Simple Summary
Enhancing the survival of the ichneumonid parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae remains a significant technical challenge for large-scale indoor reproduction. This study develops a novel methodology to promote cocoon formation in C. chlorideae by utilizing the host protein Haserpin-e to inhibit the insect’s innate immune responses. To elucidate the mechanism underlying enhanced cocoon formation, we found that Haserpin-e protein reduced encapsulation, inhibited melanization processes, and suppressed the expression of antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) in the host Helicoverpa armigera. Furthermore, this study extends our understanding of the functionalities of Haserpin-e proteins.
Abstract
The ichneumonid parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae is an important natural enemy of lepidopteran pests in different agro-ecosystems, specifically targeting early larvae (second- and third-instar). Enhancing the survival of C. chlorideae, especially within hosts, remains a significant technical challenge for large-scale indoor reproduction. This study investigates the use of endogenous serpin-e protein, derived from the host Helicoverpa armigera (Haserpin-e), to improve the survival rate of C. chlorideae in indoor reproduction. The results demonstrated that Haserpin-e protein significantly enhanced cocoon production in C. chlorideae, with no observable adverse effects on the life history traits of both F0 and F1 generations of C. chlorideae. By investigating the mechanism underlying cocoon formation promotion, it was found that Haserpin-e protein reduced the encapsulation, inhibited melanization, as well as suppressed the expression of antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) in H. armigera. This study provides novel insights into improving the survival of C. chlorideae by inhibiting host immune responses through the application of its endogenous Haserpin-e protein during large-scale indoor reproduction efforts. Additionally, this research further elucidates the multifaceted functionality of Haserpin-e proteins by demonstrating their role in regulating innate immune processes in H. armigera, including negatively regulating encapsulation, melanization, and AMP expression.
1. Introduction
Campoletis chlorideae Uchida (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) is an important natural enemy of more than 30 Lepidopteran pest species, such as Helicoverpa armigera Hübner, Spodoptera litura Fabricius, Spodoptera frugiperda Smith, Agrotis ipsilon Hufnagel, Mythimna separata Walker, and so on [1,2,3,4,5]. This parasitoid specifically targets early larvae (second- and third-instar) of the Lepidopteran species, exerting significant control over the population size of these pests in agricultural fields. A study in Hunan province, China, reported that this parasitoid’s parasitism rate on H. armigera larvae ranged from 25.1% to 63.1% [3]. Furthermore, it has shown a notable efficacy in reducing pest numbers by 20% through parasitism on plants, achieving an impressive 80.5% parasitization rate on H. armigera larvae in chickpea fields [6,7]. Consequently, C. chlorideae is recognized worldwide as a promising biological control agent for managing Lepidopteran pest populations.
Despite the high efficacy of C. chlorideae in controlling Lepidopteran pests, the survival capacity after parasitism remains a significant challenge for the mass-rearing of C. chlorideae due to the strong immune responses elicited by the host. The survival of parasitoids depends on their ability to overcome the host’s immunological rejection. Endoparasitic insects develop as larvae within the host’s body cavity, where both the oviposited eggs and the developing larvae have evolved various strategies to evade or suppress host immune responses, manipulate host immunity, and regulate their growth and development [8]. On the one hand, C. chlorideae disrupts cellular immune responses by interfering with apoptosis [9,10], inactivating hemocytes [11], degrading the cytoskeleton [12], and disrupting encapsulation [13,14]. On the other hand, it inhibits humoral immune responses by suppressing melanization [15,16] and reducing the production of defense molecules such as antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) [17].
Most of the host’s immune responses are classified as innate immunity. Insects employ innate immunity as their primary defense mechanism against pathogen attacks. Serpins within insects negatively regulate cascades of serine protease activation triggered by innate responses, which encompass hemocyte clotting, melanization, the hemocyte-mediated melanotic encapsulation response, and the expression of AMPs [18,19]. Normally, host encapsulation occurs after C. chlorideae lays eggs within the host’s body. Host encapsulation is subsequently followed by melanization, a process that effectively kill the exogenous parasite. Melanization, a rapid localized blackening response activated by phenol oxidase (PO), occurs at wound sites and in response to foreign objects such as parasitic wasp eggs [20]. During this process, polyphenol oxidase (PPO) zymogen is converted into active PO by a clip domain serine proteinase [21,22]. The resulting active PO catalyzes the oxidation of phenols to form quinones, which then spontaneously polymerize to generate melanin [23,24]. This process is tightly regulated by serpins that specifically target certain serine proteases responsible for melanization regulation [19]. Several serpins have been identified as melanization regulators in insects, such as SRPN1 and SRPN2 in Aedes agypti [25]; serpin-5 and serpin-9 in H. armigera [26]; SRPN2 in Anopheles gambiae Meigen [27], serpin-5, -6, -15, and -32 in B. mori [28,29,30,31]; serpin-1, serpin-3, serpin-4, serpin-5, serpin-6, serpin-7, serpine-9, serpine-12, and serpine-13 in Manduca sexta Blanchard [32,33,34,35]; SPN40, SPN48, and SPN55 in Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus [36], and serpin-4 in Ostrinia furnacalis Guenée [37].
Previously, we have identified a serpin protein in H. armigera (Haserpin-e) that exhibits inhibitory activity against midgut serine proteases [38,39]. However, it is not known whether Haserpin-e negatively regulates the serine protease cascade triggered by innate immune responses, thereby improving the survival of C. chlorideae in the host. If Haserpin-e could improve the survival of C. chlorideae, this will facilitate the mass-rearing of C. chlorideae and contribute to its application as a biocontrol agent for managing Lepidopteran pest populations. In this study, we first examined the impact of Haserpin-e on the cocoon formation rate of C. chlorideae (where cocoon formation indicates that C. chlorideae successfully completed its growth and development within the host). Subsequently, we assessed the effects of Haserpin-e on the life history traits of C. chlorideae, including cocoon formation rate, cocoon size and adult size, sex ratio, mating rate, adult survival time, mature eggs, and number of ovarioles, and these life history traits of F1 generation. These factors are critical in determining the quality of C. chlorideae and ensuring sustainable field reproduction. Finally, we explored the functions and mechanisms of Haserpin-e in H. armigera and the cocoon formation promotion process. This research aims to develop a new methodology for the large-scale propagation of C. chlorideae, thereby facilitating efficient biological control of Lepidopteran pests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Haserpin-e
The H. armigera larvae were obtained from Henan Jiyuan Baiyun Industry Co., Ltd. (Jiyuan, China) and reared in the laboratory using an artificial diet free of insecticides, following previously established protocols [40].
The C. chlorideae colony, originally collected from the Xuchang Campus of Henan Agricultural University on 7 June 2023, has been maintained in the laboratory for multiple generations by rearing on H. armigera larvae at a controlled temperature of 25 ± 1 °C, 55% humidity, and photoperiod of 16 h light and 8 h dark [41].
The Haserpin-e expression vector was obtained from Zhang et al. [38] and the Haserpin-e protein was expressed and purified by Hangzhou Huanan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). The Haserpin-e protein was produced using the Haserpin-e-pet-28a (+) expression plasmid in Escherichia.coli expression Rosetta (DE3) strain. After culturing, the bacterial cells were induced with IPTG (Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside) to express the raw Haserpin-e protein. Subsequently, the raw protein was extracted through ultrasonic disruption and centrifugation, followed by resuspension. Gradient dialysis with urea was performed using a nickel column, and the protein was finally concentrated using an ultrafiltration tube and dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The final protein concentration was determined by the Bradford method.
