Abstract
Among its various targets on restoring natural habitats and ecosystems in the EU, the recently adopted Nature Restoration Law (NRL) introduces ambitious targets for restoring surface water bodies (SWBs) as well. Simultaneously, the Italian CAP Strategic Plan for the implementation of the Common Agricultural Policy 2023–2027 has been designed to enhance sustainable agricultural practices, including water resource management. This paper provides a comparative analysis of the synergies, gaps, and challenges between these two regulatory frameworks, focusing on sustainable water use in Italian agriculture. A two-level comparative matrix methodology is employed to evaluate the alignment between the NRL’s objectives for freshwater ecosystems and the measures taken by the Italian CAP Strategic Plan on water resources. The results highlight key areas of convergence, existing shortcomings, and necessary steps for aligning Italian agricultural policies with the EU’s water restoration goals. The findings offer insights for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders engaged in water governance, biodiversity conservation, and agricultural sustainability.
1. Introduction
Freshwater habitats are biodiversity hotspots that deliver essential ecosystem services, including food production, carbon sequestration, water purification, flood control, and erosion control. Nonetheless, the pressures on freshwater ecosystems are unprecedented. Roughly 75% of the world’s wetlands have been eradicated, endangering 28,000 freshwater species with extinction [1]. Freshwater biodiversity is, indeed, one of the most endangered components of the biosphere [2]. It is deteriorating at a significantly accelerated rate compared to terrestrial and marine ecosystems [3], attributable to anthropogenic pressures from land utilization throughout entire river basins, the accumulation of pollutants, organic-rich effluents, fine sediments, pesticides, and contaminants (nanoplastics and pharmaceuticals) [2,4]. Furthermore, fresh waters are degraded by hydromorphological alterations that have negatively affected ecological functioning and biodiversity of freshwater systems in Europe, such as climate change and the consequent rising temperatures, limited water availability, the presence of non-native species, and changes in river morphology [5,6,7,8].
These stressors affect ecosystem functioning, resulting in only about 40% of the more than 100,000 European river water bodies routinely monitored achieving good ecological condition in 2015 [9,10]. In addition, inputs of chemical and physical substances from agricultural practices, industrial activities, and urban development have the potential to contaminate both surface and groundwater bodies, thereby affecting the overall health and stability of catchments [11]. Nonetheless, freshwater habitats remain inadequately safeguarded worldwide, necessitating immediate conservation measures to mitigate these hazards via legislative initiatives [12,13]. In this regard, the EU has implemented a water policy known as the Water Framework Directive (WFD 2000/60/CE) [14], which aims to reduce pressures and achieve good status for all water bodies in Europe. The Directive takes a systems approach and aims to achieve ‘good status’ for rivers, lakes, coastal waters, and groundwater, and to prevent their deterioration [15]. As a result, EU Member States (MSs) have assessed the status of rivers, lakes, and coastal waters within their borders and implemented action plans to reduce negative impacts on the status of these water bodies [16].
Agriculture is recognized as a major contributor to the degradation of freshwater ecosystems [17]; it is a significant source of chemical pollution of surface water and groundwater due to the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals (nitrogen, phosphates, and nitrates) [18,19,20,21,22]. These contaminants can infiltrate rivers and lakes, resulting in eutrophication and detrimental effects on aquatic organisms. Moreover, agricultural runoff can contaminate groundwater, an essential supply of potable water for numerous people [23]. Consequently, to mitigate the impact of agricultural practices on water quality, coordinated research and policy initiatives are essential.
The recently approved Reg. (EU) 2024/1991, named “Nature Restoration Law” (NRL), [24,25,26,27] appears as a promising EU piece of legislation for the full recovery and protection of natural habitats towards the achievement of the Green Deal goals [28,29]. Despite some criticisms [30,31,32,33], this regulation may serve as a fundamental element of Europe’s aspirations to rejuvenate biodiversity and ecosystem services for the foreseeable future and exemplify worldwide leadership in tackling persistent environmental challenges [34,35]. In this scenario, the agricultural sector is undoubtedly one of the sectors most influenced by the objectives of the NRL due to its links with biodiversity and habitat conservation, food security, and climate change [36,37]. The application of the NRL is essential for achieving multiple objectives related to water resources, such as the restoration of freshwater ecosystems, the removal of obsolete river barriers, river-floodplain connectivity, river-coast-marine connectivity, and peatland rewetting [38]. However, it must be highlighted how the scientific research investigating the connections between the CAP instruments for water resources, on the one hand, and the NRL, on the other, is still taking its first steps. In fact, there is a lack of studies focusing on the potential synergies between the CAP Strategic Plans’ interventions and the NRL objectives specifically targeting freshwater resources [34,39].
The article aims to identify, for the first time, synergies between the NRL targets and the CAP to enhance the alignment of conservation priorities with policy and practice. The authors explore how these synergies can contribute to the effectiveness of conservation efforts of natural ecosystems, particularly freshwater resources. This work provides a spotlight on the Italian scenario. The structure of the paper is as follows: first, the authors provide a context analysis (Section 2), which includes an overview of the current state of Italian internal surface water bodies (SWBs) (Section 2.1), the NRL targets for freshwater resources (Section 2.2), and a review of water resource management within the framework of the 2023–2027 CAP reform (Section 2.3). The subsequent section (Section 3) outlines the methodology used to assess the potential alignment between NRL targets for freshwater resources and the CAP Specific Objectives (SOs). Finally, in the Results and Discussion section (Section 4) the authors first scrutinize the alignment between the NRL targets and the CAP 2023–2027 objectives at a more general level (Section 4.2); then, they offer an insight on the Italian scenario, assessing the synergies between the national CAP Strategic Plan and the NRL targets for freshwater resources (Section 4.2).
2. Context Analysis
2.1. The Current Situation of Italian Internal Surface Water Bodies (SWBs)
According to the latest data published in the 3rd River Basin Management Plan (RBMP) cycle (2021–2027), 43% of inland water bodies (rivers and lakes) are at high and good ecological status, while the ecological status of 10% of these water bodies is unknown. Apart from the number of lakes in good ecological status, which increased from 17% to 35%, the ecological status of SWBs shows a slight improvement compared to the 2nd RBMP cycle (2015–2021), where about 42% of rivers and lakes were in high and good ecological status [22,23].
