Abstract
The pyrite bioretention system has been increasingly used to control dissolved nutrients in stormwater runoff. However, its low electron supply rate cannot adapt to the demand for denitrification under high nitrogen-loading conditions. To address this limitation, we constructed a mixed biochar–pyrite bioretention system (BP) by optimizing the structural composition of the fill media. Under simulated complex rainfall conditions, the nitrogen removal efficiency, by-product generation, and filler physicochemical properties of system were evaluated. Results demonstrated that the BP system significantly enhanced denitrification performance, achieving average NOx−-N and TN removal rates of 63.3% and 67.8%, respectively. This represented improvements of 79.1% and 45.9% over the conventional pyrite bioretention system. Moreover, the composite system exhibited a sustained and effective denitrification even under low C/N ratio conditions. This enhancement is attributed to biochar’s dual role as an electron shuttle and an electron reservoir, which facilitated microbial nitrate reduction. XPS analysis further confirmed that biochar addition effectively reduced the oxidation degree of pyrite, thereby protecting it from rapid oxidative degradation. Microbial analysis revealed that biochar supplementation in the BP system increased microbial diversity in the saturated zone, which contributed to improved ecosystem function and stability, including the promotion for key denitrification processes.
1. Introduction
Climate change and rapid urbanization have contributed to a significant increase in stormwater runoff from impervious surfaces in urban areas, which not only exacerbates non-point source pollution but also leads to considerable economic losses [1]. In response to the challenges posed by excessive stormwater runoff during heavy rainfall events, various stormwater control measures (SCMs) have been implemented globally [2].
As one of the most widely adopted SCMs, bioretention systems (also known as rain gardens or stormwater biofilters) play a crucial role in mitigating runoff volume, intercepting particulate pollutants and purifying stormwater quality [3]. However, traditional sand-based or soil-based bioretention systems often exhibit limited effectiveness in removing dissolved nutrients, which constrains their ability to meet increasingly stringent water quality requirements. For instance, Bratieres et al. reported that nitrate removal rates in conventional systems can be as low as −630% under certain conditions [4], indicating possible nitrate release. This is particularly concerning given that biologically available dissolved nutrients can constitute over half of the total nutrient load in urban runoff. Excessive nitrogen in stormwater runoff is a major contributor to eutrophication in receiving water bodies, underscoring the need for more effective nutrient control strategies.
In recent years, many studies have attempted to enhance nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency by promoting biochemical processes such as adsorption, biotransformation, and precipitation through strategies including the creation of submerged zones and modifications to filter media [5]. However, current research indicates that the nitrogen removal efficiency of bioretention systems remains highly unstable. While conventional bioretention systems generally achieve 70–90% removal of NH4+-N from surface runoff, their NOx−-N removal rates fluctuate dramatically between 40% and 70% [6]. Consequently, the development of improved bioretention systems using low-cost and readily available substrates to achieve efficient pollutants removal from stormwater runoff has emerged as a prominent research focus.
The establishment of submerged zones in bioretention system facilitates the formation of a composite structure consisting of both aerobic and anaerobic zones. This configuration enables the spatial separation of nitrification and denitrification processes, thereby enhancing overall nitrogen removal efficiency [4]. Kong et al. discovered that adding pyrite to the submerged zone as an electron donor, replacing organic waste such as the wood chips, and leveraging sulfur autotrophic denitrification can effectively achieve simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal while minimizing the risk of dissolved organic carbon leakage [7]. However, the relatively low electron-donating capacity of pyrite constrains further improvements in denitrification performance. Therefore, enhancing the denitrification efficiency of pyrite-based substrates media remains a key challenge. Biochar has attracted growing interest as a multifunctional environmental material due to its electrochemical properties. When incorporated into soil, biochar not only indirectly influences chemical properties by altering physical structure and composition but also directly facilitates electron transfer processes. By serving as an electron shuttle, biochar enhances the electron transfer activity of microorganisms [8]. Despite these advantages, no studies to date have systematically investigated the efficacy of biochar in enhancing nitrogen removal from stormwater runoff using pyrite-based bioretention systems.
In this study, the removal efficiency of pollutants such as nitrogen, TP, and COD in stormwater runoff was evaluated using bioretention system packed with an in situ mixed biochar–pyrite composite. The results are expected to provide valuable insights for optimizing the design of bioretention systems and enhancing their pollutant removal performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioretention Systems Establishment
To ensure optimal hydraulic performance, the structure configuration and fillers composition of the bioretention systems were first optimized, and three groups of bioretention systems were established, each configuration was constructed in duplicate, resulting in a total of six bioretention columns (Figure 1). The entire reaction equipment consists of an inlet water tank, a peristaltic pump, a water distribution ring, and a reactor. The reactor is made of acrylic material with an inner diameter of 10 cm and a height of 120 cm. Seven packing sampling ports (S1–S7) and six pore water outlet ports (O1–O5) were installed along the reactor’s side wall for collecting packing material and pore water, respectively. To minimize the influence of temperature on treatment performance and microbial activity, the laboratory environment was maintained at a constant temperature of 25 °C.