2.2. Effect of Haserpin-e on C. chlorideae
The artificial diet of H. armigera was prepared and supplemented with PBS buffer or Haserpin-e proteins (with final concentrations of 6 or 10 μg/g Haserpin-e proteins). Previous experiments have demonstrated that these two concentrations (6 and 10 μg/g) can effectively enhance the cocoon formation rate; however, the cocoon formation rate does not continue to increase with higher concentrations of Haserpin-e. On the one hand, 480 (120 H. armigera for each treatment, 30 H. armigera for each repetition in each treatment) early second-instar H. armigera were prepared. And these H. armigera were provided with diets corresponding to the treatment concentration for a duration of 24 h prior to parasitism. After eating Haserpin-e or PBS, each of the H. armigera would be parasitized. On the other hand, sixty successfully mated female C. chlorideae adults, aged 5–7 days (this stage exhibits the greatest reproductive capacity), were selected and used to parasitize the previously treated larvae. H. armigera in each treatment (120) were parasitized by 15 C. chlorideae, with 8 H. armigera individuals parasitized per C. chlorideae to ensure that the evaluated parasitoid wasps represent the population characteristics. One C. chlorideae was placed in a finger tube (25 mL) and positioned upside down on the table. The tube was quickly lifted, and one H. armigera was introduced. The C. chlorideae promptly pricked the H. armigera (within 5 s), indicating that an egg had been laid inside the H. armigera. The parasitized H. armigera were fed under laboratory conditions, and the life history traits of F0 generation were recorded in each treatment, including the cocoon production rate after 7 days, the emergence rate after 14 days, cocoon size and adult size, sex ratio, mating success rate, adult lifespan, number of ovarian ducts, and the mature eggs in the dead adults. The size of cocoons was used to indicate the size of pupae, and measurements were taken for both the length and width of the cocoons [42]. Following the emergence of C. chlorideae, the cocoons were carefully collected and placed on transparent glass cups. They were then secured with double-sided adhesive tape before being examined under an OLYMPUS-SZX7 microscope for determination. The tibial length of the hind legs was utilized as an indicator of adult size [42]. Tibial segments from the hind feet of naturally deceased C. chlorideae were carefully removed with pointed forceps while gently holding the carapace, arranged neatly on a clean glass plate, and then a photograph was taken using a stereoscope and measured their length under the stereoscope. Photographs of C. chlorideae cocoons under various experimental treatments were taken using a stereoscope (SZX7, OLYMPUS, Tokyo, Japan). Upon emergence, <24 h C. chlorideae female were paired with males. Each pair was placed in a 25 mL cup for 15 min. Successful mating was determined by the sustained wing vibration exhibited by the male and the occurrence of copulation. If the females are not mated on the first day, they will be provided with additional opportunities for mating on the following days using the aforementioned methods. Finally, the number of mated female adults was recorded for each treatment group. The adults C. chlorideae were reared in 25 mL cups and provided with 10% honey-soaked cotton balls placed inside the cup (replaced daily) within a temperature-controlled incubator set at 26 ± 1 °C and 55% humidity until their demise. Five to seven days after the above C. chlorideae adults emerged, 15 mated C. chlorideae in each treatment were randomly selected for a total of 60 C. chlorideae. These C. chlorideae were used to investigate the effects of Haserpin-e or PBS on F1 generation (Figure S1). Each C. chlorideae in each treatment parasitized 6 normal H. armigera (90 H. armigera for each treatment, with 30 H. armigera per repetition in each treatment).
To further investigate the specific effects of Haserpin-e on reproduction, we prepared 360 H. armigera (90 H. armigera for each treatment, with 30 H. armigera per repetition in each treatment). Additionally, 60 C. chlorideae were used for parasitization (each parasitizing 6 H. armigera). The dissection of C. chlorideae occurred at the sixth day (the reproductive peak) after their emergence, where the head was firmly pressed with a dissecting needle, while gentle pressure was applied with another dissecting needle on the abdomen of the female wasps to carefully extract the intact ovary tube. Subsequently, they were immersed in a PBS solution with a pH of 7.2. The ovaries were meticulously dissected using dissecting forceps under a stereomicroscope (SZ2-LGB, Shenzhen, China, Olympus Corporation of Japan), and then placed on slides for the quantification of ovarian tubes the using an OLYMPUS-SZX7 microscope. After that, the oviducts were broken to count the number of mature eggs inside (Figure S1).
The second-instar H. armigera is the most suitable parasitic stage, and with the increase in instar the host immunity is enhanced and the survival rate of C. chlorideae decreases [43]. In order to further verify the effect of Haserpin-e on promoting cocoon formation and prolonging parasitic time for convenient breeding, we further verified the effect of Haserpin-e at the instar for 1 day and 2 days using 360 3rd (1 day or 2 days) H. armigera (90 H. armigera for each treatment, with 30 H. armigera per repetition in each treatment). Additionally, 60 C. chlorideae were used for parasitization (each parasitizing 6 H. armigera). The cocoon production rate and the emergence rate were investigated (Figure S1).
2.3. Effect of Haserpin-e on Encapsulations of Host
A total of 600 early second-instar H. armigera larvae were prepared (150 for each treatment, with 50 as a replication per treatment) and treated with either PBS or Haserpin-e prior to being monoparasitized by C. chlorideae (Figure S1). A total of 60 C. chlorideae were used to parasitize, and each one parasitized 6 H. armigera (Figure S1). After incubation at 34 °C for 48 h, the H. armigera were dissected under a dissecting microscope (SOPTOP s1200-3, Yuyao, China, Ningbo Sunny Instruments Co., Ltd.) to observe encapsulation. The encapsulation rate was calculated as the number of capsules in each group divided by the total number of embryos.
2.4. The Effect of Haserpin-e on Hemolymph In Vitro
Hemolymph extraction: One hundred third-instar H. armigera were chilled on ice for 5 min to prepare them. Hemolymph fluid was collected using the aforementioned method. The collected hemolymph was then subjected to centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C, followed by collection of the supernatant for subsequent testing. For the following experiments, three technical repetitions were performed.
Haemolymphatic darkening analysis: The prepared hemolymph was mixed with Haserpin-e (final concentration of 0.2 μg/μL). The control group was treated with an equal volume of PBS. Subsequently, the samples were thoroughly mixed and sealed with a film. It was kept at room temperature. At 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 120 h time points, 1.5 μL of the solution was extracted and deposited onto a glass slide for photography. After each usage, it was resealed with the film until the completion of photography at 120 h.
The method for determining the activity of the PO enzyme was adapted from a previous study [44]. Hemolymph samples were prepared by mixing with PBS or Haserpin-e (final concentration of 0.2 μg/μL) incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Only hemolymphs without any additives served as the blank control. Subsequently, the PO enzyme activity was determined using a commercially available PO kit (Grace, Suzhou, China), and measured using a microplate reader (BioTEK, Charlotte, VT, USA) at a wavelength of 490 nm.
Following the same procedures as for PO enzyme activity, samples were prepared to measure PPO and trypsin enzyme activities. PPO enzyme activity was analyzed using the PPO enzyme activity kit (Grace, Suzhou, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions [45]. The absorbance of PPO enzyme activity was measured at a wavelength of 420 nm using a microplate reader. Trypsin enzyme activity was analyzed using the trypsin kit (Grace, Suzhou, China) and measured at a wavelength of 405 nm using a microplate reader [46].
2.5. The Impacts of Haserpin-e on Enzyme Activities in Non-Parasitized and Parasitized H. armigera Larvae
A total of 240 H. armigera were prepared as the above PBS or Haserpin-e treated (60 for each treatment, 20 as a replication in each treatment) without being parasitized (Figure S1). A total of 240 H. armigera (60 for each treatment, 20 as a replication in each treatment) were also prepared as the above PBS or Haserpin-e treated, and these were parasitized once by the C. chlorideae (Figure S1). Then, the treated H. armigera ate a normal artificial diet for 24 h in 26 ± 1 °C incubator. Later, the H. armigera were dissected to remove cephalic shells, the epidermis, and food residue, and the remaining tissues were collected in 1.5 mL tubes. The collected tissues were weighed, and PBS was added at a ratio of 1 mg to 9 mL. Following complete grinding, the tissues were centrifuged at 6000 rpm at 4 °C for 10 min. Subsequently, the supernatant was transferred and further diluted 10 times in PBS, using a BCA protein assay kit (Nanjing, Beijing, China) to test the protein concentration before determining the enzyme activity. Subsequently, the activities of trypsin, PO, and PPO enzymes were quantified using the corresponding enzyme activity kit as described above. Each enzyme activity was tested three times for each sample.
