Abstract
The match relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services (ESs) is a cornerstone of achieving sustainable development. However, the evolution patterns of urbanization/ecosystem service (UES) synergies under economic polarization in the rapid urbanization process remain poorly understood. This study integrates bivariate local Moran’s index and correlation analysis methods to examine the match relationship between urbanization and three key ESs (water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production) from 2000 to 2020 and explores the impact of intra-city disparities on the match relationship of urbanization and ESs. The findings revealed that urbanization and three ecosystem services showed increasing trends during 2000–2020 simultaneously. The spatial aggregation pattern of urbanization and ecosystem services showed smaller variations from 2000 to 2020. There was a High-High aggregation between urbanization and water yield in urban built-up areas and primarily High-Low aggregations between urbanization, carbon sequestration, and food production. Furthermore, the impact of urbanization on ESs decreased with increasing urban polarization. In particular, the Beijing–Tianjin–Tangshan region still demonstrated pronounced economic polarization, suggesting disparities in economic development within its urban core. This study highlights the importance of mitigating the adverse effects of urban polarization on ESs and fostering resilient and sustainable urban ecosystems in rapidly developing regions.
1. Introduction
As the principal economic engine among China’s three national growth poles [], the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH) region has undergone rapid urbanization []. This transformation has altered the interactions between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere [], triggering cascading effects on critical ecosystem services (ESs)—defined as benefits from nature that sustain human well-being []. Additionally, ESs play a vital role in maintaining the quality of life in the urban environment and land use planning []. Moreover, carbon sequestration, water yield, and food production are key ESs that from essential resource foundations for socioeconomic development [,]. Consequently, understanding the match relationship between urbanization and ESs in the BTH region could help optimize ecological conservation strategies and related policies during the process of land urbanization.
The relationship between urbanization and ESs has become a focal point in environmental and urban studies, reflecting the challenge of balancing socioeconomic development with ecological sustainability. Empirical evidence highlights both synergistic and antagonistic dynamics. Urban ecological interventions (e.g., green infrastructure projects) can enhance cultural and regulating ESs by improving air quality and public health [,]. Conversely, rapid population expansion often degrades natural habitats, intensifies soil erosion, and reduces hydrological regulation capacities, particularly in water-stressed regions [,]. Recent studies have further revealed nonlinear urbanization/ES trajectories, such as an inverted U-shaped pattern where environmental quality initially declines but later stabilizes or improves with urban growth, driven by technological advancements or policy shifts [,]. Methodologically, interdisciplinary approaches—including spatial econometric models, linear correlation, and coupling coordination degree analyses—have advanced our understanding of these dynamics [,]. However, most studies treat urban agglomerations as homogeneous units, overlooking intra-city disparities in rapid urbanization and ESs.
In the BTH region, Beijing and Tianjin have highly concentrated populations [], and the per capita GDP of Beijing and Tianjin is 2.86 times higher than that of Hebei Province. The megacity proliferation exacerbates regional asymmetries []. Additionally, there are developmental imbalances within cities []. As the concept of social development changes, nature-based solutions and sustainable strategies are applied the urban development []. China’s urban development mode has evolved into an eco-civilization in which economic growth must respect the ecological carrying capacity [,]. Therefore, understanding the interplay between economic polarization, urbanization, and ESs is essential for designing equitable and sustainable development policies. However, although prior work has examined the relationship between urbanization and ESs, few studies have systematically analyzed how economic polarization influences the spatial alignment (or mismatch) between urbanization intensity and ES capacity over time.
To tackle these issues, this study first assessed the match relationship between urbanization and three key ESs (water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production) in the BTH urban agglomeration during 2000–2020 and then quantified the economic polarization. Finally, we analyzed the impact of economic polarization on the relationship between urbanization and ESs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The BTH urban agglomeration, positioned as China’s political/cultural core and a pivotal economic hub, encompasses Beijing and Tianjin municipalities alongside 11 Hebei prefectures (Baoding, Tangshan, Langfang, Shijiazhuang, Qinhuangdao, Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Cangzhou, Hengshui, Xingtai, and Handan), with a total area of 21.6 × 104 km2 []. Furthermore, the region exhibits a pronounced topographic dichotomy: northwestern highlands (Yanshan–Taihang mountain ranges) gradually descend to southeastern alluvial plains, and the landforms are mainly plains, with hills and terraces distributed sporadically (Figure 1). The region has a continental climate characterized by four distinct seasons and concurrence of rainfall and warmth. Notably, the area recorded a 2023 GDP exceeding CNY 10 trillion (accounting for 8.7% of national output), sustained by 110 million residents and a 70.61% urbanization rate (above the national average of 4.45%). In the future, the region should foster synergistic development, evolving into a significant area of potent international competitiveness and influence. It endeavors to play an even more prominent role in guiding and sustaining the nation’s economic and social progress [].
