Abstract
Electrical properties tomography (EPT) is an imaging method that uses a magnetic resonance (MR) system to non-invasively determine the spatial distribution of the conductivity and permittivity of the imaged object. This manuscript starts by providing clear definitions about the data required for, and acquired in, EPT, followed by comprehensively formulating the physical equations underlying a large number of analytical EPT techniques. This thorough mathematical overview of EPT harmonizes several EPT techniques in a single type of formulation and gives insight into how they act on the data and what their data requirements are. Furthermore, the review describes machine learning-based algorithms. Matlab code of several differential and iterative integral methods is available upon request.
1. Introduction
The electrical properties (EPs; conductivity and permittivity ) of tissue have the potential to be used as biomarkers in many clinical applications. Tissue EPs depend on the tissue structure and composition. The conductivity varies largely as a function of fluid volumes and ionic concentrations, while the permittivity is largely influenced by the cellular membrane extent [1]. Cancer causes local changes of EPs relative to healthy tissues. The EPs of benign tissue compared to tumors are significantly different and have been reported to offer advantages in separating them from each other [2,3,4]. Similarly, the conductivity in cerebral ischemia is significantly decreased [5,6]. Conductivity measurements can therefore be helpful for better characterization of brain tumors [7,8], but they have also shown promising results for pelvic tumors [9], breast cancer [10] and ischemic stroke [11,12]. Knowledge of the EPs additionally allows for the calculation of the electromagnetic (EM) fields inside tissue. This makes them interesting for a wide range of clinical applications, such as electroencephalography (EEG) and electrocardiography (ECG) measurements to accurately localize internal electrical activities, deep brain stimulation to mitigate Parkinson’s disease symptoms, radio frequency (RF) ablation to remove arrhythmic genesis foci and RF hyperthermia for cancer treatment [13]. Additionally, they are critical to accurately determine the specific absorption rate (tissue heating) induced by EM waves [1].
Several EP mapping approaches are explored to map the electrical properties of tissue in vivo. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT), for example, uses electrode mounting to detect currents injected into the sample [14]. This method is cost-effective and yields high temporal resolution, but poor spatial resolution due to the ill-posed nature of the inverse problem [13,15]. Magnetic induced tomography (MIT) applies an oscillating magnetic field to induce eddy currents in the object and detects the resulting magnetic fields outside the object [16]. However, it suffers from the same issues as EIT. Magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography (MR-EIT) utilizes MRI to detect the magnetic field induced by the probing current [17]. This provides higher spatial resolution, but has a poor signal-to-noise ratio due to limitations on the amount of current injection [13,18,19]. Hall effect imaging (HEI) induces currents through surface electrodes and detects the emitted acoustic wave to reconstruct EPs [20]. This also has the potential to reach high resolution images, but all of the current injection based methods may suffer from shielding artifacts of non-conductivity tissue. Magneto-acoustic tomography with magnetic induction (MAT-MI) circumvents this shielding problem by inducing acoustic signals with time varying magnetic fields which are detected with ultrasound measurements [21]. However, methods that involve acoustic measurements are often limited to the surface of the object.
Electrical properties tomography (EPT) non-invasively images the conductivity and permittivity maps (simultaneously) in vivo from the radio frequency field signals obtained with MRI. The method does not require electrode mounting, does not induce additional external energy other than the inherent RF fields, and the RF fields can easily penetrate into most biological tissue. It uses a standard MRI system with regular RF coils. This concept was first introduced in 1991 by Haacke et al. [22] and first demonstrated in 2003 by Wen et al. [23]. The topic, however, only recently gained considerable interest by various research groups [1,13,19,24].
Several review papers discuss existing methods and review clinical applications [1,13,19,24]. These reviews, however, do not discuss the mathematical methodology in depth, which hampers the overview in terms of intrinsic assumptions. Here, however, a mathematical description of the acquired MR data and several differential and integral EPT approaches are described more thoroughly to give clear insights into the relations and differences between a large number of methods. This review thereby allows accurate comparisons between different methods and outlines their relative strengths and weaknesses. Extensions and generalizations are also mentioned. The EPT approaches are harmonized in terms of mathematical formulation, while maintaining as much as possible the structure of the original implementations to keep the transition from this manuscript to the references straightforward.
This review manuscript is organized as follows. First, general RF background information is presented together with a general formulation of an acquired MR image, which are necessary to understand some of the problems arising in EPT data acquisition. Second, some fundamental EPT equations are presented, from which the bulk of the analytical EPT approaches can be derived. The subsequent two sections discuss a large number of physical model-based EPT strategies, starting with methods that are based on transmit field data, followed by receive field-based methods. The review continues with a discussion about training-based EPT approaches. Finally, a general discussion is provided and EPT reconstruction examples are presented.
2. Phasor Representations for the RF Field
In EPT, knowledge about the RF field within the body is used to retrieve the dielectric properties (conductivity and permittivity) of tissue. This RF field is called the field and phasors are typically used to describe its behavior. What may lead to confusion is that there are actually two time conventions in common use to represent the RF field in terms of phasors. In particular, for a given time-domain RF field operating at a frequency , phasors are introduced via the representation
or alternatively the representation
is used to describe the RF field. The vector is the phasor of the RF field when the time factor is used, while is the phasor of the RF field in the situation where a time factor is used.
For a given time convention, the phasor that corresponds to a given RF field is unique, and, since the time-domain RF field is real-valued, the phasors of the two representations are related by
where the asterisk denotes complex conjugation. In other words, for a given RF field, the phasors of the two representations are the complex conjugate of each other. We note that if Equation (2) is used to represent RF fields, the letter j is often used for the imaginary unit instead of the letter i. We adopt this notation here as well and write the representation of Equation (2) as
Unless otherwise stated, we use the phasor representation of Equation (4) to describe the RF field.
Suppose now that we orient our reference frame such that the static background field is directed in the longitudinal z-direction (, ) and we have available a transverse RF field with x- and y-components only. The corresponding phasor of this RF field is given by
which can be written as
with
where we have introduced the and fields defined as
and
respectively. Substitution of Equation (6) into Equation (4) leads to the time-domain RF field decomposition
with
Finally, we decompose the scalar and fields into their real and imaginary parts as
Using these decompositions in Equation (7) and substituting the results in the field expressions for and as given by Equation (11) gives
and
From the above expressions, we observe that the vector traces out a circle in the transverse -plane and the radius of this circle is given by . The vector also traces out a circle but this circle has a radius and is traversed in the opposite direction compared with the direction in which the circle of the field is traversed. Since in both cases the fields trace out a circle in the transverse plane, the and fields are called circularly polarized.
The direction of rotation depends upon the direction of the static background field. In particular, assume that our reference frame is such that the static field is in the negative z-direction: with . From Equations (12) and (13), we observe that in this case the and fields rotate, respectively, in a left- and right-handed manner about the field. When the background field is directed in the positive -direction, the situation is reversed and the circularly polarized fields and rotate, respectively, in a right- and left-handed manner about the field.
To summarize, any transverse RF field can be decomposed into two circularly polarized fields, where one is polarized in a left-handed manner with respect to background field, while the other is polarized in a right-handed manner with respect to the background field. Explicitly, we have
where and rotate in a left- and right-handed manner about the field, respectively. In the case that this background field is in the negative -direction, we have
while if the background field is in the positive -direction we have
2.1. Transmit and Receive Fields
As is well known, a circularly polarized RF field that operates at the Larmor frequency and that also rotates in a left-handed manner about the field influences the orientation of the magnetization, which ultimately leads to measurable MR signals. During transmission then, the left-handed circularly polarized part of the RF field, , is of interest. In the case that the background field is in the negative -direction, it is the scalar field that determines , while, if the background field is in the positive -direction, it is the scalar field that determines .
Now, in the MRI literature, the left-handed circularly polarized RF field is always described in terms of a scalar field, which seems to contradict the above observation that this field is described by in the case that the static background field is in the positive -direction. It is important, however, to realize that the scalar and fields are defined in terms of phasors that correspond to a particular time factor that is used to represent the RF field. Moreover, the phasors of the same RF field that correspond to the two different time factors are the complex-conjugate of each other (Equation (3)). Consequently, we have
and
In other words, the field always describes a left-handed circularly polarized field provided that the phasors of Equation (4) are used for defined in the negative z-direction, while the phasors of Equation (1) have to be used for defined in the positive z-direction. Since transmitting a left-handed circularly polarized field operating at the Larmor frequency enables us to manipulate the magnetization, the field is often referred to as the transmit field. Similarly, received signals can be expressed in terms of the right-handed circularly polarized field , which is completely described by the field if the phasors of Equation (4) are used in its definition for defined in the negative -direction and the phasors of Equation (1) are used if the background field is in the positive -direction. For this reason, the field is often referred to as the receive field.
