Abstract
Gestational hypertension is a notable concern with ramifications for maternal and fetal health. Preemptive measures, including physical activity (PA), are crucial. There is a pressing need for comprehensive investigations into the impact of various forms of PA on hypertensive disorders. A systematic review and meta-analysis (CRD42022372468) following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines was performed. Our review exclusively considered randomized clinical trials (RCTs) between 2010 and 2023, using the following databases: EBSCO, including Academic Search Premier, Education Resources Information Center, PubMed/MEDLINE, SPORTDiscus, and OpenDissertations; Clinicaltrials.gov; Web of Science; Scopus; the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; and the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). The primary outcome was hypertensive disorders occurring during pregnancy (14 studies). Diagnosed preeclampsia (15 studies) and blood pressure levels were also examined (17 studies). PA during pregnancy was significantly associated with a reduced risk of hypertensive disorders (RR = 0.44, 95% CI = 0.30, 0.66). The data also indicate a positive correlation between PA during pregnancy and both systolic (MD = −2.64, 95% CI = −4.79, −0.49) and diastolic (MD = −1.99, 95% CI = −3.68, −0.29) blood pressure levels. The relationship between PA and the incidence of diagnosed preeclampsia did not demonstrate a statistically significant association (RR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.59, 1.11; p = 0.20). Random effects were used for all analyses. PA during pregnancy promises to improve maternal health by reducing the risk of gestational hypertension and positively affecting systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
1. Introduction
Epigenetics has profoundly revolutionized the comprehension and analysis of numerous essential processes, with pregnancy standing out as one of the domains most profoundly influenced by this paradigm shift. It underscores the pivotal role of the intrauterine environment as a determining factor for the offspring’s lifelong health trajectory. Consequently, maintaining a state of equilibrium within various domains of the female organism (including cardiovascular, metabolic, and emotional aspects) during gestation emerges as a linchpin for ensuring the prospective well-being of the developing human [1].
Conversely, complications and pathologies arising during pregnancy wield the potential to impose enduring health ramifications, some of which might manifest chronically over time. The wealth of the scientific literature substantiates these assertions, firmly grounding them within empirical evidence [2]. Within this context, the journey of pregnancy and childbirth stands unparalleled in its transformative nature, given the substantial quantitative and qualitative metamorphoses that the female body must undergo to facilitate optimal fetal growth and development. Moreover, the female physique must adeptly navigate the critical juncture of delivery, orchestrating the efficient expulsion of the fetus into the extracorporeal milieu while upholding the proficiency of its multifaceted systems [3].
Foremost among these systems, the cardiovascular apparatus assumes paramount significance, being subjected to heightened demands throughout gestation and particularly during delivery. Over 40 weeks, the cardiovascular system of the pregnant woman undergoes structural and functional adaptations spurred by two fundamental factors: escalating requisites due to ongoing fetal development and the mechanical consequence of the enlarging uterus causing the repositioning of specific structures. Mastery of these modifications and preserving a harmonious maternal–fetal equilibrium, with a vigilant eye on averting cardiovascular complications and pathologies, stand as formidable challenges confronting the pregnant woman [4].
Extensive research signals the perils of an imbalanced cardiovascular milieu during pregnancy. Gestational hypertension is characterized by elevated blood pressure levels that manifest specifically during pregnancy. Diagnosis typically involves the identifying two consecutive elevated blood pressure readings equal to or exceeding 140/90 mmHg (classified within the mild range) after the 20th week of gestation, with the readings taken at least 4 h apart. Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-related condition characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to organ systems, often the liver and kidneys. Preeclampsia is defined as newly elevated blood pressure ≥140/90 after 20 weeks of gestation in addition to proteinuria, defined as 300 mg or more in a 24-h urine specimen, or a protein/creatinine ratio of 0.3 or more, or 2+ protein on urine dipstick (used if other quantitative methods are unavailable). Eclampsia is a severe complication of preeclampsia, characterized by seizures in pregnant women. HELLP syndrome involves hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count, further escalating the risks associated with preeclampsia. Notably, gestational hypertension emerges as a conceivable complication, the repercussions of which reverberate across maternal, fetal, and neonatal domains, wielding lasting ramifications for the subsequent well-being of the individual [5,6].
Graver aberrations such as preeclampsia, elusive to effective control, engender pregnancies fraught with intensive medical monitoring and even imperil fetal viability. The imperative of preemptive measures, operative across the gestational timeline, becomes evident in this intricate landscape. Among these measures, moderate physical activity emerges as a promising prophylactic agent, yielding favorable outcomes across various facets of the female anatomy. Particular attention should be given to mitigating metabolic imbalances, notably excess maternal weight gain, and addressing the epigenetic repercussions of an adverse intrauterine environment [1,2,3,7].
The World Health Organization recommends at least 150 min of moderate-intensity aerobic activity spread throughout the week for pregnant women, barring contraindications. This promotes overall health and may reduce the risk of gestational hypertension [8].
Numerous studies have investigated the influence of physical activity (PA) on gestational hypertension. However, the findings have been inconclusive, lacking a definitive conclusion. In this context, implementing new research methodologies characterized by high reliability and rigor, such as a systematic review and meta-analysis (SR + MA), can significantly contribute to advancing scientific knowledge in this area.
We hypothesize that engaging in physical activity during pregnancy may serve as a preventive factor against hypertensive disorders and associated complications in pregnant women.