In terms of chemical status, 78% of Italian rivers are in good chemical status, 13% are not good, and 9% have not been classified. For lakes, 69% are in good condition, 11% are not good, and 20% are not classified. Overall, there has been a general increase in the number of surface water bodies classified as good and unclassified compared to the 2nd RBMP, when 75.2% of rivers were in good chemical status, 6.8% were not in good status, and 17.9% were in unknown status. For lakes, in 2018, 48.1% were in good chemical status, 10.1% were not in good chemical status, and 41.8% were in unknown chemical status. It should also be noted that the number of water bodies changed between the 2nd and 3rd RBMPs. Notably, for rivers, there were 7493 water bodies in the 2nd RBMP compared to 6878 in the 3rd RBMP, while for lakes, the number of water bodies increased by one (348) in the 3rd RBMP [22,23,40,41].
Regarding river barriers, according to a recent survey conducted under the AMBER project (2022)1, Italy has just under 66,000 barriers along 135,000 km of river, or one every two kilometers, which is slightly lower than the European average [42]. In Italy, for example, 31% of the barriers surveyed are weirs, which were used in the past to extract water for watermills, sawmills, and foundries. Another important component of the existing river barriers in Italy is ramps or sills, which comprise about 12% of the barriers surveyed. Eventually, only 2% of river barriers in Italy are dams, which regulate the flow of water and raise the water level, forming a reservoir. Of all the barriers mentioned, dams cause a significant change in the flow of the river and interrupt the transport of sediments; their scarce presence in Italy should be a guarantee of greater continuity of the hydrographic network and the protection of biodiversity, avoiding damage to the fish fauna and reducing the consequences in terms of ecological and hydrogeological risks. Despite being few, dams provide a significant contribution in terms of water savings and reserves.
2.2. The NRL Targets for Freshwater Resources
The NRL is specifically designed to set binding targets for the recovery of the EU’s terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems as part of the overall strategy envisaged by the European Green Deal for climate neutrality by 2050 [28,43,44]. Regarding freshwater resources, the NRL aims to restore aquatic ecosystems and improve river connectivity to ensure a balance between environmental protection and sustainable use of water resources. Notably, the NRL requires MSs to consider measures to achieve good quantitative, ecological, and chemical status of water bodies in accordance with the WFD2, in addition to the removal of barriers to free-flowing rivers [45].
The NRL sets specific targets to be implemented progressively towards the full restoration of ecosystems across the EU. First, article 4 of the NRL requires that by 2030 at least 30% of the total area of all habitat types that are not in good condition must be restored: MSs must give priority to restoration in areas within the Natura 2000 network, which is an ecological network encompassing the entire territory of the Union, established in accordance with the Habitats [46] and Birds Directive [47] to ensure the long-term preservation of vulnerable or rare habitats and species. By the conclusion of 2018, 30% of Natura 2000 sites remained without conservation measures, management plans, or comparable instruments delineating conservation and restoration activities; among the 70% of Natura 2000 sites possessing conservation measures and management plans, compliance with EU criteria was frequently inadequate [35]. The same restoration measures must be carried out on at least 60% of the same habitat types by 2040 and on at least 90% of these sites by 2050, even if some derogations apply.
Article 9 (Restoration of the natural connectivity of rivers and the natural functions of the associated floodplains) is the only provision of the NRL that establishes specific restoration targets for SWBs tout court. Under this article, MSs are required to compile a list of artificial barriers affecting the connectivity of SWB, considering their socio-economic role. Moreover, MSs should identify which barriers should be removed to achieve the restoration targets set out in Article 4, including the objective of restoring at least 25,000 km of rivers in the EU to a free-flowing status by 2030. In the process of barrier removal, each MS shall give priority to the removal of obsolete barriers (i.e., those which are no longer needed for renewable energy production, inland navigation, water supply, flood protection, or other uses).
Similarly, to the above-mentioned implementation model for the 2023–2027 CAP reform, MSs will be required to draw up a National Restoration Plan (NRP) for the implementation of the NRL3. The NRP is the operational tool through which the NRL will be implemented, translating the ambitious European objectives into concrete actions at the national level. The plan should identify the specific areas to be restored and define the restoration measures to be implemented. The drafting of the NRP requires the creation of an inventory of existing river dams, with the goal of restoring the free flow of rivers. This process also includes considering interventions in water infrastructure supported by the Rural Development and Cohesion Policy; these will affect over 1600 km of water network, of which 1200 km will be dedicated to adaptation and conversion measures aimed at reducing losses and improving the efficiency of the irrigation network. Most of this water will be left in watercourses to ensure a better supply to already irrigated areas (especially during periods of water scarcity). Moreover, in the case of ecologically critical abstractions, they will ensure an effective reduction in abstractions contributing to the protection objectives of the WFD and the objectives of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [48,49]. Eventually, the NRPs will have to include the measures necessary to achieve good quantitative, ecological, and chemical status of water bodies, as defined in the programs of measures of the RBMPs, in accordance with the WFD.
2.3. Water Resources in the Context of the Reform of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) 2023–2027
In line with Reg. (EU) 2021/2115 [50], the Italian CAP Strategic Plan [51] provides a result-oriented intervention strategy structured around the Strategic Objectives (SOs) of the CAP 2023–2027 in accordance with the so-called new delivery model introduced in the latest reform. Among the CAP objectives, the one which is most concerned with the protection and quality of water resources is SO5 “Promoting sustainable development and efficient management of natural resources such as water, soil and air, including by reducing chemical dependency”. The CAP Strategic Plan, under OS5, aims to reduce pollution and environmental degradation caused by plant protection products and fertilizers, mitigate erosion and improve soil fertility, reduce water pollution, and protect air quality. Actions include eco-schemes, sectoral interventions, and productive investments for rural development, with a budget of €9 billion.
In this framework, Result Indicators (RI), included in the CAP Strategic Plans, are used to set milestones and targets quantified by each MS in relation to the achievement of the envisaged SOs. Planned interventions must contribute directly and significantly to the result indicators to demonstrate the effectiveness of implementation. The SOs and the corresponding indicators are listed in Reg. (EU) 2021/2115. The RIs associated with the SO5 indicator are shown in Figure 1.
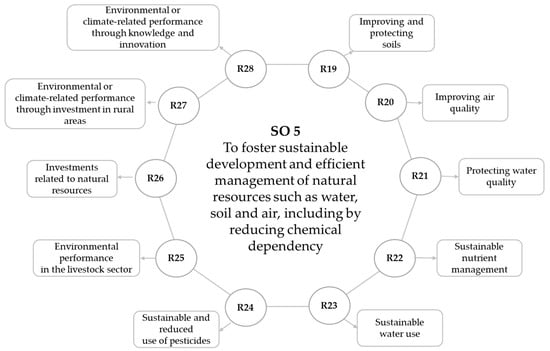
Figure 1.
SO5—Promote sustainable development and efficient management of natural resources such as water, soil and air. Source: Reg. (EU) 2021/2115.