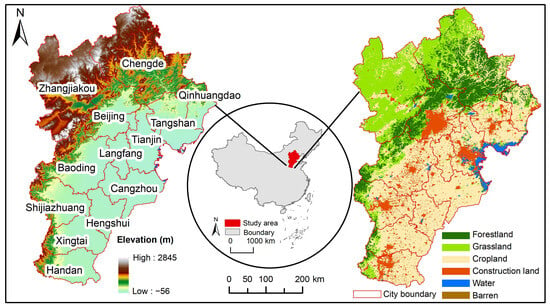
Figure 1.
Study area. Note: Elevations were derived from NASA SRTM Digital Elevation 30 m and land cover of 2020. The boundary of China was obtained from the Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform.
2.2. Framework
This study employs a multi-stage analytical framework (Figure 2) to investigate the relationship between urbanization and ESs. First, we accessed climate data, land cover, population, GDP, and statistical yearbook data to quantify urbanization and ESs on the BTH urban agglomeration during 2000–2020. Urbanization was assessed using a composite index integrating population, economic, and land urbanization. Subsequently, we calculated key ecosystem services, including water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production. We then investigated the temporal changes in both urbanization and ESs from 2000 to 2020. To explore the potential impacts of urbanization on ESs, we further examined the match relationship between urbanization and ESs based on bivariate local Moran’s index and correlation analysis methods. Finally, we evaluated the impact of intra-city disparities to match the relationship between urbanization and ESs, thereby providing insights into the dynamics of UES interactions within the BTH urban agglomeration.
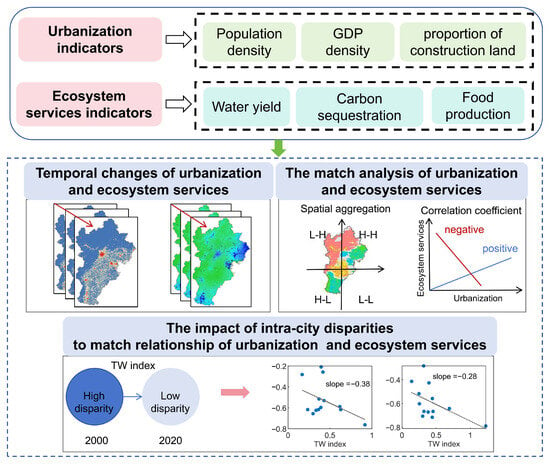
Figure 2.
Framework of the study.
2.3. Materials
We obtained the climate datasets, including monthly precipitation and potential evapotranspiration during 2000–2020. The datasets, with a spatial resolution of 0.0083333° (approximately 1 km), were sourced from Third Pole Environment Data Center at https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/ (accessed on 22 October 2024). We then calculated the annual accumulative precipitation and potential evapotranspiration by summing the monthly data. These datasets served as the pivotal inputs for calculating the annual water yield. To access the carbon sequestration capacity, we utilized Net Primary Productivity (NPP) datasets from 2000 to 2020, available at 5-year intervals from the GLASS product (version 6.0) with a spatial resolution of 500 m. Additionally, we used multi-scale land cover products to capture land use dynamics. The high-resolution annual land cover composites (30 m spatial resolution) derived from the China Land Cover Dataset (CLCDv2, 2000–2020) facilitated precise mapping and delineation of construction land at https://zenodo.org/records/4417810 (accessed on 27 September 2024). To access the spatial extent of urbanization, we aggregated the 30 m-resolution land cover data to a 1 km grid, thereby quantifying the proportion of construction land across the study area. We also used the MODIS MCD12Q1 v6.1 product, providing land cover classification consistent with the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP) at a 500 m spatial resolution at https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v061/ (accessed on 30 October 2024) [,]. Furthermore, to characterize spatially economic and demographic patterns, we utilized 1 km gridded GDP and population density datasets from 2000 to 2020, sourced from the Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform at https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 9 December 2024). Additionally, we obtained gross output values encompassing agriculture, forestry, husbandry, and fisheries from statistical yearbooks as inputs of food production.
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Assessment of Ecosystem Services
- (1)
- Water yield
The InVEST water yield module (version 3.14.2) was implemented to quantify hydrological provisioning services across the BTH urban agglomeration. The model operates on the Budyko framework, solving the water balance equation at a 1 km resolution []. The formula used is as follows:
where is the pixel-scale water yield (mm yr−1), is the pixel-scale potential evapotranspiration (mm yr−1), is the precipitation (mm yr−1), is the evapotranspiration component of the water balance, using the expression derived from the Budyko curve.
- (2)
- Food production
Because there is a positive linear covariation between food production and NDVI values, this study used the NDVI distribution method to calculate the supply at the grid scale []. The gross output values of agriculture, forestry, and animal husbandry were spatially disaggregated using the NDVI values of cropland, forestland, and grassland, respectively, and fishery outputs were allocated proportionally to the water area []. The formula used is as follows:
where is the food production in pixel x (yuan/ha), is the value of NDVI in pixel x, is the sum of NDVI values in land use type corresponding to distinct industry j, is the gross output value of industry j (CNY).
- (3)
- Carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the net creation of organic matter by plant photosynthesis and serves as a key parameter characterizing terrestrial ecological processes, proxied by NPP products in the study. Furthermore, the GLASS NPP product is derived by simulating the autotrophic respiration-to-GPP ratio using 10 dynamic vegetation models from the TRENDY project.