2.2. MR Imaging
The transmit field can be written in polar form as , where is the amplitude or magnitude of the transmit field and its phase. Similarly, the receive field can be written in polar form as , with its amplitude and its phase. Note that, to define a phase that is unique, we have restricted the transmit phase and the receive phase to the principle branch . Spatial information is encoded into the signal using magnetic field gradients, applied after the field has tipped the magnetization into the transverse plane. Due to the interaction with the body, the transmit field has a spatial dependence, denoted . The polar decomposition is used to express the acquired spatially dependent MR image as [13,19,24,25]
with the proton density, the gyromagnetic ratio and the RF pulse duration and where is the complex conjugate of . In this simplified expression for the acquired MR image, system dependent factors and contrast terms that underlie an MR image, such as and relaxation, are ignored. Of the transmit and receive fields, only the magnitude of the transmit field shows a non-linear impact on the MR image. This non-linear relation allows for the direct measurement of the transmit magnitude by combining images from different scans such that confounding factors cancel. However, the acquired phase is always the superposition of the phases of and , called the transceive phase, which can not be disentangled from measurements and are therefore difficult to determine exactly. It has been observed that at 1.5 and 3 T the transmit phase closely resembles the phase of (see also the example given in Figure 1), and in those cases the transmit phase is therefore typically estimated as half the transceive phase: this is termed the transceive phase assumption [23,26]. Similarly, the (magnitude of the) receive field is weighted by the proton density, which is also difficult to disentangle. If the proton-density is not negligible, the proton-density or magnitude of the receive field can be extracted from their product term based on symmetry patterns of the transmit and receive fields in the case of a symmetrical object and imaging setup [27,28]. Additionally, the proton-density could be removed via suitable modeling based on image segmentation [27]. However, knowledge of the transmit phase, receive phase or receive magnitude individually is not always necessary, but could also potentially be determined through EPT.
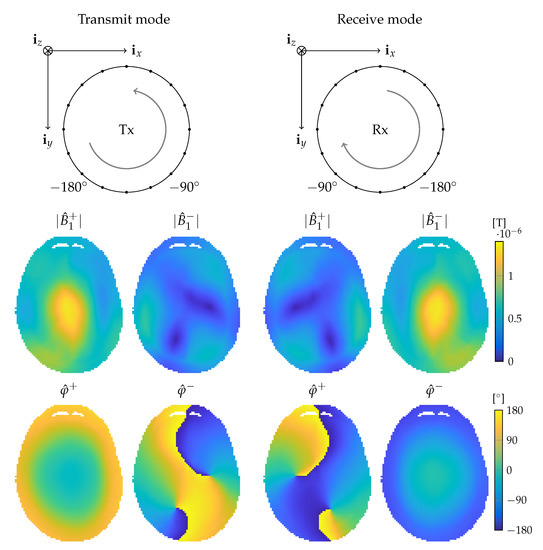
Figure 1.
The transmit and receive mode of a tuned 16 rung 7 T MR head coil loaded with the Duke body model [29] and their corresponding transmit and receive fields (magnitude and phase).
2.3. Transmit and Receive Fields in Terms of Measurable Quantities
Consider a multi-element RF antenna with P transmit and Q receive channels. The transmit field from channel p () measured at receive channel q can then be written in measurable (known) and unknown terms as
with the transceive phase (note that is sometimes defined as the argument of , such that the transceive phase is given by ), the absolute transmit phase of transmit channel p and the absolute receive phase of receive channel q. The term is the measurable term, while is the unknown term. Note that this formulation is applicable for RF coils in general with , while the subsequent two formulations in terms of relative transmit phases are only applicable for multi-element RF arrays with and/or . The transmit field from channel p can be written in terms of relative phase distributions as
with the transmit phase of channel p relative to the reference transmit phase of channel r. is the measurable term, while is the unknown term. Additionally, the receive phase can also be written in a similar formulation. The measurable term is, however, weighted by the proton density. For the conjugate of the receive field, we have
with the receive phase of reference channel r relative to channel q. is the measurable term, while is the unknown term.
In summary, we use the phasor representation of Equation (4) to describe the RF field and orient the field in the negative -direction such that enables the manipulation of magnetization. Furthermore, we describe the transmit and receive fields with Equations (8) and (9), such that and described by the phasor representation of Equation (4) correspond to the and fields described by the phasor representation of Equation (1), respectively. Additionally, the MR image can be described by Equation (15), which shows that the transmit and receive field phases, as well as the proton density and the receive field magnitude, are entangled and therefore not directly available from MR acquisitions. Instead of making assumptions about the acquirable data to obtain absolute transmit or receive field maps, the transmit and receive fields can also be expressed in terms of known (directly derived from measurements) and unknown terms, as depicted in Equations (16)–(18).
3. Fundamental EPT Equations
Physical model-based EPT approaches all rely on a few fundamental equations from which their central equations are derived. To derive and understand the approaches, knowledge about the Maxwell’s equations, the Helmholtz equation and the scattering field formalism is required. These are summarized below.
3.1. First-Order Differential Equations: Maxwell’s Equations
Maxwell’s equations for time-harmonic fields are given by
with and , which are, respectively, the per-unit-length admittance and impedance of the medium. Here, , , and are the conductivity, permittivity, permeability and angular (RF) frequency, respectively. Additionally, in the MR setting, is an external current density distribution present on the MR coil that generates the EM fields. Since these sources are located outside the body and since the permeability of biological tissue is assumed to be constant and equal to that of vacuum, the RF field inside the body satisfies the Maxwell equations
with . Furthermore, introducing the vectors
we have for the transmit and receive fields the expressions and . Similarly, we define and and introduce the differentiation operators (Wirtinger derivatives)
Taking the inner product of and the second Maxwell equation now gives an explicit expression for the transmit field, while taking the inner product of , and this second Maxwell equation gives an explicit expression for the receive field. Explicitly, we have
These relations tell us that the and fields result from a difference between transverse variations of the longitudinal electric field (as determined by the Wirtinger derivatives) and longitudinal variations of the transverse and fields. These equations are used as a starting point in the EPT method discussed in Section 4.7. For completeness, we mention that, if a similar procedure is followed for the first Maxwell equation, we obtain
3.2. Second-Order Differential Equation: The Generalized Helmholtz Equation
Since the objective is to obtain the dielectric tissue parameters from magnetic field data, a second option is not to consider the electric field at all and to eliminate this field from the source-free first-order Maxwell system as given by Equations (21) and (22). To this end, we take the curl of Equation (21) and obtain
Since
and
Equation (26) can be written as
Finally, taking the divergence of the second Maxwell equation (Equation (22)), we get and substituting this result in the above equation, we obtain the generalized Helmholtz equation
where is the complex wave number with . Note that, for homogeneous media, is constant and the second term on the left-hand side vanishes. In this case, we have the Helmholtz equation
Taking the inner product of the vector and Equation (28) gives the Helmholtz equation for the field
which serves as a starting point for the EPT methods discussed in Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 5.1 and Section 5.2. It is important to realize that the above Helmholtz equation is valid for homogeneous media ( is constant) only. For general inhomogeneous media ( is not constant), we have the generalized Helmholtz equation (Equation (27)). Dotting this equation with the vector , we end up with the generalized Helmholtz equation for the field given by
This equation serves as a starting point for the EPT methods discussed in Section 4.4, Section 4.5 and Section 4.6, but with the second term on the left-hand side rewritten in terms of and . Specifically, in the EPT methods of Section 4.4 and Section 4.5, the generalized Helmholtz equation is rewritten in terms of the gradient of and , while, in the methods of Section 4.6, the generalized Helmholtz equation is written as a convection–reaction equation.
3.2.1. The Gradient-Type Generalized Helmholtz Equation
Let us first consider rewriting the generalized Helmholtz equation (Equation (30)) in terms of the gradient of the field and , the z-component of the magnetic field. As a first step, we introduce the vector and write . The second term on the left-hand side in Equation (30) can now be written as
Since
this can be written as
Furthermore, using , we have
and substituting this relation in Equation (31) leads to
with
With this result, we end up with the gradient-type generalized Helmholtz equation
3.2.2. The Generalized Helmholtz Equation as a Convection–Reaction Equation
To arrive at the convection–reaction form of the generalized Helmholtz equation as used in EPT, we return to Equation (32) and rewrite this equation as
Substitution of this result in Equation (31) gives
where
The generalized Helmholtz equation now becomes
Dividing this equation by and using the definition of vector , we arrive at our final form
with . Equation (36) is the generalized Helmholtz equation in convection–reaction form, where is the reaction component and is the convective field. Observe that the components of the convective field are directly related to the dielectric medium parameters and the z-component of the electric field strength via (cf. Equations (24) and (25))
These relations are used as a starting point in the EPT methods discussed in Section 4.7 and Section 4.8.
3.2.3. Helmholtz Equations for the Receive Field
For completeness, we mention that a similar procedure can be carried out for the field. In particular, taking the inner product of the vector and Equation (27), we end up with
which is the generalized Helmholtz equation for . This equation can also be written in terms of gradients of the field and as
with
where we introduce , or as a convection–reaction equation as
with
For the vectorial Helmholtz equation of Equation (28), dotting with the vector gives
which is the Helmholtz equation for the field in the case of homogeneous media.
3.3. Volume Integral Equations
The fundamental integral equations are obtained through a scattering formalism by exploiting the linearity of Maxwell’s equations. Specifically, the total electromagnetic field in the presence of an object in an MR coil is denoted by , and this field is written as the sum of an incident and scattered field as
where the incident field is defined as the field that is present in an empty (air-filled) RF coil. This incident field is generated by an external current density distribution representing the MR coil that occupies the bounded source domain . The governing equations for the incident field are
with the wave number of the background medium, the electromagnetic wave speed of free space and the admittance of the background medium. In the above field expressions, the vector potential is given by
where is the Green’s function of the background medium given by
When there is an object present, scattered fields will be generated due to an induced scattering current density distribution having the object domain as its support. The scattered fields are given by
where the vector potential is given by
with the scattered current density distribution. Note that the scattering current density and consequently the scattered field vanish if the object is absent () and the total electromagnetic field is equal to the incident field. Finally, we mention that the field can be obtained from the vector potential as
where . The dielectric tissue parameters only influence , that is, the effects of the medium parameters on the field have been separated from the excited incident field. These relations are used as starting point for the EPT methods discussed in Section 4.9, Section 4.10 and Section 4.11.