The RIs most closely related to the protection of water resources are R21 “Protect water quality”, R23 “Sustainable Use of Water”, and R26 “Natural Resources Investments”. The R21 indicator sees a fundamental contribution from commitments relating to the grassing of tree crops and specific measures for pollinators, as well as the management of permanent meadows and pastures, and support for organic farming. There are many commitments financed by rural development in the field of environment and climate that can contribute to the protection of water quality. Reference is made to integrated production, reduced soil tillage techniques, grassing of tree crops, conversion of arable land to meadows and pastures, afforestation/afforestation systems on non-agricultural land, non-returnable crops ecological corridors ecological strips, reduction of the use of pesticides, specific commitments for the sustainable use of nutrients, precision farming practices, set-aside of arable land from production.
The R23 indicator derives from the estimate of the surfaces used for the grassing of tree crops, the surfaces with reduced soil tillage techniques and the surfaces that adopt precision agriculture practices. The indicator includes specific commitments for the sustainable use of water and the greening of tree crops. The R26 indicator aims to capture operations linked to natural resource management within the framework of productive investments for farm competitiveness, environmental, climate, and animal welfare improvements, and non-productive agri-environmental investments.
Most of the interventions related to these indicators fall within the agri-forestry-climate-environmental management measures foreseen in the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development4 (EAFRD) interventions. The new CAP provides various instruments for water management, including agri-environmental measures, investments contributing to environmental objectives, and investments for irrigation (article 74), which are in line with the WFD [38].
In light of the discussion, it is necessary to apply a methodology to assess all CAP SOs and their connection with NRL targets.
3. Materials and Methods
The goal of this paper is to compare the CAP 2023–2027 SOs, reflected in the Italian CAP Strategic Plan, with the targets established by the NRL for the restoration of natural ecosystems with a particular focus on the restoration of freshwater resources, assessing their potential synergies, gaps, and challenges. To conduct this research, a systematic approach was adopted, based on the selection of a homogeneous set of objects of the same type (cases) and noting their status with respect to specific properties, which were transformed into variables through operational definitions [52].
Methods
The information acquisition process was implemented through a systematic and structured approach, following the methodological framework described previously. Each phase of the process was carried out with specific resources, criteria, and procedures aimed at ensuring accuracy, transparency, and replicability. The following sections provide a detailed account of the reporting phase.
- (1)
- Identification of normative texts subject to analysis.
The first phase consisted in the selection of the legislative texts relevant to the research objectives. This was achieved through a systematic review of key regulatory documents at both the European and national levels.
Sources and selection criteria:
- -
- European Union Legislation: Regulation (EU) 2021/2115 on the CAP Strategic Plans and Regulation (EU) 2024/1991 on NRL);
- -
- National Legislation: The Italian CAP Strategic Plan was obtained from the official website of the Italian Ministry of Agriculture.
Inclusion criteria were derived inductively from the actual selection process and reflect the operational assumptions that guided the identification of relevant documents.
- (2)
- Identification of keywords in the NRL targets.
The second phase involved extracting keywords from the objectives set out in the NRL. A textual analysis of the regulation’s content was conducted to identify central themes and concepts.
Procedures:
- -
- The text of the NRL was examined article by article.
- -
- Key expressions and concepts (e.g., “ecosystems”, “restoration”, “habitats”) were identified through manual annotation;
- -
- The frequency, recurrence, and thematic relevance of each term were assessed to determine its inclusion.
- -
- A structured list of keywords was compiled and organized by thematic cluster (Table 1).
 Table 1. Keywords identified in the NRL.
Table 1. Keywords identified in the NRL.
- (3)
- Systematic review of the Italian CAP Strategic Plan using keywords.
In the third phase, the Italian CAP Strategic Plan was systematically reviewed using the previously identified keywords as reference points. The goal was to map the presence and relevance of these keywords within the Strategic Plan.
Implementation:
- -
- The full document was analyzed using digital search functions to locate keyword occurrences;
- -
- Each occurrence was contextualized to verify its substantive relevance to NRL targets, rather than simple terminological presence;
- -
- This phase allowed for the preliminary identification of potentially relevant interventions.
- (4)
- Identification of relevant interventions in the CAP Strategic Plan.
Following the keyword search, interventions explicitly linked to the identified terms were extracted from the CAP Strategic Plan.
Operational Steps:
- -
- All interventions containing at least one relevant keyword were compiled;
- -
- For each intervention, the surrounding text was reviewed to assess thematic alignment with NRL targets;
- -
- Interventions were included only if the keyword appeared in a context directly related to ecosystem restoration, biodiversity, or nature protection;
This process resulted in a subset of CAP interventions for in-depth analysis.
- (5)
- Analysis of objectives, outcome indicators, and financial allocations.
Each intervention selected in the previous phase was subjected to a detailed analysis focused on three core components:
- -
- Associated CAP SOs: The specific policy goal addressed by the intervention;
- -
- Results indicators (RI): the expected results and measurement metrics provided within the CAP documentation;
- -
- Financial allocation: the monetary resources allocated to the intervention.
- (6)
- Creation of the comparative matrix (Table 2).
 Table 2. Comparative matrix: SOs of the CAP 2023–2027 and the NRL targets.
Table 2. Comparative matrix: SOs of the CAP 2023–2027 and the NRL targets.
A comparative matrix was constructed to analyze the synergies between CAP objectives and NRL targets.
Structure of the matrix:
- -
- Rows: represent the specific objectives of the CAP (SO1, SO2, …, SOn);
- -
- Columns: represent the targets of the NRL (Art. 1, Art. 2, …, Art.n);
- -
- Cells (Dx,y): indicate whether a synergy exists between objective x and target y, based on the presence and characteristics of relevant interventions.
Criteria for Assigning Synergies:
- -
- Number of interventions linked to a given NRL target;
- -
- Financial weight of the intervention within the CAP Plan;
- -
- Relevance and strength of outcome indicators;
- -
- Qualitative assessment of the contribution to NRL objectives, based on alignment with the regulation’s strategic vision.
The matrix provided a structured and comparable overview of the connections between agricultural policy interventions and environmental restoration goals, serving as a central tool for qualitative analysis and interpretation. This comprehensive approach allowed for the identification of synergies, mismatches, and areas for policy improvement in the intersection between the CAP and the NRL.
4. Results and Discussions
The comparative matrix analysis facilitated an evaluation of the synergies and gaps between the NRL targets and the CAP 2023–2027 objectives. Notably, thanks to the adopted methodology (keywords identification and in-text review), a two-tiered analysis was conducted: first, an overview was provided to asses the alignment between the CAP SOs and the NRL targets; second, the focus shifted to the Italian scenario highlighting the alignment between the already-discussed NRL targets, on one side, and the interventions envisaged by the Italian CAP Strategic Plan regarding freshwater resources, on the other.