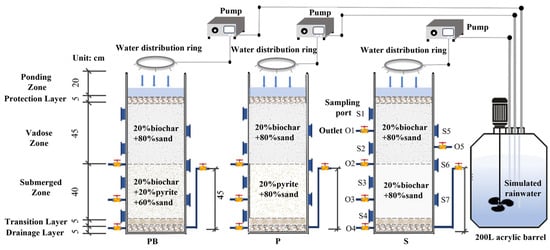
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a traditional sand-based bioretention system (S), a pyrite-based bioretention system (P), and a mixed biochar–pyrite bioretention system (BP).
A 5 cm drainage layer was placed at the bottom of each reactor, incorporating perforated pipes covered with pebbles to facilitate effluent discharge. To avoid media leakage, a 5 cm transition layer filled with pebbles approximately 1 cm in diameter was added between the reactor’s submerged zone and drainage layer. To enhance denitrification, a submerged zone was created by elevating the outlet pipe by 40 cm. The vadose zone incorporates 20% biochar (by volume) as a carbon source, with the remaining 80% consisting of quartz sand. Different amendments were added to the submerged zone as detailed in Table S1. Sludge is added to the submerged zone at 5 cm intervals, with each addition comprising to 200 mL of sludge at a concentration of 2000 mg/L. Above the media layers, a 20 cm ponding zone and a 5 cm top protection layer were installed. The bioretention column is not planted with vegetation to avoid interference with the overall system performance.
2.2. Simulated Stormwater Preparation
To investigate the denitrification efficiency of bioretention systems under adverse conditions, this study referenced previous research on pollutant concentrations in urban stormwater runoff and selected higher pollutant levels as the target concentration [9]. Simulated rainfall runoff was prepared using KNO3, NH4Cl, C2H5NO2, KH2PO4, and CH3COONa·3H2O to obtain target pollutant concentrations of 4 mg/L NO3−-N, 2 mg/L NH4+-N, 3 mg/L dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), 0.5 mg/L PO43−-P, and 18.2 mg/L COD.
In this study, the rainfall intensity was calculated based on the empirical rainfall intensity model for Shapingba District, Chongqing, China (1), while the rainfall design was calculated according to the Technical Guidelines for Sponge City Construction—Low Impact Development Stormwater System Construction (Trial) (2):
where q (mm/min) is the rainfall intensity, P (a) is the return period, and t (min) is the rainfall duration. Q (L/s) is the design flow rate of rainwater, φ is the runoff coefficient (assumed to be 0.7), and F (m2) is the catchment area (assumed the ratio of the bioretention surface area to the service area is 8.5%).
2.3. Experimental Procedures
A rainfall simulation experiment was conducted over 270 days and divided into three phases to investigate the impact of complex rainfall conditions on the pollutant removal efficiency of different bioretention systems. The objective of the first phase was to stabilize the performance of the experimental column. Since 89% of rainfalls in Chongqing are less than 25 mm, classified as heavy rain, 25 mm was selected as the constant design rainfall intensity for this phase [9]. The inflow cycle was set at one event every 3 days, with each rainfall lasting 2 h. After each discharge cycle, the effluent was collected into a 10 L polyethylene container. Following thorough mixing, a 50 mL water sample was extracted for analysis. The second phase commenced after the effluent had stabilized, with its focus on examining the effects of different operating conditions. Five distinct conditions were established (Table S2); each condition was run three times. The third phase was initiated following two runs under condition 5 of the second phase, with the aim of elucidating the nitrogen removal mechanism. For this purpose, water samples (20 mL each) were collected from the submerged zone at the O3 sampling port at 3 h, 6 h, 15 h, 27 h, 39 h, 51 h, 63 h, 75 h, 87 h, 99 h, 111 h, 123 h, and 135 h after water ingress for water quality analysis. Each sampling was performed in duplicate, following the same methodology as in the first phase.
2.4. Sample Collection and Analysis
After collecting water samples and filtering them through 0.45 μm filter membranes, water quality analysis followed. Ion chromatography (DIONEX-600, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to determine NO3−-N and SO42−. Moreover, COD, NH4+-N, TN, and total Fe (TFe) concentrations were determined according to the standard method [10]. Protein content was determined using the Coomassie Brilliant Blue method.
At the end of the rainfall experiment, substrate samples were collected from the side sampling port of the bioretention column. Surface morphology and elemental distribution of biochar and pyrite as well as the original samples were analyzed using SEM coupled with energy dispersive spectroscopy (ZEISS Sigma 300, Carl Zeiss Jena, Oberkochen, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Kalpha, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was employed to examine the pyrite, Identifying its surface compound’s elemental composition and content, molecular structure, chemical bonds, and so on.
2.5. Determination of Biochar Electron Donation and Electron Acceptance Capacities
The denitrification process requires exogenous electrons as electron donors to ensure its progression. Electron transfer system activity (ETSA) reflects the intensity of microbial respiration. Based on research by Wan et al., ETSA was measured for the submerged zone fillers in different biological systems [11]. The calculation formula is as follows:
where ABS490 is absorbance of the sample at 490 nm, V0 (mL) is volume of the sample to be tested, V1 (mL) is volume of methanol, t (min) is incubation time, and m (mg) is protein mass.