This systematic review and meta-analysis (SR+MA) aimed to examine the effects of diverse modalities of PA during pregnancy on the prevention of gestational hypertension.
2. Materials and Methods
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed in the current study. It was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO, Registration No. CRD42022372468). The Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, and Study Design (PICOS) framework was used to analyze the search sources [9].
2.1. Population
The population included pregnant individuals without obstetric contraindications to exercise during pregnancy who participated in a prenatal PA program [10].
2.2. Intervention
The analyzed characteristics of the intervention were as follows: (a) weekly frequency of PA sessions; (b) intensity, where all included studies utilized a moderate load intensity, defined as 55–65% of the maximum maternal heart rate or the perceived effort on the Borg Scale (range 12–14); (c) duration of the PA program; (d) type of PA, including yoga, Pilates, aerobic exercises, strength training, or pelvic floor training; (e) supervision of the PA program; and (f) duration of the individual sessions, as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of analyzed articles.
2.3. Comparison
Since all the studies analyzed were randomized clinical trials (RCTs), women who participated in an exercise or PA program during pregnancy were compared with those who did not. Intervention characteristics were collected and compared, as presented in Table 1.
2.4. Outcomes
The primary outcome was hypertensive disorders occurring during pregnancy. Diagnosed preeclampsia and blood pressure levels were also examined.
2.5. Study Design and Selection Process
As previously mentioned, all eligible articles were RCTs. The literature search was conducted between September 2022 and May 2023 at Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (INEF), using the following databases: EBSCO, including Academic Search Premier, Education Resources Information Center, PubMed/MEDLINE, SPORTDiscus, and OpenDissertations; Clinicaltrials.gov; Web of Science; Scopus; the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; and the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). The search encompassed articles written in English or Spanish that were published between 2010 and 31 May 2023. The search terms used were:
English: (“physical activity” OR “exercise” OR “training” OR “physical exercise” OR “fitness” OR strength training” OR “physical intervention” OR “maternal exercises” OR “cointervention”) AND (“pilates” OR “yoga” OR “strengthening” OR aerobic OR “resistance training” OR “walking”) AND (“pregnancy” OR “maternal” OR “antenatal” OR “pregnant” OR “gestation”) AND (“health” OR “wellbeing”) AND (“randomized clinical trial” OR “RCT” AND (“hypertensive disease” OR “hypertensive disorders” OR “hypertension”) AND (“blood pressure”) AND (“preeclampsia”) AND (“Systolic” AND “diastolic”).
Spanish: (“actividad física” OR “ejercicio” OR “entrenamiento” OR “ejercicio físico” OR “fitness” OR entrenamiento de fuerza” OR “intervención física” OR “ejercicios maternos” OR “cointervención”) AND (“pilates” OR “yoga” OR “fortalecimiento” OR “aeróbico” OR “entrenamiento de resistencia” OR “caminar”) AND (“embarazo” OR “materno” OR “prenatal” OR “embarazada” OR “gestación”) AND (“salud” OR “bienestar”) AND (“ensayo clínico aleatorizado” OR “ECA” AND (“enfermedad hipertensiva” OR “trastornos hipertensivos” OR “hipertensión”) OR (“presión arterial”) OR (“preeclampsia”) OR (“Sistólica y Diastólica”).
The eligible articles for review comprised studies that measured PA or exercise intervention (excluding articles that solely provided advice for an active pregnancy or those that included a measurable PA questionnaire but lacked an exercise intervention). The characteristics of the PA or exercise program were also considered. The protocol for screening records and extracting data was performed by two researchers (D.Z. and M S-P). This process is illustrated in Figure 1. Two reviewers (R.B. and C.S.-J.) independently screened titles and abstracts of all identified citations, and potentially eligible articles were selected. Full-text articles were independently assessed by the two reviewers for eligibility criteria. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus.
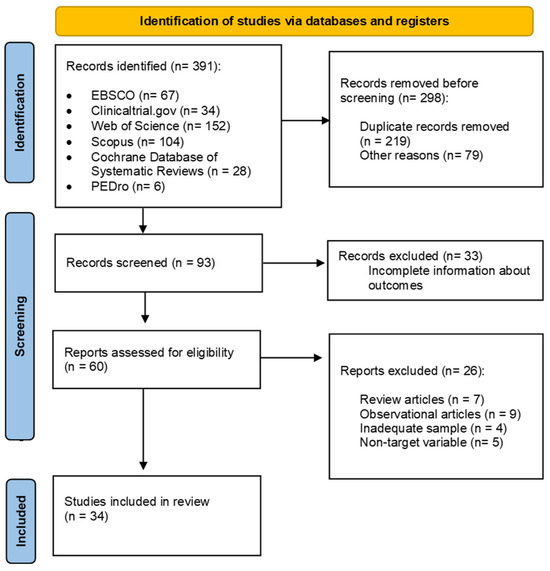
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the analyzed articles [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,45,46].
Additionally, secondary outcomes such as physiological, sociodemographic, and delivery outcomes were examined by two reviewers (D.Z. and M.S.-P.) to evaluate the effects of each intervention on maternal health. However, these secondary outcomes were not included in the meta-analyses. From each selected study, we extracted the following information: author(s), publication year, country where the study was conducted, study design type, number of participants, characteristics of the intervention program, and the variables analyzed (both primary and secondary outcomes).
