Binary Neutron Star Merger Simulations with a Calibrated Turbulence Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. WhiskyTHC
2.2. GRLES
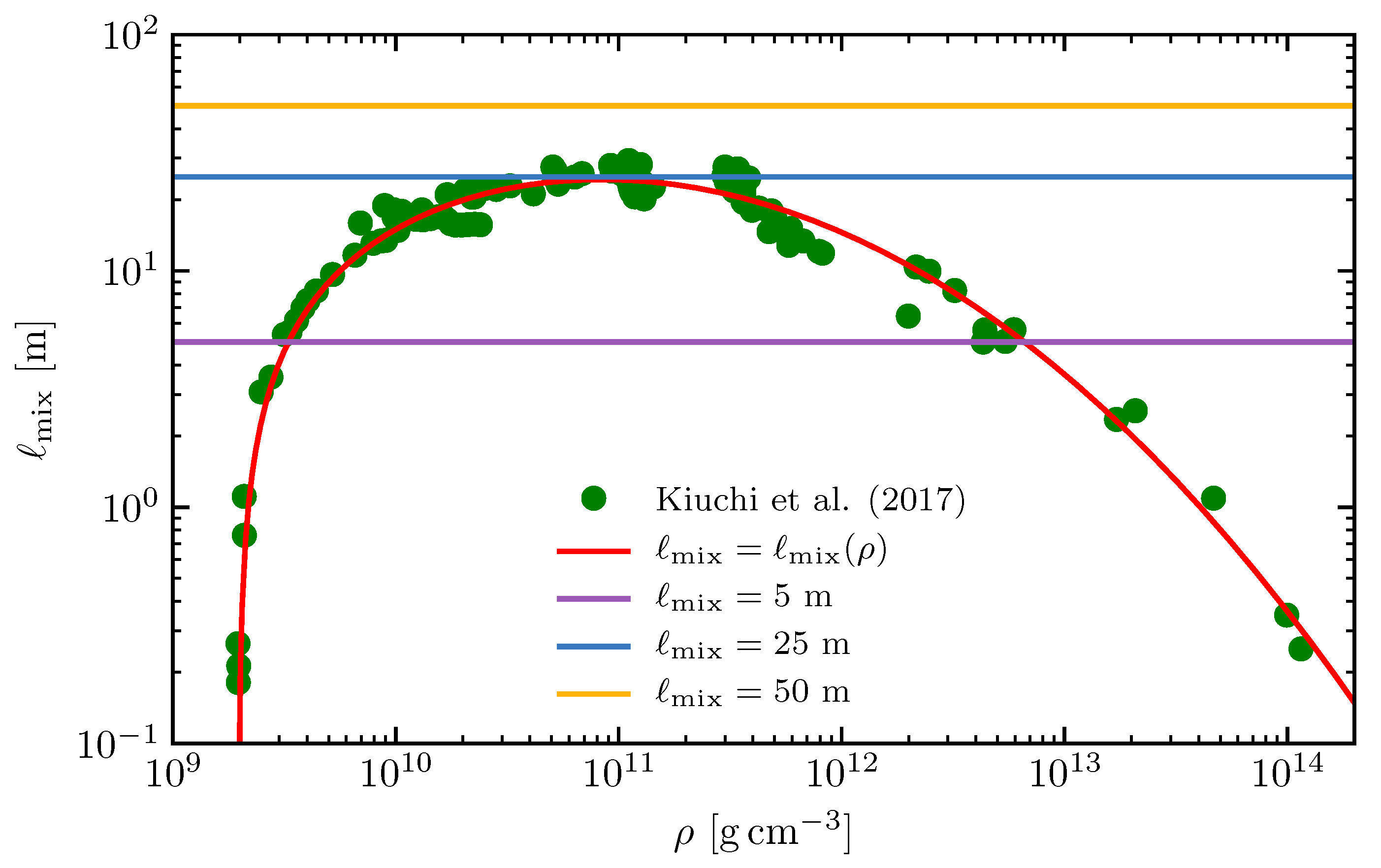
2.3. Models and Simulation Setup
3. Results
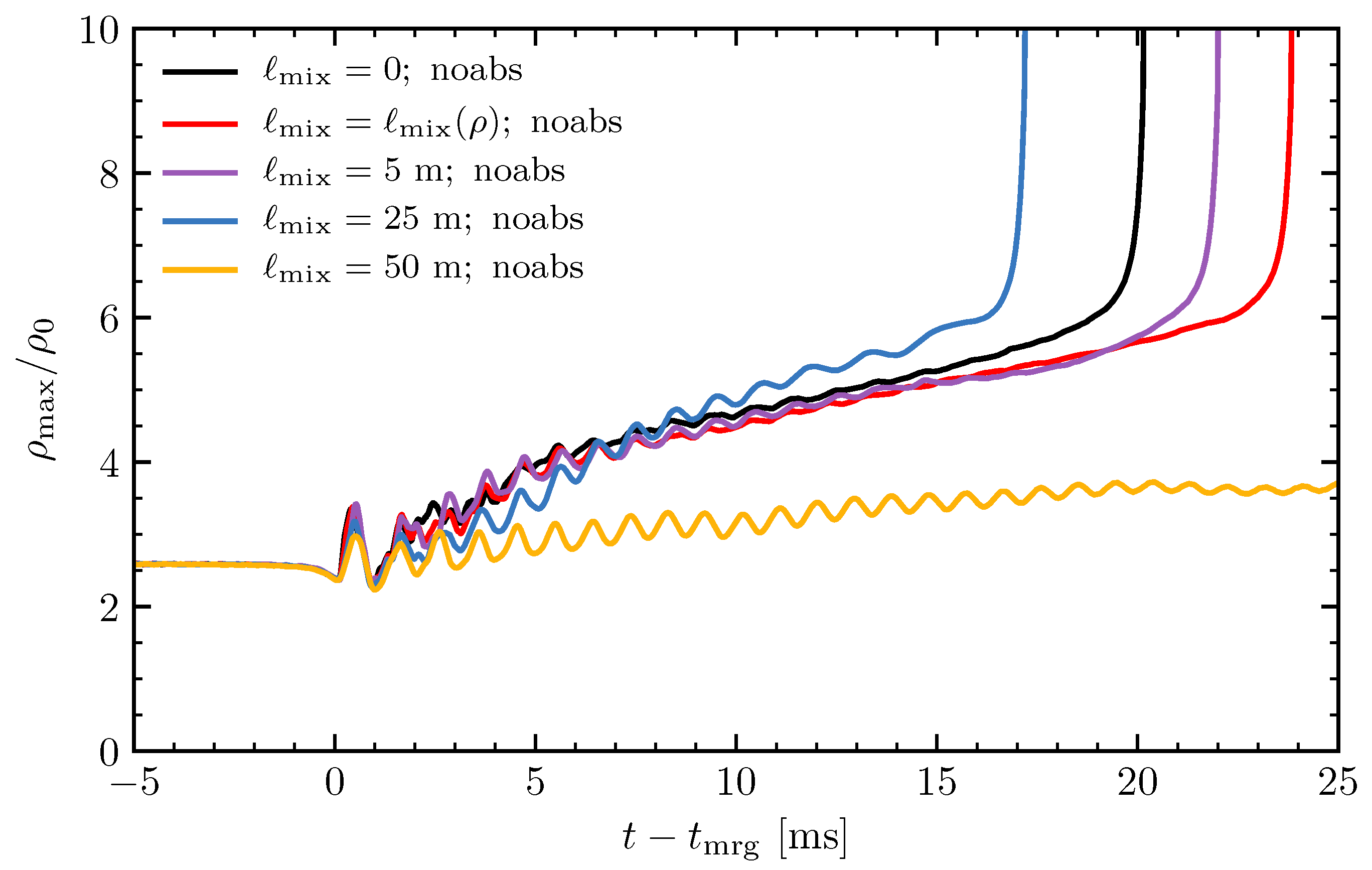
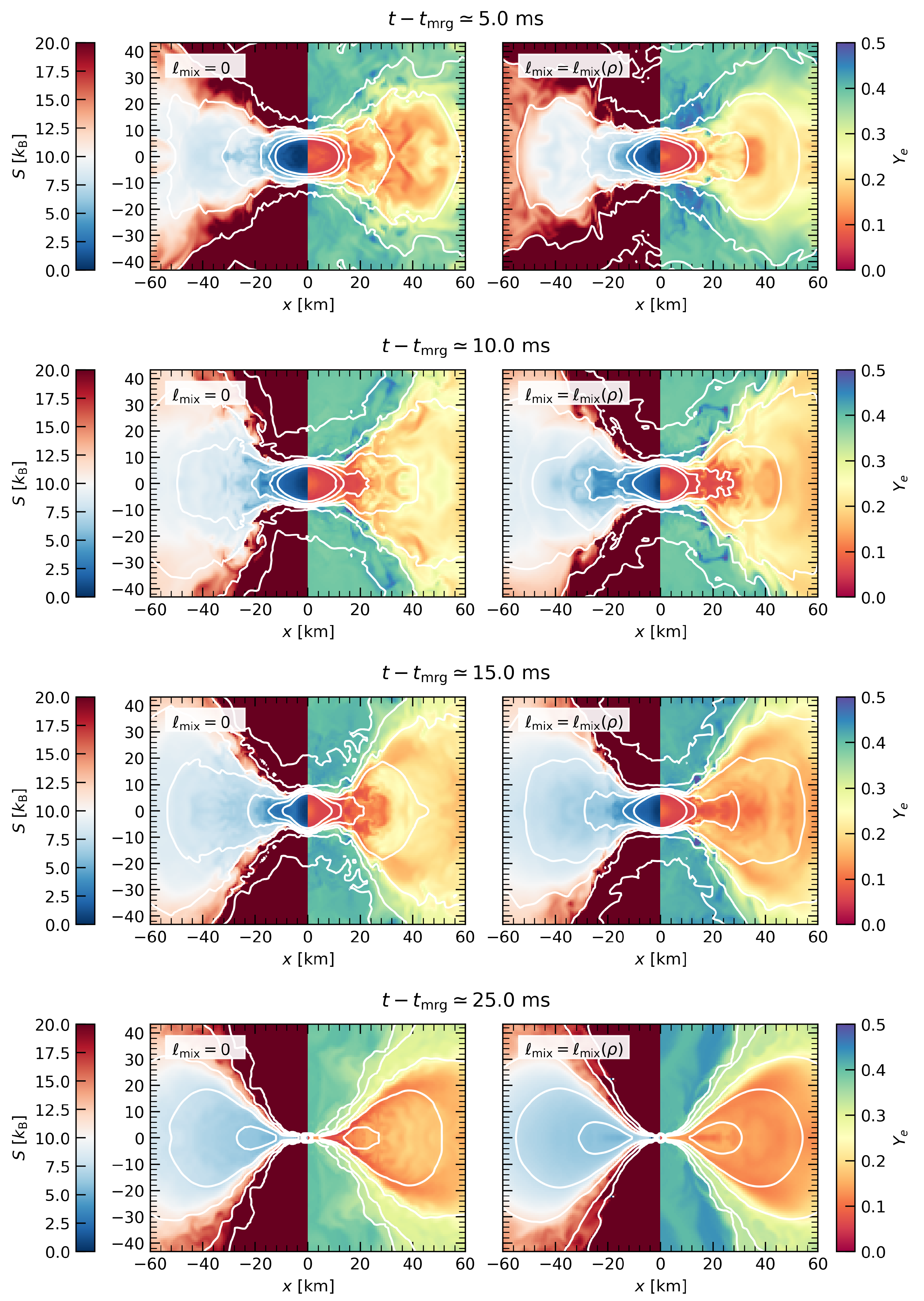
3.1. Qualitative Dynamics
3.2. Gravitational Waves
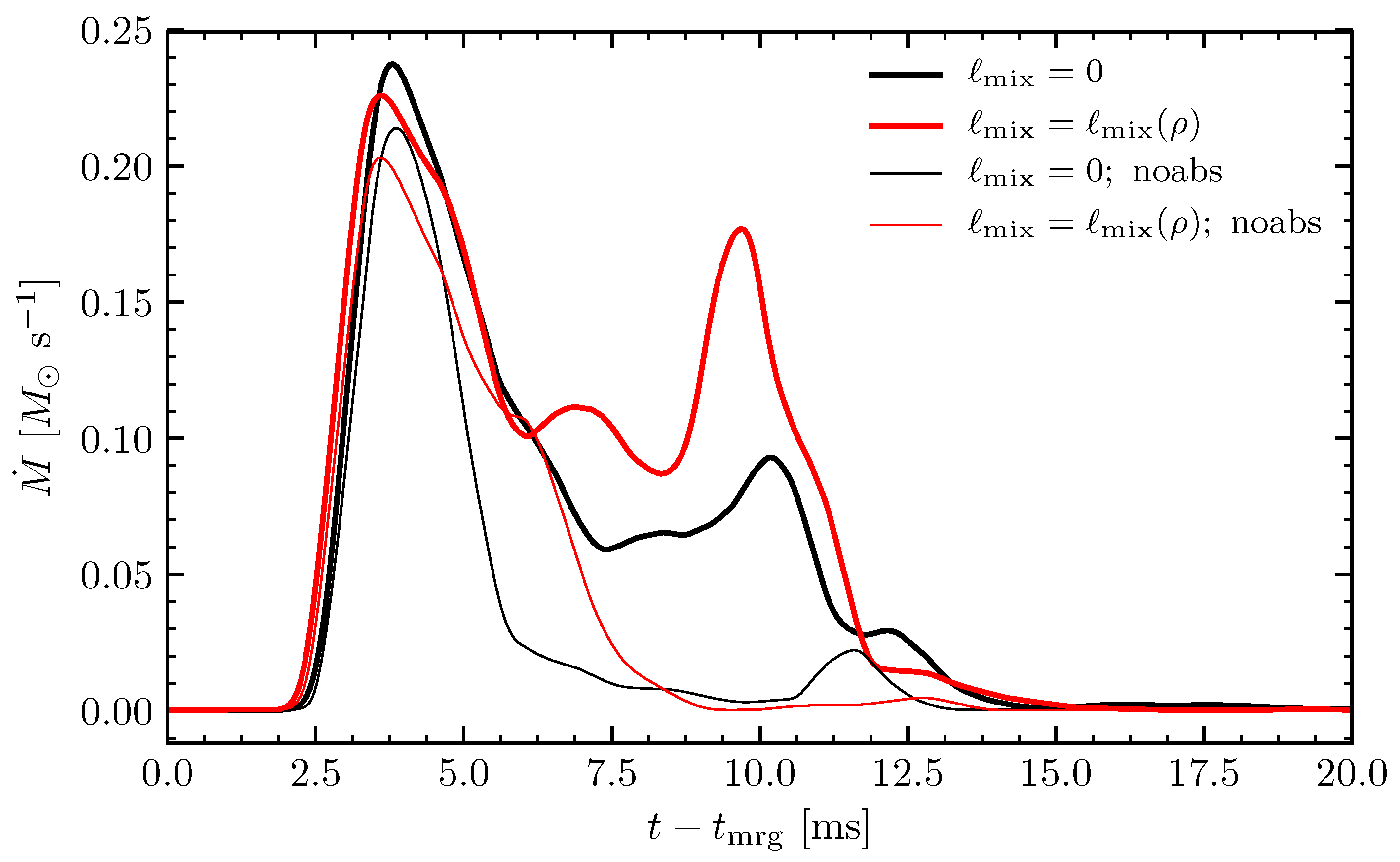
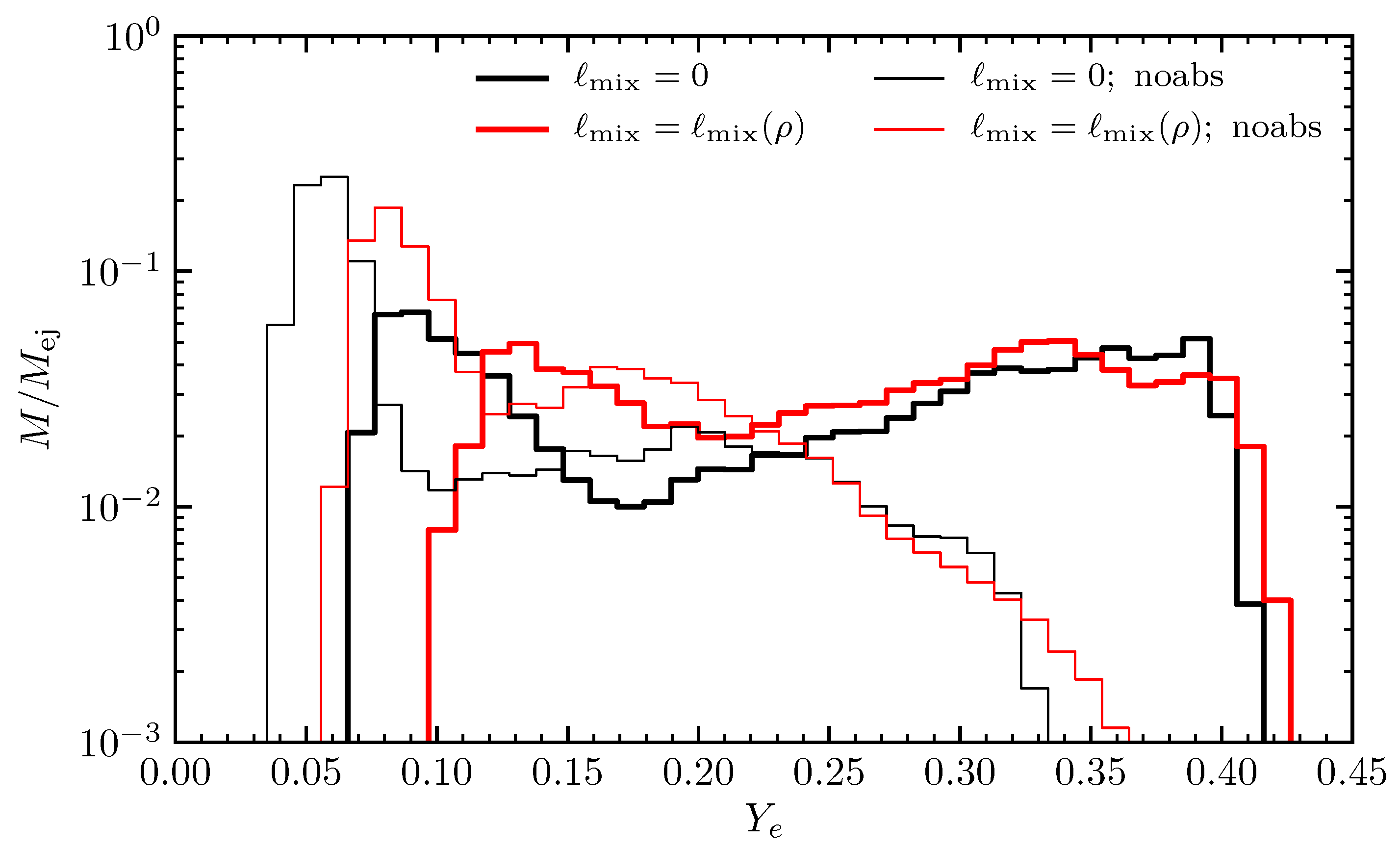
3.3. Outflows
4. Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aasi, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.; Abernathy, M.R.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Advanced LIGO. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acernese, F.; Agathos, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Aisa, D.; Allemandou, N.; Allocca, A.; Amarni, J.; Astone, P.; Balestri, G.; Ballardin, G.; et al. Advanced Virgo: A second-generation interferometric gravitational wave detector. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Michimura, Y.; Somiya, K.; Ando, M.; Miyakawa, O.; Sekiguchi, T.; Tatsumi, D.; Yamamoto, H. Interferometer design of the KAGRA gravitational wave detector. Phys. Rev. 2013, D88, 043007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D.; Livio, M.; Piran, T.; Schramm, D.N. Nucleosynthesis, Neutrino Bursts and Gamma-Rays from Coalescing Neutron Stars. Nature 1989, 340, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Paczynski, B.; Piran, T. Gamma-ray bursts as the death throes of massive binary stars. Astrophys. J. 1992, 395, L83–L86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E. Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 43–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Zhang, B. The physics of gamma-ray bursts & relativistic jets. Phys. Rep. 2014, 561, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Metzger, B.D. Electromagnetic Signatures of Neutron Star Mergers in the Advanced LIGO Era. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2016, 66, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D. Kilonovae. Living Rev. Rel. 2020, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E. The electromagnetic counterparts of compact binary mergers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.05659. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Properties of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. 2019, X9, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanajo, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M. Production of all the r-process nuclides in the dynamical ejecta of neutron star mergers. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Beniamini, P.; Piran, T. Neutron Star Mergers as sites of r-process Nucleosynthesis and Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2018, D27, 1842005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.J.; Sneden, C.; Lawler, J.E.; Aprahamian, A.; Wiescher, M.; Langanke, K.; Martínez-Pinedo, G.; Thielemann, F.K. Origin of the Heaviest Elements: The Rapid Neutron-Capture Process. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01410. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. GW190425: Observation of a Compact Binary Coalescence with Total Mass ∼3.4M⊙. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.J.; Coulter, D.A.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Piro, A.L.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Schwab, J. Updated Parameter Estimates for GW190425 Using Astrophysical Arguments and Implications for the Electromagnetic Counterpart. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIGO-Virgo Scientific Collaboration. Gravitational-Wave Candidate Event Database. Available online: https://gracedb.ligo.