2.6. Sample Preparation, cDNA Synthesis and Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analyses
Referring to the above method in Section 2.5, the samples for each treatment were prepared (Figure S1). Then, the total RNA was extracted using RNAiso Plus (TaKaRa, Kusatsu, Japan). The reverse transcription kit HiScript®III RT Su-perMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper) (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) was employed for cDNA synthesis, following the provided instructions. The real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) reaction system and process, as well as the calculation methods, were performed following the methodology outlined by Wei et al. [47]. All the relative primers of AMPs (cecropin 1, cecropin D, gloverin, and moricin) and the gene ID were listed in Table S1. The reference genes used in this study were EF-1α and β-Actin of H. armigera. Each of the genes expressions were tested three times for each sample.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Two-way and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to statistically analyze the above data with SPSS 22.0 at the p < 0.05 level of significance. Before analysis of variance, all the data were tested under the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variance. When the data did not meet the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variance, the data were transformed by arcsine or log, and then variance analysis was conducted. If all the transformations could not meet the analysis requirements, the two-way non-parametric ANOVA method was used, as seen in Shen et al. [48]. Then, the Tukey method was used for multiple comparisons, and the false discovery rate was used to correct the comparison results. One-way analysis of variance in the life history traits, including cocoon production, cocoon dimensions (length and width), adult size, sex ratio, mating rate, female and male adults’ longevity, ovarian count, and mature egg count, and the activities of trypsin, PO, PPO, encapsulation rate, and AMPs expression among the four treatments (CK, PBS, and 6 and 10 μg/g Haserpin-e) were compared with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. And the significantly differences in the activities of trypsin, PO, PPO, and TH enzymes among the three treatments (CK, PBS, and Haserpin-e) were compared with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The differences in trypsin, PO, PPO, and TH enzyme activities, as well as the AMPs expression between no-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae, were analyzed by t test with p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. The Impact of Haserpin-e on the Cocoon Production of C. chlorideae
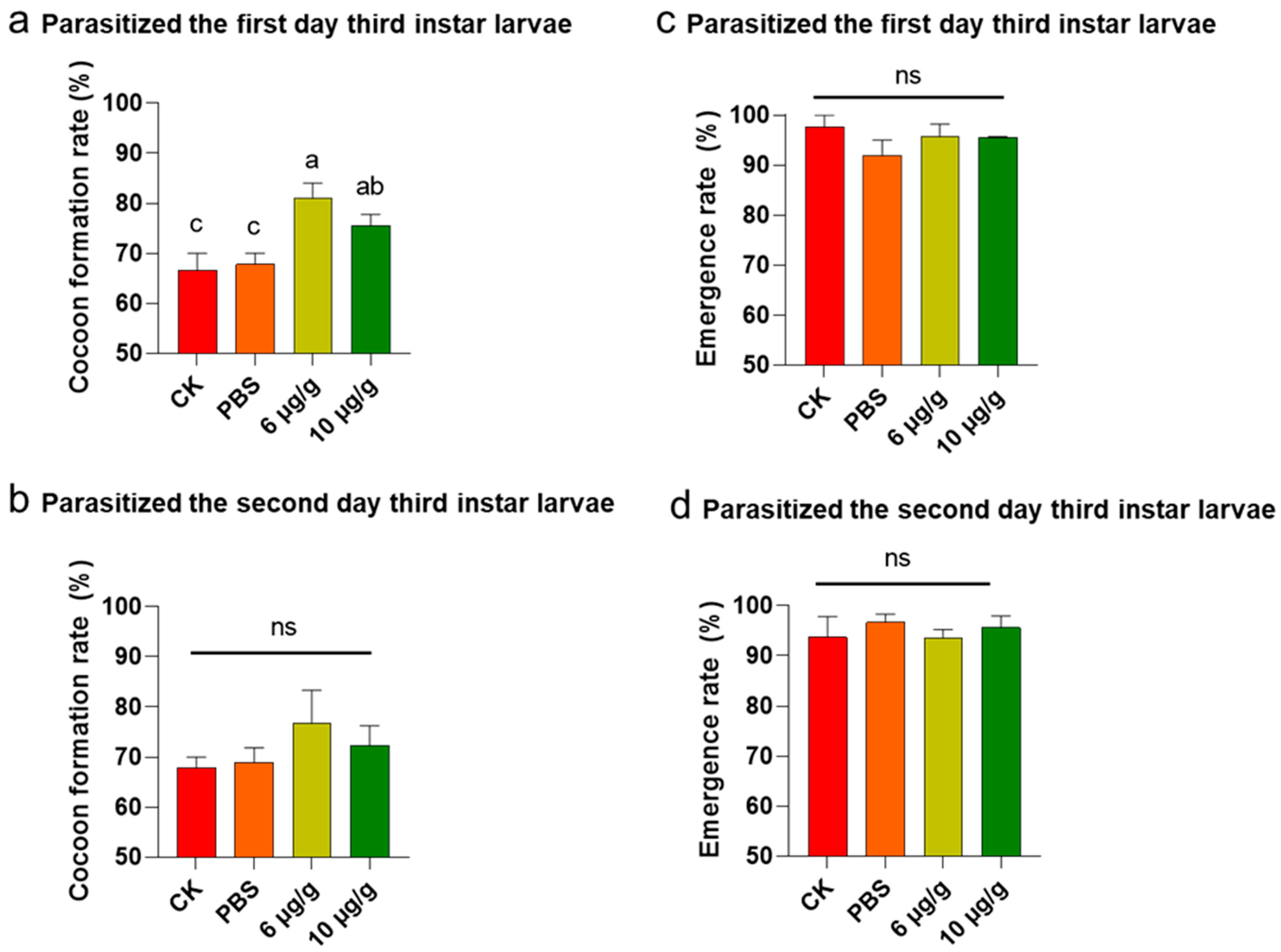
The Haserpin-e protein was purified and dissolved in PBS (Figure S2). The cocoon production significantly increased when H. armigera ate Haserpin-e, compared to the blank control and PBS treatment groups (Table 1). Specifically, the cocoon yield of C. chlorideae derived from parasitized second-late-stage H. armigera showed a significant increase of 7.22% and 4.44% compared to the CK (blank control) and PBS treatment groups when treated with 6 μg/g Haserpin-e, respectively (df = 15, F = 9.31, p = 0.002; Table 1). Moreover, the cocoon production exhibited a significant increase of 13.34% and 10.56% compared to the CK and PBS treatment groups under the treatment of 10 μg/g Haserpin-e, respectively (df = 15, F = 9.31, p = 0.002; Table 1). The cocoon yield of C. chlorideae from hosts parasitized at the third-instar (day 1) Haserpin-e treated H. armigera (df = 10, F = 6.609, p = 0.022, Figure 1a) was also significantly increased compared to the CK (blank control) and PBS treatment groups, although parasitization of late instar host larvae will result in a decrease in cocooning rate. After H. armigera was fed with 6 μg/g Haserpin-e, the cocoon yield increased by 14.45% and 13.34% compared with the CK and PBS treatment groups, respectively (Figure 1a). Similarly, providing H. armigera with 10 μg/g Haserpin-e led to cocoon yields that were 8.89% and 7.78% higher compared to the CK and PBS groups, respectively (Figure 1a). The cocoon yield of C. chlorideae from hosts parasitized at the third-instar (day 2) H. armigera, despite the fact that the effect of Haserpin-e has not yet reached a statistically significant level of impact, the is still an observed increase in cocoon production (Figure 1b, df = 10, F = 0.99, p = 0.437). C. chlorideae emerged seven days after cocoon formation. For the three stages of parasitism, Haserpin-e did not have any effect on the emergence rate of C. chlorideae (Table 1, Figure 1c,d). The second-instar of H. armigera is the optimal parasitic stage. We observed the F1 generation of the C. chlorideae that parasitized the H. armigera at this stage. The C. chlorideae of the F0 generation that indirectly contacted Haserpin-e exhibited a higher cocoon production rate; however, this effect was not sustained in the F1 generation (Table 1). A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction effect between the F0 and F1 generations (df = 1, F = 66.39, p < 0.0001; Table 1), with the cocoon formation rate of C. chlorideae in the F0 generation significantly higher than that in the F1 generation.

Table 1.
The impact of Haserpin-e supplementation on H. armigera larvae on life history traits of C. chlorideae.
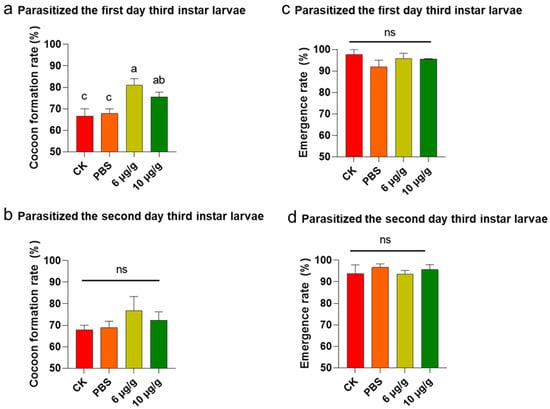
Figure 1.
The impact of Haserpin-e supplementation to different developmental stages hosts on the survival capability of F0 C. chlorideae. (a,b) The changes in cocoon formation rate when parasitized third-instar (day 1) larvae and third-instar (day 2) larvae feed on Haserpin-e. (c,d) The effects on the emergence rate of F0 generation when parasitized the third-instar (day 1) larvae and third-instar (day 2) larvae that feed on Haserpin-e. Values shown are means and standard errors. The data were transformed by arcsine before analysis. Statistically significant differences for experimental comparisons are indicated by different lowercases (p < 0.05 level) (based on the Tukey test, SPSS 22.0). The ns indicated no significantly difference among different treatments.
