A Reliable Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection of Human Antibodies Directed to SARS-CoV-2 NP Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Micro-Neutralization (MN) Assay
2.3. Development and Optimization of COVID-19 NP Human IgG ELISA
2.4. COVID-19 S-Based IgG ELISA
2.5. COVID-19 S-Based IgG CLIA
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Data Curation
3. Results
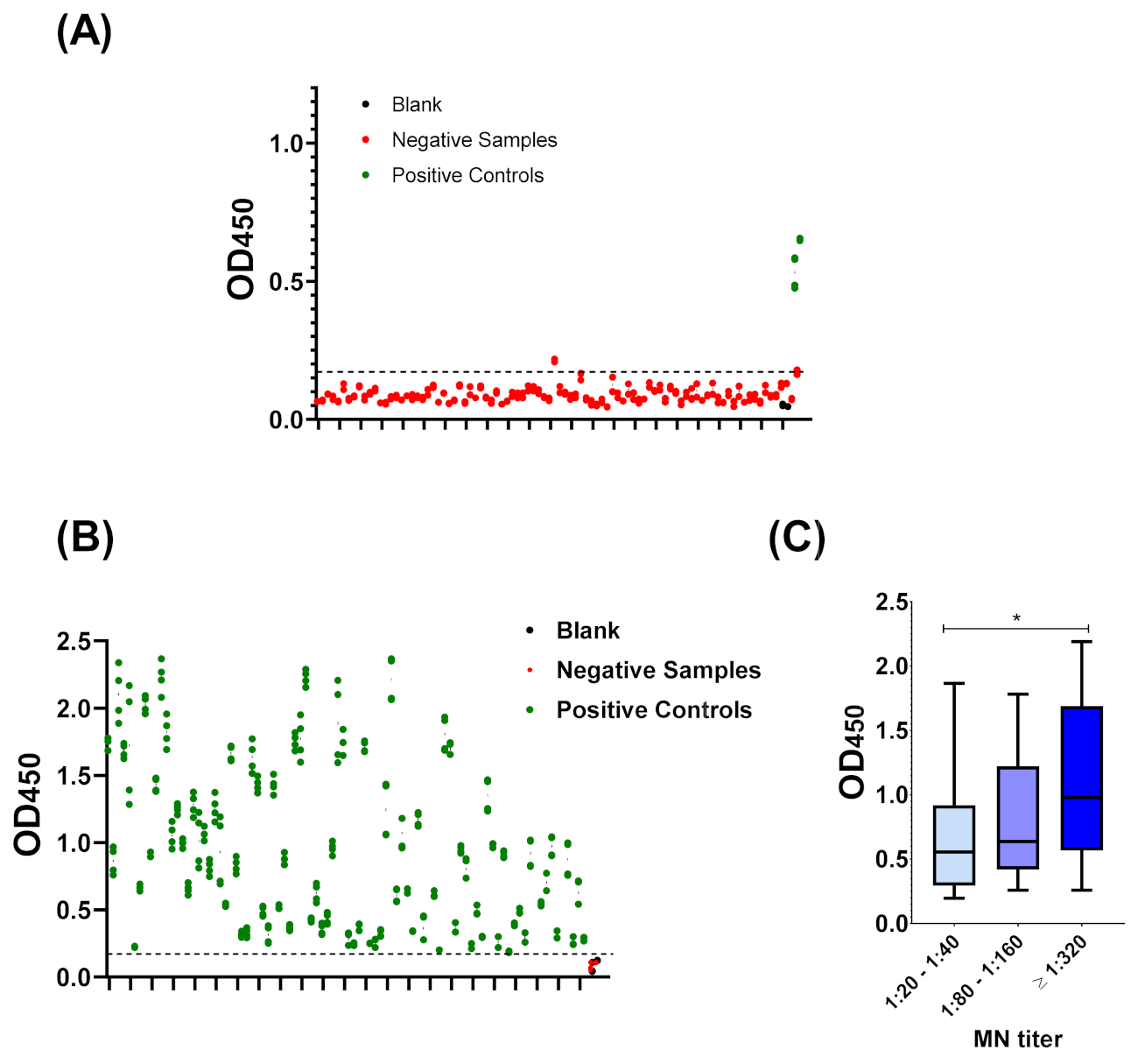
3.1. Sero-Status of Samples
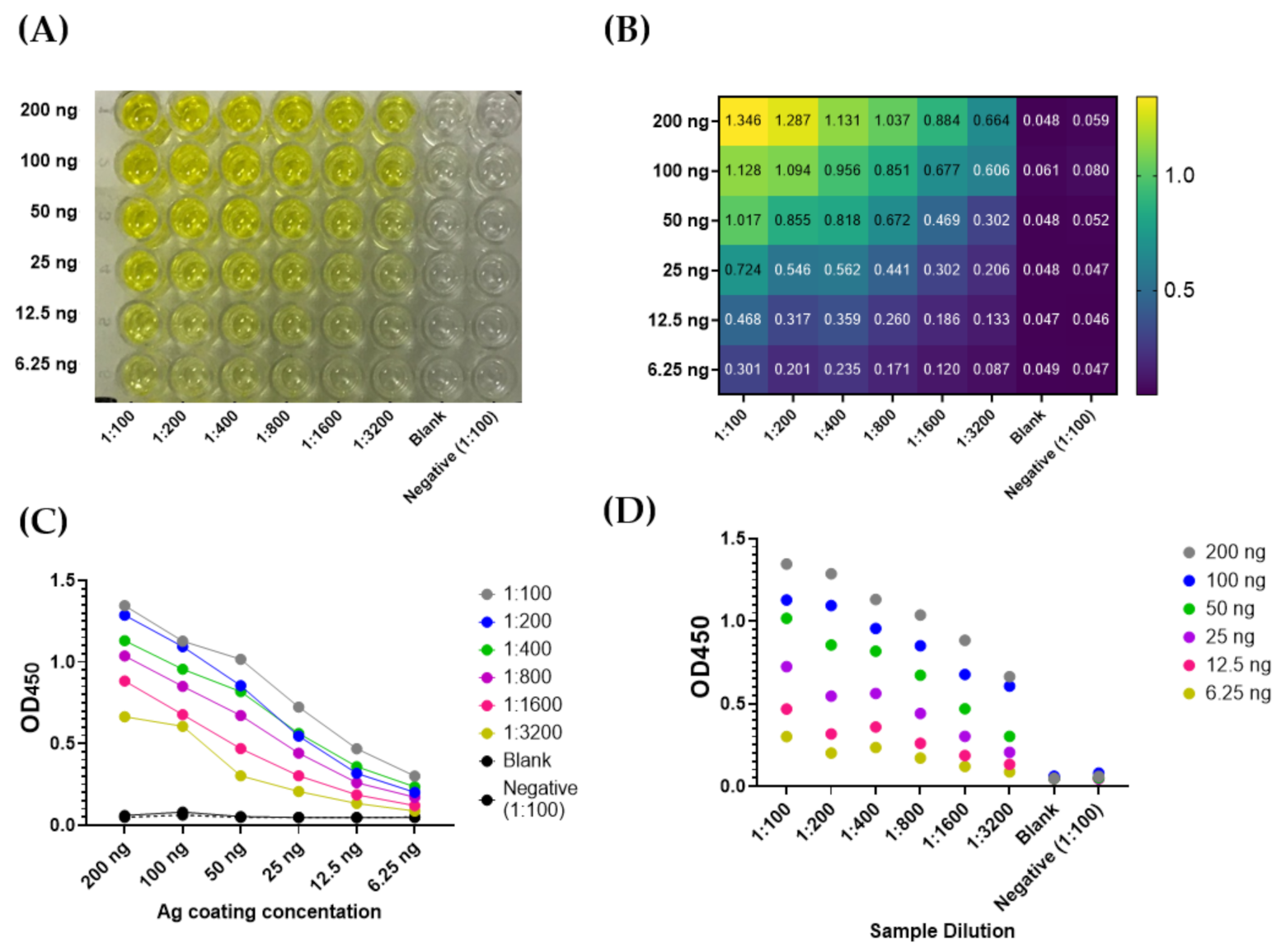
3.2. Optimization of COVID-19 NP IgG ELISA
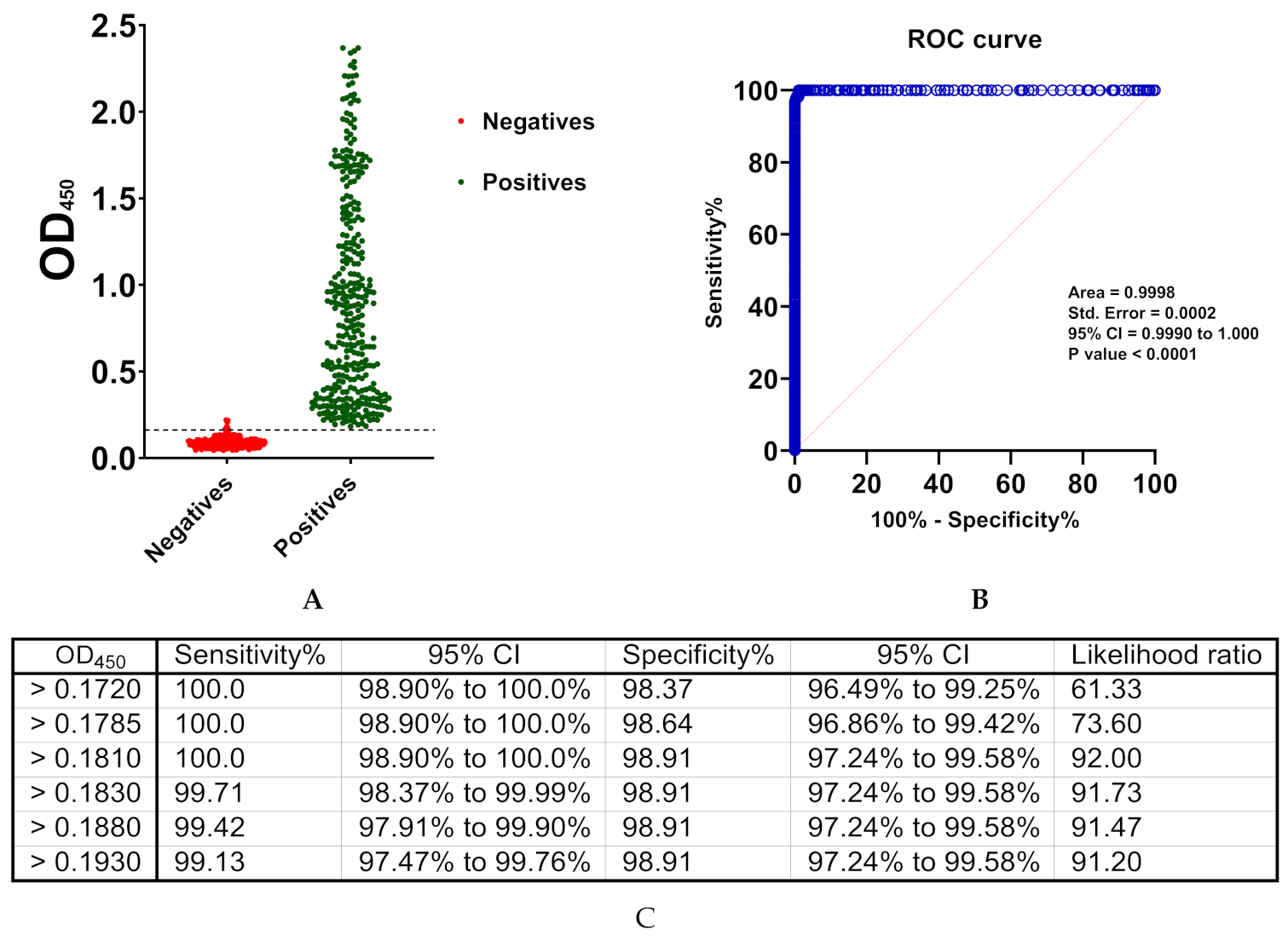
3.3. Cut-Off Value and Assay Validation
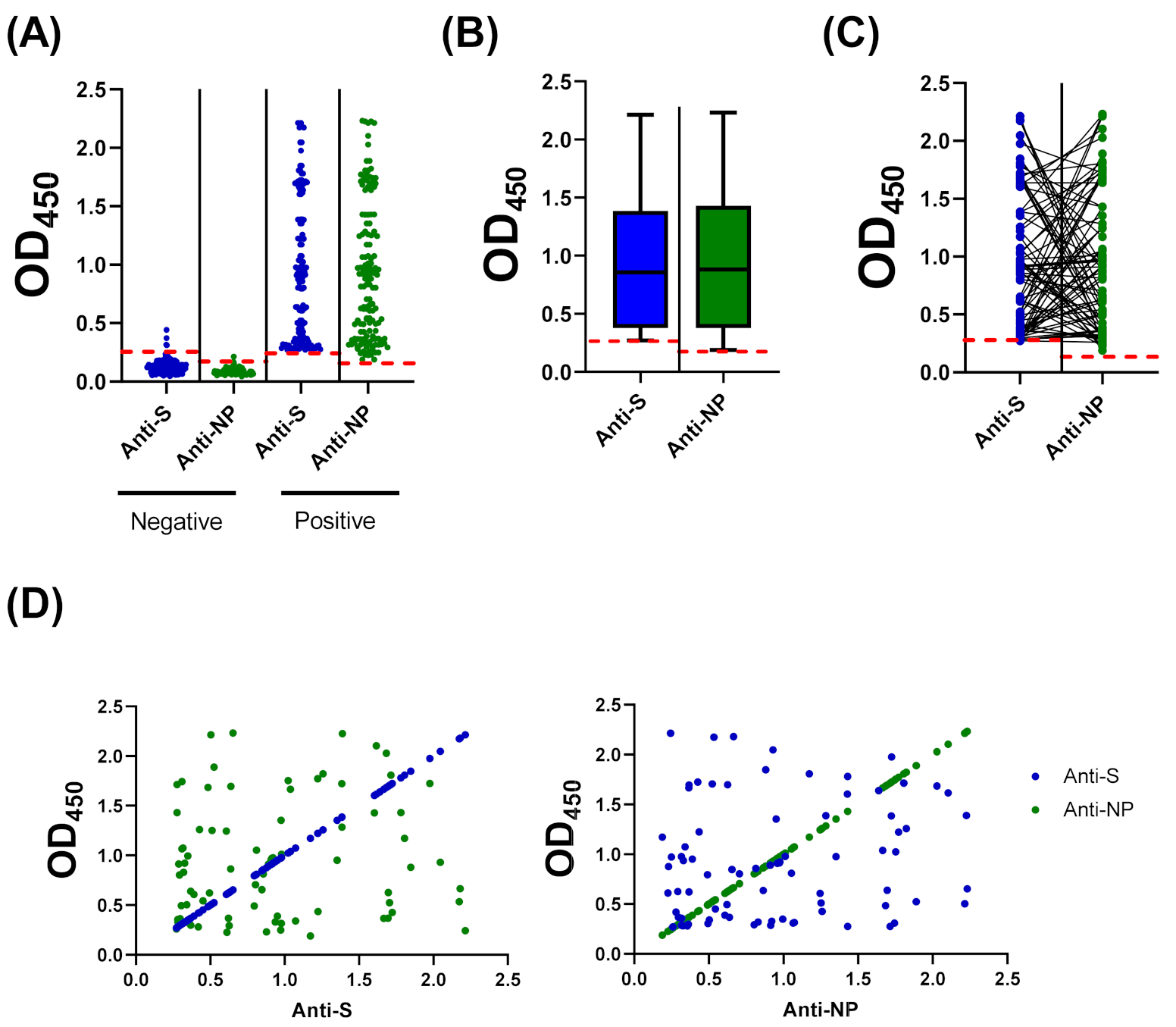
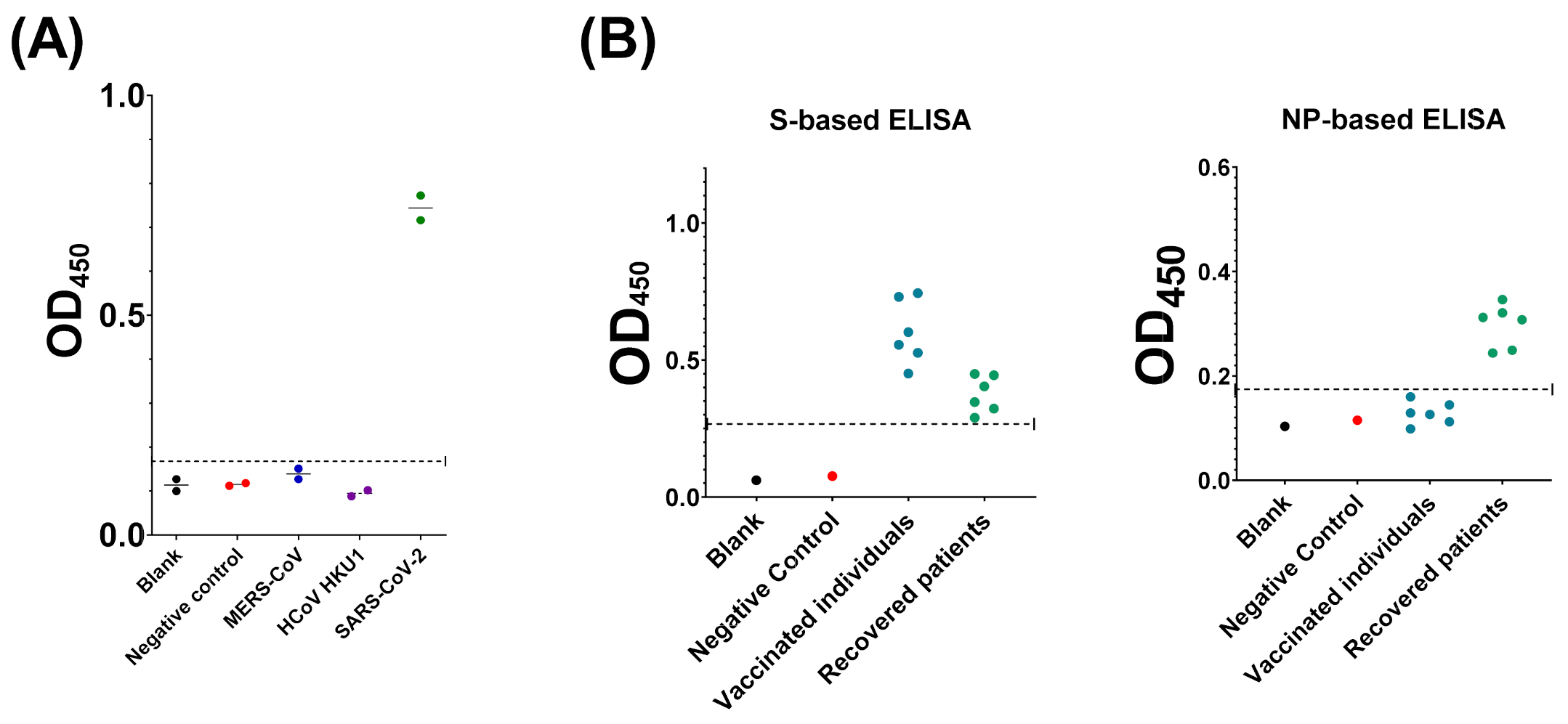
3.4. Compairson with SARS-CoV-2 S-Based ELISA and CLIA
3.5. Evaluation of Assay Cross-Reactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Wu, Z.Q.; Xiang, Z.C.; Guo, L.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Li, X.W.