4.1. The Alignment Between the NRL Targets and the CAP 2023–2027 Objectives
A strong alignment is identified between CAP’s environmental sustainability objectives—SO4, SO5, and SO65 (green rows in Table 2)—and key objectives of the NRL (see Table 1). These CAP objectives, which focus on efficient natural resource management, biodiversity preservation, and climate change mitigation, exhibit significant interconnections with Article 4 of the NRL (Restoration of terrestrial, coastal, and freshwater ecosystems). They also relate closely to Article 11 (Restoration of agricultural ecosystems) and Article 12 (Restoration of forest ecosystems), which address the restoration of agricultural and forest ecosystems, respectively. In particular, biodiversity conservation and habitat restoration emerge as crucial points of convergence between these frameworks. Furthermore, article 13 of the NRL, which aims to plant three billion additional trees, can be supported by CAP subsidies that encourage reforestation and the conversion of non-productive agricultural land into forested areas [58]6.
However, the analysis highlights certain misalignments regarding the economic sustainability objectives of the CAP (gray rows in Table 2). In fact, the objectives related to farmers’ income support, agriculture competitiveness, and the strengthening of farmers’ position in the value chain (SO1, SO2, SO3) have only a weak connection with the NRL targets. The most significant, albeit weak, connection is identified between SO1 (which envisages some income support to beekeepers in the form of direct payments) and Article 10 of the NRL (Restoration of pollinator populations), which addresses the decline of pollinators and their impact on agricultural productivity, particularly in beekeeping. Eventually, a weak connection is identified between the CAP social sustainability objectives (orange rows in Table 2)—SO8 (Vibrant rural areas) and SO9 (To protect food and health quality) and the NRL targets (notably, with articles 4, 6, 8, 11, 12). No connections are found between SO7 (Generational Renewal) and any NRL targets.
This misalignment reflects a broader trend within the CAP 2023–2027 framework, where economic sustainability objectives, particularly those aimed at enhancing farmers’ income and competitiveness (SO1, SO2, SO3), are often prioritized over social and, foremost, environmental goals [60,61,62]. As the EU Court of Auditors recently observed, the CAP Strategic Plans for 2023–2027 are greener than those from the previous period, but they fall short of meeting the EU’s climate and environmental ambitions, while also lacking key elements needed to assess green performance [62].
Last, but not least, a crucial aspect of CAP’s contribution to the NRL restoration goals is its cross-cutting objective on knowledge and innovation (OS10) (blue row in Table 2). The dissemination of technical expertise and the adoption of innovative solutions are essential for achieving sustainability and facilitating the transition towards improved water management. This is particularly relevant to Article 9 of the NRL, which focuses on restoring river connectivity and floodplain functions. Without knowledge-sharing mechanisms and technical support, these restoration goals would be difficult to achieve [34]. Innovation also plays a key role in optimizing water use in agriculture [63]. Technologies such as precision irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and artificial intelligence applied to river basin management can significantly enhance water conservation efforts [64]. Integrating these advancements within the CAP framework could improve the effectiveness of water restoration measures, ensuring a balance between agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability.
Several CAP-supported agricultural practices contribute directly to the NRL’s goals, particularly in Natura 2000 sites, which benefit from sustainable land management strategies aimed at conserving biodiversity [65]. Farmers operating in these areas can receive financial compensation for adhering to conservation restrictions. The NRL sets specific restoration targets for protected areas, and properly aligned agricultural practices can contribute to improving their ecological quality. For example, restoring wetlands within agricultural lands can enhance biodiversity and water retention, offering mutual benefits for both agriculture and nature restoration [27,32].
Other examples of synergies between the CAP-supported agricultural practices to NRL targets in Italy can be found in the case of the so-called “Bio-distretti” (“Eco-Regions”, in English), which operate in almost every Italian region. Eco-Regions represent an innovative form of territorial governance in which citizens, institutions, farmers and other actors in the agricultural chain enter into a pact for sustainable land management, according to the principles of organic farming [66,67]. Experiences such as the Lazio Eco-Regions demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating the CAP with local initiatives in favoring production models with a low environmental impact, with particular attention to the protection of aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity [68]. For example, several organic farms in the Tuscia and Sabina areas (Lazio region) are already applying conservative soil management and low-consumption irrigation practices, combined with the creation of on-farm wetlands and rainwater harvesting basins, in line with the objectives of the NRL. These experiences show how the coordinated application of agricultural and environmental policies can lead to concrete solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change, promote ecological connectivity and ensure efficient management of water resources, while increasing agricultural incomes and territorial resilience.Despite all these actual and potential synergies, the comparative analysis also reveals the NRL targets that remain outside the CAP’s scope. For instance, the restoration of marine ecosystems (article 5) falls outside the CAP (and under the Common Fisheries Policy instead), and measures related to national defense do not intersect with CAP objectives. Nevertheless, establishing strong synergies between agriculture and biodiversity restoration remains essential for achieving the Green Deal’s ambitious sustainability goals. To this end, EU Member States must ensure that their National Restoration Plans align with the CAP Strategic Plans, reinforcing the interconnectedness of agricultural and environmental policies7.
Besides, we highlighted how recent CAP initiatives have demonstrated just a limited commitment to the greening of agriculture [39,62]. In this regard, to ensure effective implementation, an integrated monitoring system between the CAP and NRL is recommended. CAP requires continuous evaluation of its environmental measures, while the NRL relies on data to track ecosystem restoration progress. A joint monitoring approach could assess improvements in agricultural areas contributing to nature restoration, greenhouse gas emissions, and biodiversity levels. Advanced technologies such as satellite imagery, drones, and environmental sensors could enhance the accuracy and reliability of ecosystem monitoring. Additionally, digital platforms could facilitate data-sharing among institutions, farmers, and researchers, improving coordination and decision-making [69].
In summary, the integration of CAP and NRL policies presents an opportunity to promote sustainable agriculture [70]. A key factor in successful implementation is the active involvement of local communities and farmers, ensuring that restoration measures and sustainable water management strategies are tailored to regional needs. Strengthening collaboration between agricultural stakeholders and environmental policymakers will be essential in achieving the long-term sustainability goals of both the CAP and the NRL.