2.6. DNA Extraction and Microbial Community Analysis
To investigate the structural characteristics of different microbial communities, purity and concentration-extracted DNA was detected using a NanoDrop2000 ultra-micro spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and an agarose gel electrophoresis. The V4-V5 region of the 16SrRNA gene was amplified by using primers 338 F (5′-ACTCCTACGGAGGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806 R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) [12]. Finally, PCR-amplified products were sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq platform, and the raw data obtained were further analyzed via the I-Sanger cloud platform.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pollutant Removal Efficiency of Bioretention Systems Under Different Rainfall Conditions
3.1.1. Nitrogen Removal Efficiency
The nitrogen removal performance of BP, P, and S systems under different rainfall conditions is shown in Figure 2. All groups achieved NH4+-N removal rates exceeding 68% under various rainfall conditions, with similar removal efficiencies. Variations in rainfall intensity and the antecedent drying duration (ADD) did not significantly affect NH4+-N removal (Figure 2a,d). As in many biological treatment processes, adsorption and ion exchange serve as key mechanisms for contaminant removal in bioretention systems [13]. During rainfall, low oxygen levels in the system slightly inhibit nitrification, making media adsorption the dominant pathway for NH4+-N removal [14]. Although biochar added to the submerged zone of the BP system contributes to NH4+-N adsorption, the anoxic conditions in this zone are unfavorable for the growth of nitrifying bacteria. Consequently, adsorbed NH4+-N continuously occupied the adsorption sites on the biochar. After multiple influent cycles, the biochar approached saturation with respect to NH4+-N, which explains why the BP system did not exhibit enhanced NH4+-N removal compared to the other systems.
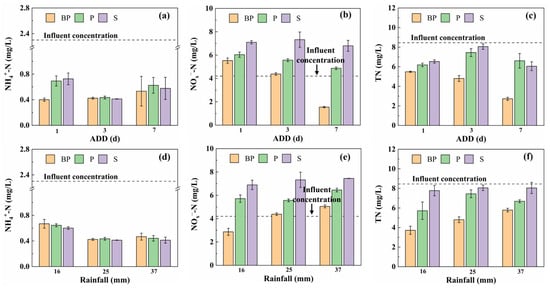
Figure 2.
Effects of ADD on (a) NH4+-N, (b) NOx−-N, and (c) TN concentrations in the effluent (rainfall of 25 mm), and the influence of rainfall intensity on (d) NH4+-N, (e) NOx−-N, and (f) TN effluent concentrations in the BP, P, and S groups (ADD of 3 days). The error bars represent the standard deviation.
As shown in Figure 2b,e, rainfall intensity and ADD significantly influence NOx−-N removal efficiency, with the exception of the BP group with ADD of 7 (rainfall of 25 mm) and under 16 mm rainfall (ADD of 3d), where all BP, P, and S groups exhibited NOx−-N leakage; however, the BP group consistently demonstrated superior NOx−-N removal performance than the other two groups. During the rainfall process, NOx−-N sources include raw influent, nitrification of NH4+-N, and mineralization of DON. Consequently, the actual NOx−-N load treated by the system is substantially higher than the influent concentration. Furthermore, NOx−-N removal relies on denitrifying bacteria, which are often unable to achieve complete denitrification within the short duration of rainfall [7]. Hydraulic retention time (HRT) also plays a critical role in microbially mediated nutrient removal, particularly denitrification. Intensive rainfall can lead to insufficient HRT and rapid leaching from organic carbon in pore water, thereby limiting the denitrification efficiency [15]. In contrast, the incorporation of biochar in the BP group enhanced NOx−-N removal, attributable to its released organic matter as a heterotrophic denitrification electron donor.
The removal trends of TN in different groups were analogous to NOx−-N (Figure 2c,f). The BP group demonstrated the highest TN removal efficiency, with an average effluent TN concentration of 2. 73 mg/L under ADD value of 7d (rainfall of 25 mm), corresponding to a removal rate of 67.8%, which was higher than the 62.3% reported by Xu et al. [16]. On the one hand, the BP group maintained a constant environmental temperature of 25 °C and no planting layer to avoid temperature variations affecting microbial activity and plant influence on system performance. On the other hand, adding biochar to the submerged zone of the BP group significantly enhanced the denitrification performance of system. This improvement can be attributed to the ability of biochar to stimulate the electrochemical activity of bacterial extracellular polymers, thereby promoting the electron transfer efficiency between microorganisms and pyrite and increasing the utilization efficiency of pyrite [17]. During the initial influent, oxygen-centered radicals in biochar (e.g., semiquinone radicals) rapidly donate electrons, synergistically supporting microbial denitrification and compensating for the relatively slow autotrophic denitrification rate of pyrite [18]. During the ADD, microorganisms can utilize biochar as an electron acceptor, transferring excess electrons generated in denitrification processes to biochar for temporary storage [8]. This electron-buffering mechanism allows biochar to function as a storage battery, ultimately contributing to higher TN removal efficiency in the BP group.
3.1.2. By-Product Leaching
The concentrations of secondary pollutants in the BP, P, and S groups are shown in Figure 3. SO42− in the effluent originates from the autotrophic denitrification of pyrite or direct oxidation of pyrite. Under different rainfall conditions, the SO42− concentration in BP, BP, and S groups ranged from 35.17 mg/L to 78.39 mg/L. The BP group exhibited a higher SO42− concentration compared to the P group, indicating a stronger capacity for sulfur autotrophic denitrification by microorganisms in the BP system. Nevertheless, all three systems complied with the effluent SO42− standard of 150 mg/L. Furthermore, the TFe concentration in the effluent from each group remained consistently ≤0.1 mg/L, meeting the Class I water standard requirements specified in the Chinese National Standard for Groundwater Quality (GB/T 14848-2017) [19].
