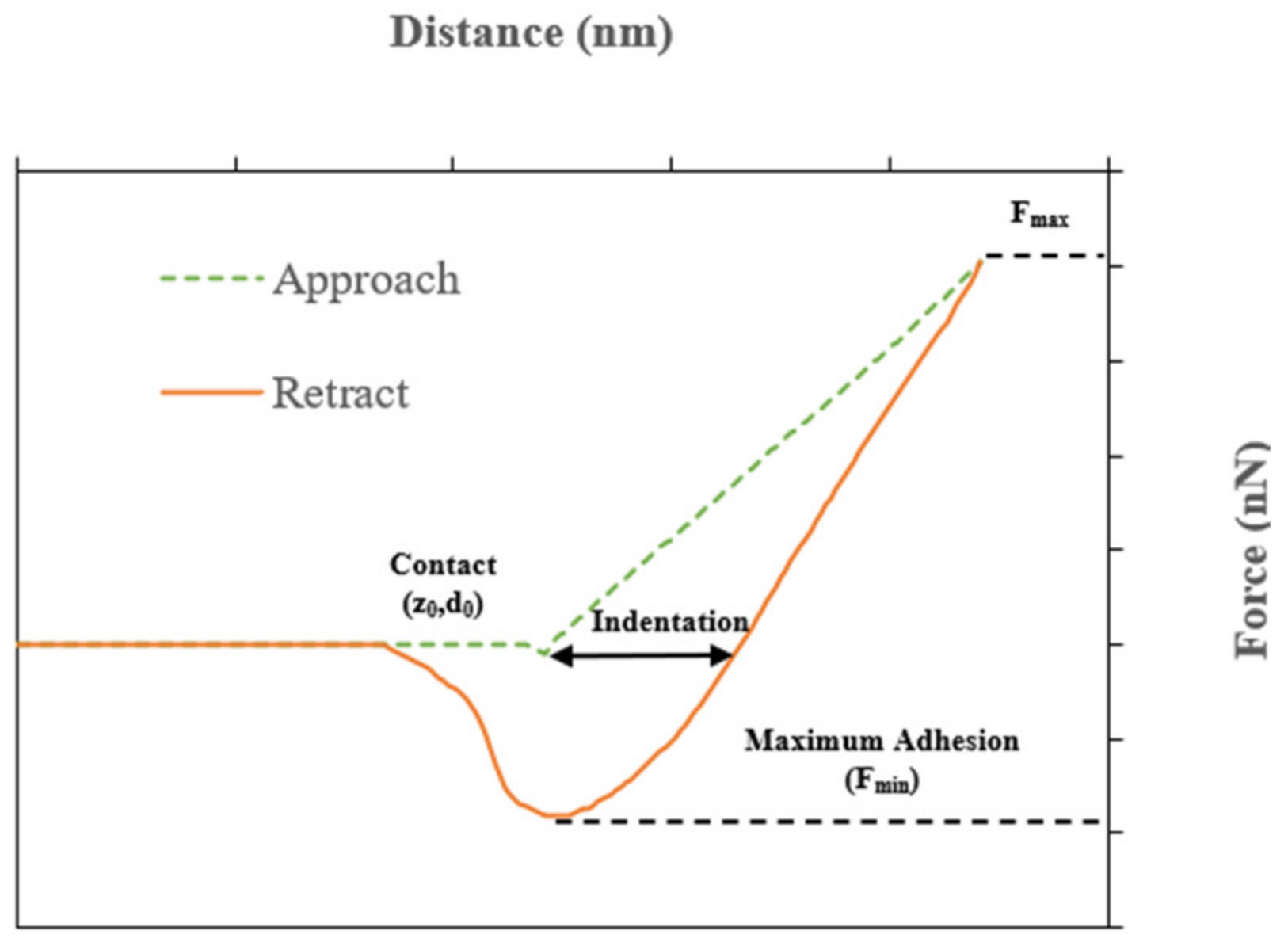
The force spectroscopy AFM technique was used at a constant temperature of 25 °C to evaluate the interaction between the rPETE and asphalt binder in the rPETE-modified binders by measuring the adhesive/cohesive forces. In this mode, the cantilever-tip assembly approaches and retracts from the sample surface by moving a half-cycle downward and upward in the z-direction, respectively. Figure 2 presents a typical force–distance curve generated from a single indentation experiment. The curve consists of two steps: the approaching step and the retracting step. In the first step, as the tip approaches closer to the surface, a slight increase in the force between the tip and the sample starts to appear; then, a remarkable increase in cantilever deflections occurs when the tip contacts the surface. The tip then continues to penetrate the sample until reaching the preselected indentation depth. In the second step, the tip starts retracting from the sample surface until it completely separates when it overcomes the adhesion force between itself and the asphalt sample surface.
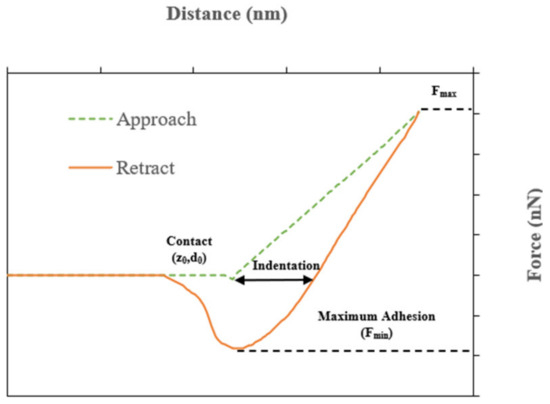
Figure 2.
Typical force–distance curve generated from AFM force spectroscopy mode testing.
The reduced elastic modulus of the binder samples as well as the bonding energy (the total energy required for tip separation) were calculated by analyzing the force–distance curves resulting from the force spectroscopy indentation. The calculation of the reduced elastic modulus (Ereduced) was conducted using Equation (1), which was proposed by Fischer-Cripps [45] and is based on Sneddon’s modification of the Hertzian model for a stiff-tip indentation in a flat, soft sample.
where
F: measured force (nN); δ: indentation depth (μm) = z − d; α: half-opening angle of the tip (degrees); d: cantilever deflection (μm); and z: piezo-driver displacement.
Equation (2) was also used to estimate the total bonding energy needed for tip separation (Ebonding) by calculating the area of the negative forces under the force–distance curve in the retraction region [46].
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Results of Rheological Testing
4.1.1. Results of DSR Testing
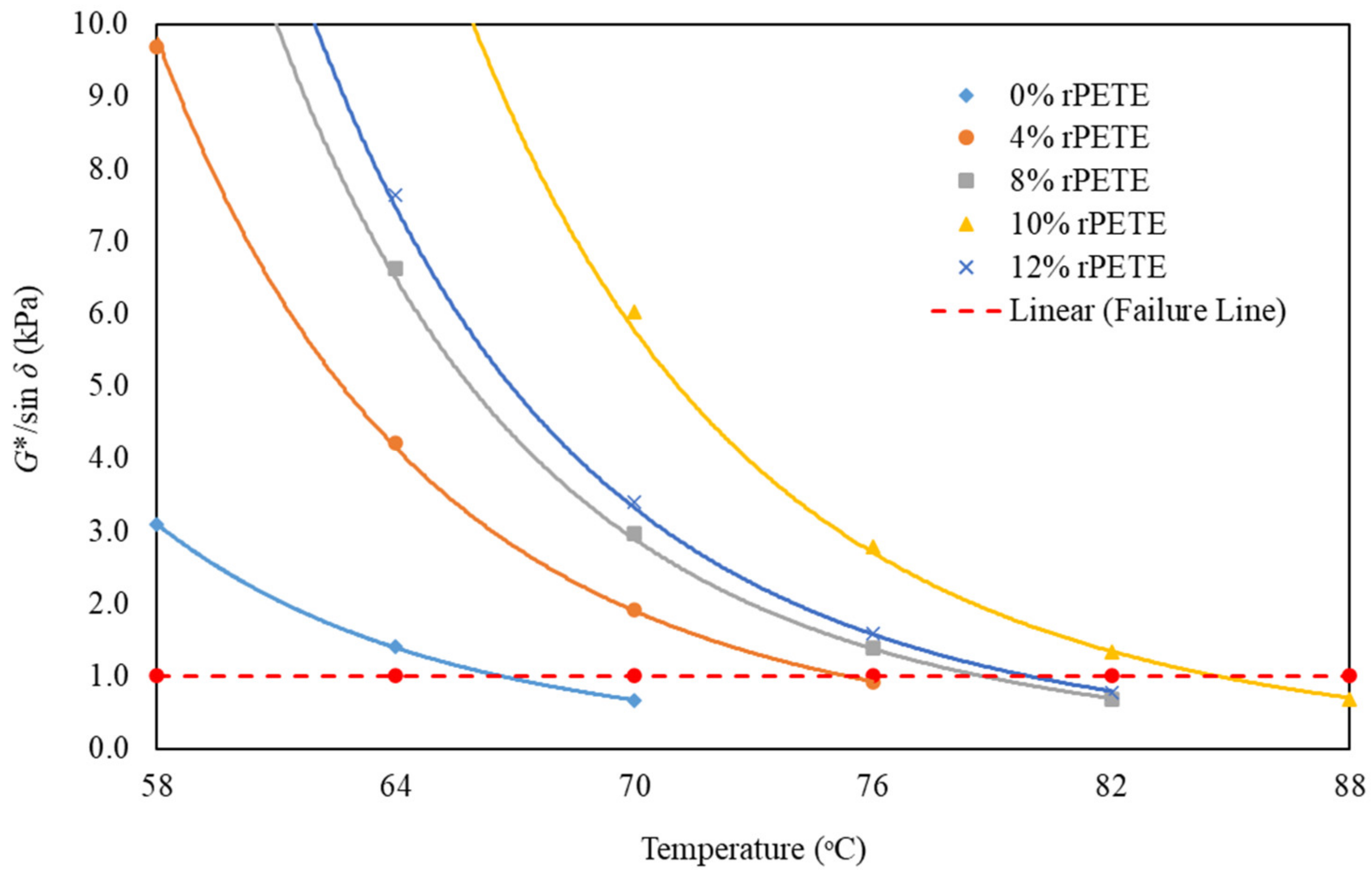
Rutting is one type of distress that occurs in pavement at high temperatures owing to heavy traffic loads. The parameter G*/Sinẟ corresponds to the ability for the binder to resist rutting. The rutting parameter is a stress-controlled parameter. Maximizing the value of G*/Sinẟ for the asphalt binder must be achieved to minimize each cycle’s dissipated energy and reduce the distress potential. The Superpave system assigned the limits for the rutting parameter to minimum values of 1 kPa for the unaged binder and 2.2 kPa for the RTFO-aged binder. Figure 3 presents the plot for the rutting parameter versus the testing temperature for the unmodified binder and rPETE-modified binders obtained from DSR testing of unaged binder samples. As the test temperature increased, the rutting parameter value decreased exponentially at a high rate at low temperatures and at a lower rate at higher temperatures. The rutting parameter remarkably increased when adding the rPETE modifier to the asphalt binder, indicating an improved rutting resistance for the rPETE-modified binder. In addition, the value of the rutting parameter increased with increasing content of rPETE inside the binder up to 10% and then started to decrease when 12% rPETE content was added to the binder, indicating an excessive amount of rPETE, which resulted in lower resistance to permanent deformation (G*) and higher values of the phase angle. This suggests that adding 10% rPETE content can be considered as the best in improving the rutting resistance of the asphalt binder.
