Abstract
The purpose of this review was to investigate the correlation between magnetism and crystallographic structures as it relates to the martensite transformation of Ni2MnGa type alloys, which undergo martensite transformation below the Curie temperature. In particular, this paper focused on the physical properties in magnetic fields. Recent researches show that the martensite starting temperature (martensite transformation temperature) TM and the martensite to austenite transformation temperature (reverse martensite temperature) TR of Fe, Cu, or Co-doped Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys increase when compared to Ni2MnGa. These alloys show large field dependence of the martensite transformation temperature. The field dependence of the martensite transformation temperature, dTM/dB, is −4.2 K/T in Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18. The results of linear thermal strain and magnetization indicate that a magneto-structural transition occurred at TM and magnetic field influences the magnetism and also the crystal structures. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy was also determined and compared with other components of Ni2MnGa type shape memory alloys. In the last section, magnetic field-induced strain and magnetostriction was determined with some novel alloys.
1. Magnetic Properties of Ni2MnGa Type Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys
1.1. Outline
Ferromagnetic shape memory alloys (FSMAs) have been extensively studied as potential candidates for smart materials. Among FSMAs, Ni2MnGa is the most familiar alloy [1]. It has a cubic L21 Heusler structure (space group Fm3m) with lattice parameter a = 5.825 Å at room temperature, and it orders ferromagnetically at the Curie temperature TC ≈ 365 K [2,3]. Upon cooling from room temperature, a martensite transformation occurs at the martensite transformation temperature TM ≈ 200 K. Below TM, a superstructure is formed because of lattice modulation [4,5]. For the Ni–Mn–Ga Heusler alloys, TM varies from 200–330 K by non-stoichiometrically changing the concentration of the chemical composition.
Several studies on Ni–Mn–Ga alloys have addressed martensite transformation and correlation between magnetism and crystallographic structures [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Ma et al. [7] studied the crystallography of Ni50+xMn25Ga25-x alloys (x = 2–11) by powder X-ray diffraction and optical microspectroscopy. In the martensite phase, typical microstructures were observed for x < 7. The martensite variants exhibit configurations typical of self-accommodation arrangements. The typical width of a variant is about 1 μm, by means of the TEM image of Ni54Mn25Ga21, which is shown in [7], and the strict twin structure of the microstructure is beneficial to the thermoelasticity of its martensitic transformation. A few studies discussed the interaction between magnetism and crystallographic rearrangements [1,8,9,17,18]. The memory strain, which means the second thermal cycle and the relative elongation obtained before the pre-deformation, was observed in single crystal Ni2MnGa and polycrystal Ni53.6Mn27.1Ga19.3 [10]. As for magnetism, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant KU in the martensite phase is 1.17 × 105 J/m3, which is four times higher than that in the austenite phase (0.27 × 105 J/m3) [1]. Manosa et al. [8] indicated that the martensite transformation takes place in the ferromagnetic phase, and the decrease in magnetization observed at fields between 0 and 1 T is due to the strong magnetocrystalline anisotropy of the martensite phase in association with the multi-domain structure of the martensite state. Sánchez-Alarcos et al. [9] investigated the influence of atomic order on the magnetic properties in a polycrystal Ni49.5Mn28.5Ga22 ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. Different thermal treatments were performed to modify the degree of the atomic order of the alloy. They analyzed the effect of the different thermal treatments on the magnetic and structural characteristics by a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements. Magnetic and structural properties of the alloys are modified as a consequence of the atomic order change. The martensitic transformation temperatures increase as long as the degree of the atomic order of the alloy increases. On the other side, the Curie temperature and magnetization saturation also reflect the degree of the atomic order of the alloy, but seem to be linked to the particular order of the Mn sub-lattice.
1.2. Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy
Likhachev et al. [17] stated that the magnetic driving force responsible for twin boundary motion is practically equal to the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant KU. The magnetic driving force applied to twin boundaries is equal to a difference in magnetization free energies between the different twin variants of martensite. This difference also characterizes the energy of uniaxial magnetization anisotropy and can be calculated from the corresponding magnetization measurements. The magnetic driving force achieves its maximal value of 0.13 MPa in a magnetic field higher than 0.8 T. This value is sufficient to explain the high 5% magnetic field-induced strain in some Ni–Mn–Ga alloys, which have very low (2 MPa) twinning stress. They also pointed out that there is a definite analogy between the deformation effects caused by the mechanical and magnetic driving forces. For instance, in both cases, the macroscopic twining strain – driven by the mechanical stress or the magnetic field applied – can be expressed through the same universal function dependent on the corresponding mechanical or magnetic driving force. This universality rule allows performing the quantitative calculations of the magnetic field induced-strain as a function of field by using the mechanical testing results. The magnetization results indicate that the martensite Ni–Mn–Ga alloys have higher magnetocrystalline anisotropy compared to Mn ferrites. Furthermore, magnetization results indicate that the coercivity and saturation field at the martensite phase are higher than those of the cubic austenite phase [11,12,13,14,15]. Zhu et al. [11] investigated the lattice constant change Δc/c of −4.8% of Ni51.9Mn23.2Ga24.9by means of X-ray diffraction study around martensite transformation temperature. Chernenko et al. [12] also studied about magnetization and X-ray powder diffractions, and clear changes were found at TM for both measurements. Murray et al. [18] studied the polycrystal Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. The magnetization step at TM was also observed, which is a reflection of the magnetocrystalline anisotropy in the tetragonal martensite phase. In the martensite phase, strong magnetocrystalline anisotropy exists. Then the magnetization that reflects the percentage of the magnetic moments parallel to the magnetic field is smaller than that in the austenite phase where the magnetocrystalline anisotropy is not strong in the weak magnetic field. Therefore, the magnetization step is observed at TM. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment was performed by Golub et al. [13] to investigate the correlation between magnetic properties and local structure in Ni–Mn–Ga systems from a microscopic view. NMR experiments indicate Mn-Mn indirect exchange via the faults in Mn-Ga layers interchange caused by excessive Ga. This result indicates that the exchange interaction between Mn-Mn magnetic moments is sensitive with the lattice transformation. Then the magnetism changes from soft magnet in the austenite phase to hard magnet in the martensite phase, which is due to higher magnetocrystalline anisotropy.
To use Ni–Mn–Ga alloys as advanced materials for actuators in daily use, magnetic actuators should be used around room temperature (300 K). Therefore, we selected the Ni52Mn25Ga23 alloy, which shows ferromagnetic transition at the Curie temperature TC (about 360 K), and the martensite transformation occurs around 330 K.
Recently, Sakon et al. [19] investigated the correlation between magnetism and crystallographic structures as it relates to the martensite transformation of Ni52Mn25Ga23, which undergoes the martensite transformation below TC [6,7]. The current study particularly focused on the physical properties in magnetic fields. Here, we analyzed that by using the polycrystal samples, it is possible to provide information on the easy axis of the magnetization in the martensite structure with temperature-dependent strain measurements under the constant magnetic fields. Thermal strain, permeability, and magnetization measurements were performed for polycrystal Ni52Mn25Ga23 in magnetic fields (B), and magnetic phase diagrams (B–T phase diagram) were constructed [19]. Thermal strain measurements (linear thermal expansion) and magnetostriction measurements were performed using strain gauges (Kyowa Dengyo Co. Ltd., Chofu, Japan) under steady fields. The magnetic permeability measurements were performed in AC fields with a frequency, f = 73 Hz, and a maximum field, Bmax = 0.0050 T. AC fields were applied along the longitudinal axis of the sample. Permeability increases above 330 K, and suddenly decreases around 360 K. The temperature dependence of permeability μ and differential of the permeability dμ/dT are shown in Figure 1a,b, respectively. When cooling from a high temperature, permeability shows a sudden increase at about 356 K and decreases at 327 K. The clear peaks at these temperatures are shown in Figure 1b. The sudden changes in permeability indicate that the ferromagnetic transition occurs around 358 K. The temperature dependence of permeability for Ni52Mn25Ga23 is similar to that for Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23, which shows the transition from a ferromagnetic–martensite (Ferro–M) phase to a ferromagnetic– austenite (Ferro–A) phase [20]. The step around 333 K (heating process) and 327 K (cooling process) for Ni52Mn25Ga23 in Figure 1a reflects stronger magnetocrystalline anisotropy in the tetragonal martensite phase [8,18]. Polycrystal Ni49.5Mn28.5Ga22, Ni50Mn28Ga22 and Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 alloys also indicate the magnetization (or permeability) step at TM [9,18,20] below the field of 10 mT. Figure 2 shows the permeability of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 by means of SQUID magnetometer under the field of 10 mT. After the zero field cooling from room temperature, this measurement was performed. The difference of permeability between increasing temperature and cooling temperature (field cooling) is supposed to the reorientation of the magnetic domains. The permeability of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 also shows abrupt change at TM = 284 K. The magnetization results are also shown in Figure 3, Figure 4. As for the temperature dependence of the magnetization (Figure 4), the magnetization at B = 0.5 T, 1 T, and 5 T just above TM is smaller than that below TM, which is different from the temperature dependence of the permeability in Figure 2. It is conceivable that the magnetocrystalline anisotropy in the martensite phase is larger than that in the austenite phase. As for Ni49.5Mn28.5Ga22 [9], the permeability measurement results indicate that the ferromagnetic transition from the paramagnetic–austenite (Para–A) phase to the Ferro–A phase occurs around 358 K. On the other hand, for Ni52Mn25Ga23, the linear strain does not show noticeable anomaly at the ferromagnetic transition around 358 K (Figure 5). When cooling from 370 K, the thermal strain shows a peak at 329 K for Ni52Mn25Ga23. This may be attributed to the intermingling of the L21 austenite lattices and the 14M martensite lattices at the martensite transformation. The sequential phenomenon is observed in single crystal Ni2.19Mn0.81Ga [21]. Zhu et al. [11] suggest that the small satellite peaks in heat flow plot of Ni51.9Mn23.2Ga24.9, which flanks the central peak, indicate that the structural transition takes place in multiple steps. The results of thermal strain in a magnetic field and magnetic field-induced strain yield information about the twin boundary motion in the fields.
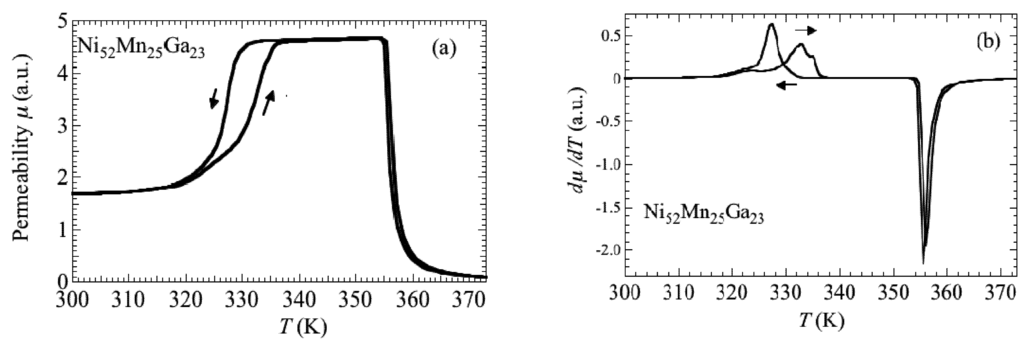
Figure 1.
(a) Temperature dependence of the permeability of Ni52Mn25Ga23. (b) Temperature dependence of the differential of the permeability.
Figure 1.
(a) Temperature dependence of the permeability of Ni52Mn25Ga23. (b) Temperature dependence of the differential of the permeability.
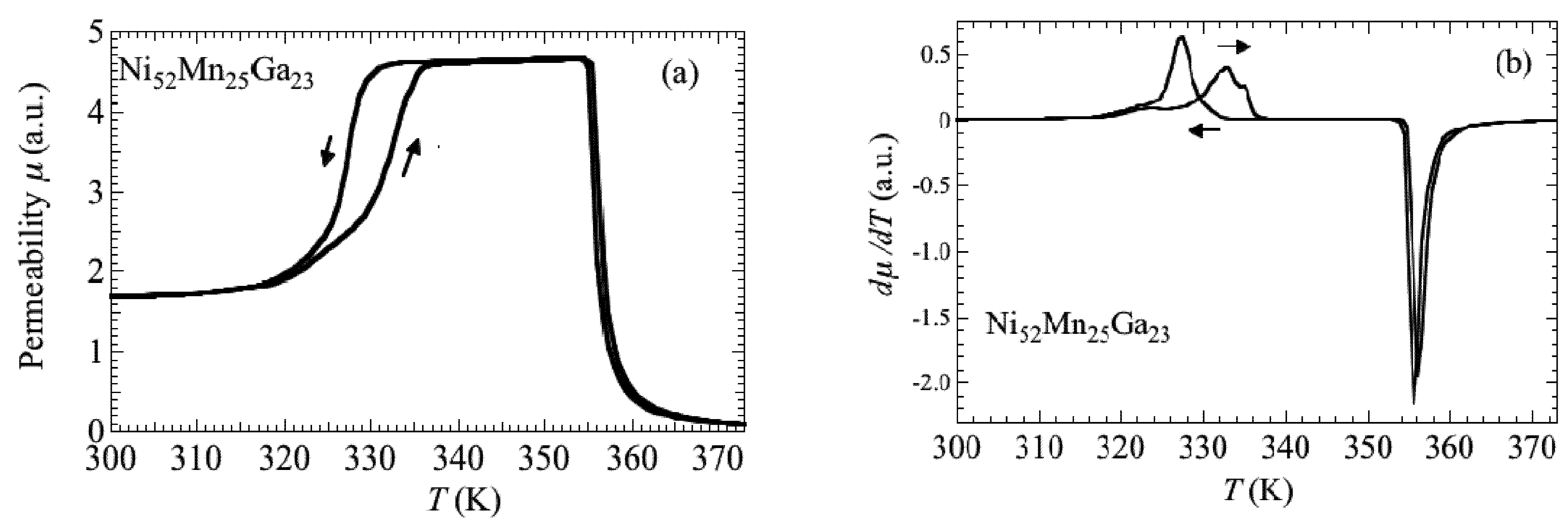
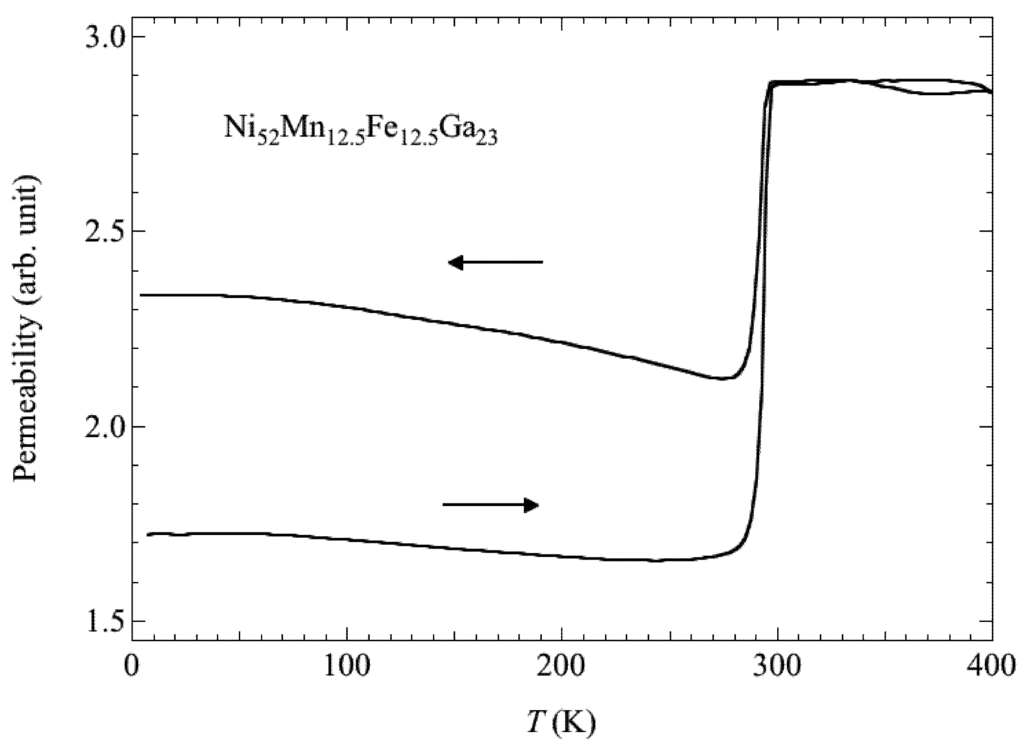
Figure 2.
