Rate of Responders for Post-Exercise Hypotension after Beach Tennis, Aerobic, Resistance and Combined Exercise Sessions in Adults with Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Characteristics of the Experimental Sessions
2.2.1. Beach Tennis
2.2.2. Aerobic Exercise
2.2.3. Combined Exercise
2.2.4. Resistance Exercise
2.3. Classification of Responders and Non-Responders
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Franklin, B.A.; Fagard, R.; Farquhar, W.B.; Kelley, G.A.; Ray, C.A.; American College of Sports Medicine American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and Hypertension. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 533–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Whelton, P.K. 2017 ACC/AHA Hypertension Guideline Writing Committee Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Synopsis of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Hypertension Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frediani, J.K.; Krustrup, P.; Lobelo, F. Cardiometabolic Adaptations and Benefits of Recreational Group Sports. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hermoso, A.; López-Gil, J.F.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Alonso-Martínez, A.M.; Izquierdo, M.; Ezzatvar, Y. Adherence to Aerobic and Muscle-Strengthening Activities Guidelines: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 3.3 Million Participants across 31 Countries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 57, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Ju, Y.J.; Lee, J.E.; Hyun, I.S.; Nam, J.Y.; Han, K.-T.; Park, E.-C. The Relationship between Sports Facility Accessibility and Physical Activity among Korean Adults. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Goodman, J.; Nolan, R.; Lacombe, S.; Thomas, S.G. Blood Pressure Responses to Acute and Chronic Exercise Are Related in Prehypertension. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio-Rivera, E.; Moncada-Jiménez, J.; Salazar-Rojas, W.; Solera-Herrera, A.; Carpio-Rivera, E.; Moncada-Jiménez, J.; Salazar-Rojas, W.; Solera-Herrera, A. Acute Effects of Exercise on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analytic Investigation. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2016, 106, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, L.B.; Cadore, E.L.; Ferrari, R. Hemodynamic Responses of Resistance Exercise Performed with Repetitions to Failure and Not to Failure in Adults with Hypertension. Blood Press. Monit. 