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Prospects for Observing and Localizing Gravitational-Wave Transients with Advanced LIGO, Advanced Virgo and KAGRA. Living Rev. Rel. 2018, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, T. Tidal Love numbers of neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 2008, 677, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Nagar, A. Relativistic tidal properties of neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2009, D80, 084035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damour, T.; Nagar, A.; Villain, L. Measurability of the tidal polarizability of neutron stars in late-inspiral gravitational-wave signals. Phys. Rev. 2012, D85, 123007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalit, B.; Metzger, B.D. Constraining the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars From Multi-Messenger Observations of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annala, E.; Gorda, T.; Kurkela, A.; Vuorinen, A. Gravitational-wave constraints on the neutron-star-matter Equation of State. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 172703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Finstad, D.; Lattimer, J.M.; Brown, D.A.; Berger, E.; Biwer, C.M. Tidal Deformabilities and Radii of Neutron Stars from the Observation of GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 091102, [Erratum: Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 259902, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.259902]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L.; Tsokaros, A. GW170817, General Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations, and the Neutron Star Maximum Mass. Phys. Rev. 2018, D97, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauswein, A.; Just, O.; Janka, H.T.; Stergioulas, N. Neutron-star radius constraints from GW170817 and future detections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Zappa, F.; Bernuzzi, S. GW170817: Joint Constraint on the Neutron Star Equation of State from Multi-messenger Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 852, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, E.R.; Weih, L.R.; Rezzolla, L.; Schaffner-Bielich, J. New constraints on radii and tidal deformabilities of neutron stars from GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 261103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, I.; Margueron, J.; Reddy, S. Critical examination of constraints on the equation of state of dense matter obtained from GW170817. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 98, 045804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Dai, L. Multi-messenger Parameter Estimation of GW170817. Eur. Phys. J. 2019, A55, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Revisiting the lower bound on tidal deformability derived by AT 2017gfo. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 876, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Zhou, E.; Kiuchi, K.; Fujibayashi, S. Constraint on the maximum mass of neutron stars using GW170817 event. Phys. Rev. 2019, D100, 023015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capano, C.D.; Tews, I.; Brown, S.M.; Margalit, B.; De, S.; Kumar, S.; Brown, D.A.; Krishnan, B.; Reddy, S. Stringent constraints on neutron-star radii from multi-messenger observations and nuclear theory. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10352. [Google Scholar]
