Abstract
The use of mercury in gold mining, as well as the presence of uncontrolled and illegal releases to the environment, continues to create severe pollution and public health risks for over 14 million people worldwide, particularly in developing countries. This study presents a modeling framework to estimate the fate and transport of mercury on a national-scale river network, where a physical-based conceptual model is implemented. Using the model, mercury concentrations are estimated for every river segment in the network, serving as a tool for effective management and control nationwide, enabling establishing intervention priorities. To test the framework’s suitability, it was applied to Colombia’s river network, a country with documented mercury pollution issues from gold mining. Results revealed persistent concentrations above 0.001 µg/L in all major basins, and concentrations close to 7 µg/L in active mining areas. The release of nearly 300 mines led to the contamination of river distance between 50 and 285 km downstream, exceeding local drinking water standards. The model results were validated with mercury concentration data of available studies in the country, showing small deviations between modeled and measured concentrations (<0.95 µg/L), confirming the robustness and suitability of the proposed framework as a screening assessment for national-scale mercury transport and fate.
1. Introduction
Mercury (Hg) is a significant threat to human and environmental well-being due to its bioaccumulative nature and ecosystem persistence. Categorized as a chemical of global concern [1,2] mercury exists in three primary forms: elemental mercury (Hg0), inorganic (Hg (II)), and organic (MeHg) [3,4]. The toxicity of mercury is determined by its speciation, which also affects its interactions within ecosystems. Effectively managing mercury releases requires a comprehensive understanding of several aspects. These aspects include the transport and fate of mercury, its interactions with the environment, its sources, and which of the primary forms are released.
Human activities, such as mining and precious metal production, particularly in South and Central America, contribute to mercury releases along with natural processes like volcanic activity [5]. Earth’s mercury reservoirs include the atmosphere, land, and aquatic ecosystems, each exhibiting distinct interactions and temporal dynamics. In freshwater ecosystems, despite uncertainties in available data related to artisanal and small-scale gold mining (ASGM), it is estimated that the proportion released to the environment is approximately 40–50% of the global inventory [6].
The creation of the Minamata Convention on Mercury (MCM), which came into effect in 2017, reflects global efforts to reduce anthropogenic emissions of mercury [7]. This convention has served as a guide to control mercury releases from anthropogenic sources [8], and led to the development of national action plans in various countries (e.g., Colombia, Costa Rica, Indonesia, Senegal [9]). Despite these efforts, artisanal and alluvial gold mining, mostly taking place in developing countries, continues to contribute to elevated levels of mercury in soil and water around mining sites and follows an incremental trend since the mid-20th century [5]. Gold mining and refining are significant sources of mercury pollution, with large amounts released into the atmosphere, land, and water bodies. These mercury releases are primarily linked to gold production and extraction processes where the contaminant reaches waste piles, storage ponds, and adjacent rivers [5].
Despite the global acknowledgment of mercury as a substance of concern, the transport and fate of mercury released to aquatic ecosystems from mining activities remain understudied [10]. Even when the MCM aims to reduce mercury use, achieving the convention’s goals and enhancing public health regulations require an understanding of how gold mining releases interact with aquatic biota and affect the food chain by bioaccumulating on fish.
Colombia is one of the world’s largest per capita mercury polluters due to artisanal gold mining [11,12]. Approximately 46.30% of mercury used in extraction processes is lost with tailings [11], leading to mercury releases on land or into water bodies. The Mojana region, located in the lowlands of the Cauca and Magdalena River valleys, two of the largest and most populated river basins in Colombia, is impacted by alluvial and artisanal gold mining and experiences high contamination levels [13]. Analyses of water and soil around mining areas in this region show elevated mercury levels, exceeding 2.0 μg/L, in rivers used for water supply [14]. Colombia’s water quality is additionally compromised due to a lack of investment in water treatment and a limited enforcing capacity of riverine pollution control permits [15]. There are also challenges related to guaranteeing safe drinking water for the population within maximum admissible concentrations. For instance, European Union guidelines set the limit of mercury in surface waters at 0.07 μg/L [16], while Colombia enables up to 2 μg/L in water bodies selected for potable water treatment [17], and 1 μg/L for drinking water [18]. Guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO) suggest that the limit of total mercury in potable water should be 1 μg/L [19].
To estimate these concentrations in rivers, numerous water quality models have been developed to simulate and predict the dynamics of various pollutants, including mercury, in aquatic systems (e.g., CE-QUAL-W2 [20], DynQual [21], MIKE [22], and Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP) [23]). These numerical models are commonly used at catchment and river reach scales to understand the transport and fate of pollutants under different flow conditions. Various examples modeling mercury transport, transformations, and concentrations are available in the literature, including the case of the East Fork Poplar Creek in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, with MIKE [24]; the Taihu basin, China, with WASP [25]; and the Mediterranean basin, with upgraded PCFLOW3Dmodel [26]. Despite the numerous studies on the topic, these studies focus on a local scale, covering a single river or watershed, and few models, such as DynQual, have the capacity to model greater scales [21]. The local approach is problematic when trying to establish mercury hotspots and intervention priorities on large scales, such as areas covering entire nations, since they often cover multiple rivers and watersheds. Therefore, tools enabling screening such large areas are a persistent necessity.
To address this need, in this work, we propose a framework to model mercury concentrations across a nationwide river network. The primary objective of the framework is to understand the processes governing the transport and fate of mercury in surface water systems on such a scale. By simulating mercury concentrations at this scale, this framework additionally facilitates the identification of pollution hotspots, and provides critical insights for regulatory assessments, policy enhancements, and improved management strategies. Therefore, the framework can support global mercury control initiatives, such as the MCM.
It is important to highlight a key feature of our framework, which is its ability to generate spatially explicit outputs through geographical information systems (GIS). This feature enables stakeholders to visualize mercury contamination patterns and prioritize intervention areas. Unlike traditional models focusing on local and single-watershed scales, our work is fully based on open-source programming languages and GIS software (QGIS 3.28), making it accessible, scalable, and replicable in other locations, even with limited resources to work with proprietary software.
2. Materials and Methods
This study proposes a framework to assess the transport and fate of mercury in river networks by integrating geographic, hydrometric, and pollutant loads data into a numerical model. As a result, the framework evaluates the downstream impacts of mercury pollution sources by calculating the river polluted length (RPL), defined as the cumulative distance where mercury concentrations exceed a user-defined threshold. This approach provides insights into identifying hotspots of contamination and informing management strategies.
2.1. Input Data
To build an accurate model for a specific country or region, two primary datasets were required for implementing the model: river network data and pollutant loads information. To ensure compatibility with geospatial analysis tools, these datasets were organized as shapefiles (.shp) in this framework.
The river network file included topological information, segment connectivity, and hydraulic attributes including discharge, velocity, and slope. Elevation and slope data were derived from Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) with a minimum resolution of 30 m. Hydraulic parameters, namely river width and travel time, were estimated using the relationships developed by Jimenez et al. [27,28]. Discharge for each river reach was obtained from long-term flow studies [29,30], ensuring that water balance was maintained at the connection nodes of river segments.
The file containing pollutant loads and sources included information on mercury release locations, identified by the number of the river reach in the network where they were located, as well as the corresponding mercury load poured into the network. Mercury emissions from gold mining activities were estimated using the Hg:Au ratio, representing the amount of mercury used to produce one gram of gold, and then discharged to the stream. Each mercury release location was linked to the nearest river reach, providing spatial context, and the corresponding concentration was computed using discharge data from the river network.
Further details regarding data acquisition, processing, and parameter estimation for input data are provided as Supplementary Materials (see Section S1).