4. EPT Methods Requiring Transmit Field Mapping
This section discusses analytical EPT approaches based on transmit field mappings. The section starts with direct local differential methods and roughly transitions to end with forward global integral methods. More specifically, the EPT methods discussed in this section are
- Section 4.1: Helmholtz-based EPT (H-EPT)
- Section 4.2: Simplified H-EPT (SH-EPT)
- Section 4.2.1: Poisson-based Conductivity Mapping (P-CM)
- Section 4.3: Local Maxwell tomography (LMT)
- Section 4.4: Modified dual-excitation EPT (MDE-EPT)
- Section 4.5: Gradient-based EPT (G-EPT)
- Section 4.6: Convection–reaction EPT (CR-EPT)
- Section 4.6.1: Phase-only convection–reaction conductivity mapping (PCR-CM)
- Section 4.7: Transverse EPT (T-EPT)
- Section 4.8: First-order induced-current EPT (foIC-EPT)
- Section 4.9: Variational Born iterative method EPT (VBIM-EPT)
- Section 4.10: Global Maxwell tomography (GMT)
- Section 4.11: Contrast source inversion EPT (CSI-EPT)
Other methods that do not require transmit field mapping are discussed in Section 5. Machine-learning approaches are discussed in Section 6.
4.1. Helmholtz-Based EPT
Helmholtz-based EPT (H-EPT) assumes a homogeneous medium () and is based on the Helmholtz equation (Equation (29)) [22,23,30]. Explicitly, assuming that the field is known, the tissue parameters are determined from
and the definition of the wave number as
This explicit method is extremely simple, easy to implement and fast to compute. However, the homogeneity assumption results in errors at tissue boundaries; the second-order derivative that acts on the data makes the method sensitive to noise [31,32,33]; and the method requires knowledge of the absolute transmit phase which is not directly available. To mitigate noise effects, filtered Laplacians with increased kernel size can be used, however, this leads to a severe numerical boundary error propagation [32,34]. The second-order differential has been reduced to first-order derivatives in an alternative formulation based on Gauss’ integral theorem, but image segmentation is required to implement this method [35,36]. Since the absolute transmit phase is in practice unavailable, it is typically estimated with the transceive phase assumption. However, since the Laplacian of a variable is the divergence of the gradient of the variable, this assumption can be prevented with multiple acquisitions from a multi-element array. This system namely allows for the determination of the gradient of the transmit phase of a reference transmit channel () from relative transmit phases [37] or the gradient of the receive phase of the receive channel () from transceive phase measurements [27].
4.2. Simplified H-EPT
Simplified H-EPT (SH-EPT) derives the conductivity and permittivity independently from the phase and magnitude of the , respectively [8,35]. Starting point is again the Helmholtz equation (Equation (29)) for the field. However, here the polar decomposition of is substituted, which gives
and, equating the real and imaginary parts in the above equation, we obtain
Finally, assuming that , we obtain
Note that, if the Helmholtz equation accurately describes the behavior of the field and if the above approximation holds, then only the phase of the field is required to determine the conductivity. We remark that, if we write the field in polar form as well and follow similar steps as for the field, we obtain from the Helmholtz Equation (41)
where is the phase of the field. Consequently, if the transceive phase is available, we have
Similarly, the assumption results in
Clearly, in this case only the magnitude of the field is required to determine the permittivity.
This EPT method is similar to H-EPT, but allows for conductivity or permittivity mapping without requiring the availability of both the magnitude and phase of the field if the corresponding additional assumptions hold. The validity of these assumptions need to be investigated further. If only one of the EP maps is required, this approach enables, for example, shorter acquisition times or an increase in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the transmit field map.
4.2.1. Poisson-Based Conductivity Mapping
Poisson-based conductivity mapping (P-CM) considers Equation (50) as a Poisson equation for the phase. More precisely, in P-CM, we consider the Poisson equation
on and observe that the right-handed side has the object domain as its support. Requiring that decays sufficiently fast at infinity ( decreases as uniformly in as ), we have
where is the 3D static Green’s function given by
In P-CM, we assume that the phase of the transmit field is known within the object, let in Equation (52), set for and retrieve a conductivity profile by minimizing Equation (52) in a least-squares sense.
P-CM is an integral formulation of the methods described in [38,39]. Its global integral approach has an inherent noise suppression effect which makes this method more robust to noise than local differentiation methods. Additionally, the minimization process allows for the inclusion of regularization as well. However, the method has an increased computational complexity compared to differential Helmholtz-based EPT approaches.
4.3. Local Maxwell Tomography
The simplified form of Local Maxwell Tomography (LMT) assumes the availability of a multi-element array and substitutes the polar decomposition of the field as presented in Equation (16) into the Helmholtz equation (Equation (29)) [40]. We then obtain
This local equation is assumed to hold inside the object domain and can be written as
with
and
Requiring that Equation (54) holds at N different locations with position vectors , (e.g., with N the total number of pixels/voxels and the position vector of the center of the nth pixel/voxel), we obtain the set of equations for , which can be written as an underdetermined system , where is an N-by- matrix given by
and
Since there are five unknowns associated with each point of interest , at least five linearly independent transmit field measurements are carried out, producing the set of equations , , where is the total number of transmit field measurements. The total set of field equations can now be written as
and this square () or overdetermined () system is solved in the least-squares sense to obtain vector . Finally, the EPs at location can be obtained by equating the fifth entry in to .
This method requires no knowledge of the unavailable absolute transmit phase. However, since there are multiple unknowns for each point of interest, several independent transmit field measurements are required, which are typically only available on 7 T MRI systems, to derive a unique solution. The amount of required transmit fields can be reduced by extending the method with receive field measurements. The same procedure as described above can be carried out for the receive field in terms of measurable quantities, as presented in Equation (18), and, under the assumption of homogeneous proton density, a similar equation may be derived [40]. When more field maps are available, this last assumption can be prevented and the gradient and Laplacian of the proton density can also be determined [40]. LMT can be further generalized to also take the spatial variations of the tissue EPs into account, such that it becomes free from object and field assumptions. This, however, comes at the cost of increasing the number of unknowns and therefore requiring a larger amount of transmit and/or receive field maps [41].
4.4. Modified Dual-Excitation EPT
Modified dual-excitation EPT (MDE-EPT) uses Equation (33) as a starting point and it assumes that the gradient of the z-component of the magnetic flux density vanishes [28]. We then obtain
This local equation is assumed to hold inside the object domain and can be written as
where and are 3-by-1 vectors given by
and . Requiring that Equation (59) holds at N different locations with position vectors , , leading to a system of equations , where the N-by- matrix , the -by-1 vector and the N-by-1 vector are of similar form as in LMT (cf. Equations (55) and (56)). Since there are three unknowns (, , and ) associated with each point of interest , at least three linearly independent transmit field measurements are carried out, producing the set of equations , , where is the total number of transmit field measurements. The total set of field equations can now again be written as Equation (57) and this square () or overdetermined () system is solved in the least-squares sense to obtain vector . Finally, the EPs at location can be obtained by equating the third entry in to .
This approach does not require homogeneity of the object, which allows for improved tissue boundary reconstructions. However, since there are three unknowns, at least three independent transmit fields are required. Additionally, the method is restricted to regions with spatially invariant z-component of the magnetic field. Note that the original form, dual-excitation EPT, assumed knowledge of the unavailable x- and y-components of the magnetic fields [42] and therefore required only two linearly independent excitations/measurements to determine the EP maps. MDE-EPT, however, can be extended by including Equation (39), again under the assumption of vanishing gradient of the z-component of the magnetic field, into the system of equations. The name dual-excitation is then again justified, in the sense that two independent excitations result in four equations if both the transmit and receive fields are acquired [43].
4.5. Gradient-Based EPT
Gradient-based EPT (G-EPT) continues from Equation (58) and writes it in terms of absolute and relative transmit phases with respect to a reference element, as presented in Equation (17) [44,45,46,47,48]. We then obtain
with the unknown absolute transmit phase of reference channel r. First, the gradient is determined. Similar to LMT and MDE-EPT, the above equation is written in the form
where
and . Equation (61) is required to hold at N different locations of interest with position vectors , , leading to a system of equations , where the N-by- matrix , the -by-1 vector and the N-by-1 vector are of a similar form as in LMT and MDE-EPT (cf. Equations (55) and (56)).
Since there are four unknowns associated with each point of interest (the elements of vector ), at least four linearly independent transmit field measurements are carried out and these produce the set of equations , , with the total number of transmit field measurements. The total set of equations can now again be written as in Equation (57) and this square () or overdetermined () system is solved in the least-squares sense to obtain vector . From this vector, can be determined from the second or third entry of .
Second, the gradient is integrated using the definition and an additional least-squares minimization process, where seed points (point belonging to a subdomain of the object domain where the EPs are known) are used to obtain absolute EP maps.
The additional integration step in G-EPT acts as a low-pass filter and makes the approach relatively robust to noise. Additionally, using the relative phase has the benefit that influences of receive field, chemical shift, magnetic susceptibility and eddy currents on the phase are mitigated. The method, however, requires multiple transmit elements as well as knowledge of seed points to derive absolute EP maps. The seed points can be derived by surrounding the object with a gel with known EPs, (dubbed boundary informed G-EPT) [48]. Additionally, since the transverse gradients of the absolute phase of the reference channel can also be derived from and in the first step of G-EPT, the seed points can be selected in an automated fashion by using the Helmholtz-based EPT approach in homogeneous regions (dubbed automated G-EPT) [47].
