Apoptosis and Relevant Genes Are Engaged in the Response of Apis mellifera Larvae to Ascosphaera apis Invasion
Simple Summary
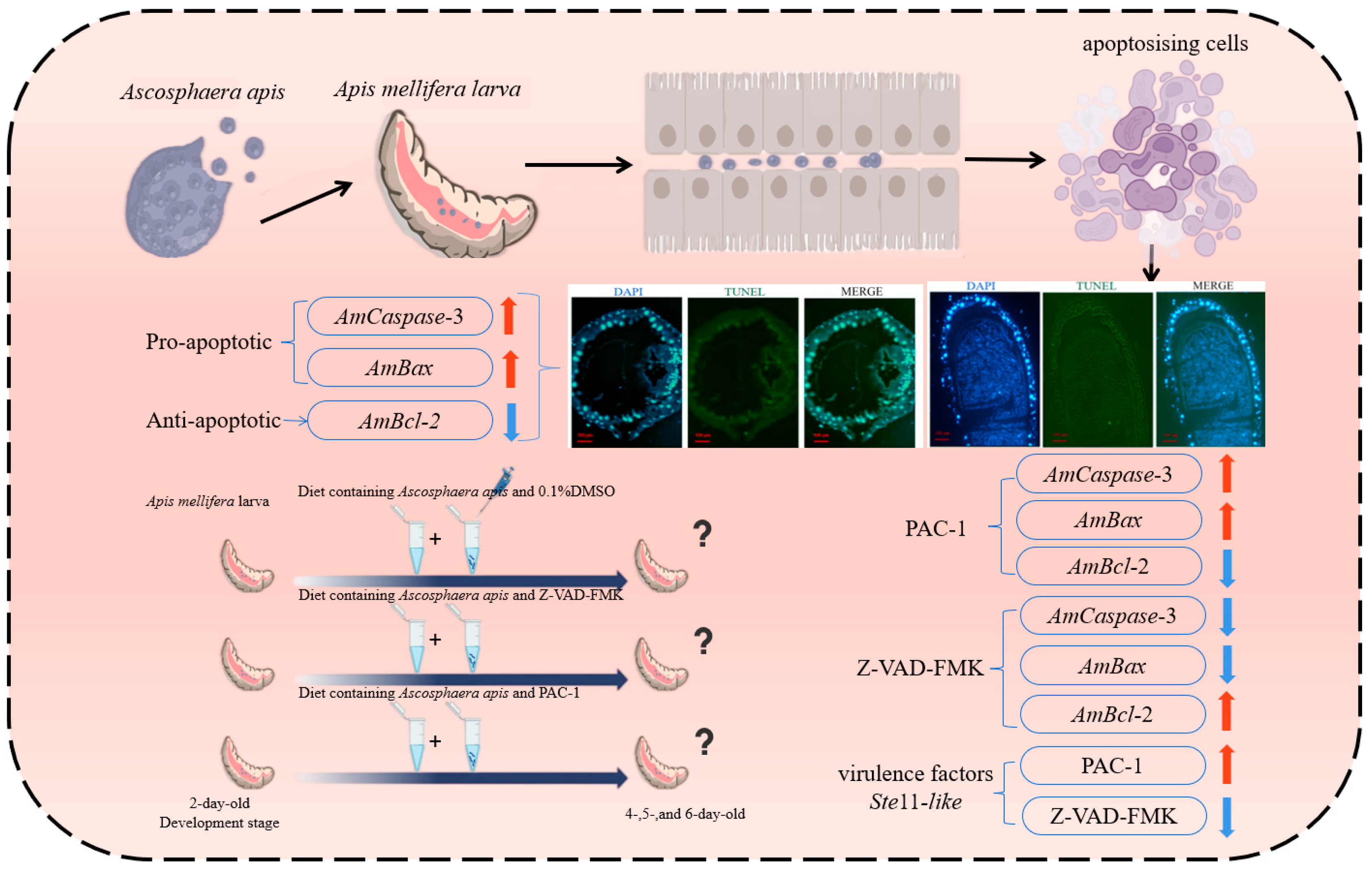
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bee Larvae and Fungal Spores
2.2. Preparation of Gut Samples
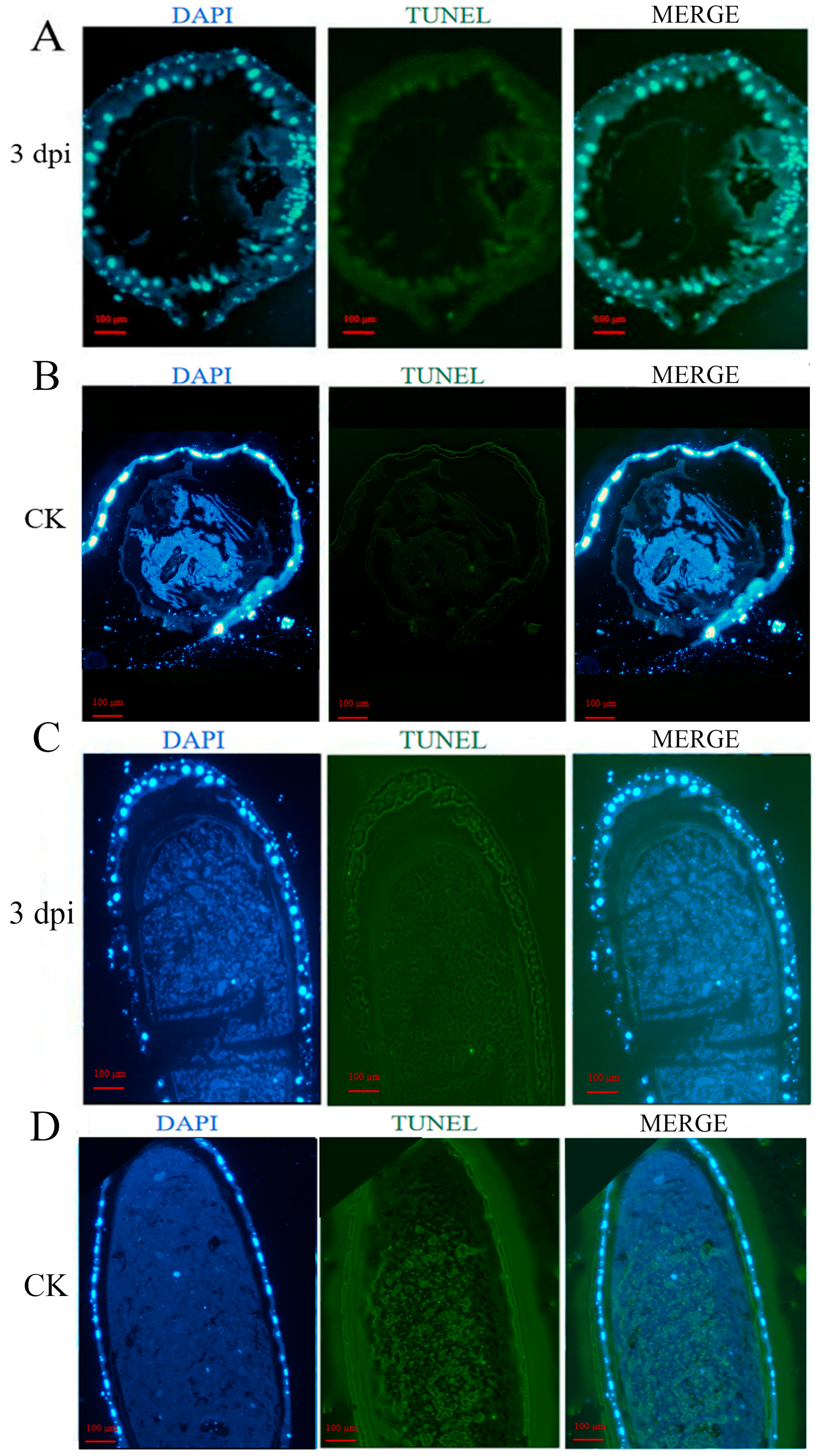
2.3. TUNEL Assay
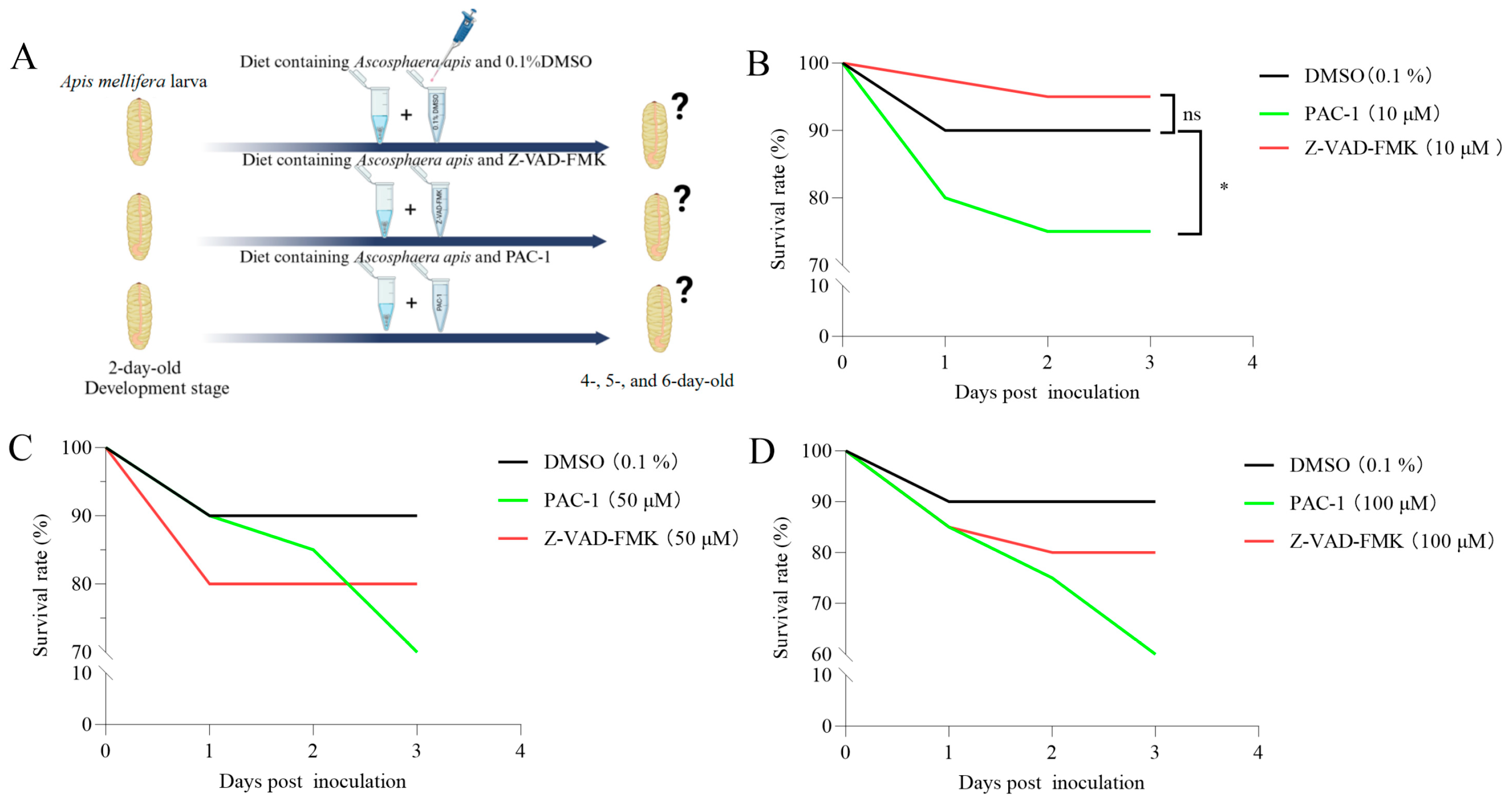
2.4. Inhibition and Activation of Apoptosis
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. A. apis Infection Induces the Apoptosis of the A. mellifera Worker Larval Gut Cells
3.2. A. apis Affects the Survival of Worker Larvae Through the Apoptosis Process
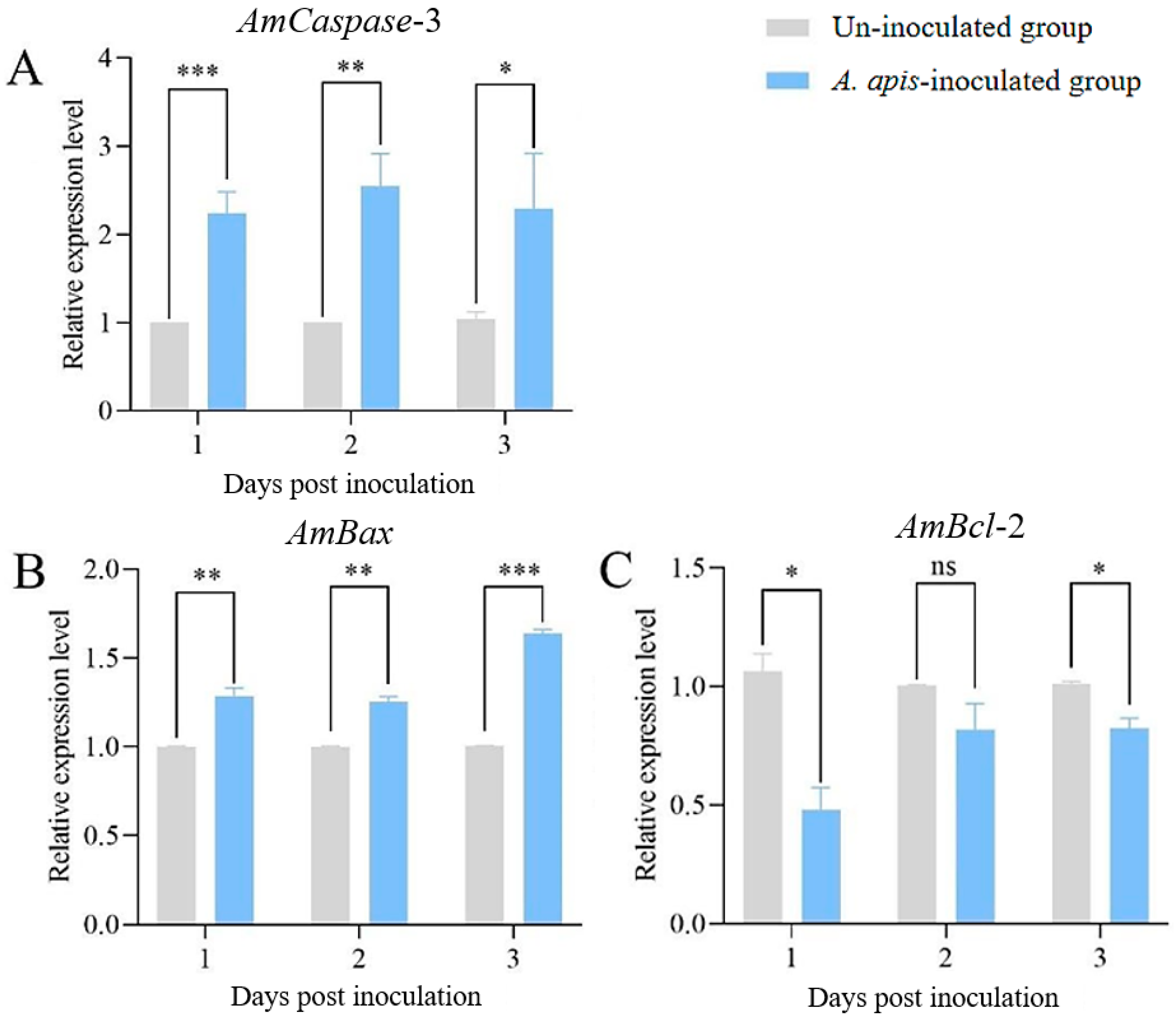
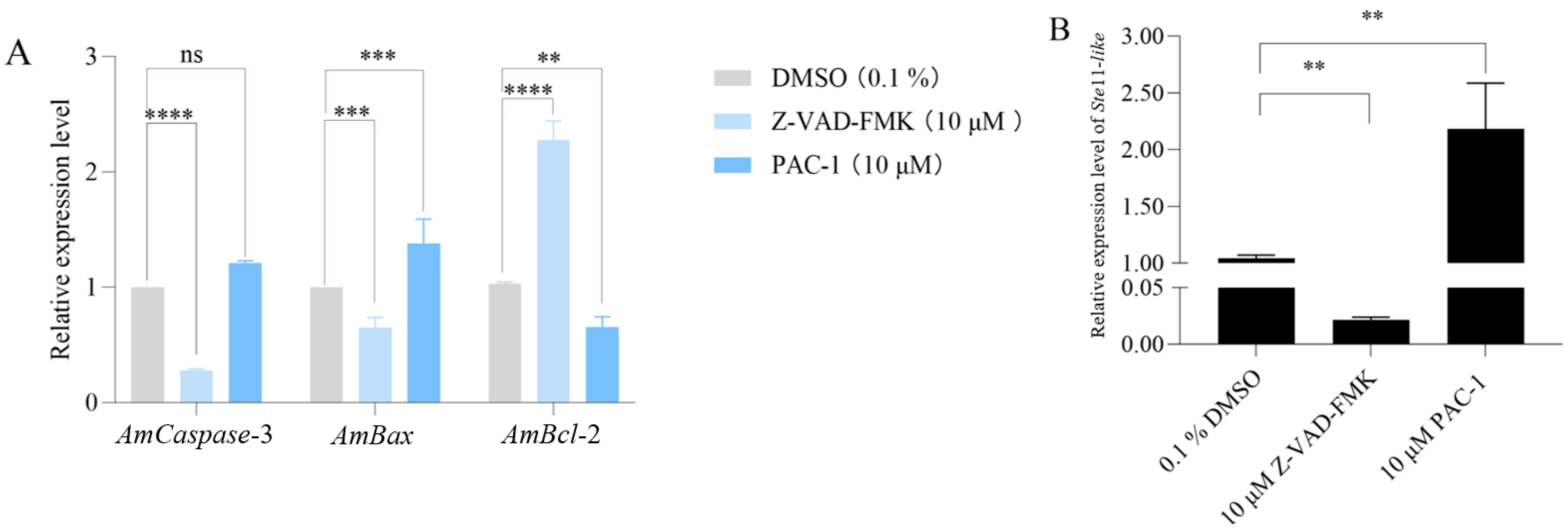
3.3. Inhibition and Activation of Apoptosis Affected the Expression of Apoptosis-Relevant Genes in the Infected Larval Guts and A. apis Virulence Factor Ste11-like Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aronstein, K.A.; Murray, K.D. Chalkbrood disease in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S20–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, M.A.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Cunningha, S.A.; Klein, A.M. How much does agriculture depend on pollinators lessons from long-term trends in crop production. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Knoblauch, T.; Jensen, A.B.; Mülling, C.K.W.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; Genersch, E. Chalkbrood disease caused by Ascosphaera apis in honey bees (Apis mellifera)-morphological and histological changes in infected larvae. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, I.; Phui, A.; Elekonich, M.M.; Abel-Santos, E. Requirements for in vitro germination of Paenibacillus larvae spores. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, E.; Genersch, E. Honey bee larval peritrophic matrix degradation during infection with Paenibacillus larvae, the aetiological agent of American foulbrood of honey bees, is a key step in pathogenesis. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genersch, E. Honey bee pathology: Current threats to honey bees and beekeeping. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, D.F. Apicultural Protection, 2nd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, A.B.; Palmer, K.A.; Boomsma, J.J.; Pedersen, B.V. Varying degrees of Apis mellifera ligustica introgression in protected populations of the black honeybee, Apis mellifera mellifera, in northwest Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertyporokh, L.; Hułas-Stasiak, M.; Wojda, I. Host-pathogen interaction after infection of Galleria mellonella with the filamentous fungus Beauveria bassiana. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Song, S.; Wei, X.; Tang, G.; Wang, C. Activation of microlipophagy during early infection of insect hosts by Metarhizium robertsii. Autophagy 2022, 18, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainu, F.; Shiratsuchi, A.; Nakanishi, Y. Induction of Apoptosis and subsequent phagocytosis of virus-infected cells as an antiviral mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sun, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, T.; Luo, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, L. Enhanced toxicity of entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana with bacteria expressing immune suppressive dsRNA in a leaf beetle. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 193, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Meng, H.; Jiang, X.; Huang, S. Bombyx mori UFL1 facilitates BmNPV proliferation by regulating host cell apoptosis through PERK. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 116, e22127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrońska, A.K.; Kaczmarek, A.; Kazek, M.; Boguś, M.I. Infection of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera) larvae with the entomopathogenic fungus Conidiobolus coronatus (Entomophthorales) induces apoptosis of hemocytes and affects the concentration of eicosanoids in the hemolymph. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 774086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Xiao, H.Y.; Li, N.; Yang, C.J.; Huang, G.H. An ascovirus utilizes different types of host larval regulated cell death mechanisms to produce and release vesicles. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0156622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. P53 and Apoptosis in the Drosophila model. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1167, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Higes, M.; Juarranz, Á.; Dias-Almeida, J.; Lucena, S.; Botías, C.; Meana, A.; García-Palencia, P.; Martín-Hernández, R. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis of Nosema ceranae (Microsporidia: Nosematidae) in honey bees (Apis mellifera). Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.J.; Guo, R.; Luo, Q.; Xiong, C.L.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, C.L.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.N.; Huang, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; et al. De novo transcriptome assembly for Apis cerana cerana larval gut and identification of SSR molecular markers. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Du, Y.; Xiong, C.L.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Fu, Z.M.; Xu, G.J.; Wang, H.P.; Chen, H.Z.; Geng, S.H.; Zhou, D.D.; et al. Differentially expressed MicroRNA and their regulation networks during the developmental process of Apis mellifera ligustica larval gut. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 4197–4209. [Google Scholar]
- Getachew, A.; Abejew, T.A.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Tan, J.; Wu, P.; Tu, Y.; Kang, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals insertional mutagenesis suppressed the expression of candidate pathogenicity genes in honeybee fungal pathogen, Ascosphaera apis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Blanco, A.; García-Sáez, A.J. Bax, Bak and beyond—Mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; McDonnell, J.M.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, S.; Chan, P.K.; Guinot, A.; Hartmannsdottir, H.; Jenni, S.; Dobay, M.P.; Bourquin, J.P.; Bornhauser, B.C. Efficient apoptosis requires feedback amplification of upstream apoptotic signals by effector caspase-3 or -7. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroschein-Stevenson, S.L.; Foley, E.; O’Farrell, P.H.; Johnson, A.D. Phagocytosis of Candida albicans by RNAi- treated Drosophila S2 cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 470, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Y.X.; Xie, H.X.; Li, D.; Ma, X.Y.; Geng, F.N.; Liu, R. Mesaconine inhibits apoptosis through the BAX/BCL-2/Caspase 3 signaling pathway to improve renal fibrosis in rats with chronic renal failure. Chin. Med. Pharmaco. Clin. 2024, 40, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Lu, B.Y.; Luo, S. Value of combined diagnosis using serum Caspase-1 and MMP-1 for postoperative pelvic infection in ovarian cyst patients and analysis of pathogenic characteristics. Anhui Med. J. 2025, 46, 483–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 8, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, D. Candida albicans, plasticity and pathogenesis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzalli, M.H.; Kagan, J.C. Apoptosis and necroptosis as host defense strategies to prevent viral infection. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyamvada, S.; Jayawardena, D.; Bhalala, J.; Kumar, A.