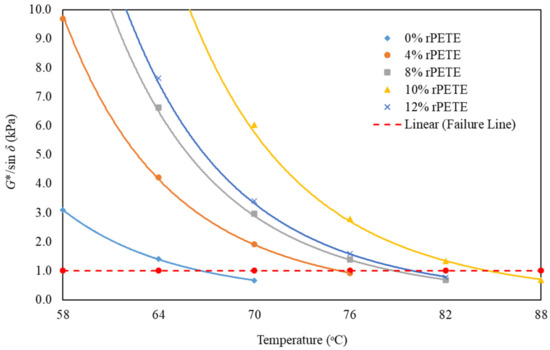
Figure 3.
Results for rutting parameter versus temperature for unaged asphalt binders.
Fatigue cracking in thin pavements is considered as a strain-controlled parameter, and it can be minimized by decreasing the dissipated energy per load cycle. Table 3 presents the results of the failure temperature for the control binder and rPETE-modified binder with different rPETE contents, as obtained from DSR testing of unaged samples of these binders. As seen in Table 3, the addition of the rPETE modifier to the asphalt binder raised the failure temperature compared with that of the unmodified (control) asphalt binder. The addition of 10% rPETE to the binder resulted in the best enhancement effect on the unaged binder’s rheology, with a resulting failure temperature of 84.53 °C, which enables the PG high-temperature grade of the unaged binder to be raised from 64 to 82 when adding 10% rPETE. Adding 8% of the rPETE modifier to the asphalt binder resulted in increasing the failure temperatures to values above 76 °C, which enables the PG grade to be raised to 76 instead of 64. The binders containing 4% or 12% of the rPETE modifier exhibited the lowest failure temperatures among the rPETE-modified binders, but they were still higher than the value obtained for the unmodified binder, and the PG high-temperature grade for the 4% rPETE binder or 12% rPETE binder could be raised from 64 to 70.

Table 3.
Results for DSR testing on control and rPETE-modified unaged binders.
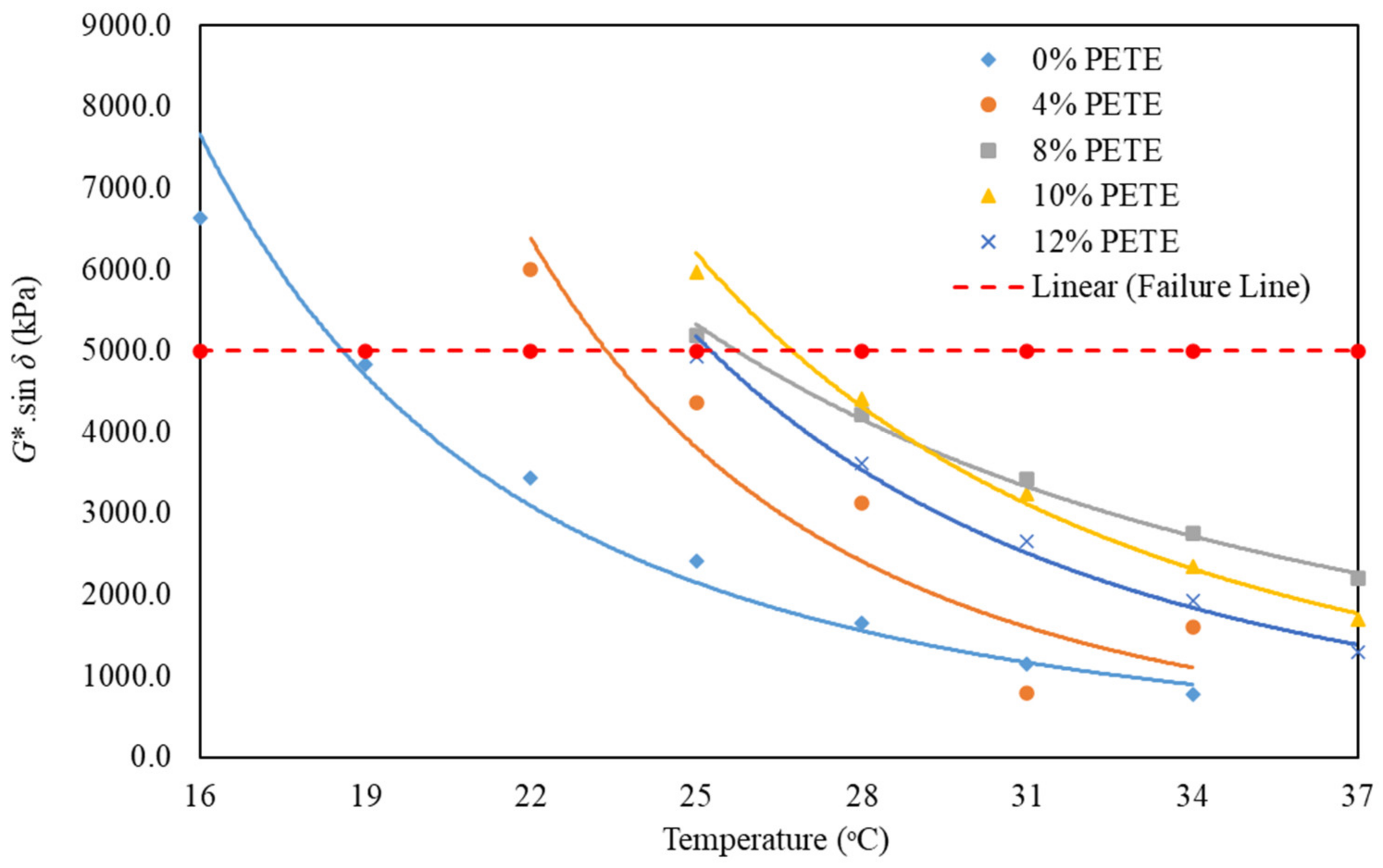
Figure 4 presents the plot of the fatigue parameter versus the test temperature for the unmodified binder and rPETE-modified binders obtained from DSR testing of PAV-aged binder samples. As test temperature increased, the G* · Sinẟ value decreased exponentially at a higher rate at low temperatures and at a lower rate at high temperatures. The fatigue parameter increased with increasing content of the rPETE inside the binder up to 10% and then started to decrease when a 12% rPETE content was added to the binder, indicating an excessive amount of rPETE, which resulted in lower resistance to permanent deformation (G*) and higher values of the phase angle.
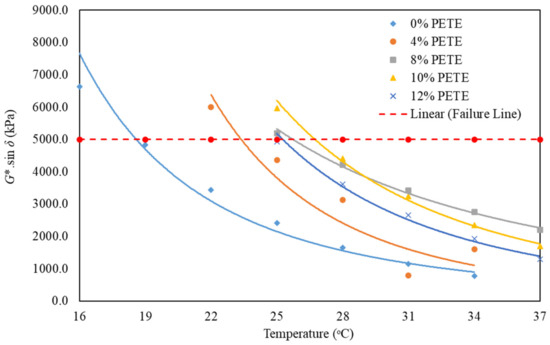
Figure 4.
Results of fatigue parameter versus temperature for PAV-aged asphalt binders.
4.1.2. Results of BBR Testing
Table 4 presents the results of the BBR testing for the PAV-aged samples obtained from the control and rPETE-modified binders. The values of the creep stiffness (S60) and m-value at 60 s were obtained for each binder at −6 °C and −12 °C to calculate the continuous lower grade. As seen in the table and both figures, the creep stiffness of the asphalt binder increased exponentially with increasing rPETE content at both testing temperatures. However, the values were still lower than the 300 MPa Superpave limit. On the other hand, the m-value decreased exponentially with increasing rPETE content at both temperatures, which indicates that adding higher contents of rPETE to the asphalt binder will have a negative effect on its stiffness. All the rPETE-modified binders except the 4% rPETE-modified binder failed at the −12 °C testing temperature because the m-value for these binders were lower than the lower limit (0.3) at that temperature. Therefore, the continuous lower-temperature grade was obtained for each binder to determine the failure temperature for each binder (Table 4). The binder with the 4% rPETE content had the coldest temperature among all the rPETE-modified binders, with a performance grade value of −22 °C. This suggests that adding this content of rPETE to the asphalt binder can result in a slightly lower resistance to low-temperature failure compared to the control binder. Asphalt binders modified with 8% or 10% rPETE contents showed almost similar lower grade values (failure temperatures), with a slightly higher value for the 10% rPETE-modified binder. Adding 12% rPETE to the binder had a remarkably negative impact on the low-temperature properties of the modified binder because it had a very warm failure temperature compared with that of the control binder. Table 4 also presents the results of the ΔTc parameter, which corresponds to the relaxation properties of the asphalt binder resulting from non-load-related cracking or aging-related embrittlement distresses in the asphalt pavement. The ΔTc parameter basically defines the relationship between the stiffness and the relaxation of the asphalt binder. Positive ΔTc values indicate a stiffness-controlled asphalt binder, whereas negative ΔTc values indicate an m-value-controlled asphalt binder [47]. Equation (3) was used to calculate the values of the ΔTc parameter for the control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders using the results of the stiffness and m-value obtained from BBR testing.
where:
- : The critical low temperature of the asphalt binder at S60 is exactly equal to the specification value of 300 MPa;
- : The critical low temperature of the asphalt binder at the m-value is exactly equal to the specification value of 0.3.

Table 4.
Results of BBR testing on control and rPETE-modified PAV-aged binders.
Table 4.