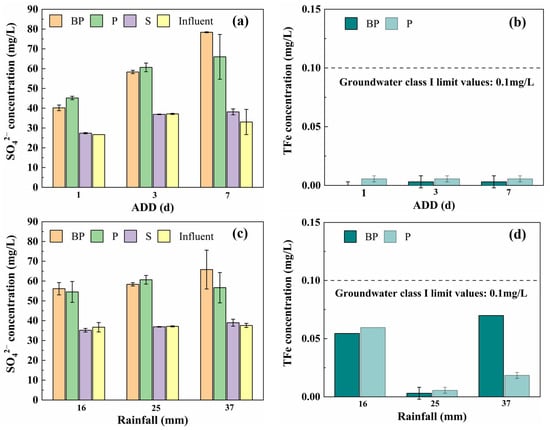
Figure 3.
The effect of different ADD on (a) SO42− concentration in BP, P, and S groups and on (b) TFe concentration in BP and P groups (rainfall of 25 mm); rainfall intensity influence on (c) SO42− concentration in BP, P, and S groups and on (d) TFe concentration in BP and P groups (ADD of 3 days).
3.2. Porewater Pollutant Concentration Variation in the Submerged Zone During ADD
Figure 4 illustrates the variation in NOx−-N concentrations within the submerged zone of the BP, P, and S bioretention systems during the 7-day ADD. As shown in Figure 4a, BP, P, and S groups in the submerged zone were 5.31 ± 0.09, 6.14 ± 0.08, and 9.9 ± 0.08 mg/L, respectively, higher than the influent of 4 mg/L. This indicates that NOx−-N accumulated in the vadose zone entered the submerged zone via rainwater runoff, thus raising the NOx−-N concentration required for treatment in the submerged zone. The NOx−-N concentration in all groups decreased over time, indicating a certain denitrification capacity in each system. In the BP group, a rapid decline in NOx−-N concentration occurred between 6 and 15 h, dropping from 5.22 ± 0.07 mg/L to 4.19 ± 0.04 mg/L. This accelerated reduction can likely be attributed to the electron-donating capacity of biochar, which enhanced the denitrification process. The NOx−-N removal behavior across the groups was further evaluated using first-order kinetics, which revealed that BP system had the highest removal rate constant. Additionally, after 135 h of reaction, the NOx−-N concentrations in the submerged zones of the BP, P, and S groups were 0.16 ± 0.13 mg/L, 4.34 ± 0.11 mg/L, and 7.75 ± 0.11 mg/L, respectively. The BP group achieved a high removal rate of 96.98% for NOx−-N, substantially higher than that of the P and S groups (Figure 4b).
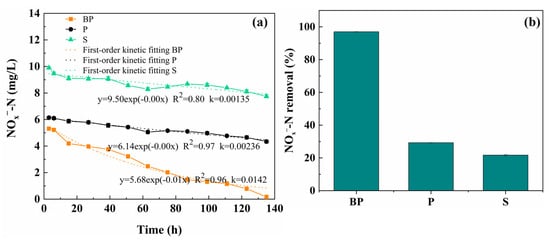
Figure 4.
Changes of NOx−-N in the submerged zone of BP, P, and S groups during the 7-day ADD: (a) NOx−-N kinetic fitting model (first-order kinetics) and (b) NOx−-N removal rate.
3.3. Chemical Property Changes in Bioretention System Media Materials
3.3.1. Biochar Surface Morphology and Electrochemical Properties
SEM characterization of pristine biochar and biochar in the vadose zone and submerged zone (BP group) after rainfall are shown in Figure 5a. The raw biochar exhibits a smooth surface with a dense structure and closely packed granular protrusions. After prolonged rainfall washing, the particulate structure of the vadose zone biochar diminished, resulting its surface smoothness. In contrast, biochar from the submerged zone underwent significant surface morphology changes due to prolonged exposure to microorganisms and pore water. Its originally smooth surface was largely replaced by numerous pits and irregularities. This increased surface roughness promotes microbial adhesion, creating favorable conditions for microbial colonization and growth. Biochar oxidation is a surface-mediated process. The surface of biochar in the boundary zone oxidized to form humus, with oxygen atoms adsorbing onto the biochar surface by forming functional groups, resulting in altered surface morphology [20]. Furthermore, biochar in the submerged zone remains continuously saturated with water. Its distinctive pore structure establishes a marked water potential gradient between the interior and exterior of the pores. As water permeates, the pore dimensions gradually expand, causing structural swelling and eventual fragmentation [21].
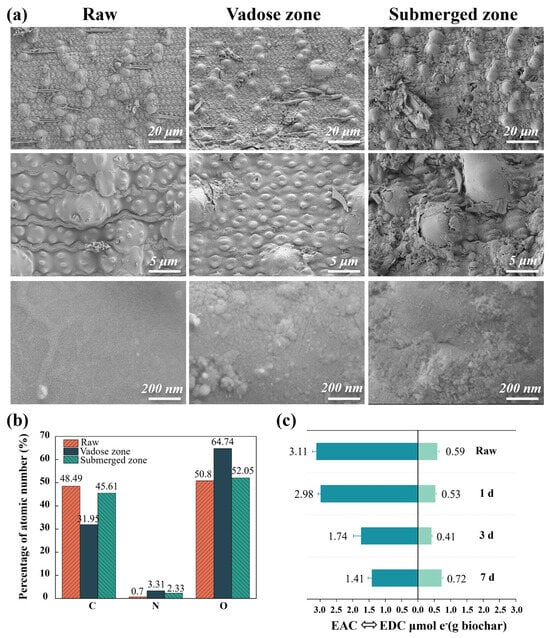
Figure 5.