2.2. Mercury Transformation Processes
This framework focuses on simulating phenomena occurring to mercury in freshwater ecosystems, particularly in rivers, where gold mining emissions are the main source of contamination. Three species of mercury are simulated within the water column: inorganic mercury (Hg (II)), methylmercury (MeHg), and elemental (Hg0(aq)). To determine the percentage of mercury species, present at different pH values, simulations with the “multiproblem/sweep” function of the VisualMINTEQ 3.1 software [31] are employed.
Eight physicochemical processes of mercury are considered during simulation (Table 1), which focus on those occurring in the water column. Note that volatilization and sedimentation processes are included to consider the interaction of the column with the atmosphere and sediments, but bedload sediment transport is omitted. Each of the eight transformation processes is described using either decay rates (i.e., oxidation, reduction and methylation) or loss velocities (i.e., volatilization and settling), as reported by the U.S EPA [32]. The magnitudes of these rates and velocities are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Rates and constants of mercury processes in the water column that are modeled in the proposed framework.
2.3. Conceptual Mercury Transport and Fate Model
The proposed conceptual model to represent the transport and fate of mercury in this framework is based on the Aggregated Dead Zone Model (ADZ) [33,34,35,36]. The ADZ model considers the river reach as an imperfectly mixed system where the solute suffers pure advection followed by longitudinal dispersion [37]. To model solute advection, an explicit time delay (τ) parameter is defined. The model introduces the concept of “dead” or “storage” zones to include the dispersive effects on the solute, assuming the major dispersive effects reside in the effective dead-zones-residence-time rather than the Fickian diffusion term. The dispersive effects in the ADZ model are represented by the dispersive fraction (DF), a parameter defining the solute’s mixing characteristics in the reach, and a relationship between the travel time () and τ [36,38,39].
With this mathematical structure, a DF of 0 indicates advection dominance (), while a DF of 1 represents pure dispersion (). The travel time ( is calculated as where is the length of the river’s reach and is the mean flow velocity, which can be calculated from the river’s hydraulic geomorphology or field data. Here, these values were calculated from the expressions derived by Jiménez et al. [27,28].
Meanwhile, is determined from Equation (1) using a dispersive fraction from the literature. Specifically, studies have shown that a dispersive fraction equal to 0.27 ± 0.015 is suitable for mountain rivers [40,41], while a range between 0.33 and 0.45 is more appropriate for alluvial rivers [42]. Hence, this framework utilized these DF values depending on the geomorphologic characterization of each river segment. This characterization was determined as a function of the river’s slope, as defined by Flores et al. [43].
For non-conservative pollutants, like is the case of mercury in this framework, the reactive transport model needs to account for processes like decay, sedimentation, volatilization, and other sources and sinks, as defined in Table 1. To this end, the reactive transport equation is defined as [34,36,38].
where is the known concentration at the beginning of a river segment, is the first order reaction or decay rate of the pollutant, is the pollutant concentration at the output of the same segment downstream, and other variables are previously defined. In this framework, the steady-state version of this equation was used, which can be derived from Equation (2) as
Note that, according to Equation (3), the computation of the downstream concentration () depends on the upstream concentration (), the decay constant (k), and temporal parameters defined by the river geomorphology and the dispersive fraction. Hence, this algebraic equation can be applied to all headwater nodes to their corresponding downstream locations, and efficiently solves the transport and fate of mercury across the entire river network.
A set of equations based on the ADZ steady-state model (Equation (3)) are proposed in this work to determine the transport and transformations of elemental mercury, divalent mercury, and the organic species of methylmercury. Further models required to understand the fate and transport of mercury, such as the pH and solids models, are presented as Supplementary Materials (see Section S3).
2.3.1. Elemental Mercury (Hg (0))
Elemental mercury ( is the only species capable of volatilization. This process is simulated by the volatilization velocity () and the depth of the water interface (H). In addition, oxidation and reduction of elemental mercury depend on the pH and redox potential. Here, oxidation and reaction constants are considered, respectively, and , with typical values reported in the literature (Table 1). The values of the reaction and decay constants are summarized in Table 1. The steady-state reactive equation for elemental mercury is therefore given by
where KHgo is given by Correa-Caselles [44]
where Hg2 is the inorganic mercury concentration at the reach, which is also a source of Hg0 as it reduces, and is the upstream concentration of elemental mercury in the reach. is calculated from the loads released from the sources and the existing concentration at the upstream reach as follows,
where corresponds to the total mercury releases from the sources, is the ratio of Hg0(aq) to total mercury, is the elemental mercury concentration at the upstream node of the reach, and Q is discharge.
2.3.2. Inorganic Mercury (Hg (II))
In the case of inorganic mercury (), the oxidation and reduction rates ( and ) describe the redox process and also depend on the pH value. Additionally, sedimentation is included as a sink where only the particulate fraction () settles at a settling velocity ( or ), depending on the concentration of TSS, POM, and the partition coefficient (Kd) value. Finally, the methylation process is incorporated as a temperature-dependent rate (). The default values of the rates and constants are presented in 2. The resulting steady-state Equation (4) for inorganic mercury is therefore given by
where KHG2 given by Correa-Caselles [44]
where Hg0 is the concentration of elemental mercury at the reach which is a source of Hg2 concentration when it oxidates, and is the upstream concentration of inorganic mercury. is calculated from the loads released from the sources and the existing concentration at the upstream reach as follows,
where represents total mercury releases from the sources, is the ratio of Hg (II) to total mercury, is the Hg (II) concentration from the upstream reach, and Q is the flow of the reach.
2.3.3. Organic Mercury (MeHg)
The methylmercury model considers two decay phenomena. The first consists of the sedimentation process associated with the solids present. This process is modelled using the sedimentation velocity ( or ), depending on the concentration of TSS, POM, and Kd. The second process consists of decay due to bioaccumulation. To simulate this phenomenon, a simple approximation is considered where a reaction constant () simulating the entry process to the trophic chain is used. The steady-state Equation (4) for organic mercury results as
where kMeHG given by Correa-Caselles [44]
where Hg2 is the inorganic mercury concentration at the reach which is a source of MeHg concentration when it methylates, and is the upstream concentration of organic mercury which considers releases from the sources and the existing concentration from the previous reach as follows,
where correspond to total mercury releases from the sources, is the fraction of total mercury that corresponds to methylmercury, is the methyl-mercury concentration from the upstream node, and Q is the flow of the reach.
2.4. Numerical Model Implementation
The numerical model is implemented in Python 3.0 and runs in the Python console of QGIS 3.28. The model solves the steady-state equations presented in Section 2.3 as a coupled model. The numerical model has three main phases. The first one orders and stores the information that characterizes the river network and the sources of pollution. In the second phase, a model preparation is carried out, where constants, rates, mercury speciation and additional models are computed. Finally, the mercury model is computed (Figure 1).
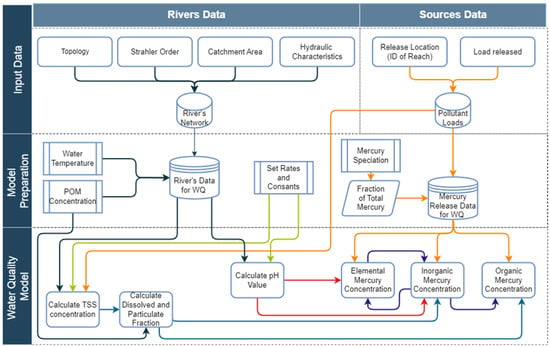
Figure 1.
Water quality model flowchart. In the input data phase is outlined the required datasets for modeling mercury dynamics in a river system, which include key data sources such as river hydraulic characteristics, and mercury release data. In the model preparation phase the datasets and input information are processed and the rates and constants are set. In the final phase critical parameters, including pH, Total Suspended Solids (TSS), and the distribution between dissolved and particulate fractions are calculated. These components integrate into a modeling framework to simulate the impacts of mercury speciation and release on water quality, providing insights into environmental dynamics and pollutant behavior in river systems.