Results of BBR testing on control and rPETE-modified PAV-aged binders.
| rPETE Content (%) | T (°C) | S60 (MPa) | m-Value | Pass/Fail (m-Value ≥ 0.3 and S ≤ 300 MPa) | Stiffness Continuous Grade (°C) | m-Value Continuous Grade (°C) | ΔTc (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −6 | 68.7 | 0.36 | Pass | −30.60 | −22.28 | −10.32 |
| −12 | 163.7 | 0.303 | Pass | ||||
| 4 | −6 | 79.4 | 0.337 | Pass | −30.75 | −22.1 | −8.65 |
| −12 | 169.1 | 0.301 | Pass | ||||
| 8 | −6 | 81.6 | 0.328 | Pass | −30.73 | −19.86 | −10.87 |
| −12 | 172.4 | 0.284 | Fail | ||||
| 10 | −6 | 84.1 | 0.327 | Pass | −28.48 | −19.64 | −8.84 |
| −12 | 187.9 | 0.283 | Fail | ||||
| 12 | −6 | 85.1 | 0.314 | Pass | −26.85 | −17.57 | −8.46 |
| −12 | 204.7 | 0.26 | Fail |
As seen in Table 4, the value of the ΔTc parameter was negative for all the asphalt binders tested using BBR; this indicates that all the binders are m-value-controlled asphalt binders.
4.1.3. Results of ABCD Testing
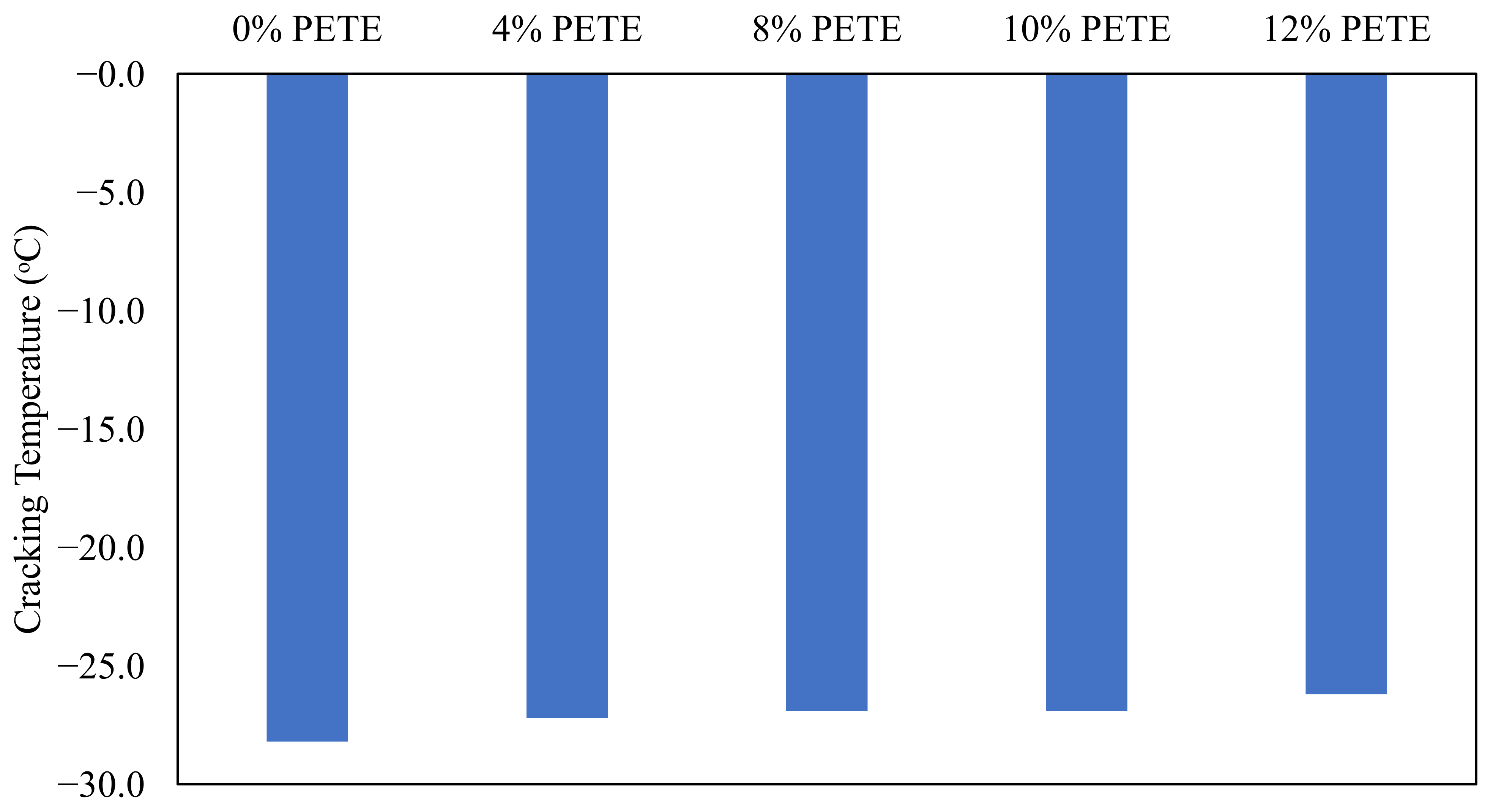
Figure 5 presents the results of the cracking temperatures obtained from ABCD testing conducted on the control and rPETE-modified binders. As seen in Figure 5, the addition of the rPETE modifier to the asphalt binder did not lead to an increase in resistance to low temperatures for the modified binder, and the cracking temperature increased with increasing rPETE content inside the binder. These results agree with the results obtained from the BBR test. Table 5 presents the cracking temperatures and low-temperature PG grades obtained from the ABCD tests. It is noted that even though the PG grade decreased with increasing rPETE content inside the binder, the noted failure temperature was colder than that obtained from BBR testing. This may be attributed to the limitation of the BBR to evaluate the inclusion of the rPETE inside the binder because it measures the stiffness of the binder without evaluating the fracture (cracking) performance. ABCD tests can be used to investigate the fracture performance of the asphalt binder at low temperatures, which makes them more suitable for obtaining binder properties at these low temperatures. It was reported in [47] that the stiffness and relaxation parameters alone do not fully characterize the cracking resistance of asphalt binders even though they are related to the cracking resistance of binders to some extent. In addition, the failure properties of the strain tolerance of complex and modified asphalt binders cannot be fundamentally and fully understood with measurements in the linear viscoelastic (LVE) range without inducing damage to the binder sample. Therefore, a new parameter, ΔTf, (the binder failure index) was proposed in the new approach to combine the temperature at the critical stiffness (Tc at S = 300 mPa), as obtained from BBR testing, and the ABCD cracking temperature, Tcr, as shown in Equation (4). “A positive ΔTf suggests that a binder used in a surface layer similarly aged and subjected to ABCD cooling rates would crack at a temperature below the temperature corresponding to 300 MPa (Tc(S)) and vice-versa” [48].
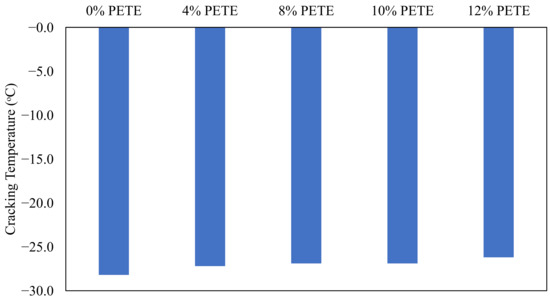
Figure 5.
Results for cracking temperature versus rPETE content for PAV-aged asphalt binders.

Table 5.
Results for ABCD testing on control and rPETE-modified PAV-aged binders.
Table 6 presents the results of the binder failure indices for the unmodified and rPETE-modified binders, as calculated from the results of the BBR and ABCD testing. As seen in Table 6, the asphalt binders modified with higher contents of rPETE (10% and 12%) showed higher (better) values than the control binder and binders modified with lower rPETE contents.

Table 6.
Results of binder failure indices calculated from BBR and ABCD testing results.
4.1.4. Summary of Asphalt Binder Performance-Grading Tests
Based on the results of the DSR, BBR, and ABCD tests discussed in previous sections, the performance grades for the unmodified and rPETE-modified binders could be determined. A summary of the rheological testing results and the corresponding PG grades is shown in Table 7. It can be seen in Table 7 that the addition of rPETE to the asphalt binder resulted in increasing the high-temperature PG grade compared with that of the control binder and decreasing the low-temperature maximum PG grade by one unit (−6 °C), except for the binder modified with a 4% rPETE content, which showed a minimal negative effect on the low-temperature PG grade of the modified binder that had a value similar to that of the control binder (−22 °C). These results for the 4% rPETE content can be considered as being better than the improvement resulting by adding other additives to the asphalt binder, such as fibers, Sasobit or other waxes, or some nano-materials. The improvement in the asphalt binder’s rheology by adding 4% rPETE can also be compared with the improvement resulting from adding polymers to the binder, especially by adding the SBS polymer, which improves the high- and intermediate-temperature performances of the binder without reducing the low-temperature performance.

Table 7.
Asphalt binder performance grades for unmodified binder and rPETE-modified binders.