2.4.2. Measurement of the Comprehensive Urbanization Index
Urbanization can be assessed through four distinct dimensions: population, economic growth, land use, and social integration [,]. Population growth and economic development serve as the cornerstones of urbanization, while the expansion of urban land represents the spatial manifestation of this process. Social urbanization is predominantly reflected in the enhanced convenience of human lifestyles. However, acquiring and qualifying data on social urbanization presents significant spatial challenges. The composite urbanization metric for the BTH region was developed using three ket proxies: (1) population intensity, (2) economic output density, and (3) built-environment footprint []. The formula used is as follows:
In this expression, CUI is the comprehensive urbanization index, and PU, EU, and LU are the standardized values of population density, GDP density, and proportion of construction land, respectively.
2.4.3. Economic Polarization Model
The Tsui-Wang (TW) index is the polarization measurement index using the two-part ranking axiom of increased bipolarity and spread [], combined with the derivation of the Wolfson index, and can better reflect the trend of “polarization” and “diffusion” in the regional economy. We used the TW index to measure the economic polarization of different cities in the BTH urban agglomeration. The formula is as follows:
In this expression, is a positive constant scalar that reflects the sensitivity of the spatial polarization index, where is 0.5. N and n are the total population and number of counties in a specified city, respectively; S(i) and q(i) are the population and GDP of the i-th county in a specified city, respectively; m is the median GDP in a specified city; and r is 0.5.
2.4.4. Analysis of Match Relationship Between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
We employ both bivariate local Moran’s index and correlation analysis to elucidate the match relationship between urbanization and ESs. The bivariate local Moran’s index is a powerful tool for investigating the spatial correlation and regional clustering effects between two variables, offering insights into their geographical interplay []. The spatial aggregation patterns can be divided into four types, including High-High, High-Low, Low-High, and Low-Low. The High-High pattern signifies regions characterized by both high levels of urbanization and elevated ecosystem services. The interpretations of the remaining three pattern types follow a similar logical framework. Utilizing this index, we meticulously assessed the spatial clustering patterns between urbanization and key ESs, specifically water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production. Additionally, we conducted a thorough analysis using the Pearson correlation coefficient to examine the municipal-scale relationships between urbanization and ESs and to understand how these relationships fluctuate with changes in polarization.
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Change of Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
Urbanization, water yield, NPP, and food production all showed increasing trends from 2000 to 2020 (Figure 3). Urbanization exhibited a slower rate of increase after 2015 (Figure 3a). However, water yield and NPP showed continuous upward trends, and food production first increased and then decreased in 2015 (Figure 3b–d).
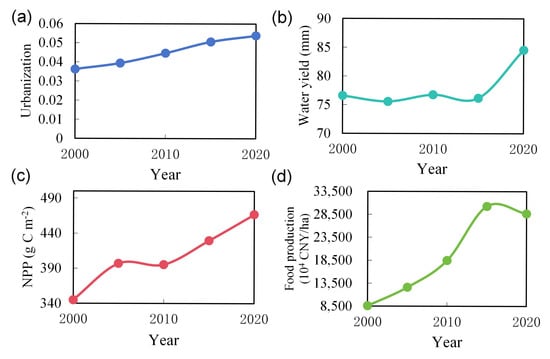
Figure 3.
Temporal change in regional mean value of (a) urbanization, (b) water yield, (c) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP), and (d) food production on the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration in the years of 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020.
Furthermore, urbanization exhibited a distinct pattern, with high values concentrated in the central and eastern regions and lower values in the north. Notably, Beijing, Tianjin, and the Bohai Rim region stood out as areas with particularly high urbanization levels (Figure 4a). Over time, changes in urbanization expanded from the center to the periphery (Figure S1). Regarding the spatial distribution of ecosystem services, water yield was abundant in the central, eastern, and southern regions, whereas it was relatively scarce in the north (Figure 4b). Conversely, NPP was high in the north, where forests were abundant, and was lower in the northwest, central, and eastern areas (Figure 4c). Food production followed a pattern of high yields in the southeast and lower yields in the central and northwestern regions (Figure 4d).
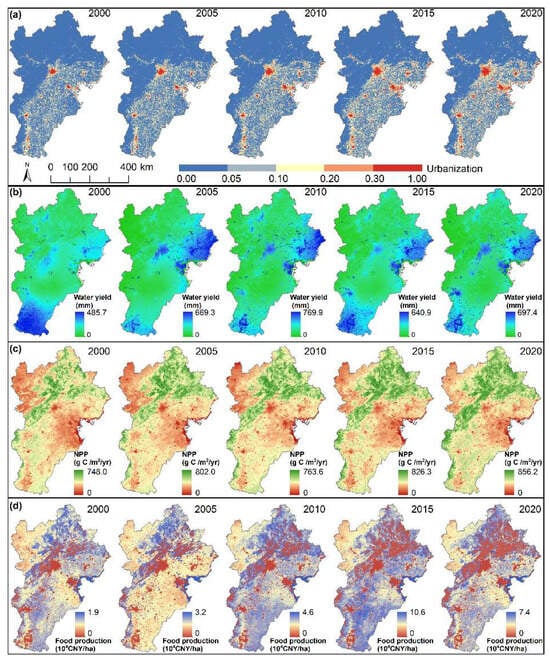
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of (a) urbanization, (b) water yield, (c) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP), and (d) food production in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020.