4.6. Convection–Reaction EPT
Convection–reaction EPT (CR-EPT) [49,50,51] assumes that the field is known and solves the generalized Helmholtz equation in convection–reaction form (Equation (36)), for convenience repeated here,
in a least-squares sense for the inverse admittance parameter u under the assumption of invariance of the z-component of the magnetic flux density in the convective field (Equation (35)), and derives the tissue parameters as
This method is again not restricted to regions with homogeneous tissue structures, does not require seed points and does not require a multi-element array. However, the absolute transmit phase is again required, which is not directly available from measurements but can be accurately estimated for many cases as half the transceive phase. Furthermore, the method is restricted to regions with spatially invariant z-component of the magnetic field. Additionally, the method suffers from a reconstruction artifact in the region with low convective field.
4.6.1. Phase-Only Convection–Reaction Conductivity Mapping
Phase-only convection–reaction conductivity mapping (PCR-CM) [52] simplifies the generalized Helmholtz equation in convection–reaction form (Equation (36)) by dividing it by and assuming and , which gives
with
The same procedure can be performed for the generalized Helmholtz equation in convection–reaction form in terms of receive fields (Equation (40)), which yields
with
The addition of these two equations gives
with
In the case that , the imaginary part of this equation can be written as a convection–reaction equation in terms of the resistivity as
which can be solved in a least-squares sense. This equation is in the form of a convection–diffusion–reaction equation with zero diffusion term. A diffusion term would act as a low-pass filter and increases numerical stability of the approach. To suppress spurious oscillations, an artificial diffusion term is typically added to the fundamental equation, where c is an empirically determined constant diffusion coefficient. The conductivity is finally retrieved as the inverse of the resistivity .
This method can be seen as a generalized version of phase-only Helmholtz-based EPT implementation as discussed in Section 4.2, which allows for large spatial variations of the tissue conductivity. However, the method has an increased computational complexity and the required assumptions do not hold for high field strengths.
4.7. Transverse EPT
Transverse EPT (T-EPT) [53] assumes that the RF field has a so-called E-polarized field structure within a certain transverse plane, by which we mean that longitudinal variations of the transverse electric field and the longitudinal variation of the magnetic field essentially vanish within this plane (, and for ). Usually, the plane is taken to be the midplane of a birdcage coil, since it has been observed that the RF field has an approximate E-polarized field structure within this midplane [54]. Note that, for two-dimensional configurations with no spatial variations in the z-direction and a z-directed external electric current source, the E-polarized field structure is exact.
Taking the E-polarized field assumption into account, it follows from Maxwell’s equations that (cf. Equations (24) and (37))
In T-EPT, these two equations are combined into a single normalized functional given by
where is an -norm defined on . Ths functional is iteratively minimized in an alternate fashion using conjugate-gradient-type update formulas for , followed by a direct update of . This two-step update procedure is repeated until convergence or a maximum number of iterations is reached. Finally, the conductivity and permittivity reconstructions follow from the reconstructed admittance as
In the remainder of this manuscript, these multi-step inversion methods are summarized in a listing (see Listing 1 for the update process of T-EPT).
This method has no second-order but only first-order derivatives that act on the measurement data, increasing noise robustness. Additionally, the method computes the z-component of the electric field strength, which can be helpful in SAR computations. However, the method is restricted to regions where the RF field is approximately E-polarized, such as in the midplane of a birdcage RF coil.
| Listing 1. Transverse EPT (T-EPT). |
|
4.8. First-Order Induced-Current EPT
First-order induced-current EPT (foIC-EPT) considers E-polarized RF fields and thus assumes that the electric field strength is mainly directed in the longitudinal z-direction [56]. For E-polarized fields, we have (cf. Equations (37) and (44))
where we introduce the vector potential operator
Combining these two equations, together with the linearity of Maxwell’s equations (see Equation (42)), gives
which can be solved for the z-component of the electric field strength, if its incident component is known. Finally, the conductivity and permittivity can be derived via
This approach has only first-order derivatives that act on the measured transmit field data, and an integral formulation for the electric field strength determination, making the method robust to noise. However, the method is again restricted to a region with an E-polarized field structure. Additionally, the method requires knowledge of the incident field, which cannot be measured directly. Incident fields are typically estimated from a simulation setup or from a reference scan of a phantom with known EPs. Note that the formulation is presented as a three-dimensional problem, but, in the case of an E-polarized field structure, it can be simplified to a two-dimensional setting. Cauchy-based EPT shares a lot of similarities with foIC-EPT, but the electric field strength is derived via a Cauchy integral which allows for the computation of the EPs in a direct manner through complex analysis [57,58,59,60].
4.9. Variational Born Iterative Method EPT
The variational Born iterative method EPT (VBIM-EPT) is a volumetric integral method that iteratively updates the tissue parameters based on improved estimations of the transmit field by solving forward and inverse problems [61,62]. Given knowledge of the incident fields and an initial estimation for the contrast function, the electric field strength is derived from (cf. Equations (42) and (44))
with . Equation (74) is a forward problem. Based on the derived electric field strength and the estimated contrast function, an estimate of the scattered part of the transmit field is computed as (cf. Equation (45))
and the residual is derived according to . The residual in the contrast function is then determined by solving
for , which is an inverse problem. The contrast function is then updated as . Based on this new estimation of the contrast function, the procedure is repeated until a convergence criterion has been reached (see Listing 2). Finally, the conductivity and permittivity maps are derived via
This method does not apply any derivatives on the measured transmit field. Instead, it makes use of an integral formulation, making the method noise robust. However, the method requires knowledge of the incident fields, and solving the forward and inverse problems iteratively is computationally prohibitively expensive.
| Listing 2. Variational Born Iterative Method-EPT (VBIM-EPT). |
|
4.10. Global Maxwell Tomography
Global Maxwell tomography (GMT) is a volumetric integral method that iteratively updates the tissue parameters based on improved estimations of the transmit field by solving a forward problem and minimizing an objective function [63,64,65]. GMT makes use of the identity [66]
and transforms the electric field integral representation of Equation (74) into a current density volume integral representation, given by
Given knowledge of the incident field and an initial contrast function, this equation is solved for the scattered current density distribution (a forward problem), which is used to estimate the scattered component of the transmit field via Equation (45). An objective function is introduced
Based on its gradient with respect to the contrast function is updated. This process is iterated until a convergence criterion has been reached (see Listing 3). Finally, the EPs are derived from the contrast function via Equation (77).
This method is similar to VBIM-EPT, but removes the inverse problem in every iteration. Even though a computational expensive inverse problem is removed, the method remains computationally expensive since the gradient updates typically require a large amount of iterations. The presented formulation still requires knowledge of the absolute transmit phase; however, this has been addressed by reformulating the objective function to only consider the magnitude of the transmit field or, in the case of a multi-element transmit system, by reformulating it in terms of magnitude and relative phases [64,65].
| Listing 3. Global Maxwell Tomography (GMT). |
|
4.11. Contrast Source Inversion EPT
Contrast-Source Inversion EPT (CSI-EPT) formulates the inversion problem as a purely optimization problem in which a single functional is iteratively minimized [67,68]. CSI-EPT combines the multiplication of the contrast function and the electric field strength into a single variable, the so-called contrast source . The scattered electric field strength is then given by (cf. Equation (44))
and the scattered transmit field operator is then given by (cf. Equation (45))
which are used to set up an objective functional (cf. Equation (74))
which is minimized in a two-step “fix-one-minimize-for-the-other” update process. First, the contrast function is fixed and the contrast source is updated from the gradient of the cost function with respect to . Once the contrast source is updated, the electric field strength is calculated as
and the contrast function is updated by solving the least-squares problem , which gives
or by fixing the contrast source and updating the contrast function from the gradient of the cost functional with respect to . This two-step update procedure is iteratively repeated until a stopping criterion has been reached (see Listing 4). Finally, the tissue parameters are derived from the contrast function via Equation (77).
This approach only applies fast forward computations and does not have to solve any forward problem as in VBIM-EPT or GMT. However, since the approach typically still requires a lot of iterations, the method remains time consuming compared to direct methods such as H-EPT. Additionally, the transmit phase remains required, which can only be accurately approximated in specific cases. Naive [69,70,71,72], two-dimensional [73,74,75,76,77,78], magnitude-based [79] and segmented [80,81] implementations have been proposed to improve for example convergence or applicability.
| Listing 4. Contrast Source Inversion-EPT (CSI-EPT). |
|
5. EPT Methods Not Requiring Transmit Field Mapping
The previously discussed EPT approaches can be extended with receive fields. However, there are also methods that do not require transmit fields. The followin EPT approaches are discussed in this section:
- Section 5.1: Single-acquisition EPT (SA-EPT)
- Section 5.2: Image-based EPT (I-EPT)
5.1. Single-Acquisition EPT
Single-acquisition EPT (SA-EPT) [82] rewrites the Helmholtz equation for the receive field (Equation (41)) as
which shows that knowledge of the rate of change of the field is sufficient to derive the EPs. By introducing the receive field of channel q relative to reference channel r as
we obtain through the Laplacian of the relative receive field [82]
since each element measures the same EPs. This local equation is assumed to hold inside the object domain and can be written as
where and are 3-by-1 vectors given by
and . Equation (84) is required to hold at N different locations of interest with position vectors , , leading to a system of equations , where the N-by- matrix , the -by-1 vector and the N-by-1 vector are of a similar form as in LMT, MDE-EPT and G-EPT (cf. Equations (55) and (56)). Once the term is obtained, the tissue parameters can be determined from Equation (81).
