Research Progress on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Concept of High-Entropy Alloys
2.1. Definition of High-Entropy Alloys
- (1)
- Low-entropy alloys: alloys mainly composed of one or two components, such as traditional alloys, ΔSmix is less than R.
- (2)
- Medium-entropy alloys: alloys mainly binary to quaternary, the mixing entropy is between R and 1.5R.
- (3)
- High-entropy alloys: alloys mainly consisting of five to thirteen elements, when the mixing entropy ΔSmix is greater than 1.5R.
2.2. Characteristics of High-Entropy Alloys
3. Influence of Alloying Elements on the Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys
3.1. Metal Elements
3.1.1. Light Metal Elements
3.1.2. Transition Metal Elements
3.1.3. Refractory Metal Elements
3.2. Non-Metallic Elements
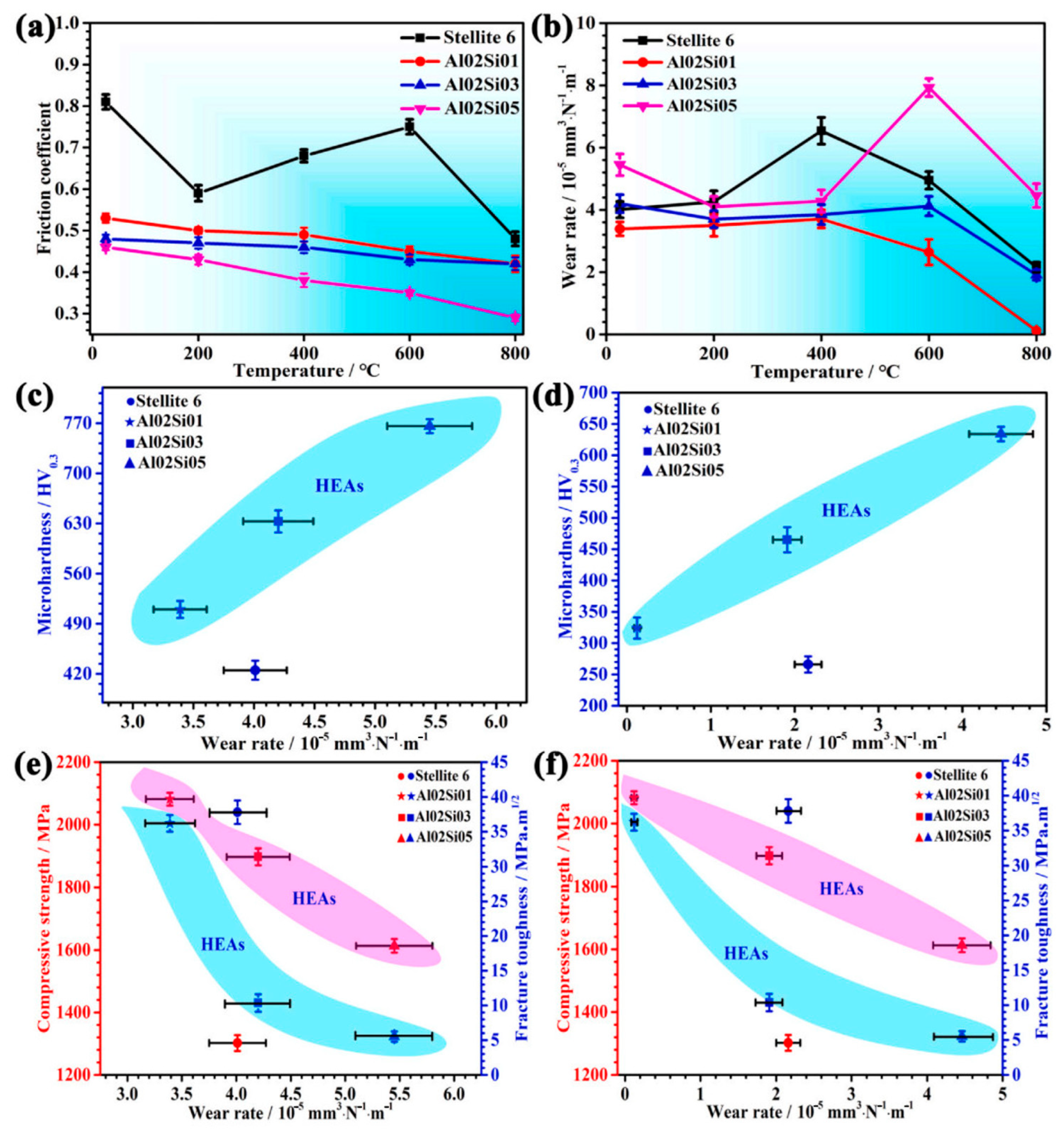
4. Influence of Friction Environment on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys
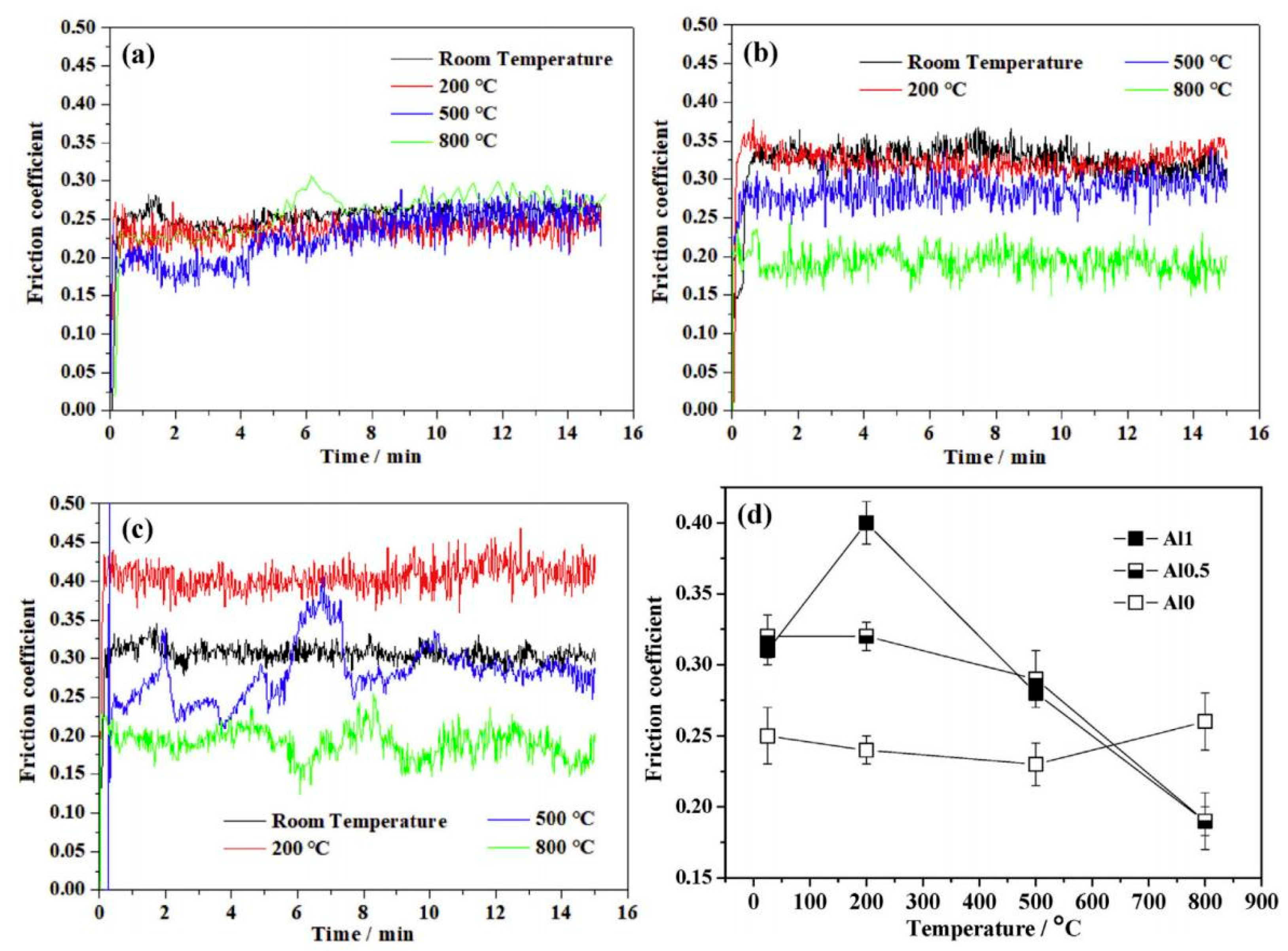
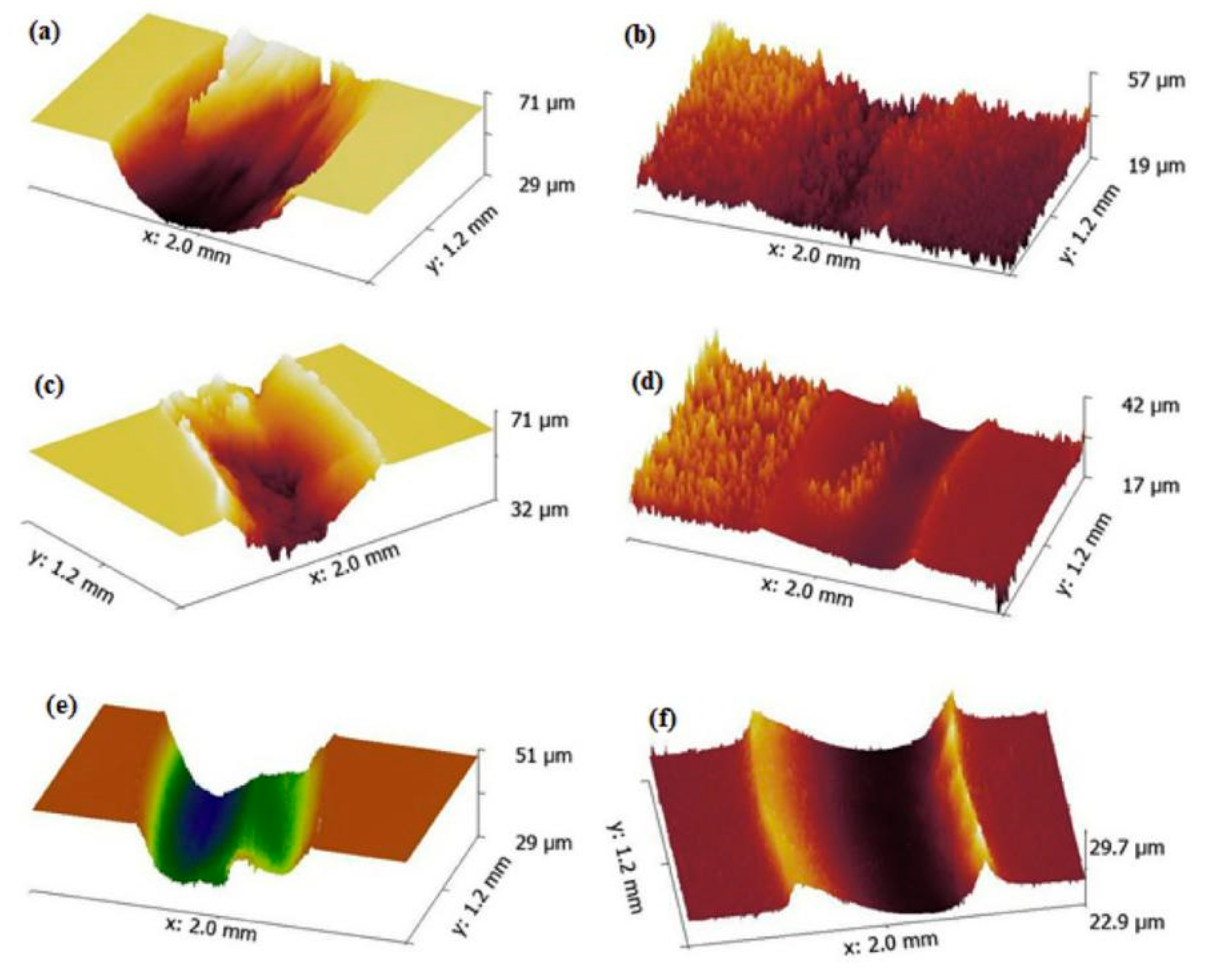
4.1. High-Temperature Environment
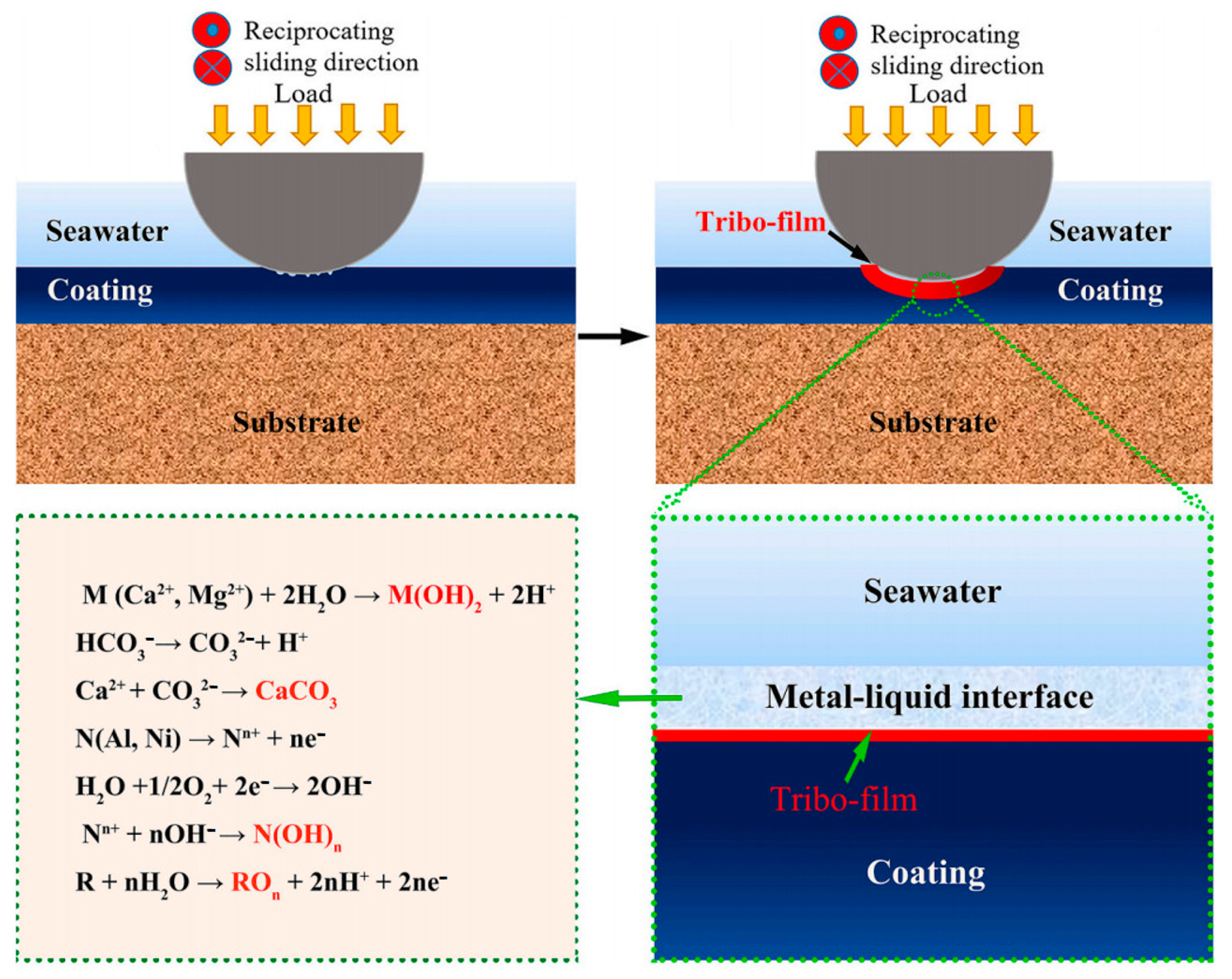
4.2. Marine Environment
4.3. H2O2 Environment
5. Influence of Test Conditions on the Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys
5.1. Load
5.2. Sliding Velocity
5.3. Friction Pair
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Xu, L.; Zhu, C.; Li, Z.; Wei, S. Research progress of high entropy alloy: Surface treatment improves friction and wear properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 752–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, D.; Sarkar, M.; Kopperi, H.; Das, A.; Ray, B.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Pathak, B.; Peter, S.C. High entropy alloy formation derived from high entropy oxide: Unlocking the active sites for green methanol production from CO2. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2504180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Couillard, M.; Tang, Z.; Shin, H.; Poitras, D.; Cheng, C.; Naboka, O. Continuous synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles by in-flight alloying of elemental metals. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Wang, S.D.; Lu, Y.P.; Cao, Z.Q.; Wang, T.M.; Li, T.J. Research progress and prospect of high-entropy alloy materials. Chin. Eng. Sci. 2023, 25, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in passenger cars. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oketola, A.M.; Adegbola, T.A.; Jamiru, T.; Ogunbiyi, O.; Salifu, S. Advances in high-entropy alloy research: Unraveling fabrication techniques, microstructural transformations, and mechanical properties. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2025, 11, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, L.J.M.; Ileana, M.M.; Victor, G.; Ionelia, V. New FeMoTaTiZr high-entropy alloy for medical applications. Metals 2025, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.Z. Mixed-up metals make for stronger, tougher, stretchier alloys. Nature 2016, 533, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Metall. Mater. Soc. 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, S.K. High-Entropy Alloys-A New Era of Exploitation. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 560, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principalelements novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Su, J.L.; Chin, T.S.; Gan, J.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chou, S.Y. Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-Valloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J.; Li, R.G.