Activation of BmToll9-1 in Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Larval Midgut by Escherichia coli and Regulation of Growth
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Bacterial Culture
2.2. RNA Protocol and Bacterial Challenge to Larvae
2.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
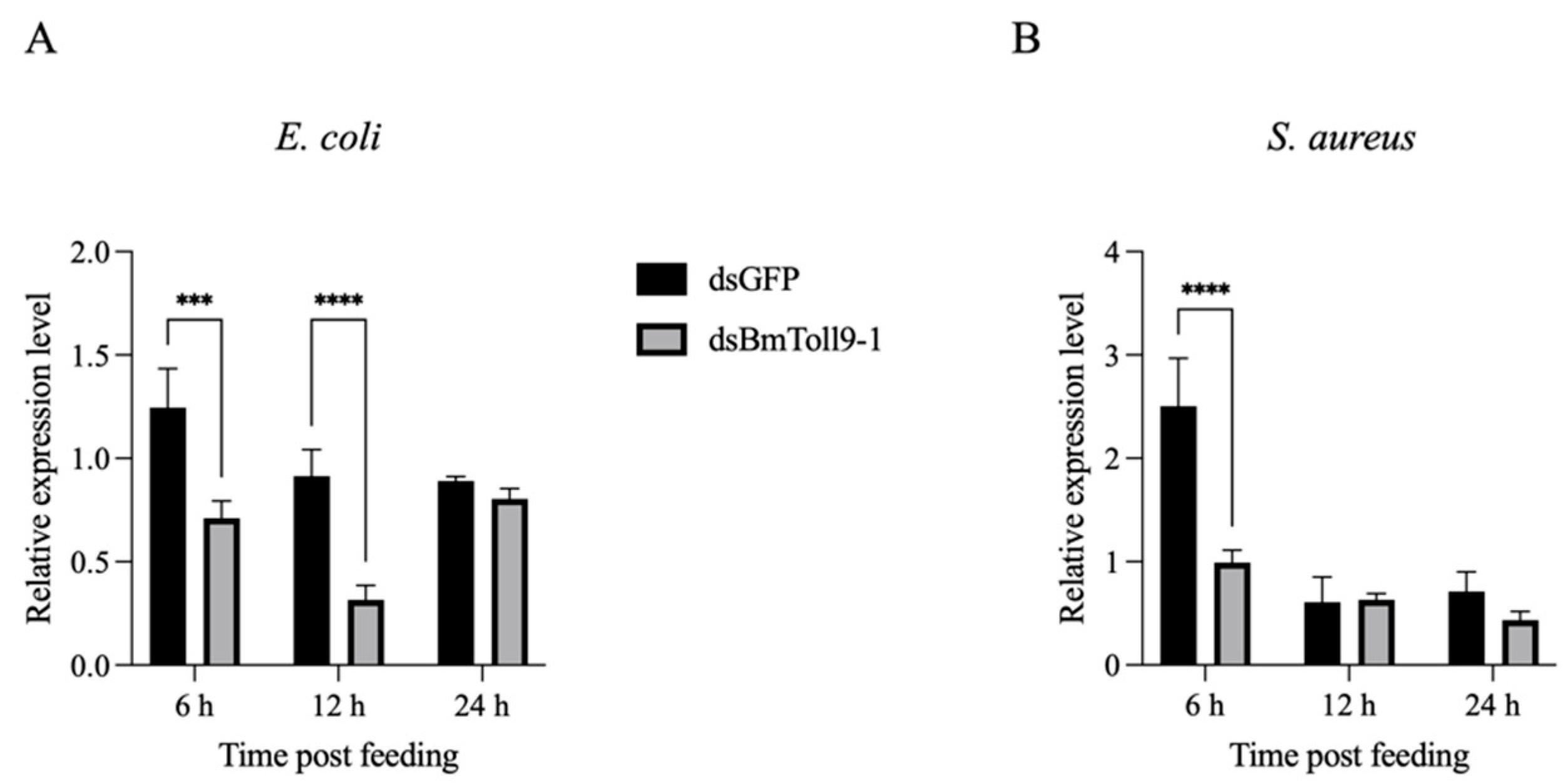
3.1. Activation of BmToll9-1 by Bacterial Challenges Following RNAi of BmToll9-1
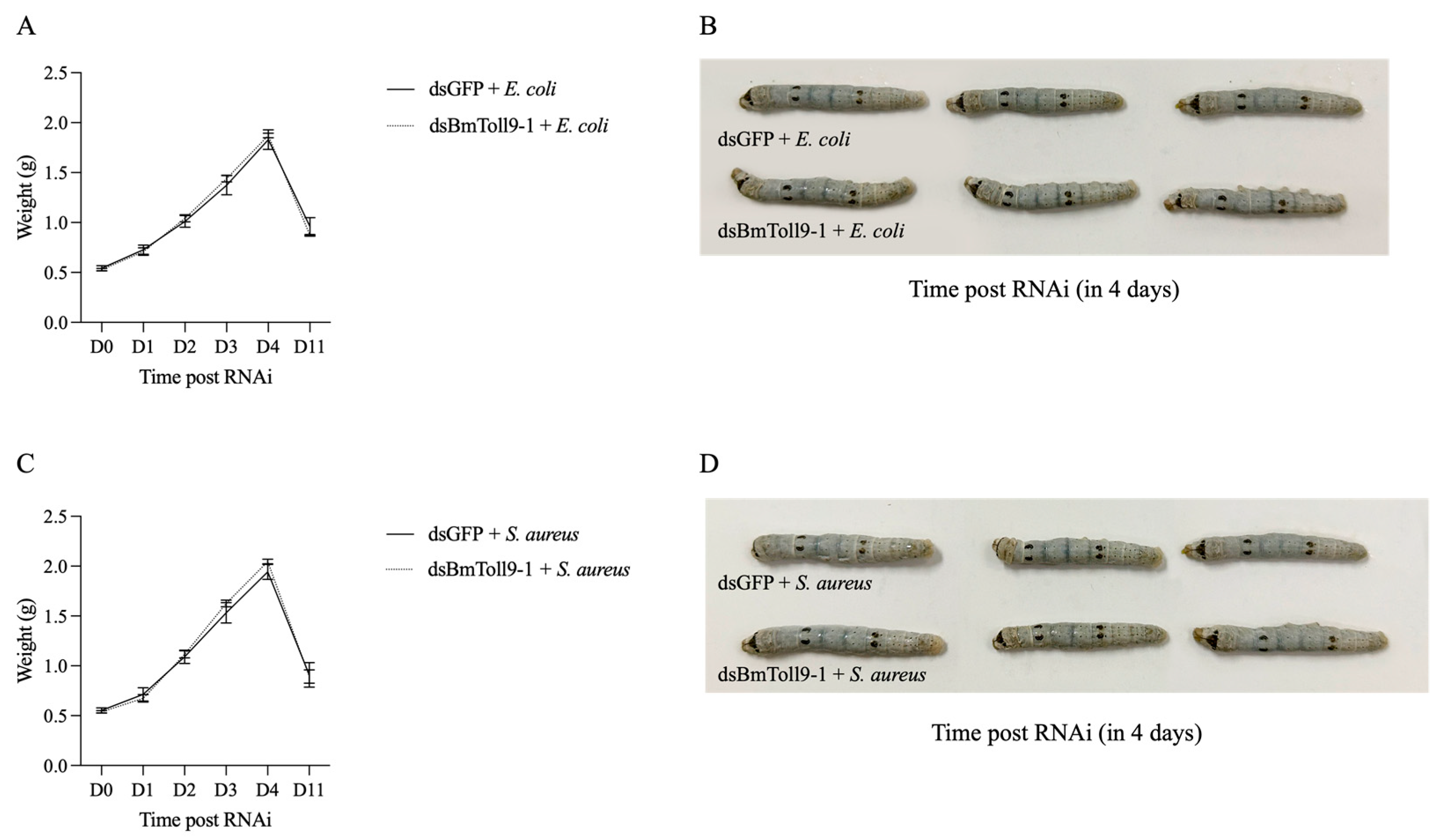
3.2. Bacterial Challenges Following Injection of dsBmToll9-1 Mitigated the Diminished Growth Phenotype
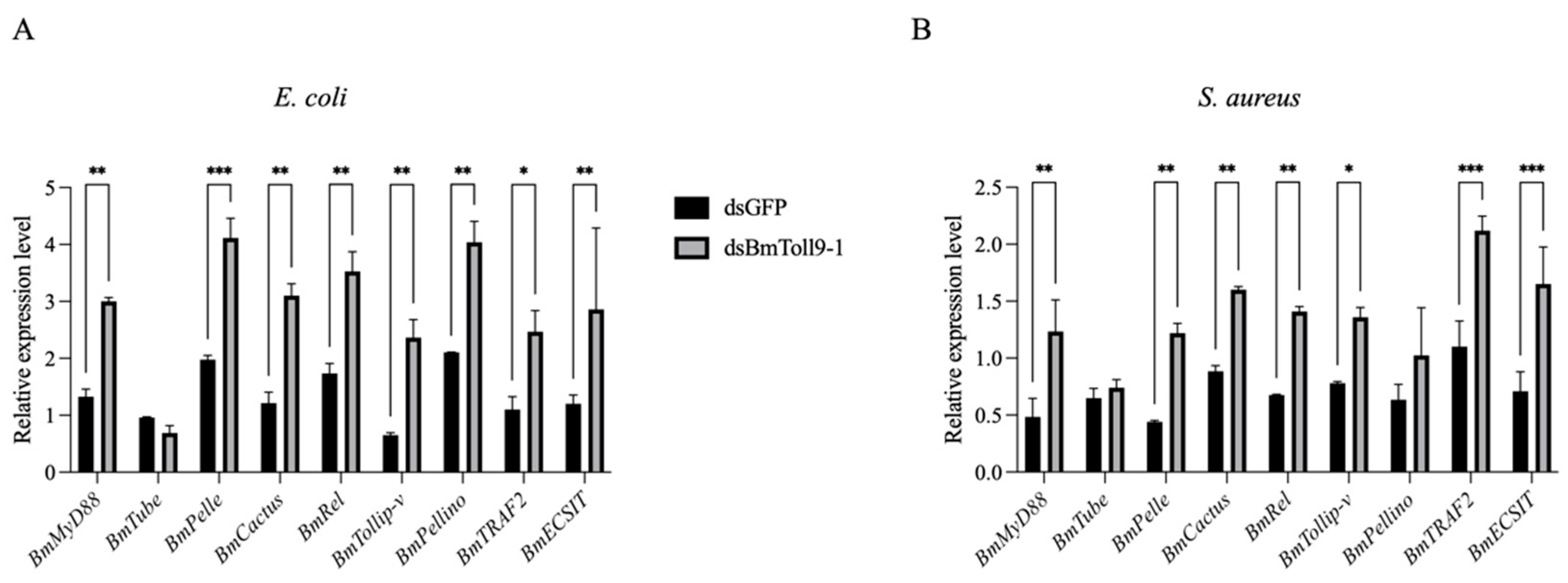
3.3. Bacterial Challenges Following RNAi of BmToll9-1 Induced Signaling Genes in Toll Pathway
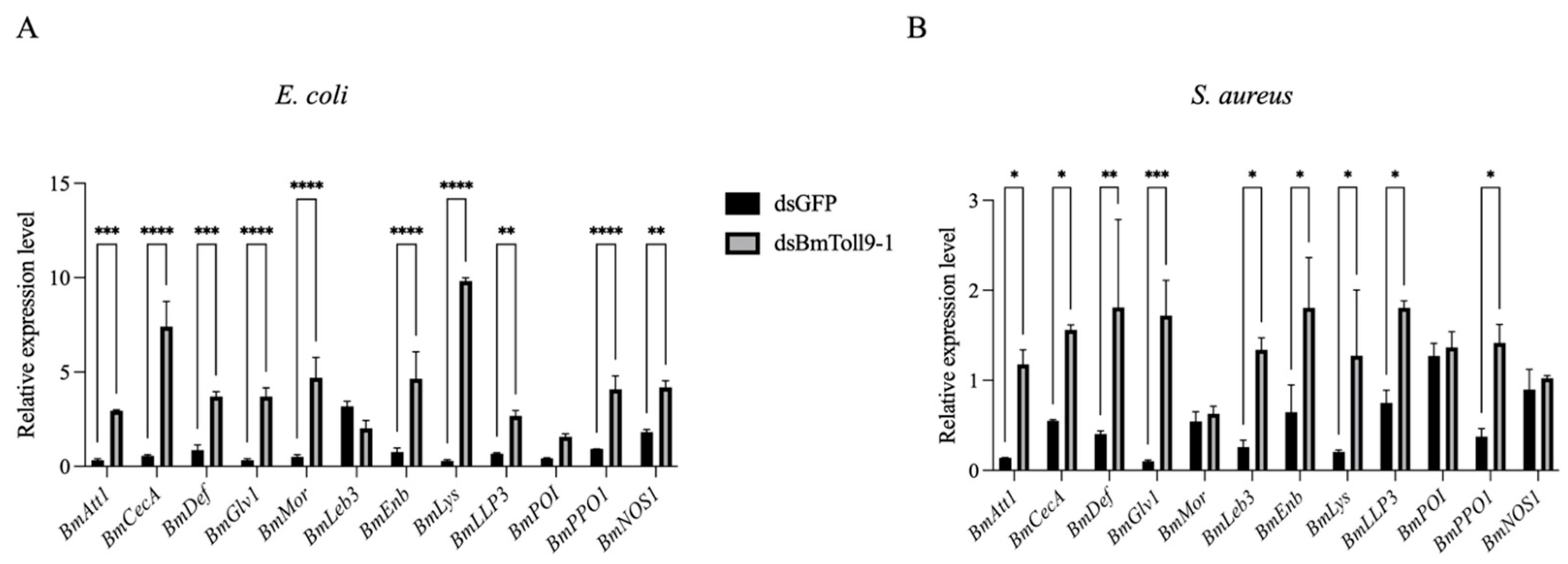
3.4. Bacterial Challenges Following RNAi of BmToll9-1 Induced Downstream Effector Genes
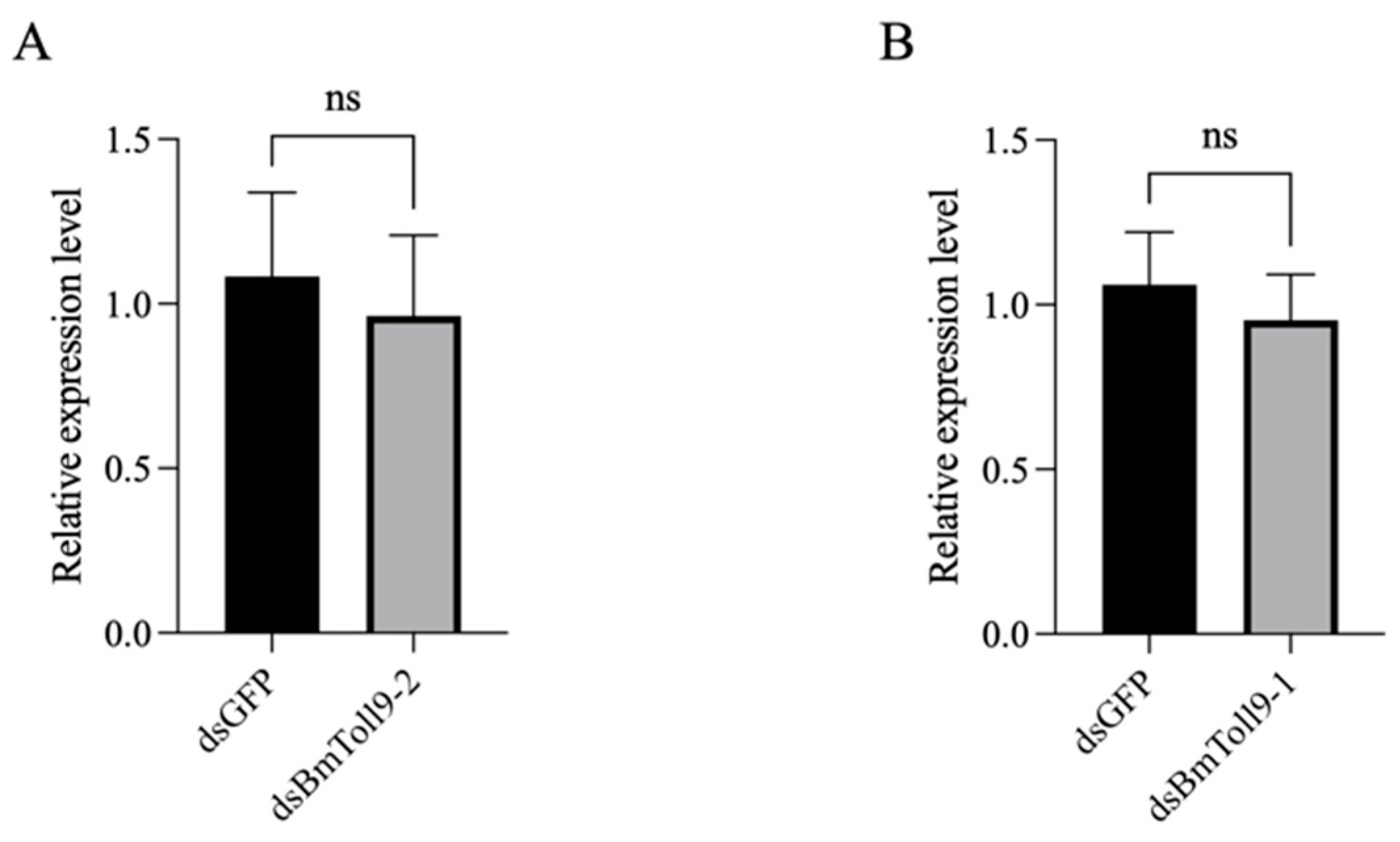
3.5. Silencing BmToll9-1 Did Not Affect the Expression of BmToll9-2
4. Discussion
4.1. BmToll9-1 Might Be Involved in Immune Response to Regulate Development of the Silkworm
4.2. BmToll9-1 Is Preferentially Triggered by Gram-Negative Bacteria
4.3. BmToll9-1 and BmToll9-2 Have Separate Functions in the Silkworm Gut
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merkling, S.H.; van Rij, R.P. Beyond RNAi: Antiviral defense strategies in Drosophila and mosquito. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, R.T.V.; Hillyer, J.F. Hemolymph circulation in insect flight appendages: Physiology of the wing heart and circulatory flow in the wings of the mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3945–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, C.; Xu, P.Z.; Gao, Z.H.; Xia, Q.Y.; Xiang, Z.H. Identification and analysis of Toll-related genes in the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüsslein-Volhard, C.; Lohs-Schardin, M.; Sander, K.; Cremer, C. A dorso-ventral shift of embryonic primordia in a new maternal-effect mutant of Drosophila. Nature 1980, 283, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.J.; Keith, F.J. Drosophila Toll and IL-1 receptor. Nature 1991, 351, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Situ, J.