The spatial distribution of change in water yield diverged from those in NPP and food production. Between 2000 and 2020, the water yield decreased in the south and northwest but increased in the Bohai Rim region, with the most significant decline in the south and the greatest increase in the Bohai Rim occurring between 2000 and 2005 (Figure S2a). In contrast, the NPP showed overall upward trends across most regions, with the northern NPP experiencing the fastest growth during 2010–2015 (Figure S2b). Food production increased in the northeast, north, and coastal areas over the same period, with a steady increase from 2000 to 2015, followed by a slowdown in 2015 (Figure S2c).
3.2. The Match Relationship Between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
To provide the spatial aggregation pattern observed between urbanization and ESs, we conducted an analysis using the bivariate local Moran’s index to assess their spatial correlation. The spatial aggregation pattern of urbanization and water yield showed smaller variations from 2000 to 2020, which were dominated by Low-Low aggregation in the northwest, High-High aggregation in the central and southern regions, and High-Low aggregation in the south-central region (Figure 5a). Moreover, the spatial aggregation pattern of urbanization and NPP showed similar patterns from 2000 to 2020, which were dominated by Low-High and Low-Low aggregation in the north and northwest, High-Low aggregation mainly in the central and eastern regions, and few regions achieving High-High agglomeration (only 2.84%) (Figure 5b). In addition, the spatial aggregation patterns of urbanization and food production showed greater changes (Figure 5c). The areas of High-High aggregation increased from 1.39% in 2005 to 14.1% in 2015, distributed in southern regions, and Low-Low and Low-High aggregation were distributed in the northern regions. The High-Low aggregation was clustered around the urban built-up areas.
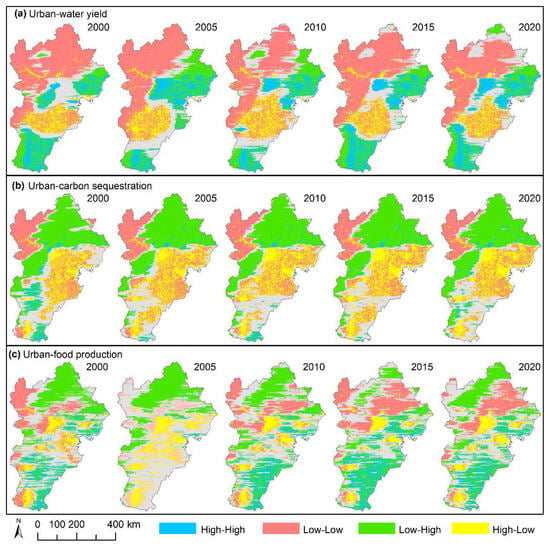
Figure 5.
Spatial aggregation distribution of urbanization and (a) water yield, (b) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP), and (c) food production in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020. Note: The gray coloration indicates regions where the bivariate local Moran’s index failed to achieve statistical significance at p < 0.05.
Furthermore, we also analyzed the correlation between urbanization and ESs. Urbanization and water production all showed significant positive correlations during 2000–2020 (p < 0.01), and the correlation coefficient exhibited increasing trends, indicating that urbanization contributed to an increase in water production to a certain extent (Figure 6a). However, urbanization, NPP, and food production were significantly negatively correlated (p < 0.01, Figure 6b). The correlation coefficients between urbanization and NPP showed increasing trends, with slower rates of change after 2015, which indicated urbanization could decrease the vegetation productivity of the regions. Furthermore, urbanization and food production showed a significantly negative correlation, with fluctuations in the correlation coefficients that have decreased in recent years (Figure 6c).
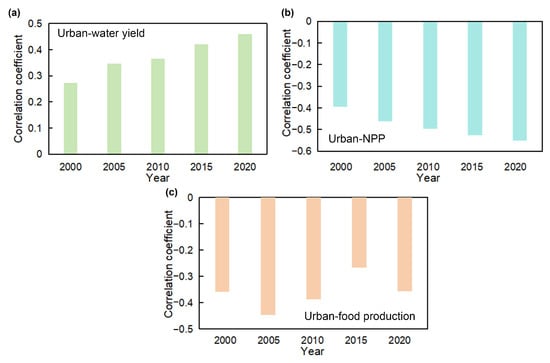
Figure 6.
The Pearson correlation coefficient in mean urbanization and (a) water yield, (b) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP), and (c) food production across the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020.
Additionally, notable variations in the correlation coefficients between urbanization and ESs were observed among different cities. Specifically, the correlation between urbanization and water yield exhibited an increasing trend in the Central Plains region, encompassing Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Langfang, Tangshan, and Qinhuangdao from 2000 to 2020 (Figure 7a). Notably, the relationship between urbanization and water yield shifted from negative to positive in Cangzhou and Zhangjiakou during this timeframe. Similarly, the negative correlation between urbanization and NPP intensified, primarily in the central regions (Figure 7b). In contrast, urbanization and food production demonstrated a negative relationship, with increasing trends in Handan, Xingtai, and Tianjin and decreasing trends in Chengde, Baoding, and Beijing (Figure 7c).