3.2. The Impact of Haserpin-e on the Life History Traits of C. chlorideae
Haserpin-e significantly affected the length (df = 267, F = 31.42, p < 0.0001) and slightly influenced the width of the F0 C. chlorideae cocoon, while exerting minimal effects on both dimensions in the F1 generation (Table 1). However, the length and the width of the F0 C. chlorideae cocoon is significantly longer than that of F1 C. chlorideae cocoon (df = 1, F = 108.25, p < 0.0001; df = 1, F = 29.74, p < 0.0001; Table 1, Figure S3a). For F0 C. chlorideae adults, Haserpin-e significantly affects the tibial length of hind legs (df = 239, F = 7.11, p < 0.0001; Table 1, Figure S3b), but not for F1 C. chlorideae adults. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction effect between the F0 and F1 generations (df = 1, F = 52.016, p = 0.008; Table 1), and the tibial length of hind legs of C. chlorideae in the F0 generation is significantly higher than that in the F1 generation. Ten μg/g Haserpin-e could cause a decrease in the sex ratio in the F0 generation, but it caused a higher mating rate. This effect did not carry over into the F1 generation. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction effect of mating rate (df = 1, F = 10.312, p = 0.004; Table 1) and sex ratio (df = 1, F = 142.10, p < 0.0001; Table 1) between the F0 and F1 generations. When treated with Haserpin-e, no significant changes were observed in the male or female survival time for the F0 and F1 generations, and between the F0 and F1 generations. After the adults were dead the mature eggs were recorded, and Haserpin-e did not affect the mature eggs not only in the F0 generation, but also in the F1 generation. And also there were significant interaction effects of mature eggs (dead adults) between the F0 and F1 generations (df = 1, F = 14.495, p < 0.0001; Table 1). For understanding the effects on the reproduction of F0 C. chlorideae, mature eggs and ovarioles were observed during the reproductive peak of C. chlorideae (Table 1, Figures S4 and S5). No adverse effects were detected (Table 1, Figures S4 and S5).
3.3. The Effects of Haserpin-e Protein on the Encapsulation of C. chlorideae in H. armigera
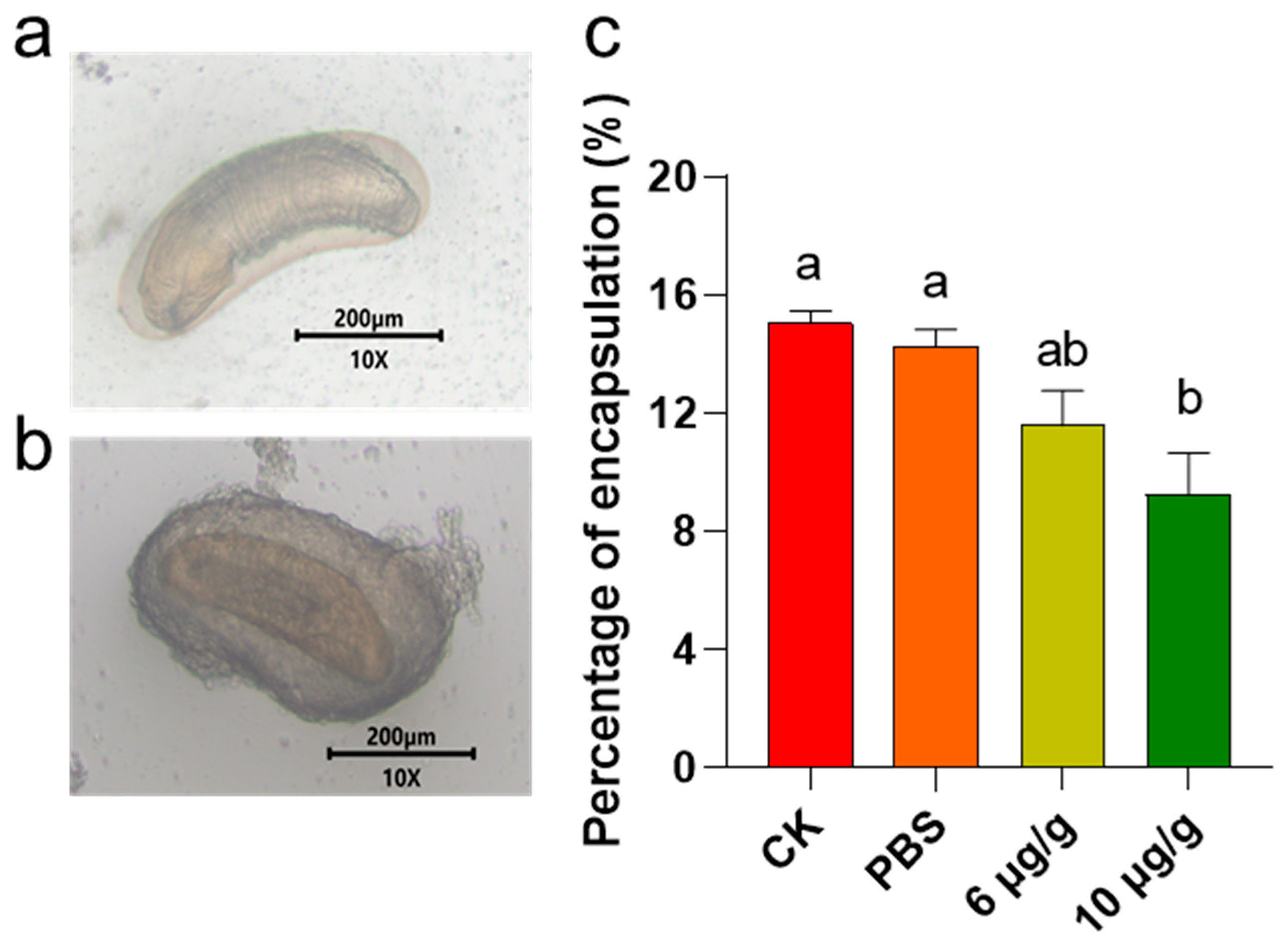
Encapsulation is a common response to exogenous invasion. The results indicated that a treatment with 6 μg/g Haserpin-e led to a reduction in the encapsulation of C. chlorideae in H. armigera by 3.46% and 2.69%, compared to the CK and PBS treatment groups, respectively (Figure 2). Furthermore, administering 10 μg/g Haserpin-e resulted in a reduction in encapsulation by 5.78% relative to the CK group and by 5.01% compared to the PBS group, respectively (df = 11, F = 7.124, p = 0.015; Figure 2).
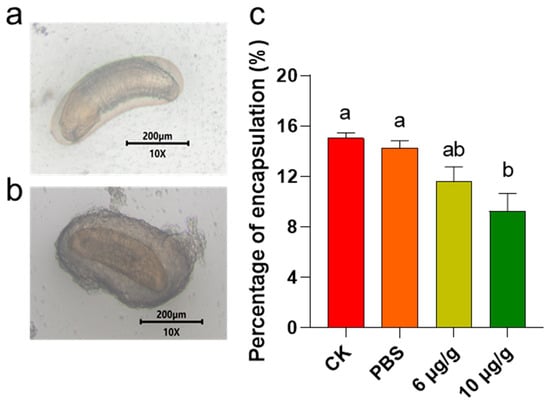
Figure 2.
The impact of Haserpin-e on the encapsulation of H. armigera. (a) Photographs of unencapsulated C. chlorideae. (b) Photographs of encapsulated C. chlorideae. (c) Percentage of encapsulation of C. chlorideae in H. armigera. Values shown are means and standard errors. The data were transformed by arcsine before analysis. Statistically significant differences for experimental comparisons are indicated by different lowercases (p < 0.05 level) (based on Tukey test, SPSS 22.0).