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Lai, M.; Huang, F.; Li, B. BmToll9-1 is a positive regulator of the immune response in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insects 2024, 15, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, C.; Hudson, K.L.; Anderson, K.V. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell 1988, 52, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valanne, S.; Wang, J.; Rämet, M. The Drosophila Toll Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Kawamura, K.; Hori, A.; Salim, E.; Fukushima, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kuraishi, T. Characterization of Spz5 as a novel ligand for Drosophila Toll-1 receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Li, C.F.; He, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Ip, Y.T.; Strand, M.R.; Yu, X.Q. Toll family members bind multiple Spatzle proteins and activate antimicrobial peptide gene expression in Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10172–10181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldon, E.; Kooyer, S.; D’Evelyn, D.; Duman, M.; Lawinger, P.; Botas, J.; Bellen, H. The Drosophila 18 wheeler is required for morphogenesis and has striking similarities to Toll. Development 1994, 120, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauszig, S.; Jouanguy, E.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Imler, J.-L. Toll-related receptors and the control of antimicrobial peptide expression in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10520–10525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.Y.; Yagi, Y.; Hu, X.; Ip, Y.T. The Drosophila Toll-9 activates a constitutive antimicrobial defense. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, R.; Tanji, T.; Yagi, Y.; Ip, Y.T. Toll and Toll-9 in Drosophila innate immune response. J. Endotoxin Res. 2004, 10, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbakken, M.H.; Tørresen, O.K.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Seppola, M.; Gregers, T.F.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Jentoft, S. Evolutionary redesign of the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) Toll-like receptor repertoire by gene losses and expansions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.J. The 18-wheeler mutation reveals complex antibacterial gene regulation in Drosophila host defense. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6120–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambris, Z.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Imler, J.-L.; Capovilla, M. Tissue and stage-specific expression of the Tolls in Drosophila embryos. Gene Expr. Patterns 2002, 2, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikov, T.; Beckendorf, S.K. 18 Wheeler regulates apical constriction of salivary gland cells via the Rho-GTPase-signaling pathway. Dev. Biol. 2007, 307, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppo, A.; Matani, P.; Sharrow, M.; Tiemeyer, M. Induction of neuron-specific glycosylation by Tollo/Toll-8, a Drosophila Toll-like receptor expressed in non-neural cells. Development 2003, 130, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chung, S.; Yoon, J.; Choi, K.W.; Yim, J. Ectopic expression of Tollo/Toll-8 antagonizes Dpp signaling and induces cell sorting in the Drosophila wing. Genesis 2006, 44, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronstein, K.A.; Saldivar, E. Characterization of a honey bee Toll related receptor gene Am18w and its potential involvement in antimicrobial immune defense. Apidologie 2005, 36, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophides, G.K.; Zdobnov, E.