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.B.; Zhong, Y.B.; Ren, W.L.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, T.X.; Peng, J.C.; Liang, X.L.; et al. Hierarchical crack buffering triples ductility in eutectic herringbone high-entropy alloys. Science 2021, 373, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Asta, M.; Ritchie, R.O. Melts of CrCoNi-based high-entropy alloys: Atomic diffusion andelectronic/atomic structure from ab initio simulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coury, F.G.; Butler, T.; Chaput, K.; Saville, A.; Copley, J.; Foltz, J.; Mason, P.; Clarke, K.; Kaufman, M.; Clarke, A. Phase equilibria, mechanical properties and design of quaternary refractory high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dwivedi, V.K.; Dwivedi, S.P. Development of high entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today 2021, 43, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Min, L.J.; Lai, Z.H.; Han, T.Y.; Yang, D.N.; Zhu, J.C. Alloying effect on phase stability, elastic and thermodynamic properties of Nb-Ti-V-Zr high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 101, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, G.Q.; Zhang, L.M. Microstructure and mechanical property of a novel ReMoTaW high-entropy alloy with high density. Int. J. Refract. Meth. 2018, 77, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, D.; King, D.J.M.; Laws, K.J.; Knowles, A.J.; Aughterson, R.D.; Lumpkin, G.R.; Obbard, E.G. Cr-Mo-V-W: A new refractory and transition metalhigh-entropy alloy system. Scripta. Mater. 2019, 158, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Gwalani, B.; Soni, V.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Banerjee, R. Influence of Cr substitution and temperature on hierarchicalphase decomposition in the AlCoFeNi high entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Recent progress in high entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Guo, S.; Luan, J.; Shi, S.; Liu, C.T. Entropy-driven phase stability and slow diffusion kinetics in an Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2012, 31, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, X. Thermodynamic analysis of the simple microstructure of AlCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy with multi-principal elements. Acta Metall. Sin. 2009, 22, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, S.K. Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.J.; Chen, M.R.; Chen, S.K. Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Wilks, G.B.; Mauger, L.; Munoz, J.A.; Karapetrova, E. Absence of long-range chemical ordering in equimola FeCoCrNi. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 251907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, P.C.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del, G.M.F.; Bozzolo, G.; Hugo, O.M. Determination of the transition to the high entropy regime for alloys of refractory elements. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 534, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chang, S.Y.; Hong, Y.D.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J. Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of CuNiAlCoCrFeSi alloy systems with multi-principal elements. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, S. Research and application progress of high-entropy alloys. Coatings 2023, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H. Physical Properties of high entropy alloys. Entropy 2013, 15, 5338–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.R.; Yeh, J.W.; Tseng, K.K.; Natesan, K. Irradiation effects in high entropy alloys and 316H stainless steel at 300 degrees C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 510, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucza, W.; Dabrowa, J.; Danielewski, M.; Kulik, T.; Cieslak, G. Interdiffusion in the FCC-structured Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high entropy alloys: Experimental studies and numerical simulations. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 674, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Trubel, S.; Murty, B.S.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V. Ni tracer diffusion in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi highentropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 688, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.J.; Ruan, H.H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.P. High thermal stability and sluggish crystallization kinetics of high-entropy bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, W.M.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, L. Experimental and numerical studies on the sluggish diffusion in face centered cubic Co-Cr-Cu-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottke, J.; Laurent-Brocq, M.; Fareed, A.; Wilde, G. Tracer diffusion in the Ni-CoCrFeMn system: Transitionfrom a dilute solid solution to a high entropy alloy. Scripta Mater. 2019, 159, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.; Kim, H.S. High-entropy alloys: Potential candidates for high-temperature applications–an overview. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Song, H.; Li, P.J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Duan, P.G.; Hu, X. A new method for removal of nitrogen in sewage sludge-derived hydrochar with hydrotalcite as the catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, S. Alloyed pleasures: Multimetallic cocktails. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Vicario, I.; Albizuri, J.; Guraya, T.; Garcia, J.C. Phase prediction, microstructure and high hardness of novel light-weight high entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Tian, C.; Li, Y. The role of Nb on the high temperature oxidation behavior of CoCrFeMnNbxNi high-entropy alloys. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108088.1–108088.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.X.; Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.T. Cocktail effects in understanding the stability and properties of face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloys at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Choudhuri, D.; Soni, V.; Ren, Y.; Styles, M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nam, S.J.; Ryu, H.; Hong, S.H.; Banerjee, R. Cu assisted stabilization and nucleation of L12 precipitates in Al0.3CuFeCrNi2fcc-based high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 129, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Jones, N.G. High-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Suhane, A. Mechanically alloyed high entropy alloys: Existing challenges and opportunities. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 2431–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Chen, H.C. Adhesive wear behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content. Wear 2006, 261, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.M.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Z.L. Effect of Al content on properties of CrFeNiAlxSi high entropy alloy. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 35, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Fang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, C.; Xue, S. Tribological properties of nano/ultrafine-grained fecocrnimnalx high-entropy alloys over a wide range of temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 817, 153305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, B.S.; Yu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhu, S.S.; Lou, X.; Wang, Z.Z. Study of high temperature friction and wear performance of (CoCrFeMnNi)85Ti15 high-entropy alloy coating prepared by plasma cladding. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 384, 125337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.M.; Zhan, Y.Z.; Nie, N. Development of novel CoCu0.5FeNiVTix (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, D.L. Effect of Ti on the wear behavior of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy during unidirectional and bi-directional sliding wear processes. Wear 2021, 476, 203650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukanov, S.; Loginov, P.; Fedotov, A.; Bychkova, M.; Antonyuk, M.; Levashov, E. The effect of copper on the microstructure, wear and corrosion resistance of CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys manufactured by powder metallurgy. Materials 2023, 16, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
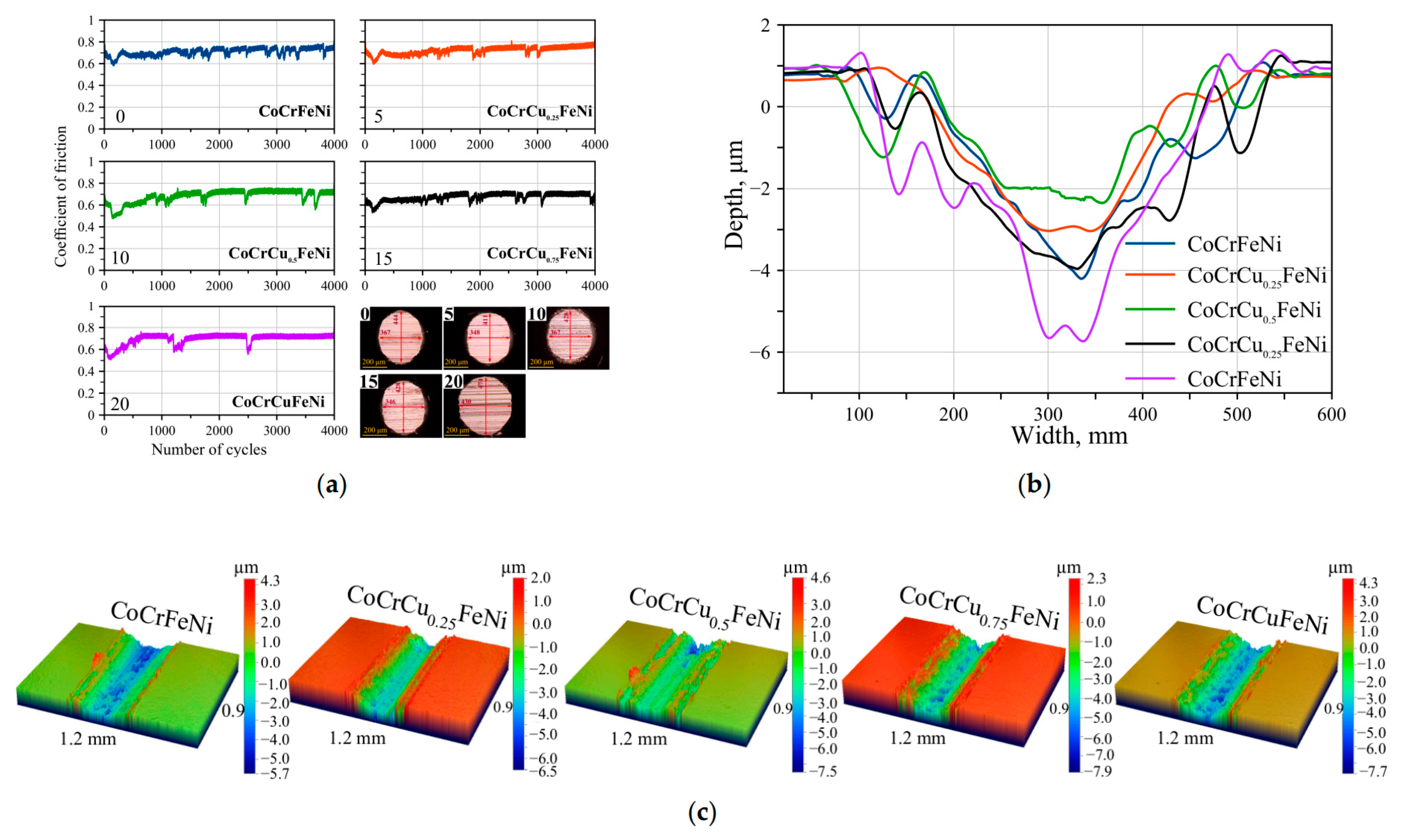
- Verma, A.; Tarate, P.; Abhyankar, A.C.; Mohape, M.R.; Gowtam, D.S.; Deshmukh, V.P.; Shanmugasundaram, T. High temperature wear in CoCrFeNiCux high entropy alloys: The role of Cu. Scr. Mater. 2019, 161, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Sheu, T.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K. Effect of iron content on wear behavior of AlCoCrFexMo0.5Ni high-entropy alloys. Wear 2010, 268, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.; Yang, B.; Dong, S.; Zhao, H.Y.; Xu, B.S.; Xu, F.J.; Liu, B.; He, P.; Feng, J.C. Effects of Fe-to-Co ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded FeCoCrBNiSi high-entropy alloy coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Patnaik, A.; Pradhan, A.K.; Kumar, V. Dry sliding wear behavior of Al0.4FeCrNiCox(x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2019, 8, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.B.; Liang, X.B.; Xu, B.S. Effect of Nb addition on the structure and mechanical behaviors of CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 240, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, F.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, J. Effects of temperature and microstructure on the triblogical properties of cocrfeninbx eutectic high entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 775, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, H. Mechanical and dry sliding tribological properties of CoCrNiNb medium-entropy alloys at room temperature. Tribol. Int. 2021, 163, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.Y.; Tieu, A.K.; Su, L.H.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Lan, X.D.; Cui, S.G.; Zhu, H.T. Investigation into reciprocating dry sliding friction and wear properties of bulk CoCrFeNiMo high entropy alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering and subsequent cold rolling processes:role of Mo element concentration. Wear 2020, 460, 203440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, X.M.; Chen, W.J.; Shang, L.; Jia, L.M. Microstructural evolution, mechanical and wear properties, and corrosion resistance of as-cast CrFeNbTiMox refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2023, 155, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.G.; Zhang, K.F.; Feng, K. Tribological properties of CoCrFeNiWx high-entropy alloys at room temperature and 900 °C. Tribology 2024, 44, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.K.