(a) SEM characterization of pristine biochar and biochar from the vadose zone and submerged zone after the experiment, left to right, at different magnification levels; (b) elemental composition of C, N, and O on the samples surface; and (c) distribution of EDC and EAC in raw biochar and biochar at different times after water inflow completion.
The atomic percentage of carbon in the raw, vadose zone, and submerged zone biochar were 48.49%, 31.95%, and 45.61%, respectively; those of nitrogen were 0.7%, 3.31%, and 2.33%; and those of oxygen were 50.8%, 64.74%, and 52.05%, respectively (Figure 5b). By the end of the experiment, the N content on the surface of all biochar samples increased, indicating adsorption NH4+-N from the influent. The higher N content observed in the vadose zone biochar compared to that in the submerged zone confirmed that the NH4+-N adsorption sites on the submerged biochar surface remained occupied for extended periods, resulting in reduced adsorption capacity. The increase in the oxygen atoms percentage in the vadose zone biochar reflects a higher degree of oxidation. In contrast, the oxygen content on the surface of submerged biochar showed no significant change from that of the raw biochar. The discrepancy between SEM observations and elemental scanning results may be attributed to distinct aging mechanisms in the vadose and submerged zones. In the vadose zone, biochar aging is primarily driven by chemical oxidation under alternating wet and dry conditions, whereas in the submerged zone, aging is mainly influenced by microbial metabolic activities, which modify the biochar surface structure. Cao et al. reported that wet–dry cycles alter biochar structure, leading to reduced carbon content and increased oxygen content, thereby modifying its polarity, aromaticity, and hydrophilicity [22]. Furthermore, microorganisms contribute to biochar solubilization, resulting in exfoliation of its outer layer.
Biochar enhances microbial electron transfer activity by facilitating extracellular electron transfer (IET) through its electron-conducting properties [23]. To evaluate the electron transfer properties of biochar in the submerged zone, its redox capabilities were examined. The electron acceptance capacity (EAC) response to current and electron donation capacity (EDC) response to current are shown in Figures S1 and S2, respectively. The calculated trends in EAC and EDC of the biochar are shown in Figure 5c. The results reveal that EAC continues to decrease overtime after water addition was completed, indicating sustained electron uptake by biochar. In contrast, EDC initially decreased and then increased. This is attributed to a mismatch in electron transfer kinetics among functional groups. Specifically, the slower electron release rate of the quinone group causes a lag in the recovery of biochar’s EDC [24].
3.3.2. Pyrite Surface Morphology and XPS Characterization
The microscopic morphology of raw pyrite and pyrite from BP and P groups after rainfall experiments are shown in Figure 6. Under identical influent conditions, the surface morphology of pyrite differed significantly between the BP and P groups. Compared with raw pyrite, the BP group exhibited a rougher surface with abundant pores, which considerably increased the specific surface area and favored microbial attachment [25]. In contrast, a dense mineral film was formed on the pyrite surface in the P group. Based on EDS scanning results (Figure S3), this layer is inferred to be composed mainly of iron oxides. Such a coating likely hinders pyrite-driven autotrophic denitrification. Therefore, with prolonged reactor operation, the service life of the BP group is expected to be significantly longer than that of the P group. These findings further demonstrate the advantage of the substrate configuration used in the BP group.
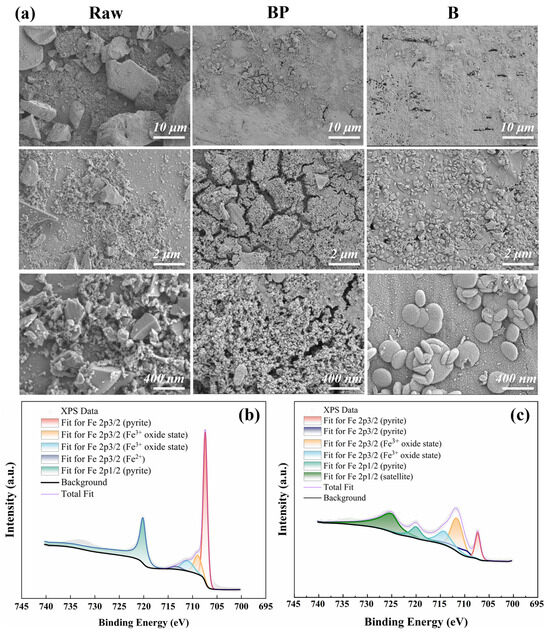
Figure 6.
(a) SEM characterization images of raw pyrite and after rainfall experiments for BP and P groups, along with fitted XPS Fe 2p spectra: (b) BP and (c) P.