The temperature dependence of the permeability of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
Figure 2.
The temperature dependence of the permeability of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
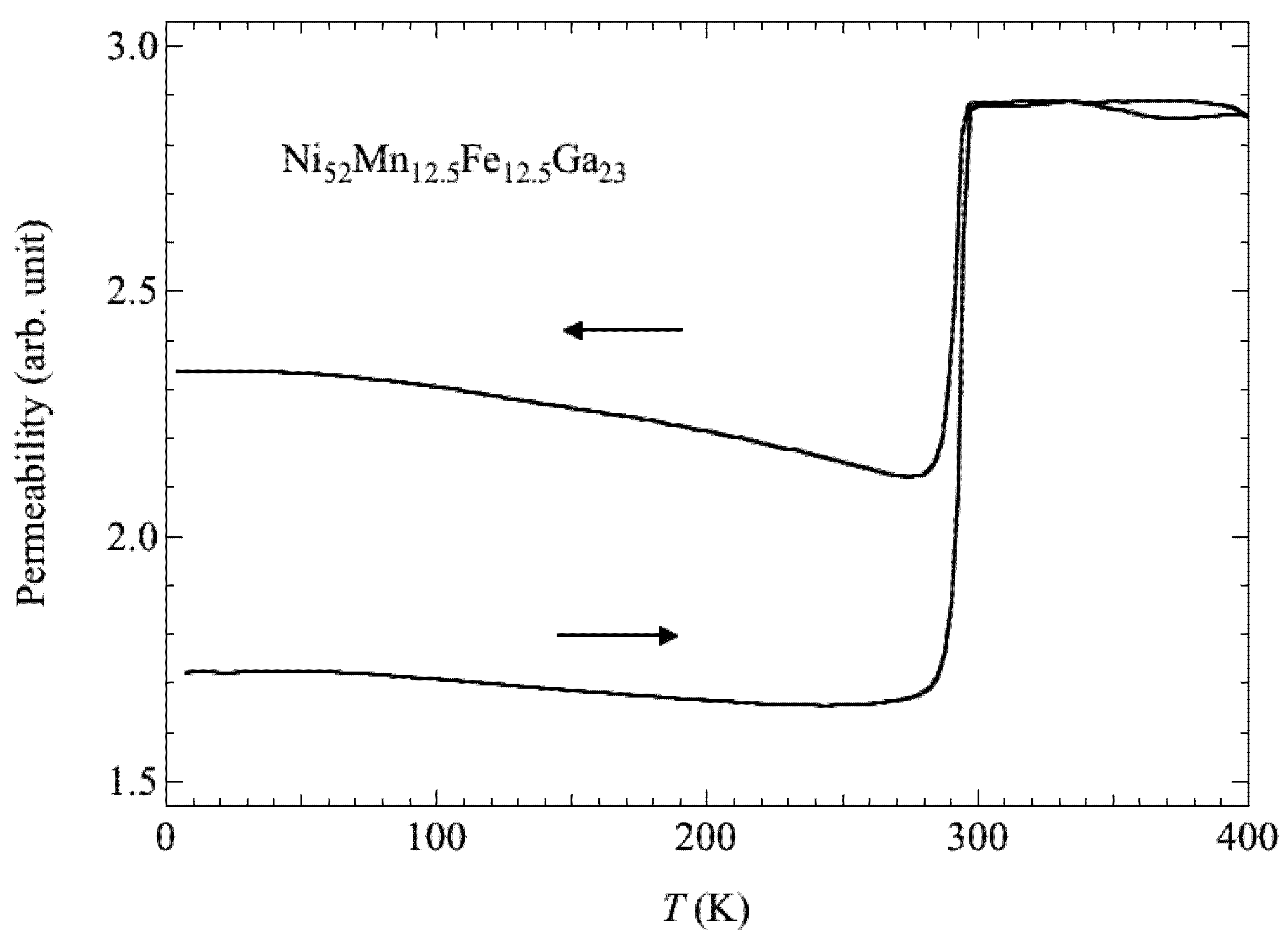
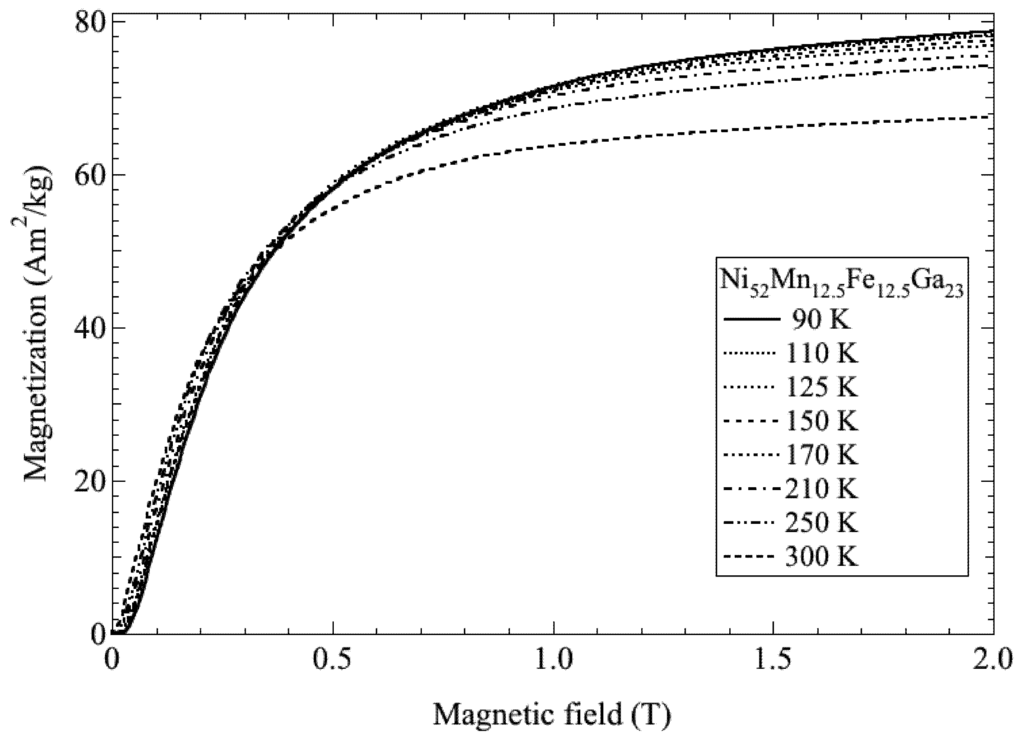
Figure 3.
The magnetic field dependence of the magnetization of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
Figure 3.
The magnetic field dependence of the magnetization of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
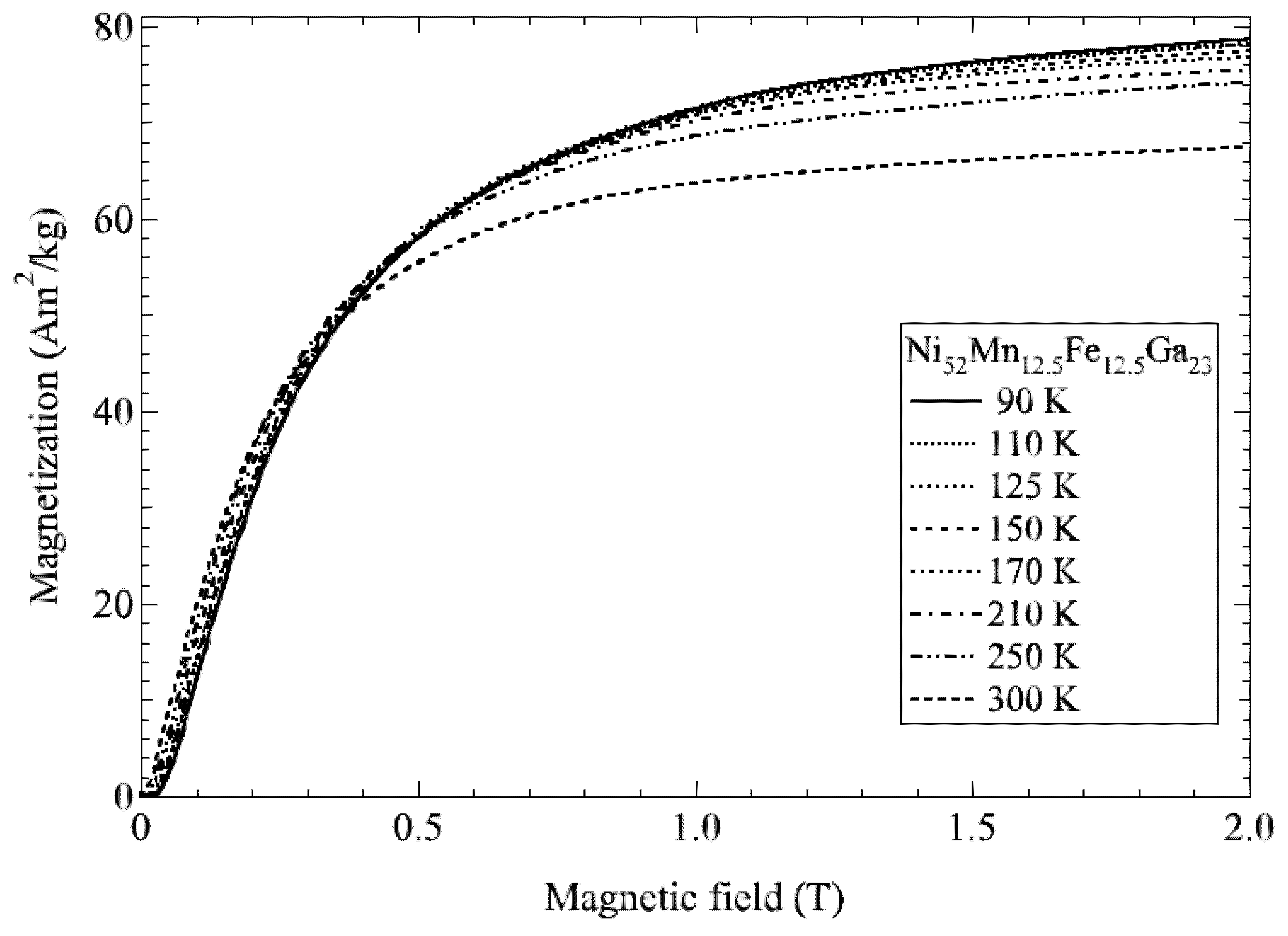
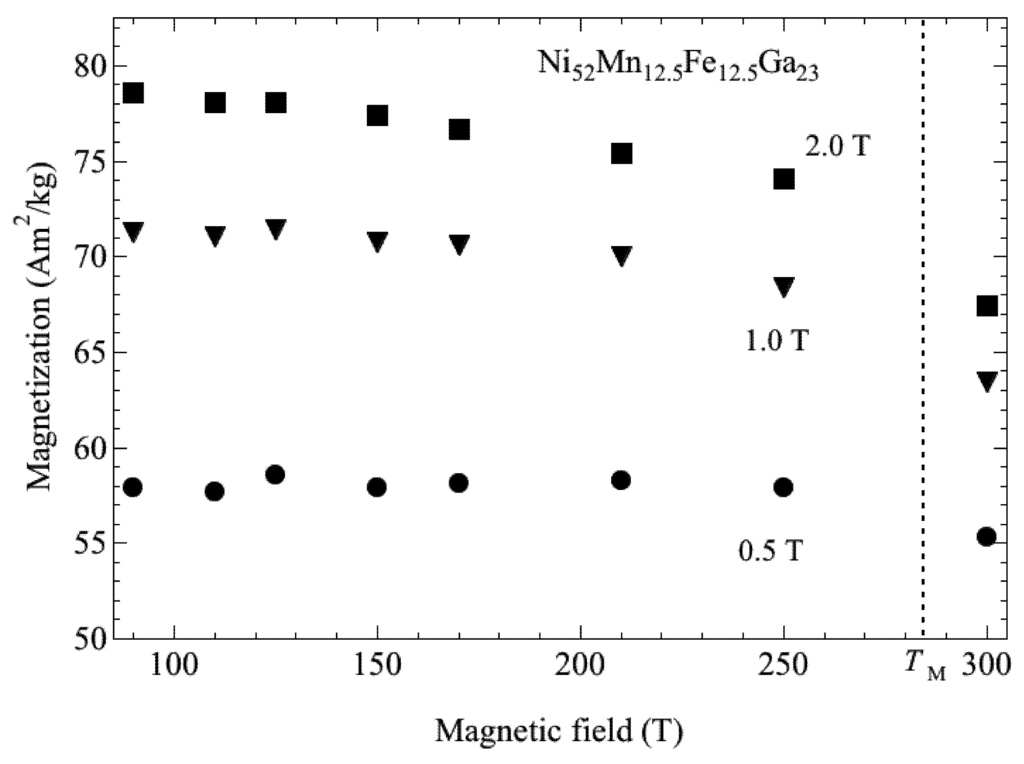
Figure 4.