From the input data, the code uses the river network topology, Strahler order, and accumulated catchment area to characterize flow direction. In addition, from the sources’ file, it extracts the pollutant loads and the release locations. In the second phase, the river network is prepared and loaded into the model with site-specific information, such as rates and constants, mercury speciation, water temperature, POM concentration.
Utilizing the flow direction, the hydraulic characteristics of each segment, and the TSS load released to the network, the concentrations of TSS are calculated from the upstream to the downstream nodes. Using the TSS and POM concentrations the numerical model determines the values of and (See Supplementary Materials, Section S2). Next, the pH model (See Supplementary Materials, Section S3) is used to compute the pH value at each node, from which the predominance of oxidation or reduction processes are determined, and the mercury concentrations are calculated. Finally, the numerical model computes the concentration for each mercury species simultaneously as a function of pH.
Concentrations are calculated from upstream locations to downstream locations following the direction of flow. This emphasizes the importance of a well-connected network to ensure the correct transport of pollutant concentration, as the one used in this framework (HydroShed [45]). After the numerical code calculates the concentrations for each segment, it generates a comma-separated values (.csv) output file that can be easily linked to the input shapefiles by joining the segment IDs in the river network with the corresponding concentrations stored in the CSV archive. The results are analyzed for each mercury species or as the sum of the species concentrations to obtain total mercury values. Nevertheless, as all species undergo different decay and transformation processes, understanding total mercury behavior requires first calculating the concentration of each species.
2.5. Impact Assesment
The results of the fate and transport model are useful to estimate the impact caused by a mercury source, using indicators calculated from the resulting concentrations. In this framework, the indicator is the river polluted length (RPL), which is an estimate of the distance located downstream of a contamination source that exceeds a defined standard [46]. The RPL is a metric that indicates the downstream impact caused by pollution sources and serves to compare modelling scenarios by showing mercury concentrations above a user-defined threshold [46]. This length is calculated by accumulating the length of the segments showing concentrations above the threshold or standard value, which is usually relevant to secure water supply following local environmental regulations.
Since the sources are georeferenced and linked with a polluted length downstream, using QGIS 3.28 or any other GIS software, it is easy to identify the regions or municipalities that require sanitation treatment or appropriate regulation of the industry. The releases that cause larger polluted lengths downstream can be prioritized, and this information can be used in the decision-making process.
2.6. Validation and Sensitivity Analysis
The processes of calibration and validation are usually conducted to assess the reliability and predictive capacity of model simulations by contrasting observed and simulated data [47]. During the parameter calibration process, it is possible to both understand how the parameter uncertainty affects model results and to identify the uncertainty of a model. However, this procedure is appropriate for site-specific applications and is not suitable for multisystem screening analyses since each system has a wide range of characteristics [48]. Note that, multisystem screening analysis corresponds to analyzing various basins and rivers at a time, and their calibration is challenging due to their diverse dynamics and lack of data for all of them, thus metrics commonly used to evaluate model performance that require observations, such as R-squared or RMSE are not suitable to measure model robustness.
For this level of modeling application, the analysis should be focused on planning, management goals, and questions that are being addressed by decision makers [48]. Thus, site-specific calibration was not conducted due to the large-scale and multisystem scope of this study, but a sensitivity analysis was performed to evaluate the robustness of the framework. The Sobol method, a global sensitivity analysis approach, was used to analyze the influence of three input variables on the outcomes. These variables correspond to BOD, TSS concentrations, and Au:Hg ratio, which were chosen since these are input variables relevant to pollution management and control.
Quasi-random parameter sets were generated, and sensitivity indices were calculated to assess the contribution of individual parameters and factor correlations [49,50]. The first-order sensitivity index (S1) captures the direct impact of individual parameters, while the total sensitivity index (ST) quantifies the variation in the outputs while considering factor correlations.
3. Case Study
Colombia is in the northwestern part of South America. The country is characterized by mountainous territories and valleys, which run from the south to the north of the Andes. The country is known for its biodiversity and water availability. However, unregulated releases of pollutants into rivers and unenforced regulations threaten the ecosystems’ health and the availability of safe drinking water [15]. Mercury releases have been associated with gold mining and production in over 70 countries in Asia, Africa, and South America, where approximately 15% of gold production comes from ASGM [51]. In South America, studies, such as [11,12] showed that Colombia has a major problem with mercury pollution derived from gold mining, and it has been declared as a major global mercury polluter [11,12]. Thus, the framework proposed is implemented in Colombia’s river network, as a case study to put the framework to test and model the transport and fate of mercury from alluvial gold mines in this country.
The model was applied on a national scale, and the input data were obtained from previous and updated studies [52,53,54,55]. Also, the model results were compared with available data from measuring campaigns conducted at site-specific locations. The water network employed is based on data generated by the HydroSHED v1and HydroRivers v1.0 software [45]. Using geographic information systems, the required manipulations in our methods are made to obtain the network for the entire country. The network employed has the required flow attributes, such as flow directions and links between sections, as well as information regarding flow orders, which is required for the macro network routing algorithm.
The geomorphology of each river reach is determined as a function of the slope, adopting the default equations and relationships given by [27,28,56]. Depending on the river type (step-pool, plane bed, pool-riffle, etc.) a different approximation is used to compute the travel time and the dispersive fraction. As mentioned in Section 2.3, for mountain rivers, the adopted dispersive fraction is 0.27, and for alluvial rivers, it is 0.35. Thus, for each type of geomorphology, a DF is assigned to compute the delay time using Equation (1).
In Colombia, maps of precipitation and evapotranspiration are available, and the long-term flows were determined at the scale of the network resolution [29,30]. In the calculation of long-term flows, we used geographic information tools and raster operations to obtain the values at each node of the river network considering the mass balance of water. In the case of precipitation, the most precise map available for Colombia, when compared to observed values, is the one calculated from the KDE method. On the other hand, in the case of evapotranspiration, it is calculated using the map obtained by the TURC method [30].
Due to the lack of data on mercury releases in Colombia, the mercury concentrations released by gold mines used in this study are calculated based on the concept of the ratio of Hg lost and Au produced [57,58]. In Colombia, this ratio can vary between 2 kg and 7 kg of mercury per kilogram of gold obtained [13]. An average ratio is 4:1 [14]; thus, for each kilogram of gold produced, 4 kg of mercury are released into the ecosystem.
The production of gold in Colombia is overseen by the mining-energy planning unit (UPME) in the mining-energy information system (SIMCO) [59]. To examine the application and results of the framework that is being proposed, the average values of gold production are taken as a starting point for the determination of mercury pollutant loads. The data of SIMCO show that the Colombian states with the highest production are Antioquia, Chocó, Bolívar, and Nariño. The municipalities with the highest content of mercury are all located within these four Colombian states [13]. This demonstrates that the information collected and adopted to determine mercury loads is valid and has a credible basis. The mercury released from each mine is calculated as .
As presented in Section 2.3, it is required to know the POM and TSS concentrations in each segment. Since the framework is implemented on a national scale and this type of data is sparse, presumptive loads are used as sources of these types of pollutants. These loads are calculated using the number of inhabitants of the municipalities and are released in the nearest upstream node of the river network. Note that this procedure is used given that domestic wastewater treatment is effectively only approximately 10% in the country [15] and therefore domestic loads of POM and TSS are far the largest sources of pollution of these determinants, more than diffuse loads.