4.2. Results for AFM Nano-Scale Testing
4.2.1. Results for AFM Tapping Mode
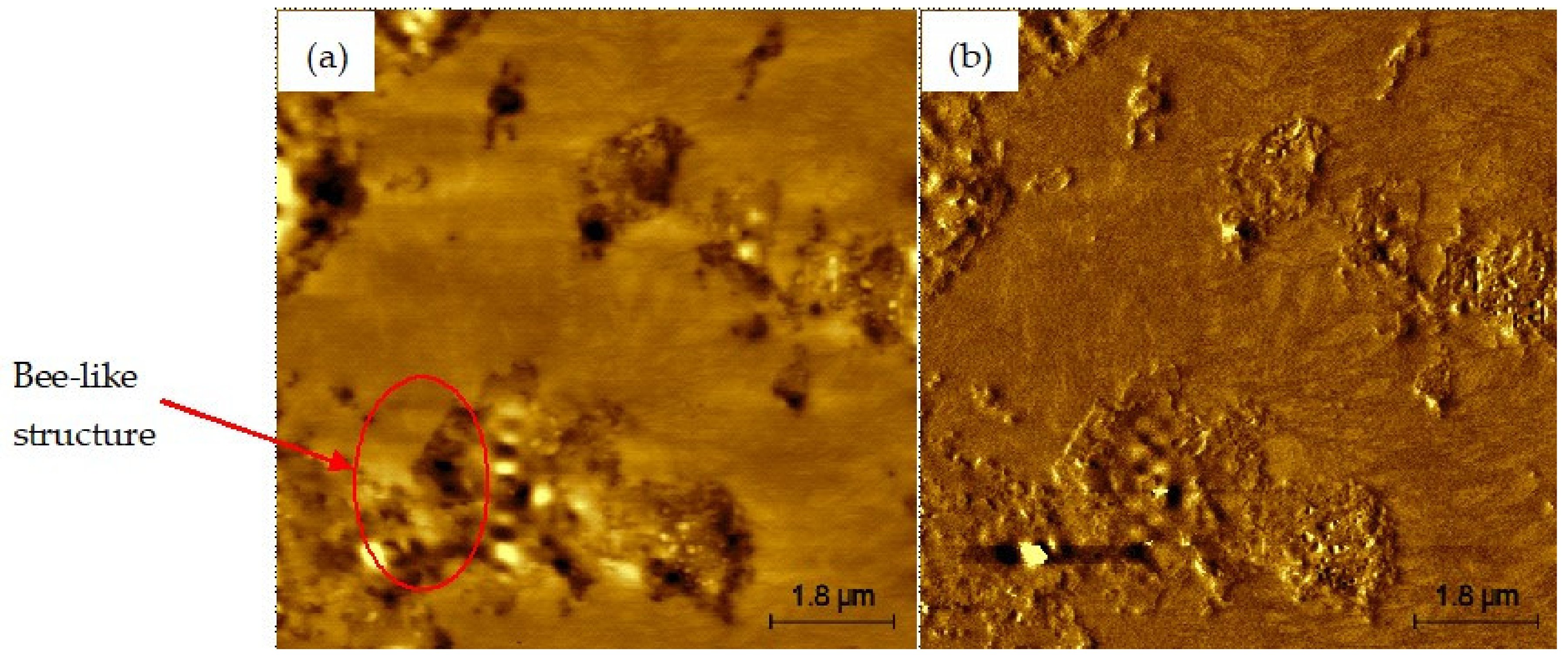
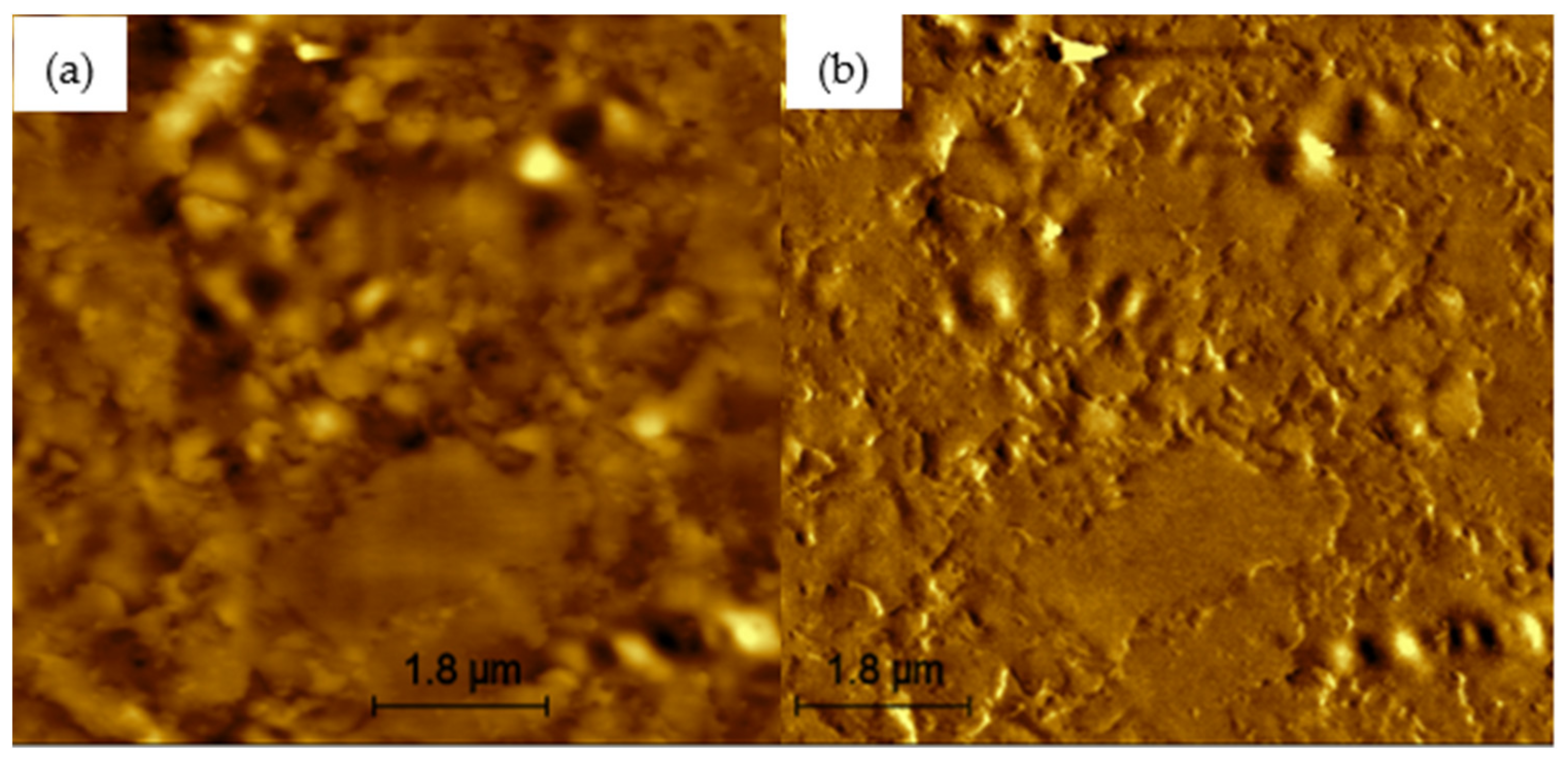
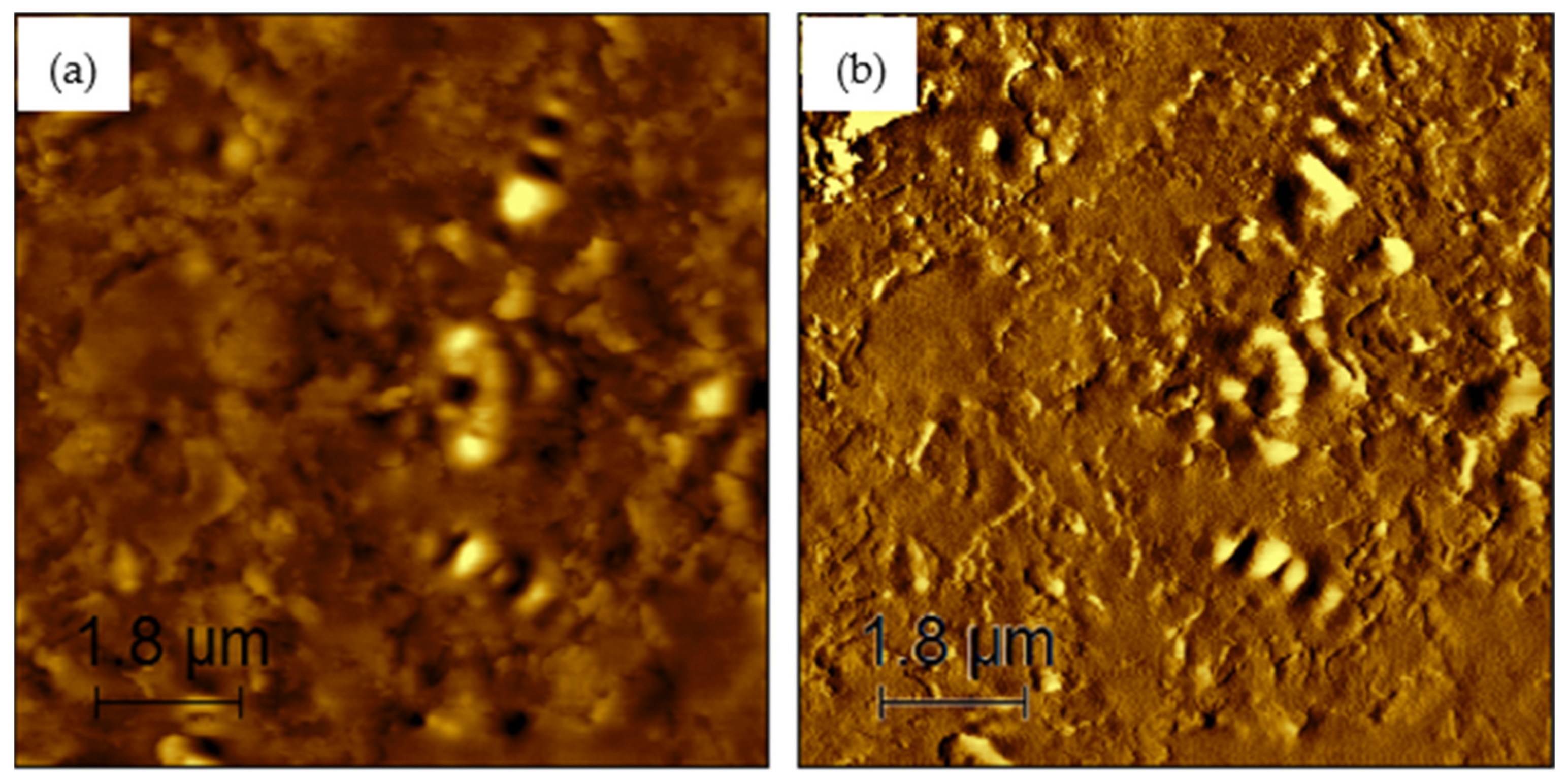
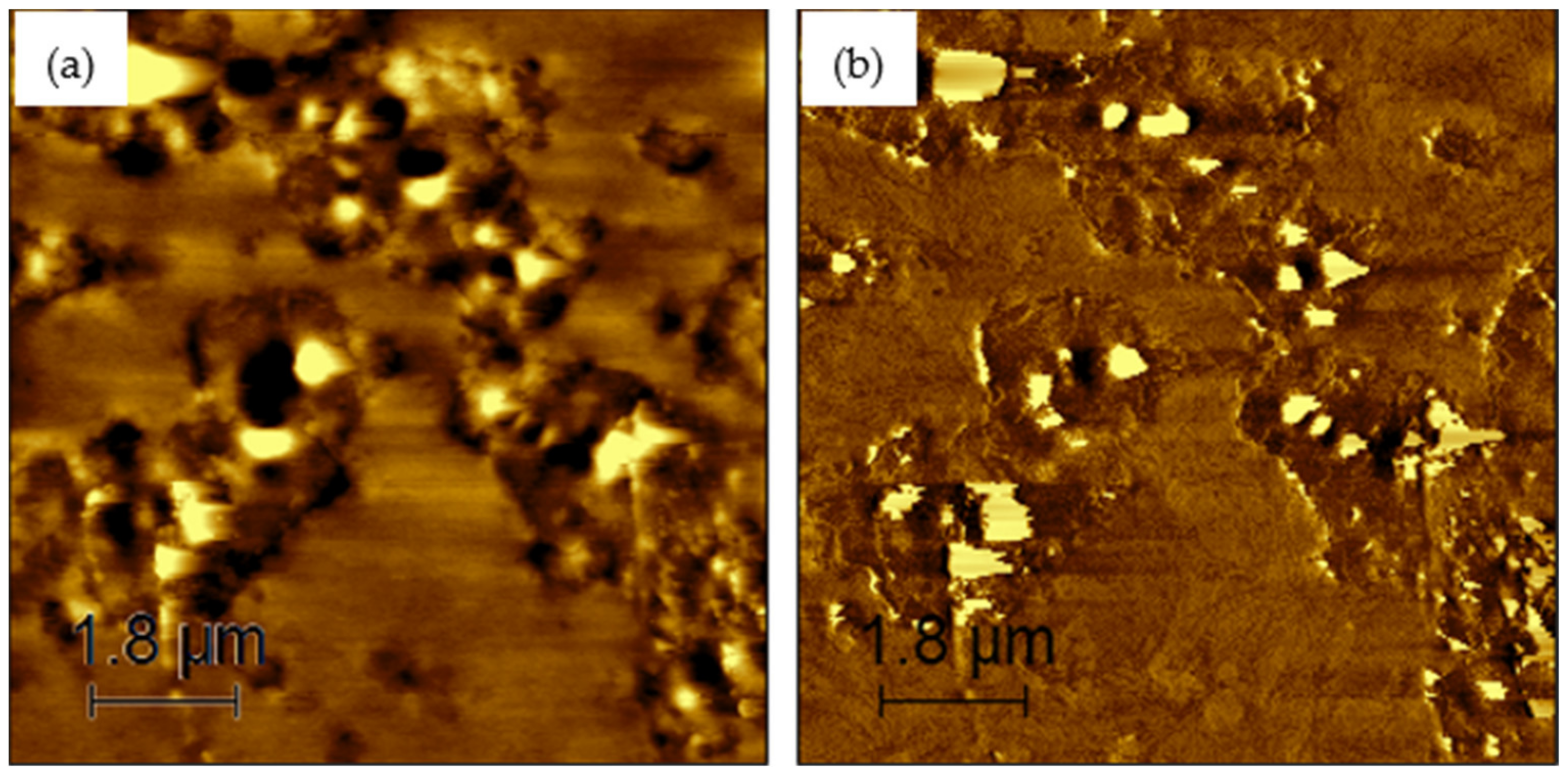
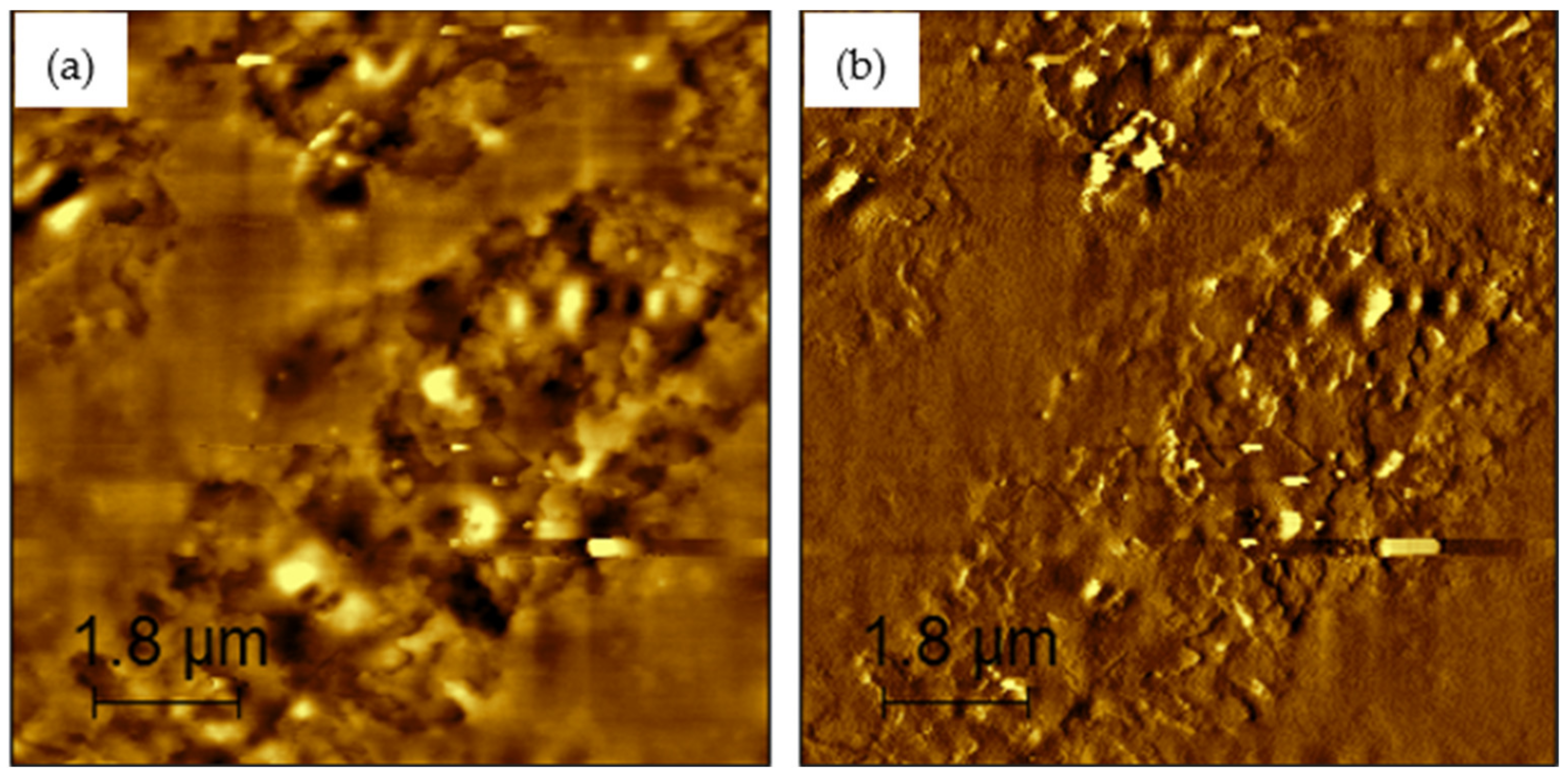
Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 present the topographical and phase images of the PG 64-22 control and rPETE-modified binders. It can be seen that some nonhomogeneity exists within the asphalt matrix, as represented by the revealed dispersed black and white successions of elongated structures within the relatively flat matrix. These black and white successions are called “bee-like” structures and have been identified in many previous studies [49,50,51,52,53,54]. They were attributed, in many studies, to the asphaltene content in the asphalt binder [50,55]. The topographical and phase images for the rPETE-modified asphalt binder samples indicate that the inclusion of rPETE in the asphalt binder reduced the size of the bee-like structures to appear in long chains with a much smaller width than those in the control binder. This may be attributed to