The temperature dependence of the magnetization of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
Figure 4.
The temperature dependence of the magnetization of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23.
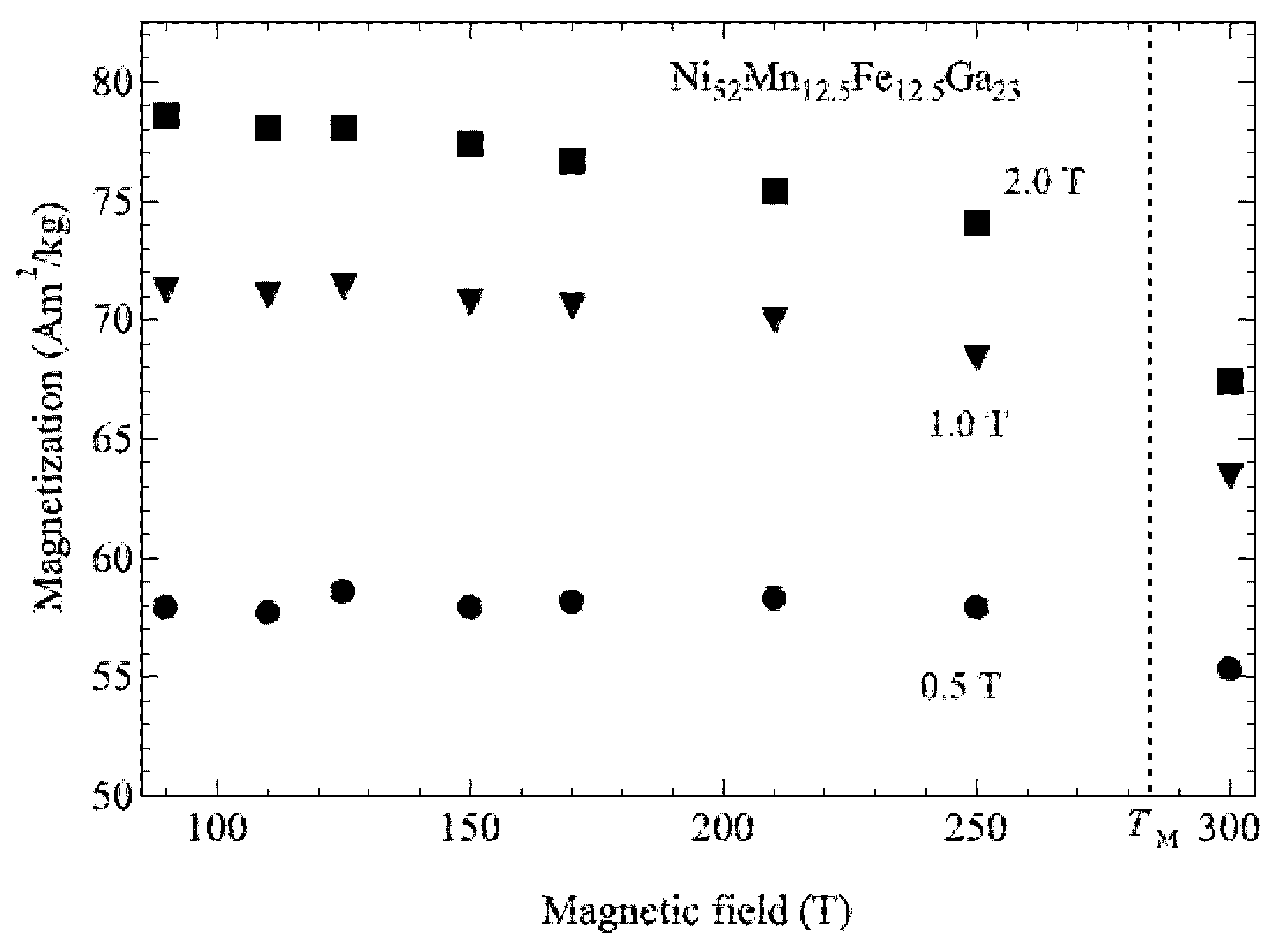
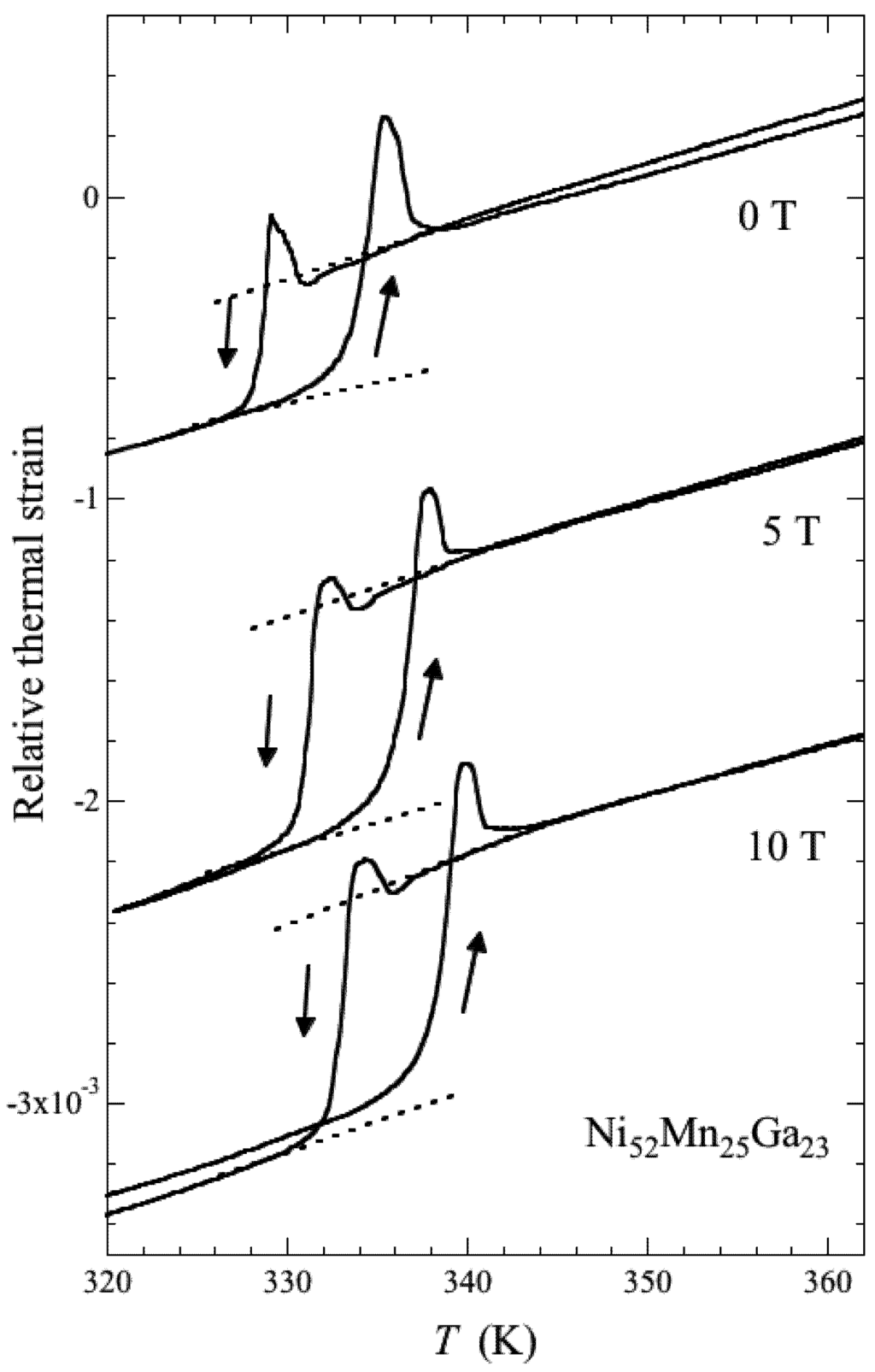
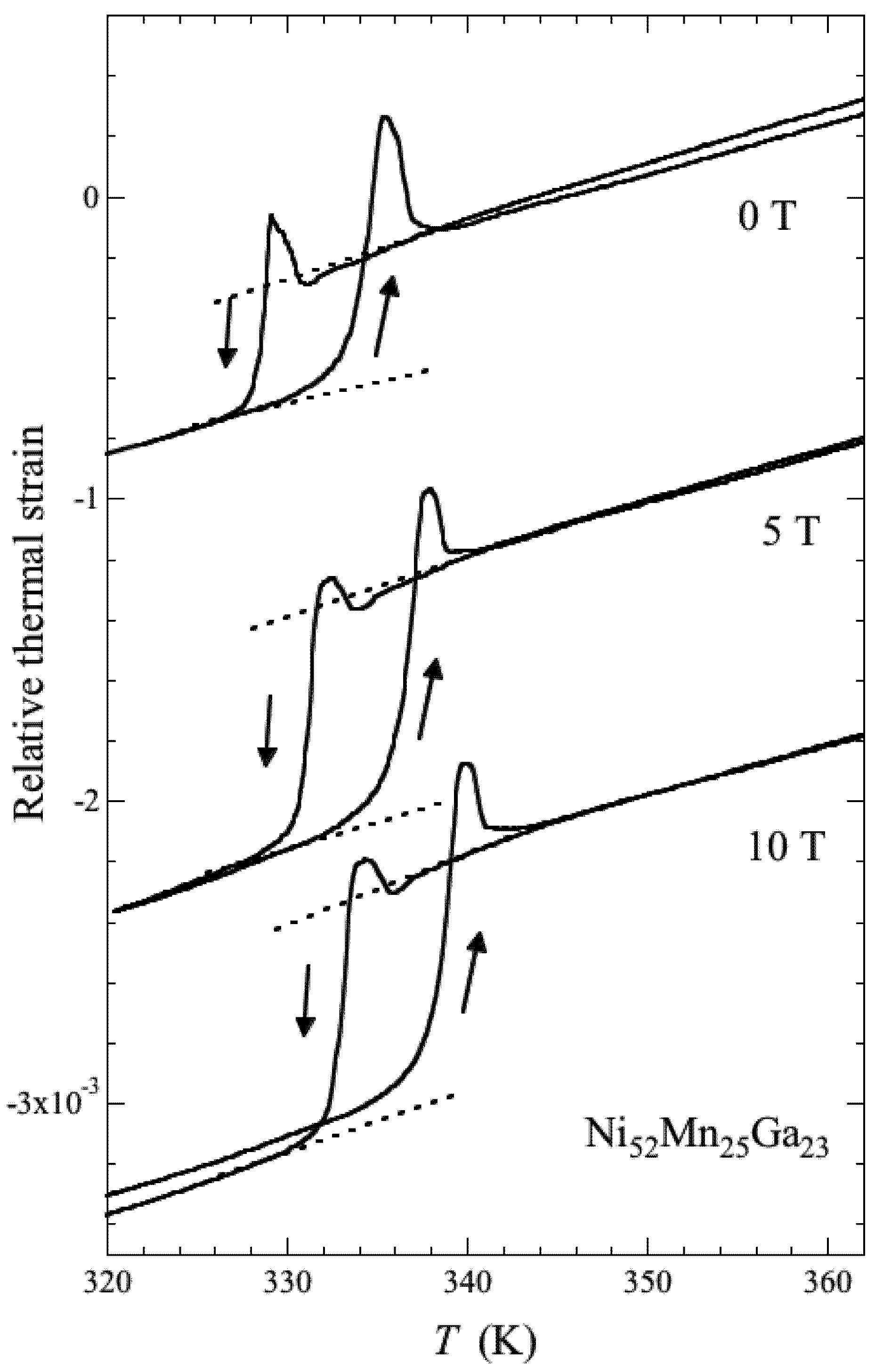
Figure 5.
The linear thermal strain of Ni52Mn25Ga23 along the applied magnetic fields.
Figure 5.
The linear thermal strain of Ni52Mn25Ga23 along the applied magnetic fields.
The difference of magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant KU between the value in the martensite phase and that in the austenite phase for a Ni2MnGa single crystal [1] indicates that the magnetocrystalline anisotropy is about four times larger in the martensite phase than the austenite phase. The Zeeman energy and/or magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy that is sufficient to induce motion of the twin boundary is denoted as MSBS/2 = KU [1], where, MS is the saturated magnetization and BS is the saturated magnetic field. Kim et al. [14] also mentioned that the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy is of the order of 105 J/m3. From the permeability and magnetization measurements, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant KU of Ni52Mn25Ga23 can be calculated [19]. Spontaneous magnetization is provided from the value that M2 intersects the y-axis in the Arrott plot (M2 vs. B/M plot) in order to obtain a spontaneous magnetization. Spontaneous magnetization in Ni52Mn25Ga23 at 333 K, just below TR, is 42.2 Am2/kg (=emu/g), which was obtained by the Arrott plot. When using this value as MS, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy in the martensite phase of Ni52Mn25Ga23 is MSBS/2 = KU = 1.04 × 105 J/m3, which is in the same order as the martensite phase of Ni2MnGa. These magnetic properties were also shown for Ni51.9Mn23.2Ga24.9 [11], Ni49.7Mn29.1Ga21.2 [12], and Ni54Mn21Ga25 [13]. These results are indicative of high magnetocrystalline anisotropy.