This method does not require absolute transmit field data, but relies only on relative receive fields which are directly available. This results in the elimination of specific artifacts, since common terms for the different elements can be eliminated. These receive fields can be derived from a single acquisition; however, this requires a multi-element array with a minimum of four receive elements, since at least three linearly independent relative receive fields are required to determine a unique solution. Additionally, since the gradient term is derived in a minimization process based on second-order derivatives and an additional divergence is applied on the gradient term, the method relies on third-order derivatives giving strong dependence on the SNR of the images.
5.2. Image-Based EPT
Image-based EPT (I-EPT) uses the acquired MR image directly for the reconstruction of the tissue parameters. For a low flip angle , we have , thus the MR image for any low-flip-angle sequence is essentially given by (cf. Equation (15))
In I-EPT, information from this image is used, instead of estimated transmit or receive fields. The relevant equation applied to this image is derived by multiplying Equation (29) with and Equation (41) with and adding them together, which gives
By taking and defining and , we obtain
and by using the product rule of the scalar Laplacian () and dividing by , we find
The underbraced term denoted by is an error term that can be simplified to [83] and can be neglected when and are similar to each other. This results in the following Helmholtz equation
Equation (88) remains valid when the term is multiplied by a constant, since it drops out of the equation. The variables in front of the term in Equation (88) are relatively constant throughout space in regions where the Helmholtz equation applies, and the image as described in Equation (85) can therefore be applied in Equation (88).
This method does not require the acquisition of transmit and receive fields, which results in reduced scan time and an increase in SNR, since the image SNR is greater than that of transmit or receive field maps. Additionally, in this formulation, the errors resulting from and differences are reduced to a first-order effect with respect to the difference compared to the conventional H-EPT method. A zero echo-time sequence has been proposed due to its immunity to eddy current and static magnetic field () inhomogeneity-induced phase changes, as well as its speed and SNR efficiency [83]. The method has also been proposed with a fast spin echo sequence together with a relaxation pattern between echoes to increase noise robustness [84]. A generalized image-based EPT form which includes the gradient of the EPs has also been proposed [85].
6. Data Driven Deep Learning Approaches for Solving Inverse Problems
Solving inverse problem by data-driven deep learning approaches is an emerging field with recent examples from the fields of gravitation [86], radioastronomy [87], medical imaging reconstruction [88] and electromagnetics [89,90]. The basic advantage of these data-driven approaches is that it allows insertion of more tailored a priori information about the specific inverse problem under study. A key aspect is the learning-based approach where during a training phase deep neural networks learn to perform a specific task in the inverse process by feeding them with many ground truth examples. After training the neural network, the inference is extremely fast, sometimes only a few seconds. This constitutes a clear computational gain over more conventional iterative approaches to solve inverse problems. Other advantages include a higher level of tolerance to noise on the input data and a higher flexibility on the required input data as neural networks can act as learned surrogate models.
6.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
The most popular for image processing and reconstruction are convolutional neural networks (CNN) [91,92,93]. These neural networks employ convolutions in their architecture whose kernels are optimized during training for their given task. The training phase is a very computationally intensive process involving the backpropagation of the errors during the training (in fact, a large scale optimization process itself) over the various weights between the nodes (often >1 million) in the network. This process takes place on a GPU and is facilitated by mature software packages that are able to exploit the parallel nature of the GPU in an efficient manner.
To obtain an idea on what information a trained CNN triggers, it is insightful to process an input image through the trained network and generate the output of the various units in the layers as images (so-called feature maps) comprising of local and global predictive information to perform the task it was trained for. Although CNNs are also heavily used for classification problems such as image segmentation, for use in the EPT reconstruction, only the regression task is relevant. In a regression CNN, where the famous U-NET [93] is a prime example, an encoder and the image information is processed by various convolutional kernels and pooling operations and fed through activation layers which constitute non-linear elements and are essential for the ability to learn. During the downsampling path, spatial contextual information is learnt. In regression problems, this is followed by the decoder where convolution and upsampling takes place to recover the spatial information of the desired output matrix size. In fully convolutional networks, the architecture solely employs operations such as convolution, pooling, activation and upsampling. Avoiding fully connected layers makes the inference much faster as fewer weights are needed, and the network can work regardless of the original image size. Skip connections short-circuiting corresponding layers in the encoder and decoder such as in the popular U-NET [93] are essential to recover fine-grained spatial information lost in the pooling or downsampling layers.
6.2. Deep Learning for EPT Reconstruction: Single Feedforward Approaches
An important distinction can be made between deep learning inverse approaches where single feed forward networks are employed and hybrid approaches where deep neural networks are themselves embedded in the iterative optimization process of solving the inverse problem. In principle, both approaches can be applied to EPT. Using the feedforward approach, Mandija et al. [94] employing convolutional neural networks demonstrated that deep learning EPT (DL-EPT) can reconstruct more noise robust dielectric parameter maps than conventional Helmholtz based EPT. An essential element of this feed forward approach is that the network constitutes a surrogate EPT reconstruction model implicitly learnt from the training data and takes the measured complex transmit field information as the input. This learning-based approach creates more flexibility than state-of-the-art MR-EPT techniques, which require electromagnetic quantities dictated by electromagnetic first principles which are not accessible with MRI. As example, in DL-EPT, a feedforward network can be trained with MR accessible quantities (e.g., the transceive phase) only. Interestingly, Mandija et al. [94] demonstrated that, also for a deep learning approach, almost all predictive features to reconstruct electrical conductivity are contained in the transceive phase maps in accordance with our insight from electromagnetic principles underpinning conventional EPT.
6.3. Training Data and Generalization to Unseen Data
Essential of course is the availability of training data which can nowadays be easily generated by electromagnetic simulations including realistic RF coil models, phantoms and body models. In this way, a high degree of a priori knowledge, such as the specific MRI coil setup, can be introduced. The advantage of using this simulation-based approach to generate the training transmit field data with superimposed artificial noise, is that the ground truth is available. However, in silica training data might not reflect realistic experimental conditions. Therefore, approaches that employ training data reconstructed with more conventional EPT reconstruction schemes are also used [95]. In the work of Gavazzi et al. [96], a 3D patch neural network approach was used where the receptive field is more local (size of the 3D patch) forcing it to perform dielectric parameter estimation from more local magnitude and phase information. A further advantage is that it can work with varying matrix size of the input data. A key question is of course how a single feed forward neural network approach behaves when it is tested on unseen input data that was not directly included in the training data, e.g., pathologic tissue with different dielectric parameter values or in the presence of motion artifacts on the maps. An obvious mitigation is to augment the training data sufficiently (e.g., part of the transmit maps can be artificially corrupted with motion artifacts) to obtain more robust results.
6.4. Deep Learning EPT: Integrating Deep Learning into Iterative EPT Schemes
Another option to improve the generalization to unseen data is to retain the physics in the reconstruction framework while still benefiting from the advantages of deep learning. A first approach was published for EPT by Leijsen et al. [97], who demonstrated that initial estimates provided by deep learning led to better convergence for 3D CSI-EPT. This integration can be further improved. New hybrid approaches are now emerging in medical image construction where neural networks are embedded in conventional iterative reconstruction schemes [98,99,100,101,102]. The physics related to the reconstruction problem is still explicitly included by means of a physics-based forward operator (e.g., Fourier transform in case of MR image reconstruction). Experiences from the medical image reconstruction demonstrated that this leads to much better generalization to unseen data in the training [100]. The neural networks can be inserted in the iterative procedure for various tasks. For example, neural networks can be trained to learn regularization filters much more tailored to the specific application than applying standard regularization kernels [101]. Alternatively, the networks can be used to perform the update task, i.e., determining the update direction based on the data mismatch and the regularization term [98]. Employing such an approach, the convergence is often much faster as a priori information on the optimization landscape is learned in the training phase, enabling faster convergence. These hybrid approaches should also be possible to combine with iterative EPT schemes such as 3D CSI-EPT where the physics is included by a forward operator (e.g., Green’s function approach) linking a certain electrical property distribution to the measured data ( magnitude and transceive phase information). Such a methodology would be an ideal scenario as it would harvest the power of deep learning to accelerate reconstruction and include tailored a priori information from the learning phase, while still retaining to the physics-based modeling and the data consistency.
6.5. Outlook
It is clear that deep learning offers much benefit for EPT in terms of achieving higher quality reconstructions. The feedforward approaches using CNNs have demonstrated clear potential in terms of noise robustness, flexibility on inputs and computational speed. A key question is the generalization to data not encountered in the training. Interestingly, also in EPT’s sister field of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping deep learning improves the quality of susceptibility reconstruction over conventional methodology [103,104]. Promising results have been achieved here on the generalization issue. An attractive alternative might be the integration of learned networks into a conventional iterative EPT approach as occurs in medical image reconstruction. This still retains the physics, offering better generalization, while also being able to include more a priori information and providing faster reconstructions.
7. Discussion and Conclusions
This paper presents a mathematical analysis of a large number of different methods for EPT, each with their own relative strengths and weaknesses. By comparing the results from each approach, one can make a number of general statements, the most important of which are listed below.
7.1. Approach Description
EPT approaches can be sorted into several different categories. These categories can give some general insight into how the methods work, and what kind of restrictions exist. Here, we sort the methods into three categories.
- Differential methods or integral methods
- Local methods that reconstruct the EPs at a specific location by only taking the information from the direct neighbourhood into account, or global methods that take the whole imaging domain into account to reconstruct the EP maps as a whole
- Direct methods that act directly on the data to reconstruct the EPs, also called backward methods since they run ‘backwards’ from the measured field map to the underlying EPs, or forward methods that employ forward models or solve forward problems in the inversion scheme and act ‘indirectly’ on the data
For each of the transmit field-based methods discussed in the manuscript, the approach descriptions are assigned in Table 1.