4.2. A Focus on Italy: Assessing the Alignment Between the National CAP Strategic Plan and the NRL Targets for Freshwater Resources
As foreseen in the afore-mentioned Reg. (EU) 2021/2115, the CAP Strategic Plans for the 2023–2027 programming period address the issue of water protection under the SO5 (“Promoting sustainable development and efficient resource management”), with reference to the specific issues of both quantity (making the use of water resources in agriculture efficient and sustainable) and quality (protecting surface and deep waters from pollution). The CAP Strategic Plan defined by Italy for the period 2023–2027 supports sustainable water management through the financing of investments (SRD), both at farm and non-farm level, and through the programming of the use of resources for agri-environmental commitments (ACA) and compensatory payments (SRC) that have a positive impact on the use of water resources. Among these interventions, the only one fully dedicated to water resources is the SRA 02 ACA 2 (Specific commitments for the sustainable use of water), which responds to two SOs of the CAP 2023–2027: SO4 (Contributing to climate change mitigation and adaptation, including by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon sequestration, and promoting sustainable energy), and the just-mentioned SO5 [38]. The intervention, therefore, contributes to the management optimisation of available irrigation volumes, and it also promotes farmers′ active role in adapting to climate change by adapting irrigation practices (volumes and irrigation times) to actual weather patterns and climate change-related variability. This intervention of the Italian CAP Strategic Plan aims to promote sustainable water management in agriculture. The objective is to reduce water wastage and improve the adaptation of farms to the effects of climate change through the introduction of innovative systems that support the farmer in irrigating according to actual crop needs. The commitment was foreseen in the Rural Development Complements 2023–2027 by six out of the twenty Italian regions (Calabria, Campania, Lazio, Toscana, Umbria, and Veneto) with specific adaptations to the territorial needs. It provides for an annual payment to farmers who voluntarily commit to advanced water management practices. These practices consist of the use of expert systems for calculating the soil-plant-atmosphere water balance that estimate the irrigation volumes needed for each crop according to the phenological phase and seasonal climatic conditions. These tools allow a sustainable use of water, ensuring efficiency in both the volumes delivered and the timing of irrigation interventions.
Several commitments are required from the beneficiary. First of all, water must be withdrawn according to regionally defined irrigation methods from authorised sources such as surface networks or groundwater tables, and high-efficiency irrigation systems such as micro-irrigation or sprinkling must be used, excluding low-efficiency systems such as run-off or lateral infiltration from furrows. Each plot must be equipped with a farm meter to monitor the irrigation volumes distributed. In addition, the farmer must subscribe to a regional web-based irrigation assistance system that provides indications on the volumes to be administered and the timing of interventions. The volumes actually distributed must comply with the system’s indications, and irrigation operations must be supervised to avoid malfunctions. Each intervention must be accurately recorded, including dates of sowing, harvesting, and all irrigations carried out. Records must be kept in digital or paper format. Then, adhesion to the measure involves specific eligibility criteria. Individual and associated farmers or public bodies managing agricultural holdings may join, but the regions have established additional requirements, such as the minimum area under commitment in relation to the farm area and the list of eligible crops. Eligible crops vary according to the regional context and range from horticultural and floricultural crops to irrigated arable land, fruit, olive trees, and vines.
At the regional level, intervention is implemented in a differentiated manner. In the Calabria Region, for example, horticultural, floricultural, arboreal, and irrigated arable crops are eligible, and all selection criteria are applied to favour environmental effectiveness. The Lazio Region limits eligible crops to spring-summer arable crops, kiwi, and hazelnuts, and focuses on vulnerable areas. The Region of Tuscany only includes species for which irrigation assistance is available, with a focus on protected and Natura 2000 areas. In the Umbria Region, intervention is only available for certain crops such as vegetables, tobacco, and fruit. The Veneto Region activates the intervention only in the plain and hills, in regional irrigation districts, with the obligation of drawing from the surface network and excluding the water table. Each Region also establishes the amount of support, which varies from a minimum of around 100 euros to over 800 euros per hectare per year, with degressivity thresholds applied only in some Regions.
In sum, the SRA02—ACA 2 intervention aims to support the climate resilience of agro-ecosystems, while contributing to the objectives of the WFD and the NRL by facilitating the transition to low water use production models. The expected impacts of its implementation are:
- Active farmer participation. It encourages the adoption of monitoring and decision-making systems based on climate data, promoting dynamic management of irrigation volumes and times.
- Optimisation of irrigation volumes. A structural reduction in agricultural water withdrawals is envisaged through precision irrigation techniques and improved system efficiency.
- Climate adaptation. It will strengthen the ability of farms to respond to periods of water stress and mitigate production losses due to drought and extreme weather events.
- Contribution to biodiversity conservation. It reduced water abstraction and calibrated water use limits pressure on aquatic ecosystems and promotes the conservation of associated habitats.
On the other hand, some barriers to the SRA02—ACA 2 implementation are:
- Limited access to initial investment. Modernising irrigation practices requires large financial resources, which are not always available to small farms, especially in marginal or disadvantaged areas.
- Low levels of digitalisation and technical skills. The transition to “data-driven” irrigation practices requires advanced technical skills that not all farms have, especially in less innovative areas.
- Fragmented institutional coordination. The complex governance of water resources in Italy involves multiple actors such as river basin districts, regional authorities, and irrigation consortia.
- Climatic variability and lack of data. The rapidity of meteorological changes and the lack of local monitoring stations hinder the correct planning and calibration of irrigation practices.
The following table (Table 3) summarizes the key impacts and the main obstacles regarding the implementation of the intervention at the regional level:

Table 3.
Key impacts and the main obstacles regarding the implementation of the SRA02—ACA 2 at the regional level.
Besides, the measure aligns with the agricultural actions provided for in the National Plan for Adaptation to Climate Change (NPACC) [72], which aim to promote and strengthen methods and practices for the rational use of water resources and to improve the adaptation of farms to climate change, reducing their vulnerability to the extreme weather events that currently characterise the climate.
In general, the Italian CAP Strategic Plan and the NRL share several key objectives regarding the sustainable management of water resources. Their synergies include:
- Sustainable irrigation practices. The CAP promotes efficient irrigation systems and precision agriculture to optimise water use in agriculture (SRA24—ACA24—Precision farming practices), in line with the objectives of the NRL to reduce water extraction from natural ecosystems.
- Restoration of agricultural wetlands. Both policies support the restoration of wetlands and riparian zones to enhance biodiversity, improve water retention and mitigate the effects of droughts and floods.
- Reducing agricultural pollution. The CAP includes measures to reduce nitrogen and pesticide run-off, which complements the Nature Conservation Act’s aim to improve water quality in rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
- Climate-smart agriculture. To promote agro-ecological approaches and soil conservation techniques helps to maintain the water balance in agricultural landscapes and supports wider environmental restoration efforts.
By integrating the principles of the European Water Resilience Strategy [73]8, the NRL and the Italian CAP Strategic Plan, the EU aims to create a more sustainable and resilient agricultural and environmental framework to ensure the long-term availability and quality of water resources. The European Water Resilience Strategy will establish a comprehensive, multi-annual, cross-sectoral plan with key milestones set for 2030 and 2040. This strategy aims to ensure the sustainable management of water resources while addressing water scarcity and promoting innovation in the water sector. The approach will encompass both EU-wide and global actions, reinforcing Europe’s commitment to water security and sustainability.