Straka et al. [22] performed a study on temperature dependence of magnetocrystalline anisotropy of three different martensites known to exist in the Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. The anisotropy constants were determined from magnetization curves measured at different temperatures. The anisotropy of Ni50.5Mn29.4Ga20.1 five-layered modulated tetragonal martensite single crystal is uniaxial with easy magnetization direction along the short crystallographic axis. At room temperature, K1 (rt) = 1.65 × 105 J/m3 and K2 is negligible, where coefficients K1 and K2 are correspondingly the first- and second-order anisotropy constants. Ni50.5Mn29.4Ga21.2 seven-layered modulated orthorhombic martensite single crystal exhibits easy magnetization direction along the shortest crystallographic axis. K1 (rt) = 1.7 × 105 J/m3 and K2 (rt) = 0.9 × 105 J/m3 referring to hard and mid-hard magnetization axes. Nonmodulated tetragonal martensite possesses a uniaxial anisotropy with easy plane and hard magnetization direction along the long crystallographic axis with K1 = −2.3 × 105 J/m3 and K2 = 0.55 × 105 J/m3 at room temperature. For uniaxial anisotropy, the temperature dependence of the first anisotropy constant K1 below Tc can be described by magnetization power law [23,24]:
where, Ms is the saturation magnetization. Co follows this power law with exponent n = 3. Fe follows with exponent n = 4 [25].
K1(T)/K1(0) = [Ms(T)/Ms(0)]n
The temperature dependence of K1 (T) follows magnetization power law with exponent n = 3 in Equation (1) suggesting a single ion origin of the magnetocrystalline anisotropy in Ni–Mn–Ga marten site. The temperature dependence of K1 and K2 does not follow power law with exponent n = 3; rather n is between two and three.
Okamoto et al. [26] measured the magnetizations of 10 M martensite in Ni2MnGa and 2 M martensite in Ni2.14Mn0.92Ga0.94 single crystals. As for Ni2MnGa, the magnetic easy axis is the c axis. On the contrary, the magnetic easy axis is the a axis for Ni2.14Mn0.92Ga0.94. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (Ku) of Ni2MnGa and Ni2.14Mn0.92Ga0.94 is 5.9 × 105 J/m3 and 4.3 × 105 J/m3, respectively. Concerning the magnetization power law, Equation (1), for Ni2MnGa and Ni2.14Mn0.92Ga0.94, it follows power law with exponent n = 3. The difference of the Ku between the Ni2MnGa alloys is presumed that the variant types in the martensite phase are different with each other.
The magnetocrystalline anisotropy of nonmodulated Ni–Mn–Ga alloy was investigated by Heczko et al. [27]. Five-layered modulated nearly tetragonal 5 M with c < a = b, seven layered orthorhombic 7M with c < b < a, and nonmodulated (NM) tetragonal phases with c > a = b. The absolute value of anisotropy constant of NM Ni50.5Mn30.4Ga19.1 single crystal increases from 2.6 × 105 J/m3 at 300 K to 5 × 105 J/m3 at 10 K under the tensile stress of 40 MPa. The obtained exponent in power law of Equation (1) is n = 2.5.
Now we compare the Ni–Mn–Ga alloys with 4f rare earth compounds and 5f uranium compounds, which have a highly magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The magnetization of Nd2Fe17 single crystal indicates that the c-axis is the hard axis and the b-axis is the easy one [28]. The magnetocrystalline anisotropy constants of the Nd-sublattice were estimated to be K1Nd = −5.7 × 107 J/m3and K2Nd = 2.6 × 107 J/m3. The temperature dependence of the second order magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant K2° in Equation (1) strayed out from the curve of power law with n = 3. The saturation magnetization is mainly dominated by the Fe-sublattice moment, where the magnetocrystalline anisotropy is strongly dominated by the Nd-sublattice anisotropy. The sharp drop of the anisotropy constant K2° is mainly due to the large thermal fluctuation of the magnetic moment of theNd-sublattice with temperature, compared with the Fe-sublattice.
As for 5f electron compound UGe2 single crystal [29], it has a highly magnetocrystalline anisotropy because the magnetization curves reflect the large magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant K1 = 3.4 kJ/kg. The density value ρ = 10.26 g/cm3 = 1.026 × 104 kg/m3 [30]. Then K1 = 3.4 × 103 J/kg × 1.026 × 104 kg/m3 = 3.5 × 107 J/m3. This value is comparable with that of K1Nd for Nd2Fe17 single crystal. The exponent n in Equation (1) is 1. This is smaller than n = 3. This analysis indicates that UGe2 retains magnetocrystalline anisotropy until high temperature.

Table 1.
Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant K and temperature dependence of K.
| Sample | Structural phase | K(104 J/m3) | Exponent n in Equation (1) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Bcc | 4.8 | 4 | [24] |
| Co | Hcp | 45 | 3 | [24] |
| αFe2O3 (hematite) | (32/m) | 120 | [24] | |
| Ni2MnGa | Martensite | 11.7 | single crystal [1] | |
| Ni2MnGa | L21austenite | 2.7 | single crystal [1] | |
| Ni2MnGa | 10M martensite | 59 | 3 | single crystal [26] |
| Ni2.14Mn0.92Ga0.94 | 2M martensite | 43 | 3 | single crystal [26] |
| Ni52Mn25Ga23 | 14M martensite | 10.4 | polycrystal [19] | |
| Ni50.5Mn30.4Ga19.1 | NM martensite | 26 (300 K) 50 (10K) | 2.5 | single crystal 40 MPa tensile stress [27] |
| Ni50.5Mn29.4Ga20.1 | 5M martensite | K1 16.5 K2 negligible | 2~3 | single crystal room temp. [22] |
| Ni50.5Mn29.4Ga21.2 | 7M martensite | K117 K29 | 2~3 | single crystal room temp. [22] |
| Nd2Fe17 | Rhombohedral Th2Zn17 | K1Nd = −5700 K2Nd = 2600 | Stray out from Equation (1) | single crystal 4.2 K [28] |
| UGe2 | Orthorhombic Cmmm ThGe2 | 3500 | 1 | single crystal 4.2 K [29] |
Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant K and the exponent of Equation (1) are summarized in Table 1. With an increase in constant K, the exponent n comes smaller. In strong correlated electron systems such as 4f or 5f electron compounds, which have highly anisotropic electron orbital, itinerant bands predominate the magnetic properties.
In the next section, we mention the theoretical studies about the phase diagram of Ni2MnGa type Heusler alloys considering the magnetocrystalline anisotropy [31].
2. Structural and Magnetic Properties in Magnetic Fields
In this section, we mention the substitution Fe, Cu, or Co atoms for Mn or Ga atoms in Ni2MnGa alloys.
Ni-Fe-Ga Heusler alloys are the new promising FSMAs for which TM varies from 150 K to room temperature and exhibits excellent ductility [32,33,34]. The Ni54Fe19Ga27 alloy transforms from high temperature L21 phase to the martensite phase having a monoclinic structure [33,34]. Kikuchi et al. [20] have reported the magnetic properties of Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x (0 ≤ x ≤ 5.5) ferromagnetic alloys, which were produced by replacing Ga with Ni in Ni50Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga25 alloy. The measurements of temperature dependence of magnetization for this series were performed [35]. It was observed that TC gradually decreases with the concentration x, while TM and the reverse martensitic transformation temperature TR increases with x and exhibits saturation behavior for x ≥ 3.0. The linear thermal expansion measurements of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 were performed in static magnetic fields. When cooling from 310 K (Ferro-A phase), the alloy shrinks gradually in zero magnetic fields. Small elongation was observed at 288 K. Then, sudden shrinking occurs below 286 K, which indicates transformation from the austenite to martensite phase. The TM of this alloy is 284 K. The reason of small elongation at 288 K is considered to be that L21 and 14M structures coexist each other. Therefore, apertures between L21 and 14M structures were originated and a small expansion occurred. As for Ni2+xMn1-xGa alloys, small elongation was observed just above TM [36]. The phase below TM is Ferro-M. When heating from 270 K, expansion occurs at about TR = 288 K, which indicates reverse martensitic transformation [20]. Small elongations just above the temperatures of TM and TR were also observed in polycrystal Ni2+xMn1−xGa (0.16 ≤ x ≤ 0.20) [36].
TM and TR gradually changed with increasing magnetic fields. The strain at TM and TR was about −2.5 × 10−3 (−0.25%) and was almost the same as that in magnetic fields. Kikuchi et al. [20] performed the X-ray diffraction experiments of Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x. The X-ray patterns at room temperature (T = 300 K, austenite phase) for the samples of 0 ≤ x ≤ 2.0 were indexed with the L21 Heusler structure. In the X-ray diffraction pattern at room temperature of the sample with x = 2.0, a very weak reflection from a γ phase was observed, where the γ phase has a disordered face-centered cubic (fcc) structure. The lattice parameter a of x = 2.0 was found to be 5.7927 Å [37]. On the other hand, the martensite phase appeared at room temperature. The martensitic structure of x = 3.0 was indexed as a monoclinic structure with 14 M (7R) structure. The lattice parameters of the sample were determined as a = 4.2495 Å, b = 2.7211 Å, c = 29.340 Å, and β = 93.36° at room temperature. We estimated the strain of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 (x = 2.0) at TM using the lattice parameter of x = 2.0 in the austenite phase and x = 3.0 in the martensite phase [35]. In the austenite phase, for the L21 cubic structure, the lattice parameter a was 5.7927 Å. The distance between Mn–Mn atoms was 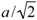 = 4.0961 Å, and the volume of the unit cell was VA = (a/√2)3 = (4.0961)3 = 68.72 Å3. Furthermore, the volume VM in the martensite phase was estimated and compared with VA in the same area. In the 14 M (7R) martensite phase, a = 4.2495 Å in the basal plane is parallel to one of the a axis in the L21 structure, and is of the same unit. The other axis in the martensite phase corresponds to one of the a axis in the L21 structure of the Mn–Mn ridge in the basal plane (
= 4.0961 Å, and the volume of the unit cell was VA = (a/√2)3 = (4.0961)3 = 68.72 Å3. Furthermore, the volume VM in the martensite phase was estimated and compared with VA in the same area. In the 14 M (7R) martensite phase, a = 4.2495 Å in the basal plane is parallel to one of the a axis in the L21 structure, and is of the same unit. The other axis in the martensite phase corresponds to one of the a axis in the L21 structure of the Mn–Mn ridge in the basal plane ( 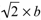 ). The c axis is almost normal (β = 93.36°) to the basal plane and the seven Mn–Mn cycles at c = 29.340 Å. Therefore, the volume,
). The c axis is almost normal (β = 93.36°) to the basal plane and the seven Mn–Mn cycles at c = 29.340 Å. Therefore, the volume,
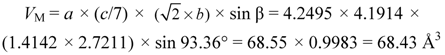
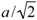 = 4.0961 Å, and the volume of the unit cell was VA = (a/√2)3 = (4.0961)3 = 68.72 Å3. Furthermore, the volume VM in the martensite phase was estimated and compared with VA in the same area. In the 14 M (7R) martensite phase, a = 4.2495 Å in the basal plane is parallel to one of the a axis in the L21 structure, and is of the same unit. The other axis in the martensite phase corresponds to one of the a axis in the L21 structure of the Mn–Mn ridge in the basal plane (
= 4.0961 Å, and the volume of the unit cell was VA = (a/√2)3 = (4.0961)3 = 68.72 Å3. Furthermore, the volume VM in the martensite phase was estimated and compared with VA in the same area. In the 14 M (7R) martensite phase, a = 4.2495 Å in the basal plane is parallel to one of the a axis in the L21 structure, and is of the same unit. The other axis in the martensite phase corresponds to one of the a axis in the L21 structure of the Mn–Mn ridge in the basal plane (  ). The c axis is almost normal (β = 93.36°) to the basal plane and the seven Mn–Mn cycles at c = 29.340 Å. Therefore, the volume,
). The c axis is almost normal (β = 93.36°) to the basal plane and the seven Mn–Mn cycles at c = 29.340 Å. Therefore, the volume,
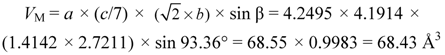
The linear strain of a polycrystal is one-third of the volume strain. Therefore, we estimate the linear strain Δε as,
Δε = {(VM − VA)/VA} × 1/3 = {(68.43 − 68.72)/68.72} × 1/3 = (−0.29/68.72) × 1/3 = −0.14%
This estimated value is approximately comparable to the strain value Δε = −0.25% of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 obtained from the experimental study in [35].
TM and TR gradually changed with increasing magnetic fields. The strain at TM and TR was about −2.5 × 10−3 (−0.25%) and was almost the same as that in magnetic fields. For Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23, the shifts of TM in magnetic fields (B) were estimated as dTM/dB ≈ 0.5 K/T from the thermal strain measurement results in magnetic fields. The shifts of TM indicate that magnetization influences martensite transformation and the increase of TM in accordance with the magnetic fields is proportional to the difference between the magnetization of the austenite phase with that of the martensitic phase.