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus causing severe pneumonia in human: A descriptive study. Chin. Med J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, T.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: What we know. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Tang, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, H. Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2. Gastroenterology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.W.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.W.; Wen, X.J.; Mao, T.H.; Peng, S.W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.M.; Lu, F.M. Exploring the mechanism of liver enzyme abnormalities in patients with novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2020, 28, E002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, K.; Ding, Y.; Lu, W.L.; Wang, J. ACE2 expression in kidney and testis may cause kidney and testis damage after 2019-nCoV infection. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. Science 2005, 309, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouzard, S.; Chu, V.C.; Whittaker, G.R. Activation of the SARS coronavirus spike protein via sequential proteolytic cleavage at two distinct sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5871–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Wedderburn, C.J.; Garcia, P.J.; Boeras, D.; Fongwen, N.; Nkengasong, J.; Sall, A.; Tanuri, A.; Heymann, D.L. Serology testing in the COVID-19 pandemic response. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, G.; Strumia, A.; Piliego, C.; Bruno, F.; Del Buono, R.; Costa, F.; Scarlata, S.; Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: A comprehensive review. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Okba, N.M.A.; Igloi, Z.; Bogers, S.; Embregts, C.W.E.; Laksono, B.M.; Leijten, L.; Rokx, C.; Rijnders, B.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; et al. An evaluation of COVID-19 serological assays informs future diagnostics and exposure assessment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.J.; Naing, Z.; Ospina Stella, A.; Yeang, M.; Caguicla, J.; Ramachandran, V.; Isaacs, S.R.; Agapiou, D.; Bull, R.A.