2.6. Statistical Analysis, Quality of Evidence Assessment, Risk of Bias, and Publication Bias
Meta-analyses were conducted, with the dependent variable being the ratio of occurrence of hypertensive disorders in each study, categorized as either “yes” or “no”. The number of events observed in each study group and their respective relative risks (RRs) were recorded. A random effects model calculated the total risk ratio (RR) sum [47]. Each study was assigned a weight based on its sample size, contributing to the overall analysis, and establishing a weighted average. The I2 statistic was utilized to quantify the heterogeneity observed in the results due to variations in interventions and study designs, indicating the extent of variability in the effects of each intervention, which were non-random. The following criteria were used to classify heterogeneity levels: low heterogeneity (25%), moderate heterogeneity (50%), and high heterogeneity (75%) [48].
The quality of evidence for each study’s primary outcome was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) framework, with RCT studies rated as moderate or high quality. The certainty of evidence was high [49]. The Cochrane Handbook guidelines were followed to evaluate the potential risk of bias (including selection, performance, attrition, detection, and reporting bias) [45]. RCTs were initially considered to have a “low” risk of bias due to their study design and intervention compared with non-randomized interventions. However, their risk of bias could be either increased or decreased depending on the presence of “high” or “low” scores across the different bias sources [49].
In order to assess potential publication bias in each developed meta-analysis, the Egger regression test was used due to its enhanced sensitivity in detecting publication bias under conditions of weak or moderate heterogeneity. Typically, this test yields a metric indicating significant publication bias when p < 0.1 [46].
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
A total of 391 articles were initially identified during the first stage of the search of which 298 were removed before screening: duplicate records removed (n = 219) and other reasons (n = 79) such as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. After record screening, 33 articles were excluded. Subsequently, 26 articles were excluded for the following reasons: being review (n = 7) or observational (n = 9) studies, inadequate sample (n = 4), and non–target variable (n = 5). Ultimately, 34 studies were included for further meta-analysis (Figure 1).
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
The quality of evidence across the studies exhibited a spectrum ranging from low to high. Achieving blinding of participants to either the intervention or control group, as well as blinding of the instructor, was often unattainable due to the inherent characteristics of the PA intervention. Consequently, this led to an unclear or high risk of bias, particularly with regard to performance bias, depending on how it was documented. In some instances, other potential sources of bias included the unavailability of the study protocol for public scrutiny, preventing a comparison between the planned and observed outcomes. Additionally, there were instances of a need for more transparency in reporting the randomization process. However, on the whole, the majority of the studies demonstrated a low risk of bias across the five categories of bias that were evaluated. The detailed risk of bias analysis can be found in Figure 2.
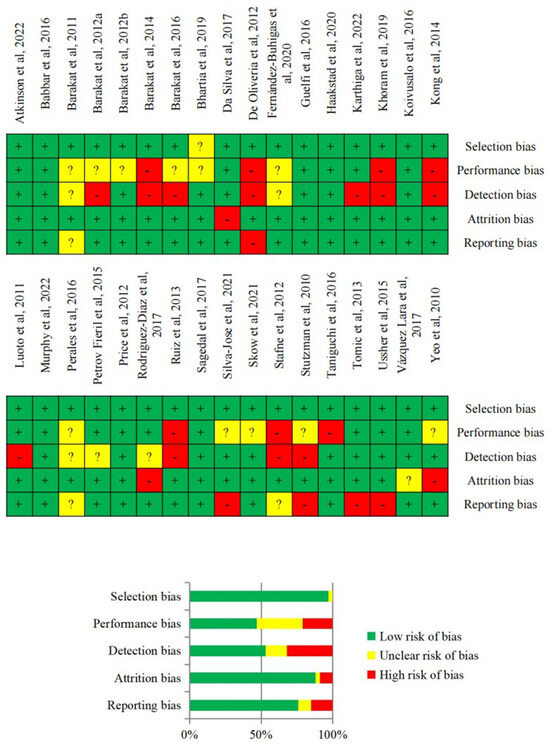
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49].
3.3. Effect of PA on the Occurrence of Hypertensive Disorders
A total of 14 distinct RCTs were incorporated into the present analysis, which investigated the incidence of hypertensive disorders in women within both experimental and control groups during pregnancy. The results revealed a significant correlation between PA during pregnancy and the occurrence of hypertensive disorders (RR = 0.44, 95% CI = 0.30, 0.66, p = 0.0002; I2 = 53%, Pheterogeneity = 0.01). Figure 3 depicts a forest plot corresponding to the conducted meta-analysis. The quantification evaluation of the risk of publication bias test in the analyzed articles showed that there was no potential publication bias (p = 0.44) in this analysis.
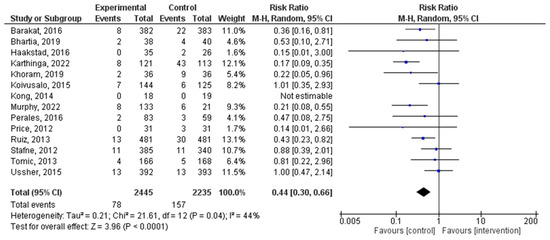
Figure 3.
Effect of PA on the occurrence of hypertensive disorders [22,23,28,29,30,31,32,34,35,37,39,46,47].
3.4. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Diagnosed Preeclampsia
A total of 15 distinct RCTs were included in the present analysis, which examined the incidence of diagnosed preeclampsia in women within both experimental and control groups during pregnancy. The results did not reveal a significant statistical association between PA during pregnancy and the diagnosed preeclampsia (RR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.59, 1.11; I2 = 26%, Pheterogeneity = 0.18). Figure 4 illustrates a forest plot corresponding to the conducted meta-analysis. The quantitative assessment of publication bias risk in the analyzed articles indicated the absence of potential publication bias (p = 0.99) in this analysis.