Kataoka et al. [31] have reported the magnetic properties of Ni2Mn1-xCuxGa (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) alloys, which were obtained by replacing Mn with Cu in Ni2MnGa alloy. The samples with 0.23 ≤ x ≤ 0.30 show martensite transformation at about 300 K. The magnetic and crystal states above and below TM are the paramagnetic austenite phase (Para-A), and the ferromagnetic martensite phase (Ferro-M), respectively. Such Heusler alloys show martensitic transformation around room temperature. The temperature dependence of magnetic permeability and linear thermal expansion of Ni2Mn0.75Cu0.25Ga in zero magnetic fields, were performed [35]. When cooling from a high temperature in the parent austenite phase, it shrinks and the permeability increases at about TM = 308 K. The permeability at the austenite phase is very low compared to the martensite phase. These results indicate that the region above TM or TR is Para-A and the region below TM or TR is Ferro-M. When heating from a low temperature, the expansion occurs at about TR = 316 K, which indicates reverse martensitic transformation. The strain at TM or TR is about 3.0 × 10−3 (0.30%). Kataoka et al. [31] studied the X-ray powder diffraction of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40). The X-ray diffraction measurement of Ni2Mn0.75Cu0.25Ga indicates that the austenite phase is cubic L21 phase and the martensite phase is 14 M phase. From the temperature dependence of the linear thermal expansion of Ni2Mn0.75Cu0.25Ga in static magnetic fields, it was revealed that TM and TR gradually changed with increasing magnetic fields. The shifts of TM in magnetic fields (B) were estimated as dTM/dB = 1.2 K/T. The value is twice larger than that of Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23, which is mentioned above. The reason is that, for Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23, martensite transformation occurred in a ferromagnetic phase. On the contrary, magnetic transition and structural transition (martensite transformation) occurred at the same temperature. Magneto-structural phase transition largely influences the shifts of TM in magnetic fields.
Thermal expansion, permeability, and magnetization measurements of ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, Ni2MnGa0.88Cu0.12, were performed across TM and TR at atmospheric pressure [38]. When cooling from the austenite phase, a steep decrease was found in thermal expansion due to martensite transformation. The permeability indicates a sharp peak around TM and ferromagnetism below TM. Considering the permeability and magnetization results of Ni2MnGa0.88Cu0.12, the region above TM or TR is the Para-A phase and the region below TM or TR is the Ferro-M phase. TM and TR increased gradually with increasing magnetic field. The shift of TM in magnetic fields around zero magnetic fields were estimated as dTM/dB = 1.3 K/T. The shift of TM also indicates that magnetization influences martensite transformation and the increase of TM in accordance with the magnetic fields is proportional to the difference between the magnetization of austenite and martensite phases.
Albertini et al. [39] investigated the composition dependence of the structural and magnetic properties of the Co-doped Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloy around the Mn-rich composition Ni50Mn30Ga20. The magnetic and structural properties displayed noticeable discontinuities across the martensite transformation; there was a remarkable jump (ΔM) in the values of the saturation magnetization at the transformation, which indicates that a metamagnetic transition occurred under the magnetic field. The field dependence of the martensite transformation temperature (dTM/dB) and that of the crystalline volume change (ΔV/V) was reported and found to be considerably enhanced by the additional In-doping of the quaternary alloy. The most remarkable alloy is Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18 [39]. When cooling from 500 K, it shows a ferromagnetic transition at TCA = 456 K in the austenite phase. At the martensite transformation temperature, TM = 420 K, its AC susceptibility drastically decreased. Below 300 K, its AC susceptibility gradually increased and a distinct peak was found at TCM = 257 K in the martensitic phase. When heating from 200 K, the Curie temperatures TCM and TCA were the same as the temperatures in the cooling process. The reverse martensitic temperature TR was 436 K. Thus, AC susceptibility indicates re-entrant magnetism, ferromagnetic-paramagnetic, or weak ferromagnetic-ferromagnetic states, which may be related to the crystal structures. Thermal strain, magnetostriction, and magnetization measurements of the polycrystal ferromagnetic shape memory alloy, Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5, were performed across TM and TR, at atmospheric pressure [40]. The AC susceptibility also indicates re-entrant magnetism. The isothermal magnetization curve (M vs. B) shows S-shape metamagnetic transition between 320 K and 390 K. Strong magneto-structural coupling was indicated by the magnetic properties and phase transitions. When cooling from the austenite phase, a steep decrease in the thermal expansion due to the martensite transformation at TM was found. When heating from the martensitic phase, a steep increase in the thermal expansion due to the reverse martensite transformation at TR was observed. These transition temperatures decreased gradually with increasing magnetic field. The field dependence of the martensite transformation temperature, dTM/dB, is −4.2 K/T and that of the reverse martensite transformation temperature, dTR/dB, is −7.9 K/T in Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5. The metamagnetic transition appeared between 330 K and 390 K. The results of thermal strain and magnetization indicate that a magneto-structural transition occurred at TM. Ni50−xCoxMn31.5Ga18.5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 9) was also investigated across the martensite transformation temperature TM and the reverse martensite transformation temperature TR at atmospheric pressure [41]. By means of X-ray powder diffraction, the samples were confirmed as a single phase with D022 tetragonal structure at 298 K in the martensite phase. These transition temperatures increased gradually with increasing Co component x. Moreover, temperature hysteresis in the thermal cycles of the magnetization across the TR and TM became larger with the increasing of x. Wide temperature hysteresis of TM − TR = −65 K at zero fields was observed in the thermal strain measurement.

Table 2.
Spontaneous magnetization and dTM/dB in Heusler Ni2MnGa type magnetic shape memory alloys. MM and MA indicate the spontaneous magnetizations in the martensite phase and austenite phase, respectively. Ferro and Para mean the ferromagnetic and the paramagnetic phases, respectively. TCM indicates the Curie temperature in the martensite phase, and TCA indicates the Curie temperature in the austenite phase.
| Sample | MM | MA | (MM − MA)/MM | dTM/dB(K/T) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni2MnGa | 90 Am2/kg at 180 K (*1) Ferro | 80 Am2/kg at 220 K (*1) Ferro | 0.11 | 0.20 (*2) 0.40 ± 0.25 (*3) | *1 [2] *2 [25] *3 [26] |
| Ni2.19Mn0.81Ga | 2.0 (a.u.) (*4) at 300 K Ferro | 0 (a.u.) (*4) at 350 K Para | 1.0 | 1.0 (*4) | *4 [28] |
| Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 | 63.1 Am2/kg at 250 K Ferro | 52.7 Am2/kg at 300 K Ferro | 0.16 | 0.5 | [20] |
| Ni2Mn0.75Cu0.25Ga | 42.4 Am2/kg at 300 K Ferro | 0 Am2/kg at 307 K Para | 1.0 | 1.2 | [20] |
| Ni2MnGa0.88Cu0.12 | 37.3 Am2/kg at 330 K Ferro | 0 Am2/kg at 340 K Para | 1.0 | 1.3 | [29] |
| Ni52Mn25Ga23 | 42.2 Am2/kg at 333 K Ferro | 34.2 Am2/kg at 335 K Ferro | 0.19 | 0.43 | [19] |
| Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 | 0 Am2/kg at 270 K Para | 70 Am2/kg at 320 K Ferro | −1.0 | −4.3 | [42] |
| Ni43Co7Mn31Ga19 | 20 Am2/kg at TCM ≤ T ≤ TM Para or weak Ferro | 59.2 Am2/kg at TM ≤ T ≤ TCA Ferro | −0.64 | −2.95 | [39] |
| Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18 | 4.0 Am2/kg at TCM ≤ T ≤ TM Para or weak Ferro | 53.3 Am2/kg at TM ≤ T ≤ TCA Ferro | −0.92 | −2.8 | [39] |
| Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 | 12 Am2/kg at TCM ≤ T = 316 K ≤ TM Para or weak Ferro | 79 Am2/kg at TM ≤ T = 388 K ≤ TCA Ferro | −0.84 | −4.2 | [40] |
Single crystal Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 (13.3 In), which was studied by Kainuma et al. [42], also shows the re-entrant ferromagnetic property. The TM and TR decreased with the increasing of magnetic fields. The thermo-magnetization curve (M vs. T) indicates that the decrease of TM, ΔTM from 0.05 T to 7.0 T is about 30 K. Large hysteresis was shown in the thermo-magnetization curve. Monroe et al. [43] suggested that Kinetic Arrest effect phenomenon appeared in Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys. The magnetic field change of the TM, dTM/dB, is −4.3 K/T. The isothermal magnetization curve (M vs. B) shows S-shape metamagnetic transition between 270 K and 310 K [42,44].
Spontaneous magnetizations at the martensite phase MM and the austenite phase MA are shown in Table 2. The dTM/dB is also shown. It is clear that the dTM/dB of the alloys of which magnetic transition and martensite transiton occurs at almost the same temperature are large. Some Ni-Co-Mn-Ga and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys indicate minus dTM/dB values, which indicate the re-entrant magnetism. These results indicate that the magneto-structural interactions are large in the alloys, which have large dTM/dB values.
The change in transition temperature (ΔT) induced by a change in magnetic field (ΔB) is approximately given by the Clausius–Clapeyron relation in the magnetic phase diagram as
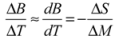 where ΔM and ΔS are the differences in magnetization and entropy change between the austenite and martensitic phases, respectively [42,45]. From the experimental results in this study, dTR/dB is determined as −7.9 K/T in Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18. Therefore, dB/dTR is −0.13 T/K. The entropy change, ΔS, obtained from the DSC measurement is 7.3 J/kg K. From the magnetization results, ΔM is 40 Am2/kg, and then, −ΔS/ΔM = dB/dT is −0.18 T/K, given by Equation (2). However, the measured dTR/dB = −0.13 K/T is 30% smaller than the calculated value. The latent heat of the martensite transformation is not small. Therefore, the ambiguity for the value of ΔS is large, thereby giving rise to the large ambiguity present in this calculation.
where ΔM and ΔS are the differences in magnetization and entropy change between the austenite and martensitic phases, respectively [42,45]. From the experimental results in this study, dTR/dB is determined as −7.9 K/T in Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18. Therefore, dB/dTR is −0.13 T/K. The entropy change, ΔS, obtained from the DSC measurement is 7.3 J/kg K. From the magnetization results, ΔM is 40 Am2/kg, and then, −ΔS/ΔM = dB/dT is −0.18 T/K, given by Equation (2). However, the measured dTR/dB = −0.13 K/T is 30% smaller than the calculated value. The latent heat of the martensite transformation is not small. Therefore, the ambiguity for the value of ΔS is large, thereby giving rise to the large ambiguity present in this calculation.
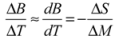
Satyanarayan et al. [46] and Nishiyama [47] mentioned the relation between free energy and TM or TR in magnetic fields. It is well known that the TM of Iron steels increase with increasing magnetic fields. The dTM/dB is about few K/T. The increase of the martensite α' phase is a few percent for 1 T field increase. In usual Iron steels, γ phase is the nonmagnetic phase and α' phase is the ferromagnetic phase.
The free energy of α' phase is lower in magnetic fields and then, the percentage of α' phase increases. This is because the free energy lowers due to Zeeman energy in ferromagnetic α' phase. Figure 6 shows the temperature and magnetic field dependence of Gibbs’s free energy. In zero fields, the martensite transformation occurs at the TM, where the motive force ΔF is equal to the difference of the free energy between the martensite α' phase and γ phase. In magnetic fields, the free energy of α' phase is lowered due to the Zeeman energy magnetic energy ΔE. Consequently, the TM increases, as shown in Figure 6(a). The relation between ΔF,ΔE, TM, and ΔT, the temperature change of TM, is,
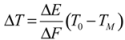 where,
where, 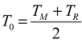 .
.
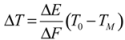
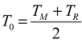 .
.In some Iron steels, experimental results and calculated results obtained by Equation (3) are almost the same [46]. This approach could be applicable to ferromagnetic Heusler alloys Ni2MnGa and Ni2+xMn1−xGa.
Meanwhile, the TM of Ni-Co-Mn-Ga and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys decreases with increasing magnetic fields, as shown in Figure 6(b). The phase just below the TM of these alloys is the martensite paramagnetic (or weak ferromagnetic) phase and the phase just above the TM is the ferromagnetic austenite phase. In magnetic fields, the free energy of the austenite phase lowers and the percentage of the austenite increases due to Zeeman energy. Consequently, in the magnetic B-T phase diagram, the domain of the austenite phase increases and the TM decreases.
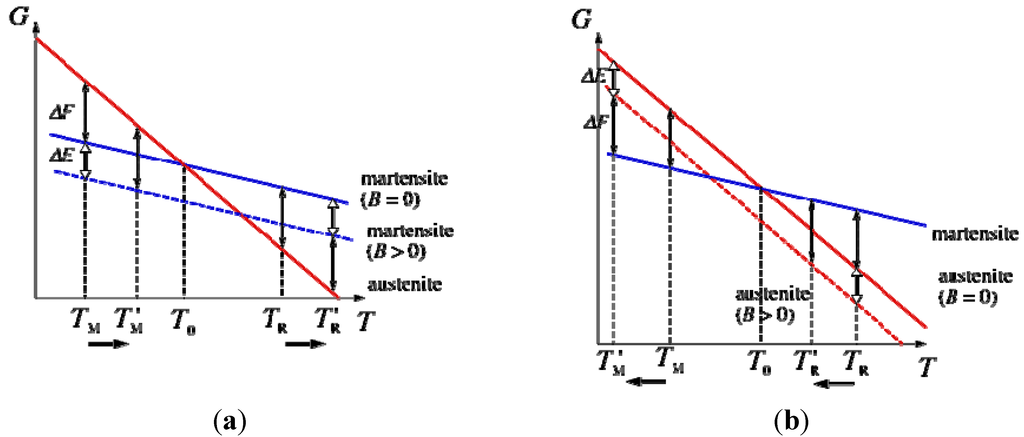
Figure 6.
Temperature and magnetic field dependence of Gibbs’s free energy. (a) The diagram when the martensite phase is ferromagnetic and the austenite phase is paramagnetic. ΔF and ΔE indicate the motive force for inducing a martensite transition, and the Zeeman energy, respectively. Dashed bold line indicates the free energy under the magnetic field at the martensite phase. (b) The diagram when the martensite phase is paramagnetic and the austenite phase is ferromagnetic. Dashed bold line indicates the free energy under the magnetic field at the austenite phase.
Figure 6.
Temperature and magnetic field dependence of Gibbs’s free energy. (a) The diagram when the martensite phase is ferromagnetic and the austenite phase is paramagnetic. ΔF and ΔE indicate the motive force for inducing a martensite transition, and the Zeeman energy, respectively. Dashed bold line indicates the free energy under the magnetic field at the martensite phase. (b) The diagram when the martensite phase is paramagnetic and the austenite phase is ferromagnetic. Dashed bold line indicates the free energy under the magnetic field at the austenite phase.