The speciation ratios (Figure 2) were obtained using [31] the maximum value of the interquartile range of total mercury concentration released to the network. Also, to represent the presence of organic matter, the associated Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) concentration is adopted. The total mercury released is mostly represented by inorganic mercury and a small fraction is methylmercury for a pH greater than 5. On the other hand, for acid environments, the fraction of organic mercury increases. As a result, for a pH greater than or equal to 5 the fraction of divalent mercury ( has a value of 99.999% and has a value of 0.001%. For a pH less than 5, is 99.98% while is 0.02%.
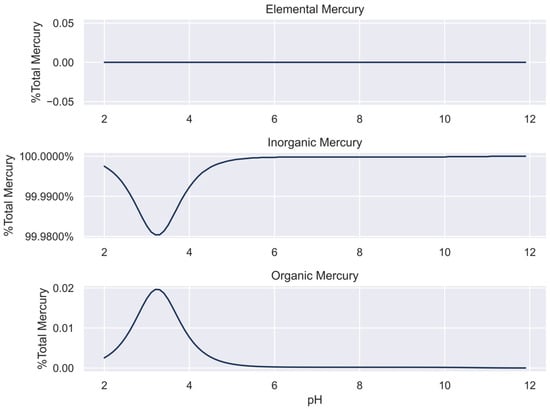
Figure 2.
Mercury speciation in the water column based on the pH level. Results from VisulaMinteq [31]. The speciation shows that inorganic mercury is the predominant form of mercury in the water column and only in low pH levels is the presence of organic mercury results relevant.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Mercury Distribution Across Colombia’s Rivers
The results demonstrate significant spatial variability in mercury concentrations across Colombia’s river network. Most of the rivers had total mercury concentrations below the local regulatory limit (1 µg/L) (Figure 3a). Yet, certain regions exceed this threshold, with concentrations ranging up to 16 µg/L. These hotspots were predominantly located in gold mining districts, such as Antioquia, Bolívar (Figure 3b), and Chocó, where artisanal mining activities have a long history of releasing mercury into the environment.
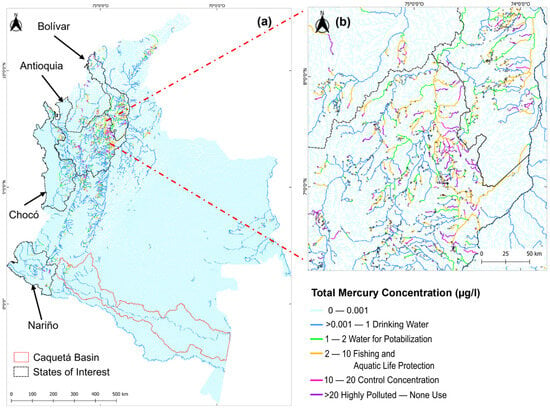
Figure 3.
(a) Total mercury spatial distribution on Colombia’s River Network (concentration in μg/L). The results prove the ability of mercury to persist in water and maintain the same concentration over long distances, as shown in the Caquetá basin. (b) Total Mercury spatial distribution in the Antioquia and Bolivar gold mining districts. The overall results showed the predominance of high mercury concentrations in gold mining districts such as the states of Antioquia, Chocó and Bolívar.
One of the most impacted regions was Bajo Cauca, located within the departments of Antioquia and Bolívar, with a high density of mines (Figure 4). Here, concentrations in the Nechí River ranged between 7 μg/L and 10 μg/L near the headwaters of several tributaries. Municipalities such as El Bagre, Zaragoza, and Segovia experienced mercury concentrations exceeding the limits for human consumption (>1 µg/L) and fishing (>2 µg/L), highlighting the potential public health risks due mercury releases from gold mining.
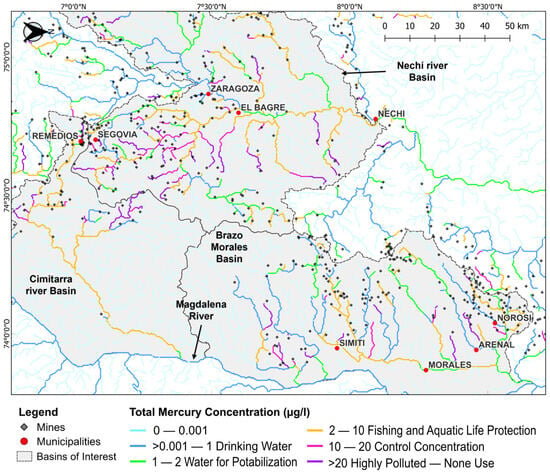
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of total mercury (HgT) concentration at Bajo Cauca watercourses (States of Antioquia and Bolívar. Concentration in μg/L). Mercury concentrations in the Nechí River and its tributaries, as well as the Cimitarra River and the Brazo Morales basin, exceeded recommended levels for safe human consumption and fishing. Concentrations reached as high as 10 μg/L in the Nechí River headwaters and 16 μg/L in the Brazo Morales basin, indicating significant environmental impact from mining activities.
Similarly, the Cimitarra River showed concentrations between 1 and 6 µg/L (Figure 4), limiting the use of water for human consumption and fishing. Thus, it is important to monitor mercury concentrations in the area to ensure the viability of fishing and to protect aquatic life. Moreover, the Brazo Morales basin (Bolívar), a highly influential watershed in the country as a direct tributary of the Magdalena River, one of Colombia’s major rivers, has mercury concentrations posing risks for safe human consumption and, in some sectors, limiting fishing activities. Specifically, in Brazo Morales, mercury concentrations ranged from 1.9 μg/L and 16 μg/L, demonstrating the high environmental impact of gold mining districts.
Among the mining districts highlighted (Figure 3a), the one in the state of Chocó stands out for having elevated concentrations (Figure 5). In this area, the Atrato river basin was significantly impacted, particularly in the sub-basins of the Quito, Andagueda, and Alto Atrato rivers. Results showed concentrations reaching 10 μg/L in the Alto Atrato headwaters, and 2 μg/L near the town of Lloró. These elevated values restrict economic activities, including artisanal fishing practices, in the nearby municipalities. Similarly, in the Andagueda River, near Bagado, mines located at the headwaters generate concentrations between 1 μg/L and 5 μg/L, which also limits the river’s water uses.
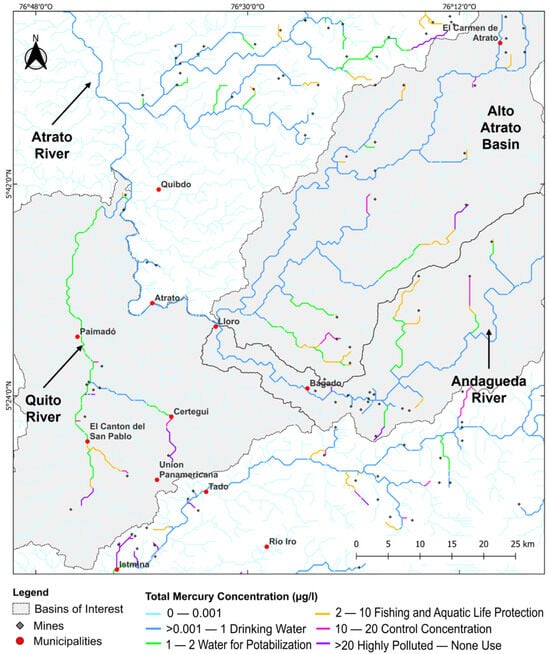
Figure 5.
Total mercury concentration (HgT) spatial distribution at Atrato River basin (State of Chocó). Concentration in μg/L. The Quito, Andagueda, and Alto Atrato sub-basins were significantly impacted by mercury pollution. Concentrations reached up to 10 μg/L in the Alto Atrato headwaters and 2 μg/L near Lloró, restricting economic activities like artisanal fishing.