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Birney, E.; Blandin, S.; Blass, C.; Brey, P.T.; Collins, F.H.; Danielli, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Immunity-Related Genes and Gene Families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Evans, J.D.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Williams, M.; Sumathipala, N.; Hetru, C.; Hultmark, D.; Jiang, H. Comparative genomic analysis of the Tribolium immune system. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Ishibashi, J.; Fujita, K.; Nakajima, Y.; Sagisaka, A.; Tomimoto, K.; Suzuki, N.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; et al. A genome-wide analysis of genes and gene families involved in innate immunity of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, C.; Cheng, D.; Dai, F.; Li, B.; Zhao, P.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T.; Chai, C.; et al. A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 2004, 306, 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mita, K.; Kasahara, M.; Sasaki, S.; Nagayasu, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kanamori, H.; Namiki, N.; Kitagawa, M.; Yamashita, H.; Yasukochi, Y.; et al. The genome sequence of silkworm, Bombyx mori. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X. Larval RNA Interference in Silkworm Bombyx mori through Chitosan/dsRNA Nanoparticle Delivery. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 212, e67360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Lin, Q.; Swevers, L.; Liu, J. BmPGPR-L4 is a negative regulator of the humoral immune response in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 115, e22093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Swevers, L. Successful oral RNA interference efficiency in the silkworm Bombyx mori through nanoparticle-shielded dsRNA delivery. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2025, 161, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, P.; Beerntsen, B.T.; Ling, E. BmToll9, an Arthropod conservative Toll, is likely involved in the local gut immune response in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Smagghe, G.; Swevers, L. Transcriptional response of BmToll9-1 and RNAi machinery genes to exogenous dsRNA in the midgut of Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kolliopoulou, A.; Smagghe, G.; Swevers, L. Modulation of the transcriptional response of innate immune and RNAi genes upon exposure to dsRNA and LPS in silkmoth-derived Bm5 cells overexpressing BmToll9-1 receptor. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 66, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Ren, F.; Yi, H.; Deng, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Toll9 from Bombyx mori functions as a pattern recognition receptor that shares features with Toll-like receptor 4 from mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103021118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Liao, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Bu, X.; Huang, S.; Jiang, W.; Swevers, L. Immunological function of Bombyx Toll9-2 in the silkworm (Bombyx mori) larval midgut: Activation by Escherichia coli/lipopolysaccharide and regulation of growth. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 116, e22130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Swevers, L. Similarly to BmToll9-1, BmToll9-2 Is a Positive Regulator of the Humoral Immune Response in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insects 2024, 15, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Huang, Y.; Hou, C.; Qin, G.; Lv, D.; Guo, X. Inductive expression patterns of genes related to Toll signaling pathway in silkworm ( Bombyx mori ) upon Beauveria bassiana infection. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Xia, Q.Y.; Cheng, D.J.; Duan, J.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Reference genes identified in the silkworm Bombyx mori during metamorphism based on oligonucleotide microarray and confirmed by qRT-PCR. Insect Sci. 2008, 15, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Shuai, J.; Chen, X.; Ling, E. Expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in Bombyx mori gut modulated by oral bacterial infection and development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Swevers, L.; Liu, J. Silencing of the immune gene BmPGRP-L4 in the midgut affects the growth of silkworm (Bombyx mori) larvae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Keesey, I.W.; Hansson, B.S.; Knaden, M. Gut microbiota affects development and olfactory behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb.192500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Tang, J.; Ding, G.; Mashilingi, S.K.; Huang, J.; An, J. Gut microbiota is a potential factor in shaping phenotypic variation in larvae and adults of female bumble bees. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Yao, Z.; Raza, M.F.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, H. Regulatory mechanisms of microbial homeostasis in insect gut. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Accession Number | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primers for qRT-PCR | |||
| BmToll9-1 | PP496203 | F: CGCAGACCGTTGAGTACATG | 149 |
| R: CCAGACTGTCGTACCTTGGT | |||
| BmToll9-2 | PP716770 | F: GGTTACAAGCGAACGGTAGC | 80 |
| R: CCAAATATCCGGACTGCTGC | |||
| BmTIF4A | DQ443290 | F: TTCGTACTGGCTCTTCTCGT | 174 |
| R: CAAAGTTGATAGCAATTCCCT | |||
| BmTIF3s4 | DQ443238 | F: ACTTCAAGTTCAGGGCAGAT | 110 |
| R: TTAATTGTTTTGTGGAGGCT | |||
| Signaling | |||
| BmMyD88 | XM_028186400 | F: AACGGTCACGACTCGAACTC | 105 |