The primary goal of the European Water Resilience Strategy is to make Europe water-resilient by implementing effective water management policies and tackling issues related to water scarcity. The European Water Resilience Strategy aligns closely with the NRL, which aims to restore degraded ecosystems, enhance biodiversity, and mitigate climate change effects. The intersection between the two policies is outlined below.
- Ecosystem-Based Water Management: Both strategies emphasize the importance of restoring wetlands, rivers, and floodplains to improve natural water retention, reduce flood risks, and enhance water purification.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Healthy aquatic ecosystems contribute to biodiversity preservation. The restoration of natural habitats under the NRL will support the goals of the Water Resilience Strategy by ensuring sustainable water bodies and improved ecological conditions.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The integration of nature-based solutions, such as reforestation and wetland restoration, will enhance resilience to droughts and extreme weather events, contributing to both water security and broader environmental sustainability.
- Circular and Sustainable Water Use: By promoting water reuse and reducing pollution, the Water Resilience Strategy complements the objectives of the NRL, ensuring that water ecosystems remain viable and productive for future generations.
The European Water Resilience Strategy will serve as a crucial step towards securing water resources for future generations, supporting economic growth, and enhancing environmental sustainability in the EU and beyond.
5. Conclusions
The CAP plays a fundamental role in the sustainable management of natural resources, such as water and soil, which are essential for ecosystem restoration and for the achievement of the ambitious targets of climate neutrality set by the European Green Deal. Protecting these resources is crucial not only for the continuity of agricultural activities but also for the health and resilience of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Agricultural practices that reduce chemical inputs contribute significantly to improving water and soil quality, thus supporting the recovery of degraded ecosystems and biodiversity. Sustainable soil and water management, particularly through efficient irrigation and agroecological practices, also enhances climate resilience by stabilizing the water cycle and preventing soil erosion.
The CAP aligns with the NRL in its aim to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by supporting sustainable agricultural practices and ecosystem restoration activities. The strong alignment between CAP objectives SO4, SO5, and SO6 with key NRL targets, particularly those related to terrestrial, agricultural, and freshwater ecosystem restoration, underscores CAP’s role in addressing environmental challenges such as climate change, natural resource management, and biodiversity loss. Moreover, CAP funding mechanisms, including subsidies for reforestation and the conversion of non-productive agricultural land into forests, directly support initiatives such as NRL’s goal to plant three billion additional trees. However, economic sustainability objectives of the CAP (SO1, SO2, and SO3) exhibit only weak connections with the NRL targets, with the most notable link being CAP’s limited income support for beekeepers, which aligns with NRL’s focus on pollinator restoration.
Despite CAP’s substantial budget allocation for environmental sustainability, with approximately 40% dedicated to green initiatives, challenges remain in local implementation. Some restoration measures may face resistance from farmers who perceive them as constraints to productivity. Financial incentives, training programs, and knowledge dissemination are therefore essential to ensure that sustainability goals are met without compromising agricultural profitability. Notably, CAP’s cross-cutting objective on knowledge and innovation (SO10) is crucial for facilitating the transition to sustainable water management. Advanced technologies such as precision irrigation, soil moisture sensors, and AI-driven river basin management can optimize water use and enhance conservation efforts. Another hurdle lies in the implementation of the environmental commitments envisaged by the CAP and the NRL, namely the area where an enhanced alignment is highly desirable in view of the climate neutrality targets set by the Green Deal. In fact, it must be highlighted how, thanks to the high degree of decentralization and flexibility envisaged by the new delivery model of the CAP 2023–2027, a relevant part of the actual environmental ambition largely depends on MS’s implementation choices and on farmers’ voluntary measures. Therefore, without stringent guidelines, monitoring, and accountability, there is a risk of minimal environmental progress.
Looking at the Italian context, the CAP Strategic Plan 2023–2027 incorporates interventions for sustainable water management, aligning with the NRL’s freshwater resource restoration goals. The integration of these policies under the European Water Resilience Strategy can enhance long-term water security and sustainability, supporting ecosystem-based water management, biodiversity conservation, and circular water use. In Italy, particular emphasis should be placed on restoring internal aquatic ecosystems, such as river networks, wetlands, and freshwater habitats, which play a critical role in maintaining water quality and biodiversity. Efforts to reduce nitrogen and pesticide runoff, as well as initiatives to restore riparian zones and floodplains, are essential for improving the resilience of Italy’s freshwater ecosystems.
Ensuring greater synergy between infrastructure, environmental, and agricultural policies is essential. Investments in multi-purpose reservoirs, renewable energy integration, and governance innovations can optimize water resource management. The restoration of river ecosystems, a key priority under the NRL, requires an integrated approach addressing pollution, habitat degradation, and hydrological modifications. Italy must also prioritize the protection and rehabilitation of internal aquatic ecosystems, ensuring that river connectivity projects align with broader sustainability goals.