3.4. The Effects Haserpin-e Protein on Melanization of H. armigera Larvae Hemolymph In Vitro
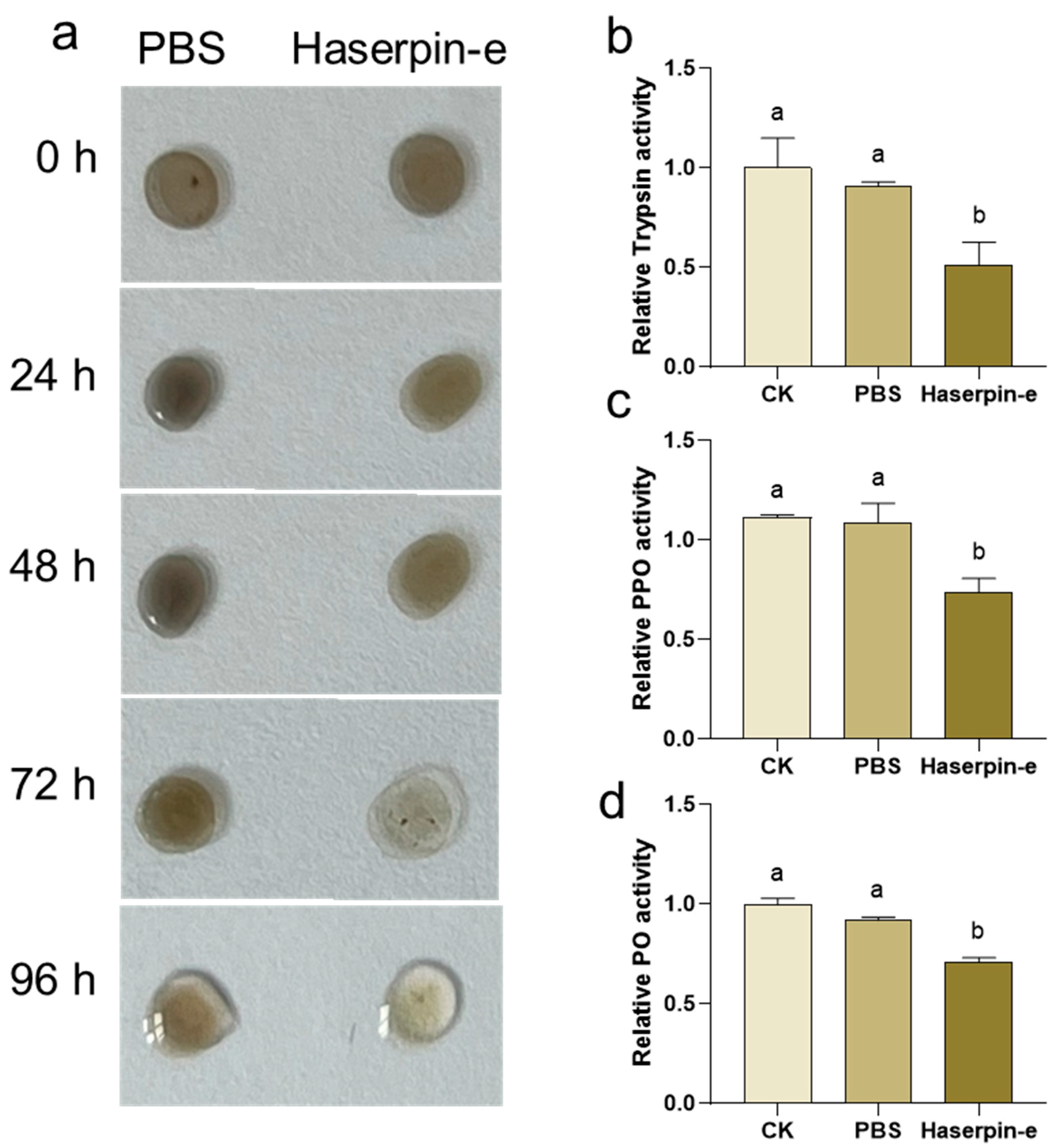
Since Haserpin-e acts as a trypsin inhibitor, it can suppress the enzymatic activities of trypsin 38. Moreover, serpin has been reported to play a role in insect melanization upon external invasion [49]. Therefore, the impact of Haserpin-e on the melanization process in H. armigera larvae hemolymph in vitro was investigated. When mixed with H. armigera larvae hemolymph, Haserpin-e significantly inhibited melanization after 72 h (Figure 3a). Furthermore, the analysis of key enzymes involved in melanization including trypsin, PPO, and PO revealed that Haserpin-e significantly suppressed the enzyme activities of trypsin (df = 10, F = 5.047, p = 0.038; Figure 3b), PPO (df = 8, F = 7.529, p = 0.019; Figure 3c), and PO (df = 10, F = 40.18, p < 0.001; Figure 3d).
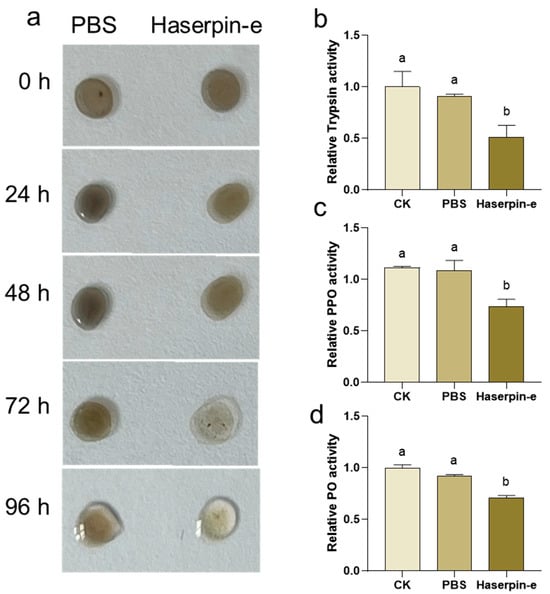
Figure 3.
The impact of Haserpin-e on melanization of hemolymph form H. armigera larvae. (a) Haserpin-e exhibits reactivity with the color of the hemolymph. (b–d) Haserpin-e modulates the activities of trypsin, polyphenol oxidase (PPO), and phenol oxidase (PO) in the hemolymph. Values shown are means and standard errors. Statistically significant differences for experimental comparisons are indicated by different lowercases (p < 0.05) (based on a Tukey test, SPSS 22.0).
3.5. The Effects Haserpin-e Protein on Melanization of H. armigera In Vivo
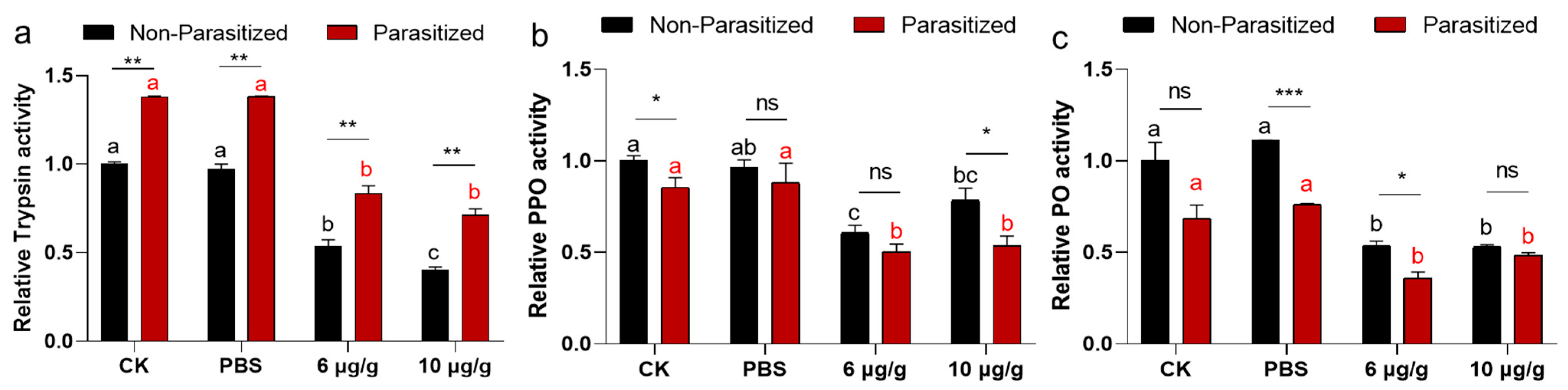
A two-way ANOVA revealed no significant interaction effect between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in trypsin activities (df = 3, F = 1.333, p = 0.6795; Figure 4a). Similarly, parasitized status has independent effects on trypsin activities (df = 1, F = 224.422, p < 0.0001; Figure 4a). Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects on trypsin activities (df = 3, F = 202.695, p < 0.0001; Figure 4a). The results revealed a significantly higher trypsin activity in parasitized H. armigera compared to non-parasitized H. armigera in every treatment (Figure 4a). However, Haserpin-e treatment led to suppressed trypsin activities in both parasitized and non-parasitized H. armigera (Figure 4a). For the enzyme activities of PPO, there was no significant interaction effect between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in PPO activities (df = 3, F = 0.975, p = 0.8599; Figure 4b). Similarly, parasitized status has independent effects on PPO activities (df = 1, F = 12.168, p = 0.0016; Figure 4b). Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects on PPO activities (df = 3, F = 22.779, p = 0.0001; Figure 4b). Additionally, Haserpin-e was found to significantly inhibit both parasitized (p < 0.0004) and non-parasitized (p < 0.0001) H. armigera, respectively, with no significant difference between the parasitized and non-parasitized in each treatment (Figure 4b). For the enzyme activities of PO, there was no significant interaction effect between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in PO activities (df = 3, F = 3.191, p = 0.057; Figure 4c). Similarly, parasitized status has independent effects on PO activities (df = 1, F = 35.236, p < 0.0001; Figure 4c). Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects on PO activities too (df = 3, F = 41.742, p < 0.0001; Figure 4c). In terms of PO, there was a notable decrease in enzyme activity among parasitized H. armigera within each treatment group (Figure 4c), and Haserpin-e effectively inhibited PO activities in both parasitized and non-parasitized individuals (Figure 4c).
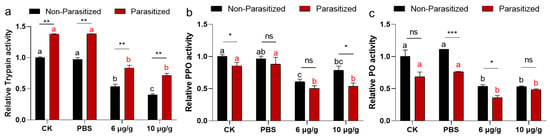
Figure 4.
The impacts of Haserpin-e on trypsin (a), polyphenol oxidase (PPO) (b), and phenol oxidase (PO) (c) activities in non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae. Values shown are means and standard errors. Statistically significant differences among different Haserpin-e treatments in no-parasitized or parasitized H. armigera larvae are denoted by lowercase letters for p < 0.05, based on a Tukey test using SPSS 22.0 software. The statistically significant differences between non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae in each treatment group are represented by different lowercase letters (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, based on t test, SPSS 22.0). The ns indicated no significant difference between non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae.