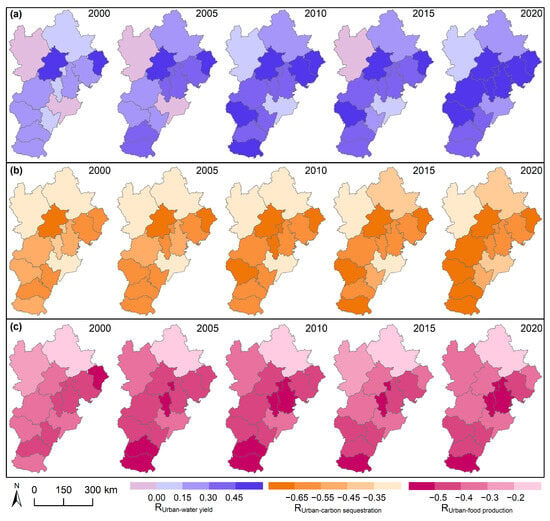
Figure 7.
The Pearson correlation coefficient in urbanization and (a) water yield, (b) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP), and (c) food production among various cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020.
3.3. The Impact of Intra-City Disparities to Match Relationship Between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
Economic polarization will highly concentrate elements such as resources, population, and economic activities in a few core cities, forming an unbalanced pattern of regional development. Meanwhile, this unbalanced development may lead to different changes in ecosystem services. To further clarify the impact of economic polarization on the match relationship between urbanization and ESs, we analyzed the change in economic polarization and its impacts on the match relationship. Among the 13 cities in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, economic polarization has intensified in 7 of them (Figure 8 and Figure S3). Specifically, Hengshui and Xingtai showed slight changes. Additionally, the Beijing, Tangshan, Cangzhou, and Qinhuangdao regions experienced substantial economic polarization, underscoring significant disparities in economic development across different parts of these cities. In contrast, economic polarization within cities decreased during 2000–2020, particularly in Handan, Zhangjiakou, Shijiazhuang, and Chengde (Figure 8 and Figure S3). It is particularly noteworthy that within these cities, the rate at which economic polarization declined outpaced the rate at which it increased, which indicated that there was a phenomenon of weakened economic polarization in most areas in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region during 2000–2020.
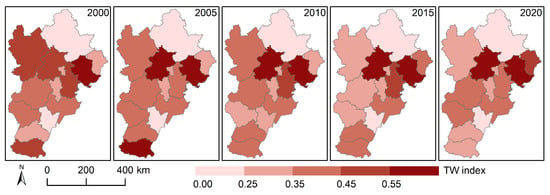
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of economic polarization (Tsui-Wang index, TW) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020.
The scatter plot of the TW index and the correlation coefficient between urbanization and ESs clearly reflect the influence of economic polarization on the match relationship between the two variables. The influence of urbanization on ESs diminishes as urban polarization intensifies (Figure S4), suggesting that advanced stages of urban development rely less on land use, particularly for carbon sequestration capacity. In 2000, the scatter plot of the TW index versus the correlation coefficient for mean urbanization and water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production exhibits a decentralized distribution, with trends of 0.44, −0.30, and −0.14, respectively (Figure 9). This indicates that urban polarization had a more pronounced impact on the correlation between urbanization and ESs in the earlier stages of development. However, in later periods (e.g., 2015 and 2020), the scatter plot shows a clustered distribution with a lower TW index (Figure 9), suggesting a decreased influence of economic polarization on the relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services. The trends of polarization’s impact on urbanization related to water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production were 0.41, −0.28, and -0.05, respectively. The impact of urbanization on ESs has gradually weakened and stabilized, particularly for food production. This suggests that shifts in urban construction and development concepts have led urbanization to transition from exclusive land occupation to sustainable human/land relationships.
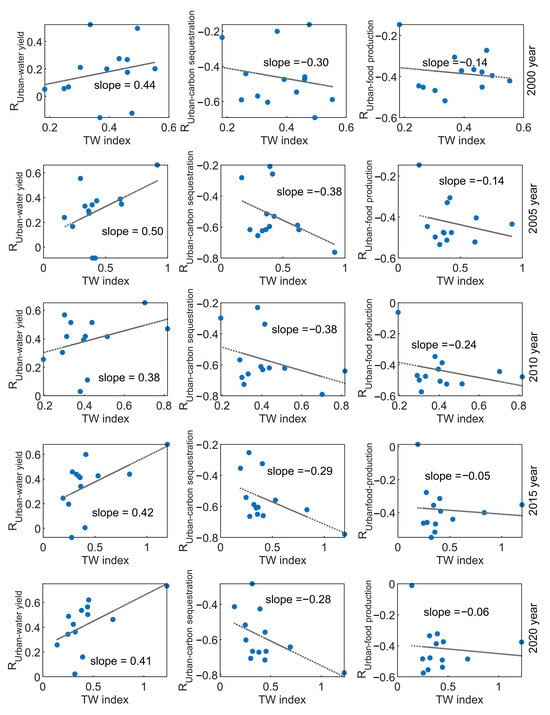
Figure 9.