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; et al. SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays. Viruses 2021, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kekäläinen, E.; Ahava, M.J.; Loginov, R.; Kallio-Kokko, H.; Vapalahti, O.; Jarva, H.; Kurkela, S.; Lappalainen, M. Performance of six SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in comparison with microneutralisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandijany, T.A.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Tolah, A.M.; Sohrab, S.S.; Faizo, A.A.; Hassan, A.M.; Alsubhi, T.L.; Othman, N.A.; Azhar, E.I. Development and optimization of in-house ELISA for detection of human IgG antibody to SARS-CoV-2 full length spike protein. Pathogens 2020, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandijany, T.A.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Qashqari, F.S.; Faizo, A.A.; Tolah, A.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Sohrab, S.S.; Hindawi, S.I.; Badawi, M.A.; et al. Lack of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 among Blood Donors during COVID-19 Lockdown: A Study from Saudi Arabia. Healthcare 2021, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.A.; Dada, A.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Sohrab, S.S.; Faizo, A.A.; Tolah, A.M.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Bajrai, L.H.; Moalim, H.M.; Aly, M.H.; et al. Seroprevalence of neutralizing antibodies to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) among healthcare workers in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashte, S.; Gulbake, A.; El-Amin Iii, S.F.; Gupta, A. COVID-19 vaccines: Rapid development, implications, challenges and future prospects. Hum. Cell 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Lessells, R.J.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Msomi, N.; Mlisana, K.; Bhiman, J.N.; von Gottberg, A.; Walaza, S.; et al. Sixteen novel lineages of SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa. Nat. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.E.; Zhang, X.; Case, J.B.; Winkler, E.S.; Liu, Y.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Liu, J.; Errico, J.M.; Xie, X.; Suryadevara, N.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees-Spear, C.; Muir, L.; Griffith, S.A.; Heaney, J.; Aldon, Y.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Thomas, P.; Graham, C.; Seow, J.; Lee, N.; et al. The effect of spike mutations on SARS-CoV-2 neutralization. Cell Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F. SARS-CoV-2 variants lacking a functional ORF8 may reduce accuracy of serological testing. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 488, 112906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England. Evaluation of the Ortho Clinical Diagnostics Vitros Immunodiagnostic Products Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Serology Assay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies; Public Health England: Birmingham, UK, 2020.
