Abstract
In the inspired extension of the minimal supersymmetric (SUSY) standard model (MSSM), a single discrete symmetry permits suppressing rapid proton decay and non-diagonal flavor transitions. If matter parity and symmetry are preserved in this SUSY model (SESSM), it may involve two dark matter candidates. In this article, we study a new modification of the SESSM in which the cold dark matter is composed of gravitino and the lightest neutral exotic fermion. We argue that, in this case, the dark matter nucleon scattering cross-section can be considerably smaller than the present experimental limit.
1. Introduction
The possible unification of all interactions remains one of the most appealing motivations for studying supersymmetric (SUSY) extensions of the Standard Model (SM). At very high energies, the minimal supersymmetric standard model (MSSM) and its extensions can be embedded into Grand Unified Theories (GUTs). In SUSY GUTs based on the gauge group, all SM bosons and fermions can belong to a single 248 representation of . This representation involves three , which are fundamental and anti-fundamental representations of , adjoint 78 representation of and 8 components that do not participate in the gauge interactions. In SUSY GUTs, three fundamental representations of may include Higgs doublet and three families of the SM fermions. The SM gauge bosons are contained in the adjoint representation of . It is expected that near the scale the extended SUSY is broken down to supersymmetry while the breakdown of (or ) gauge group can lead to
where is a SM gauge group.
The exceptional supersymmetric standard model (ESSM) [1,2] (for recent review, see Ref. [3]) implies that around the GUT scale rank-6 model with two extra symmetries and is reduced further to an effective rank-5 model based on the SM gauge group together with an additional factor, i.e.,
where is the so-called matter parity, which is a discrete subgroup of and . In Equation (2) the gauge symmetry is defined as
In these inspired extensions of the MSSM the right-handed neutrinos do not participate in the gauge interactions and may be superheavy [1,2]. Therefore, a see-saw mechanism can be used to shed light on the origin of the mass hierarchy in the lepton sector, providing a comprehensive understanding of the neutrino oscillations data. The successful leptogenesis is a distinctive feature of the extensions of the MSSM because the heavy Majorana right-handed neutrinos may decay into final states with lepton number , creating a lepton asymmetry in the early Universe [4,5].
In the inspired extensions of the MSSM gauge anomalies become cancelled if the particle spectrum at low-energies contains complete representations of . To ensure that the ESSM is anomaly-free one is forced to extend the minimal matter content by extra matter beyond the MSSM which, together with ordinary SM fermions, form three complete 27-plets of ( with ). Each 27-dimensional representations of involves one generation of ordinary matter, a SM singlet field , that carries non-zero charge, up- and down-type Higgs doublets and , as well as charged exotic quarks and . The presence of extra exotic matter may give rise to non-diagonal flavor transitions and rapid proton decay. In the ESSM a set of discrete symmetries can be used to suppress the corresponding operators [1,2].
In this article, we examine the dark matter-nucleon scattering cross section within the modification of the ESSM (SESSM) [6,7] in which a single discrete symmetry forbids tree-level flavor-changing transitions, as well as the most dangerous baryon and lepton number violating operators. The conservation of symmetry and matter parity/R-parity implies the existence of at least two stable states that may account for all or some of the observed cold dark matter density. At the same time null results from direct detection experiments [8,9,10] placed stringent limits on the dark matter nucleon scattering cross-section. Here, we explore a new variant of the SESSM in which two stable states are gravitino and the lightest neutral exotic fermion. In general, the spin-independent part of the dark matter-nucleon scattering cross section can be much larger in this case than the corresponding experimental limit. Nevertheless, the results of our analysis indicate that there is a part of the SESSM parameter space, in which this cross section is sufficiently strongly suppressed.
2. The SESSM
Since 2006, several modifications of the ESSM have been explored [1,2,6,7,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. The implications of the extensions of the MSSM were considered for Z– mixing [20], neutralino sector [20,21,22], electroweak (EW) symmetry breaking (EWSB) [21,23,24], the renormalization group (RG) flow of couplings [21,25], the renormalization of vacuum expectation values (VEVs) [26,27], non-standard neutrino models [28], and dark matter [19,29,30]. Within the ESSM, the upper bound on the lightest Higgs mass near the quasi-fixed point was examined in [31]. The corresponding quasi-fixed point is an intersection of the invariant and quasi-fixed lines [32,33]. The particle spectrum in the constrained ESSM (cESSM) and its modifications was analyzed in [34,35,36,37]. The degree of fine tuning and threshold corrections were explored in Refs. [38,39] and [40], respectively. Extra exotic matter in the ESSM may result in distinctive LHC signatures [1,2,12,15,41,42,43,44] and can give rise to non-standard Higgs decays [7,45,46].