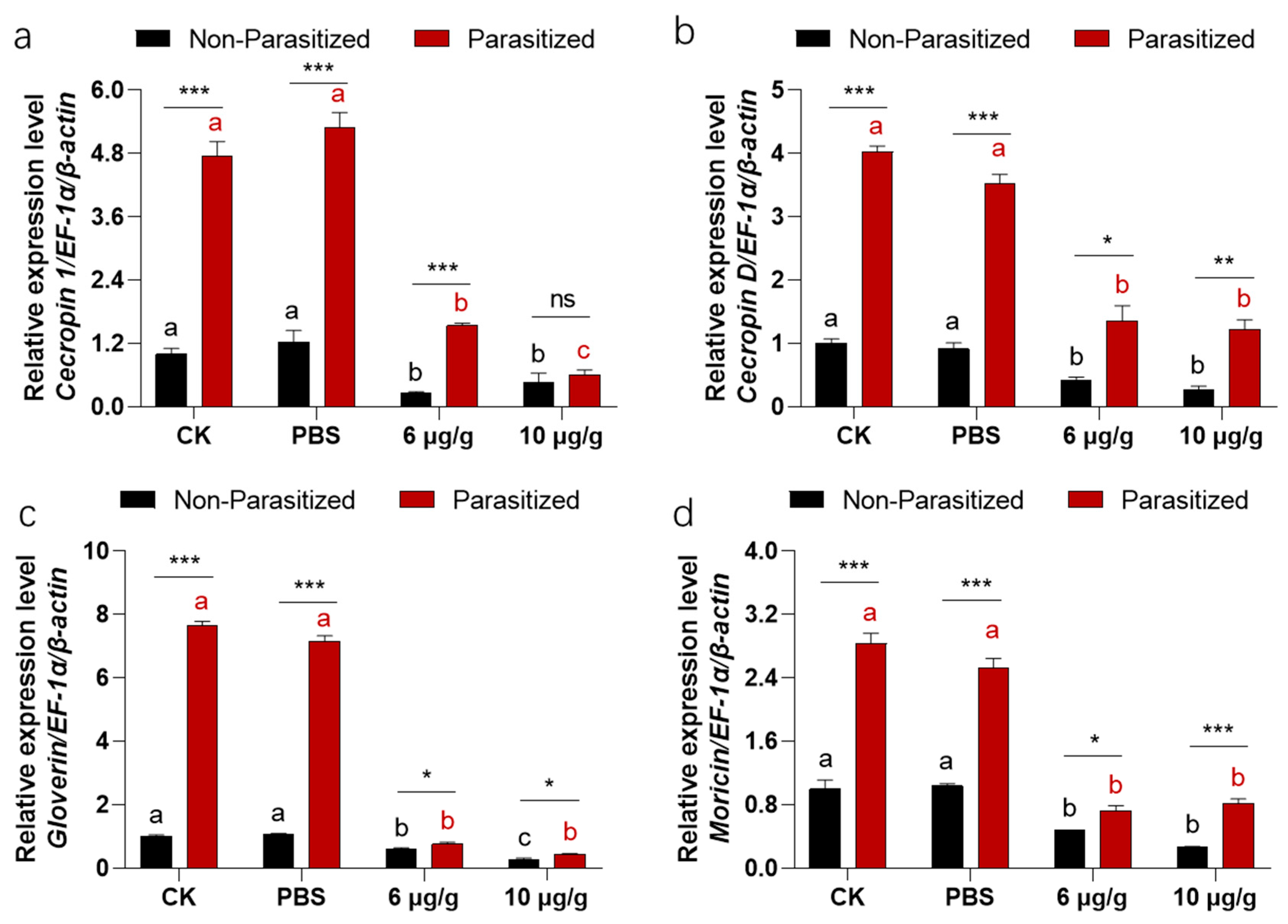
3.6. Haserpin-e Suppresses the Expression of AMPs Expression in H. armigera
A two-way ANOVA revealed significant interaction effects between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in cecropin 1 (df = 3, F = 118.51, p < 0.0001; Figure 5a), cecropin D (df = 3, F = 38.15, p = 0.0.776; Figure 5b), gloverin (df = 3, F = 912.942, p < 0.004; Figure 5c), and moricin (df = 3, F = 55.033, p = 0.0017; Figure 5d). Similarly, parasitized status has independent effects on cecropin 1 (df = 1, F = 57.77, p = 0.0002; Figure 5a), cecropin D (df = 1, F = 451.42, p < 0.001; Figure 5b), gloverin (df = 1, F = 2996.12, p = 0.0210; Figure 5c), and moricin (df = 1, F = 416.17, p < 0.0210; Figure 5d). Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects on cecropin 1 (df = 3, F = 334.32, p < 0.0001; Figure 5a), cecropin D (df = 3, F = 103.85, p < 0.0002; Figure 5b), gloverin (df = 3, F = 1288.70, p < 0.0001; Figure 5c), and moricin (df = 3, F =214.14, p < 0.0001; Figure 5d). After being parasitized by C. chlorideae, the expressions of cecropin 1 (Figure 5a), cecropin D (Figure 5b), gloverin (Figure 5c), and moricin (Figure 5d) were all significantly increased, repectively. However, upon Haserpin-e administration, the expression of cecropin 1 (Figure 5a), cecropin D (Figure 5b), gloverin (Figure 5c), and moricin (Figure 5d) all were significantly suspressed by Haserpin-e.
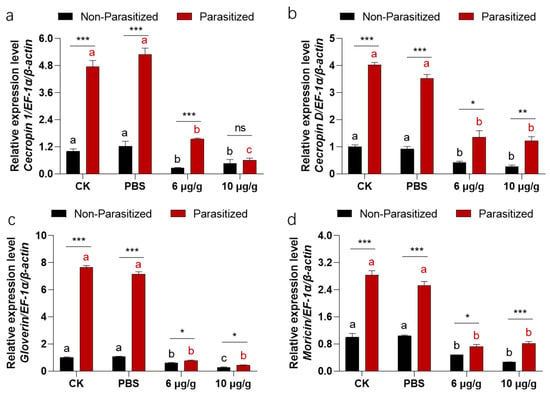
Figure 5.
The impacts of Haserpin-e on the expression of cecropin 1 (a), cecropin D (b), gloverin (c), and moricin (d) in non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae. Values shown represent means with standard errors. Statistically significant differences among different Haserpin-e treatments in non-parasitized or parasitized H. armigera larvae are denoted by lowercase letters for p < 0.05, based on a Tukey test using SPSS 22.0 software. The statistically significant differences between non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae in each treatment group are represented by different lowercase letters (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, based on t test, SPSS 22.0). The ns indicated a significantly difference between non-parasitized and parasitized H. armigera larvae.
4. Discussion
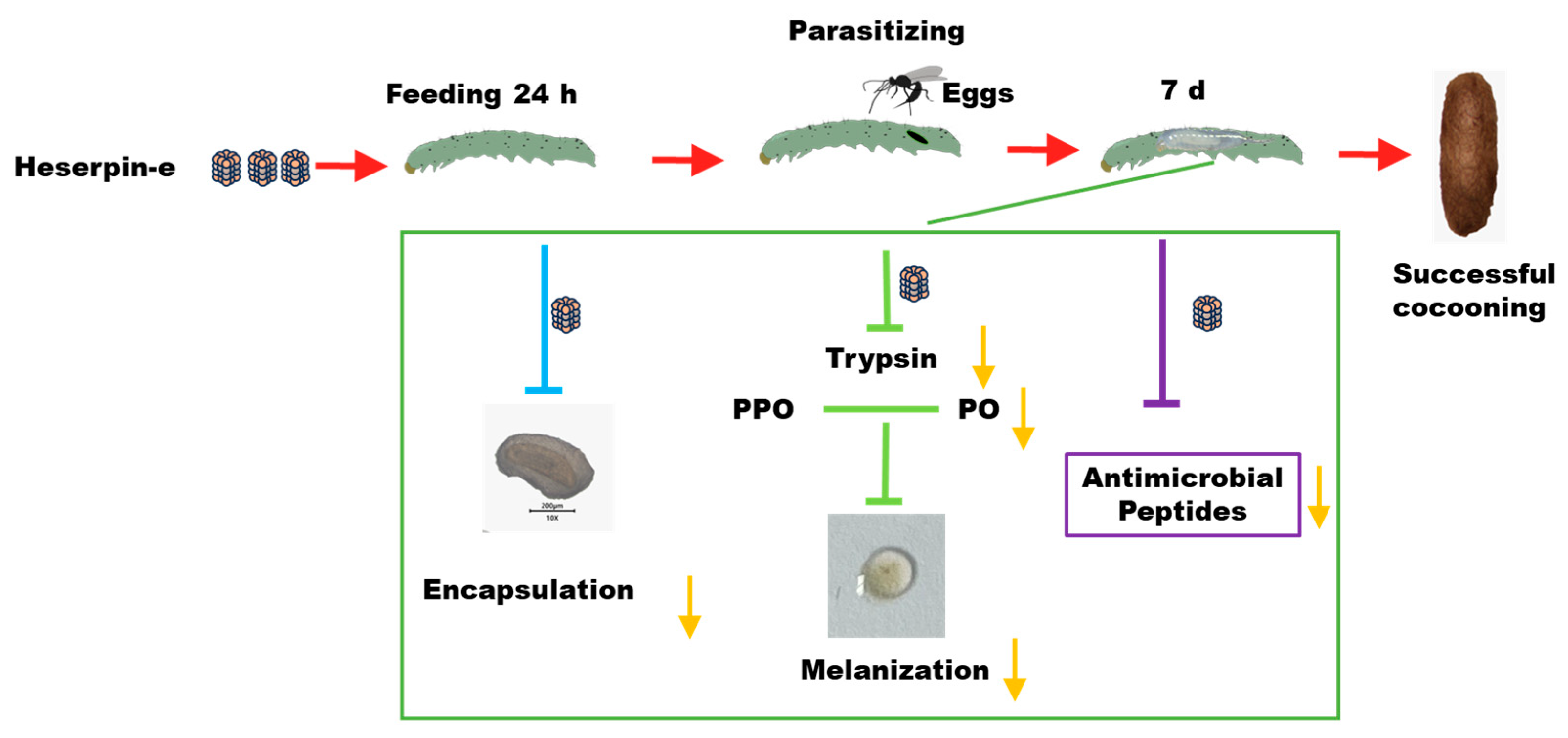
C. chlorideae serves as one of vital biological control agents against Lepidopteran pests due to their significant impact on host populations [1] and high rates of parasitism observed in field studies [5]. To improve the rearing efficiency of C. chlorideae, Zhang et al. [49] documented that superparasitism could significantly increase the C. chlorideae cocoon production. Here, our study firstly provides a different methodology for large-scale propagation of C. chlorideae by feeding the host with Haserpin-e protein to inhibit host’s innate immune responses, which does so by inhibiting melanization, decreasing encapsulation, and reducing the expression of AMPs (cecropin 1, cecropin D, gloverin, and moricin), ultimately enhancing C. chlorideae survival (Figure 6). Compared to superparasitism, this method conserves the number of eggs utilized, as regardless of the number of eggs deposited only a single parasitic wasp will fully develop within the host insect. This finding holds significant implications for large-scale indoor reproduction of C. chlorideae.