Table 1.
Approach description for the EPT approaches as described in this manuscript.
7.1.1. Differential vs. Integral
A general observation is that differential approaches have an inherent noise amplification, while integral approaches are more noise robust due to the inherent low-pass filtering properties of the relevant integrals. The higher is the order of the differentials acting on the data, the larger is the noise amplification. A comparison between a second-order differential approach and an integral approach is shown for simulated three-dimensional noisy data (SNR = 100, as defined in [94]) in Figure 2. It shows that integral methods are in essence more noise robust and that typical noise reduction implementations such as regularization do not overcome this disadvantage.
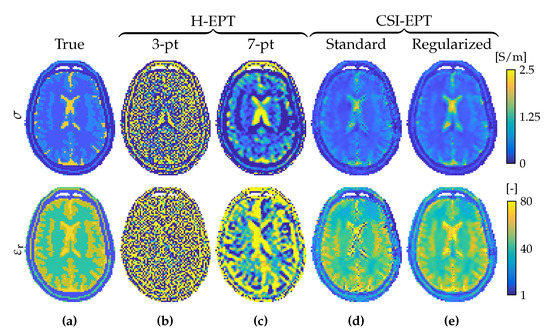
Figure 2.
Direct differential method and forward integral method comparison on simulated three-dimensional noisy data () from a 7 T head coil. Methods are three-dimensional implementations without and with noise suppression in the form of using a larger differential kernel [32] or by including multiplicative total variation regularization [73]. True model (a), Helmholtz-based EPT with a 3-point kernel (b), Helmholtz-based EPT with a 7-point kernel (c), standard contrast source inversion EPT (d) and regularized contrast source inversion EPT (e). Conductivity (top row) and relative permittivity (bottom row).
7.1.2. Local vs. Global
A commonality among many approaches is that there appears to be a trade-off between having an adverse noise effect in local methods due to higher-order derivatives (second order and up) acting on the data or having the bias effect of the EM field structure in global methods. A comparison between two-dimensional implementations of local and global approaches that assume knowledge of the complex transmit signal is shown for simulated two-dimensional noiseless data in Figure 3. The reconstructions of the local method H-EPT shows boundary errors due to assumed homogeneity of the underlying tissue, but the method is accurate in regions which have locally spatially invariant tissue properties. The reconstructions of the global methods (T-EPT, foIC-EPT and CSI-EPT) take the inhomogeneity of the EPs into account, but suffer from a bias related to the low electric field strength (low convective field). Additionally, global methods have the potential to reach local minima in their optimization process.
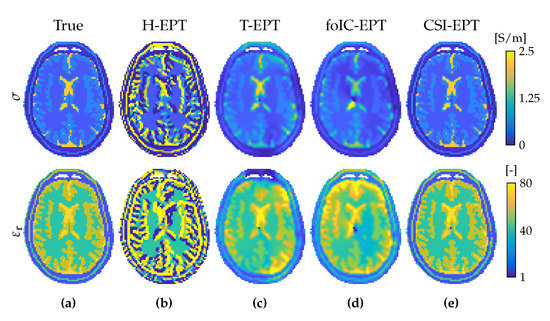
Figure 3.
Local method and global methods comparison on simulated two-dimensional noiseless data from a 7 T head coil. Methods are two-dimensional implementations. True model (a), Helmholtz-based EPT (b), Transverse EPT (c), first-order Induced-Current EPT (d) and contrast source inversion EPT (e). Conductivity (top row) and relative permittivity (bottom row).
Global methods allow for the inclusion of regularization in the optimization problem which can be employed to correct for the bias, resolve local minima or improve noise robustness.
7.1.3. Direct vs. Forward
A general observation is that direct methods are relatively fast, while forward methods tend to be computational expensive and time consuming, especially those that require the results of forward and/or inverse problems iteratively. Forward methods have yet to be demonstrated to be clinically feasible. Forward methods, however, typically simultaneously reconstruct additional field maps, such as the electric field strength which would be useful for SAR computations.
7.2. Data Requirements
EPT approaches can also be categorized on which type of data they require, or what kind of assumptions about the data are required. For each of the transmit field-based methods discussed in the manuscript, data requirements are assigned in Table 2.

Table 2.
Data requirements for the EPT approaches as described in this manuscript. Note that data requirements can be influenced by extensions or generalizations of the methods.
7.2.1. Measurable and Non-Measurable Data
For accurate reconstruction of the EPs, ideally measurements of all three components of the field would be possible. However, the z-component cannot be measured. Additionally, the x- and y-components cannot be acquired in a direct fashion, and determination would require the absolute transmit field as well as the absolute receive field. The absolute magnitude of the transmit field can be acquired in a direct fashion, while the absolute transmit phase and absolute receive field can not. Measured phases are always a superposition of the transmit and receive phase, and the magnitude of the receive field is always weighted by the proton-density. This data unavailability is one of the fundamental challenges that makes EPT complicated.
EPT approaches that assume availability of the complex transmit field typically estimate the absolute transmit phase by applying the transceive phase estimation (TPA), while methods that incorporate absolute receive fields go hand-in-hand with homogeneity or symmetry assumptions to eliminate the proton-density bias. To bypass these assumptions, solutions are often sought by reformulating the problem in terms of only directly-available field quantities. With regular RF coils, this comes down to formulating the inverse problem in only magnitude data or (in combination with) transceive phase data. However, with multi-element RF coil arrays, the acquisition of relative fields are possible, by dividing the complex signal measured in an element by the signal obtained in a particular reference element. This allows the derivation of the (gradient of the) transmit (and receive) phase, as well as EPT formulations based on the relative phase, instead of absolute or transceive phase, or formulations based on receive fields only. Additionally, this type of coil can eliminate specific artifacts since common terms for the different channels can be eliminated. However, the acquisition of multiple fields requires lengthy scans which can compromise patient comfort, throughput or SNR. Moreover, these multi-element RF coil elements are not yet widely available in clinical settings. About 50% of clinical MR scanners have a field strength of 1.5 T and have a body coil with a single transmit channel. About 45% of clinical MR scanners have a field strength of 3 T, of which the older ones have the same arrangement, and the newer one typically have two independent transmit channels that can produce different degrees of elliptically polarized RF fields. High field scanners, such as 7 T scanners, can have up to eight transmit channels with independent magnitude and phase control; however, there are only about 100 of these worldwide available.
Integral methods often require knowledge of the incident electric and magnetic field strength which are inaccessible with MRI. Typically, a reference scan from a phantom with known EPs or a simulation setup is used for estimation of the incident fields. However, since the incident fields are dependent on the loading of the coil, they are to a certain level patient-specific. Patient-specific coil–subject interactions remain unknown and a source of error.
7.2.2. Field/Object Structure
The inverse problem in EPT can be significantly simplified by assuming local homogeneity of the object. Methods that apply this local homogeneity assumption (LHA) are most often used in clinical studies due to their simplicity and ease of implementation. These methods however suffer from significant errors at tissue boundaries where the LHA is violated, making them impractical in regions with small tissue structures. For larger tissue structures, tissue segmentation can be used to improve boundary reconstructions.
The EPT problem can also be simplified by assuming an E-polarized field structure, i.e., assuming negligible (gradients of the) longitudinal component of the magnetic flux density, sometimes in combination with the assumption of vanishing (gradients of the) transverse components of the electric fields strength. This approximation is typically applied in the transverse midplane of a birdcage coil, where they are relatively small [13].
7.3. State Of Development
One might select a method based on different criteria, for example based on the SNR level, on the availability of multiple transmit or receive elements or incident fields, or whether or not the region of interest contains a homogeneous medium, a low electric field region or E-polarized fields. Due to the large number of EPT approaches with a large variety in requirements, assumptions and complexity, and since the EPT field is relatively new, most methods are not at the stage of clinical use yet (see Table 3). To facilitate development, comparison and prototyping of EPT approaches, MATLAB code of the approaches presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3 is available upon request from the corresponding author.

Table 3.