The results showed that mercury concentrations were the highest in the primary gold mining districts of Colombia (Antioquia, Chocó, Bolívar), where artisanal mining is a common practice. This indicates that local mining activities and the density of mines in an area contribute to elevated pollution levels. For instance, these gold mining districts caused exceedance of safe consumption limits and restricted fishing activities for the nearby population. In contrast, areas with less mining density, such as the Caquetá basin (Figure 3a), demonstrated lower mercury concentrations but highlighted the persistence of mercury over long distances, reflecting the persistent nature of the pollutant. These findings underline the critical role of mining density in influencing regional contamination patterns, emphasizing the need to control pollution sources to mitigate widespread contamination.
4.2. Mercury Speciation and Implications for Ecosystem
The previous results focused on synthesizing concentration values and water restrictions associated with total mercury, considering that local regulations do not establish limits for other mercury forms or species. Nevertheless, analyzing these species of mercury is important since their individual impacts on ecosystems and public health vary. Thus, it is convenient to show at the national level the concentration of each species (Figure 6).
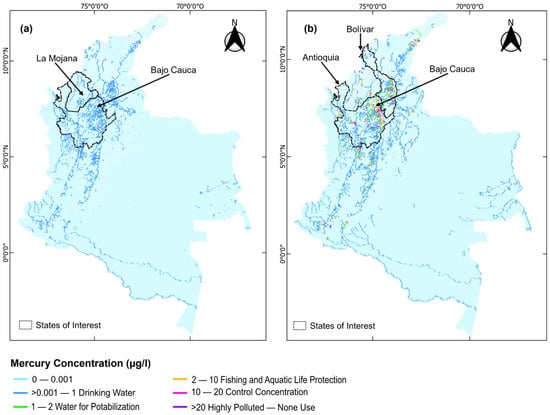
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of mercury concentrations by type of form. (a) Shows the distribution of methylmercury; (b) shows divalent mercury. Methylmercury concentrations were generally below 1 μg/L in most of the country’s river network but reached 60 μg/L to 2.4 μg/L in the Bajo Cauca and La Mojana regions. Divalent mercury was the predominant species, with concentrations close to the levels observed for total mercury.
Mercury speciation results reveal distinct regional patterns, with Hg (II) as the predominant across most of the river network. Concentrations of Hg (II) closely match total mercury values (Figure 6b), indicating that this species accounts for the majority of the mercury load. In contrast, methylmercury concentrations were generally below 1 μg/L (Figure 6a) nationwide, except in mining-intensive regions such as Bajo Cauca (Antioquia) and La Mojana (Córdoba) where levels ranged between 2.4 μg/L and 60 µg/L (Figure 6a). These elevated methylmercury levels raise significant concerns about bioaccumulation and biomagnification in aquatic food webs since methylmercury concentrations in fish can range between 46 and 109 µg-Hg/kg-fish [60]; therefore, further studies on the bioaccumulation and biomagnification phenomena are important to further understand Hg dynamics in streams and food web relationships.
In contrast, Hg0 concentrations were consistently low, as analyzed in the speciation results (Figure 2), ranging from 1 ng/L to 9 ng/L (nanograms per liter). While Hg0 has limited direct toxicity on water, its potential for volatilization and atmospheric deposition highlights the need for comprehensive mercury management strategies. The findings emphasize the importance of understanding speciation dynamics to address the ecological and human health impacts of mercury pollution.
4.3. Public Health and Pollution Impacts
The results for key mining districts illustrate the intersection of mercury contamination, hydrology, and human health risk. The findings for key mining districts reveal that mercury pollution is not only a widespread environmental issue but also a public health concern for communities in mining sites. Mining districts in Antioquia, Choco and Bolivar have been affected due to intensive gold mining activities. These areas rely on rivers for drinking water, fishing and agricultural irrigation which increases their vulnerability to mercury exposure.
To provide insights into the extent of mercury contamination, the RPL metric provides an assessment of the impacts of gold mining in Colombia. Regions with the highest total mercury concentrations, such as Antioquia and Bolívar, also had the largest RPL values, with lengths up to 286 km with concentrations exceeding the standard for drinking water without treatment (1 µg/L) (Figure 7a). For potabilization water use, mercury released from 78 mines resulted in an RPL between 50 km and 162 km with concentrations greater than 2 µg/L. Municipalities like Remedios (Antioquia) (Figure 7d) accounted for the largest number of mines generating concentrations above the human consumption standard. These results were consistent with the high historic levels and water quality assessments in the departments of Antioquia, Chocó, and Bolívar [11,12,13,58]. These areas require detailed water quality modeling studies and interventions. On the national level, results revealed that the potential mercury public health problem is found in the Bajo Cauca area (Figure 4, Figure 7c,d). These areas require detailed water quality modeling studies.
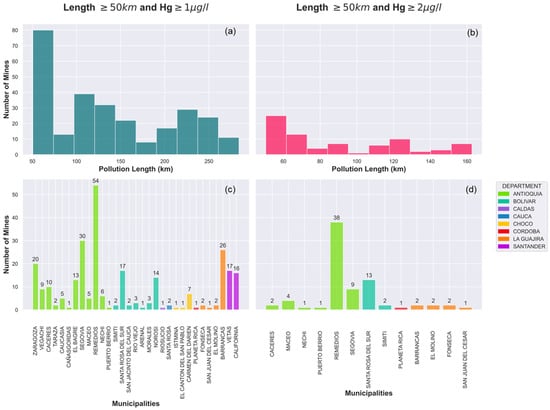
Figure 7.
Mine and spatial distribution of pollution length greater than 50 km compared to a standard concentration. (a,b) show the distribution of pollution length in terms of number of mines and (c,d) show the spatial distribution of the mines that have a pollution length greater or equal to 50 km. (a,c) correspond to concentrations of mercury greater than 1 µg/L, and (b,d) correspond to concentrations greater than 2 µg/L.
4.4. Validation and Comparative Analysis
The validation of the model’s national-scale results is restricted by the limited amount of data. Hence, the validation was performed with the sparse datasets collected from previous studies [61,62]. These studies were in the Quito River, located at the northeastern region of Colombia within the department of Chocó (Figure 8). The region is widely known for its rich biodiversity and active gold mining activities [63], which, given the lack of environmental controls, have resulted in significant mercury deposits in local ecosystems [64]. The studies provide values of mercury concentrations in water and sediments at different points located downstream of the mining area of the Quito River.
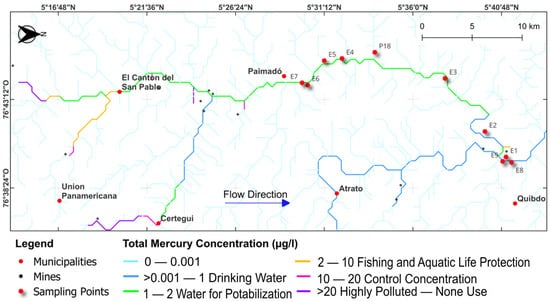
Figure 8.
Quito River and localization of sampling sites, along with model results.
When comparing the results of the model with measured concentrations reported in these two studies, at the same sampling locations, the magnitudes were very similar (Table 2) (error < 1 μg/L). The difference between them can be associated with missing releases of mercury or unregulated sources. These validation results suggest that even with limitations of data availability for a countrywide verification, the implementation of the modelling framework was appropriate, as well as the assumptions. Hence, although further validation is required upon the availability of more data, our modeling approach is a strong tool to estimate the transport and fate of mercury.

Table 2.
Sampling points with mercury concentrations in water.
To strengthen the reliability of the results, a comparative analysis with existing studies is necessary to contextualize the findings. The gold mining districts, as recognized by the Ministry of Mines and Energy are in municipalities within the departments of Antioquia, Chocó and Bolívar (Figure 3a). Examples of said municipalities are El Bagre and Remedios in Antioquia, Morales and Arenal in Bolívar (Figure 4). The model results showed that the highest calculated mercury concentrations (>20 µg/L) are found in these mining districts, demonstrating congruence with other studies conducted in the country [11,13,14,65,66].