XPS analysis was performed on pyrite samples from different groups. The fitted curves of the Fe 2p spectra for the BP and P groups are shown in Figure 6b and Figure 6c, respectively. The results reveal a notable decrease in the peak intensity of ferrous sulfide in the P group pyrite, accompanied by a marked increase in the proportion of the iron oxide/hydroxide species. The Fe 2p3/2 characteristic peaks of raw pyrite and the post-reaction BP and P groups are generally consistent (Figure S4). The peak at 707.4 eV is primarily attributed to pyrite or other Fe2+ and S species [26]. In the P group, the intensity of the peak decreased substantially, indicating chemical transformation of pyrite and the formation of new surface compounds. In contrast, the BP group showed no significant difference compared to the raw pyrite. A minor characteristic peak at 702.5 eV is most likely a Fe2+ electron vacancies resulting from the breaking of Fe-S bonds on the pyrite surface [27]. Peaks at 709.0 eV and 711.35 eV correspond primarily to Fe2+ and Fe3+ compounds, which may include FeSO4, FeOOH, FeO, or related phases, with the surface likely comprising multiple coexisting species. Combined with the O 1 s fitting results (Figure S5a–c), the pyrite in the BP group predominantly consists of Fe(OH)3, whereas the P group contains both Fe(OH)3 and FeOOH [28]. In summary, introducing biochar reduces the trivalent iron coating on pyrite surfaces, protecting the pyrite and delaying its degradation. As a result, the exposed pyrite can release more electron donors, thereby maintaining stable sulfur autotrophic denitrification performance.
3.4. Microbial Community Characteristics of Bioretention Systems
To further validate the microbial processes discussed above, the microbial communities in the submerged zones of the BP, P, and S bioretention systems were analyzed, At the phylum level, all systems showed similar major microbial compositions, predominantly consisting of Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, Chloroflexi, Bacteroidota, and Acidobacteriota (Figure 7a). The relative abundance of Proteobacteria was higher in the BP group than in the P and B groups. As the dominant microbial community in most bioretention systems, Proteobacteria are known to participate in denitrification, phosphorus removal, and organic matter degradation. Therefore, the increased proportion of Proteobacteria likely enhances nitrogen and phosphorus removal in the submerged zone of the BP system. Actinobacteriota, which play an important role in hydrolyzing organic matter [29], accounted for only 3.5% of the community in the BP group, significantly lower than in the P and S groups. This suggests that the presence of biochar may reduce dissolved oxygen levels in the submerged zone, thereby influencing microbial composition. Chloroflexi and Bacteroidota can utilize organic matter derived from biomass as electron donors for denitrification. While the relative abundance of Chloroflexi was similar across all groups [30], that of Bacteroidota differed significantly, with the BP group exhibiting 2.37- and 3.88-times higher abundance than the P and S groups, respectively. The elevated relative abundance of the Bacteroidota in the BP group implies a more efficient nitrogen cycle, promoting the reduction of NOx−-N to N2.
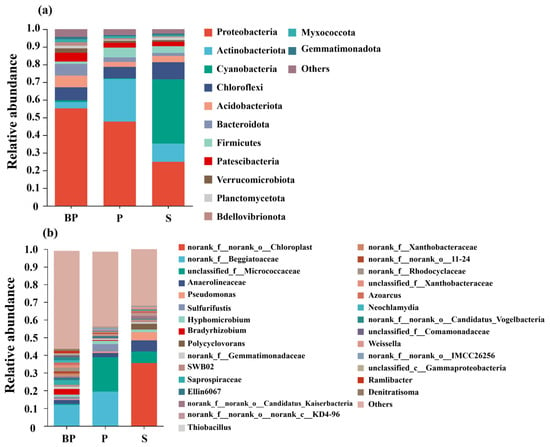
Figure 7.
Taxonomic classification of the bacterial communities at (a) phylum and (b) genus levels in different bioretention system.
At the genus level, microbial communities in the submerged zones of BP and P groups exhibited high similarity but differed significantly from those in the S group (Figure 7b). Beggiatoaceae was the dominant genus in both the BP and P groups. This genus is capable of oxidizing sulfides to sulfates using oxygen or nitrate, forming elemental sulfur as an intermediate product in the process [31]. unclassified_f__Micrococcaceae, commonly found in contaminated soils and able to tolerate low-nutrient environments [32], showed a relative abundance of only 5.98% in the BP group, compared to 19.4% in the P group and 6.5% in the S group. norank_f__Saprospiraceae had a relative abundance of 2.67% in the BP group but was extremely low and undetectable in the P and S groups. The presence of this genus in the BP group, in contrast to its absence in the P group, demonstrates that the lower dissolved oxygen levels in the BP submerged zone influenced community structure [33]. Bradyrhizobium accounted for 3.5% of the community in BP group but only 0.4% in the P group. The lower NH4+-N concentration in the BP submerged zone, along with a more complete microbial denitrification pathway yielding more N2, likely supported the growth of Bradyrhizobium.
In summary, the BP group enhanced microbial diversity in the submerged zone through the addition of biochar, resulting in a more balanced distribution of bacterial genera. This contributes to improved ecosystem function and stability, including support for key processes such as denitrification.