the obstruction in the movement of the asphaltene molecule chains owing to the presence of resin thermoplastic polymer molecules of rPETE. As seen from the phase images of the control asphalt binder (Figure 6) and the rPETE-modified binder (Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10), an increase in the phase contrast between the dispersed domains and the flat matrix was noted with the addition of rPETE. Based on that, stiffer dispersed domains will result after adding rPETE, which may result in improving the stiffness properties of the rPETE-modified asphalt as compared with those of the control asphalt binder.
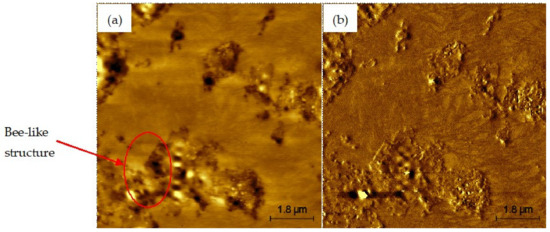
Figure 6.
AFM images of PG 64-22 control binder: (a) topographical image; (b) phase image.
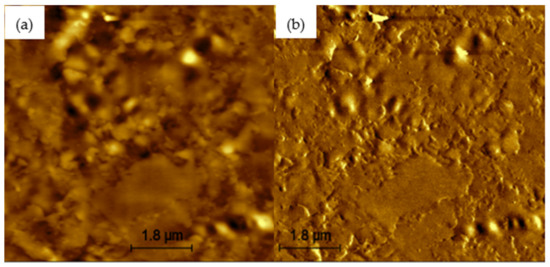
Figure 7.
AFM images of 4% rPETE-modified binder: (a) topographical image; (b) phase image.
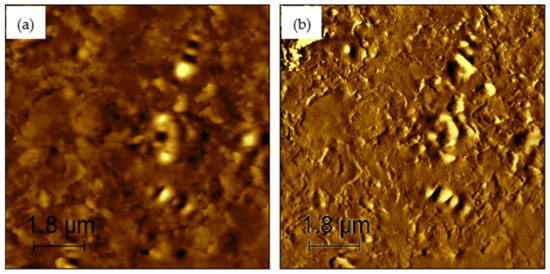
Figure 8.
AFM images of 8% rPETE-modified binder: (a) topographical image; (b) phase image.
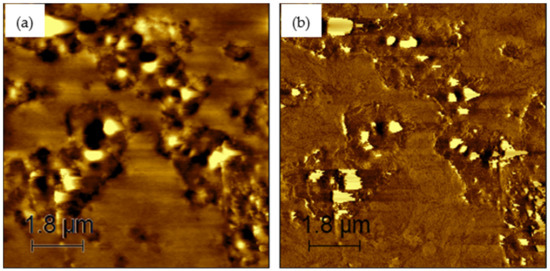
Figure 9.
AFM images of 10% rPETE-modified binder: (a) topographical image; (b) phase image.