| R: TCTGCCCAGATTCTTCATCC | |||
| BmTube | XM_028173146 | F: GGCAGAAAGTTATGGCTTGG | 82 |
| R: ATCCTCAAATGCTCGCTGTT | |||
| BmPelle | XM_028182154 | F: ACATCAAGCCGGCTAACATC | 117 |
| R: ACCGTGAGACCTTCAGATGC | |||
| BmCactus | XM_028180230 | F: ACAGTCGTGCGTACATTTGG | 97 |
| R: CAGCCTCTCCCTATCGTCAA | |||
| BmTollip-d | XM_021351983 | F: GACGAGTCAGTCCCTCTTGC | 92 |
| R: GTGGCTGGTGGAATTCGTAG | |||
| BmTollip-v | XM_028186930 | F: TGCTACTTCTGACGGTGTGG | 91 |
| R: AGGGCCACTTTGTGGTACTG | |||
| BmPellino | XM_028184930 | F: AGAGTCGCTCAGCACAACAA | 95 |
| R: CAATGTGGCTCCACACAGAT | |||
| BmTRAF2 | XM_028172769 | F: TCGCTCCTATGGGCATAACT | 118 |
| R: CCGCATGTTGTGATTACTGG | |||
| BmECSIT | XM_028171307 | F: ATGCCGCCTTAGCTAGAATG | 86 |
| R: GCCTTTGGGCAGTACGTCTA | |||
| Effectors | |||
| BmAttacin1 | NM_001043541 | F: CAGTGAACTCGGATGGAACC | 97 |
| (BmAtt1) | R: GGCGCTGAGTACGTTCTTGT | ||
| BmCecropinA | NM_001043997 | F: CCGTCATAGGGCAAGCGAAA | 230 |
| (BmCecA) | R: AGCAATGACTGTGGTATGTCAA | ||
| BmDefensin | AB_367525 | F: GTTAAGTGCGGCGTTGACTG | 104 |
| (BmDef) | R: TGACAGGGAAAGTGGAAGGG | ||
| BmGloverin1 | AB_289654 | F: GCTGGGATAGAAGCATCAGC | 107 |
| (BmGlv1) | R: ACATCAGGCCTTCTGTGACC | ||
| BmMoricin | AB_006915 | F: TGTGGCAATGTCTCTGGTGT | 117 |
| (BmMor) | R: CTGGCGATATTGATGGCTCT | ||
| BmLebocin3 | NM_001126260 | F: CTCGATCCAAACCGAAGGTA | 105 |
| (BmLeb3) | R: CGGCTGGTCAAGTCCAGTAT | ||
| BmEnbocin | FJ373019 | F: ACCTCGCACAACTAGTTCGG | 116 |
| (BmEnb) | R: CCAACAGAACAAACCCACTCG | ||
| BmLysozyme | NM_001043983 | F: TAACGGCTCGAAGGACTACG | 103 |
| (BmLys) | R: GAGGTCGGAGCACTTAACGT | ||
| Lysozyme-like protein | XM_012696687 | F: GTTTAATCGAGCAGGGCAGC | 120 |
| (BmLLP3) | R: CACCCTTGCGACCTTCTTTG | ||
| Phenoloxidase inhibitor | XR_001139981 | F: GGATACGTGACTGGAAATGCA | 102 |
| (BmPOI) | R: GTCATAATCCACGGGTTTGTCC | ||
| Prophenoloxidase 1 | AF_178462 | F: AGTGGGAAGCCATTCTCCTT | 81 |