Changes in the Pearson correlation coefficient in mean urbanization and water yield (RUrban-water yield), carbon sequestration (RUrban-carbon sequestration), and food production (RUrban-food production) with the economic polarization index (Tsui-Wang index, TW) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration from 2000 to 2020. Note: The slope represents the impact of the TW index on the correlation between urbanization and ecosystem services.
4. Discussions
4.1. The Changes in Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
The BTH urban agglomeration experienced rapid urbanization during 2000–2020 (Figure 3 and Figure 4a). At the same time, water yield, carbon sequestration, and food production also showed increasing trends (Figure 3 and Figure 4b–d). However, there is spatial heterogeneity in the changes in urbanization and ESs. The areas with more pronounced urbanization growth are mainly located along the Beijing–Tianjin, Beijing–Baoding–Shijiazhuang, and Beijing–Tangshan–Qinhuangdao development axes. This pattern of urban expansion is related to geographical factors and policy directives [,].
The overall landscape distribution of the BTH urban agglomeration is characterized by northwestern mountains, southeastern plains, and an eastern coastline. Consequently, urban development progresses more slowly in the northwest than in the central and southeastern regions owing to the topography []. Additionally, Beijing, as the capital, serves as a hub for politics, culture, international communication, and scientific and technological innovation, attracting industries and resources, which fuels its rapid expansion []. Tianjin capitalizes on its coastal location and proximity to Beijing, enabling it to harness Beijing’s resources for its own growth []. Meanwhile, cities such as Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Tangshan, and Qinhuangdao are significantly influenced by the spillover effects of Beijing and Tianjin while also benefiting from the accelerated development of transportation networks and urbanization [,]. However, Zhangjiakou and Chengde exhibit slower urbanization rates because of their roles in ecological conservation.
The increase in water yield is strongly influenced by climatic factors such as precipitation []. NPP has demonstrated an upward trend in the northern and northwestern regions, primarily attributed to ecological restoration projects. Since 2002, the BTH region has comprehensively implemented a range of measures, including the conversion of farmland to forests and grasslands, execution of large-scale ecological initiatives, and enforcement of grazing bans since 2010 []. Food production also showed an increasing trend, especially in the southeast plains of Hebei Province and coastal areas, which could benefit from high-intensity agricultural production and the South–North Water Diversion Project []. In addition, coastal areas have abundant high-value fishery resources.
4.2. The Reasons for the Match Relationship Between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services
Urbanization can exert a significant influence on ESs []. This study revealed that spatial clustering and interdependencies between urbanization and ESs evolve over time and are marked by considerable spatial variations. Notably, regions of High-High aggregation of urbanization and water yield were mainly in urban built-up areas and showed increasing trends during 2000–2020, suggesting that high urbanization could increase water yield (Figure 5). However, urbanization demonstrated a pattern of High-Low aggregation with carbon sequestration and food production. This pattern arises due to the proliferation of impervious surfaces in highly urbanized areas, leading to the contraction of ecological lands and a reduction in regional evapotranspiration, which in turn results in lower NPP, lower food production, and higher water yield [,]. Urbanization, carbon sequestration, and food production also showed a negative correlation between 2000 and 2020 (Figure 7). The regions that experienced the most substantial negative impact of urbanization on carbon sequestration were mainly Beijing, Shijiazhuang, Handan, and Baoding, whereas Tianjin and Handan were the areas where urbanization had the strongest adverse effect on food production. This suggests that the expansion of urban land encroaches on arable land and premium ecosystems, subsequently resulting in a decrease in ESs, and this impact is obvious in these regions []. Despite the negative impacts of urbanization on ESs, the impact of urbanization on ESs diminished after 2015 (Figure 9). With the development of urban processes, governments have increasingly acknowledged the significance of ecological preservation, prompting the rollout of protective policies. Notably, the Outline of the Plan for Coordinated Development for the BTH Region, released in April 2015, emphasized the synergy between ecological protection and economic development. In addition, by the end of 2017, the BTH region delineated the red line for ecological protection, marking a further escalation in environmental conservation efforts. These initiatives have served as pivotal guides in the urbanization trajectory, mitigating the detrimental impacts of urban sprawl on ecosystems.
4.3. Urbanization Under Sustainable Development
This study found a positive relationship between urbanization and water yield, in contrast to the negative associations for carbon sequestration and food production. Furthermore, the correlation between urbanization and ESs strengthened during 2000–2020. This indicated that urbanization adversely affected carbon sequestration and food production while augmenting water yield. In addition, the impact of intra-city disparities on the relationship between urbanization and ESs showed a decreasing trend, suggesting that urbanization from exclusive land occupation transferred to sustainable human/land relations. This is consistent with previous studies. Existing studies have also found economic polarization in the process of urbanization [,]. Furthermore, the relationship between urbanization and ESs in the BTH region showed an upward fluctuating trend from 1996 to 2014 and experienced a lag in urbanization to a lag in ESs, suggesting that the ESs maintained good development under high urbanization []. In addition, research on urbanization in China has also shown that the more intensive the land use, the lower the impact on ecosystems []. Our study complements this perspective by demonstrating a decreasing impact of intra-city disparities on the UES relationship, which may reflect improvements in land use efficiency and the adoption of more sustainable urban planning practices.