The elevated mercury concentrations observed in the Bajo Cauca (7–16 µg/L) region align with trends reported in other mining-intensive areas. For instance, studies in the Amazon Region of Brazil found high mercury levels in water, sediments, and fish, exceeding safe consumption levels by up to five times [67,68]. Similarly, in Ghana studies reported widespread mercury pollution in small-scale gold mining sites, with concentrations several orders higher than background levels [69].
Studies in the Peruvian Amazon observed a strong correlation between mercury imports and gold production, highlighting the significant contribution of gold mining to mercury pollution in the region [70]. Similarly, studies in the Yellow River basin in China showed that total mercury concentrations vary spatially and temporally, with higher concentrations during the water-sediment regulation. This variability underscores the role of sediment dynamics and dam operations in mercury transport and distribution [71].
Unlike previous studies focused on localized contamination in specific rivers or sub-basins, this nationwide assessment examines mercury transport and persistence across a broader scale. For example, studies in Peru’s Madre de Dios region found that mining activities introduced mercury into the environment and created artificial lakes. The work showed that total mercury concentrations were strongly linked to suspended sediment levels [72], highlighting sediment’s role in mercury transport. While such regional studies provide detailed insights, this study offers a more comprehensive view of mercury behavior across multiple basins, accounting for variations in hydrology, sediment loads, and mining intensity.
This study provides a comprehensive understanding of mercury dynamics in mining-affected regions by combining a nationwide perspective with insights into mercury transport processes. This study addresses the interactions between regional drivers and broader environmental factors, making its findings crucial for policy development and environmental management.
4.5. Sensitivity Analysis Results
Three factors influencing mercury concentration in water were selected for the sensitivity analysis. These factors were the Hg:Au ratio, the TSS per-capita load, and the BOD per-capita load. The parameter ranges were estimated from existing literature and field data, Hg:Au ratio from 2 to 7 [13,73]; TSS from 150 to 400 g/d·per-capita; and BOD from 25 to 50 g/d·per-capita [74,75,76,77,78]. As mentioned in the material and section we chose these parameters since they correspond to input variables that can address answers related to water pollution management and are essentially oriented to understanding the influence of policy-controlling factors in the model outputs. The Sobol indices results are shown in Figure 9. The indices were calculated to understand the variation in three mercury concentration metrics: the median, 25th quartile (Q25), and 75th quartile (Q75) as shown in Figure 9.
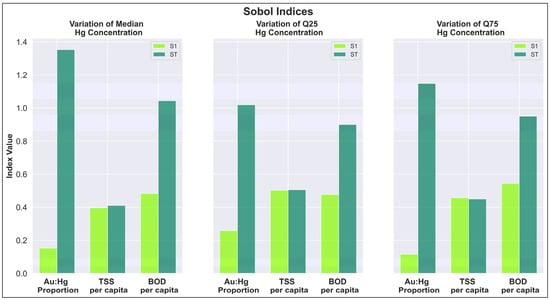
Figure 9.
Sobol indices results. The S1 index indicates that TSS and BOD have the strongest influence on output variation when parameter correlation is not considered. The ST index shows that the Au:Hg ratio is the most influential parameter when accounting for parameter correlation, though varying only this ratio would not lead to significant changes in the model results.
The behavior of the S1 index shows the influence of each parameter on the output variation. TSS and BOD have the strongest influence on the output variation (near 90% of variance in some cases) when no correlation between parameters is considered (Figure 9). The S1 index results are consistent with the adsorption and sedimentation phenomena that predominate for the species present in the water. On the other hand, the ST index shows that when correlation between parameters is considered, the Au:Hg ratio is the parameter that influences the response of the model the most. However, if only this parameter was varied, there would be no significant variation in the results of the model.
From the sensitivity analysis, it is possible to conclude that the results of the model depend on the input loads to the system. In this case, it is observed that there is a direct dependence associated with the values of suspended solids, either organic matter or inorganic solids. The results given by the S1 index led to the conclusion that the results do not have a high sensitivity to the variation in the Au:Hg ratio when it is varied by itself. Hence, the outputs do not have a direct dependence on the Au:Hg ratio. This is relevant since this ratio can become the source of major uncertainty due to the lack of field data.
5. Conclusions and Suggestions for Further Work
This study presents a robust framework for assessing mercury concentrations in river networks at a national scale, providing an essential tool for prioritizing pollution mitigation efforts under resource constraints. By simulating the transport and fate of mercury across multiple basins, the framework enables the identification of pollution hotspots and offers valuable insights into spatial dynamics and patterns, which are critical for regulatory and management planning including prioritization strategies.
The framework’s reliability was demonstrated through sensitivity analysis and a validation process using limited field data from the Quito River basin. Results indicate close values to observed concentrations, underscoring the model’s ability to assess mercury dynamics despite data limitations. The sensitivity analysis highlighted the dominant role of TSS, BOD, and Au:Hg ratio in influencing mercury transport, emphasizing their influence for effective pollution management.
Applied to Colombia, the framework identified several critical regions, corresponding to major gold mining districts, where mercury concentrations in rivers exceed safety limits for drinking water (1 µg/L) and fishing (10 µg/L). Metrics like the RPL quantified the extent of mercury impacts, showing pollution distances of up to 285 km caused by mining activities. These findings highlight the urgent need for targeted sanitation measures and stricter mercury release regulations in mining-affected areas.
The framework’s scalability and flexibility are valuable features. This enables analyses at the national and basin scales, making it useful for decision makers at different levels of government. The open-source programming and GIS integration ensure the framework is accessible for applying similar studies in other countries or basins. This supports global efforts under the MCM to address mercury pollution.
While the framework offers a powerful tool for large-scale mercury assessments, limitations remain. The partial consideration of sediment–water interactions provides an approximation of mercury concentrations without fully accounting for sediment transport dynamics. Similarly, the reliance on registered mining data may overlook contributions from illegal mining activities. Future research could incorporate more advanced models for sediment dynamics and account for unregistered mercury sources. Additionally, addressing data gaps at the national scale by enhancing monitoring networks and considering mineral weathering processes could further improve the framework’s accuracy and utility.
This framework represents a significant advancement in mercury pollution assessment by integrating spatial analysis, sensitivity evaluation, and national-scale applicability. This study’s implementation in Colombia underscores the pressing need for targeted interventions in mining-affected regions. This framework serves as a model for future large-scale efforts to address mercury’s harmful effects on ecosystems and public health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17020250/s1. These materials comprise a document including all additional models’ equations and technical information used to develop the numerical model in Python. Data and code are also available as described in the Data Availability Statement below. References [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89] are citied in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.C.-C. and L.A.C.; methodology, D.C.-C. and L.A.C.; software, D.C.-C. and N.F.; validation, D.C.-C., L.A.C. and N.F.; formal analysis, D.C.-C.; investigation, D.C.-C.; resources, L.A.C.; data curation, D.C.-C. and N.F.; writing—original draft preparation, D.C.-C.; writing—review and editing, L.A.C. and N.F.; visualization, D.C.-C.; supervision, L.A.C.; project administration, L.A.C.; funding acquisition, L.A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universidad de los Andes as part of the teaching and research projects related to the achievement of sustainable development goals (SDGs). This publication is part of the project “Update of the multi-criteria prioritization of wastewater treatment implementation needs in Colombia”. Funding Number: F-ODS-2021.