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Alrefai, W.A.; Borthakur, A.; Dudeja, P.K. Cryptosporidium parvum infection induces autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cheng, T.; Xu, P.; Cheng, D.; Fang, T.; Xia, Q. A genome-wide survey for host response of silkworm, Bombyx mori during pathogen Bacillus bombyseptieus infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, R.A.; Román, E.; Nombela, C.; Pla, J. The MAP kinase signal transduction network in Candida albicans. Microbiology 2006, 152, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaForce, F.M. Anthrax. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, W.; Kohout, E. Anthrax. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 1971, 6, 209–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, N.H.; Anderson, E.C.; Swenson, E.E.; Janes, B.K.; Fisher, N.; Niemeyer, M.M.; Miyoshi, A.D.; Hanna, P.C. Transcriptional profiling of Bacillus anthracis during infection of host macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3434–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qiu, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Qiang, L.; et al. A bacterial phospholipid phosphatase inhibits host pyroptosis by hijacking ubiquitin. Science 2022, 378, eabq0132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: CACCTTCTGCAAAATTATGGCG R: ACCTTTGCCAAGTCTAACTGTTAA | Reference gene for RT-qPCR |
| Caspase-3 | F: ACCTGATCACTCGTTCCACT R: AGCAAGATGGAAAACGTGTGT | RT-qPCR |
| Bcl-2 | F: GAATATGTAGCCCGCATCTTTT R: CTTTGTTGATTAGACTTGCCGA | |
| Bax | F: CTGCTGCAGGAGTTTACATTCA R: AAGTAAAGGACCCAGGCCAA | |