2021, 26, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casonatto, J.; Goessler, K.F.; Cornelissen, V.A.; Cardoso, J.R.; Polito, M.D. The Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect of a Single Bout of Resistance Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 1700–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buford, T.W.; Roberts, M.D.; Church, T.S. Toward Exercise as Personalized Medicine. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loenneke, J.P.; Fahs, C.A.; Abe, T.; Rossow, L.M.; Ozaki, H.; Pujol, T.J.; Bemben, M.G. Hypertension Risk: Exercise Is Medicine* for Most but Not All. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.H.R.A.; Miranda, A.S.; Correia, M.A.; Soares, A.H.G.; Cucato, G.G.; Sobral Filho, D.C.; Gomes, S.L.; Ritti-Dias, R.M. Individual Blood Pressure Responses to Walking and Resistance Exercise in Peripheral Artery Disease Patients: Are the Mean Values Describing What Is Happening? J. Vasc. Nurs. Off. Publ. Soc. Peripher. Vasc. Nurs. 2015, 33, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, C.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Cristi-Montero, C.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Izquierdo, M. Prevalence of Non-Responders for Blood Pressure and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Among Prehypertensive Women After Long-Term High-Intensity Interval Training. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpes, L.; Jacobsen, A.; Domingues, L.; Jung, N.; Ferrari, R. Recreational Beach Tennis Reduces 24-h Blood Pressure in Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Umpierre, D.; Vogel, G.; Vieira, P.J.C.; Santos, L.P.; de Mello, R.B.; Tanaka, H.; Fuchs, S.C. Effects of Concurrent and Aerobic Exercises on Postexercise Hypotension in Elderly Hypertensive Men. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Périco, B.; Kothe, G.B. Acute Effects of Body-Weight Resistance Exercises on Blood Pressure and Glycemia in Middle-Aged Adults with Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2021, 43, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado Filho, J.; Machado, C.L.F.; Tanaka, H.; Ferrari, R. Postexercise Hypotension After Muscle Power Training Session in Older Adults With Hypertension. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2020, 28, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimitt, R.P.; O Carpes, L.; Domingues, L.B.; Tanaka, H.; Fuchs, S.C.; Ferrari, R. Effects of a Single Bout of Power Exercise Training on Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Older Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 54, 102554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, W.K.S.; Rodrigues, C.I.S.; Bortolotto, L.A.; Mota-Gomes, M.A.; Brandão, A.A.; Feitosa, A.D.d.M.; Machado, C.A.; Poli-de-Figueiredo, C.E.; Amodeo, C.; Júnior, D.M.; et al. Diretrizes Brasileiras de Hipertensão Arterial—2020. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2021, 116, 516–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Merchant, R.A.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Aprahamian, I.; Arai, H.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Bernabei, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 824–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescatello, L.S.; Buchner, D.M.; Jakicic, J.M.; Powell, K.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Bloodgood, B.; Campbell, W.W.; Dietz, S.; Dipietro, L.; George, S.M.; et al. Physical Activity to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R.; Taylor, J.A.; Eckberg, D.L. Impaired Sympathetic Vascular Regulation in Humans after Acute Dynamic Exercise. J. Physiol. 1996, 495 Pt 1, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R.; Buck, T.M.; Lacewell, A.N.; Romero, S.A. Postexercise Hypotension and Sustained Postexercise Vasodilatation: What Happens after We Exercise? Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwill, J.R. Mechanisms and Clinical Implications of Post-Exercise Hypotension in Humans. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett-O’Keefe, Z.; Kaplon, R.E.; Halliwill, J.R. Sustained Postexercise Vasodilatation and Histamine Receptor Activation Following Small Muscle-Mass Exercise in Humans. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.C.; Dantas, T.C.B.; Junior, L.F.d.F.; Frazão, D.T.; Prestes, J.; Moreira, S.R.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Tibana, R.A.; Duhamel, T.A. Inter- and Intra-Individual Analysis of Post-Exercise Hypotension Following a Single Bout of High-Intensity Interval Exercise and Continuous Exercise: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecchio, R.Y.; Queiroz, A.C.C.; Ritti-Dias, R.; Costa, E.C.; Forjaz, C.L.M. Post-Dynamic Resistance Exercise Hypotension: Exploring Individual Responses and Predictors. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 787444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejeune, T.M.; Willems, P.A.; Heglund, N.C. Mechanics and Energetics of Human Locomotion on Sand. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Skoradal, M.-B.; Randers, M.B.; Weihe, P.; Uth, J.; Mortensen, J.; Mohr, M. Broad-Spectrum Health Improvements with One Year of Soccer Training in Inactive Mildly Hypertensive Middle-Aged Women. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krustrup, P.; Hansen, P.R.; Randers, M.B.; Nybo, L.; Martone, D.; Andersen, L.J.; Bune, L.T.; Junge, A.; Bangsbo, J. Beneficial Effects of Recreational Football on the Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Untrained Premenopausal Women. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20 (Suppl. S1), 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