To ensure the sustainable development of both urbanization and ESs, it is imperative to enhance their collaboration through the implementation of the BTH collaborative development strategy. First, the economic development layout should be optimized. The economic development of northwestern regions (such as Chengde and Zhangjiakou) is greatly constrained by natural geographical factors, and the development of regional urbanization is weak, while the advantages of natural resources are obvious. These cities should change their economic development mode and combine their natural resource advantages to stimulate their economic development potential with models such as tourism cities around Beijing and Tianjin or urban oxygen bars. Beijing, Tianjin, Shijiazhuang, Baoding, and Qinhuangdao should focus on the effective unification of resource protection and urban development while urban construction is underway and take the construction of ecological civilization as the fundamental guideline to promote long-term and effective economic development. Handan, Xingtai, Hengshui, and other regions, which are in the main grain-producing areas, should optimize their industrial layout and promote synergistic regional development based on the principle of the red line for the protection of cultivated land. Furthermore, this strengthens the intra-city cluster cooperation. Significant variations also exist among cities, such as within the Beijing region, where there is a considerable disparity in economic development between the core area and suburbs. It is crucial to leverage the spatial spillover effect and establish an intra-regional synergy mechanism to foster collaborative development. This will facilitate the efficient circulation of population, economy, and resources across various parts of the city, ultimately contributing to the advancement of surrounding areas.
4.4. Implications and Limitations
The patterns and the interaction between urbanization and ESs are likely to be relevant in other rapidly urbanizing parts of the world. For example, in Southeast Asia or Africa, where many cities are experiencing rapid growth [,], the lessons from our study can inform policies to balance urban expansion with the preservation of ecosystem functions. Additionally, policymakers could use our findings to design urbanization strategies that minimize negative impacts on the environment and ensure food security.
However, there are still some deficiencies. Firstly, we used the model to calculate the water yield, though these methods were widely applied in ES research [,]. Nevertheless, the model still has uncertainty about the accuracy of the results. Secondly, the determination of food production was based on the gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery, and inflation between years is not considered. In the future, price differences due to inflation need to be amended.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the match relationship between urbanization and ESs and further explored the impact of intra-city disparities on the match relationship in the BTH region from 2000 to 2020. We revealed that urbanization, water production, NPP, and food production in the BTH region showed increasing trends but with large spatial variations. Using the bivariate local Moran’s index analysis, there were different characteristics in the spatial aggregation patterns of urbanization and ESs, and urbanization was significantly positively correlated with water yield and negatively correlated with NPP and food production, with significant differences in correlation coefficients among different cities. Economic polarization led to unbalanced regional development and affected ecosystem service functions. The analysis showed that economic polarization was weakening in most areas of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, and the impact of economic polarization on the match relationship between urbanization and ESs was weakening over time. This suggests that the concept of urban construction and development is shifting from pure land occupation to sustainable human/land relations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land14061196/s1, Figure S1: Spatial distribution of change of urbanization on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2020; Figure S2: Spatial distribution of change of (a) water yield, (b) carbon sequestration (Net Primary Productivity, NPP) and (c) food production on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2020; Figure S3: Temporal change of Tsui-Wang (TW) index on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2020; Figure S4: Temporal change of impact of Tsui-Wang (TW) index to correlation between urbanization and ecosystem services on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2020.
Author Contributions
J.L.: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing—original draft; C.D.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing; Q.Y.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—review and editing; H.L.: Data curation, Software, Writing—review and editing; L.F.: Methodology, Writing—review and editing; X.W.: Software, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Henan Key Laboratory Program of Remote Sensing and GIS (No. SZKF202302) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No. AR2203).
Data Availability Statement
The climate data that support the findings of this study are available at https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/ (accessed on 22 October 2024). The Net Primary Productivity data that support the findings of this study are available at https://www.glass.hku.hk/archive/NPP/MODIS/500M/GLASS_NPP_500M_V60/ (accessed on 31 October 2024). The land cover data of 30 m that support the findings of this study are available at https://zenodo.org/records/4417810 (accessed on 27 September 2024) and land cover data of 500 m that support the findings of this study are available at https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v061/ (accessed on 30 October 2024). The GDP and population density datasets that support the findings of this study are available in the Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform at https://doi.org/10.12078/2017121102 and https://doi.org/10.12078/2017121101 (accessed on 9 December 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this study.