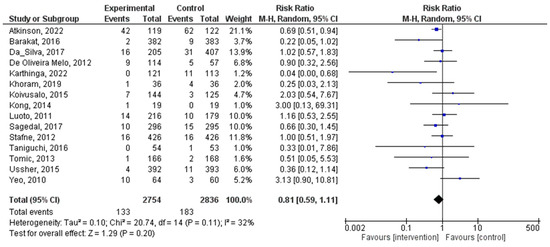
Figure 4.
Effect of PA during pregnancy on diagnosed preeclampsia [16,22,24,25,29,30,31,32,33,40,43,45,46,47,49].
3.5. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Systolic Blood Pressure
There was a total of 17 studies that were incorporated into this analysis. Regular PA during pregnancy had a significant relationship with systolic blood pressure (MD = −2.64, 95% CI = −4.79, −0.49, I2 = 78%, Pheterogeneity = 0.00001). The forest plot corresponding to the current meta-analysis is illustrated in Figure 5. The quantification evaluation of the risk of publication bias test in the analyzed articles showed that there was no potential publication bias (p = 0.8) in this analysis.
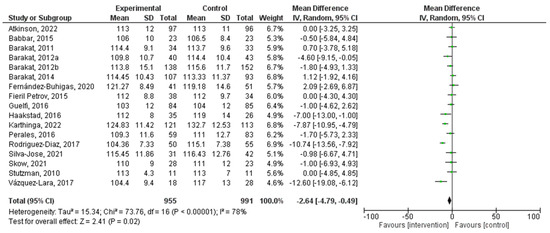
Figure 5.
Effect of PA during pregnancy on systolic blood pressure [16,17,18,19,20,21,26,27,28,29,35,36,38,41,42,44,48].
3.6. Effect of PA during Pregnancy on Diastolic Blood Pressure
There was a total of 17 studies that were incorporated into this analysis. Regular exercise or PA during pregnancy had a significant relationship with diastolic blood pressure (MD = −1.99, 95% CI = −3.68, −0.29, I2 = 79%, Pheterogeneity = 0.00001). The forest plot corresponding to the current meta-analysis is illustrated in Figure 6. The quantitative assessment of publication bias risk in the analyzed articles indicated the absence of potential publication bias (p = 0.63) in this analysis.
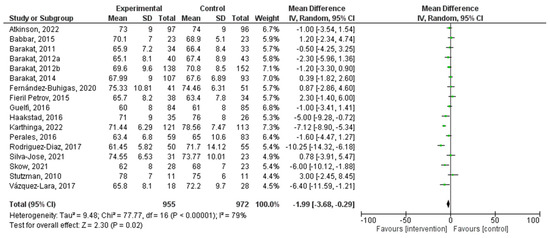
Figure 6.
Effect of PA during pregnancy on diastolic blood pressure [16,17,18,19,20,21,26,27,28,29,35,36,38,41,42,44,48].
4. Discussion
In light of the current study’s findings, it is evident that active women during pregnancy exhibit a noteworthy decrease in hypertensive disorders. Additionally, a favorable impact of physical activity during pregnancy on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure is discernible. These results provide valuable insights into the potential benefits of exercise for expectant mothers and their overall maternal health, supporting international recommendations for a minimum amount of moderate PA during pregnancy (150 min per week) as a facilitator of positive effects of PA during pregnancy on maternal, fetal, and newborn outcomes [8,10,50].
The rigorous study selection aimed to ensure the inclusion of only high-quality research in this meta-analysis. This careful selection process enhances the reliability and validity of the meta-analysis results.
The mechanism underlying the beneficial impact of moderate exercise on blood pressure in pregnant women is a multifaceted interplay of physiological adaptations that contribute to cardiovascular health. Several studies have indicated that engaging in regular, moderate-intensity physical activity during pregnancy can improve cardiac function, regulate body weight, reduce oxidative stress, and enhance vascular endothelial function. The type and intensity of exercise should be adapted to the woman’s pre-existing fitness level. Aerobic exercises, such as those included in our meta-analysis, have been associated with increased cardiac output and stroke volume. These cardiovascular adaptations play a crucial role in maintaining optimal blood flow to vital organs, including the placenta, supporting the overall well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus [51,52].
Moreover, the positive effects of moderate exercise extend to its impact on body weight, which is a significant factor in blood pressure regulation. Exercise during pregnancy has been shown to contribute to healthy weight management, reducing the risk of excessive gestational weight gain, a known factor associated with elevated blood pressure [53].
Oxidative stress, implicated in the pathogenesis of hypertensive disorders, is another aspect influenced by moderate exercise. Regular physical activity has been linked to reducing oxidative stress markers and promoting an environment conducive to blood pressure homeostasis [54].
Additionally, improvements in vascular endothelial function, facilitated by exercise, contribute to the dilation of blood vessels, enhancing blood flow and reducing the resistance that can lead to elevated blood pressure. The adaptability of the vascular system is particularly crucial during pregnancy, where adequate blood supply is essential for the developing fetus [55].