Data Availability Statement
In addition to the Supplementary Materials, the datasets, results, and code developed for the present project are available for download in the following online repository: Correa, Daniela (2024), “Water Quality Datasets & Models for Nationwide Surface Waters”, Mendeley Data, V1, https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/mkf3xkfwtm/1, accessed on 1 January 2025. Software Requirements: QGIS 3.28.11 or the latest, Programming Language: Python 3.0.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Andrew Conolly at the Department of Languages and Culture for his help proofreading this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury Toxicity and Neurodegenerative Effects. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Minamata Convention on Mercury. 2019. Available online: https://minamataconvention.org/en/documents/minamata-convention-mercury-text-and-annexes (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- World Health Organization. Preventing Disease through Healthy Environments: Exposure to Mercury: A Major Public Health Concern. 2021. Available online: https://who.int/publications/i/item/9789240023567 (accessed on 8 October 2023).
- Bernhoft, R.A. Mercury Toxicity and Treatment: A Review of the Literature. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 460508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Horowitz, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Lu, Z.; Levin, L.; ter Schure, A.F.H.; Sunderland, E.M. Total Mercury Released to the Environment by Human Activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5969–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N.E. A Review of Global Environmental Mercury Processes in Response to Human and Natural Perturbations: Changes of Emissions, Climate, and Land Use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, M.S.; Bank, M.S.; Bishop, K.; Bowman, K.; Branfireun, B.; Chételat, J.; Eckley, C.S.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Lamborg, C.; Lyman, S.; et al. Mercury Biogeochemical Cycling: A Synthesis of Recent Scientific Advances. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment Programme. Minamata Convention in 2022: Progress Report on Activities; UN Environment Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- UN Environment Programme. National Action Plans; UN Environment Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Brush, M.; McLagan, D.S.; Biester, H. Fate of Mercury from Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Tropical Rivers: Hydrological and Biogeochemical Controls. A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 437–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordy, P.; Veiga, M.M.; Salih, I.; Al-Saadi, S.; Console, S.; Garcia, O.; Mesa, L.A.; Velásquez-López, P.C.; Roeser, M. Mercury Contamination from Artisanal Gold Mining in Antioquia, Colombia: The World’s Highest per Capita Mercury Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Arriaga, F.A. Mercurio En La Minería Del Oro: Impacto En Las Fuentes Hídricas Destinadas Para Consumo Humano. Rev. Salud Pública 2015, 16, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Minas y Energía; Universidad de Córdoba. Estudio de La Cadena de Mercurio En Colombia Con Énfasis En La Actividad Minera de Oro; Ministerio de Minas y Energía y Unidad de Planeación Minero-Energética: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014. Available online: https://rds.org.co/apc-aa-files/ba03645a7c069b5ed406f13122a61c07/cadena_mercurio_tomo_i.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Diaz, F.A.; Katz, L.E.; Lawler, D.F. Mercury Pollution in Colombia: Challenges to Reduce the Use of Mercury in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Light of the Minamata Convention. Water Int. 2020, 45, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.A. The Paradox of the Availability of Poor Water Quality in the Colombian Rural Sector. Rev. Ing. 2020, 49, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament and of the Council. Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water Policy, Amending and Subsequently Repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and Amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. 2008. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/105/2013-09-13 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible. Decreto 1076 de 2015. Colombia, 2015. Available online: https://www.funcionpublica.gov.co/eva/gestornormativo/norma.php?i=78153 (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Resolución de Colombia. Ministerio de Ambiente Vivienda y Desarrollo Territorial; Ministerio de Protección Social. 2007. Available online: https://minvivienda.gov.co/sites/default/files/normativa/2115%20-%202007.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- World Health Organization. Mercury in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.M.; Wells, S.A. CE-QUAL-W2: A Two-Dimensional, Laterally Averaged, Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, Averaged, Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, Version 3.5. 2006. Available online: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/cengin_fac/130/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Jones, E.R.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wanders, N.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Vliet, M.T.H. DynQual v1.0: A High-Resolution Global Surface Water Quality Model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 4481–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute. MIKE 11 A Modelling System for Rivers and Channels User Guide; Danish Hydraulic Institute: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wool, T.; Ambrose, R.B.; Martin, J.L.; Comer, A. WASP 8: The next Generation in the 50-Year Evolution of USEPA’s Water Quality Model. Water 2020, 12, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek-Mohammadi, S.; Tachiev, G.; Cabrejo, E.; Lawrence, A. Simulation of Flow and Mercury Transport in Upper East Fork Poplar Creek, Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Remediation 2012, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhuang, W.; Qian, Y.; Xia, B.; Yang, Y.; Qian, X. Estimating and Predicting Metal Concentration Using Online Turbidity Values and Water Quality Models in Two Rivers of the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žagar, D.; Petkovšek, G.; Rajar, R.; Sirnik, N.; Horvat, M.; Voudouri, A.; Kallos, G.; Četina, M. Modelling of Mercury Transport and Transformations in the Water Compartment of the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Chem. 2007, 107, 64–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.A.; Wohl, E. Solute Transport Modeling Using Morphological Parameters of Step-Pool Reaches. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.A.; Vélez, J.I.; Camacho, L.A. Stream Morphology and Downstream Hydraulic Geometry Relations for Bankfull Width, Universidad Nacional de Colombia; Universidad de los Andes: Bogotá, Colmbia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Villa, O.D.; Vélez, J.I.; Poveda, G. Improved Long-Term Mean Annual Rainfall Fields for Colombia. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2194–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, O.D.; Vélez, J.I.; Poveda, G. Incertidumbre Asociada Con El Balance Hídrico de Largo Plazo. In XXIII Congreso Latinoamericano de Hidráulica; International Association for Hydro-Environmental Engineering and Research (IAHR): Cartagena de Indias, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.P. Visual MINTEQ, ver. 3.1. Available online: https://vminteq.com/ (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. WASP Mercury Processes. Hydrologic Modelling Community of Practice. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hydrowq/wasp7-course#toxicants (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Beer, T.; Young, P.C. Longitudinal Dispersion in Natural Streams. J. Environ. Eng. 1983, 109, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.C.; Wallis, S.G. Solute Transport and Dispersion in Channels. In Channel Network Hydrology; Beven, K.J., Kirkby, M.J., Eds.; Wiley: Mason, MI, USA, 1993; pp. 129–174. [Google Scholar]
