Validation of the Accuracy of Automatic Measurement of Blood Volume in Culture Bottles for Blood Culture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
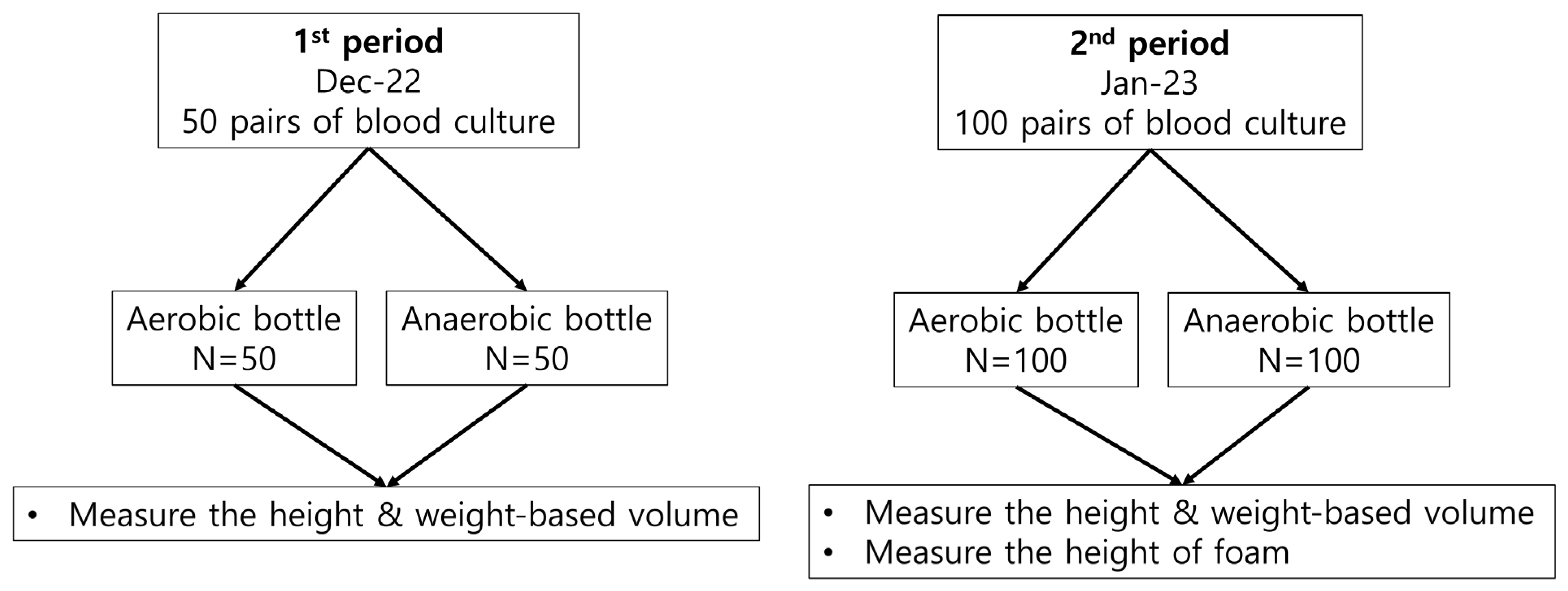
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Measurement of Blood Volumes and Foam
2.3. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection, and Cut-Off of the Height-Based Volume
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
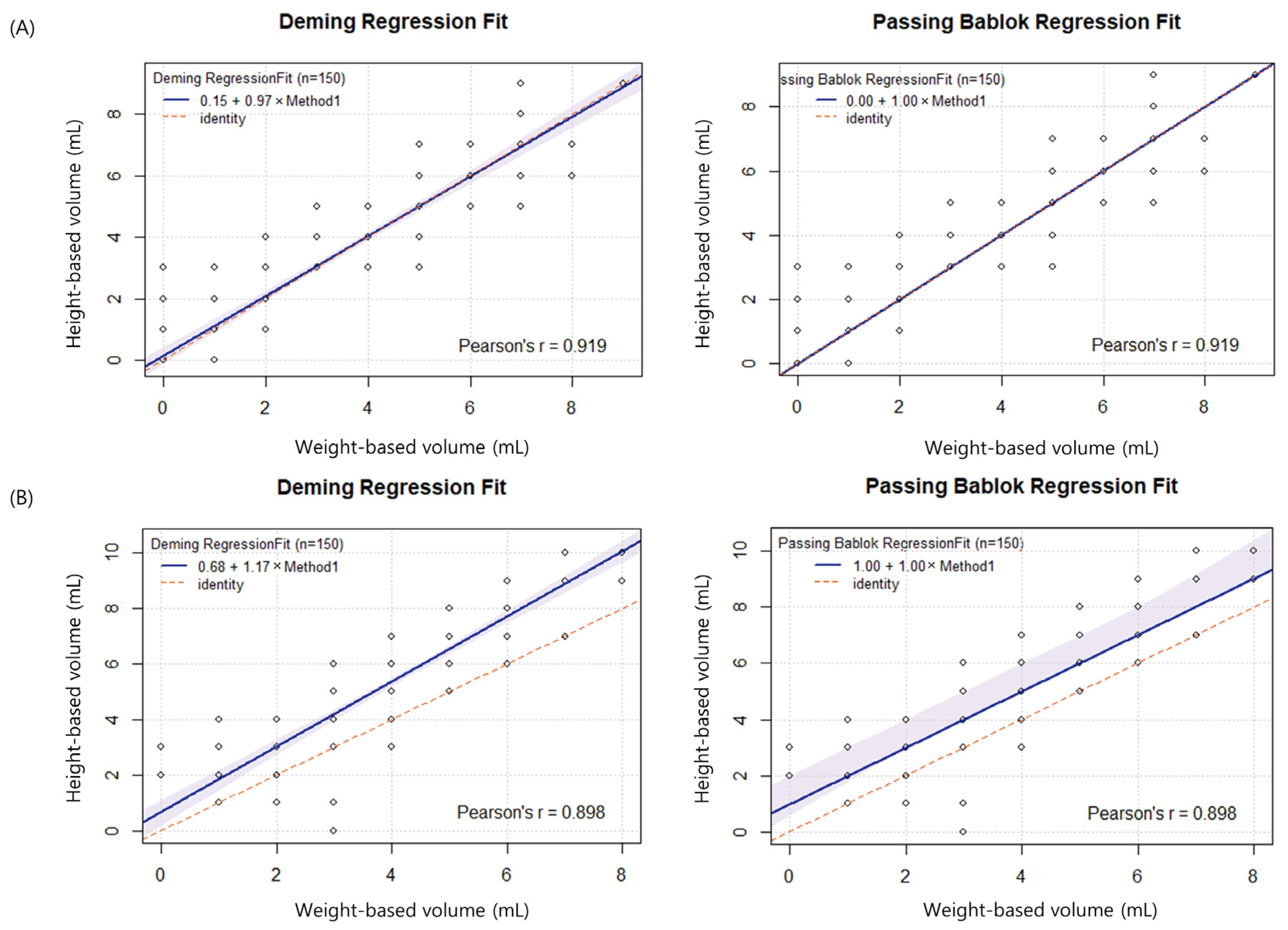
3.1. Height- vs. Weight-Based Volumes
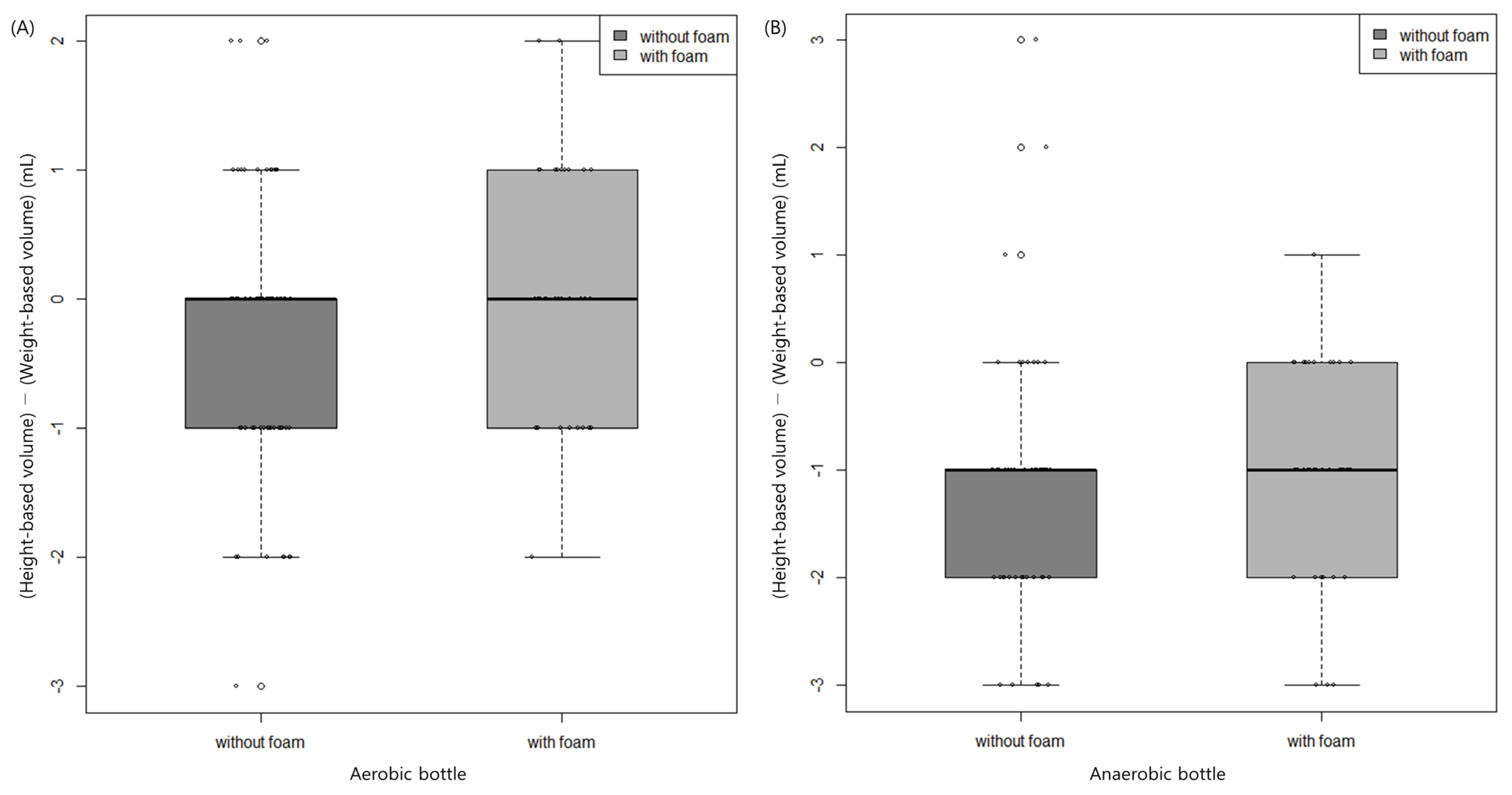
3.2. Effect of Foam
3.3. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection, and Cut-Off Value of Height-Based Volume
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hattori, H.; Maeda, M.; Nagatomo, Y.; Takuma, T.; Niki, Y.; Naito, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Ishino, K. Epidemiology and risk factors for mortality in bloodstream infections: A single-center retrospective study in Japan. Am. J. Infect. Control 2018, 46, e75–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.H. Bloodstream infections and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in South Korea. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 931–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjandra, K.C.; Ram-Mohan, N.; Abe, R.; Hashemi, M.M.; Lee, J.-H.; Chin, S.M.; Roshardt, M.A.; Liao, J.C.; Wong, P.K.; Yang, S. Diagnosis of Bloodstream Infections: An Evolution of Technologies towards Accurate and Rapid Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, B.; Dargère, S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Parienti, J.