3.5. Mechanism of Denitrification in Bioretention Systems Modified with Biochar and Pyrite
Figure 8 illustrates the denitrification mechanism in biochar-pyrite-enhanced bioretention systems. During rainfall, microorganisms utilize abundant carbon sources in precipitation to conduct aerobic nitrification, effectively removing NH4+-N adsorbed on biochar surfaces in the vadose zone as well as NH4+-N from rainwater runoff. In the submerged zone, the incorporation of biochar, which exhibits electron-storage properties analogous to a battery, enables denitrifying bacteria to utilize electrons retained in the biochar for denitrification. Concurrently, the high water retention capacity of biochar reduces dissolved oxygen levels in the surrounding capillary water, establishing favorable anoxic conditions for denitrification by microorganisms attached to the biochar surface. During aerobic nitrification and heterotrophic denitrification processes, microorganisms used carbon sources as an electron donor for metabolic activities. However, not all electrons released during carbon oxidation are fully utilized by microorganisms. The surplus electrons can transfer to the biochar surface and undergo reversible redox reactions with quinone functional groups, thereby allowing the biochar to act as an electron acceptor. As no new rainfall is entering the bioretention system, dissolved oxygen concentrations decrease, inducing sulfur-mediated autotrophic denitrification in the submerged zone. This process slowly reduces NOx−-N while simultaneously transferring additional electrons to the biochar. These stored electrons are subsequently released during subsequent rainfall events, providing a readily available electron source to support denitrification.
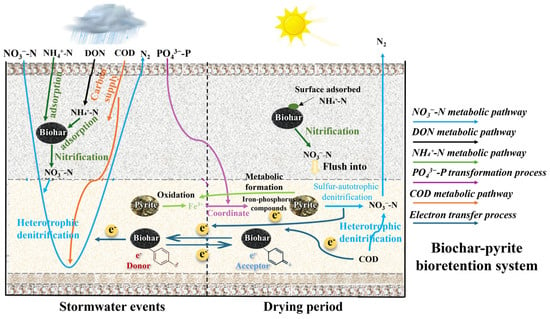
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of nutrient transformation and removal processes in biochar–pyrite bioretention systems under a stormwater event and drying period.
4. Conclusions
This study established a bioretention system incorporating biochar into a pyrite matrix. The impact of in situ mixed biochar on runoff pollutant removal in the pyrite-based bio-retention system under different rainfall intensity and ADD was clarified. Firstly, the BP group achieved average removal efficiencies of 63.3% for NOx−-N and 67.8% for TN, which were 79.1% and 45.9% higher, respectively, than conventional pyrite bioretention systems. During the ADD, the EDC of biochar initially decreased and then increased, while the EAC continuously decreased; this pattern confirms the role of biochar as an electron buffer in the bioretention system. Additionally, biochar reduced the trivalent iron coating on pyrite surfaces, protecting the pyrite and delaying its degradation, and exposed pyrite released more electron donors, maintaining stable sulfur autotrophic denitrification performance. Finally, the introduction of biochar to the submerged zone enhanced microbial electron transfer activity and promoted a more balanced distribution of microbial population abundance, thereby extending the life of the bioretention system.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17223263/s1: Figure S1: Reductive current responses to increasing amounts of biochar, analyzed by mediated electrochemical reduction (MER, Eh = −0.49 V, pH = 7). The numbers of electrons transferred from the biochar, Q, increased linearly with increasing masses of biochar analyzed (inserts): (a) raw biochar; (b) submerged zone biochar one day after the end of inflow; (c) submerged zone biochar three days after the end of inflow; (d) submerged zone biochar seven days after the end of inflow; Figure S2: Oxidative current responses to increasing amounts of pine wood biochar, analyzed by mediated electrochemical oxidation (MEO, Eh = +0.61 V, pH = 7). The numbers of electrons transferred from the biochar, Q, increased linearly with increasing masses of biochar analyzed (inserts): (a) raw biochar; (b) submerged zone biochar one day after the end of inflow; (c) submerged zone biochar three days after the end of inflow; (d) submerged zone biochar seven days after the end of inflow; Figure S3: Percentage of atomic number of each element of raw pyrite and pyrite in BP and P groups at the end of the rainfall experiment; Figure S4: Raw pyrite XPS Fe 2p spectra; Figure S5: Fitted energy spectra of pyrite O 1s for each group at the end of the rainfall experiment (a) raw pyrite, (b) BP, and (c) P; Table S1: Media composition and parameters of submerged zone in bioretention systems; Table S2: Experimental conditions of stage 2.