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Martini, A.; Zhang, C. Effect of carbon content on microstructure, hardness and wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNiCx high-entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 847, 156533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.Q.; Zhang, N.N.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.Y. Phase evolution and wear mechanism of AlCoCrFeNiSix high-entropy alloys produced by arc melting. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 096505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Swarnakar, A.K.; Basu, A.; Chopkar, M. Effects of processing route on phase evolution and mechanical properties of CoCrCuFeNiSix high entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 748, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.B.; Zhang, A.J.; Han, J.S.; Meng, J.H. Improving mechanical properties and tribological performance of Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5 high entropy alloys via doping Si. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 869, 159122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T.; Lei, W.B.; Ma, L.J.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, J.; Cui, J.Z. Effect of boron on the microstructure, phase assemblage and wear properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Zhang, N.N.; He, B. Tribological properties of FeCoCrNiAlB-x high-entropy alloys coating prepared by lasercladding. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2017, 24, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, S. Research progress of laser cladding coating on titanium alloy surface. Coatings 2024, 14, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, H.; Abedi, H.R.; Zhang, Y. A study on outstanding high-temperature wear resistance of high-entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Recent advances in tribology of high entropy alloys: A critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 136, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.G. A review on the tribological performances of high-entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.W.; Feltrin, A.C.; Akhtar, F. Processing, microstructure and high temperature dry sliding wear of a Cr-Fe-Hf-Mn-Ti-Ta-V high-entropy alloy based composite. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Cai, Z.B.; Guan, Y.J.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, M.L.; Zhang, D. High temperature wear performance of laser-cladded FeNiCoAlCu high-entropy alloy coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.M.; Lan, L.W.; Zhu, S.; Yang, H.J.; Shi, X.H.; Liaw, P.K.; Qiao, J.W. Effects of temperature on the tribological behavior of Al_(0.25)CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Qiao, D.; Miao, J.; Cao, Z.; Wang, T. Anomalous microstructure and tribological evaluation of AlCrFeNiW0.2Ti0.5 high-entropy alloy coating manufactured by laser cladding in seawater. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Miao, J.W.; Gao, B.Y.; Deng, D.W.; Wang, T.M.; Lu, Y.P.; Cao, Z.Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, T.J.; Kang, H.J. Microstructure and tribological properties of AlCrFe2Ni2W0.2Mo0.75 high-entropy alloy coating prepared by laser cladding in seawater, NaCl solution and deionized water. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Qiao, Z.H.; Duan, H.T.; Li, J.S.; Li, J.; Liu, W.M. Corrosive and tribological behaviors of AlCoCrFeNi-M high entropy alloys under 90 wt. % H2O2 solution. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xin, Y.L.; Hai, T.D.; Jun, Y.; Zhu, H.Q.; Jian, L.; Jin, S.L. Outstanding self-lubrication of SiC ceramic with porous surface/AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy tribol-pair under 90wt% H2O2 harsh environment. Mater. Lett. 2020, 276, 128025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.T.; Wu, Y.; Hua, M.; Yuan, C.Q.; Wang, D.; Tu, J.S.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J. Tribological properties of AlCoCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy in hydrogen peroxide solution and in oil lubricant. Wear 2013, 297, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
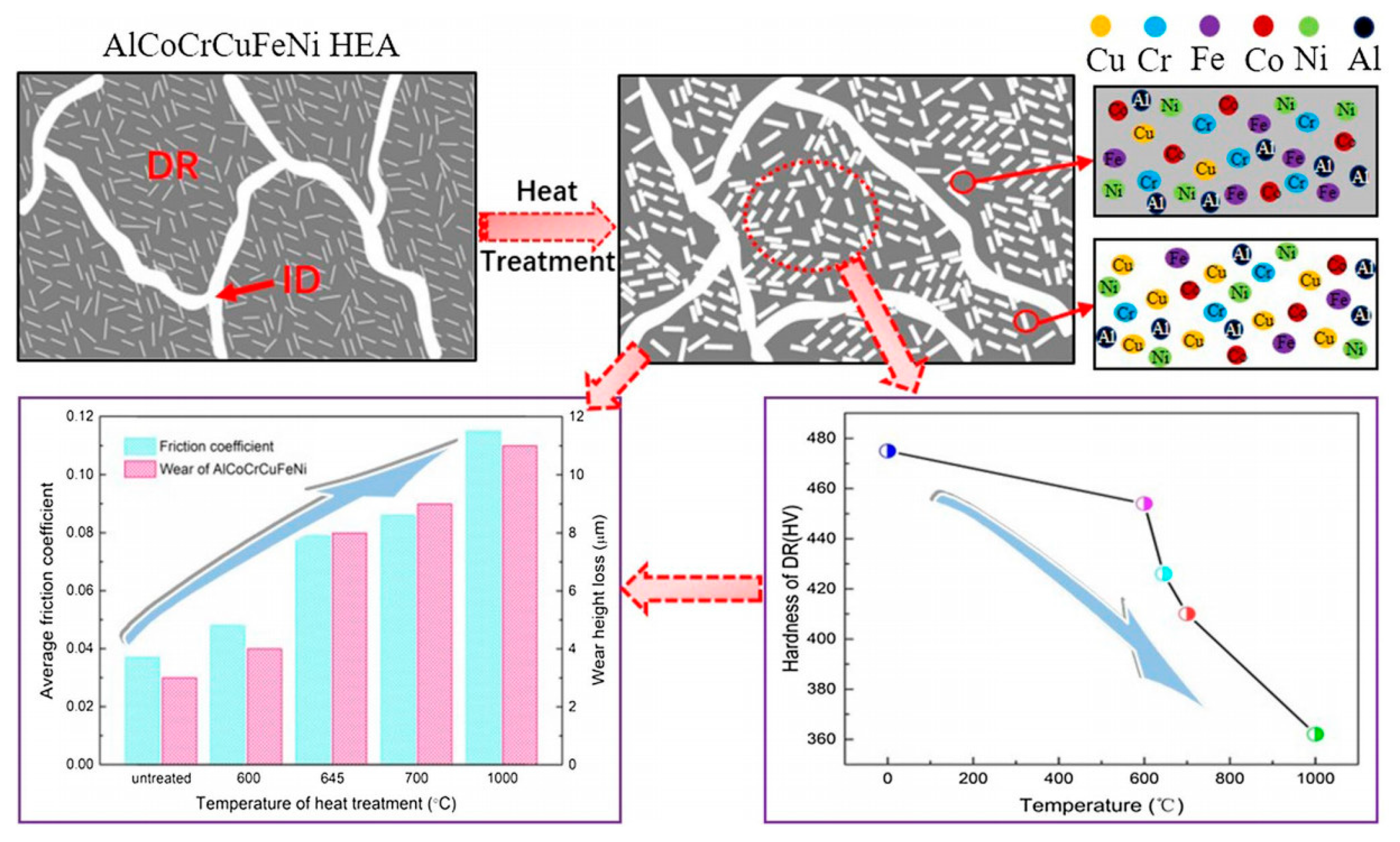
- Luo, X.S.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.L.; Hu, C.P.; Jia, D.; Zhan, S.P.; Yu, Y.; Hua, M.; Duan, H.T. Heat treatment influence on tribological properties of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy in Hydrogen Peroxide-Solution. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirari, T.; Trabadelo, V. A review on wear, corrosion, and wear-corrosion synergy of high entropy alloys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheenepalli, N.; You, H.J.; Suseong, A.; Song, J.W.; Jeong, K.Y.; Madavali, B.B.; Gian, S.; Na, Y.S.; Jong, W.W.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Worn surface and subsurface layer structure formation behavioron wear mechanism of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy in different sliding conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 549, 149202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.S.; Kou, H.C.; Niu, S.Z.; Zhu, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.M. Dry-sliding tribological properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, J.S.; Jin, J.S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, B.; Hu, Z.G.; Gong, P. Effect of grain size on the tribological behavior of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Haghdadi, N.; Annasamy, M.; Kada, S.R.; Fabijanic, D. On the enhanced wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperature. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.Y.; Tieu, A.K.; Lan, X.D.; Su, L.H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, H.T. Effects of normal load and velocity on the dry sliding tribological behaviour of CoCrFeNiMo0.2 high entropy alloy. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.; Tran, B.; Tieu, A.K.; Wexler, D.; Deng, G.Y.; Nguyen, C. Effects of oxidation on friction and wear properties of eutectic high-entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi2.1. Tribol. Int. 2021, 160, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Patnaik, A.; Pradhan, A.K.; Kumar, V. Room temperature wear study of Al0.4FeCrNiCox (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mol) high-entropy alloys under oil lubricating conditions. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.W.; Wang, X.J.; Guo, R.P.; Yang, H.J.; Qiao, J.W. Effect of environments and normal loads on tribological properties of nitrided Ni45(FeCoCr)40(AlTi)15 high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firstov, S.A.; Gorban, V.F.; Krapivka, N.A.; Karpets, M.V.; Kostenko, A.D. Wear resistance of high-entropy alloys, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2017, 56, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jia, Q.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Greiner, C.; Hua, K.