-J.; Tattevin, P. How to optimize the use of blood cultures for the diagnosis of bloodstream infections? A state-of-the-art. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermel, L.A.; Maki, D.G. Detection of bacteremia in adults: Consequences of culturing an inadequate volume of blood. Ann. Intern. Med. 1993, 119, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Principles and Procedures for Blood Cultures, 2nd ed.; CLSI guideline M47; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Coorevits, L.; den Abeele, A.-M.V. Evaluation of the BD BACTEC FX blood volume monitoring system as a continuous quality improvement measure. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattoir, L.; Claessens, J.; Cartuyvels, R.; den Abeele, A.M.V. How to achieve accurate blood culture volumes: The BD BACTEC FX blood volume monitoring system as a measuring instrument and educational tool. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.; Choi, B.; Yoon, N.S.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.N. Impact of monitoring blood volume in the BD BACTECTM FX blood culture system: Virtual volume versus actual volume. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 81, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S. Accuracy of BacT/Alert Virtuo for measuring blood volume for blood culture. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures, 2nd ed.; CLSI guideline EP17-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Song, S.A.; Kim, M.-N.; Lee, N.Y.; Kim, E.-C.; Kim, S.; Koo, S.-H.; Ryoo, N.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Cho, J.-H. Comprehensive analysis of blood culture performed at nine University Hospitals in Korea. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2011, 31, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Plato, F.; Fontana, C.; Gherardi, G.; Privitera, G.P.; Puro, V.; Rigoli, R.; Viaggi, B.; Viale, P. Collection, transport and storage procedures for blood culture specimens in adult patients: Recommendations from a board of Italian experts. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WESTGARD QC. Available online: https://www.westgard.com/lesson34.htm (accessed on 9 June 2023).
| Type (No.) | Weight-Based Volumes (Mean, mL) | Height-Based Volumes (Mean, mL) | Difference (mL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerobic (150) | 3.71 | 3.76 | 0.05 | 0.5693 |
| Anaerobic (150) | 3.61 | 4.9 | 1.29 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Total (300) | 3.66 | 4.33 | 0.67 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Type (No.) | No. of High Weight-Based Volumes (≥5 mL) | No. of Low Weight-Based Volumes (<5 mL) | Agreement (95% CI) | Kappa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of High Height-Based Volumes (≥5 mL) | No. of Low Height-Based Volumes (<5 mL) | No. of High Height-Based Volumes (≥5 mL) | No. of Low Height-Based Volumes (<5 mL) | |||
| Aerobic (150) | 56 | 11 | 5 | 78 | 0.893 (0.834–0.933) | 0.782 |
| Anaerobic (150) | 61 | 0 | 24 | 65 | 0.84 (0.773–0.890) | 0.688 |
| Total (300) | 117 | 11 | 29 | 143 | 0.867 (0.824–0.901) | 0.732 |