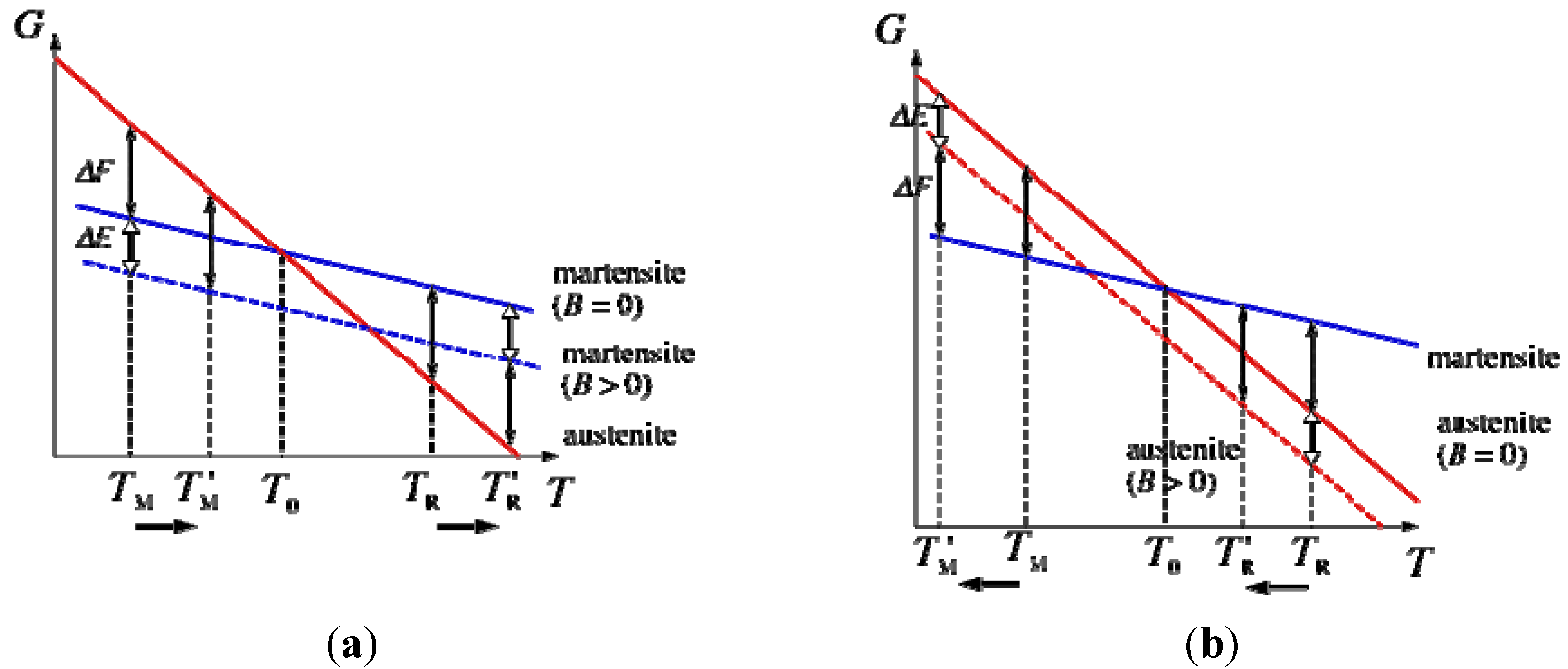
Now we apply Equation (3) to Ni41Co9Mn32Ga18. TM = 315 K, TR = 380 K, To = 348 K at zero fields. ΔT = To −TM = 33 K. ΔEm= MB = 100 J/kgT (at 8 T) × 8 T = 800 J/kg. [J/kg] = [emu/g] = [Am2/kg]. From the DSC measurement, ΔF = 1.0 kJ/kg. Then, ΔT =  K for ΔB = 8 T. ΔT/ΔB = 3.3 K/T decrease. The difference between the experimental value of dTM/dB is −4.2 K/T and the calculated value is supposed to the latent heat of the first order martensite transformation.
K for ΔB = 8 T. ΔT/ΔB = 3.3 K/T decrease. The difference between the experimental value of dTM/dB is −4.2 K/T and the calculated value is supposed to the latent heat of the first order martensite transformation.
 K for ΔB = 8 T. ΔT/ΔB = 3.3 K/T decrease. The difference between the experimental value of dTM/dB is −4.2 K/T and the calculated value is supposed to the latent heat of the first order martensite transformation.
K for ΔB = 8 T. ΔT/ΔB = 3.3 K/T decrease. The difference between the experimental value of dTM/dB is −4.2 K/T and the calculated value is supposed to the latent heat of the first order martensite transformation.Kataoka et al., studied about the martensite transformation and ferromagnetic transition of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) [31] and Ni2MnGa1−yCuy (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) [48] alloys and made x − T, or y − T phase diagrams. They suggested that the characteristics of the phase diagrams are very similar to those of Ni2+x Mn1−xGa (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) alloys [49]. Kataoka et al. [31] explained the phase diagram of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) alloys using the Landau-type phenomenological free energy as a function of the martensitic distortion and magnetization. Their analysis showed that the bi-quadratic coupling term, together with a higher order term, of the martensitic distortion and magnetization plays an important role in the interplay between the martensite phase and the ferromagnetic phase. Their calculation based on the phenomenological free energy is shown as
where, Ftot is the total free energy, Fela the free energy of the elastic strain eij, Fmag the free energy of the magnetic system including the magnetic exchange energy and the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy, and Fmag-ela the energy of the interaction between the distortion and the magnetization. The calculated x – T phase diagram of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa agrees well with the phase diagram, which was obtained from the experimental results. In addition, they suggested that the bi-quadratic term, 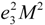 , in Fmag-ela affects the large magneto-structural coupling. Thus, strong magneto-structural coupling was displayed to play an important role in the magnetic properties and phase transitions of FSMAs. In the last part of Section 1, we mentioned about the magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The large magnetocrystalline anisotropy influences the magneto-elastic coupling Fmag-ela by means of the bi-quadratic term,
, in Fmag-ela affects the large magneto-structural coupling. Thus, strong magneto-structural coupling was displayed to play an important role in the magnetic properties and phase transitions of FSMAs. In the last part of Section 1, we mentioned about the magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The large magnetocrystalline anisotropy influences the magneto-elastic coupling Fmag-ela by means of the bi-quadratic term, 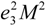 . In Ni50−xCoxMn31.5Ga18.5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 9), magnetization M increases with the magnetic field between 338 K and 388 K [41]. The thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain also decreases at high magnetic fields. Other Heusler compounds such as Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x, show an x–T phase diagram similar to that of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa [20]. In comparison with the experimental results of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 and Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa, it is considered that the thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain that decreases with increasing magnetic field is an indication of strong magneto-structural coupling in Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5. The magnetic field-induced strain in single crystal, or magnetostriction in polycrystal in Ni2MnGa, Ni-Co-Mn-Ga, and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys also suggest a strong magneto-structural coupling. In the next section, we will mention the magnetic field-induced strains of the magnetic shape memory alloys.
. In Ni50−xCoxMn31.5Ga18.5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 9), magnetization M increases with the magnetic field between 338 K and 388 K [41]. The thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain also decreases at high magnetic fields. Other Heusler compounds such as Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x, show an x–T phase diagram similar to that of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa [20]. In comparison with the experimental results of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 and Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa, it is considered that the thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain that decreases with increasing magnetic field is an indication of strong magneto-structural coupling in Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5. The magnetic field-induced strain in single crystal, or magnetostriction in polycrystal in Ni2MnGa, Ni-Co-Mn-Ga, and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys also suggest a strong magneto-structural coupling. In the next section, we will mention the magnetic field-induced strains of the magnetic shape memory alloys.
Ftot = Fela + Fmag + Fmag-ela
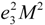 , in Fmag-ela affects the large magneto-structural coupling. Thus, strong magneto-structural coupling was displayed to play an important role in the magnetic properties and phase transitions of FSMAs. In the last part of Section 1, we mentioned about the magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The large magnetocrystalline anisotropy influences the magneto-elastic coupling Fmag-ela by means of the bi-quadratic term,
, in Fmag-ela affects the large magneto-structural coupling. Thus, strong magneto-structural coupling was displayed to play an important role in the magnetic properties and phase transitions of FSMAs. In the last part of Section 1, we mentioned about the magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The large magnetocrystalline anisotropy influences the magneto-elastic coupling Fmag-ela by means of the bi-quadratic term, 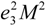 . In Ni50−xCoxMn31.5Ga18.5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 9), magnetization M increases with the magnetic field between 338 K and 388 K [41]. The thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain also decreases at high magnetic fields. Other Heusler compounds such as Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x, show an x–T phase diagram similar to that of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa [20]. In comparison with the experimental results of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 and Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa, it is considered that the thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain that decreases with increasing magnetic field is an indication of strong magneto-structural coupling in Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5. The magnetic field-induced strain in single crystal, or magnetostriction in polycrystal in Ni2MnGa, Ni-Co-Mn-Ga, and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys also suggest a strong magneto-structural coupling. In the next section, we will mention the magnetic field-induced strains of the magnetic shape memory alloys.
. In Ni50−xCoxMn31.5Ga18.5 (0 ≤ x ≤ 9), magnetization M increases with the magnetic field between 338 K and 388 K [41]. The thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain also decreases at high magnetic fields. Other Heusler compounds such as Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x, show an x–T phase diagram similar to that of Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa [20]. In comparison with the experimental results of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 and Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa, it is considered that the thermal hysteresis of the thermal strain that decreases with increasing magnetic field is an indication of strong magneto-structural coupling in Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5. The magnetic field-induced strain in single crystal, or magnetostriction in polycrystal in Ni2MnGa, Ni-Co-Mn-Ga, and Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys also suggest a strong magneto-structural coupling. In the next section, we will mention the magnetic field-induced strains of the magnetic shape memory alloys.3. Magnetic Field-Induced Strain and Magnetostriction in Shape Memory Alloys
Large magnetic field-induced strains (MFISs) have been observed in several Heusler single crystal alloys. These materials based on a Ni2MnGa alloys have been characterized on the basis of the rearrangement of martensitic structural variants due to an external field [1,50,51]. MFISs of 6.0% have been produced at room temperature in single crystals of Ni49.8Mn28.5Ga21.7 (TM = 318 K) by application of fields of order 400 kA/m (=0.50 T) under an opposing stress of order 1 MPa [52]. The strain is the result of field-induced twin boundary motion. A disordered Fe-31.2%Pd (at.%) alloy (A1-type cubic) [53,54], and an ordered Fe3Pt (L12-type cubic) ferromagnetic alloy [55,56], have attracted considerable interest due to the large MFISs. The Ni-Mn-Ga, Fe-Pd, and Fe-Pt alloy shave attracted considerable attention as materials for magnetic actuators. Recently, MFIS experiments at an AC magnetic field or pulse magnetic field have been carried out and the dynamical MFIS response of the Ni-Mn-Ga alloy has been reported by Henry et al. [57]. The 3% MFIS of FSMA Ni49.8Mn28.5Ga21.7 at uniaxial bias stress of 1.6 MPa and an AC magnetic field of 2 Hz has been observed at the AC fields of 6 kOe. Even at a faster AC field, a strain of 2.5% at 150 Hz and a strain of 0.6% at 332 Hz have been observed. On the other hand, the MFISs without a bias stress have been observed in the Fe-Pd and Fe-Pt alloys. As for a Fe-31.2%Pd (at.%) single crystal alloy, a strain of 0.4% has been observed in single-shot pulse fields at the fields of 12 kOe with a frequency of 80 Hz at 77 K, which is much lower than the martensite transformation temperature TM = 230 K [58]. With regard to the Fe3Pt single crystal alloy, an MFIS of 1.7% has been observed and a recoverable strain of about 0.6% has been induced in single-shot pulse fields at the fields of 20 kOe with a frequency of 160 Hz at 4.2 K in the martensite state (TM = 85 K) [59].
New alloys in the Ni-Mn-In, Ni-Mn-Sn, and Ni-Mn-Sb Heusler alloy systems, which are ferromagnetic shape memory alloys, have been studied by a Tohoku University group of researchers [60]. These alloys indicate a very small magnetization in the martensite phase compared to the parent phase. Oikawa et al. [61] studied the magnetic and martensite transformation behaviors of a Ni46Mn41In13 alloy through various techniques, such as scanning calorimetry and vibrating sample magnetometry. A metamagnetic transition from the paramagnetic martensite phase to the ferromagnetic austenite phase was detected and a magnetic field-induced reverse martensite transformation was confirmed in a high magnetic field. This alloy is a metamagnetic shape memory alloy with a magnetic field-induced shape memory effect and is used as a magnetocaloric material. Ni-Co-Mn-In alloys, in which Co is added to Ni-Mn-In to increase Curie temperature, show a basic shape memory behavior in a compression stress-strain measurement. As for Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 (13.3In), which was mentioned in Section 2, a large MFIS has been observed [42]. After a compression prestrain of about 3% was applied to the 13.3In alloy, the steady magnetic field was applied parallel to the compression axis of the sample. The MFIS was measured by a three-terminal capacitance method. The expansion of 3% was observed at around 35 kOe, indicating an almost complete shape recovery induced by a magnetic field. Using this expansion, a stress of about 100 MPa was generated in the material on the application of a magnetic field. This stress level is about 50-fold higher than those of other shape memory alloys.
Polycrystal samples are better for magnetostriction measurements as MFIS is hindered by the grain boundaries [62]. Therefore, the realistic magnitude of the magnetostriction can be observed. Barandiarán et al. [62] observed the magnetostriction in polycrystal Ni51.1Mn24.9Ga24.0. The sign of the longitudinal magnetostriction is negative and the magnitude is 100 ppm or smaller. The magnitude of the longitudinal magnetostriction at 1.5 T is −67 ppm at 180 K. The minus sign indicates the contraction. They mentioned that the observed behavior can only be understood if the short easy axes of tetragonal martensitic lattice (c-axis) are preferably aligned perpendicularly to the slab plane.