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, J. A wear-resistant metastable CoCrNiCu high-entropy alloy with modulated surface and subsurface structures. Friction 2022, 10, 1722–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Nie, Q.; Qi, Z.; Cao, Z. Microstructures and wear resistance of CoCrFeNi2V0.5Tix high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Crystals 2020, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Dong, L.G.; Dong, X.W.; Zhao, W.H.; Liu, J.H.; Xiong, J.X.; Xu, C.Y. Study on wear behavior of FeNiCrCoCu high entropy alloy coating on Cu substrate based on molecular dynamics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 570, 151236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ren, K.; Xie, J.; Zhang, C.; Tang, W.C. Friction and wear behavior of single-phase high-entropy alloy FeCoNiCrMnunderMoS2-oil lubrication. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2019, 72, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Xiao, M.; Shen, Y. Effect of iron content on microstructure and properties of FexNi2Co2CrTiNb high-entropy alloy coating. Optik 2020, 204, 164168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Li, X.M.; Qiu, Z.J.; Zhang, R.Z. Molecular dynamics study on friction of high-entropy alloy FeNiCrCoCu. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Z.; Xu, Z.H.; Song, J.R.; Hu, C.X.; Miao, L.L.; He, X.D. Molecular dynamics simulation of a new inhomogeneous concentration distribution model based on frictional behavior of FeNiCrCoCu high-entropy alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.S.; Kou, H.C.; Duan, H.T.; Li, J.; Liu, W.M. Tribological behavior of AlCoCrCuFeNi and AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloys under hydrogen peroxide solution against different counterparts. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthoula, P.; Emmanuel, G.; Angela, L.; Alexander, K. Dry-sliding wear response of MoTaWNbV high entropy alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1600535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yi, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P. Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 788, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, A.; He, J.; Meng, J.; Lu, Y. Tribological behavior of an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy sliding against different counterfaces. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentzaris, K.; Poulia, A.; Georgatis, E.; Lekatou, A.G.; Karantzalis, A.E. Analysis of microstructure and sliding wear behavior of Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5 High-Entropy Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 5177–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, J. Influence of MoSi2 on the microstructure and elevated-temperature wear properties of Inconel 718 coating fabricated by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 424, 127665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiou, C.; Poulia, A.; Georgatis, E.; Karantzalis, A.E. Microstructural features and dry—Sliding wear response of MoTaNbZrTi high entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
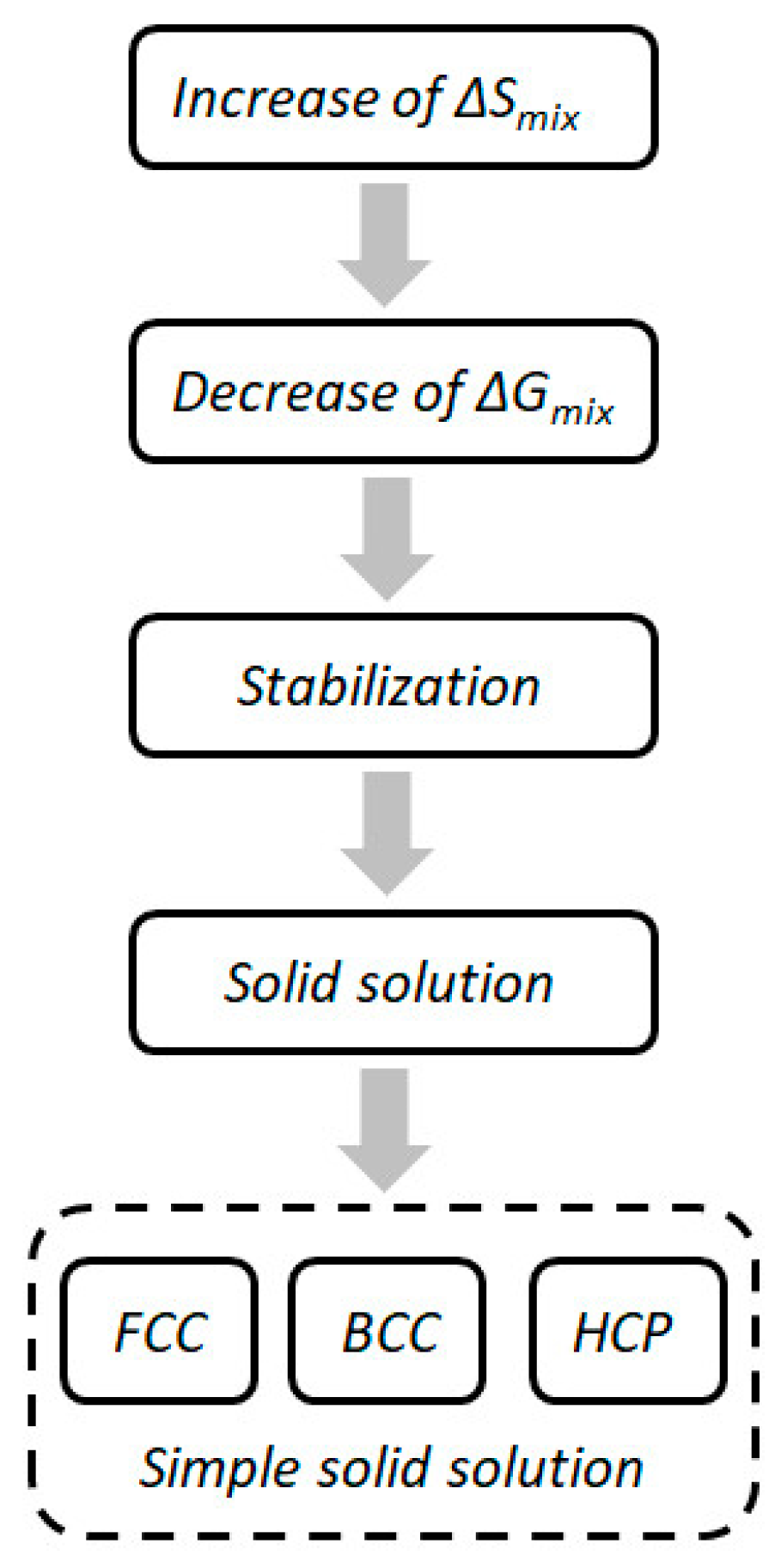
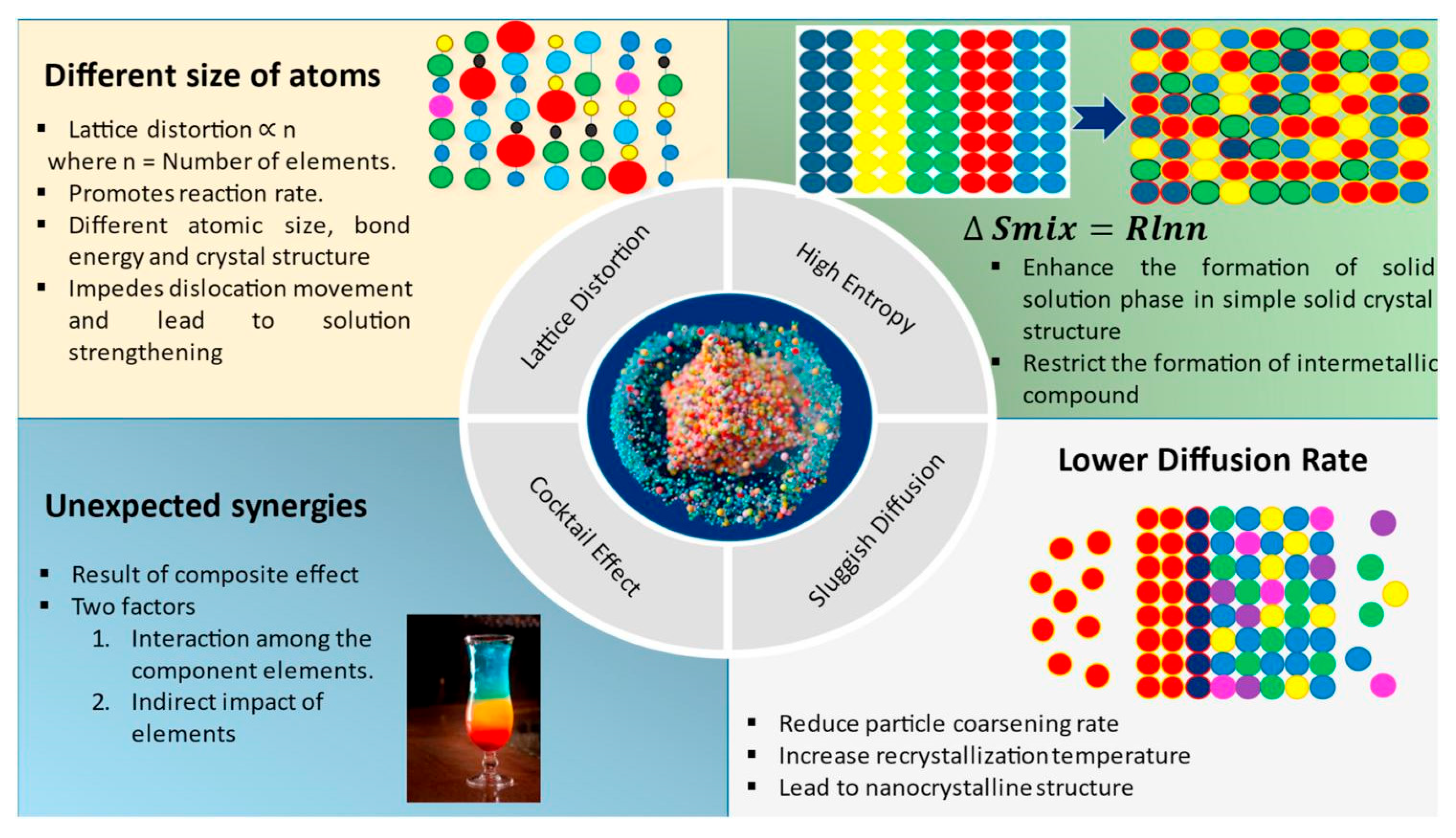
| Dimension | Traditional Alloys | High-Entropy Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Composition design | Based on 1–2 elements (proportion > 50%) | 5 or more principal elements (atomic ratio 5–35%) |
| Phase diagram position | Biased towards endpoints (dominated by a single principal element) | Located in the central region (mixed by multiple principal elements) |