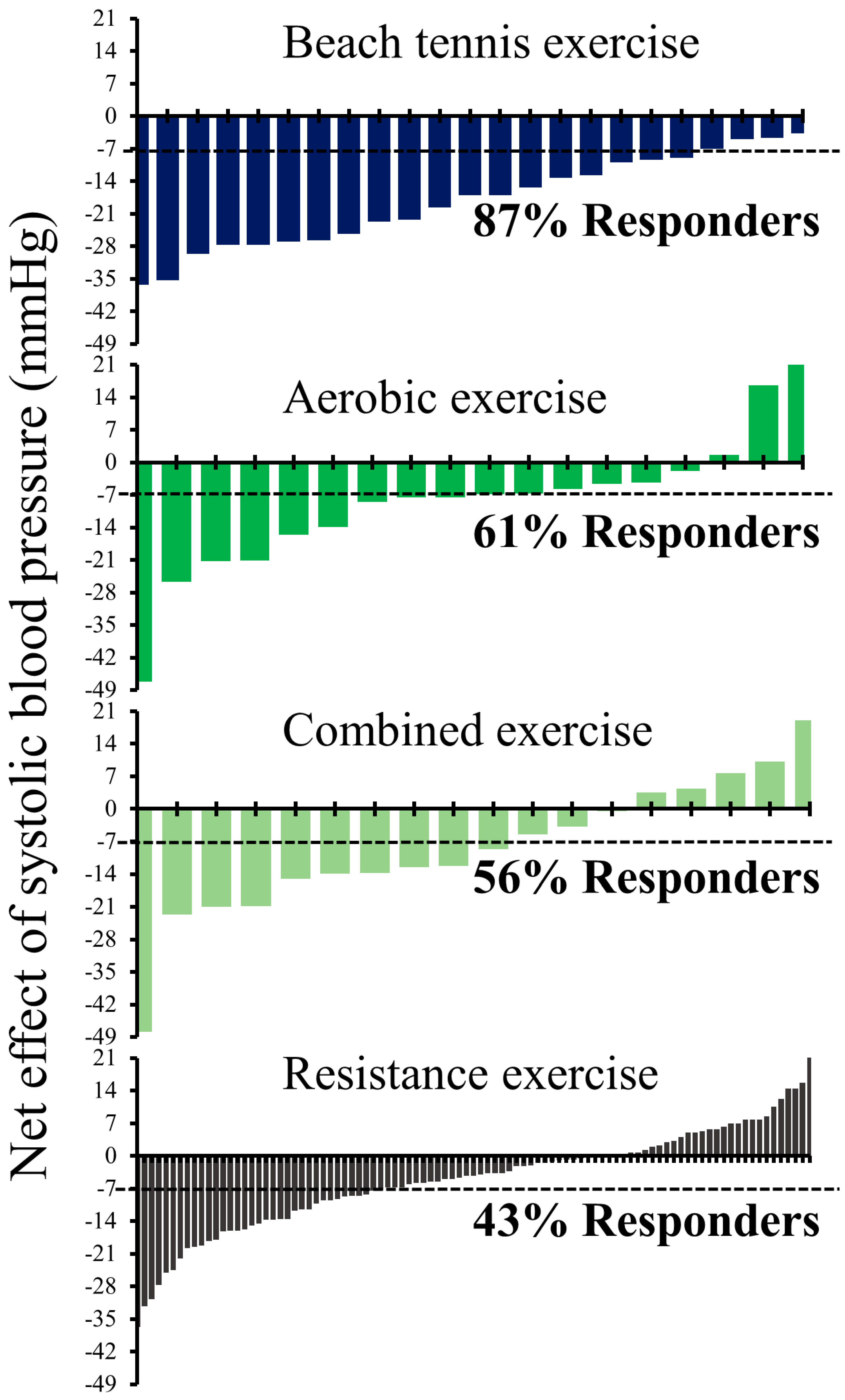
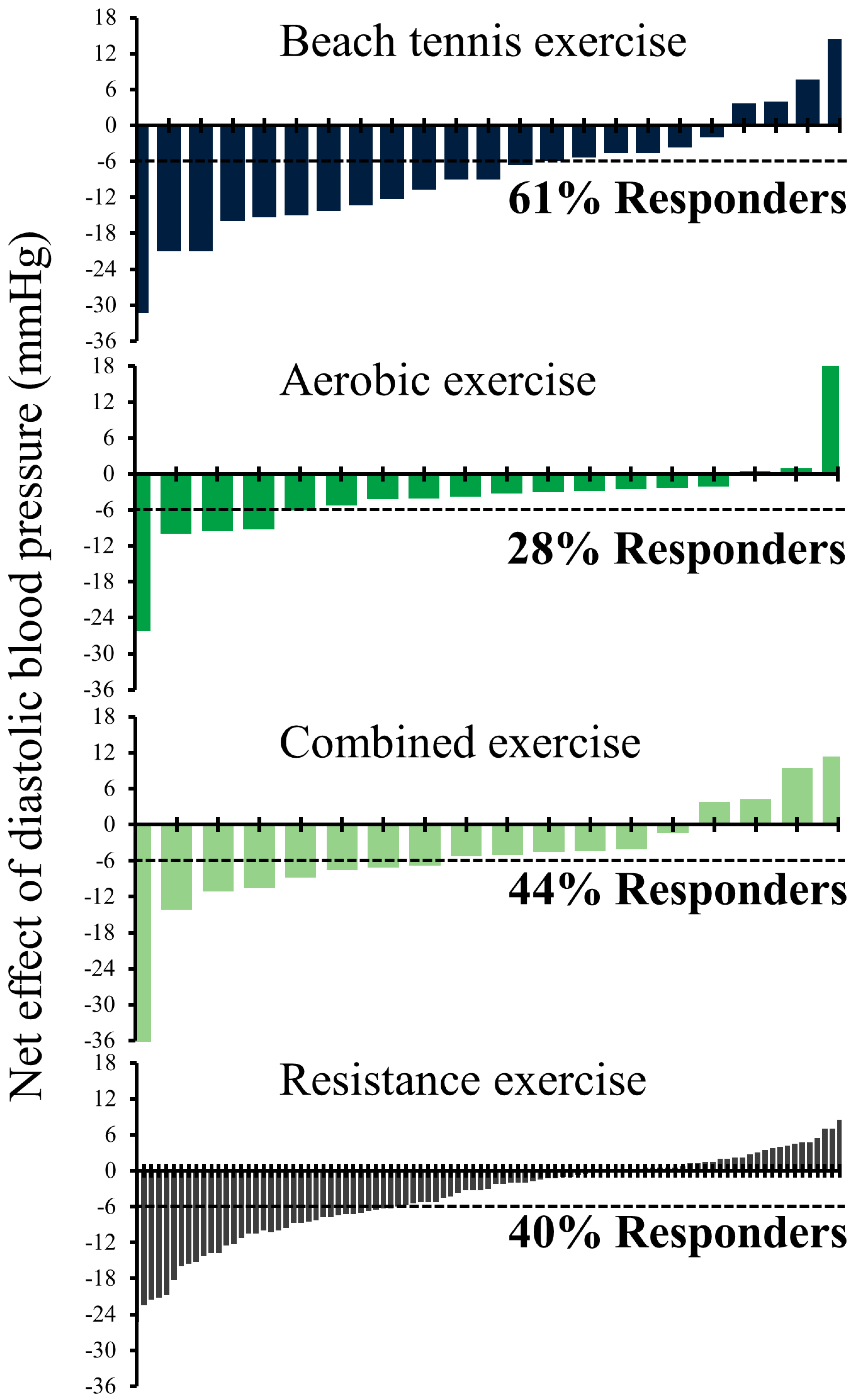
| Responder | Non-Responder | Δ | Effect Size | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic exercise | 11 (61) | 7 (39) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 123 ± 10 (117 to 130) | 114 ± 6 (109 to 120) | 9 ± 4 (1 to 18) | 1.03 | 0.042 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 115 ± 7 (111 to 120) | 113 ± 10 (104 to 121) | 2 ± 4 (−6 to 11) | 0.24 | 0.524 | |
| Pre Control | 120 ± 10 (113 to 126) | 123 ± 16 (108 to 138) | −3 ± 6 (−16 to 10) | 0.24 | 0.601 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 127 ± 14 (119 to 137) | 117 ± 12 (106 to 129) | 10 ± 6 (−3 to 24) | 0.75 | 0.116 | |
| Net effect | −17 ± 12 (−25 to −8) | 4 ± 12 (−7 to 15) | −21 ± 6 (−33 to −8) | 1.75 | 0.003 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 75 ± 12 (67 to 83) | 68 ± 7 (62 to 75) | 7 ± 5 (−4 to 17) | 0.67 | 0.208 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 71 ± 9 (65 to 77) | 70 ± 8 (62 to 77) | 1 ± 4 (−7 to 10) | 0.12 | 0.696 | |
| Pre Control | 74 ± 9 (68 to 80) | 68 ± 13 (57 to 80) | 6 ± 5 (−5 to 16) | 0.56 | 0.271 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 77 ± 10 (70 to 83) | 70 ± 9 (62 to 78) | 7 ± 5 (−2 to 17) | 0.73 | 0.134 | |
| Net effect | −7 ± 7 (−11 to −2) | 0 ± 10 (−9 to 9) | −7 ± 4 (−15 to 2) | 0.85 | 0.129 | |
| Combined exercise | 10 (56) | 8 (44) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 128 ± 7 (122 to 133) | 118 ± 10 (109 to 126) | 10 ± 4 (1 to 19) | 1.18 | 0.027 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 117 ± 5 (111 to 124) | 116 ± 10 (108 to 125) | 1 ± 5 (−9 to 11) | 0.13 | 0.800 | |
| Pre Control | 120 ± 10 (111 to 127) | 123 ± 15 (110 to 135) | −3 ± 6 (−15 to 10) | 0.24 | 0.631 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 129 ± 14 (117 to 139) | 117 ± 11 (108 to 126) | 12 ± 6 (1 to 25) | 0.94 | 0.049 | |
| Net effect | −19 ± 11 (−28 to −11) | 4 ± 8 (−2 to 11) | −23 ± 5 (−33 to −13) | 2.35 | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 76 ± 11 (67 to 85) | 71 ± 7 (65 to 77) | 5 ± 5 (−5 to 15) | 0.63 | 0.324 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 71 ± 5 (70 to 74) | 70 ± 9 (62 to 77) | 1 ± 3 (−6 to 8) | 0.14 | 0.789 | |