The SESSM implies that below the scale three complete 27–plets are accompanied by SM singlet superfield , which does not participate in the interactions, and a set of pairs of supermultiplets and , which belong to additional and representations, respectively. Because and carry opposite quantum numbers gauge anomalies still cancel. In the simplest case, the set of and involves three pairs of doublets, i.e., and , and , and , as well as a pair of superfields, S and . The field content of the SESSM may originate from the orbifold GUT model in six dimensions in which the appropriate splitting of the bulk supermultiplets can be achieved [6].
The supermultiplets , S, , , , , and are required to be even under the custodial symmetry whereas all other supermultiplets are odd [7]. In the SESSM superpotential, the symmetry allows the interactions that comes from and but it forbids all terms which originate from , where indexes are associated with the supermultiplets while family indexes run over three generations. Such structure of the superpotential ensures that it does not involve any operators that give rise to rapid proton decay. Because the set of supermultiplets includes only two Higgs doublets and , the up-type quarks couple to just , whereas the down-type quarks and charged leptons couple to only. Therefore, the flavor-changing processes are suppressed in the SESSM at tree-level.
In the simplest scenario and become combined with the superposition of the corresponding components from the , forming vector-like states with masses of order . The components of the supermultiplets and , as well as S and are expected to gain the TeV scale masses. The presence of and at low energies permits the lightest exotic quarks to decay within a reasonable time, as well as facilitates the gauge coupling unification [25] and the generation of the baryon asymmetry of the Universe [5].
Using the method discussed in [47], it was revealed that in the ESSM and its simplest modifications the lightest R-parity odd states (lightest SUSY particles) have to be lighter than 60–65 GeV [46]. These states are predominantly linear superpositions of the fermion components of the superfields . Although the couplings of these lightest exotic fermions to the SM particles are very small the lightest SUSY particle (LSP) could account for some of the cold dark matter relic density if the LSP had a mass close to half the Z boson mass [46]. However, in this case the SM-like Higgs boson decays mostly into the lightest exotic fermions whereas its other branching ratios are suppressed. LHC experiments have already excluded such a scenario. When the lightest exotic fermions are substantially lighter than , the LSP annihilation cross section tends to be too small resulting in too large cold dark matter density. In the simplest phenomenologically viable scenario, the sparticle spectrum of the SESSM includes the lightest SUSY particles with masses which are much smaller than . These lightest exotic fermions form hot dark matter in our Universe. Nevertheless, they give a minor contribution to the total density of dark matter. The existence of neutral fermions with tiny masses may lead to very interesting implications for the neutrino physics [48].
The variant of the SESSM explored here implies that in addition to all states mentioned above the low-energy matter content of the model involves at least three singlet superfields which are odd under the symmetry. This allows to avoid the appearance of the lightest exotic fermions with tiny masses in the particle spectrum. It is expected that the components of the supermultiplets
where and , have masses either of the order of or considerably lower. The right-handed neutrino superfields are assumed to be much heavier then . The and charges of all matter supermultiplets in the SESSM are summarised in Table 1.

Table 1.
The and charges of matter supermultiplets in the SESSM. The superfields , , and have zero and charges.
Integrating out the right-handed neutrino superfields and neglecting all suppressed non-renormalisable interactions, the low-energy superpotential of the new variant of the SESSM can be written as
It is worth noting that the extra gauge symmetry forbids the term in the superpotential (5), but allows all other terms in . In Equation (5) the part of the superpotential describes the interactions of , , and with the even supermultiplets , S, , , and .
The sector responsible for the breakdown of the gauge symmetry in the SESSM is formed by the scalar components of , S, , , and . In the limit the D-term contribution to the effective scalar potential can force the minimum of such potential to be along the D-flat direction [49]. Indeed, if the coupling vanishes the part of the scalar potential that depends on S and takes the form
where is the charge of S and , is the gauge coupling whereas and are the soft SUSY breaking mass parameters. The last term in Equation (7) is associated with the D-term contribution. For the quartic term vanishes. If, in this case , then the scalar potential (7) has a run-away direction . The F-term contribution to the scalar potential (7) induced by the small coupling stabilizes the run-away direction so that the SM singlet superfields acquire VEVs which are much larger than the sparticle mass scale , i.e.,
resulting in an extremely heavy boson. All extra exotic states can be also rather heavy in this limit.
The conservation of and symmetries implies that R-parity and symmetry are also conserved where [6]. The transformation properties of different supermultiplets under the , and symmetries are summarized in Table 2. Here, we assume that gravitino is the lightest R-parity odd state. Therefore, it has to be stable and potentially contributes to the density of dark matter. There is a large class of models in which gravitino can be much lighter than the superpartners of other particles [50,51,52,53]. Recently, the cosmological implications of the gravitino with mass were discussed in Ref. [54]. Since gravitino is the lightest SUSY particle with the lightest exotic state with must be absolutely stable as well [6].

Table 2.
Transformation properties of different supermultiplets under the discrete symmetries , and . The signs + and − correspond to the states which are even and odd under different symmetries.