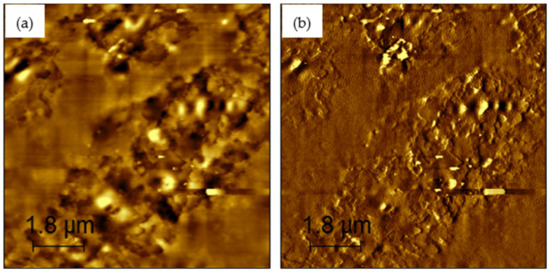
Figure 10.
AFM images of 12% rPETE-modified binder: (a) topographical image; (b) phase image.
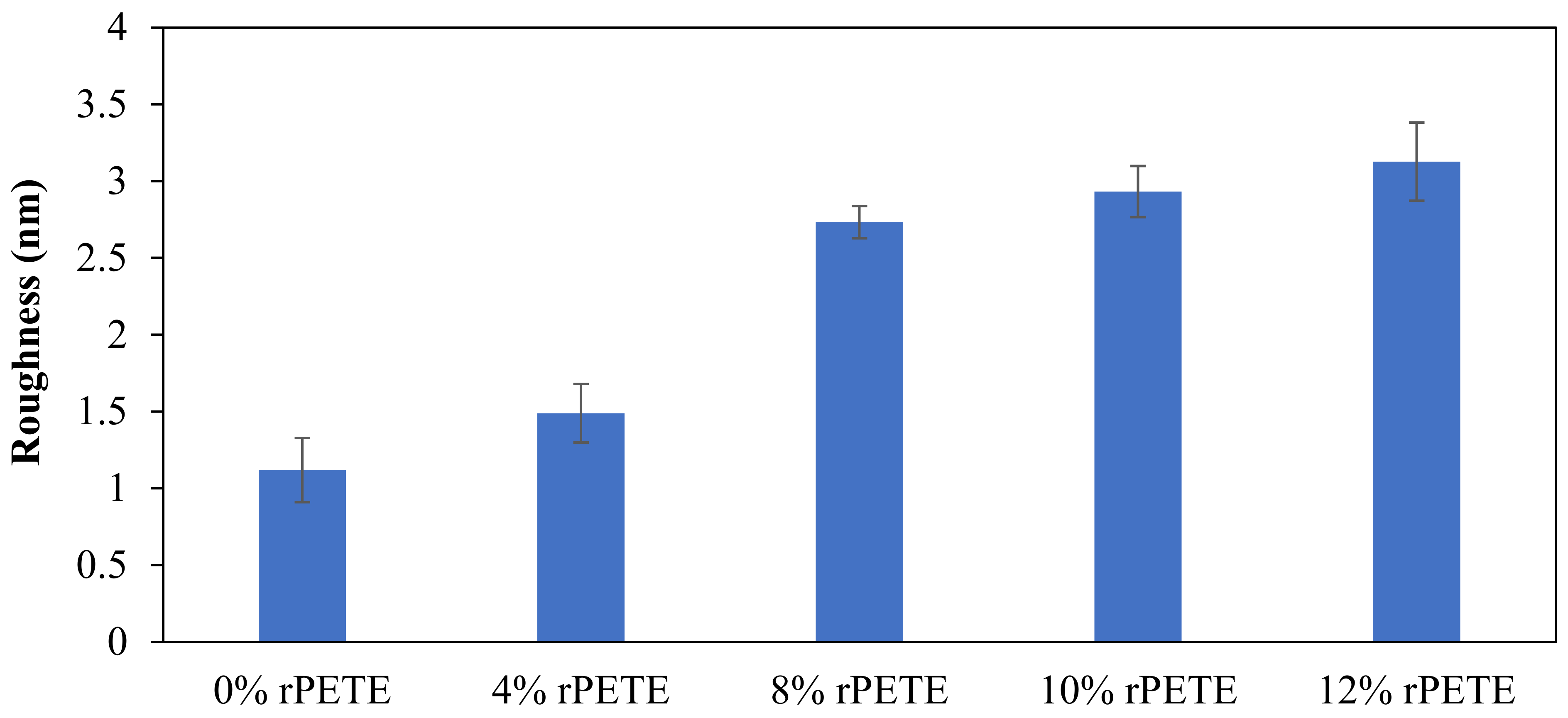
The surface roughness of the control and rPETE-modified binders was also evaluated by conducting a roughness analysis on the obtained topographical images of each binder sample using WSxM version 5.0 software [56]. In this analysis, the average roughness was estimated by calculating the absolute mean of the difference between the average height and the height of each single point of the sample. Figure 11 presents the average roughness values for the PG 64-22 control and rPETE-modified binders. As seen in Figure 11, the rPETE-modified binder samples had much higher roughness values compared with those of the control binder sample, and the roughness value increased with increasing rPETE content. This may be attributed to the increased number of bee-like structures in the modified binders, which have long chains with a smaller width.
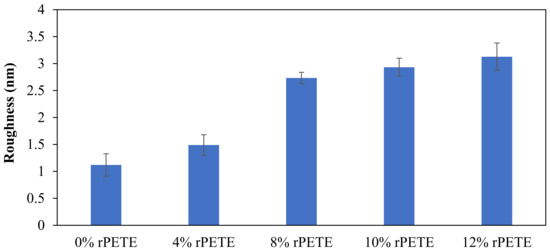
Figure 11.
Results of surface roughness for control and rPETE-modified binders.
4.2.2. Results of AFM Force Spectroscopy Mode
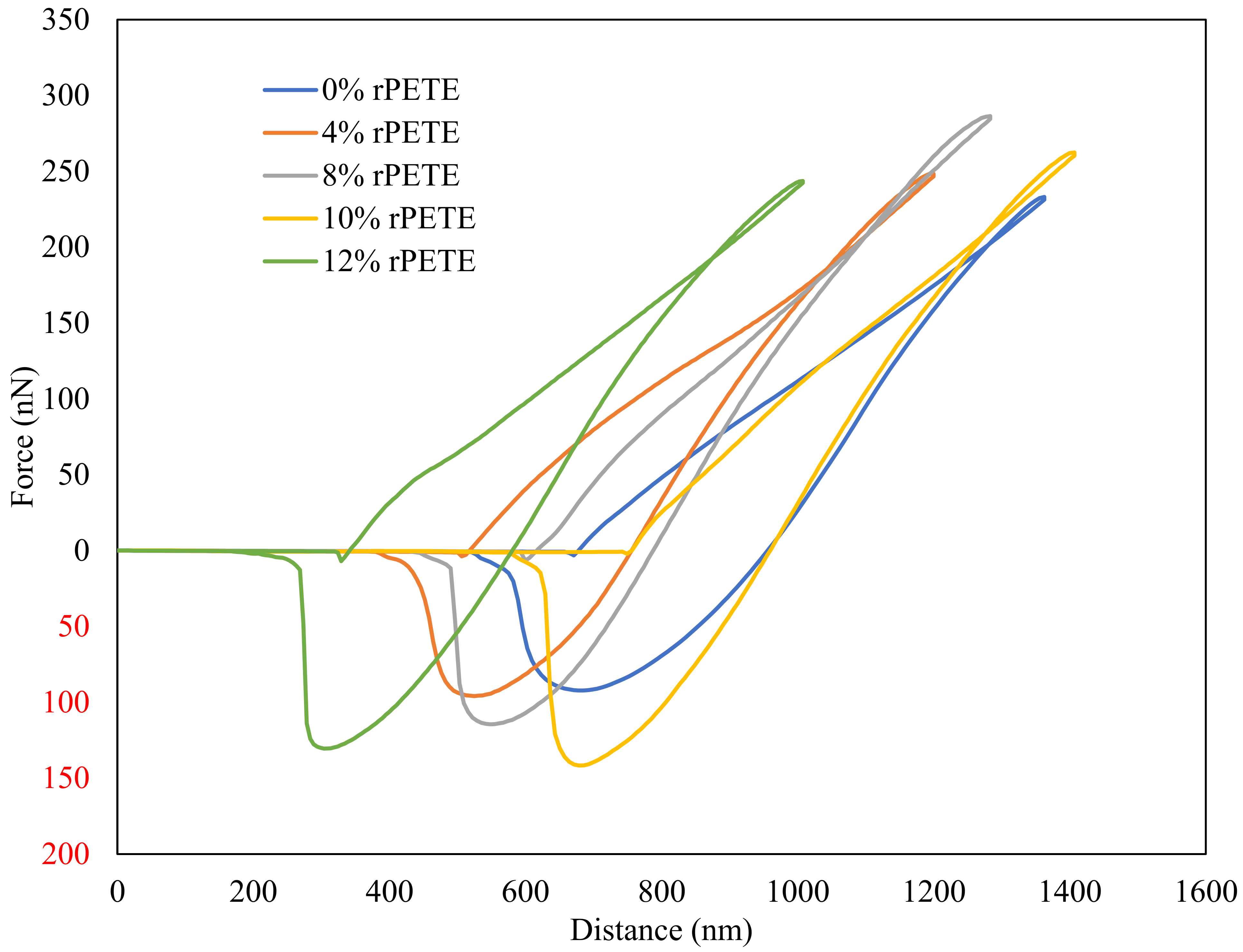
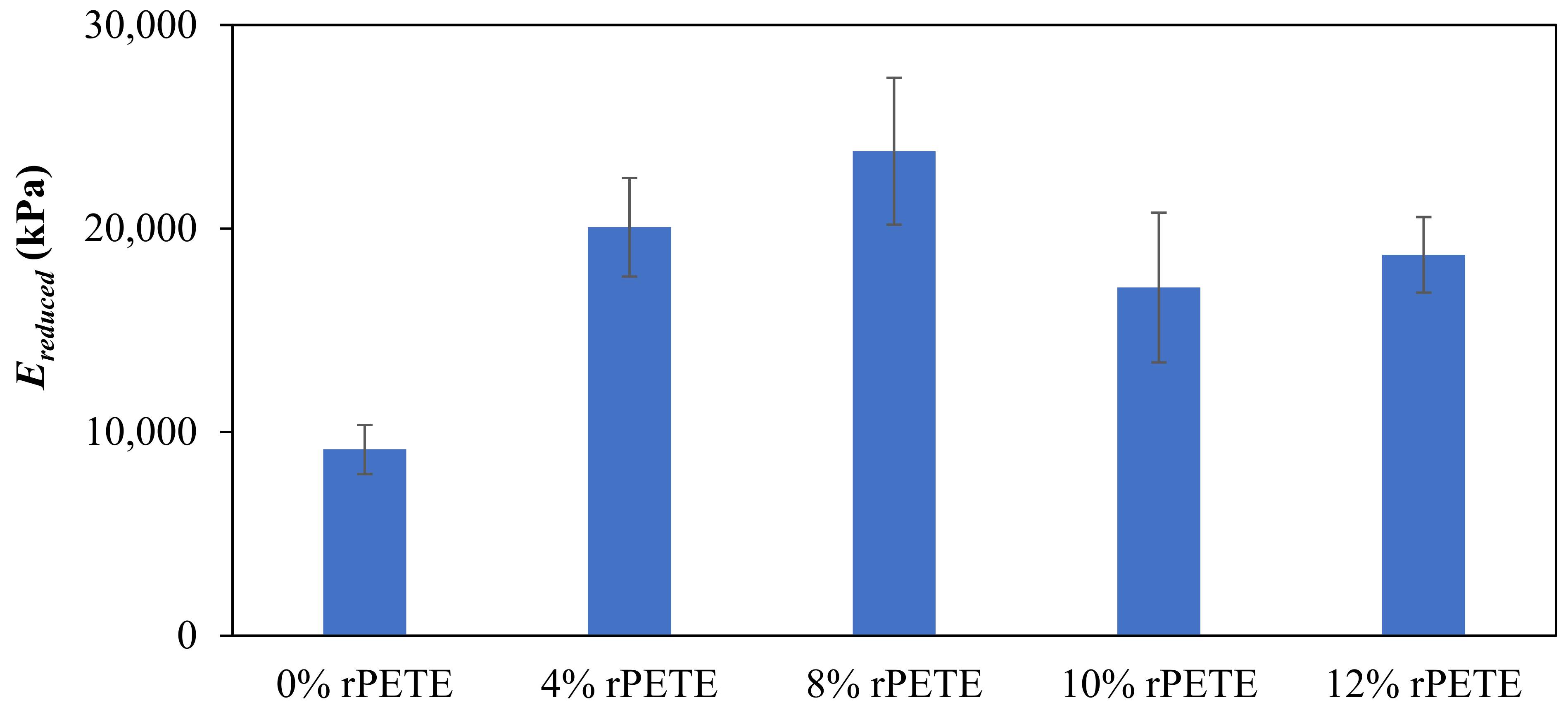
Figure 12 presents typical force–distance curves for the different binder types considered in this study. Figure 13 presents the results of the reduced modulus (Ereduced) for the PG 64-22 control and rPETE-modified binders. The reduced modulus values for the rPETE-modified binders were remarkably higher than that of the control binder; this may be attributed to the short-term aging resulting from the mixing of the rPETE with the binder at a relatively high temperature. Also, this may be attributed to the properties of the rPETE material, which improved the stiffness of the binder. The binder with the 8% rPETE content showed the highest reduced modulus value among all the binders, followed by the binder with 4% rPETE. This means an excessive level of stiffness is achieved by the binder, especially when adding 8% rPETE. The asphalt binders modified with 10% or 12% rPETE contents showed higher values of the reduced modulus than the control binder. However, these values were considered as being reasonable because the modified binders did not exhibit higher levels of stiffness that might affect their adhesion properties.