| Pre Control | 73 ± 10 (64 to 80) | 71 ± 11 (61 to 80) | 2 ± 5 (−9 to 13) | 0.19 | 0.712 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 77 ± 10 (69 to 84) | 70 ± 9 (63 to 78) | 7 ± 4 (−3 to 16) | 0.73 | 0.142 | |
| Net effect | −9 ± 11 (−18 to −1) | −1 ± 8 (−8 to 6) | −8 ± 5 (−18 to 1) | 0.82 | 0.093 | |
| Resistance exercise | 41 (43) | 54 (57) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 128 ± 14 (124 to 132) | 127 ± 14 (123 to 131) | 1 ± 3 (−5 to 6) | 0.07 | 0.792 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 119 ± 24 (111 to 127) | 129 ± 13 (125 to 132) | −10 ± 4 (−17 to −2) | 0.54 | 0.018 | |
| Pre Control | 126 ± 13 (122 to 130) | 132 ± 13 (128 to 135) | −6 ± 3 (−11 to −1) | 0.46 | 0.025 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 135 ± 17 (129 to 140) | 132 ± 14 (128 to 136) | 3 ± 3 (−3 to 3) | 0.20 | 0.351 | |
| Net effect | −14 ± 9 (−17 to −12) | 2 ± 7 (0 to 4) | −16 ± 2 (−19 to −12) | 2.02 | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 77 ± 11 (74 to 80) | 75 ± 9 (72 to 77) | 2 ± 2 (−2 to 7) | 0.20 | 0.231 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 71 ± 15 (66 to 76) | 76 ± 8 (74 to 78) | −5 ± 2 (−10 to −1) | 0.43 | 0.032 | |
| Pre Control | 76 ± 11 (73 to 79) | 77 ± 9 (74 to 79) | −1 ± 2 (−5 to 3) | 0.10 | 0.716 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 80 ± 10 (77 to 83) | 79 ± 9 (77 to 82) | 1 ± 2 (−3 to 5) | 0.11 | 0.741 | |
| Net effect | −8 ± 8 (−11 to −6) | −1 ± 5 (−3 to 0) | −7 ± 1 (−9 to −4) | 1.08 | <0.001 | |
| Beach tennis exercise | 20 (87) | 3 (13) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 129 ± 12 (124 to 134) | 127 ± 6 (113 to 140) | 2 ± 7 (−12 to 17) | 0.17 | 0.740 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 112 ± 12 (107 to 118) | 117 ± 2 (112 to 122) | −5 ± 7 (−19 to 10) | 0.44 | 0.491 | |
| Pre Control | 126 ± 13 (120 to 132) | 128 ± 14 (91 to 164) | −2 ± 8 (−19 to 16) | 0.15 | 0.842 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 130 ± 12 (124 to 135) | 122 ± 10 (97 to 147) | 8 ± 7 (−8 to 23) | 0.68 | 0.349 | |
| Net effect | −21 ± 9 (−25 to −16) | −5 ± 1 (−6 to −3) | −16 ± 2 (−20 to −12) | 1.87 | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 82 ± 8 (78 to 86) | 70 ± 4 (60 to 80) | 12 ± 5 (2 to 22) | 1.56 | 0.025 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 75 ± 8 (71 to 78) | 70 ± 3 (63 to 80) | 5 ± 5 (−5 to 14) | 0.65 | 0.350 | |
| Pre Control | 80 ± 10 (75 to 85) | 73 ± 5 (60 to 85) | 7 ± 6 (−5 to 20) | 0.73 | 0.249 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 82 ± 10 (78 to 87) | 72 ± 9 (51 to 94) | 10 ± 6 (−3 to 23) | 1.01 | 0.111 | |
| Net effect | −10 ± 9 (−14 to −5) | 1 ± 5 (−12 to 14) | −11 ± 4 (−21 to −1) | 1.26 | 0.038 | |