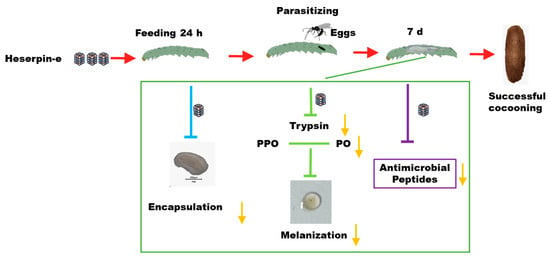
Figure 6.
The Haserpin-e derived from H. armigera negatively regulates encapsulation, melanization, and AMPs expression in larvae, thereby enhancing large-scale indoor reproduction of C. chlorideae.
In addition, assessments of life history traits in both F0 and F1 generations revealed that Haserpin-e nearly showed no adverse effect on the growth, development, and reproduction in F0 and F1 generation, except for the size of C. chlorideae (Table 1). A significant reduction in H. armigera weight was observed when they were fed Haserpin-e (Figure S6). Consequently, it is plausible that the reduced size of F0 and F1 C. chlorideae could be attributed to their consumption of thinner H. armigera. However, rate of cocoon production, emergence rate, sex ratio, mating rate, the size of C. chlorideae, and number of mature eggs (in dead adults) all showed significant interaction effects between the F0 and F1 generations (Table 1). Based on our extensive experience in indoor rearing, it is hypothesized that this phenomenon may be attributed to the degradation of the indoor experimental population of C. chlorideae, because there were no changes between the Haserpin-e treatments and the CK (or PBS treatment) group in F0 or F1 generations. Degradation in insect populations under long-term laboratory conditions has been frequently documented in previous studies [50].
By exploring functions and mechanisms of Haserpin-e in H. armigera and the cocoon formation promotion process, we observed that Haserpin-e exhibited the ability to reduce encapsulation in H. armigera (Figure 2). This result is consistent with the report that the introduction of serpin27A into D. melanogaster Meigen larvae with high immune competence significantly impaired their ability to form melanotic capsules around eggs of L. boulardi [18]. In addition, this study also found no significant interaction effect between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in trypsin, PPO, and PO activities, but parasitized status or Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects, respectively, which indicated that both parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments could inhibit melanization of the host (Figure 3 and Figure 4). These are consistent with previous reports that C. chlorideae could inhibit melanization by polydnaviruses [43] and serpin had the functions of inhibiting melanization in many insects [25,26,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Although the exact mechanism by which orally administered Haserpin-e reaches systemic immunity in the host remains unclear, many protein fragments expressed by prokaryotes can indeed enter insects and perform their functions. For example, proteins such as cadherin, ALP, and ATP synthase subunit α fragments, when ingested orally by H. armigera, enhance the toxicity of Cry1A toxins to H. armigera [51,52,53]. This provides evidence of Haserpin-e’s role in regulating encapsulation and melanization, which deepens our understanding of Haserpin-e’s effects.
In addition, this study revealed significant interaction effects between the parasitized status and Haserpin-e treatments in four AMP genes, and showed that parasitized status or Haserpin-e treatments have independent effects on four AMP genes (Figure 5). This phenomenon of up-regulated AMPs overexpression due to parasitism has also been observed in silkworms. In response to Exorista japonica Townsend parasitoid attack, the expressions of 13 AMP genes from families such as lysozyme, gloverin, cecropin, enbocin, attacin, and moricin were all up-regulated [54]. AMPs play a crucial role in the humoral defense responses of insects and are negative regulated by serpins [31,55,56]. We discovered that upon administration of Haserpin-e, the expression levels of cecropin 1, cecropin D, gloverin, and moricin were all significantly suppressed by Haserpin-e treatment, and this effect was particularly pronounced in parasitized H. armigera (Figure 5), suggesting that Haserpin-e contributes to the survival of C. chlorideae by reducing the expression of AMPs induced by parasitism. It is hypothesized that Haserpin-e may directly or indirectly modulate certain antimicrobial peptide synthesis pathways; however, the precise mechanism remains to be elucidated. Our findings here provide additional evidence for the regulatory function of Haserpin-e on AMPs’ expression.
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this study represents a pioneering approach in promoting the survival of C. chlorideae in large-scale indoor reproduction involving endogenous Haserpin-e protein derived from the host H. armigera. Additionally, this study expands on the functionalities of Haserpin-e proteins by showing for that Haserpin-e affects the encapsulation, melanization, and AMP expression in H. armigera.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/insects16050474/s1, Figure S1: Experiment design and sample sizes in this study; Figure S2: Purification of HaSerpin-e protein; Figure S3: The impact of Haserpin-e on the size of Campoletis chlorideae cocoons (a) and the length of their tibiae (b); Figure S4: The impact of Haserpin-e on the ovarin of Campoletis chlorideae; Figure S5 The impact of Haserpin-e on the mature eggs of Campoletis chlorideae e; Figure S6 The impact of Haserpin-e on the weight of H. armigera. (a) Photographs of H. armigera under different treatments. (b) The weight of H. armigera under different treatments at 72 h. (c) The weight of H. armigera under different treatments at 96 h; Table S1: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
J.W., S.B. and Y.W. conceived the idea and designed the methodology. J.W. procured funding. L.H., X.Y., N.Z. and S.W. conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. J.W., Y.W. and S.A. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Central Plains Science and Technology Innovation Youth Top Talent Program, Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (24HASTIT051).