The scalar components of the supermultiplets , , , and do not develop VEVs. Their fermion components compose the exotic chargino and neutralino states. In the limit, when all components of are considerably heavier than the bosons and fermions from the supermultiplets , , and , the superfields can be integrated out so that the part of the SESSM superpotential reduces to:
Hereafter, we use the field basis in which and .
In this article, we focus on the scenarios in which the lightest exotic state with is predominantly formed by the fermion components of the supermultiplets and while all sparticles except gravitino and all other exotic states have masses which are much larger than . If and mostly interact with , and , whereas all other couplings of and are negligibly small, the part of the mass matrix, that determines the masses of the lightest exotic neutralino states, can be written in the following form:
where , and are the VEVs of the Higgs doublets and , i.e., and . Instead of and it is more convenient to use and . Hereafter, we neglect the contribution of loop corrections to the mass matrix (10). In this case, the mass of the charged fermion components of and is determined by , i.e., .
When is much larger than and v, the perturbation theory method can be used to diagonalise the mass matrix (10) (see, for example, [55,56,57,58]). This method yields
From Equation (11), it follows that the masses of the lightest exotic chargino and neutralino states in the leading approximation are set by . If the mass difference is as small as , the inelastic scattering processes , where N is a nucleon, may occur. In this article, we restrict our consideration to the part of the SESSM parameter space where . Because of this the inelastic scattering processes do not take place. Moreover, the lifetime of is much smaller than that allows to preserve the success of the Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN).
In the scenarios under consideration, the contribution of the lightest neutral exotic fermion to the cold dark matter relic density can be estimated using the approximate formula:
which was derived in the case of the Higgsino dark matter within the MSSM (see, for example, [59,60]). Because the Planck observations lead to [61]:
in the phenomenologically viable scenarios is expected to be lower than . If then gravitino may account for some or major part of the observed cold dark matter density.
In general, to find a viable cosmological scenario with stable gravitino one has to ensure that the decay products of the lightest unstable R-parity odd (or exotic) particle Y do not alter the abundances of light elements induced by BBN. The decays of state Y change the abundances of light elements the more the longer its lifetime is. This problem can be evaded if sparticle Y decays before BBN, i.e., . The lifetime of state Y decaying into its SM partner (or lightest exotic fermion) and gravitino can be estimated as [62]:
where is its mass and is the reduced Planck mass. In order to obtain for we should restrict our consideration to .
If gravitinos mostly originate from scattering processes of particles in the thermal bath then their abundance is approximately proportional to the reheating temperature after inflation. In the leading approximation one finds [63,64]:
where is a gluino mass. Taking into account that , for and one obtains an upper bound on the reheating temperature, i.e., [65]. However even for so low reheating temperatures the appropriate amount of the baryon asymmetry can be induced within the SESSM via the decays of the lightest right-handed neutrino/sneutrino into exotic states [5].
3. Dark Matter Nucleon Scattering Cross-section
Since the couplings of gravitino to the SM particles are negligibly small, in the scenarios under consideration the interactions of the cold dark matter with the baryons are determined by the couplings of the lightest neutral exotic fermion . The low energy –quark effective Lagrangian is:
The first term in the brackets gives rise to a spin-independent interaction, while the second one is associated with a spin-dependent interaction.
For spin-independent interactions experiments quote the cross-section to scatter off a nucleon, which is given by [66,67]:
where A and Z are the nucleon number and charge of the target nucleus, whereas and are related to the quantities entering . To simplify our analysis, we assume that while:
From Equations (17) and (18), one can see that depends rather strongly on the hadronic matrix elements, i.e., the coefficients , which are related to the -nucleon term and the spin content of the nucleon. Here, we set , , and . These values of the hadronic matrix elements are the default values used in micrOMEGAs, as determined in Ref. [68] from lattice results (see also Refs. [69,70,71,72]).
Because in the SESSM the exotic neutralino states do not couple to quarks and squarks, the coefficients receives only contributions from the t-channel exchange of CP-even Higgs bosons. In the scenarios under consideration, the mass of the lightest Higgs particle is much smaller than the masses of all other Higgs bosons. Therefore, in our analysis we ignore all contributions induced by the heavy Higgs exchange. Moreover, in this case, the lightest Higgs scalar manifests itself in the interactions with the SM fermions and gauge bosons as a SM-like Higgs so that:
When the coupling of the SM-like Higgs to the lightest exotic neutralino is given by:
The dominant contribution to the coefficients in Equation (16) comes from t-channel Z boson exchange. In the field basis , the two lightest exotic neutralinos are made up of the following superposition of interaction states:
where . In Equation (21), is the exotic neutralino mixing matrix defined by:
where is exotic neutralino mass matrix given by Equation (10). Using the above compositions of the lightest exotic neutralino states (21), it is straightforward to derive the couplings of these states to the Z-boson. The part of the Lagrangian that describes the interactions of Z with and can be written as:
Then, the coefficients and the corresponding cross-section can be presented in the following form:
where is the third component of isospin. For fractions of the nucleon spin carried by a given quark q we use (see also [60])
Using the compositions of and one can obtain the analytical expressions for the couplings of these states to the lightest Higgs boson, i.e.,
The perturbation theory method allows to compute the entries of the exotic neutralino mixing matrix . Substituting into Equation (26) one can reproduce the analytical Formula (20) for and find the approximate expression for . If and is larger than and , we get:
Here, we restrict our considerations to low values of . In this case, the particle spectrum of the SESSM may include the SM-like Higgs state with mass around 125 GeV if . Indeed, in this SUSY model the upper bound on the lightest Higgs boson mass is given by:
where and are the charges of and whereas is the contribution of loop corrections. When the sum of the first two terms can be larger than for moderate values of . As a consequence, for the Higgs state can be obtained. In this part of the SESSM parameter space, all Higgs states except the lightest Higgs boson tend to have masses beyond the multi-TeV range and cannot be observed at the LHC experiments [1,2,41,42].