References
- Zhong, W.; Song, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, S. Revealing the nexus among energy-economy system with Haken model: Evidence from China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatio-temporal investigation of the interactive relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: Case study of the Jingjinji urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Chen, W.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial-temporal risk assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services based on pressure-status—Response framework. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, R.C.; Camerin, F.J.F. The application of ecosystem assessments in land use planning: A case study for supporting decisions toward ecosystem protection. Futures 2024, 161, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, A.; Egoh, B.N.; Lanzanova, D.; Grizzetti, B.; Bidoglio, G.; Pagliero, L.; Bouraoui, F.; Aloe, A.; Reynaud, A.; Maes, J.; et al. Mapping water provisioning services to support the ecosystem–water–food–energy nexus in the Danube river basin. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.; Willemen, L.; Hein, L. Assessing the Capacity of Ecosystems to Supply Ecosystem Services Using Remote Sensing and An Ecosystem Accounting Approach. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, M.; Ode Sang, A. Urban natural environments as nature-based solutions for improved public health—A systematic review of reviews. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.A.; Tadaki, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Arbuthnott, K.; Coutts, A.; Demuzere, M.; Dirks, K.N.; Heaviside, C.; Lim, S.; Macintyre, H.; et al. Health and climate related ecosystem services provided by street trees in the urban environment. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhai, G.; Yu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Coupling coordination between urbanization and ecosystem services value in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, B. Dynamics of ecosystem services in response to urbanization across temporal and spatial scales in a mega metropolitan area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The coupling curve between urbanization and the eco-environment: China’s urban agglomeration as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhai, N.; Mu, H.; Miao, J.; Li, W.; Li, M. Assessment of urban resilience and subsystem coupling coordination in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhao, C. Inter-Metropolitan Land-Price Characteristics and Patterns in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, H. Evaluating urban sustainability under different development pathways: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, S. Spatiotemporal dynamics of urban expansion in 13 cities across the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration from 1978 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, Y.M.; Austin, A.; Bardgett, R.; Catford, J.A.; Hector, A.; Iler, A.; Mariotte, P. The plant ecology of nature-based solutions for people, biodiversity and climate. J. Ecol. 2024, 112, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Guo, J.; Guo, Z.; Lee, J.C.K.; Liu, G.; Wang, N. Urban ecological transition: The practice of ecological civilization construction in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, T. China's Eco-City Construction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, G. Conflict or Coordination? Multiscale assessment of the spatio-temporal coupling relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: The case of the Jingjinji Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MODIS/Terra+Aqua Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 500m SIN Grid V061. 2022. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v061/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Sharp, R.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Wood, S.; Guerry, A.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide. 2018. Available online: https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/software/invest (accessed on 24 October 2024).
- Quarmby, N.A.; Milnes, M.; Hindle, T.L.; Silleos, N. The use of multi-temporal NDVI measurements from AVHRR data for crop yield estimation and prediction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, L.; Gou, M.; Chen, B.; Lv, J.; Xiao, W. Identification of Urban Ecological Security Pattern Based on Ecosystem Services Supply–Demand. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2024, 10, 0146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Huang, A.; Yin, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, L.; Lin, Z. Investigating the Impact of Urbanization on Water Ecosystem Services in the Dongjiang River Basin: A Spatial Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, W.; Cao, S.; Mo, Y.; Du, M.; He, Z. The impact of multidimensional urbanization on sustainable development goals (SDGs): A long-term analysis of the 31 provinces in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B. Coupling relationship between urbanization and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Yangtze River economic Belt and its socio-ecological driving forces: A county-level perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Tsui, K.Y. Polarization orderings and new classes of polarization indices. J. Public. Econ. Theory 2000, 2, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban. Plann. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y. Addressing the rural in situ urbanization (RISU) in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region: Spatio-temporal pattern and driving mechanism. Cities 2018, 75, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhao, J.; Yan, S.; Zhu, M. Coupling coordination of new urbanization in Chinese urban agglomeration-characteristics and driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 117082–117095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ning, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, H. Identification of Metropolitan Area Boundaries Based on Comprehensive Spatial Linkages of Cities: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, G.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Land Space and High-Speed Transportation Coordinated Development Evaluation in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China. Land 2024, 13, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.; Fu, B. Understanding the impacts of climate and landuse change on water yield. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2018, 33, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qie, X. Quantitative assessment of the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on net primary productivity of vegetation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1508433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Qi, Y.; Pei, H.; Shen, Y. Balancing water and food by optimizing the planting structure in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 262, 107326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Spatiotemporal exploration of ecosystem service, urbanization, and their interactive coercing relationship in the Yellow River Basin over the past 40 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, F.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X. The impact of land-use change on water-related ecosystem services: A study of the Guishui River Basin, Beijing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S148–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Economic and Ecological Coupled Coordination: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Land 2024, 13, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.N.; Connor, D.S.; Stuhlmacher, M.; Peng, J.; Turner Ii, B.L. More urbanization, more polarization: Evidence from two decades of urban expansion in China. NPJ Urban. Sustain. 2024, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Z. The balance between economic development and ecosystem service value in the process of land urbanization: A case study of China’s land urbanization from 2000 to 2015. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourdes, K.; Gibbins, C.; Hamel, P.; Sanusi, R.; Azhar, B.; Lechner, A. A Review of Urban Ecosystem Services Research in Southeast Asia. Land 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, H.; Pauleit, S.; Lorz, C. Mapping the Loss of Ecosystem Services in a Region Under Intensive Land Use Along the Southern Coast of South Africa. Land 2019, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).