| Actin apis | F: CATGATTGGTATGGGTCAG R: CGTTGAAGGTCTCGAAGAC | Reference gene for detection of virulence factors in A. apis |
| Ste11-like | F: GGGAAGATTGCCAGGCC R: CACTTGTAGTCCGGATG | Detection of virulence factors in A. apis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Fan, X.; Mi, S.; Guo, X.; Dai, M.; Luo, X.; Zou, P.; Tan, Q.; et al. Apoptosis and Relevant Genes Are Engaged in the Response of Apis mellifera Larvae to Ascosphaera apis Invasion. Insects 2025, 16, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090925
Zhang T, Li J, Yang J, Fan X, Mi S, Guo X, Dai M, Luo X, Zou P, Tan Q, et al. Apoptosis and Relevant Genes Are Engaged in the Response of Apis mellifera Larvae to Ascosphaera apis Invasion. Insects. 2025; 16(9):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090925
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tianze, Jingxian Li, Jiarun Yang, Xiaoxue Fan, Shiyu Mi, Xi Guo, Mengyuan Dai, Xihan Luo, Peiyuan Zou, Qingwei Tan, and et al. 2025. "Apoptosis and Relevant Genes Are Engaged in the Response of Apis mellifera Larvae to Ascosphaera apis Invasion" Insects 16, no. 9: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090925
APA StyleZhang, T., Li, J., Yang, J., Fan, X., Mi, S., Guo, X., Dai, M., Luo, X., Zou, P., Tan, Q., Chen, D., Qiu, J., & Guo, R. (2025). Apoptosis and Relevant Genes Are Engaged in the Response of Apis mellifera Larvae to Ascosphaera apis Invasion. Insects, 16(9), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090925