Within the SESSM the masses of new exotic states including the boson are set by the VEVs of S and . LHC constraints require the extra gauge boson to be heavier than [73,74]. When for the mass of the extra vector boson one finds:
In order to obtain we choose . The experimental constraints on mixing are also satisfied in this case. To avoid the experimental lower limit on the mass of the lightest exotic chargino and to ensure that the lightest exotic neutralino state gives rise to the phenomenologically acceptable dark matter density the interval of variation of is chosen so that and . This corresponds to relatively small values of . To simplify our analysis we set . In addition, we also require the validity of perturbation theory up to the scale that, in particular, constrains the allowed range of and .
The results of our analysis are summarised in Figure 1 and Figure 2. From the approximate expressions (20) and (27), it follows that the couplings and vanish if . In other words, the interactions of the lightest exotic neutralino with the baryons can be extremely weak in some part of the SESSM parameter space. Our numerical analysis indicates that the perturbation theory method describes the dependence of and on the SESSM parameter quite well when is sufficiently large (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). In particular, and grow whereas and diminish with increasing from to . Since in the scenario under consideration is chosen to be negative while is positive, and , as well as the spin-dependent and spin-independent cross sections decreases when grows.
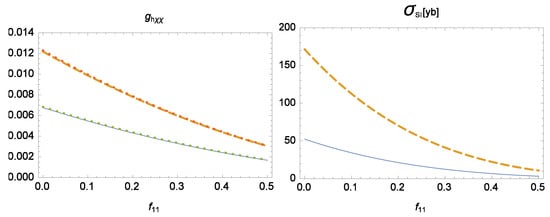
Figure 1.
(Left) The coupling and (Right) the cross-section as a function of for , , , (solid lines), and (dashed lines). The dotted lines correspond to the approximate expression for (20).
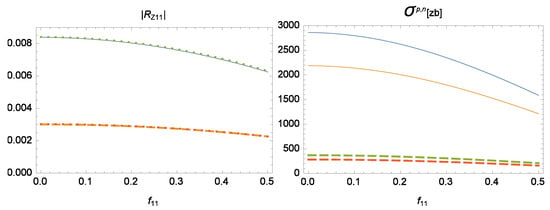
Figure 2.
(Left) The coupling and (Right) the cross-section as a function of for , , , (solid lines), and (dashed lines). The upper solid and upper dashed lines represent while lower solid and lower dashed lines are associated with . The dotted lines correspond to the approximate expression for (27).
The calculated values of and should be compared with the corresponding experimental limits. For the value of can be substantially smaller than that leads to some reduction in the number density of the lightest neutral exotic fermions. Thereby, the direct detection limits become weakened, i.e.,
where , and are computed values of these quantities for each set of the parameters of the SESSM, while and are the experimental limits on the spin-independent and spin-dependent cross-sections at the given mass . Any set of the SESSM parameters that does not satisfy the conditions (30) is basically ruled out. Hereafter, we just compare and with and .
The spin-independent cross-sections shown in Figure 1 remain always smaller than for and for () which are the values of obtained by the LUX–ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment [10]. The most stringent experimental upper bound on the WIMP-proton spin-dependent cross-section was set by the PICO-60 experiment [75]. For equals to () the value of , where . The WIMP-neutron spin-dependent cross-section is more tightly constrained. If the LZ experiment set the experimental limit [10]. All experimental bounds on the spin-dependent cross sections mentioned here are substantially larger than the values of presented in Figure 2.
In the part of the SESSM parameter space, where and become smaller than , one cannot ignore quantum corrections to the effective Lagrangian (16) which are induced by the one-loop diagrams involving the electroweak gauge bosons [76,77]. The inclusion of such corrections results in even when at the tree level [78].
The values of and presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2 are substantially smaller than the maximal possible values of the spin-dependent and spin-independent -nucleon scattering cross-sections in the SESSM. In the part of the parameter space examined in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the suppression of and is caused by the large value of , which is associated with the sparticle mass scale, as well as by the partial cancellations of different contributions to and . The maximal possible values of and are attained when and . In this case, the spin-independent -nucleon scattering cross section can reach 20–30 zb which is two orders of magnitude larger than the present experimental limit on [10]. However, even when , the desirable suppression of can be achieved if .