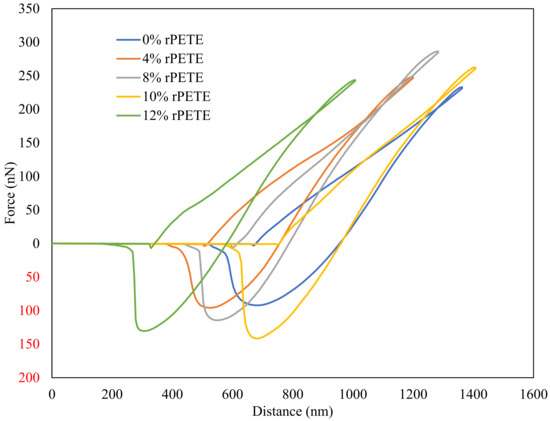
Figure 12.
Typical force–distance curves for control and rPETE-modified asphalt binders. Red numbers represent negative values.
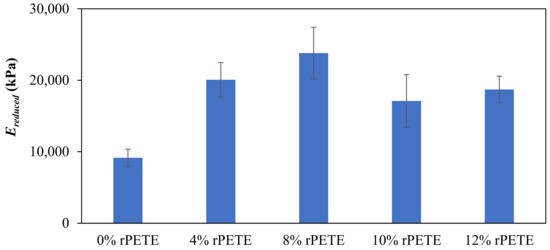
Figure 13.
Results of reduced modulus for control and rPETE-modified binders.
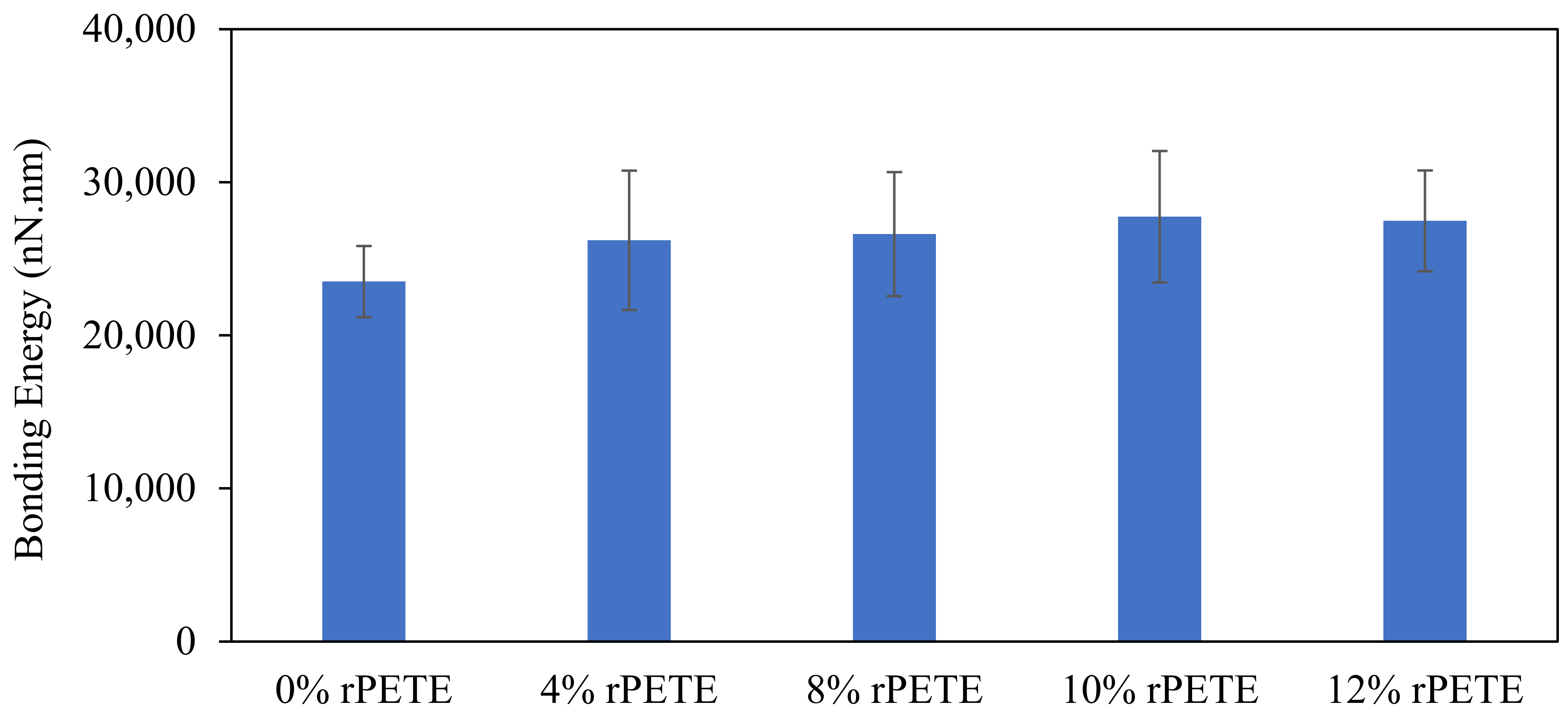
Figure 14 presents the results of the bonding energy for the PG 64-22 control and rPETE-modified binders. In general, the addition of rPETE to the asphalt binder resulted in raising the value of its bonding energy compared with that of the control binder. This improvement in the bonding energy increased with the rPETE content increasing. However, the binder with the 10% rPETE content exhibited the highest bonding energy. This indicates improved adhesion properties between the binder and the rPETE material because the AFM tip needed more energy to pull out from the sample surface after retraction, especially when the 10% rPETE content was used. Increasing the rPETE content to more than 10% will have an adverse effect, as an excessive amount of rPETE will reduce the adhesion between the tip and the binder surface, resulting in lower bonding energy values. When combining the results obtained for the reduced modulus and the bonding energy for this binder, it can be seen that adding this content to the binder resulted in excessive values of stiffness, as represented by the reduced modulus and reduced adhesion between the binder and the rPETE. Finally, the content of 10% rPETE was selected to represent the best performance in regard to the adhesive properties, stiffness, and roughness.
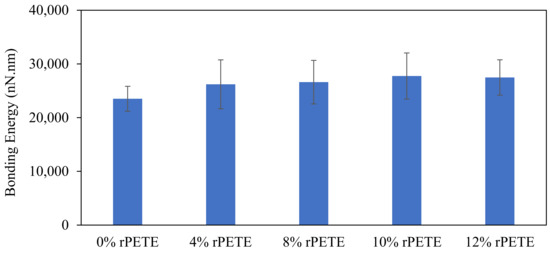
Figure 14.
Results for bonding energy for control and rPETE-modified binders.
4.2.3. Statistical Analysis of the Results for AFM Testing
The statistical evaluation of the results for the micro-scale AFM testing and the significance of the effects of the rPETE addition on the performances of the modified binder and the binder–rPETE adhesion was conducted by applying analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post-ANOVA least square means (LSMs) using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS)®. A linear completely random design (CRD) model was used in these analyses.
The results of the ANOVA on the results of the AFM bonding energy, reduced modulus, and average roughness parameters for the unaged and RTFO-aged control and rPETE-modified binders are presented in Table 8. It is noted that the p-values in Table 8 were less than 0.05 at the 95% confidence level, which indicates a statistically significant effect for the rPETE content on the results of the AFM parameters. Table 9 presents the results for the ranking of the asphalt binders based on the results of the bonding energy, reduced modulus, and roughness, as determined by the post-ANOVA LSM analysis. In Table 9, a descending-order listing was given to the groups, with the letter “A” contributing to the highest mean, followed by the other letters in the appropriate order. As seen in Table 9, the 10% rPETE content had the highest value of the bonding energy compared to the other binders, followed by the 12% rPETE content. On the other hand, the 8% rPETE content had the highest value of the reduced modulus compared to the other binders, followed by the 4% PETE content. The 12% rPETE content had the highest roughness value compared to the other binders, followed by the 10% rPETE content. However, the control binder with no rPETE addition had statistically the lowest values of the bonding energy, reduced modulus, and average roughness among all the binders.