Data Availability Statement
All the data are in the manuscript and Supplemental Document.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, S.G.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.T.; Miao, L.; Qin, Q.L. Research progress in rearing of parasitoid wasp Campoletis chlorideae. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2012, 28, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, M.K.; Sharma, H.C. Survival and development of Campoletis chlorideae on various insect and crop hosts: Implications for Bt-transgenic crops. J. Appl. Entomol. 2007, 131, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.S.; Lei, R.H.; Jiang, J.X.; BO, L.Y.; Xiao, Z.S. Bionomic of Campoletis chlorideae (Hym: Ichneumonidae) as a parasitoid of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lep: Noctuidae). Insect Sci. 2002, 9, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Keyhani, N.; Lei, X.F.; Liu, C.H.; Al Dhafer, H.M. Biocontrol performance and mass production potential of the larval endoparasitoid Campoletis chlorideae Uchida (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) against the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2024, 34, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, C. Identification of Mythmna separata induced maize volatile synomones that attract the parasitoid Campoletis chlorideae. J. Appl. Entomol. 2006, 130, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolappan, B. Misuse of Pesticides to Blame for Disappearance of Pollinators. Available online: www.thehindu.com/news/national/tamil-nadu/misuse-of-pesticides-to-blame-for-disappearance-of-pollinators/article30814702.ece (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Pandey, R.K.; Singh, G.R.; Tripathi, A. Effect of biopesticides (HaNPV) on larval population of Helicoverpa armigera on chickpea in eastern part of U.P under rainfed low-land ecosystem. National conference on role of bio-agents and bio-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture and horticulture. IISR-Lucknow 2004, 86, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.Q.; Shi, M.; Huang, J.H.; Chen, X.X. Parasitoid polydnaviruses and immune interaction with secondary hosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strad, M.R.; Clark, K.D. Plasmatocyte spreading peptide induces spreading of plasmatocytes but represses spreading of granulocytes. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1999, 42, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.R.; Pech, L.L. Immunological basis for compatibility in parasitoid-host relationships. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 40, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Lu, W.X.; Wu, B.; Qi, P.Z. Transcriptome analysis of Mytilus coruscus hemocytes in response to Vibrio alginnolyficus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, M.; Kim, Y. Transient expression of a polydnaviral gene, CpBV15beta, induces immune and developmental alterations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 100, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, M.W.; Martin, S.B.; Webb, B.A. Quantitative analysis of hemocyte morphological abnormalities associated with Campoletis sonorensis parasitization. J. Insect Sci. 2004, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Erickson, S.L.; Hersh, B.M.; Turnbull, M.W. Virus innexins induce alterations in insect cell and tissue function. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Stoltz, D.B. Comparative serology of viruses isolated from Ichneumonid parasitoids. Virology 1983, 130, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelby, K.S.; Adeyeye, O.A.; Okot-Kotber, B.M.; Webb, B.A. Parasitism-linked block of host plasma melanization. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 75, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.J.M.; Huguet, E.; Drezen, J.M. Polydnaviruses as Tools to Deliver Wasp Virulence Factors to Impair Lepidopteran Host Immunity. Insect Infection and Immunity: Evolution, Ecology, and Mechanisms; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, A.J.; Frey, F.; Carton, Y. Drosophila serpin 27A is a likely target for immune suppression of the blood cell-mediated melanotic encapsulation response. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekins, D.A.; Kanost, M.R.; Michel, K. Serpins in arthropod biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanost, M.R.; Gorman, M.J. Phenoloxidases in insect immunity. Insect Immunol. 2008, 1, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, D.X.; Hong, F.; Wang, G.R.; An, C.J. Serine proteases SP1 and SP13 mediate the melanization response of asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis, against entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 128, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Hong, F.; Liu, Q.Z.; An, C.J. Serine protease SP105 activates prophenoloxidase in Asian corn borer melanization and is regulated by serpin-3. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Park, J.W.; Roh, K.B.; Lee, H.; Park, B.J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Söderhäll, K.; et al. Molecular control of phenoloxidase-induced melanin synthesis in an insect. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25316–25323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumaran, M.; Barek, H. Critical analysis of the melanogenic pathway in insects and higher animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Shin, S.W.; Alvarez, K.S.; Kokoza, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Distinct melanization pathways in the mosquito Aedes Aegypti. Immunity 2010, 32, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.F.; Xing, L.S.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, X.; Yin, M.Y.; Wang, Q.R. Inhibition of melanization by Serpin-5 and Serpin-9 promotes baculovirus infection in cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; El Moussawi, L.; Saab, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Osta, M.A. CLIPB10 is a terminal protease in the regulatory network that controls melanization in the African malaria mosquito anopheles gambiae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 585986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.R.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Qian, C.; Wei, G.Q.; Dai, L.S.; Li, J.; Zhu, B.J.; Liu, C.L. Serpin-15 from Bombyx mori inhibits prophenoloxidase activation and expression of antimicrobial peptides. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Ma, L.; Lin, Z.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z.Q. Serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide pathways in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 73, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, P.; Xia, Q. Silkworm serpin32 functions as a negative-regulator in prophenoloxidase activation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 91, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, H.Z.; Ye, C.J.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, T.; Chen, F.S.; Xu, J.P. Bombyx Mori Serpin6 regulates prophenoloxidase activity and the expression of antimicrobial proteins. Gene 2017, 610, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Kanost, M.R. Identification of plasma proteases inhibited by Manduca sexta serpin-4 and serpin-5 and their association with components of the prophenoloxidase activation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14932–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.J.; Kanost, M.R. Manduca sexta serpin-5 regulates prophenoloxidase activation and the toll signaling pathway by inhibiting hemolymph proteinase HP6. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.J.; Ragan, E.J.; Kanost, M.R. Serpin-1 splicing isoform j inhibits the prospätzle-activating proteinase hp8 to regulate expression of antimicrobial hemolymph proteins in Manduca Sexta. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Xu, J.H.; Wang, L.L.; Guo, P.C.; Tang, Z.C.; Sun, X.T.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.A.; Cao, Y.; et al. Serpin-1a and serpin-6 regulate the Toll pathway immune homeostasis by synergistically inhibiting the Spätzle-processing enzyme CLIP2 in silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 18, e1011740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Kim, E.H.; Gong, J.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Kim, C.H.; Ryu, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Kurokawa, K.; Zhang, J.H.; Gubb, D. Three pairs of protease serpin complexes cooperatively regulate the insect innate immune responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35652–35658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.Y.; Shen, D.X.; Zhang, S.S.; Wang, L.; An, C.J. Serpin-4 facilitates baculovirus infection by inhibiting melanization in asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wei, J.Z.; Naing, Z.L.; Soe, E.T.; Liang, G.M. Endogenous serpin reduces toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 175, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Wei, J.Z.; Naing, Z.L.; Soe, E.T.; Tang, J.R.; Liang, G.M. Up-regulated serpin gene involved in Cry1Ac resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Xue, Y.Y.; Zhao, W.L.; Liu, X.G.; Du, M.F.; Yin, X.M.; Guan, R.B.; Wei, J.Z.; An, S.H. New insights on the effects of spinosad on the development of Helicoverpa armigera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.F.; Li, X.; Chen, X.X.; Cheng, J.A.; He, J.H. Interspecific competition between two endoparasitoids Cotesia vestalis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and Oomyzus sokolowskii (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 76, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Li, X.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, S.J.; Wang, K.; Tian, C.H.; Feng, H.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Yin, X.M.; Bai, S.F.; et al. Cyclosporin A acts as an insecticide candidate: Providing sustainable biocontrol potential for managing Mythimna separata. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.B.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Host preference and suitability in the endoparasitoid Campoletis chlorideae is associated with its ability to suppress host immune responses. Ecol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.P.; Li, M.W. The hemolymph melanization response is related to defence against the AcMNPV infection in Bombyx mori. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2020, 108, e21764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Li, T.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.C.; Zhang, J. Transcriptomic analysis of interactions between Iymantria dispar larvae and carvacrol. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 181, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Q.; Kong, F.; Ma, B.; Chen, D.S.; Ran, Z.S.; Ma, S.N.; Liao, K.; Cao, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, X.J.; et al. Effects of light on growth, feeding rate, digestion, and antioxidation in juvenile razor clams Sinonovacula constricta. Aquaculture 2023, 568, 739306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Deng, Z.Y.; Yin, X.M.; An, S.H.; Li, X.C. Functional assessment of cadherin as a shared mechanism for cross/dual resistance to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa zea. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1604–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.P.; Qi, H.P.; Liu, X.N.; Ren, X.W.; Li, J.S. Implementation of two-way nonparametric ANOVA in SPSS. Chin. J. Health Stat. 2013, 30, 913–914. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Gu, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Superparasitism behavior and host discrimination of Campoletis chlorideae (Ichneumonidae: Hymenoptera) toward Mythimna separata (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera). Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Ross, P.A. Rates and patterns of laboratory adaptation in (mostly) insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, C.X.; Xiao, Y.T.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, X.C.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, K.M. A toxin-binding alkaline phosphatase fragment synergizes Bt toxin Cry1Ac against susceptible and resistant Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.J.; Dong, S.; Hu, X.D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.F.; Lu, L.N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, X.J. Roles of midgut cadherin from two moths in different Bacillus thuringiensis action mechanisms: Correlation among toxin binding, cellular toxicity, and synergism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13237–13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Duan, Y.P.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zhao, W.L.; Wei, J.Z.; Li, X.C.; An, S.H. ATP synthase subunit α from Helicoverpa armigera acts as a receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac and synergizes Cry1Ac toxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6155–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Gu, H.Y.; Li, F.C.; Li, B.; Wei, J. Parasitism by the tachinid parasitoid Exorista japonica leads to suppression of basal metabolism and activation of immune response in the host Bombyx mori. Insects 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Cao, X.L.; Zou, Z.; Lu, Z.Q.; Kanost, M.R.; Jiang, H.B. Hemolymph protease-5 links the melanization and Toll immune pathways in the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23581–23587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, X.T.; Yan, X.Z.; Wang, W.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Hao, C.; Lu, Z.Q.; Ma, L. Serpin-4 Negatively Regulates Prophenoloxidase activation and antimicrobial peptide synthesis in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).