| Responder | Non-Responder | Δ | Effect Size | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic exercise, n (%) | 5 (28) | 13 (72) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 126 ± 9 (115 to 137) | 118 ± 9 (112 to 123) | 8 ± 5 (−2 to 18) | 0.89 | 0.102 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 116 ± 5 (109 to 122) | 114 ± 9 (108 to 119) | 2 ± 4 (−6 to 11) | 0.24 | 0.609 | |
| Pre Control | 115 ± 7 (106 to 124) | 123 ± 13 (115 to 131) | −8 ± 6 (−22 to 5) | 0.68 | 0.214 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 125 ± 13 (109 to 141) | 123 ± 14 (114 to 132) | 2 ± 7 (−14 to 18) | 0.15 | 0.767 | |
| Net effect | −20 ± 17 (−41 to 0) | −4 ± 13 (−12 to 4) | −16 ± 7 (−32 to −1) | 1.13 | 0.047 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 79 ± 15 (61 to 97) | 70 ± 8 (65 to 75) | 9 ± 5 (−2 to 20) | 0.88 | 0.116 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 73 ± 10 (61 to 84) | 70 ± 8 (65 to 75) | 3 ± 4 (−6 to 13) | 0.35 | 0.499 | |
| Pre Control | 71 ± 13 (55 to 88) | 72 ± 10 (66 to 78) | −1 ± 6 (−13 to 11) | 0.09 | 0.896 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 78 ± 13 (62 to 94) | 73 ± 8 (67 to 78) | 5 ± 5 (−6 to 16) | 0.11 | 0.316 | |
| Net effect | −12 ± 8 (−22 to −2) | −1 ± 7 (−5 to 3) | −11 ± 4 (−19 to −4) | 1.51 | 0.007 | |
| Combined exercise, n (%) | 8 (44) | 10 (56) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 124 ± 10 (115 to 132) | 122 ± 10 (115 to 129) | 2 ± 5 (−8 to 12) | 0.20 | 0.700 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 115 ± 10 (106 to 123) | 119 ± 9 (112 to 125) | −4 ± 4 (−14 to 5) | 0.42 | 0.378 | |
| Pre Control | 121 ± 11 (111 to 130) | 121 ± 14 (110 to 131) | 0 ± 6 (−13 to 13) | 0.00 | 0.908 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 124 ± 13 (114 to 135) | 123 ± 15 (110 to 133) | 1 ± 7 (−13 to 15) | 0.07 | 0.887 | |
| Net effect | −13 ± 19 (−28 to 3) | −5 ± 12 (−14 to 5) | −8 ± 7 (−23 to 7) | 0.52 | 0.288 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 76 ± 11 (67 to 85) | 71 ± 8 (65 to 77) | 5 ± 5 (−5 to 15) | 0.53 | 0.308 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 68 ± 6 (64 to 73) | 72 ± 8 (66 to 78) | −4 ± 3 (−10 to 4) | 0.56 | 0.335 | |
| Pre Control | 71 ± 10 (62 to 79) | 73 ± 11 (63 to 81) | −2 ± 5 (−13 to 8) | 0.19 | 0.648 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 76 ± 10 (69 to 84) | 73 ± 10 (65 to 78) | 3 ± 5 (−7 to 13) | 0.30 | 0.583 | |
| Net effect | −13 ± 10 (−21 to −5) | 0 ± 6 (−4 to 6) | −13 ± 4 (−21 to −5) | 1.63 | 0.003 | |