Table 8.
Results of ANOVA on AFM-testing of unmodified and rPETE-modified asphalt binders.

Table 9.
Results of post-ANOVA analysis on AFM testing of unmodified and rPETE-modified asphalt binders.
5. Conclusions
This paper documents the results of a research study that included the preparation of rPETE-modified asphalt binders to evaluate the effects of adding rPETE in different contents on the high-temperature, intermediate-temperature, and low-temperature performances of the modified binders, using rheological macro-scale testing, as well as on the interaction and bonding properties between the asphalt binder and rPETE at the nano-scale, using AFM testing, and to compare them with those of the unmodified binder. The following conclusions can be drawn based on the results of this study:
- The addition of the rPETE enhanced the high- and intermediate-temperature rheological properties and slightly reduced the low-temperature rheological properties of the modified PG 64-22 binder;
- The results from the AFM testing indicated that the inclusion of rPETE in the asphalt binder improved the stiffness properties of the modified binder as compared with those of the control asphalt binder. In addition, the rPETE-modified binders showed rougher surfaces and remarkably higher values of the reduced modulus than the control binder;
- As seen from the results of the AFM bonding energy, the rPETE-modified binders showed higher bonding energy values compared with those of the control binder. This improvement in the bonding energy increased with increasing rPETE content. The addition of the 10% rPETE content resulted in the highest bonding energy among all the binders;
- The mixture with the 10% rPETE content resulted in the best high- and intermediate-temperature binder performances. Although the 4% rPETE binder showed improved high- and intermediate-temperature properties without reducing the low-temperature grade of the modified binder, 4% can be considered as the optimal content of rPETE as a modifier for the asphalt binder.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.N.; Methodology, A.A.-H., M.D.N. and S.K.; Formal analysis, A.A.-H. and S.K.; Investigation, M.D.N. and A.A-H..; Data curation, A.A.-H. and T.R.; Writing—original draft, A.A.-H. and M.D.N.; Writing—review & editing, A.A.-H. and M.D.N.; Supervision, M.D.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All the data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Ahmad Al-Hosainat was employed by the company Terracon Consultants, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Shahnawaz, M.; Sangale, M.K.; Ade, A.B. Plastic Waste Disposal and Reuse of Plastic Waste. In Bioremediation Technology for Plastic Waste; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; Hamzah, M.O.; Aman, M.Y. Effects of Sasobit® content on the rheological characteristics of unaged and aged asphalt binders at high and intermediate temperatures. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, B.V.; Yılmaz, M.; Akpolat, M. Evaluation of the conventional and rheological properties of SBS+Sasobit modified binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 63, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarefder, R.A.; Yousefi, S.S. Rheological Examination of Aging in Polymer-Modified Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04015112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuzlan, K.A.; Al Assi, M.O. Sasobit-Modified Asphalt Binder Rheology. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, A.; Taamneh, M.; Khasawneh, M.A.; Al-Hosainat, A. Effect of crumb tire rubber, microcrystalline synthetic wax, and nano silica on asphalt rheology. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 757–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuaddous, M.; Taamneh, M.M.; Rabab’ah, S.R. The potential use of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (RPET) plastic waste in asphalt binder. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y.; Mendez, M.P.; Rodriguez, Y. Polymer modified asphalt. Vis. Tecnol. 2001, 9, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Gharehveran, M.M. Morphology, rheology, and physical properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 766–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wen, Y. Influencing factors and evaluation methods of reinforcement effect of fiber-modified asphalt binder. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 8986–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.; Reid, G. Recycled waste plastic for extending and modifying asphalt binders. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on Pavement Surface Characteristics (SURF 2018), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2–4 April 2018; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.F.; Razali, A.R.; Razelan, I.S.M. Utilization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in asphalt pavement: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 203, p. 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Khedaywi, T.; Haddad, M.; Bataineh, H. Effect of waste plastic polyethylene terephthalate on properties of asphalt cement. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. An Evaluation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Pavement towards a Circular Economy. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Missouri–Columbia, Columbia, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Montalvo, L. Repurposing waste plastics into cleaner asphalt pavement materials: A critical literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, D.; Borisenko, Y.; Shvachev, D.; Rudak, S. Effective Polymer-Modified Bitumen Based on PET Waste. In Proceedings of the FORM 2022: Construction the Formation of Living Environment, Moscow, Russia, 20–22 April 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi, A. Reuse of Waste Plastic as an Additive in Asphalt Concrete. ATBU J. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2022, 10, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, Z.; Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A. Production of a sustainable paving material through chemical recycling of waste PET into crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majka, T.M.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Piechaczek, M. Research on the Development of a Way to Modify Asphalt Mixtures with PET Recyclates. Materials 2023, 16, 6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Kawabata, T.; Oda, M. Current State and Perspectives Related to the Polyethylene Terephthalate Hydrolases Available for Biorecycling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8894–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanderi, K.K.; Joshi, J.R.; Patel, J.V. Recycling of polyethylene terephthalate (PET or PETE) plastics—An alternative to obtain value added products: A review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Wirth, B.; Lüder, U.; Werner, M. Behavior of selected hydrolyzed and dehydrated products during hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.; McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Elucidating hydrochar morphology and oxygen functionality change with hydrothermal treatment temperature ranging from subcritical to supercritical conditions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, P.; Yu, R.; Liu, X. Preparation process to affect stability in waste polyethylene-modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.T.; Hussein, Z.H. Evaluation of pyrolisis PET utilization in asphalt binder. Evaluation 2014, 3, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ghuzlan, K.A.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Qasem, Y. Rheological Properties of Polyethylene-Modified Asphalt Binder. Athens J. Technol. Eng. 2015, 2, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.d.A.A.e.; Lucena, L.C.d.F.L.; Rodrigues, J.K.G.; Carvalho, M.W.; Costa, D.B. Use of Micronized Polyethylene Terephthalate (Pet) Waste in Asphalt Binder. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Nasr, D. Properties of asphalt modified with devulcanized polyethylene terephthalate. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, M.D.; Abu-Qtaish, L.; Kaya, S.; Powers, D. Using Atomic Force Microscopy to Evaluate the Nanostructure and Nanomechanics of Warm Mix Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Qtaish, L.; Nazzal, M.D.; Abbas, A.; Kaya, S.; Akinbowale, S.; Arefin, M.S.; Kim, S.-S. Micromechanical and Chemical Characterization of Foamed Warm-Mix Asphalt Aging. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, A.; Nazzal, M.D.; Abu Qtaish, L.; Kim, S.S.; Abbas, A.; Arefin, M.; Quasem, T. Effect of RAP Source on Cracking Resistance of Asphalt Mixtures with High RAP Contents. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, M.D.; Abu Qtaish, L.; Al-Hosainat, A.; Abu Talha, S.; Kaya, S.; Abbas, A.R. Evaluation of Moisture Damage in Asphalt Mixtures at Macro- and Nanoscales. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO T 240; Standard Method of Test for Effect of Heat and Air on a Moving Film of Asphalt Binder (Rolling Thin-Film Oven Test). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- AASHTO T R28; Standard Practice for Accelerated Aging of Asphalt Binder Using a Pressurized Aging Vessel (PAV). American Association of State Highway Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- AASHTO T 315-22; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- AASHTO T 313-22; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- AASHTO T PP42; Standard Practice for Determination of Low-Temperature Performance Grade (PG) of Asphalt Binders. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- AASHTO TP 92–14; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Cracking Temperature of Asphalt Binder Using the Asphalt Binder Cracking Device (ABCD). Standard by American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Baaj, H.; Tighe, S.; Kringos, N. Atomic force microscopy to investigate asphalt binders: A state-of-the-art review. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2016, 17, 693–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.R. Atomic Force Microscopy. Chem. Educ. 1996, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, M.D.; Qtaish, L.A. The Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Evaluate Warm Mix Asphalt (No. FHWA/OH-2012/19); Ohio Department of Transportation: Columbus, OH, USA, 2013.
- Tarefder, R.A.; Zaman, A.M. Nanoscale Evaluation of Moisture Damage in Polymer Modified Asphalts. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuQtaish, L.; Nazzal, M.D.; Kaya, S.; Kim, S.-S.; Abbas, A.; Abu Hassan, Y. AFM-Based Approach to Study Blending between RAP and Virgin Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. Critical review of analysis and interpretation of nanoindentation test data. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 4153–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, T.; Grimes, W.; Cookman, A.; Huang, S.-C. Adherence Energy of Asphalt Thin Films Measured by Force-Displacement Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 04014089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphalt Institute Technical Advisory Committee. Use of the Delta Tc Parameter to Characterize Asphalt Binder Behavior; Asphalt Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-934154-77-9. [Google Scholar]
- Elwardany, M.; Planche, J.-P.; King, G. Universal and practical approach to evaluate asphalt binder resistance to thermally-induced surface damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeber, L.; Sutton, O.; Morel, J.; Valleton, J.-M.; Muller, G. New direct observations of asphalts and asphalt binders by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 1996, 182, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, A.; Lackner, R.; Eisenmenger-Sittner, C.; Blab, R. Identification of four material phases in bitumen by atomic force microscopy. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2004, 5 (Suppl. 1), 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, J.-F.; Leblond, V.; Margeson, J. Bitumen morphologies by phase-detection atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 221, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kringos, N.; Schmets, A.; Scarpas, A.; Pauli, T. Towards an understanding of the self-healing capacity of asphaltic mixtures. Heron 2011, 56, 45–74. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzal, M.D.; Kaya, S.; Gunay, T.; Ahmedzade, P. Fundamental Characterization of Asphalt Clay Nanocomposites. J. Nanomech. Micromech. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcombe, E.W.; Nazzal, M.D.; Mogawer, W.; Austerman, A.J.; Kaya, S. Evaluating Asphalt Binders Prepared with Different Processes to Meet the Same Performance Grade: Use of Atomic Force Microscope. Transp. Res. Rec. 2017, 2632, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeber, L.; Muller, G.; Morel, J.; Sutton, O. Bitumen in colloid science: A chemical, structural and rheological approach. Fuel 1998, 77, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcas, I.; Fernández, R.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.M.; Colchero, J.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Baro, A.M. WSXM: A software for scanning probe microscopy and a tool for nanotechnology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).