One notable aspect of the included studies was the diverse nature of the interventions. These interventions were delivered by specialized professionals and encompassed various physical activities, including aerobic exercises, strength training, and aquatic sessions. The variety in exercise modalities reflects the versatility of PA programs during pregnancy. Furthermore, the session frequency and duration flexibility allow interventions tailored to individual preferences and needs. Compared with previous studies in the field, this meta-analysis stands out due to its focused examination of specific maternal health outcomes, including the latest evidence, and its interpretation of clinical significance. While previous studies may have explored broader pregnancy-related outcomes, this study homes in on hypertensive disorders, preeclampsia, and blood pressure levels, providing a more targeted analysis.
The meta-analysis identified a significant correlation between exercise during pregnancy and the occurrence of hypertensive disorders. This finding suggests that regular PA may protect against developing hypertensive disorders in pregnant women. The RR of 0.44, with a 95% confidence interval, indicates a substantial reduction in the risk of hypertensive disorders among pregnant women participating in PA programs. However, it is essential to note that a moderate level of heterogeneity (I2 = 53%) was observed among the included studies, suggesting some variability in the results. Further research may help elucidate the sources of this heterogeneity. Our findings align with the results of the Magro-Maloso et al. 2017 and Martinez-Vizcaino et al. 2022 meta-analyses [56,57], which also assessed the impact of aerobic exercise during singleton pregnancies on hypertensive disorders. While our study includes additional evidence and focuses on specific outcomes, both analyses support the notion that exercise during pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of gestational hypertensive disorders.
Additionally, our meta-analysis and Wolferz et al.’s 2017 systematic review harmonize the exploration of aerobic exercise’s impact on gestational hypertensive disorders [58]. Both studies find that engaging in regular aerobic exercise, particularly starting early in pregnancy, holds promise in reducing the risk of these disorders. This work also emphasized that the type of exercise, specifically aerobic exercise, significantly reduced the risk of gestational hypertensive disorders. This concept resonates with our findings. While our study did not specifically investigate the impact of exercise on preterm birth rates, Wolferz et al.’s 2017 systematic review suggests that exercise during pregnancy may not influence preterm birth rates [58]. Our meta-analysis, which focused on exercise interventions during pregnancy, echoes the findings of Zhang et al.’s 2023 study [59]. While their article provides insights into the multifaceted pathogenesis of gestational hypertension, our research delves into exercise’s potential preventive and therapeutic role in addressing this complex condition. The physiological mechanisms discussed in Zhang et al.’s work, such as improvements in cardiac function, body weight, oxidative stress reduction, and vascular endothelial function with exercise, align with our findings regarding the positive effects of exercise on blood pressure regulation during pregnancy.
In contrast to the positive association with hypertensive disorders, this meta-analysis did not reveal a statistically significant relationship between exercise during pregnancy and the incidence of diagnosed preeclampsia. The RR of 0.81, with a 95% confidence interval, suggests that exercise does not substantially impact the development of preeclampsia. However, it is worth noting that there was a relatively low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 18%) among the studies, indicating a degree of consistency in the results. While exercise may not significantly reduce the risk of preeclampsia, it is essential to consider the potential benefits of PA on other aspects of maternal health. In contrast to the findings of Davenport et al. 2017 [60], our study did not observe a significant reduction in preeclampsia (PE) risk with exercise interventions during pregnancy. Magro-Malosso et al. 2017 did not find a significant difference in preeclampsia incidence between exercise and control groups, likely due to an underpowered analysis requiring a larger sample size to detect a 21% reduction in preeclampsia from a 2.3% baseline risk [56]. A Cochrane Review from 2006 and prior meta-analyses also support the positive effects of exercise on maternal health outcomes, including reductions in gestational diabetes and maternal hypertension. However, no significant impact on preeclampsia was observed [61].
Several hypotheses may explain why exercise during pregnancy did not show substantial benefits for preeclampsia in the meta-analysis as preeclampsia is a complex pathology. While beneficial for cardiovascular health, exercise may not directly address the intricate mechanisms leading to preeclampsia. Other factors, such as genetic predisposition and immunological factors, might play a more dominant role in the development of preeclampsia. The timing and intensity of exercise during pregnancy could be other critical factors. The exercise regimens in the included studies did not match the specific timing or dose required to prevent preeclampsia. Preeclampsia often develops in the later stages of pregnancy, and the impact of exercise may vary depending on when it is initiated and its intensity. Pregnant women are a diverse group, and individual responses to exercise can differ significantly. Some women may have genetic or physiological factors predisposing them to preeclampsia regardless of exercise. The included studies did not adequately consider this variability, which may have reduced the benefits and should be planned for future studies on this scientific topic.
The analysis of systolic blood pressure levels revealed a significant association with regular exercise during pregnancy. A mean difference of −2.64 (95% CI = −4.79, −0.49) suggests a modest reduction in systolic blood pressure among pregnant women who participate in PA. However, it is essential to note that a relatively high level of heterogeneity (I2 = 76%) was observed in this analysis. This heterogeneity may be attributed to variations in exercise intensity, frequency, and duration variations among the included studies. Despite the heterogeneity, the observed decrease in systolic blood pressure aligns with the overarching objective of enhancing maternal health during pregnancy.
Similarly, the analysis of diastolic blood pressure also revealed a significant difference (MD = −1.99, 95% CI = −3.68, −0.29). Similar to systolic blood pressure, this analysis exhibited a high level of heterogeneity (I2 = 81%). This heterogeneity underscores the intricacies of studying blood pressure responses to exercise during pregnancy, as multiple factors can influence blood pressure outcomes, including complex dynamics, individual variations, and measurement precision. Exercise appears to positively impact on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, despite the challenges posed by the complex nature of studying blood pressure dynamics in pregnant individuals. An understanding of these complexities can guide future research and healthcare recommendations for pregnant women seeking to enhance their cardiovascular health through exercise.