Sakon et al. [19] measured the strain for polycrystal Ni52Mn25Ga23. At zero magnetic field, the strain is 3.6 × 10−4 (Figure 5). On the other hand, the strain in a magnetic field is about 7.1 × 10−4, which is almost twice that in zero field. Ullakko et al. [1] measured the magnetic field-induced strain of a Ni2MnGa single crystal. The strain at TM in zero field was 2 × 10−4. This is only a small fraction compared to the lattice constant change for c-axis from the austenite to martensite phase, which was Δc/c = 6.56%. It is proposed that the strain accommodation occurs by different twin variant orientations. On the contrary, the thermal strain under the magnetic field of 5 T at 300 K in the ferromagnetic martensite phase was 720 ppm, indicating that the field aligned some of the twin variants. The magnetostriction at 300 K in the ferromagnetic martensite phase at 10 T is −100 ppm [19].
We discuss the difference of the driving forces of the variant rearrangements in two cases. One is martensitic transformation, shown in Figure 5, and the other is magnetostriction [19]. In the former case, the driving force is originated from phase transformation. Therefore, the magnitude is great and, as a consequence, the phase-induced variant rearrangements are easy and occur throughout the sample. For the latter case, the magnetic field-induced twin boundary motion is driven by the limited magnetic anisotropy energy, which is lower than the martensitic phase transformation driving force. Consequently, the variant orientation is limited by the mobile twin boundaries that are not pinned by any obstacles such as grain boundaries or defects. As a result, the variant rearrangement and magnetostriction are limited. Therefore, the magnetostriction is smaller than the strain at TM in the linear strain measurements. The magnetostriction of the polycrystalline Ni50Mn28Ga22 alloy was reported by Murray et al. [18]. They mentioned that the strain in the martensite phase below TM is an order of magnitude smaller than that of a single crystal of the stoichiometric compounds [1]. They attributed this to the polycrystalline nature of the material or to the presence of impurities that impede twin boundary motion. The field-induced strain of Ni50Mn28Ga22 increases on cooling from the austenite phase, leading to an abrupt increase with the appearance of the twin variant below TM. On heating from the martensite phase, an abrupt increase occurs in the field-induced strain around TM. They suggest that this is caused by lattice softening near TM. As for the thermal strain of Ni52Mn25Ga23, shown in Figure 5, peaks appear for both TM and TR in zero field and all values of the magnetic field. The peak at TR, associated with heating, is larger than that at TM, associated with cooling. These peaks indicate that the lattice expands abruptly. Dai et al. [21] studied the elastic constants of a Ni0.50Mn0.284Ga0.216 single crystal using the ultrasonic continuous-wave method. C11, C33, C66, and C44 modes were investigated; every mode indicated abrupt softening around TM. This lattice softening appears to be affected by the abrupt expansion just above TM when cooling from the austenite phase. Barandiarán et al. [62] also suggest that physical reason of large variations at the martensite transformation temperatures is the lattice softening.
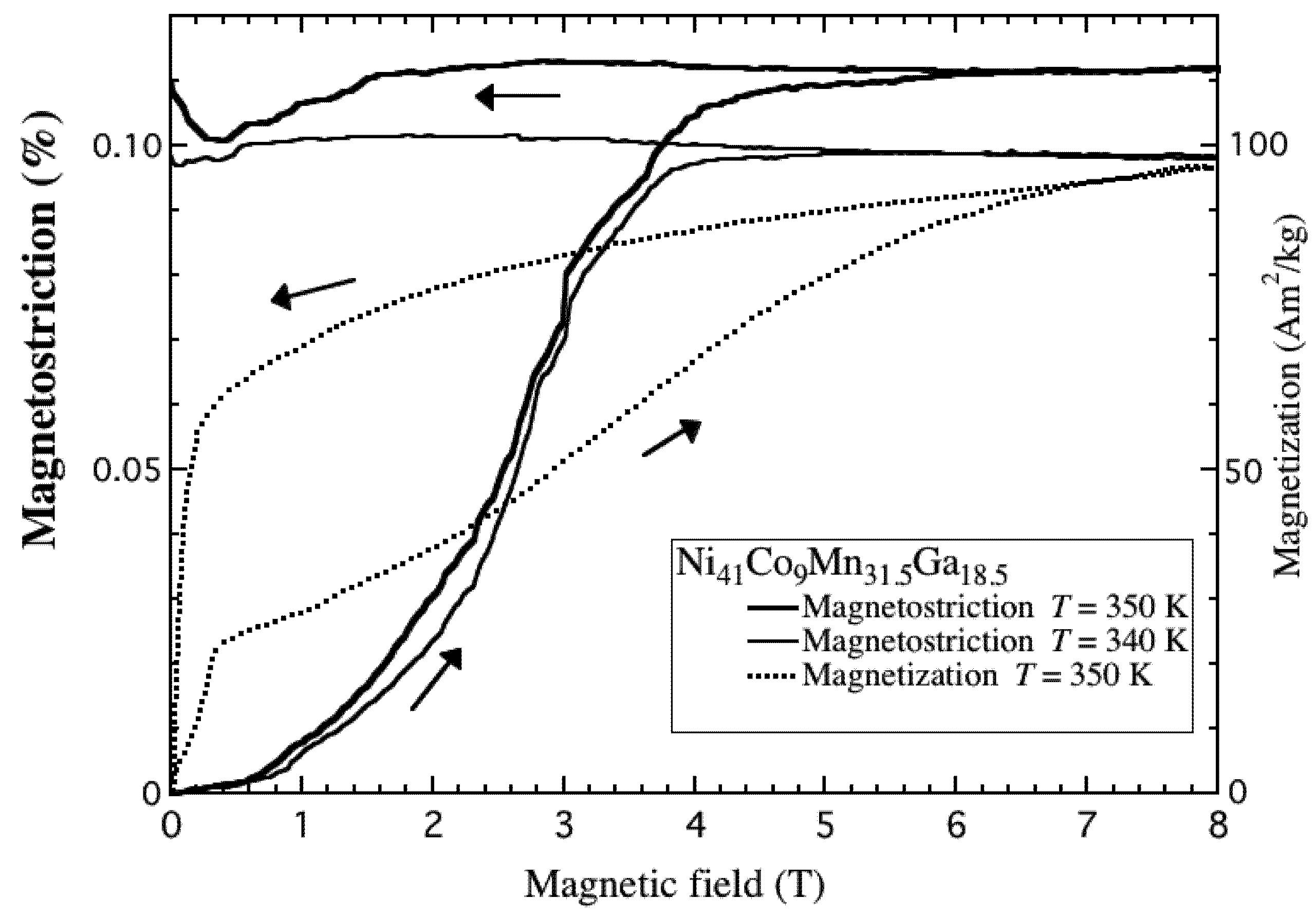
Now, we describe Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 alloy, where the martensitic transformation and magnetic transition occur at the same temperature, TM. Polycrystal Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 shows the magnetostriction in steady magnetic fields [40]. When increasing the magnetic field, distinct magnetostriction was observed at the temperatures between TM and TR. The magnetic field dependences of magnetostriction and magnetization are shown in Figure 7. These measurements were performed after zero fields cooling to the temperature of 300 K in the paramagnetic martensite phase. The magnetization shows metamagnetic transition. The magnetostriction was also observed at the same temperature, 350 K. The metamagnetism and magnetostriction are due to the magnetic field-induced magnetic transition and martensite transformation from the paramagnetic martensite phase to the ferromagnetic austenite phase. The magnitude of the magnetostriction was 1.1 × 10−3 (0.11%) at maximum between 320 K and 360 K, which was approximately the same value as that of the thermal strain for the reverse martensite transformation. The magnitude of the magnetostriction of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 is 10 times larger than that of Ni52Mn25Ga23. As for Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5, the metamagnetic transition and martensite transformation occurs simultaneously. Therefore, the magnitude is larger than the alloys, in which martensite transformation occurs in a ferromagnetic phase.
Previous MFIS measurements performed for 13.3In were under a compressive pre-strain of 100 MPa. However, the magnetostriction measurements in this study were performed under atmospheric pressure and without the compression pre-strain. The M-B curves and the thermal strain suggest that the magneto-structural transition of Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 alloy is sensitive to magnetic fields. The magnitude of the magnetic field strains and the magnetostrictions of the magnetic shape memory alloys are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The magnetic field induced strains and the magnetostrictions of shape memory alloys.
| Sample | Crystal structure | crystalline | Magnitude | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni49.8Mn28.5Ga21.7 | Fm3m | Single | 6.0% at 300 K under 1 MPa | [52] |
| Fe-31.2%Pd (at.%) | Disordered A1 | Single | 3.0% at 4.2 K | [53,54] |
| Fe3Pt | L12 | Single | 2.3% at 4.2 K | [55,56] |
| Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 | 14M | Single | 3.0% at 298 K | [42] |
| Ni51.1Mn24.9Ga24.0 | D022 | Poly | −67 ppm at 180 K | [62] |
| Ni52Mn25Ga23 | 14M | Poly | −100 ppm at 300 K | [19] |
| Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 | D022 | Poly | 0.11% at 350 K | [40] |
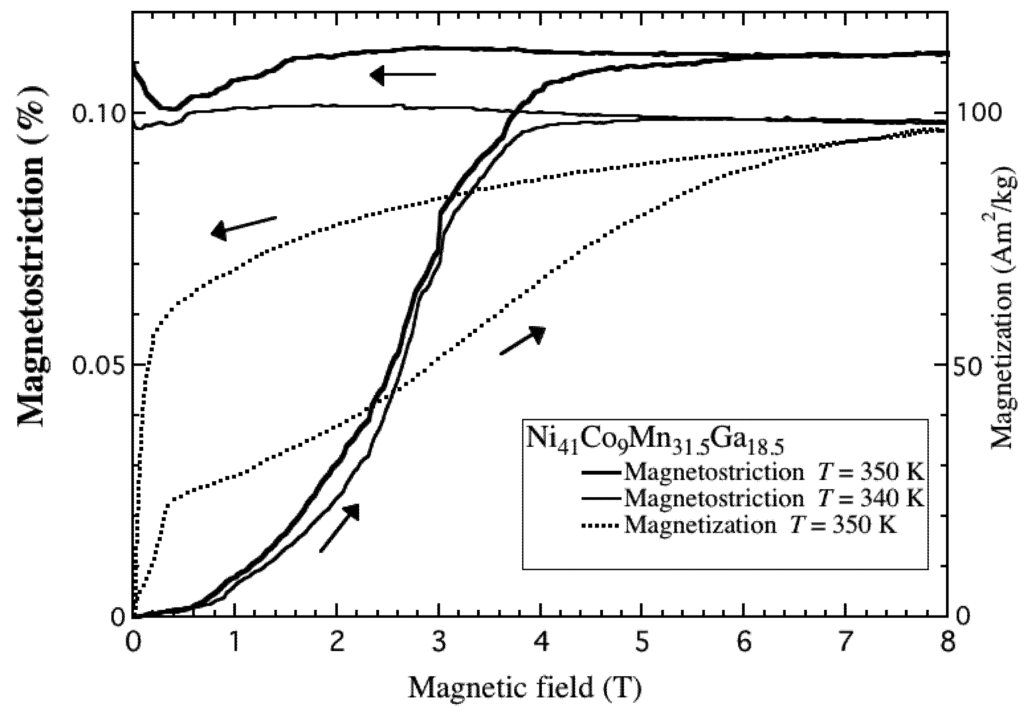
Figure 7.
The magnetic field dependence of the magnetostriction and magnetization of polycrystal Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 at the temperatures between TM and TR.
Figure 7.
The magnetic field dependence of the magnetostriction and magnetization of polycrystal Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 at the temperatures between TM and TR.
Finally, we introduce a new measurement system for the magnetostriction or magnetic transformation in pulse magnetic fields. An in situ microscopic imaging observation system has been developed by Xu et al. [63], and it was performed on Ni45Co5Mn36.7In13.3 metamagnetic shape memory alloy in pulse magnetic fields (time constant is 4.6 ms). Magnetic field-induced reverse martensitic transformation and heating-induced martensitic transformation were directly observed by means of an optical microscope between 8.5 K and 180 K with a maximum field of 31 T. A fraction of the martensite phase was evaluated by contrast change from micrographs and critical magnetic fields were determined. Isothermal growth of martensite after magnetic field application was also clearly observed. Comparison between the micrographs after the application of a magnetic field and on cooling also revealed the nature of the adiabatic process under a strong driving force.
In the last part of the reference lists in this paper, some papers concerning to the magnetic shape memory alloys are listed denoted by A to C sign. A: Magnetic field influence on martensite transformation in ferromagnetic shape memory alloys and metamagnetic shape memory alloys [64,65,66,67,68,69,70]; B: Magnetic anisotropy of the ferromagnetic shape memory alloys [71,72]; C: Magnetostriction [73,74].