| Microstructure | Prone to form intermetallic compounds or brittle phases | Tend to form simple solid solutions (FCC/BCC, etc.) |
| Performance characteristics | Single performance is prominent, but it is difficult to coordinate multiple performances | Balanced comprehensive performance, breaking through traditional performance bottlenecks |
| Common Element | Examples for Element Classification |
|---|---|
| Light metal elements | Al, Li, Be, Mg, Ca |
| Transition metal elements | Ti, Cu, Mn, Fe, Co |
| Refractory metal elements | Nb, Mo, W, Hf |
| Non-metallic elements | C, Si, B, N |
| Elements Added | Preparation Method | Material Composition | Experimental Parameter Conditions | Influence on Friction and Wear | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Laser sintering | CrFeNiAlxSi | Load 20 N, abrasive grain 40 μm, time 5 min | Wear resistance is optimal when Al content reaches x = 0.6, in line with the positive correlation between hardness and wear resistance | [53] |
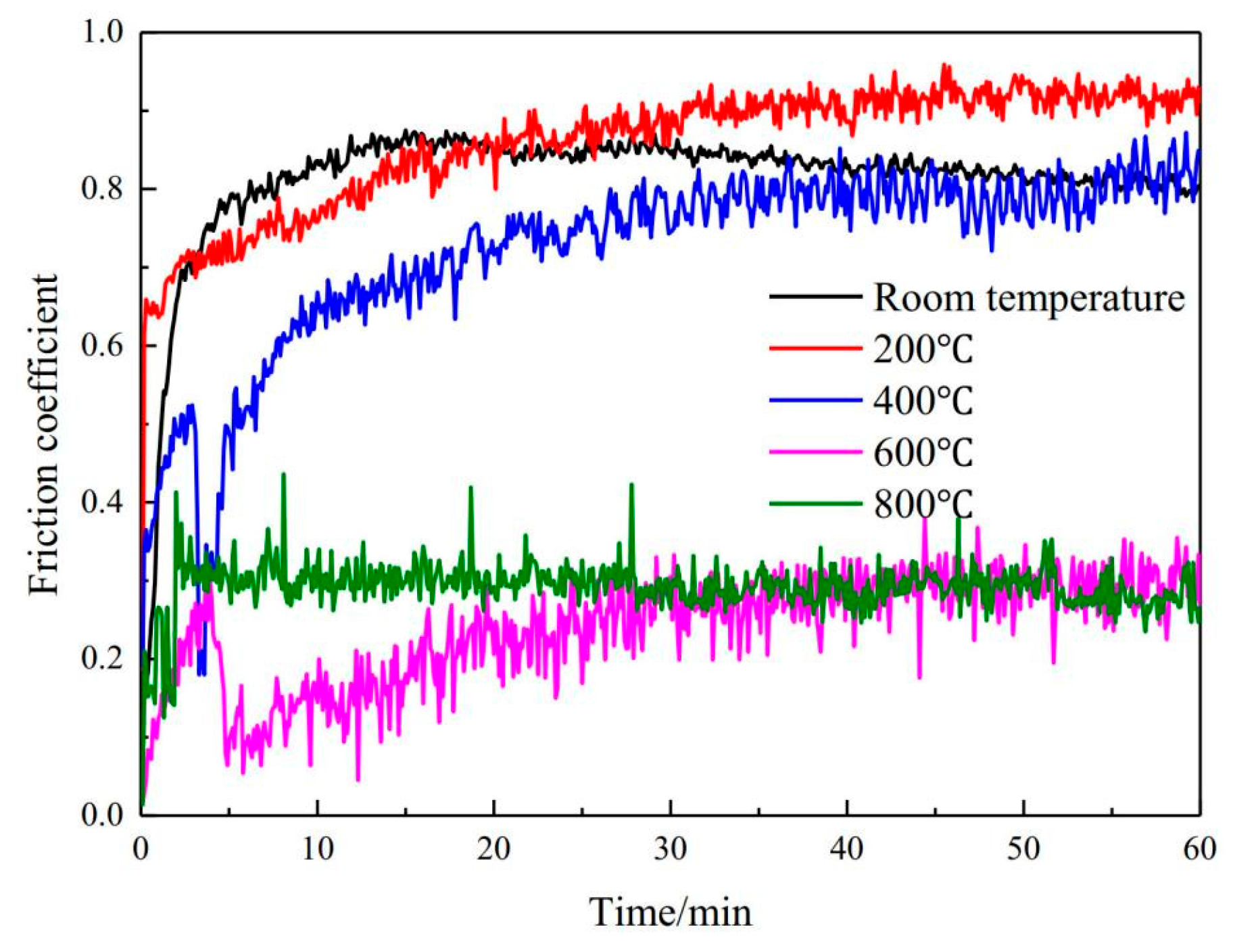
| Ti | Plasma cladding | (CoCrFeMnNi)85Ti15 coating | Load 25 N, room temperature 800 °C, rotating speed 300 rpm, time 20 min | Ti increases hardness by 6 times, and wear resistance is optimal at 400 °C | [55] |
| Cu | Arc melting | CoCrFeNiCux | Load 100 N, room temperature 600 °C, rotating speed 95 rpm, time 1000 s | Cu forms an oxide glaze layer, and high-temperature self-lubrication improves wear resistance | [59] |
| Fe | Arc melting | AlCoCrFexMo0.5Ni | Load 29.4 N, speed 0.5 m/s, time 24 h | Increase in Fe reduces σ phase, wear resistance decreases, mainly abrasive wear | [60] |
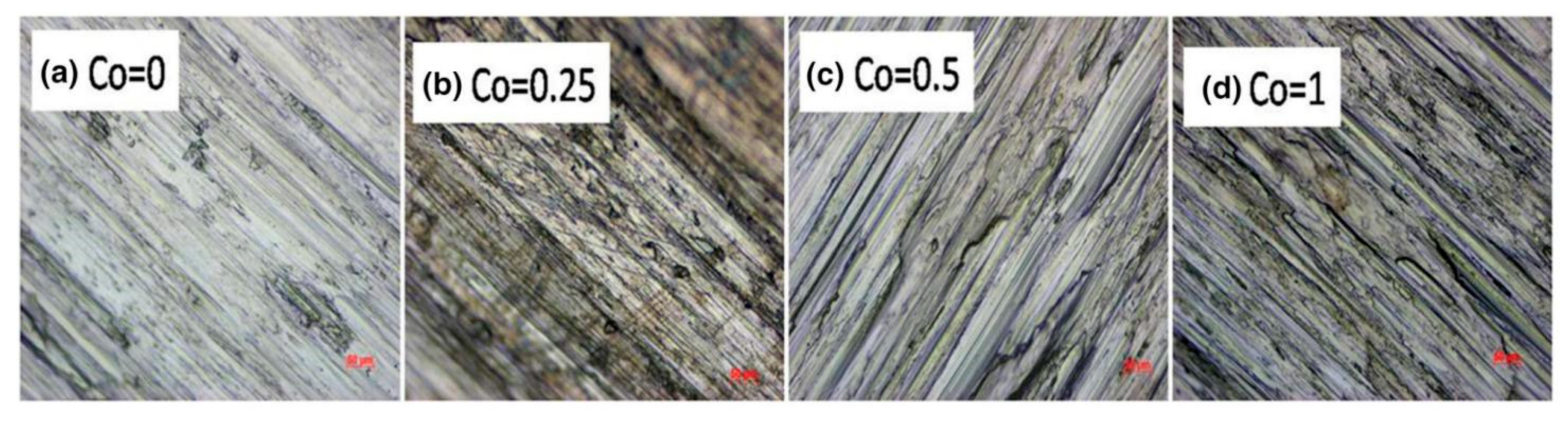
| Co | Arc melting | Al0.4FeCrNiCox | Load 5–20 N, sliding speed 0.5–2 m/s, room temperature | Increase in Co content reduces BCC phase and hardness, leading to decreased wear resistance | [62] |
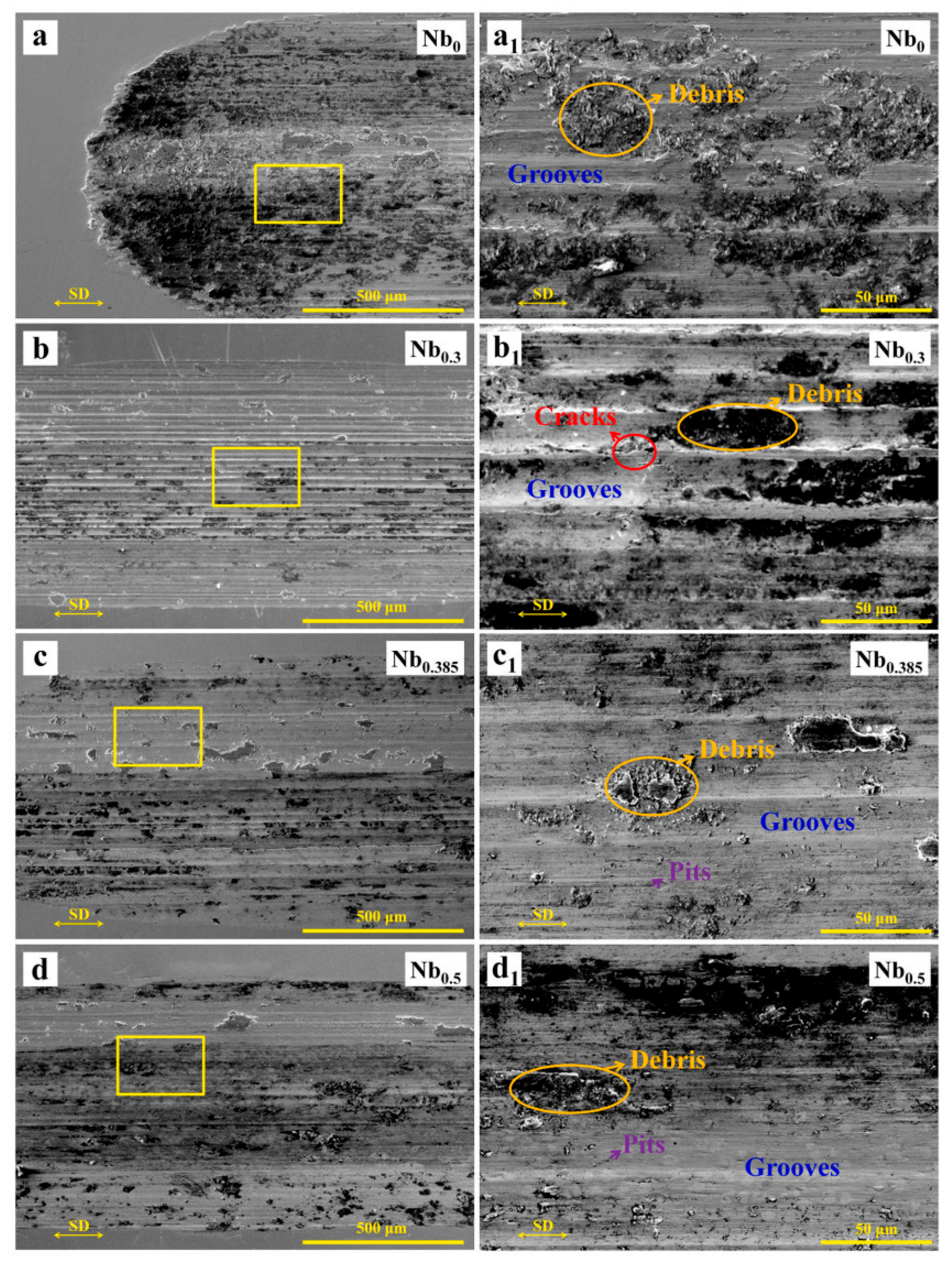
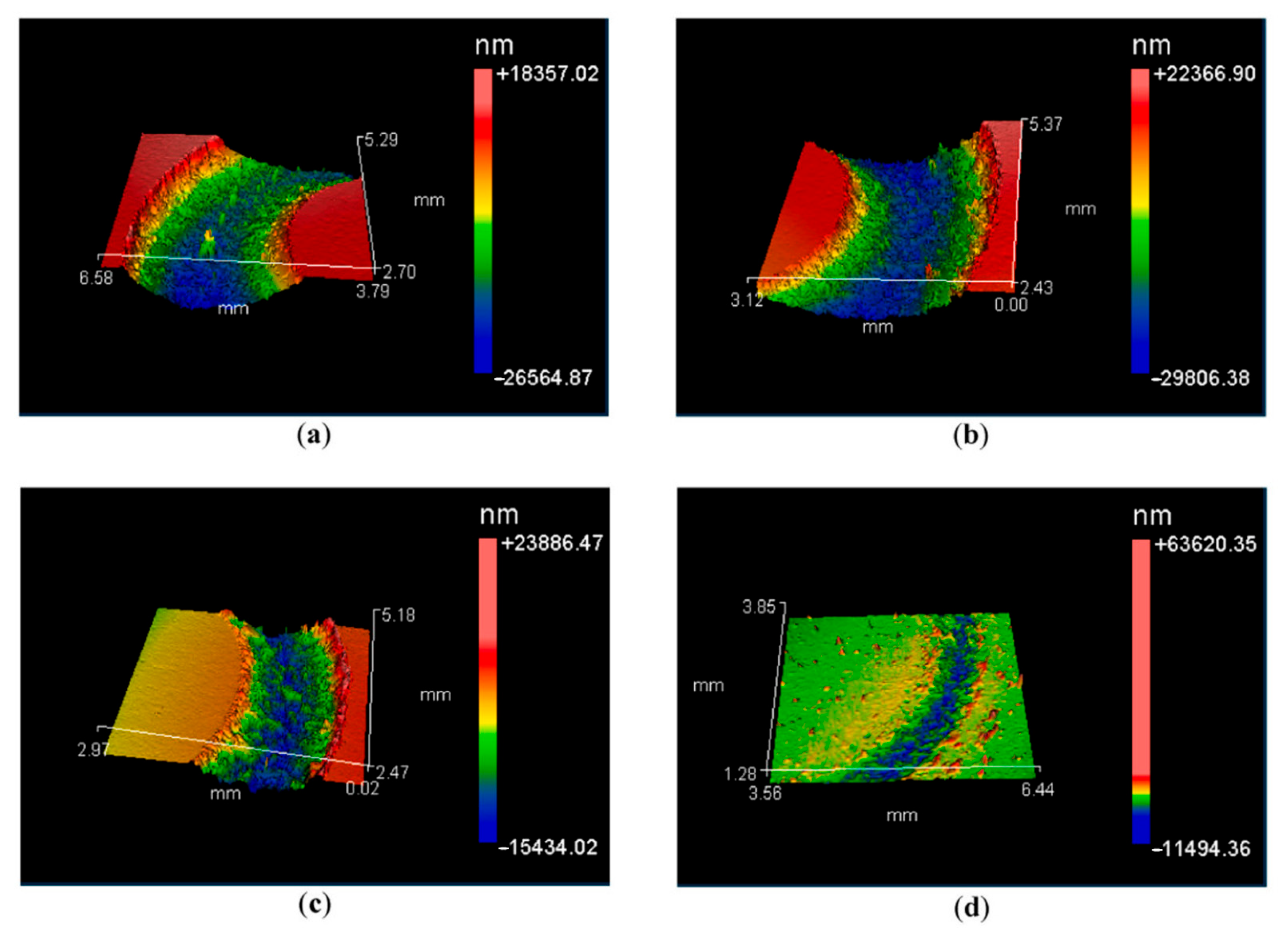
| Nb | Arc melting | CoCrFeNiNbx | Load 5 N, room temperature 800 °C, speed 0.188 m/s | A dense oxide layer forms at high temperatures, significantly reducing wear rate, at 800 °C, the oxide layer is glaze-like, and wear resistance is optimal | [64] |
| Mo | Spark plasma sintering + cold rolling | CoCrFeNiMox | Load 5 N/50 N, speed 6 mm/s | Mo solid solution strengthening improves hardness, inhibits grain coarsening, and reduces abrasive wear | [66] |
| W | Vacuum arc melting | CoCrFeNiWx | Load 10 N, room temperature and 900 °C, speed 0.3 m/s | W addition increases high-temperature hardness, and high-temperature oxidation generates WO3 to reduce friction coefficient | [68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Guo, H. Research Progress on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys. Lubricants 2025, 13, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13080342
Zhang S, Wang Z, Lin W, Guo H. Research Progress on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys. Lubricants. 2025; 13(8):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13080342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuai, Zhaofeng Wang, Wenqing Lin, and Haoyu Guo. 2025. "Research Progress on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys" Lubricants 13, no. 8: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13080342
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, Z., Lin, W., & Guo, H. (2025). Research Progress on Tribological Properties of High-Entropy Alloys. Lubricants, 13(8), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13080342