Type of experiments performed for the EPT approaches as described in this manuscript. The table is constructed to the best of the authors knowledge. For references, see the main text.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L., A.W. and R.R.; methodology, R.L.; software, R.L. and W.B.; validation, R.L., W.B., C.v.d.B., A.W. and R.R.; formal analysis, R.L.; investigation, R.L. and W.B.; resources, W.B., A.W. and R.R.; data curation, R.L. and A.W.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L., C.v.d.B., R.R.; writing—review and editing, R.L., W.B., C.v.d.B., R.R. and A.W.; visualization, R.L. and R.R.; supervision, A.W., W.B. and R.R.; project administration, R.R. and A.W.; and funding acquisition, R.R. and A.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research of R. Leijsen and A. Webb was funded by the European Research Council Advanced NOMA MRI under grant number 670629.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CR-EPT | Convection–reaction EPT |
| CSI-EPT | Contrast source inversion EPT |
| DL-EPT | Deep-learning EPT |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| EP | Electrical property |
| EPT | Electrical properties tomography |
| foIC-EPT | First-order induced-current EPT |
| G-EPT | Gradient-based EPT |
| GMT | Global Maxwell tomography |
| H-EPT | Helmholtz-based EPT |
| I-EPT | Image-based EPT |
| LMT | Local Maxwell tomography |
| MDE-EPT | Modified dual-excitation EPT |
| MR | Magnetic resonance |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| P-CM | Poisson-based conductivity mapping |
| PCR-CM | Phase-only convection–reaction conductivity mapping |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| SA-EPT | Single-acquisition EPT |
| SH-EPT | Simplified H-EPT |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| T-EPT | Transverse EPT |
| VBIM-EPT | Variational Born iterative method EPT |
References
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; He, B. Magnetic-Resonance-Based Electrical Properties Tomography: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 7, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowiec, A.J.; Stuchly, S.S.; Barr, J.R.; Swarup, A. Dielectric Properties of Breast Carcinoma and the Surrounding Tissues. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 35, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, J.; Yu, J. Dielectric properties of human glioma and surrounding tissue. Int. J. Hyperth. 1992, 8, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancu, I.; Roberts, J.C.; Bulumulla, S.; Lee, S.K. On conductivity, permittivity, apparent diffusion coefficient, and their usefulness as cancer markers at MRI frequencies. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holder, D.S. Detection of Cerebral Ischaemia in the Anaesthetised Rat by Impedance Measurement with Scalp Electrodes: Implications for Non-Invasive Imaging of Stroke by Electrical Impedance Tomography. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 1992, 13, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallert, M.A.; Mirotznik, M.S.; Downing, S.W.; Savage, E.B.; Foster, K.R.; Josephson, M.E.; Bogen, D.K. Myocardial Electrical Impedance Mapping of Ischemic Sheep Hearts and Healing Aneurysms. Circulation 1993, 87, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tha, K.K.; Stehning, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Katscher, U.; Keupp, J.; Kazumata, K.; Terasaka, S.; Van Cauteren, M.; Kudo, K.; Shirato, H. Noninvasive evaluation of electrical conductivity of the normal brain and brain tumors. Proc. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 22, 1885. [Google Scholar]
- Tha, K.K.; Katscher, U.; Yamaguchi, S.; Stehning, C.; Terasaka, S.; Fujima, N.; Kudo, K.; Kazumata, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Van Cauteren, M.; et al. Noninvasive electrical conductivity measurement by MRI: A test of its validity and the electrical conductivity characteristics of glioma. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balidemaj, E.; van Lier, A.L.; Crezee, H.; Nederveen, A.J.; Stalpers, L.J.; Van Den Berg, C.A. Feasibility of electric property tomography of pelvic tumors at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.; Nam, Y.; Kim, M.o.; Choi, N.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.H. Initial study on in vivo conductivity mapping of breast cancer using MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, A.; Kolk, A.; Brundel, M.; Hendriske, J.; Luijten, J.; Lagendijk, J.; van den Berg, C. Electrical conductivity in ischemic stroke at 7.0 Tesla: A case study. In Proceedings of the 20th Scientific Meeting of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM’12), Melbourne, Australia, 5–11 May 2012; Volume 3484. [Google Scholar]
- Gurler, N.; Oran, O.F.; Keklikoglu, H.D.; Ider, Y.Z. Application of generalized phase based electrical conductivity imaging in the subacute stage of hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. In Proceedings of the 24th Annu. Meeting ISMRM, Singapore, 7–13 May 2016; p. 2994. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Katscher, U.; He, B. Electrical Properties Tomography Based on B1 Maps in MRI: Principles, Applications, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.H. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT): A Review. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2003, 27, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; de Moortele, P.F.V.; Schmitter, S.; He, B. Complex B1 mapping and electrical properties imaging of the human brain using a 16-channel transceiver coil at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, H. Magnetic induction tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, E.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Mun, C.W. Impedance tomography using internal current density distribution measured by nuclear magnetic resonance. In Mathematical Methods in Medical Imaging III; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA USA, 1994; Volume 2299, pp. 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, E.J.; Seo, J.K. Magnetic Resonance Electrical Impedance Tomography (MREIT) for High-Resolution Conductivity Imaging. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, R1–R26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katscher, U.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, J.K. Recent Progress and Future Challenges in MR Electric Properties Tomography. Comput. Math. Method. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Shah, J.; Balaban, R.S. Hall Effect Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, B. Magnetoacoustic Tomography with Magnetic Induction (MAT-MI). Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 5175–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haacke, E.M.; Petropoulos, L.S.; Nilges, E.W.; Wu, D.H. Extraction of conductivity and permittivity using magnetic resonance imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1991, 36, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H. Noninvasive Quantitative Mapping of Conductivity and Dielectric Distributions Using RF Wave Propagation Effects in High-Field MRI. In Medical Imaging 2003: Physics of Medical Imaging; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 5030, pp. 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Katscher, U.; van den Berg, C.A.T. Electric Properties Tomography: Biochemical, Physical and Technical Background, Evaluation and Clinical Applications. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoult, D.I. The Principle of Reciprocity in Signal Strength Calculations – a Mathematical Guide. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2000, 12, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, A.L.H.M.W.; Raaijmakers, A.; Voigt, T.; Lagendijk, J.J.W.; Luijten, P.R.; Katscher, U.; van den Berg, C.A.T. Electrical Properties Tomography in the Human Brain at 1.5, 3, and 7 T: A Comparison Study. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katscher, U.; Findeklee, C.; Voigt, T. B1-based specific energy absorption rate determination for nonquadrature radiofrequency excitation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; Liu, J.; He, B. From Complex B1 Mapping to Local SAR Estimation for Human Brain MR Imaging Using Multi-Channel Transceiver Coil at 7T. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, A.; Kainz, W.; Hahn, E.G.; Honegger, K.; Zefferer, M.; Neufeld, E.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J.; et al. The Virtual Family–development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 55, N23–N38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandija, S.; Petrov, P.I.; Vink, J.J.; Neggers, S.F.; van den Berg, C.A. Brain Tissue Conductivity Measurements with MR-Electrical Properties Tomography: An In Vivo Study. Brain Topogr. 2020, 34, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, J.; Choi, N.; Woo, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, O.I.; Kim, D.H. Error Analysis of Nonconstant Admittivity for MR-Based Electric Property Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 31, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Mandija, S.; Sbrizzi, A.; Katscher, U.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Berg, C.A. Error Analysis of Helmholtz-Based MR-Electrical Properties Tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H. Redesign of the Laplacian Kernel for Improvements in Conductivity Imaging Using MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lier, A.L.; Brunner, D.O.; Pruessmann, K.P.; Klomp, D.W.; Luijten, P.R.; Lagendijk, J.J.; van den Berg, C.A. Phase Mapping at 7 T and its Application for In Vivo Electrical Conductivity Mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, T.; Katscher, U.; Doessel, O. Quantitative Conductivity and Permittivity Imaging of the Human Brain Using Electric Properties Tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulumulla, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Yeo, T.B.D. Calculation of Electrical Properties from B1+ Maps–a Comparison of Methods. Brain 2012, 68, 66-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; Schmitter, S.; He, B. Determining Electrical Properties Based on B1 Fields measured in an MR Scanner Using a Multi-Channel Transmit/Receive Coil: A General approach. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 4395–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ropella, K.M.; Noll, D.C. A Regularized, Model-Based Approach to Phase-Based Conductivity Mapping Using MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsic, A.; Perreard, I.; Mahara, A.; Halter, R.J. An Inverse Problems Approach to MR-EPT Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 35, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodickson, D.K.; Alon, L.; Deniz, C.M.; Brown, R.; Zhang, B.; Wiggins, G.C.; Cho, G.Y.; Eliezer, N.B.; Novikov, D.S.; Lattanzi, R.; et al. Local Maxwell Tomography Using Transmit-Receive Coil Arrays for Contact-Free Mapping of Tissue Electrical Properties and Determination of absolute RF Phase. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Melbourne, Australia, 5–11 May 2012; p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Sodickson, D.K.; Alon, L.; Deniz, C.M.; Ben-Eliezer, N.; Cloos, M.; Sodickson, L.A.; Collins, C.M.; Wiggins, G.C.; Novikov, D.S. Generalized Local Maxwell Tomography for Mapping of Electrical Property Gradients and Tensors. In Proceedings of the 21th Annual Meeting ISMRM, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 20–26 April 2013; p. 4175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; He, B. Imaging Electric Properties of Biological Tissues by RF Field Mapping in MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduino, A. Mathematical Methods for Magnetic Resonance Based Electric Properties Tomography. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; He, B. Gradient-Based Electrical Properties Tomography (gEPT): A Robust Method for Mapping Electrical Properties of Biological Tissues In Vivo Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; He, B. Simultaneous Quantitative Imaging of Electrical Properties and Proton Density From B1 Maps Using MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 2064–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Adriany, G.; Bischof, J.; van de Moortele, P.F.; He, B. In Vivo Imaging of Electrical Properties of an Animal Tumor Model with an 8-Channel Transceiver Array at 7 T using electrical properties tomography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; He, B. Automated Gradient-Based Electrical Properties Tomography in the Human Brain Using 7 Tesla MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 63, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; Racila, E.; Liu, J.; Bischof, J.; He, B. Mapping Electrical Properties Heterogeneity of Tumor Using Boundary Informed Electrical Properties Tomography (BIEPT) at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafalir, F.S.; Oran, O.F.; Gurler, N.; Ider, Y.Z. Convection-Reaction Equation Based Magnetic Resonance Electrical Properties Tomography (cr-MREPT). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariturk, G.; Ider, Y.Z. Optimal Multichannel Transmission for Improved cr-MREPT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, G.; Ider, Y.Z. Use of Dielectric Padding to Eliminate Low Convective Field Artifact in cr-MREPT Conductivity Images. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 3168–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurler, N.; Ider, Y.Z. Gradient-based Electrical Conductivity Imaging Using MR Phase. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijsen, R.L.; An, X.; Brink, W.M.; Webb, A.G.; Remis, R.F. Transverse-EPT: A Local First Order Electrical Properties Tomography Approach Free of Incident Fields. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Meeting of ISMRM Benelux, Arnhem, The Netherlands, 24 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- van den Bergen, B.; Stolk, C.C.; van den Berg, J.B.; Lagendijk, J.J.W.; van den Berg, C.A.T. Ultra Fast Electromagnetic Field Computations for RF Multi-Transmit Techniques in High Field MRI. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.K.; Zak, S.H. An Introduction to Optimization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, P.S.; Mandija, S.; Stijnman, P.R.; Brink, W.M.; van den Berg, C.A.; Remis, R.F. First-Order Induced Current Density Imaging and Electrical Properties Tomography in MRI. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2018, 4, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, M.; Nara, T. A Boundary-Value-Free Reconstruction Method for Magnetic Resonance Electrical Properties Tomography Based on the Neumann-Type Integral Formula over a Circular Region. SICE J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2017, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, M.; Nara, T. Boundary Value-Free Magnetic Resonance Electrical Properties Tomography Based on the Generalized Cauchy Formula with the Complex-Derivative Boundary Condition. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M Pier M 2020, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, M.; Nara, T. Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Electrical Properties Tomography Based on Linear Integral Equation Derived from the Generalized Cauchy Formula. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C Pier C 2020, 105, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, T.; Furuichi, T.; Fushimi, M. An Explicit Reconstruction Method for Magnetic Resonance Electrical Property Tomography Based on the Generalized Cauchy Formula. Inverse Probl. 2017, 33, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. 3-D MRI-based Electrical Properties Tomography Using the Volume Integral Equation Method. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 4802–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, R.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. Three-Dimensional MR Reconstruction of High-Contrast Magnetic Susceptibility by the Variational Born Iterative Method Based on the Magnetic Field Volume Integral Equation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrallés, J.E.; Daniel, L.; White, J.K.; Sodickson, D.K.; Lattanzi, R.; Polimeridis, A.G. Global Maxwell Tomography: A Novel Technique for Electrical Properties Mapping Based on MR Measurements and Volume Integral Equation Formulations. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, Puerto Rico, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1395–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Serrallés, J.E.; Giannakopoulos, I.; Zhang, B.; Ianniello, C.; Cloos, M.A.; Polimeridis, A.G.; White, J.K.; Sodickson, D.K.; Daniel, L.; Lattanzi, R. Noninvasive Estimation of Electrical Properties from Magnetic Resonance Measurements via Global Maxwell Tomography and Match Regularization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakopoulos, I.I.; Serrallés, J.E.; Daniel, L.; Sodickson, D.K.; Polimeridis, A.G.; White, J.K.; Lattanzi, R. Magnetic-Resonance-Based Electrical Property Mapping Using Global Maxwell Tomography with an 8-Channel Head Coil at 7 Tesla: A Simulation Study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polimeridis, A.G.; Villena, J.F.; Daniel, L.; White, J.K. Stable FFT-JVIE Solvers for Fast Analysis of Highly Inhomogeneous Dielectric Objects. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 269, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijsen, R.L.; Brink, W.M.; Van Den Berg, C.A.; Webb, A.G.; Remis, R.F. 3-D Contrast Source Inversion-Electrical Properties Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijsen, R.; Fuchs, P.; Brink, W.; Webb, A.; Remis, R. Developments in Electrical-Property Tomography Based on the Contrast-Source Inversion Method. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Webb, A. A New Approach for Electrical Properties Estimation Using a Global Integral Equation and Improvements Using High Permittivity Materials. J. Magn. Reson. 2016, 262, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jin, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S. An Efficient Integral-Based Method for Three-Dimensional MR-EPT and the Calculation of the RF-Coil-Induced Bz Field. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 65, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jin, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S. Reference-Based Integral MR-EPT: Simulation and Experiment Studies at 9.4 T MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Li, M.; Nguyen, P.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S. Integral MR-EPT with the Calculation of Coil Current Distributions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balidemaj, E.; van den Berg, C.A.T.; Trinks, J.; van Lier, A.L.H.M.W.; Nederveen, A.J.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Crezee, H.; Remis, R.F. CSI-EPT: A Contrast Source Inversion Approach for Improved MRI-Based Electric Properties Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2015, 34, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduino, A.; Chiampi, M.; Zilberti, L.; Bottauscio, O. Alternative Approaches to Magnetic Resonance-Based Electric Properties Tomography and Local Specific Absorption Rate Estimation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino, A.; Zilberti, L.; Chiampi, M.; Bottauscio, O. CSI-EPT in Presence of RF-Shield for MR-Coils. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2017, 36, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino, A.; Chiampi, M.; Pennecchi, F.; Zilberti, L.; Bottauscio, O. Monte Carlo Method for Uncertainty Propagation in Magnetic Resonance-Based Electric Properties Tomography. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Stijnman, P.R.; Mandija, S.; Fuchs, P.S.; van den Berg, C.A.; Remis, R.F. Transceive Phase Corrected Contrast Source Inversion-Electrical Properties Tomography. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.13451. [Google Scholar]
- Balidemaj, E.; van den Berg, C.A.T.; van Lier, A.L.H.M.W.; Nederveen, A.J.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Crezee, H.; Remis, R.F. B1-Based SAR Reconstruction Using Contrast Source Inversion-Electric Properties Tomography (CSI-EPT). Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino, A.; Bottauscio, O.; Chiampi, M.; Zilberti, L. Magnetic Resonance-Based Imaging of Human Electric Properties with Phaseless Contrast Source Inversion. Inverse Probl. 2018, 34, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, M.T.; Bellizzi, G.G.; Crocco, L.; Isernia, T. A Method for Quantitative Imaging of Electrical Properties of Human Tissues from Only Amplitude Electromagnetic Data. Inverse Probl. 2019, 35, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, M.T.; Bellizzi, G.G.; Isernia, T.; Crocco, L. A Method for Effective Permittivity and Conductivity Mapping of Biological Scenarios via Segmented Contrast Source Inversion. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Pier 2019, 164, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.P.; Sodickson, D.K.; Ipek, O.; Collins, C.M.; Gruetter, R. Single Acquisition Electrical Property Mapping Based on Relative Coil Sensitivities: A Proof-of-Concept Demonstration. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Bulumulla, S.; Wiesinger, F.; Sacolick, L.; Sun, W.; Hancu, I. Tissue Electrical Property Mapping from Zero Echo-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, M.O.; Cho, S.; Kim, D.H. Fast Spin Echo Imaging-Based Electric Property Tomography with K-Space Weighting via T2 Relaxation (rEPT). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soullié, P.; Missoffe, A.; Ambarki, K.; Felblinger, J.; Odille, F. MR Electrical Properties Imaging Using a Generalized Image-Based Method. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Huerta, E. Deep Learning for Real-Time Gravitational Wave Detection and Parameter Estimation: Results with Advanced LIGO Data. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 778, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamary, R. Astronomical Image Reconstruction with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Kos, Greece, 28 August–2 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2468–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An Overview of Deep Learning in Medical Imaging Focusing on MRI. Z. Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.G.; Teixeira, F.L.; Liu, C.; Nehorai, A.; Cui, T.J. DeepNIS: Deep Neural Network for Nonlinear Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 67, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliadò, E.F.; Raaijmakers, A.J.E.; Sbrizzi, A.; Steensma, B.R.; Maspero, M.; Savenije, M.H.F.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Berg, C.A.T. A Deep Learning Method for Image-Based Subject-Specific Local SAR assessment. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mandija, S.; Meliadò, E.F.; Huttinga, N.R.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Berg, C.A. Opening a New Window on MR-Based Electrical Properties Tomography with Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampe, N.; Katscher, U.; Van den Berg, C.A.T.; Tha, K.K.; Mandija, S. Investigating the Challenges and Generalizability of Deep Learning Brain Conductivity Mapping. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavazzi, S.; van den Berg, C.A.T.; Savenije, M.H.F.; Kok, H.P.; de Boer, P.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Lagendijk, J.J.W.; Crezee, H.; van Lier, A.L.H.M.W. Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction of In Vivo Pelvis Conductivity with a 3D Patch-Based Convolutional Neural Network Trained on Simulated MR Data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijsen, R.; van den Berg, C.; Webb, A.; Remis, R.; Mandija, S. Combining Deep Learning and 3D Contrast Source Inversion in MR-Based Electrical Properties Tomography. NMR Biomed. 2019, e4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J.; Öktem, O. Learned Primal-Dual Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2018, 37, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Taviani, V.; Malkiel, I.; Cheng, J.Y.; Tamir, J.I.; Shaikh, J.; Chang, S.T.; Hardy, C.J.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S. Variable-Density Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MRI with Deep Learning Reconstruction by Using Variational Networks. Radiology 2018, 289, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lønning, K.; Putzky, P.; Sonke, J.J.; Reneman, L.; Caan, M.W.; Welling, M. Recurrent Inference Machines for Reconstructing Heterogeneous MRI Data. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammernik, K.; Klatzer, T.; Kobler, E.; Recht, M.P.; Sodickson, D.K.; Pock, T.; Knoll, F. Learning a Variational Network for Reconstruction of Accelerated MRI Data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, F.; Hammernik, K.; Kobler, E.; Pock, T.; Recht, M.P.; Sodickson, D.K. Assessment of the Generalization of Learned Image Reconstruction and the Potential for Transfer Learning. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Gong, E.; Chatnuntawech, I.; Bilgic, B.; Lee, J.; Jung, W.; Ko, J.; Jung, H.; Setsompop, K.; Zaharchuk, G.; et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Using Deep Neural Network: QSMnet. Neuroimage 2018, 179, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; Bollmann, S.; Lee, J. Overview of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Using Deep Learning: Current Status, Challenges and Opportunities. NMR Biomed. 2020, e4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).