4. Conclusions
To ensure anomaly cancellation the extensions of the MSSM (ESSM) are expected to include at least three fundamental representations of below the GUT scale . These fundamental representations of , in particular, contain three families of Higgs-like doublets and . One pair of such Higgs-like doublet supermultiplets ( and ) gains VEVs resulting in the breakdown of the EW symmetry, while two other families ( and , where ) are normally assumed to be inert.
In addition to three 27-plets the low-energy matter content of the SESSM also involves an singlet superfield , a pair of superfields S and with opposite charges, as well as a pair of doublets and with opposite quantum numbers. The supermultiplets S, , and can come from additional and . Within the SESSM a single symmetry prevents rapid proton decay and tree-level non-diagonal flavor transitions. In this paper, we have considered new variant of this SUSY model in which the low-energy particle spectrum is supplemented by three singlet superfields which are odd under the symmetry. This permits to avoid the presence of neutral exotic fermions with tiny masses () in the spectrum of the SESSM. The scalar components of the even superfields , S and may acquire very large VEVs, i.e., , breaking the gauge symmetry and generating masses of all extra exotic fermions which can be much heavier than all SM particles.
The conservation of R–parity and the symmetry within the SESSM ensures that at least two neutral states can be stable, giving rise to dark matter density. Since no firm indication of the presence of dark matter has been observed at the direct detection experiments we assume that one of the stable states is gravitino with mass . Another stable state can be the lightest exotic fermion which is mostly composed of the neutral fermion components of the supermultiplets and . In this case, the lightest and second lightest exotic neutralino states ( and ), as well as the lightest exotic chargino are almost degenerate. If these exotic fermions have masses below they can lead to the phenomenologically acceptable density of the dark matter.
The interactions of dark matter with the baryons are defined by the couplings of because the interaction of gravitino with the SM fermions and bosons is extremely weak. In this article, we have explored the scenario in which all scalars and exotic fermions except the lightest Higgs boson, gravitino, , , and have masses of the order of a few TeV or even higher. Therefore, the spin-dependent and spin-independent -nucleon cross-sections ( and ) are dominated by the t-channel exchanges of the Z boson and the lightest Higgs scalar, respectively. Our analysis revealed that for a fixed mass of the lightest exotic fermion the values of and vanish in the leading approximation if . As a result for a given the spin-independent -nucleon cross-section varies from its maximal value, which is about 20–30 zb, to zero. When so that and , one cannot ignore the contributions to and induced by the t-channel exchanges of the heavy Higgs states. Moreover, in this case, one has to take into account the quantum corrections to the effective Lagrangian (16), which is beyond the scope of the present paper. Nevertheless, the results presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2 demonstrate that there is a part of the SESSM parameter space in which and can be considerably smaller than the corresponding experimental limits. In particular, the spin-independent dark matter nucleon scattering cross section may be less than . In the near future, the experiments XENONnT [79], LZ [80], DarkSide-20k [81], and DARWIN [82] may set even more stringent bounds on the spin-dependent and spin-independent WIMP-nucleon scattering cross-sections constraining further the SESSM parameter space.
As mentioned before, the scenario under consideration implies that two lightest exotic neutralino states and the lightest exotic chargino must be lighter than . Several collider experiments have searched for such particles. However, if the mass splitting between these states is small the decay products of and are very soft and may escape detection. This happens, for example, with the lightest ordinary neutralino and chargino states within natural SUSY, where the splitting between the heavier neutralino or the chargino and the LSP is at least a few GeV [83,84,85]. In this case, the results of the search for the lightest exotic fermions depend on .
At the LHC the pair production of such states can occur through off-shell W and Z bosons. ATLAS excluded the exotic chargino with masses below and for and , respectively [86], while CMS ruled out such chargino with masses below for [87]. On the other hand, if the exotic charginos may be long-lived. When their lifetime is longer than the time needed to pass through the detector, these states appear as charged stable massive particles. LHC experiments excluded such charginos with masses below [88].
The last experimental limit is not applicable in the case of the SESSM scenario discussed here because tends to be larger than [78,89]. The part of the SESSM parameter space explored in Figure 1 and Figure 2 is associated with relatively small mass splitting between , , and . For the value of estimated using Equation (11) changes from to when increases from 0 to . As a consequence the lightest exotic chargino decays mainly into hadrons and the lightest exotic neutralino so that it seems to be rather problematic to discover the set of these states at hadron colliders. The discovery prospects for such fermions at future International Linear Collider look more promising (for a review see [90]).