- Annala, E.; Gorda, T.; Kurkela, A.; Nättilä, J.; Vuorinen, A. Quark-matter cores in neutron stars. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.09121. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, T.; Coughlin, M.W.; Pang, P.T.H.; Bulla, M.; Heinzel, J.; Issa, L.; Tews, I.; Antier, S. New Constraints on the Supranuclear Equation of State and the Hubble Constant from Nuclear Physics—Multi-Messenger Astronomy. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11355. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.; Lang, R.N.; Paschalidis, V.; Shapiro, S.L. Binary Neutron Star Mergers: A jet Engine for Short Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 824, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Gravitational Waves and Gamma-rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; Perna, R.; Morsony, B.J.; López-Cámara, D.; Cantiello, M.; Ciolfi, R.; Giacomazzo, B.; Workman, J.C. Late time afterglow observations reveal a collimated relativistic jet in the ejecta of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 241103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zrake, J.; MacFadyen, A. Numerical Simulations of the Jet Dynamics and Synchrotron Radiation of Binary Neutron Star Merger Event GW170817/GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajela, A.; Margutti, R.; Alexander, K.D.; Kathirgamaraju, A.; Baldeschi, A.; Guidorzi, C.; Giannios, D.; Fong, W.; Wu, Y.; MacFadyen, A.; et al. Two Years of Nonthermal Emission from the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817: Rapid Fading of the Jet Afterglow and First Constraints on the Kilonova Fastest Ejecta. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 886, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; Ciolfi, R.; Perna, R. Intrinsic properties of the engine and jet that powered the short gamma-ray burst associated with GW170817. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10210. [Google Scholar]
- Rosswog, S.; Liebendoerfer, M.; Thielemann, F.K.; Davies, M.B.; Benz, W.; Piran, T. Mass ejection in neutron star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 341, 499–526. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.H.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Lopez-Camara, D. Phase transitions and He-synthesis driven winds in neutrino cooled accretion disks: Prospects for late flares in short gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, L93–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Okawa, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.i.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Mass ejection from the merger of binary neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2013, D87, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauswein, A.; Goriely, S.; Janka, H.T. Systematics of dynamical mass ejection, nucleosynthesis, and radioactively powered electromagnetic signals from neutron-star mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Rosswog, S.; Cabezón, R.M.; Korobkin, O.; Käppeli, R.; Arcones, A.; Liebendörfer, M. Neutrino-driven winds from neutron star merger remnants. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 3134–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Dynamical mass ejection from the merger of asymmetric binary neutron stars: Radiation-hydrodynamics study in general relativity. Phys. Rev. 2016, D93, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucart, F.; Haas, R.; Duez, M.D.; O’Connor, E.; Ott, C.D.; Roberts, L.; Kidder, L.E.; Lippuner, J.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A. Low mass binary neutron star mergers: Gravitational waves and neutrino emission. Phys. Rev. 2016, D93, 044019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Galeazzi, F.; Lippuner, J.; Roberts, L.F.; Ott, C.D.; Rezzolla, L. Dynamical Mass Ejection from Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 3255–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, L.; Liebling, S.L.; Palenzuela, C.; Caballero, O.L.; O’Connor, E.; Anderson, M.; Neilsen, D. Unequal mass binary neutron star mergers and multi-messenger signals. Class. Quant. Grav. 2016, 33, 184002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, T.; Ujevic, M.; Tichy, W.; Bernuzzi, S.; Bruegmann, B. Gravitational waves and mass ejecta from binary neutron star mergers: Effect of the mass-ratio. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 024029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Metzger, B.D. Three-Dimensional General-Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Remnant Accretion Disks from Neutron Star Mergers: Outflows and r-Process Nucleosynthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 231102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.; Barnes, J.; Quataert, E.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Origin of the heavy elements in binary neutron-star mergers from a gravitational wave event. Nature 2017, 551, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucart, F.; O’Connor, E.; Roberts, L.; Kidder, L.E.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A. Impact of an improved neutrino energy estimate on outflows in neutron star merger simulations. Phys. Rev. 2016, D94, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Kiuchi, K.; Nishimura, N.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Mass Ejection from the Remnant of a Binary Neutron Star Merger: Viscous-Radiation Hydrodynamics Study. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Quataert, E.; Foucart, F.; Kasen, D. Long-term GRMHD simulations of neutron star merger accretion discs: Implications for electromagnetic counterparts. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 3373–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Hotokezaka, K.; Fromm, S.A.; Bernuzzi, S.; Roberts, L.F. Binary Neutron Star Mergers: Mass Ejection, Electromagnetic Counterparts and Nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Ryan, B.R.; Dolence, J.C.; Burrows, A.; Fontes, C.J.; Fryer, C.L.; Korobkin, O.; Lippuner, J.; Mumpower, M.R.; Wollaeger, R.T. Full Transport Model of GW170817-Like Disk Produces a Blue Kilonova. Phys. Rev. 2019, D100, 023008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.; Foucart, F.; Duez, M.D.; Haas, R.; Kidder, L.E.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A. Unequal Mass Binary Neutron Star Simulations with Neutrino Transport: Ejecta and Neutrino Emission. Phys. Rev. 2020, D101, 044053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedora, V.; Bernuzzi, S.; Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Endrizzi, A.; Ortiz, N. Spiral-wave wind for the blue kilonova. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 886, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Shibata, M.; Wanajo, S.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y. Mass ejection from disks surrounding a low-mass black hole: Viscous neutrino-radiation hydrodynamics simulation in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. 2020, D101, 083029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzuela, C.; Liebling, S.L.; Neilsen, D.; Lehner, L.; Caballero, O.L.; O’Connor, E.; Anderson, M. Effects of the microphysical Equation of State in the mergers of magnetized Neutron Stars With Neutrino Cooling. Phys. Rev. 2015, D92, 044045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, E.R.; Papenfort, L.J.; Rezzolla, L. Beyond second-order convergence in simulations of magnetized binary neutron stars with realistic microphysics. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 3588–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mösta, P.; Radice, D.; Haas, R.; Schnetter, E.; Bernuzzi, S. A magnetar engine for short GRBs and kilonovae. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.06043. [Google Scholar]