| Resistance exercise, n (%) | 38 (40) | 57 (60) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 128 ± 13 (123 to 132) | 127 ± 15 (124 to 131) | 1 ± 3 (−6 to 6) | 0.07 | 0.950 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 122 ± 17 (116 to 127) | 127 ± 22 (121 to 132) | −5 ± 4 (−13 to 3) | 0.25 | 0.255 | |
| Pre Control | 125 ± 12 (121 to 129) | 132 ± 13 (128 to 135) | −7 ± 3 (−12 to −1) | 0.56 | 0.015 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 131 ± 15 (126 to 136) | 134 ± 15 (130 to 138) | −3 ± 3 (−10 to 3) | 0.20 | 0.309 | |
| Net effect | −12 ± 11 (−16 to −8) | −1 ± 8 (−3 to 2) | −11 ± 2 (−15 to −7) | 1.18 | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 78 ± 10 (75 to 81) | 75 ± 10 (72 to 77) | 3 ± 2 (−1 to 7) | 0.30 | 0.103 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 72 ± 10 (69 to 75) | 75 ± 13 (72 to 79) | −3 ± 3 (−8 to 2) | 0.25 | 0.186 | |
| Pre Control | 74 ± 9 (71 to 77) | 78 ± 10 (75 to 81) | −4 ± 2 (−8 to −1) | 0.42 | 0.036 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 79 ± 10 (76 to 82) | 80 ± 10 (77 to 83) | −1 ± 2 (−5 to 3) | 0.10 | 0.656 | |
| Net effect | −12 ± 5 (−13 to −10) | 0 ± 3 (−1 to 1) | −12 ± 1 (−14 to −10) | 3.06 | <0.001 | |
| Beach tennis exercise, n (%) | 14 (61) | 9 (39) | ||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 126 ± 12 (119 to 133) | 133 ± 7 (127 to 139) | −7 ± 5 (−16 to 3) | 0.67 | 0.145 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 108 ± 12 (102 to 115) | 120 ± 5 (115 to 124) | −12 ± 4 (−20 to −2) | 1.21 | 0.014 | |
| Pre Control | 127 ± 14 (119 to 135) | 124 ± 12 (115 to 134) | 3 ± 6 (−9 to 15) | 0.23 | 0.592 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 132 ± 12 (125 to 139) | 123 ± 11 (115 to 132) | 9 ± 5 (−1 to 19) | 0.77 | 0.088 | |
| Net effect | −22 ± 9 (−27 to −17) | −12 ± 9 (−19 to −6) | −10 ± 4 (−18 to −2) | 1.11 | 0.015 | |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | ||||||
| Pre Exercise | 83 ± 9 (76 to 88) | 76 ± 7 (70 to 82) | 7 ± 4 (−1 to 14) | 0.84 | 0.075 | |
| Mean post 1 h Exercise | 72 ± 7 (68 to 76) | 78 ± 7 (72 to 83) | −6 ± 3 (−12 to 0) | 0.86 | 0.063 | |
| Pre Control | 81 ± 12 (75 to 88) | 75 ± 4 (72 to 78) | 6 ± 4 (−2 to 15) | 0.61 | 0.121 | |
| Mean post 1 h Control | 85 ± 10 (79 to 91) | 75 ± 8 (69 to 81) | 10 ± 4 (2 to 18) | 1.08 | 0.022 | |
| Net effect | −14 ± 7 (−18 to −10) | 1 ± 7 (−4 to 6) | −15 ± 3 (−21 to −9) | 2.14 | <0.001 | |
| Aerobic Exercise | Combined Exercise | Resistance Exercise | Beach Tennis Exercise | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Responder | Non-Responder | Responder | Non-Responder | Responder | Non-Responder | Responder | Non-Responder | ||
| Systolic blood pressure | |||||||||
| Anti-hypertensive medications, n (%) | |||||||||