| Type (No.) | No. of High Weight-Based Volumes (≥8 mL) | No. of Low Weight-Based Volumes (<8 mL) | Agreement (95% CI) | Kappa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of High Height-Based Volumes (≥8 mL) | No. of Low Height-Based Volumes (<8 mL) | No. of High Height-Based Volumes (≥8 mL) | No. of Low Height-Based Volumes (<8 mL) | |||
| Aerobic (150) | 1 | 2 | 5 | 142 | 0.953 (0.907–0.977) | 0.201 |
| Anaerobic (150) | 2 | 0 | 11 | 137 | 0.927 (0.873–0.959) | 0.249 |
| Total (300) | 3 | 2 | 16 | 279 | 0.94 (0.907–0.962) | 0.23 |
| Type (No.) | LOB of Weight-Based Volumes (mL) | LOB of Height-Based Volumes (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic (20) | 0 | 0 |
| Anaerobic (20) | 0 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Park, S. Validation of the Accuracy of Automatic Measurement of Blood Volume in Culture Bottles for Blood Culture. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162685
Kim K, Park S. Validation of the Accuracy of Automatic Measurement of Blood Volume in Culture Bottles for Blood Culture. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(16):2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162685
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyoungbo, and Sunggyun Park. 2023. "Validation of the Accuracy of Automatic Measurement of Blood Volume in Culture Bottles for Blood Culture" Diagnostics 13, no. 16: 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162685
APA StyleKim, K., & Park, S. (2023). Validation of the Accuracy of Automatic Measurement of Blood Volume in Culture Bottles for Blood Culture. Diagnostics, 13(16), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13162685