| (BmPPO1) | R: GCCAGGTTTCACTCCTTGAG | ||
| Nitric oxide synthase 1 | XM_012689821 | F: TCATCACCACTAGCGCATCC | 102 |
| (BmNOS1) | R: CCTTGTCCGTTCTGTGTCCT | ||
| Primers for dsRNA synthesis | |||
| T7-BmToll9-1 | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | 531 | |
| ACTATAGGCACAGGTCGGGT | |||
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | |||
| TCGTTGTCCCATTCGCTGAT | |||
| T7-BmToll9-2 | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | 581 | |
| TAGTATTCTCCCGGCTCTC | |||
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | |||
| GAAGGGTGCCTTGTGTAATC | |||
| T7-GFP | F: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | 495 | |
| TACGGCGTGCAGTGCT | |||
| R: TAATACGACTCACTATAGG | |||
| TGATCGCGCTTCTCG | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Lai, M.; Chen, J.; Swevers, L. Activation of BmToll9-1 in Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Larval Midgut by Escherichia coli and Regulation of Growth. Insects 2025, 16, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060621
Liu J, Chen W, Lai M, Chen J, Swevers L. Activation of BmToll9-1 in Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Larval Midgut by Escherichia coli and Regulation of Growth. Insects. 2025; 16(6):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060621
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jisheng, Weijian Chen, Minchun Lai, Jiahua Chen, and Luc Swevers. 2025. "Activation of BmToll9-1 in Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Larval Midgut by Escherichia coli and Regulation of Growth" Insects 16, no. 6: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060621
APA StyleLiu, J., Chen, W., Lai, M., Chen, J., & Swevers, L. (2025). Activation of BmToll9-1 in Silkworm (Bombyx mori) Larval Midgut by Escherichia coli and Regulation of Growth. Insects, 16(6), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060621