- Jesse, J.; Duez, M.D.; Foucart, F.; Haddadi, M.; Knight, A.L.; Cadenhead, C.L.; Hébert, F.; Kidder, L.E.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A. Axisymmetric Hydrodynamics in Numerical Relativity Using a Multipatch Method. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.01848. [Google Scholar]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Bernuzzi, S.; Zhang, B. Long-lived Remnants from Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Bernuzzi, S.; Perego, A. The Dynamics of Binary Neutron Star Mergers and of GW170817. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.03863. [Google Scholar]
- Obergaulinger, M.; Aloy, M.A.; Muller, E. Local simulations of the magnetized Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in neutron-star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciantini, N.; Metzger, B.D.; Thompson, T.A.; Quataert, E. Short GRBs with Extended Emission from Magnetar Birth: Jet Formation and Collimation. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Ciolfi, R.; Harte, A.I.; Rezzolla, L. Magnetorotational instability in relativistic hypermassive neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2013, D87, 121302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Wada, T. High resolution numerical-relativity simulations for the merger of binary magnetized neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2014, D90, 041502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzo, B.; Zrake, J.; Duffell, P.; MacFadyen, A.I.; Perna, R. Producing Magnetar Magnetic Fields in the Merger of Binary Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Cerdá-Durán, P.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Efficient magnetic-field amplification due to the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. 2015, D92, 124034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Global simulations of strongly magnetized remnant massive neutron stars formed in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. 2018, D97, 124039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duez, M.D.; Liu, Y.T.; Shapiro, S.L.; Stephens, B.C. General relativistic hydrodynamics with viscosity: Contraction, catastrophic collapse, and disk formation in hypermassive neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2004, D69, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duez, M.D.; Liu, Y.T.; Shapiro, S.L.; Shibata, M. Evolution of magnetized, differentially rotating neutron stars: Simulations in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. 2006, D73, 104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Muranushi, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.i.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Remnant massive neutron stars of binary neutron star mergers: Evolution process and gravitational waveform. Phys. Rev. 2013, D88, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolfi, R.; Kastaun, W.; Kalinani, J.V.; Giacomazzo, B. First 100 ms of a long-lived magnetized neutron star formed in a binary neutron star merger. Phys. Rev. 2019, D100, 023005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilet, J.; Bauswein, A.; Just, O.; Janka, H.T. Magnetorotational instability in neutron star mergers: Impact of neutrinos. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D. General-Relativistic Large-Eddy Simulations of Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2017, 838, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Kiuchi, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.i. General relativistic viscous hydrodynamics of differentially rotating neutron stars. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 083005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyink, G.L.; Drivas, T.D. Cascades and Dissipative Anomalies in Relativistic Fluid Turbulence. Phys. Rev. 2018, X8, 011023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, F.; Viganò, D.; Palenzuela, C. Gradient subgrid-scale model for relativistic MHD large-eddy simulations. Phys. Rev. 2020, D101, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, D.; Aguilera-Miret, R.; Carrasco, F.; Miñano, B.; Palenzuela, C. GRMHD large eddy simulations with gradient subgrid-scale model. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00870. [Google Scholar]
- Rosofsky, S.G.; Huerta, E.A. Artificial neural network subgrid models of 2D compressible magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. Phys. Rev. 2020, D101, 084024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, F.; Bernuzzi, S.; Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Dietrich, T. Gravitational-wave luminosity of binary neutron stars mergers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Hotokezaka, K.; Bernuzzi, S.; Fromm, S.A.; Roberts, L.F. Viscous-Dynamical Ejecta from Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 869, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Bernuzzi, S.; Radice, D. Thermodynamics conditions of matter in neutron star mergers. Eur. Phys. J. 2019, A55, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernuzzi, S.; Breschi, M.; Daszuta, B.; Endrizzi, A.; Logoteta, D.; Nedora, V.; Perego, A.; Schianchi, F.; Radice, D.; Zappa, F.; et al. Accretion-induced prompt black hole formation in asymmetric neutron star mergers, dynamical ejecta and kilonova signals. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.06015. [Google Scholar]
- Radice, D.; Rezzolla, L. THC: A new high-order finite-difference high-resolution shock-capturing code for special-relativistic hydrodynamics. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 547, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Rezzolla, L.; Galeazzi, F. Beyond second-order convergence in simulations of binary neutron stars in full general-relativity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, L46–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Rezzolla, L.; Galeazzi, F. High-Order Fully General-Relativistic Hydrodynamics: New Approaches and Tests. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Rezzolla, L.; Galeazzi, F. High-Order Numerical-Relativity Simulations of Binary Neutron Stars. ASP Conf. Ser. 2015, 498, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bernuzzi, S.; Hilditch, D. Constraint violation in free evolution schemes: Comparing BSSNOK with a conformal decomposition of Z4. Phys. Rev. 2010, D81, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilditch, D.; Bernuzzi, S.; Thierfelder, M.; Cao, Z.; Tichy, W.; Bruegmann, B. Compact binary evolutions with the Z4c formulation. Phys. Rev. 2013, D88, 084057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollney, D.; Reisswig, C.; Schnetter, E.; Dorband, N.; Diener, P. High accuracy binary black hole simulations with an extended wave zone. Phys. Rev. 2011, D83, 044045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisswig, C.; Ott, C.D.; Abdikamalov, E.; Haas, R.; Moesta, P.; Schnetter, E. Formation and Coalescence of Cosmological Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in Supermassive Star Collapse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 151101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiuc-Hamilton, M.; Brandt, S.R.; Diener, P.; Elley, M.; Etienne, Z.; Ficarra, G.; Haas, R.; Witek, H.; Alcubierre, M.; Alic, D.; et al. The Einstein Toolkit. Zenodo 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffler, F.; Faber, J.; Bentivegna, E.; Bode, T.; Diener, P.; Haas, R.; Hinder, I.; Mundim, B.C.; Ott, C.D.; Schnetter, E.; et al. The Einstein Toolkit: A Community Computational Infrastructure for Relativistic Astrophysics. Class. Quant. Grav. 2012, 29, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, S.; Ketcheson, D.I.; Shu, C.W. High Order Strong Stability Preserving Time Discretizations. J. Sci. Comput. 