- Alandijany, T.A.; Faizo, A.A.; Azhar, E.I. Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries: Current status and management practices. J. Infect. Public Health 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peto, J. Covid-19 mass testing facilities could end the epidemic rapidly. BMJ 2020, 368, m1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J.; Beale, R. Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Science 2021, 371, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacofsky, D.; Jacofsky, E.M.; Jacofsky, M. Understanding Antibody Testing for COVID-19. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S74–s81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa Bastos, M.; Tavaziva, G.; Abidi, S.K.; Campbell, J.R.; Haraoui, L.-P.; Johnston, J.C.; Lan, Z.; Law, S.; MacLean, E.; Trajman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for covid-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, O.; Martiny, D.; Rochas, O.; van Belkum, A.; Kozlakidis, Z. Considerations for diagnostic COVID-19 tests. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathe, J.A.; Hemann, E.A.; Eggenberger, J.; Li, Z.; Knoll, M.L.; Stokes, C.; Hsiang, T.-Y.; Netland, J.; Takehara, K.K.; Pepper, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 serologic assays in control and unknown populations demonstrate the necessity of virus neutralization testing. J. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, L.L.; Ransegnola, B.P.; Jin, D.K.; Muecksch, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Bao, W.; George, P.J.; Rodriguez, M.; Tricoche, N.; Schmidt, F.; et al. Serological assays estimate highly variable SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity in recovered COVID-19 patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02005–e02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, I.; Forde, D.; Zelek, W.; Tyson, L.; Chichester, L.; Palmer, N.; Jones, R.; Morgan, B.P.; Moore, C. Temporal development and neutralising potential of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: An observational cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Feng, Y.; Mo, X.; Zheng, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, P.; Peng, P.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; et al. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM and IgG responses in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Okeagu, C.N.; Pham, A.D.; Silva, R.A.; Hurley, J.J.; Arron, B.L.; Sarfraz, N.; Lee, H.N.; Ghali, G.E.; Gamble, J.W.; et al. Economic impact of COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare facilities and systems: International perspectives. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.W.L.; Verkerke, H.; Owens, J.; Saeedi, B.; Boyer, D.; Shin, S.; Roback, J.D.; Neish, A.S.; Stowell, S.R. Serum pooling for rapid expansion of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing capacity. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2021, 28, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, H.; Ricci, V.; Tesi, G.; Soldatini, C.; Castria, M.; Vaccaro, M.N.; Tornesi, S.; Toppi, S.; Verdiani, S.; Brogi, A. Large scale production and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 whole antigen for serological test development. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faizo, A.A.; Alandijany, T.A.; Abbas, A.T.; Sohrab, S.S.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Tolah, A.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Azhar, E.I. A Reliable Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection of Human Antibodies Directed to SARS-CoV-2 NP Protein. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050825
Faizo AA, Alandijany TA, Abbas AT, Sohrab SS, El-Kafrawy SA, Tolah AM, Hassan AM, Azhar EI. A Reliable Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection of Human Antibodies Directed to SARS-CoV-2 NP Protein. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(5):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050825
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaizo, Arwa A., Thamir A. Alandijany, Ayman T. Abbas, Sayed S. Sohrab, Sherif A. El-Kafrawy, Ahmed M. Tolah, Ahmed M. Hassan, and Esam I. Azhar. 2021. "A Reliable Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection of Human Antibodies Directed to SARS-CoV-2 NP Protein" Diagnostics 11, no. 5: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050825
APA StyleFaizo, A. A., Alandijany, T. A., Abbas, A. T., Sohrab, S. S., El-Kafrawy, S. A., Tolah, A. M., Hassan, A. M., & Azhar, E. I. (2021). A Reliable Indirect ELISA Protocol for Detection of Human Antibodies Directed to SARS-CoV-2 NP Protein. Diagnostics, 11(5), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11050825