One of the key strengths of this study is its incorporation of the most recent RCTs and research available up to the present date. This study acknowledges and quantifies heterogeneity among the included studies, demonstrating a commitment to rigorous analysis. This transparency enhances the robustness and reliability of the findings, promoting greater confidence in the results. This study’s exploration of the null findings related to preeclampsia is a noteworthy strength. By offering hypotheses and insights into why exercise may not have demonstrated significant benefits for this specific condition, this study contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the intricate relationship between exercise and maternal health. While this study transparently addresses heterogeneity, it remains a challenge inherent to meta-analyses. Variations in study design, interventions, and populations may contribute to heterogeneity, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings. This study’s findings are based on the available evidence, which may predominantly represent specific populations or settings. As such, the generalizability of the results to broader people or diverse healthcare contexts may be limited. Future studies may need to fully account for variability in participants’ adherence and compliance with exercise interventions. Variations in adherence could impact the effectiveness of exercise programs and influence the outcomes observed in meta-analyses. The absence of significant results in some studies may introduce publication bias, as studies demonstrating no effect of exercise on maternal health outcomes may be less likely to be published or included in meta-analyses. This bias could influence the overall findings.
In the context of sports medicine, our meta-analysis offers valuable insights into the effects of PA during pregnancy on hypertensive disorders, preeclampsia, and blood pressure levels. These findings are significant for expectant mothers’ overall maternal health. By carefully selecting 34 studies from an initial pool of 391 articles, we aimed to ensure the inclusion of high-quality research, thus enhancing the credibility of our results. Notably, the diversity of interventions in the included studies, ranging from aerobic exercises to strength training and aquatic sessions, reflects the adaptability of pregnancy-related PA programs.
Our meta-analysis distinguishes itself by focusing on specific maternal health outcomes and emphasizing clinical significance, in contrast to previous broader studies. By integrating the latest research and addressing heterogeneity, we offer a clear perspective on the study variations. We found a substantial correlation between exercise during pregnancy and reduced hypertensive disorder risk, while preeclampsia risk reduction was inconclusive. Furthermore, exercise demonstrated a modest reduction in systolic blood pressure levels. These insights inform the complex relationship between exercise and maternal health, offering guidance for future research and healthcare recommendations.
5. Conclusions
PA during pregnancy promises to improve maternal health by reducing the risk of gestational hypertension and positively affecting systolic and diastolic blood pressure. In conclusion, our meta-analysis underscores the positive impact of PA during pregnancy on maternal health, specifically in reducing the risk of gestational hypertension and positively influencing systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The mechanisms underlying these benefits involve improvements in cardiac function, body weight regulation, oxidative stress reduction, and vascular endothelial function. Engaging in aerobic exercise and moderate physical activity three times per week appears to be the most suitable regimen throughout pregnancy. However, addressing the broader questions raised, the optimal frequency, duration, and type of exercise for pregnant women remain nuanced and should be tailored to individual preferences and needs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.B., C.S.-J., M.S.-P. and R.M.; methodology, R.B., D.Z. and R.M.; software, R.B. and M.S.-P.; validation, R.B., C.S.-J. and D.Z.; formal analysis, R.B., C.S.-J., D.Z., M.S.-P. and R.M.; investigation, R.B., C.S.-J. and R.M.; resources, I.R.; data curation, M.S.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B., C.S.-J., M.S.-P. and R.M.; writing—review and editing, R.B., C.S.-J., D.Z. and M.S.-P.; visualization, M.S.-P.; supervision, I.R. and R.M.; project administration, R.B. and R.M.; funding acquisition, I.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by Research Project UPM C2311580017. Instituto de las Mujeres. Ministerio de Igualdad de España.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to give special thanks to Alejandro Barrera and Ane Uría Minguito.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Andrawus, M.; Sharvit, L.; Atzmon, G. Epigenetics and Pregnancy: Conditional Snapshot or Rolling Event. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccarello, D.; Sorrentino, U.; Brasson, V.; Marin, L.; Piccolo, C.; Capalbo, A.; Andrisani, A.; Cassina, M. Epigenetics of pregnancy: Looking beyond the DNA code. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2022, 39, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J.D.; Carey, N. The Epigenetics of Normal Pregnancy. Obstet. Med. 2013, 6, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.S.; Cameron, N.A.; Lindley, K.J. Pregnancy as an Early Cardiovascular Moment: Peripartum Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1584–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Chang, Y.T.; Chang, Y.C. Maternal hypertensive pregnancy disorders increase childhood intellectual disability hazards independently from preterm birth and small for gestational age. Early Hum. Dev. 2023, 185, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACOG Practice Bulletin, No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, e1–e25.