2008, 38, 251–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnetter, E.; Hawley, S.H.; Hawke, I. Evolutions in 3-D numerical relativity using fixed mesh refinement. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, 1465–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.J.; Oliger, J. Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations. J. Comput. Phys. 1984, 53, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.J.; Colella, P. Local Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Shock Hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1989, 82, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisswig, C.; Haas, R.; Ott, C.D.; Abdikamalov, E.; Mösta, P.; Pollney, D.; Schnetter, E. Three-Dimensional General-Relativistic Hydrodynamic Simulations of Binary Neutron Star Coalescence and Stellar Collapse with Multipatch Grids. Phys. Rev. 2013, D87, 064023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyuls, F.; Font, J.A.; Ibanez, J.M.A.; Marti, J.M.A.; Miralles, J.A. Numerical 3+1 General Relativistic Hydrodynamics: A Local Characteristic Approach. Astrophys. J. 1997, 476, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Reprint of 1973A&A....24..337S. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astro. Astrophys. 1973, 500, 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Uryu, K. Merger of binary neutron stars with realistic equations of state in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. 2005, D71, 084021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastaun, W.; Ciolfi, R.; Giacomazzo, B. Structure of Stable Binary Neutron Star Merger Remnants: A Case Study. Phys. Rev. 2016, D94, 044060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanauske, M.; Takami, K.; Bovard, L.; Rezzolla, L.; Font, J.A.; Galeazzi, F.; Stöcker, H. Rotational properties of hypermassive neutron stars from binary mergers. Phys. Rev. 2017, D96, 043004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolfi, R.; Kastaun, W.; Giacomazzo, B.; Endrizzi, A.; Siegel, D.M.; Perna, R. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of binary neutron star mergers forming a long-lived neutron star. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 063016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Swesty, F.D. A Generalized equation of state for hot, dense matter. Nucl. Phys. 1991, A535, 331–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgoulhon, E.; Grandclément, P.; Marck, J.A.; Novak, J.; Taniguchi, K. LORENE; Paris Observatory, Meudon Section—LUTH Laboratory: Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bernuzzi, S.; Radice, D.; Ott, C.D.; Roberts, L.F.; Moesta, P.; Galeazzi, F. How loud are neutron star mergers? Phys. Rev. 2016, D94, 024023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauswein, A.; Janka, H.T. Measuring neutron-star properties via gravitational waves from binary mergers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, K.; Rezzolla, L.; Baiotti, L. Constraining the Equation of State of Neutron Stars from Binary Mergers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 091104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernuzzi, S.; Dietrich, T.; Nagar, A. Modeling the complete gravitational wave spectrum of neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 091101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breschi, M.; Bernuzzi, S.; Zappa, F.; Agathos, M.; Perego, A.; Radice, D.; Nagar, A. kiloHertz gravitational waves from binary neutron star remnants: Time-domain model and constraints on extreme matter. Phys. Rev. 2019, D100, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Kiuchi, K. Gravitational waves from remnant massive neutron stars of binary neutron star merger: Viscous hydrodynamics effects. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Takami, K. Gravitational-wave signal from binary neutron stars: A systematic analysis of the spectral properties. Phys. Rev. 2016, D93, 124051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weih, L.R.; Hanauske, M.; Rezzolla, L. Postmerger Gravitational-Wave Signatures of Phase Transitions in Binary Mergers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 171103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Hotokezaka, K. Merger and Mass Ejection of Neutron-Star Binaries. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2019, 69, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippuner, J.; Roberts, L.F. r-Process Lanthanide Production and Heating Rates in Kilonovae. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Piro, A.L.; Quataert, E. Time-Dependent Models of Accretion Disks Formed from Compact Object Mergers. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2008, 390, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Piro, A.L.; Quataert, E. Neutron-Rich Freeze-Out in Viscously Spreading Accretion Disks Formed from Compact Object Mergers. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2009, 396, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Metzger, B.D. Delayed outflows from black hole accretion tori following neutron star binary coalescence. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, O.; Bauswein, A.; Pulpillo, R.A.; Goriely, S.; Janka, H.T. Comprehensive nucleosynthesis analysis for ejecta of compact binary mergers. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 541–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Fernández, R. Red or blue? A potential kilonova imprint of the delay until black hole formation following a neutron star merger. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 3444–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Perego, A.; Arcones, A.; Thielemann, F.K.; Korobkin, O.; Rosswog, S. Neutrino-driven winds in the aftermath of a neutron star merger: Nucleosynthesis and electromagnetic transients. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Metzger, B.D. Three-dimensional GRMHD simulations of neutrino-cooled accretion disks from neutron star mergers. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M. GW170817—The first observed neutron star merger and its kilonova: Implications for the astrophysical site of the r-process. Eur. Phys. J. 2019, A55, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radice, D. Binary Neutron Star Merger Simulations with a Calibrated Turbulence Model. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081249
Radice D. Binary Neutron Star Merger Simulations with a Calibrated Turbulence Model. Symmetry. 2020; 12(8):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081249
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadice, David. 2020. "Binary Neutron Star Merger Simulations with a Calibrated Turbulence Model" Symmetry 12, no. 8: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081249
APA StyleRadice, D. (2020). Binary Neutron Star Merger Simulations with a Calibrated Turbulence Model. Symmetry, 12(8), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12081249