4. Summary
Magneto-structural properties of novel Ni2MnGa type FSMAs in magnetic fields were introduced. These alloys indicate large magnetic field dependence of dTM/dB or dTR/dB when the martensite transformation (or reverse martensite transformation) and magnetic phase transition occur at the same temperature. A consideration by means of the phenomenological analysis by Satyanarayan et al. [46] and Nishiyama [47] was performed and it was explained that the Heusler alloys, which show re-entrant magnetism (high temperature phase: ferromagnetic austenite; low temperature phase: paramagnetic martensite), the sign of dTM/dB or dTR/dB is negative. Giant magnetic field-induced strain was determined with some novel alloys. Novel measurement system for investigation of the MFIS was also introduced.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (Grant No. 24560798) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
References
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kantner, C.; O’Handley, R.C.; Kokorin, V.V. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Ziebeck, K.R.A.; Town, S.L.; Peak, M.S. Magnetic order and phase transformation in Ni2MnGa. Philos. Mag. B 1984, 49, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.J.; Crangle, J.; Kanomata, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Neumann, K-.U.; Ouladdiaf, B.; Ziebeck, K.R.A. The crystal structure and phase transitions of the magnetic shape memory compound Ni2MnGa. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, 10159–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Santamarta, R.; Chernenko, V.A.; Cesari, E. Long-Period martensitic structures of Ni-Mn-Ga alloys studied by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 083516:1–083516:7. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R.; Banik, S.; Barman, S.R.; Kumar, U.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K.; Pandey, D. Powder x-ray diffraction study of the thermoelastic martensite transition in Ni2Mn1.05Ga0.95. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 224443:1–224443:2. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Feng, G.; Gong, S.; Xu, H. Effect of Ni excess on phase transformation temperatures of NiMnGa alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 342, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Study of Ni50+xMn25Ga25−x (x = 2–11) as high-temperature shape-memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosa, L.; Moya, X.; Planes, A.; Krenke, T.; Acet, M.; Wassermann, E.F. Ni-Mn-based magnetic shape memory alloys: Magnetic properties and martensite transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481–482, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Gómez-Polo, C.; Recarte, V. Influence of the atomic order on the magnetic characteristics of a Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, e160–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudajevová, A. Analysis of the thermal expansion characteristics of Ni53.6Mn27.1Ga19.3 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 430, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.Q.; Yang, F.Y.; Chien, C.L.; Ritchie, L.; Xiao, G.; Wu, G.H. Magnetic and thermal properties of Ni–Mn–Ga shape memory alloy with Martensite transition near room temperature. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 288, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A.; L’vov, V.A.; Khovailo, V.V.; Takagi, T.; Kanomata, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kainuma, R. Interdependence between the magnetic properties and lattice parameters of Ni–Mn–Ga martensite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2004, 16, 8345–8352. [Google Scholar]
- Golub, V.O.; Vovk, A.Y.; O’Connor, C.J.; Kotov, V.V.; Yakovenko, P.G.; Ullakko, K. Magnetic and structural properties of nonstoichiometric Ni2MnGa alloys with Ni and Ga excess. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8504–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Inaba, F.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Effect of magnetic field on martensitic transformation temperature in Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Comas, A.; Obradó, E.; Mafiosa, L.; Planes, A.; Labarta, A. Magnetoelasticity in the Heusler Ni2MnGa alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 196–197, 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lanska, N.; Söderberg, O.; Sozinov, A.; Ge, Y.; Ullakko, K.; Lindroos, V.K. Composition and temperature dependence of the crystal structure of Ni–Mn–Ga alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 8074–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhachev, A.A.; Ullakko, K. Magnetic-field-controlled twin boundaries motion and giant magneto-mechanical effects in Ni–Mn–Ga shape memory alloy. Phys. Lett. A 2000, 275, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Farinelli, M.; Kantner, C.; Huang, J.K.; Allen, S.M.; O’Handley, R.C. Field-induced strain under load in Ni–Mn–Ga magnetic shape memory materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 7297–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Nagashio, H.; Sasaki, K.; Susuga, S.; Numakura, D.; Abe, M.; Endo, K.; Yamashita, S.; Nojiri, H.; Kanomata, T. Thermal strain and magnetization of the ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Ni52Mn25Ga23 in a magnetic field. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, D.; Kanomata, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishihara, H. Magnetic properties of ferromagnetic shape memory alloys Ni50+xMn12.5Fe12.5Ga25−x. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 426, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Cullen, J.; Wuttig, M. Intermartensitic transformation in a NiMnGa alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 6957–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, L.; Heczko, O. Magnetic anisotropy in Ni-Mn-Ga martensite. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8636–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callen, H.B.; Callen, E. The present status of the temperature dependence of magnetocrystalline anisotropy, and the l(l+1)/2 power law. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1966, 27, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziljistra, H. Experimental Methods in Magnetism 2; North-Holland Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Neatherland, 1967; pp. 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, C.D., Jr. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constants of iron at room temperature and below. Phys. Rev. 1958, 112, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Takeuchi, T. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant and twinning stress in martensite phase of Ni–Mn–Ga. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 948–951. [Google Scholar]
- Heczko, O.; Straka, L.; Novak, V.; Fähler, S. Magnetic anisotropy of nonmodulated Ni–Mn–Ga martensite revisited. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A914:1–09A914:3. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, K.; Fujii, H.; Canfield, P.C. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy of a Nd2Fe17 single crystal. Physica. B 1996, 226, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Saito, S.; Koyama, K.; Awaji, S.; Sato, I.; Nojima, T.; Watanabe, K.; Sato, N.K. Experimental investigation of giant magnetocrystalline anisotropy of UGe2. Phys. Scr. 2007, 75, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, P.; Daoudi, A.; Potel, M.; Noël, M.; Gross, G.M.; André, G.; Bourée, F. Crystal and magnetic structure of the uranium digermanide UGe2. J. Alloys Comp. 1997, 247, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, M.; Endo, K.; Kudo, N.; Kanomata, T.; Nishihara, H.; Shishido, T.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Nagasako, M.; Kainuma, R. Martensitic transformation, ferromagnetic transition, and their interplay in the shape memory alloys Ni2Mn1−xCuxGa. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa, K.; Ota, T.; Ohmori, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Morito, H.; Fujita, A.; Kainuma, R.; Fukamichi, K.; Ishida, K. Magnetic and martensitic phase transitions in ferromagnetic Ni–Ga–Fe shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 5201–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K.; Oikawa, K. Stress-strain characteristics in Ni–Ga–Fe ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Ota, T.; Sutou, Y.; Ohmori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Magnetic and martensitic phase transformations in a Ni54Ga27Fe19 Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2360–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Nagashio, H.; Sasaki, K.; Susuga, S.; Endo, K.; Nojiri, H.; Kanomata, T. Thermal expansion and magnetization studies of novel ferromagnetic shape memory alloys Ni52Mn12.5Fe12.5Ga23 and Ni2Mn0.75Cu0.25Ga. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’ev, A.N.; Estrin, E.I.; Khovailo, V.V.; Bozhko, A.D.; Ischuk, R.A.; Matsumoto, M.; Takagi, T.; Tani, J. Dilatometric study of Ni2+xMn1−xGa under magnetic field. Int. Appl. Electromagn. Mechan. 2000, 12, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, D. Thermomagnetic Properties of Quarternary Ni-Mn-Fe-Ga Ferromagnet Shape Memory Alloys. Master Thesis, Tohoku Gakuin University, Takajo, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sakon, T.; Nagashio, H.; Sasaki, K.; Susuga, S.; Numakura, D.; Abe, M.; Endo, K.; Nojiri, H.; Kanomata, T. Thermal expansion and magnetization studies of the novel ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Ni2MnGa0.88Cu0.12 in a magnetic field. Physica Scripta 2011, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Albertini, F.; Fabbrici, S.; Paoluzi, A.; Kamarad, J.; Arnold, Z.; Righi, L.; Solzi, M.; Porcari, G.; Pernechele, C.; Serrate, D.; et al. Reverse magnetostructural transitions by Co and In doping NiMnGa alloys: Structural, magnetic, and magnetoelastic properties. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 684, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Sasaki, K.; Numakura, D.; Abe, M.; Nojiri, H.; Adachi, Y.; Kanomata, T. Magnetic field-induced transition in Co-Doped Ni41Co9Mn31.5Ga18.5 Heusler Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Nojiri, H.; Adachi, Y.; Kanomata, T. Crystallography and Magnetic field-induced strain by Co doping NiCoMnGa Heusler alloy. TMS2013 Suppl. Proc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainuma, R.; Imano, Y.; Ito, W.; Sutou, Y.; Morino, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Oikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Kanomata, T.; et al. Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature 2006, 439, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, J.A.; Karaman, I.; Basaran, B.; Xu, X.; Ito, W.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Kainuma, R.; Koyama, K.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Kinetic arrest of martensitic transformation in Ni33.0Co13.4Mn39.7Ga13.9 metamagnetic shape memory alloy. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Kodama, Y.; Motokawa, M.; Kanomata, T.; Oikawa, K.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Magnetic field-induced strain of Ni–Co–Mn–In alloy in pulsed magnetic field. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Battle, X.; Labarta, A.; Marcos, J.; Manósa, L.; Planes, A. Entropy change and magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(SixGe1−x)4. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 100401:1–100401:4. [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayan, K.R.; Eliasz, W.; Miodownik, A.P. The effect of a magnetic field on the martensite transformation in steels. Acta Metall. 1968, 16, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Z.; Fine, M.E.; Meshii, M.; Wayman, C.M. Martensite Transformation; Academic Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Kanomata, T.; Endo, K.; Kudo, N.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Nishihara, H.; Kataoka, M.; Nagasako, M.; Kainuma, R.; Ziebeck, K.R.A. Magnetic moment of Cu-modified Ni2MnGa magnetic shape memory alloys. Metals 2013, 3, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khovaylo, V.V.; Buchelnikov, V.D.; Kainuma, R.; Koledov, V.V.; Ohtsuka, M.; Shavrov, V.G.; Takagi, T.; Taskaev, S.V.; Vasiliev, A.N. Phase transitions in Ni2+xMn1−xGa with a high Ni excess. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 224408:1–224408:10. [Google Scholar]
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kokorin, V.V.; O’Handley, R.C. Magnetically controlled shape memory effect in Ni2MnGa intermetallics. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeshita, T.; Ullakko, K. Giant magnetostriction in ferromagnetic shape-memory alloys. MRS Bull. 2002, 27, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Marioni, M.; Allen, S.M.; O’Handley, R.C. 6% magnetic-field-induced strain by twin-boundary motion in ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–Ga. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 886–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeshita, T.; Fukuda, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Kindo, K.; Endo, S.; Kishino, K. Martensitic transformation in shape memory alloys under magnetic field and hydrostatic pressure. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Kishino, K. Magnetic field-induced strain in iron-based ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeshita, T.; Fukuda, T. Conversion of variants by magnetic field in Iron-based ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 426–432, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Sakomoto, T.; Inoue, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Kishio, K. Influence of magnetic field direction on recoverable strain due to rearrangement of variants in Fe3Pt. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 29, 3059–3060. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, C.P.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Bono, D.; O’Handley, R.C.; Allen, A.M. Dynamic Magnetic Field-Induced Strain Response of Ni49.8Mn28.5Ga21.7 Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy up to 332 Hz. In The Fourth Pacific Rim International Conference. Advanced Materials and Processing (PRICM4), Hawaii, USA, 11–15 December 2001; pp. 1657–1660.
- Sakon, T.; Takaha, A.; Matsuoka, Y.; Obara, K.; Saito, T.; Motokawa, M.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Field-induced strain of shape memory alloy Fe-31.2%Pd using a capacitance method in a pulsed magnetic field. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 7467–7471. [Google Scholar]
- Sakon, T.; Takaha, A.; Obara, K.; Dejima, K.; Nojiri, H.; Motokawa, M.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Magnetic-field-induced strain of shape-memory alloy Fe3Pt studied by a capacitance method in a pulsed magnetic field. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Sutou, Y.; Imano, Y.; Koeda, N.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K.; Oikawa, K. Magnetic and martensitic transformations of NiMnX (X = In, Sn, Sb) ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4358–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Ito, W.; Imano, Y.; Sutou, Y.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Kanomata, T. Effect of magnetic field on martensite transformation of Ni46Mn41In13 Heusler alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 122507:1–122507:3. [Google Scholar]
- Barandiarán, J.M.; Chernenko, V.A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Orúe, I.; Lázpita, P. Magnetostriction in the vicinity of structural transitions in Ni2MnGa. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 262410:1–262410:5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Ito, W.; Katakura, I.; Tokunaga, M.; Kainuma, R. In situ optical microscopic observation of NiCoMnIn metamagnetic shape memory alloy under pulsed high magnetic field. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 946–949. [Google Scholar]
- Barandiarán, J.M.; Chernenko, V.A.; Cesari, E.; Salas, D.; Lazpita, P.; Gutierrez, J.; Orue, I. Magnetic influence on the martensitic transformation entropy in Ni-Mn-In metamagnetic alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 071904:1–071904:4. [Google Scholar]
- Entel, P.; Siewert, M.; Gruner, M.E.; Herper, H.C.; Comtesse, D.; Arroyave, R.; Singh, N.; Talapatra, A.; Sokolovskiy, V.V.; Buchelnikov, V.D.; et al. Complex magnetic ordering as a driving mechanism of multifunctional properties of Heusler alloys from first principles. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 65:1–65:11. [Google Scholar]
- Lázpita, P.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Gutiérrez, J.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Chernenko, V.A.; Richard, M.L. Magnetic moment and chemical order in off-stoichiometric Ni-Mn-Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. N. J. Phys. 2011, 13, 033039:1–033039:14. [Google Scholar]
- Lázpita, P.; Chernenko, V.A.; Barandiarán, J.M.; Orue, I.; Gutiérrez, J.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Rodriguez-Velamazán, J.A. Influence of magnetic field on magnetostructural transition in Ni46.4Mn32.8Sn20.8 Heusler alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 635, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Barandiarán, J.M.; Chernenko, V.A.; Lázpita, P.; Gutiérrez, J.; Feuchtwanger, J. Effect of martensitic transformation and magnetic field on transport properties of Ni-Mn-Ga and Ni-Fe-Ga Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 104404:1–104404:7. [Google Scholar]
- Chernenko, V.A.; Lv’ov, V.A.; Kanomata, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Koyama, K.; Besseghini, S. Martensitic transformation in Ni-Mn-Ga alloy under high magnetic fields. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Imano, Y.; Chernenko, V.A.; Luo, F.; Omori, T.; Sutou, Y.; Kainuma, R.; Kanomata, T.; Ishida, K. Influence of Co addition on martensitic and magnetic transitions in Ni-Fe-Ga β based shape memory alloys. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A.; L’vov, V.A.; Golub, V.; Aseguinolaza, I.R.; Barandiarán, J.M. Magnetic anisotropy of mesoscale-twinned Ni-Mn-Ga thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 054450:1–054450:7. [Google Scholar]
- L’vov, V.; Chernenko, V. Magnetic anisotropy of ferromagnetic martensites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 684, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A.; L’vov, V.A. Magnetoelastic nature of ferromagnetic shape memory effect. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 583, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’vov, V.; Zagorodnyuk, S.; Chernenko, V.; Takagi, T. Magnetic-field-induced stresses and magnetostrain effect in martensite. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