Author Contributions
Y.X. and X.Y.; organized the framework of the paper; F.L.; methodology; H.M.; proposed the study idea; C.H. and Z.X.; contributed to the testing and analysis of experimental data and participated in the writing of this paper; R.L., L.Q. and H.Z. took part in data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52200113).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Ying Xu, Cong Huang, Zheng Xu, Rui Liu, Lu Qiu, and Haifa Zu were employed by the company Power China Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| S | Sand-based bioretention system |
| P | Pyrite-based bioretention system |
| BP | Biochar–pyrite bioretention system |
| NOx−-N | Nitrate and Nitrite |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| C/N ratio | Carbon to Nitrogen ratio |
| XPS | X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| SCMs | Stormwater Control Measures |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand) |
| DON | Dissolved Organic Nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate |
| PO43−-P | Phosphorate |
| TFe | Total iron |
| ETSA | Electron Transfer System Activity |
| 16SrRNA | 16S ribosomal RNA |
| ADD | Antecedent Drying Duration |
| HRT | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| SO42− | Sulfate |
| EET | Extracellular Electron Transfer |
| EAC | Electron Acceptance Capacity |
| EDC | Electron Donation Capacity |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectrometer |
| MER | Mediated Electrochemical Reduction |
| MEO | Mediated Electrochemical Oxidation |
References
- Kayhanian, M.; Fruchtman, B.D.; Gulliver, J.S.; Montanaro, C.; Ranieri, E.; Wuertz, S. Review of highway runoff characteristics: Comparative analysis and universal implications. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6609–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Winston, R.J.; Wituszynski, D.M.; Tirpak, R.A.; Boening-Ulman, K.M.; Martin, J.F. Effects of watershed-scale green infrastructure retrofits on urban stormwater quality: A paired watershed study to quantify nutrient and sediment removal. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 186, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFevre, G.H.; Paus, K.H.; Natarajan, P.; Gulliver, J.S.; Novak, P.J.; Hozalski, R.M. Review of Dissolved Pollutants in Urban Storm Water and Their Removal and Fate in Bioretention Cells. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Zinger, Y. Nutrient and sediment removal by stormwater biofilters: A large-scale design optimisation study. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søberg, L.C.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.-T. Nitrogen removal in stormwater bioretention facilities: Effects of drying, temperature and a submerged zone. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirpak, R.A.; Afrooz, A.R.M.N.; Winston, R.J.; Valenca, R.; Schiff, K.; Mohanty, S.K. Conventional and amended bioretention soil media for targeted pollutant treatment: A critical review to guide the state of the practice. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Song, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chai, H. Biochar-pyrite bi-layer bioretention system for dissolved nutrient treatment and by-product generation control under various stormwater conditions. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Coffin, E.S.; Sheng, Y.; Duley, M.L.; Khalifa, Y.M. Microbial reduction of Fe(III) in nontronite: Role of biochar as a redox mediator. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 345, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Shao, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, G.; Wei, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of stormwater pollutants characteristics, purification process and environmental impact after low impact development practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers?ReferenceID=1870039 (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Wan, R.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Su, Y.; Li, M. Effect of CO2 on Microbial Denitrification via Inhibiting Electron Transport and Consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9915–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wu, W. Nitrogen removal performance in pilot-scale solid-phase denitrification systems using novel biodegradable blends for treatment of waste water treatment plants effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 122994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Yue, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X. A bilayer media bioretention system for enhanced nitrogen removal from road runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Dynamic adsorption behavior of methylene blue onto oil palm shell granular activated carbon prepared by microwave heating. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.W.; Valenca, R.; Miao, Y.; Ravi, S.; Mahendra, S.; Mohanty, S.K. Biochar increases nitrate removal capacity of woodchip biofilters during high-intensity rainfall. Water Res. 2019, 165, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhi, Y.; Kong, Z.; Ma, H.; Shao, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, Y.; et al. Enhancing nitrogen and phosphorus removal in plant-biochar-pyrite stormwater bioretention systems: Impact of temperature and high-frequency heavy rainfall. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Geng, R.; Sun, S.; Guan, X. Coupling of selenate reduction and pyrrhotite oxidation by indigenous microbial consortium in natural aquifer. Water Res. 2023, 238, 119987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, X. Biochar as both electron donor and electron shuttle for the reduction transformation of Cr(VI) during its sorption. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wang, H.; Feng, M.; Zhou, F.; Huang, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, W. Effects of atmospheric ageing under different temperatures on surface properties of sludge-derived biochar and metal/metalloid stabilization. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Ma, Z.; Yang, K.; Cui, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; Wu, G.-L.; Zheng, J. Effect of three artificial aging techniques on physicochemical properties and Pb adsorption capacities of different biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Hao, Y.J.H.; Wang, X. Changes in the Physicochemical Characteristics of Peanut Straw Biochar after Freeze-Thaw and Dry-Wet Aging Treatments of the Biomass. BioResources 2019, 14, 4329–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappler, A.; Wuestner, M.L.; Ruecker, A.; Harter, J.; Halama, M.; Behrens, S. Biochar as an Electron Shuttle between Bacteria and Fe(III) Minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquing, J.M.; Yu, Y.-H.; Chiu, P.C. Wood-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar) as a Microbial Electron Donor and Acceptor. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tan, S.N.; Glenn, A.M.; Harmer, S.; Bhargava, S.; Chen, M. A direct observation of bacterial coverage and biofilm formation byAcidithiobacillus ferrooxidanson chalcopyrite and pyrite surfaces. Biofouling 2015, 31, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Sumona, M.; Gupta, B.S.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Utilization of iron sulfides for wastewater treatment: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhliga, I.; Nesbittb, R.S.H.W.; Laajalehtoc, K. Surface states and reactivity of pyrite and marcasite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 179, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Dong, Y.; Fu, D.; Gao, N.; Ma, J.; Liu, X. Chloramphenicol removal by zero valent iron activated peroxymonosulfate system: Kinetics and mechanism of radical generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, R.; Xiao, L.; Zhan, X. Iron sulphides mediated autotrophic denitrification: An emerging bioprocess for nitrate pollution mitigation and sustainable wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Jing, Z.; Tao, Z.; Luo, H.; Zuo, S. Improvements of nitrogen removal and electricity generation in microbial fuel cell-constructed wetland with extra corncob for carbon-limited wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, V.; Bailey, J.V.; Teske, A. Phylogenetic and morphologic complexity of giant sulphur bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Mielczarek, A.T.; Kragelund, C.; Nielsen, J.L.; Saunders, A.M.; Kong, Y.; Hansen, A.A.; Vollertsen, J. A conceptual ecosystem model of microbial communities in enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5070–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Gu, X.; Wu, J. Response of nitrite accumulation, sludge characteristic and microbial transition to carbon source during the partial denitrification (PD) process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 165043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).