Thus, in this article we argued that within the new variant of the SESSM, in which the cold dark matter density is formed by two stable states, there are some regions of the parameter space that are safe from all current constraints. The SUSY model under consideration predicts the existence of exotic fermions and exotic scalars which are colored and carry baryon and lepton numbers simultaneously [6]. In collider experiments, such exotic quarks/squarks can only be created in pairs. The stringent LHC lower limits on the masses of scalar leptoquarks [91,92,93] are not directly applicable in the case of the SESSM. Indeed, in the inspired SUSY models ordinary scalar leptoquark can decay either to an up-type quark and charged lepton or to down-type quark and left-handed neutrino . On the other hand, in the SESSM the lightest exotic colored particle (scalar or fermion) is odd under symmetry. Therefore, its decay always gives rise to the missing energy and transverse momentum in the final state associated with the lightest exotic fermion, i.e.,
Here, X may include extra charged leptons and/or jets that can come from the decays of intermediate states. Although the masses of the exotic colored particles are expected to be in the multi TeV range can be lighter than . If is exotic colored fermion the LHC pair production cross section for decreases from to when its mass changes from to [94]. The LHC pair production cross-section for the lightest exotic squarks tends to be an order of magnitude smaller. The pair production of may lead to some enhancement of the cross sections of and if such states are relatively light. The discovery of these exotic colored states will provide a smoking gun signal of the model allowing to distinguish it from other extensions of the SM.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
R.N. thanks X. Tata for very valuable comments and remarks. R.N. acknowledges fruitful discussions with S. Khalil, S. Moretti, H. Waltari, and P. V. Zinin.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Theory and phenomenology of an exceptional supersymmetric standard model. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Exceptional supersymmetric standard model. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 634, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. A Review of the Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model. Symmetry 2020, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambye, T.; Ma, E.; Raidal, M.; Sarkar, U. Allowable low-energy E(6) subgroups from leptogenesis. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 512, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nevzorov, R. Leptogenesis as an origin of hot dark matter and baryon asymmetry in the E6 inspired SUSY models. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 779, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Nevzorov, R. E6 inspired supersymmetric models with exact custodial symmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 015029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Mühlleitner, M.; Nevzorov, R.; Williams, A.G. Non-Standard Higgs Decays in U(1) Extensions of the MSSM. J. High Energy Phys. 2015, 1501, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aprile, E. et al. [XENON Collaboration] Dark Matter Search Results from a One Ton-Year Exposure of XENON1T. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y. et al. [PandaX-4T Collaboration] Dark Matter Search Results from the PandaX-4T Commissioning Run. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 261802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalbers, J.; Akerib, D.S.; Akerlof, C.W.; Musalhi, A.K.A.; Alder, F.; Alqahtani, A.; Alsum, S.K.; Amarasinghe, C.S.; Ames, A.; Anderson, T.J.; et al. First Dark Matter Search Results from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Experiment. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.03764. [Google Scholar]
- Howl, R.; King, S.F. Planck Scale Unification in a Supersymmetric Standard Model. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 652, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howl, R.; King, S.F. Minimal E6 Supersymmetric Standard Model. J. High Energy Phys. 2008, 0801, 030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howl, R.; King, S.F. Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Models with non-Abelian Discrete Family Symmetry. J. High Energy Phys. 2008, 0805, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howl, R.; King, S.F. Solving the Flavour Problem in Supersymmetric Standard Models with Three Higgs Families. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 687, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Athron, P.; Hall, J.P.; Howl, R.; King, S.F.; Miller, D.J.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Aspects of the Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 2010, 200–202, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.P.; King, S.F. Bino Dark Matter and Big Bang Nucleosynthesis in the Constrained E6SSM with Massless Inert Singlinos. J. High Energy Phys. 2011, 1106, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, J.C.; King, S.F. E6 Models from F-theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 1304, 034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, J.C.; King, S.F.; Leontaris, G.K. Gauge coupling unification in E6 F-theory GUTs with matter and bulk exotics from flux breaking. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 1312, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; Moretti, S.; Rojas-Ciofalo, D.; Waltari, H. Multicomponent dark matter in a simplified E6SSM. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 075039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, D. Neutralino decay in the mu problem solvable extra U(1) models. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 57, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, E.; Ma, E. Generic consequences of a supersymmetric U(1) gauge factor at the TeV scale. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, E.; Ma, E. Efficacious Extra U(1) Factor for the Supersymmetric Standard Model. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suematsu, D.; Yamagishi, Y. Radiative symmetry breaking in a supersymmetric model with an extra U(1). Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1995, 10, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daikoku, Y.; Suematsu, D. Mass bound of the lightest neutral Higgs scalar in the extra U(1) models. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Gauge coupling unification in the exceptional supersymmetric standard model. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 650, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sperling, M.; Stöckinger, D.; Voigt, A. Renormalization of vacuum expectation values in spontaneously broken gauge theories. J. High Energy Phys. 2013, 1307, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, M.; Stöckinger, D.; Voigt, A. Renormalization of vacuum expectation values in spontaneously broken gauge theories: Two-loop results. J. High Energy Phys. 2014, 1401, 068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E. Neutrino masses in an extended gauge model with E(6) particle content. Phys. Lett. B 1996, 380, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.P.; King, S.F. Neutralino Dark Matter with Inert Higgsinos and Singlinos. J. High Energy Phys. 2009, 0908, 088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Thomas, A.W.; Underwood, S.J.; White, M.J. Dark matter candidates in the constrained Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 035023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorov, R. Quasifixed point scenarios and the Higgs mass in the E6 inspired supersymmetric models. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorov, R.; Trusov, M.A. Infrared quasifixed solutions in the NMSSM. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2001, 64, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nevzorov, R.; Trusov, M.A. Quasifixed point scenario in the modified NMSSM. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2002, 65, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Athron, P.; King, S.F.; Miller, D.J.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. The Constrained E6SSM. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0810.0617. [Google Scholar]
- Athron, P.; King, S.F.; Miller, D.J.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Constrained Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model with a Higgs Near 125 GeV. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 095003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Harries, D.; Nevzorov, R.; Williams, A.G. E6 Inspired SUSY benchmarks, dark matter relic density and a 125 GeV Higgs. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 760, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Harries, D.; Nevzorov, R.; Williams, A.G. Dark matter in a constrained E6 inspired SUSY model. J. High Energy Phys. 2016, 1612, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Binjonaid, M.; King, S.F. Fine Tuning in the Constrained Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Harries, D.; Williams, A.G. Z′ mass limits and the naturalness of supersymmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athron, P.; Stöckinger, D.; Voigt, A. Threshold Corrections in the Exceptional Supersymmetric Standard Model. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 095012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. Spectrum of Higgs particles in the ESSM. arXiv 2006, arXiv:hep-ph/0601269. [Google Scholar]
- King, S.F.; Moretti, S.; Nevzorov, R. E6SSM. AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 881, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Belyaev, A.; Hall, J.P.; King, S.F.; Svantesson, P. Novel gluino cascade decays in E6 inspired models. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 031702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, A.; Hall, J.P.; King, S.F.; Svantesson, P. Discovering E6 supersymmetric models in gluino cascade decays at the LHC. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 035019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorov, R.; Pakvasa, S. Exotic Higgs decays in the E6 inspired SUSY models. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 728, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.P.; King, S.F.; Nevzorov, R.; Pakvasa, S.; Sher, M. Novel Higgs Decays and Dark Matter in the E6SSM. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 075013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbach, S.; Miller, D.J.; Moortgat-Pick, G.; Nevzorov, R.; Trusov, M. Theoretical upper bound on the mass of the LSP in the MNSSM. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 662, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frere, J.M.; Nevzorov, R.B.; Vysotsky, M.I. Stimulated neutrino conversion and bounds on neutrino magnetic moments. Phys. Lett. B 1997, 394, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kolda, C.F.; Martin, S.P. Low-energy supersymmetry with D term contributions to scalar masses. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, G.F.; Rattazzi, R. Theories with gauge mediated supersymmetry breaking. Phys. Rept. 1999, 322, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovsky, S.L.; Gorbunov, D.S.; Troitsky, S.V. Gauge mechanism of mediation of supersymmetry breaking. Phys. Usp. 1999, 42, 623. [Google Scholar]
- Gherghetta, T.; Pomarol, A. Bulk fields and supersymmetry in a slice of AdS. Nucl. Phys. B 2000, 586, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghetta, T.; Pomarol, A. A Warped supersymmetric standard model. Nucl. Phys. B 2001, 602, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Khlopov, M.; Wu, L.; Yang, J.M.; Zhu, B. Light gravitino dark matter: LHC searches and the Hubble tension. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, P.A.; Nevzorov, R.B.; Ter-Martirosian, K.A. Masses of Higgs bosons in supersymmetric theories. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1998, 61, 812. [Google Scholar]
- Nevzorov, R.B.; Trusov, M.A. Particle spectrum in the modified NMSSM in the strong Yukawa coupling limit. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2000, 91, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nevzorov, R.B.; Ter-Martirosyan, K.A.; Trusov, M.A. Higgs bosons in the simplest SUSY models. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2002, 65, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nevzorov, R.; Miller, D.J. Approximate solutions for the Higgs masses and couplings in the NMSSM. arXiv 2004, arXiv:hep-ph/0411275. [Google Scholar]