To conclude, this study represents a first effort in analyzing the potential synergies between the CAP 2023–2027 and the NRL. Their integration presents an opportunity to transition towards an agricultural model that maintains productivity while preserving natural capital. Achieving the Green Deal’s sustainability goals requires enhanced collaboration among policymakers, farmers, and environmental stakeholders to implement effective restoration strategies. By aligning agricultural and environmental policies, the EU can promote biodiversity conservation, climate resilience, and sustainable water resource management, ensuring the long-term viability of both farming and natural ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Methodology, G.P.; Writing—original draft, A.M. and R.P.; Writing—review & editing, M.H., L.S. and S.C.; Supervision, A.P. and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Notes
| 1 | Website of the project: https://amber.international/. |
| 2 | Cfr. Whereas (66) of the Nature Restoration Law. |
| 3 | Cfr. Articles 14–19 of the NRL. |
| 4 | The European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD) supports rural development across EU countries as part of the CAP. It promotes sustainable land use, environmental protection, rural diversification, and modernization of agriculture. Special focus is given to climate action and support for young farmers. |
| 5 | Within the CAP 2023–2027, OS1 (to ensure a fair income for farmers), OS2 (to increase competitiveness), OS3 (to improve the position of farmers in the food chain) concern economic sustainability. OS4, OS5, OS6, discussed above, concern environmental sustainability. While OS7 (to support generational renewal), OS8 (vibrant rural areas), and OS9 (to protect food and health quality) represent the social sustainability targets. Cf. [53,54,55,56,57]. |
| 6 | Cf. also the recent EU Regulation on Deforestation-free Products, Reg. (EU) 2023/1115 [59]. |
| 7 | This is explicitly stated by Art. 14, para. 14, letter (h) of the NRL, as well as by Art. 15, para. 5, which prescribes that each National Restoration Plan shall include “an overview of the interplay between the measures included in the national restoration plan and the national CAP strategic plan”. |
| 8 | The Water Resilience Strategy is a series of initiatives and policies aimed at ensuring the sustainability and efficient management of water resources in Europe, particularly addressing challenges related to climate change, water scarcity, and pollution. |
References
- Darwall, W.; Bremerich, V.; De Wever, A.; Dell, A.I.; Freyhof, J.; Gessner, M.O.; Grossart, H.; Harrison, I.; Irvine, K.; Jähnig, S.C.; et al. The Alliance for Freshwater Life: A global call to unite efforts for freshwater biodiversity science and conservation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, F.M.; Tilley, R.M.; Tyler, C.R.; Ormerod, S.J. Microplastic ingestion by riverine macroinvertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: Recent progress and future challenges. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Sánchez, A.; Rico, A.; Vighi, M. Effects of water scarcity and chemical pollution in aquatic ecosystems: State of the art. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Clavero, M.; Sánchez, M.I.; Vilà, M. Global ecological impacts of invasive species in aquatic ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures 2018; EEA Report No 7/2018; European Environment Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Water and Agriculture: Towards Sustainable Solutions; EEA Report No 17/2020; European Environment Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, M.N.; Riza, M.; Pervez, M.d.N.; Khyum, M.M.O.; Liang, Y.; Naddeo, V. Environmental and health impacts of PFAS: Sources, distribution and sustainable management in North Carolina (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.L.; Cazalis, V.; Dudley, N.; Hoffmann, M.; Rodrigues, A.S.L.; Stolton, S.; Visconti, P.; Woodley, S.; Kingston, N.; Lewis, E.; et al. Area-based conservation in the twenty-first century. Nature 2020, 586, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Zarra, T.; Pervez, M.N.; Papamichael, I.; Zorpas, A.A.; Li, C.W.; Klontza, E.; Lekkas, D.F.; Belgiorno, V. A comparative analysis of ecological status assessment in river water quality under the European Water Framework Directive. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2000/60/EC—Water Framework Directive. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Grizzetti, B.; Lo Porto, A.; Barkved, L.; Joy, K.; Paranjape, S.; Deelstra, J.; Manasi, S. The Science-Policy-Stakeholders Interface in Water Pollution Assessment. In Science, Policy and Stakeholders in Water Management: An Integrated Approach to River Basin Management; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, S.; Rathore, S.S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, V.; Raj, R.; Yadav, D.; Shekhawat, K.; et al. Exploring agricultural waste biomass for energy, food and feed production and pollution mitigation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamam, M.; Pergamo, R.; Manganiello, V.; Ferrigno, M. Agricultural Wastewater Reuse as a Circular Economy Model: Future Scenarios Considering Reg. (EU) 2020/741. Water 2024, 16, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickner, D.; Opperman, J.J.; Abell, R.; Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Dalton, J.; Darwall, W.; Edwards, G.; et al. Bending the Curve of Global Freshwater Biodiversity Loss: An Emergency Plan. BioScience 2020, 70, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Report from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council and the European Economic and Social Committee the State of Nature in the European Union Report on the Status and Trends in 2013–2018 of Species and Habitat Types Protected by the Birds and Habitats Directives—COM (2020) 635 Final. 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:52020DC0635 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- van Rees, C.B.; Waylen, K.A.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A.; Thackeray, S.J.; Kalinkat, G.; Martens, K.; Domisch, S.; Lillebø, A.I.; Hermoso, V.; Grossart, H.-P.; et al. Safeguarding freshwater life beyond 2020: Recommendations for the new global biodiversity framework from the European experience. Conserv. Lett. 2021, 14, e12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, T.; Doropoulos, C.; Schwarzmueller, F.; Gladish, D.W.; Kumaran, N.; Merkel, K.; Di Marco, M.; Gagic, V. Global mismatch of policy and research on drivers of biodiversity loss. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistema Nazionale Protezione Ambiente (SNPA). Rapporto Ambiente—SNPA. Edizione 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.snpambiente.it/snpa/rapporto-ambiente-snpa-edizione-2023/ (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). WISE Water Framework Directive (Data Viewer). 2018. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/wise-wfd (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- European Parliament. Regulation (EU) 2024/1991 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 June 2024 on Nature Restoration and Amending Regulation (EU) 2022/869 (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32024R1991&qid=1722240349976 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Prach, K.; Janečková, P.; Walker, L.R. Europe’s Nature Restoration Law has now been adopted. What comes next? Oikos 2025, e11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, O.W.; Emma, L. Restoring the Regulated: The EU’s Nature Restoration Law; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, D.; Schürings, C.; Wenskus, F.; Blackstock, K.; Borja, A.; Birk, S.; Bullock, C.; Carvalho, L.; Dagher-Kharrat, M.B.; Lakner, S.; et al. Securing success for the Nature Restoration Law. Science 2023, 382, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. The European Green Deal—COM (2019) 640 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030. Bringing Nature Back into Our Lives—COM (2020) 380 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, N. A Critical Analysis of the Proposed EU Regulation on Nature Restoration: Have the Problems Been Resolved? Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, N.M.; Jansen, C.; Janssen, A.U.; Kuypers, P.H.L.M. (Eds.) Nature Restoration put to EU Law: Tensions and Synergies between Private Property Rights and Environmental Protection. In Spanningen Tussen Duurzaamheid en Europees Recht; Serie Onderneming en Recht; Wolters Kluwer: Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mezzacapo, E. The “undigested” restoration of the Agri-food Ecosystem under the EU Nature Restoration Law. In DIREITO AGRÁRIO Compreensão Jurídica à COP 30; Academia Brasileira de Letras Jurídicas Agrárias (ABLJA) Alcir Gursen De Miranda: Belém do Parà, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallin, E. Nature Restoration and Agriculture and Forestry: At the Opposite Side of the Fighting Ring or Compatible after All? An Analysis of the Proposal and the Final Agreement on the Nature Restoration Law. Eur. Energy Environ. Law Rev. 2024, 33, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffers, T.; Altermatt, F.; Baldan, D.; Bilous, O.; Borgwardt, F.; Buijse, A.D.; Bondar-Kunze, E.; Cid, N.; Erős, T.; Ferreira, M.T.; et al. Reviving Europe’s Rivers: Seven Challenges in the Implementation of the Nature Restoration Law to Restore Free-Flowing Rivers. WIREs Water. 