- Folk, D.M. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: Overview and Current Recommendations. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2018, 63, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, M.F.; Davenport, M.H.; Ruchat, S.M.; Davies, G.A.; Poitras, V.J.; Gray, C.E.; Garcia, A.J.; Barrowman, N.; Adamo, K.B.; Duggan, M.; et al. 2019 Canadian guideline for physical activity throughout pregnancy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.A.; Maran, A.; Dempsey, K.; Perreault, M.; Vanniyasingam, T.; Phillips, S.M.; Hutton, E.K.; Mottola, M.F.; Wahoush, O.; Xie, F.; et al. Be Healthy in Pregnancy (BHIP): A Randomized Controlled Trial of Nutrition and Exercise Intervention from Early Pregnancy to Achieve Recommended Gestational Weight Gain. Nutrients 2022, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babbar, S.; Hill, J.B.; Williams, K.B.; Pinon, M.; Chauhan, S.P.; Maulik, D. Acute feTal behavioral Response to prenatal Yoga: A single, blinded, randomized controlled trial (TRY yoga). Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 399.e1–399.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; Pelaez, M.; Montejo, R.; Luaces, M.; Zakynthinaki, M. Exercise during pregnancy improves maternal health perception: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 402.e1–402.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; Cordero, Y.; Coteron, J.; Luaces, M.; Montejo, R. Exercise during pregnancy improves maternal glucose screen at 24-28 weeks: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; Pelaez, M.; Lopez, C.; Montejo, R.; Coteron, J. Exercise during pregnancy reduces the rate of cesarean and instrumental deliveries: Results of a randomized controlled trial. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 2372–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; Perales, M.; Bacchi, M.; Coteron, J.; Refoyo, I. A program of exercise throughout pregnancy. Is it safe to mother and newborn? Am. J. Health Promot. 2014, 29, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, R.; Pelaez, M.; Cordero, Y.; Perales, M.; Lopez, C.; Coterón, J.; Mottola, M.F. Exercise during pregnancy protects against hypertension and macrosomia: Randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 649.e1–649.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhartia, N.; Jain, S.; Shankar, N.; Rajaram, S.; Gupta, M. Effects of antenatal yoga on maternal stress and clinical outcomes in north indian women: A randomised controlled trial. J. Indian. Acad. Clin. Med. 2019, 20, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, S.G.; Hallal, P.C.; Domingues, M.R.; Bertoldi, A.D.; da Silveira, M.F.; Bassani, D.; da Silva, I.C.M.; da Silva, B.G.C.; Coll, C.V.N.; Evenson, K. A randomized controlled trial of exercise during pregnancy on maternal and neonatal outcomes: Results from the PAMELA study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveria Melo, A.S.; Silva, J.L.; Tavares, J.S.; Barros, V.O.; Leite, D.F.; Amorim, M.M. Effect of a physical exercise program during pregnancy on uteroplacental and fetal blood flow and fetal growth: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 120 Pt 1, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Buhigas, I.; Brik, M.; Martin-Arias, A.; Vargas-Terrones, M.; Varillas, D.; Barakat, R.; Santacruz, B. Maternal physiological changes at rest induced by exercise during pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 220, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelfi, K.J.; Ong, M.J.; Crisp, N.A.; Fournier, P.A.; Wallman, K.E.; Grove, R.J.; Doherty, D.A.; Newnham, J.P. Regular Exercise to Prevent the Recurrence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 128, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haakstad, L.A.; Bø, K. The marathon of labour—Does regular exercise training influence course of labour and mode of delivery?: Secondary analysis from a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 251, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthiga, K.; Pal, G.K.; Dasari, P.; Nanda, N.; Velkumary, S.; Chinnakali, P.; Renugasundari, M.; Harichandrakumar, K.T. Effects of yoga on cardiometabolic risks and fetomaternal outcomes are associated with serum nitric oxide in gestational hypertension: A randomized control trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoram, S.; Loripoor, M.; Pirhadi, M.; Beigi, M. The effect of walking on pregnancy blood pressure disorders in women susceptible to pregnancy hypertension: A randomized clinical trial. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2019, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koivusalo, S.B.; Rönö, K.; Klemetti, M.M.; Roine, R.P.; Lindström, J.; Erkkola, M.; Kaaja, R.J.; Pöyhönen-Alho, M.; Tiitinen, A.; Huvinen, E. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Can Be Prevented by Lifestyle Intervention: The Finnish Gestational Diabetes Prevention Study (RADIEL): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.L.; Campbell, C.G.; Foster, R.C.; Peterson, A.D.; Lanningham-Foster, L. A pilot walking program promotes moderate-intensity physical activity during pregnancy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, R.; Kinnunen, T.I.; Aittasalo, M.; Kolu, P.; Raitanen, J.; Ojala, K.; Mansikkamäki, K.; Lamberg, S.; Vasankari, T.; Komulainen, T.; et al. Primary prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus and large-for-gestational-age newborns by lifestyle counseling: A cluster-randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.E.; Johnston, C.A.; Strom, C.; Isly, C.; Haven, K.; Newton, E.; McDonald, S.; May, L.E. Influence of exercise type on maternal blood pressure adaptation throughout pregnancy. AJOG Glob. Rep. 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, M.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Luaces, M.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Garatachea, N.; Barakat, R.; Lucía, A. Maternal Cardiac Adaptations to a Physical Exercise Program during Pregnancy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov Fieril, K.; Glantz, A.; Fagevik Olsen, M. The efficacy of moderate-to-vigorous resistance exercise during pregnancy: A randomized controlled trial. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2015, 94, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, B.B.; Amini, S.B.; Kappeler, K. Exercise in pregnancy: Effect on fitness and obstetric outcomes-a randomized trial. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2263–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Díaz, L.; Ruiz-Frutos, C.; Vázquez-Lara, J.M.; Ramírez-Rodrigo, J.; Villaverde-Gutiérrez, C.; Torres-Luque, G. Effectiveness of a physical activity programme based on the Pilates method in pregnancy and labour. Efectividad de un programa de actividad física mediante el método Pilates en el embarazo y en el proceso del parto. Enferm. Clin. 2017, 27, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Perales, M.; Pelaez, M.; Lopez, C.; Lucia, A.; Barakat, R. Supervised exercise-based intervention to prevent excessive gestational weight gain: A randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagedal, L.R.; Øverby, N.C.; Bere, E.; Torstveit, M.K.; Lohne-Seiler, H.; Smastuen, M.; Hillesund, E.R.; Henriksen, T.; Vistad, I. Lifestyle intervention to limit gestational weight gain: The Norwegian Fit for Delivery randomised controlled trial. BJOG 2017, 124, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Jose, C.; Sánchez-Polán, M.; Diaz-Blanco, Á.; Coterón, J.; Barakat, R.; Refoyo, I. Effectiveness of a Virtual Exercise Program during COVID-19 Confinement on Blood Pressure Control in Healthy Pregnant Women. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 645136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skow, R.J.; Fraser, G.M.; Steinback, C.D.; Davenport, M.H. Prenatal Exercise and Cardiovascular Health (PEACH) Study: Impact on Muscle Sympathetic Nerve (Re)Activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafne, S.N.; Salvesen, K.Å.; Romundstad, P.R.; Eggebø, T.M.; Carlsen, S.M.; Mørkved, S. Regular exercise during pregnancy to prevent gestational diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 119, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman, S.S.; Brown, C.A.; Hains, S.M.; Hains, S.M.J.; Godwin, M.; Smith, G.N.; Parlow, J.L.; Kisilevsky, B.S. The effects of exercise conditioning in normal and overweight pregnant women on blood pressure and heart rate variability. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2010, 12, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.; Sato, C. Home-based walking during pregnancy affects mood and birth outcomes among sedentary women: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2016, 22, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, V.; Sporiš, G.; Tomić, J.; Milanović, Z.; Zigmundovac-Klaić, D.; Pantelić, S. The effect of maternal exercise during pregnancy on abnormal fetal growth. Croat. Med. J. 2013, 54, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ussher, M.; Lewis, S.; Aveyard, P.; Manyonda, I.; West, R.; Lewis, B.; Marcus, B.; Riaz, M.; Taylor, A.; Daley, A.; et al. Physical activity for smoking cessation in pregnancy: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2015, 350, h2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez Lara, J.M.; Rodríguez Díaz, L.; Ramírez Rodrigo, J.; Villaverde Gutiérrez, C.; Torres Luque, G.; Gómez-Salgado, J. Calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en una población de gestantes sanas tras un programa de actividad física en el medio acuático (PAFMAE) [Quality of life related to health in a population of healthy pregnant women after a program of physical activity in the aquatic environment.]. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2017, 91, e201710042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S. Prenatal stretching exercise and autonomic responses: Preliminary data and a model for reducing preeclampsia. J. Nurs. Scholarsh 2010, 42, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira González, I.; Urrútia, G.; Alonso-Coello, P. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: Scientific rationale and interpretation. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2011, 64, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.; Vist, G.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Activity and Exercise during Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period: ACOG Committee Opinion, Number 804. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, e178–e188. [CrossRef]
- Teede, H.J.; Bailey, C.; Moran, L.J.; Bahri Khomami, M.; Enticott, J.; Ranasinha, S.; Rogozińska, E.; Skouteris, H.; Boyle, J.A.; Thangaratinam, S.; et al. Association of Antenatal Diet and Physical Activity-Based Interventions with Gestational Weight Gain and Pregnancy Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.M.; Andrade, A.; Nunes, I. Physical Exercise in Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks and Prescription. J. Perinat. Med. 2022, 50, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dipietro, L.; Evenson, K.R.; Bloodgood, B.; Sprow, K.; Troiano, R.P.; Piercy, K.L.; Vaux-Bjerke, A.; Powell, K.E. 2018 PHYSICAL ACTIVITY GUIDELINES ADVISORY COMMITTEE*. Benefits of Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Postpartum: An Umbrella Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.K.; Matchkov, V.V. Hypertension and physical exercise: The role of oxidative stress. Medicina 2016, 52, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skow, R.J.; King, E.C.; Steinback, C.D.; Davenport, M.H. Davenport; The influence of prenatal exercise and pre-eclampsia on maternal vascular function. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2223–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro-Malosso, E.R.; Saccone, G.; Di Tommaso, M.; Roman, A.; Berghella, V. Exercise during pregnancy and risk of gestational hypertensive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Sanabria-Martínez, G.; Fernández-Rodríguez, R.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Pascual-Morena, C.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Martínez-Hortelano, J.A. Exercise during pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus and hypertensive disorders: An umbrella review of randomised controlled trials and an updated meta-analysis. BJOG 2023, 130, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolferz, R.; Fotoohi, M.; Spiess, S.; Ose, D.M.P.H.; Vukelic, B.; Fortenberry, K.T. Does Exercise during Pregnancy Decrease the Risk of Developing Hypertensive Disorders? Am. Fam. Physician 2022, 106, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.P.; Wang, X.X. Effects of aerobic exercise performed during pregnancy on hypertension and gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2023, 63, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.H.; Ruchat, S.M.; Poitras, V.J.; Jaramillo García, A.; Gray, C.E.; Barrowman, N.; Skow, R.J.; Meah, V.L.; Riske, L.; Sobierajski, F.; et al. Prenatal exercise for the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, S.; Duley, L. Exercise or other physical activity for preventing pre-eclampsia and its complications. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2006, CD005942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).