- Arkani-Hamed, N.; Delgado, A.; Giudice, G.F. The Well-tempered neutralino. Nucl. Phys. B 2006, 741, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chalons, G.; Dolan, M.J.; McCabe, C. Neutralino dark matter and the Fermi gamma-ray lines. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 02, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Planck collaboration. Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Su, S.; Takayama, F. Supergravity with a gravitino LSP. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 075019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolz, M.; Brandenburg, A.; Buchmuller, W. Thermal production of gravitinos. Nucl. Phys. B 2001, 606, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, H.; Gialamas, I.D.; Spanos, V.C. Gravitino thermal production revisited. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 075025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, A.; McGehee, R.; Murayama, H. Cosmologically Viable Low-energy Supersymmetry Breaking. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.R.; Olive, K.A.; Savage, C. Hadronic Uncertainties in the Elastic Scattering of Supersymmetric Dark Matter. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 065026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, J.; King, S.F.; Roberts, J.P. Neutralino Dark Matter in the USSM. J. High Energy Phys. 2009, 2009, 066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, G.; Boudjema, F.; Pukhov, A.; Semenov, A. micrOMEGAs3: A program for calculating dark matter observables. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2014, 185, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, J.M.; Martin Camalich, J.; Oller, J.A. The chiral representation of the πN scattering amplitude and the pion-nucleon sigma term. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 051503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.W.; Shanahan, P.E.; Young, R.D. Strangeness in the nucleon: What have we learned? Nuovo Cim. C 2012, 035N04, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Chiang, C.W. Revisiting Scalar and Pseudoscalar Couplings with Nucleons. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 1207, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, J.M.; Geng, L.S.; Martin Camalich, J.; Oller, J.A. The strangeness content of the nucleon from effective field theory and phenomenology. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 730, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirunyan, A.M. et al. [CMS Collaboration] Search for resonant and nonresonant new phenomena in high-mass dilepton final states at s = 13 TeV. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 7, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Aad, G. et al. [ATLAS Collaboration] Search for high-mass dilepton resonances using 139 fb-1 of pp collision data collected at =13 TeV with the ATLAS detector. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 796, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amole, C. et al. [PICO Collaboration] Dark Matter Search Results from the Complete Exposure of the PICO-60 C3F8 Bubble Chamber. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, J.; Ishiwata, K.; Nagata, N.; Takesako, T. Direct Detection of Electroweak-Interacting Dark Matter. J. High Energy Phys. 2011, 7, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hisano, J.; Ishiwata, K.; Nagata, N. Direct Search of Dark Matter in High-Scale Supersymmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, N.; Shirai, S. Higgsino Dark Matter in High-Scale Supersymmetry. J. High Energy Phys. 2015, 1, 029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, E. et al. [XENON Collaboration] Projected WIMP sensitivity of the XENONnT dark matter experiment. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 11, 031. [Google Scholar]
- Akerib, D.S. et al. [LUX-ZEPLIN Collaboration] Projected WIMP sensitivity of the LUX-ZEPLIN dark matter experiment. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 052002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalseth C.E. et al. [DarkSide-20k Collaboration] DarkSide-20k: A 20 tonne two-phase LAr TPC for direct dark matter detection at LNGS. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalbers J. et al. [DARWIN Collaboration] DARWIN: Towards the ultimate dark matter detector. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 11, 017. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, H.; Barger, V.; Huang, P.; Mustafayev, A.; Tata, X. Radiative natural SUSY with a 125 GeV Higgs boson. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 161802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, H.; Barger, V.; Huang, P.; Tata, X. Natural Supersymmetry: LHC, dark matter and ILC searches. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, H.; Barger, V.; Huang, P.; Mickelson, D.; Mustafayev, A.; Tata, X. Radiative natural supersymmetry: Reconciling electroweak fine-tuning and the Higgs boson mass. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aad, G. et al. [ATLAS Collaboration] Searches for electroweak production of supersymmetric particles with compressed mass spectra in = 13 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 052005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirunyan, A.M. et al. [CMS Collaboration] Search for supersymmetry with a compressed mass spectrum in the vector boson fusion topology with 1-lepton and 0-lepton final states in proton-proton collisions at = 13 TeV. J. High Energy Phys. 2019, 8, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Aaboud, M. et al. [ATLAS Collaboration] Search for heavy charged long-lived particles in the ATLAS detector in 36.1 fb-1 of proton-proton collision data at =13 TeV. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 092007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirelli, M.; Fornengo, N.; Strumia, A. Minimal dark matter. Nucl. Phys. B 2006, 753, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, H.; Barklow, T.; Fujii, K.; Gao, Y.; Hoang, A.; Kanemura, S.; List, J.; Logan, H.E.; Nomerotski, A.; Perelstein, M.; et al. The International Linear Collider Technical Design Report—Volume 2: Physics. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.6352. [Google Scholar]
- Aad, G. et al. [ATLAS Collaboration] Search for pairs of scalar leptoquarks decaying into quarks and electrons or muons in = 13 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Aad, G. et al. [ATLAS Collaboration] Search for pair production of third-generation scalar leptoquarks decaying into a top quark and a τ-lepton in pp collisions at = 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 06, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Sirunyan, A.M. et al. [CMS Collaboration] Searches for physics beyond the standard model with the MT2 variable in hadronic final states with and without disappearing tracks in proton-proton collisions at s= 13 TeV. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Langacker, P.; Nelson, B.D. Theory and Phenomenology of Exotic Isosinglet Quarks and Squarks. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).