2024. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/wat2.1717 (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Management Effectiveness in the EU’s Natura 2000 Network of Protected Areas; European Environment Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, I.; Hauck, J.; Bonn, A. The alignment of agricultural and nature conservation policies in the European Union. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, A. The new Common Agricultural Policy: Reflecting an agro-ecological transition. The legal perspective. Rev. Agric. Food Environ. Stud. 2023, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergamo, R.; Ruberto, M. L’acqua tra agricoltura e ambiente: Dalla Direttiva Quadro Acque alla nuova PAC. RRN Mag. 2023, 18, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Perissi, I. Assessing the EU27 Potential to Meet the Nature Restoration Law Targets. Environ. Manag. 2025, 75, 711–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archi, F.; Piva, F. Stato Ecologico delle Acque Superficiali Interne|Indicatori Ambientali; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Archi, F.; Piva, F. Stato Chimico delle Acque Superficiali Interne|Indicatori Ambientali; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- AMBER. Amber Policy Brief 1—September 2020 (Horizon Project 2020). 2020. Available online: https://amber.international/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/AMBER-policy-Brief-1.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Chiti, E.; Giorgi, A. (Eds.) Ecological Sustainability and the Law: The European Green Deal and the New Frontiers of Sustainability; Routledge-Giappichelli: Abingdon, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EU Commission. Analysis of Links between CAP Reform and Green Deal, SWD (2020) 93 Final—Commission Staff Working Document; EU Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, A.; Pergamo, R. La Legge UE sul Ripristino della Natura in Relazione allo Stato Ambientale dei Corpi Idrici Superficiali in Italia. Pianeta PSR. 2024. Available online: https://www.pianetapsr.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/3193 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/1992/43/oj/eng (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Directive 2009/147/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32009L0147 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Manganiello, V.; Ferrigno, M. Agricoltura e Risorse Idriche in Annuario Dell’Agricoltura Italiana 2021—Volume LXXV—CREA. 2022. Available online: https://www.crea.gov.it/web/politiche-e-bioeconomia/-/annuario-dell-agricoltura-italiana (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. A/RES/70/1. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. Regulation (EU) 2021/2115—Strategic Plan Regulation; European Parliament: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; p. L 435/1. [Google Scholar]
- Italy CAP Strategic Plan (Piano Strategico della PAC) 2023–2027. 2023. Available online: https://www.reterurale.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/24037 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Marradi, A. Concetti e Metodo per la Ricerca Sociale; Giuntina: Firenze, Italy, 1980; Available online: https://marradiani.com/concetti-e-metodo-per-la-ricerca-sociale/ (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- European Commission. Modernising and Simplifying the CAP. Climate and Environmental Challenges Facing EU Agriculture and Rural Areas; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Modernising and Simplifying the CAP. Economic Challenges Facing EU Agriculture; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Modernising and Simplifying the CAP. Socio-Economic Challenges Facing Agriculture and Rural Areas; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni, A.; Mezzacapo, E. The EU pursue sustainability in the agri-food sector: The tortuous path of the Common Agricultural Policy towards a food system approach. In Ecological Sustainability and the Law: The European Green Deal and the New Frontiers of Sustainability; Chiti, E., Giorgi, A., Eds.; Routledge-Giappichelli: Abingdon, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, A. The new CAP must be linked more closely to the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Agric. Food Econ. 2020, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakiris, R.; Stara, K.; Kazoglou, Y.; Kakouros, P.; Bousbouras, D.; Dimalexis, A.; Dimopoulos, P.; Fotiadis, G.; Gianniris, I.; Kokkoris, I.P.; et al. Agroforestry and the Climate Crisis: Prioritizing Biodiversity Restoration for Resilient and Productive Mediterranean Landscapes. Forests 2024, 15, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2023/1115 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 May 2023 on the Making Available on the Union Market and the Export from the Union of Certain Commodities and Products Associated with Deforestation and Forest Degradation and Repealing Regulation (EU) No 995/2010 (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/1115/oj/eng (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- Guyomard, H.; Détang-Dessendre, C.; Dupraz, P.; Delaby, L.; Huyghe, C.; Peyraud, J.L.; Reboud, X.; Sirami, C. How the Green Architecture of the 2023–2027 Common Agricultural Policy could have been greener. Ambio 2023, 52, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPES-Food. Towards a Common Food Policy for the European Union. The Policy Reform and Realignment that Is Required to Build Sustainable Food Systems in Europe; IPES FOOD: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- European Court of Auditors. Special Report 20/2024—Common Agricultural Policy Plans. Greener, But Not Matching the EU’s Ambitions for the Climate and the Environment. 2024. Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/en/publications/sr-2024-20 (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Mannina, G.; Gulhan, H.; Ni, B.J. Water reuse from wastewater treatment: The transition towards circular economy in the water sector. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, X. Precision Agriculture and Water Conservation Strategies for Sustainable Crop Production in Arid Regions. Plants 2024, 13, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, G.; Pergamo, R. La Legge sul Ripristino della Natura e la PAC 2023-2027: Integrazioni di Politiche per il Ripristino degli Ecosistemi. Pianeta PSR. 2024. Available online: https://www.pianetapsr.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/3194 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Sturla, A. Biodistretti: Nuova Forma di Governance Territoriale per lo Sviluppo Locale. Pianeta PSR. Available online: https://www.pianetapsr.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/2288 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Bocci, R. La Lunga Avventura dei Distretti Biologici tra Leggi e Pratiche|Rete Semi Rurali. 2023 May 10. Available online: https://rsr.bio/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Crucianelli, F. Sostenibilità e Sviluppo, L’esperienza Decennale del Biodistretto della via Amerina e delle Forre. Pianeta PSR. Available online: https://www.pianetapsr.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/2304 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Borrero, J.D.; Mariscal, J. A Case Study of a Digital Data Platform for the Agricultural Sector: A Valuable Decision Support System for Small Farmers. Agriculture 2022, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe’er, G.; Finn, J.A.; Díaz, M.; Birkenstock, M.; Lakner, S.; Röder, N.; Kazakova, Y.; Šumrada, T.; Bezák, P.; Concepción, E.D.; et al. How can the European Common Agricultural Policy help halt biodiversity loss? Recommendations by over 300 experts. Conserv. Lett. 2022, 15, e12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Ministry of Agriculture. L’analisi SWOT per la Costruzione delle Strategie Regionali e Nazionale della PAC Post-2020. Documento di Indirizzo Metodologico. 2019. Available online: https://www.reterurale.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/20432 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Italian Ministry of the Environment. The National Plan for Adaptation to Climate Change (NPACC). 2023. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/en/news/the-national-plan-for-adaptation-to-climate-change-pnacc-approved (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- European Water Resilience Strategy. Ares (2025)843493 Publications Office of the European Union. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/98258000-e2e4-11ef-be2a-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 4 February 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).