| Diuretics | 5 (46) | 1 (14) | 3 (30) | 3 (38) | 22 (54) | 22 (41) | 8 (40) | 1 (33) | |
| β blockers | 4 (36) | 1 (14) | 4 (40) | 1 (13) | 6 (15) | 14 (26) | 4 (20) | 1 (33) | |
| Angiotensin converting enzyme inibitors | 3 (27) | 2 (29) | 3 (30) | 2 (25) | 5 (12) | 11 (20) | 5 (25) | 1 (33) | |
| Angiotensin receptor antagonists | 2 (18) | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | 1 (13) | 9 (22) | 6 (11) | − | − | |
| Calcium channel blockers | 4 (36) | 3 (43) | 3 (30) | 4 (50) | 3 (7) | 5 (9) | 2 (10) | 1 (33) | |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers | − | − | − | − | 7 (17) | 20 (37) | 7 (35) | 1 (33) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure | |||||||||
| Anti-hypertensive medications, n (%) | |||||||||
| Diuretics | 2 (40) | 4 (31) | 1 (13) | 5 (50) | 19 (50) | 25 (44) | 4 (29) | 5 (56) | |
| β blockers | 1 (20) | 4 (31) | 2 (25) | 3 (30) | 7 (18) | 13 (23) | 3 (21) | 2 (22) | |
| Angiotensin converting enzyme inibitors | 2 (40) | 3 (23) | 2 (25) | 3 (30) | 5 (13) | 11 (19) | 4 (29) | 2 (22) | |
| Angiotensin receptor antagonists | 0 (0) | 2 (15) | 2 (25) | 0 (0) | 7 (18) | 8 (14) | − | − | |
| Calcium channel blockers | 2 (40) | 5 (39) | 3 (38) | 4 (40) | 4 (11) | 4 (7) | 2 (14) | 1 (11) | |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers | − | − | − | − | 8 (21) | 19 (33) | 4 (29) | 4 (44) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira Carpes, L.; Domingues, L.B.; Fuchs, S.C.; Ferrari, R. Rate of Responders for Post-Exercise Hypotension after Beach Tennis, Aerobic, Resistance and Combined Exercise Sessions in Adults with Hypertension. Sports 2023, 11, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11030058
de Oliveira Carpes L, Domingues LB, Fuchs SC, Ferrari R. Rate of Responders for Post-Exercise Hypotension after Beach Tennis, Aerobic, Resistance and Combined Exercise Sessions in Adults with Hypertension. Sports. 2023; 11(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11030058
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira Carpes, Leandro, Lucas Betti Domingues, Sandra Costa Fuchs, and Rodrigo Ferrari. 2023. "Rate of Responders for Post-Exercise Hypotension after Beach Tennis, Aerobic, Resistance and Combined Exercise Sessions in Adults with Hypertension" Sports 11, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11030058
APA Stylede Oliveira Carpes, L., Domingues, L. B., Fuchs, S. C., & Ferrari, R. (2023). Rate of Responders for Post-Exercise Hypotension after Beach Tennis, Aerobic, Resistance and Combined Exercise Sessions in Adults with Hypertension. Sports, 11(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11030058