- Young, P.; Wallis, S. The Aggregated Dead Zone (ADZ) Model for Dispersion in Rivers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Quality Modelling in the Inland Natural Environment, Bournemouth, UK, 10–13 June 1986; pp. 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, M.J.; Camacho, L.; Whitehead, P. Extension of the QUASAR River Water Quality Model to Incorporate Dead-Zone Mixing. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1998, 2, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, M.J.; Camacho, L.A.; Chapra, S. On the Relationship of Transient Storage and Aggregated Dead Zone Models of Longitudinal Solute Transport in Streams. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.F.; Camacho, L.A. An Integrated Water Quality Model to Support Multiscale Decisions in a Highly Altered Catchment. Water 2022, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.A.; Lees, M.J. Multilinear Discrete Lag-Cascade Model for Channel Routing. J. Hydrol. 1999, 226, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pinzón, R. Determinación Del Comportamiento de La Fracción Dispersiva En Ríos Característicos de Montaña. Master’s Dissertation, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, L.A.; González, R.A. Calibration and Predictive Ability Analysis of Longitudinal Solute Transport Models in Mountain Streams. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, S.G.; Young, P.C.; Beven, K.J. Experimental Investigation of the Aggregated Dead Zone Model. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1989, 87, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.N.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Cuhaciyan, C.O.; Wohl, E.E. Channel-reach Morphology Dependence on Energy, Scale, and Hydroclimatic Processes with Implications for Prediction Using Geospatial Data. Water Resour Res 2006, 42, W06412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Caselles, D.F. Metodología Para La Estimación Del Destino y Transporte de Mercurio Presente En Los Ríos de Colombia. 2022. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1992/54564 (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Lehner, B. Global River Network Delineation Derived from HydroSHEDS Data at 15 Arc-Second Resolution; 2019. Available online: https://hydrosheds.org/images/inpages/HydroRIVERS_TechDoc_v10.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Díaz-Granados, M.; Barrera, S.; Ramos, J.P.; Camacho, L.A.; Rosales, R.; Escalante, N.; Torres, M. Metodología Multicriterio Para La Priorización de Inversión En Aguas Residuales Municipales En Colombia. In XX Congreso Latinoamericano de Hidráulica; IARH: La Habana, Cuba, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, N.; Camacho, L.A. Water Quality Modeling in Headwater Catchments: Comprehensive Data Assessment, Model Development and Simulation of Scenarios. Water 2023, 15, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C.; Boehlert, B.; Fant, C.; Bierman, V.J.; Henderson, J.; Mills, D.; Mas, D.M.L.; Rennels, L.; Jantarasami, L.; Martinich, J.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Harmful Algal Blooms in U.S. Freshwaters: A Screening-Level Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8933–8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.; Usher, W. SALib: An Open-Source Python Library for Sensitivity Analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Usher, W.; Herman, J. Toward SALib 2.0: Advancing the Accessibility and Interpretability of Global Sensitivity Analyses. SESMO 2022, 4, 18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.; Wadle, A.; Parham, J. Gold Rush, Mercury Legacy: Small-Scale Mining for Gold Has Produced Long-Lasting Toxic Pollution, from 1860s California to Modern Peru. The Conversation, 28 May 2020. Available online: https://theconversation.com/gold-rush-mercury-legacy-small-scale-mining-for-gold-has-produced-long-lasting-toxic-pollution-from-1860s-california-to-modern-peru-133324 (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Rojas-Aguirre, A.; Camacho, L. Aplicación de Factores de Asimilación Para La Priorización de La Inversión En Sistemas de Saneamiento Hídrico En Colombia; Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera, S.; Díaz-Granados, M.; Ramos, J.P.; Camacho, L.A.; Rosales, R.; Escalante, N.; Torre, M. Modelo Computacional Del Impacto de Las Aguas Residuales Municipales Sobre La Red Hídrica. In XX Congreso Latinoamericano de Hidráulica; International Association for Hydro-Environmental Engineering and Research (IAHR): Punta del Este, Uruguay, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, A. Factores de Asimilación de Carga Contaminante En Ríos: Una Herramienta Para La Identificación de Estrategias de Saneamiento Hídrico En Países En Desarrollo; Universidad de Los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Raciny-Alemán, I. Investigación y Extensión Del Modelo Computacional Del Impacto De Las Aguas Residuales Municipales Sobre La Red Hídrica Colombiana, 2003, Volume 18. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1992/10062 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Camacho, L.A.; Lees, M.J. Modelación Del Transporte de Solutos En Ríos Bajo Condiciones de Flujo No Permanente: Un Modelo Conceptual Integrado. In XIX Congreso Latinoamericano de Hidráulica; IAHR: Córdoba, Argentina, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Watari, T.; Seccatore, J.; Nakajima, K.; Nansai, K.; Takaoka, M. A Review of Gold Production, Mercury Consumption, and Emission in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM). Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, M. Antioquia, Colombia, the World’s Most Polluted Place by Mercury, Impressions from Two Field Trips; Normal Keevil Institute of Mining Engineering, University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2010; Prepared for UNIDO (United Nations Industrial Development Organization). [Google Scholar]
- Unidad de Planeación Minero Energética (UPME). Sistema de Información Minero Colombiano (SIMCO)—Oro. Producción de Oro. Available online: https://www1.upme.gov.co/simco/Cifras-Sectoriales/Paginas/oro.aspx (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Ramos, C.; Estévez, S.; Giraldo, E. Nivel de Contaminación Por Metilmercurio En La Región de La Mojana; Universidad de los Andes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2000; Available online: https://www.hruschka.com/hg-net/members/claudia/metilmercurio_en_la_mojana.doc (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Gaviria, S.; Angel-Amaya, J. Geoindicadores Aplicados al Estudio de Los Efectos Ambientales de La Explotación de Oro Aluvial En La Cuenca Baja Del Río Quito, Chocó (Colombia). Gestión Ambiente 2019, 22, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L. Caracterización de la Concentración de Metales en Agua, Sedimentos y Suelos a lo Largo del Río Quito (Chocó), Zona de Explotación de oro Aluvial. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1992/44787 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Ángel-Amaya, J.; Ordoñez, M.; Olivero, J.; Echavarría, C.; Ayala, H.; Cabrera, M. Consideraciones Sobre La Minería En El Departamento Del Chocó y Recomendaciones Para Mejorar La Gestión; Geopatrimonio—Universidad de Cartagena—IIAP—WWF: Cali, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios-Torres, Y.; Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Mercury Pollution by Gold Mining in a Global Biodiversity Hotspot, the Choco Biogeographic Region, Colombia. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, A.; Suemasu, K.; Veiga, M.M. Estimation of Mercury Losses and Gold Production by Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM). J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procuraduría General de la Nación. Informe Nacional: Minería Ilegal y Contaminación por Mercurio en Colombia; Procuraduría General de la Nación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2024; Available online: https://foronacionalambiental.org.co/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Informe-Nacional-Mineria-Ilegal-y-Contaminacion-por-Mercurio-en-Colombia-2.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Pfeiffer, W.C.; Drude de Lacerda, L.; Malm, O.; Souza, C.M.M.; da Silveira, E.G.; Bastos, W.R. Mercury Concentrations in Inland Waters of Gold-Mining Areas in Rondônia, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1989, 87–88, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palheta, D.; Taylor, A. Mercury in Environmental and Biological Samples from a Gold Mining Area in the Amazon Region of Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 168, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.J. Assessing Releases of Mercury from Small-Scale Gold Mining Sites in Ghana. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2017, 4, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, J.J.; Carter, C.E.; Domec, J.-C.; Delgado, C.I. Gold Mining in the Peruvian Amazon: Global Prices, Deforestation, and Mercury Imports. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, M.; Guo, J.; Lin, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, M.; Lu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Transport of Mercury in a Regulated High-Sediment River and Its Input to Marginal Seas. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.R.; Topp, S.N.; Vega, C.M.; Gardner, J.R.; Yang, X.; Fernandez, L.E.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Pavelsky, T.M. Artificial Lake Expansion Amplifies Mercury Pollution from Gold Mining. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Minas y Energía; Agencia Nacional de Minería. Plan de Acción Nacional Sobre Mercurio en la Minería Artesanal y de Pequeña Escala en Colombia; Ministerio de Minas y Energía: Bogotá, Colombia, 2023. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/col227994.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Metcalf, L.; Eddy, H.P.; Tchobanoglous, G. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal, and Reuse; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Aboulfotoh, A.; Heikal, G. Estimation of Per Capita Loading and Treated Wastewater Quality Index in Sharkia Governorate, Egypt. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosic, M.; Restrepo, J.D.; Izquierdo, A.; Lonin, S.; Martins, F.; Escobar, R. An Integrated Approach for the Assessment of Land-Based Pollution Loads in the Coastal Zone. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2018, 211, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, D.; Pulikesi, M.; Baskaralingam, P.; Ramamurthi, V.; Sivanesan, S. Production of Biogas from Municipal Solid Waste with Domestic Sewage. J. Hazard Mater 2007, 141, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katukiza, A.Y.; Ronteltap, M.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Kansiime, F.; Lens, P.N.L. Grey Water Characterization and Pollutant Loads in an Urban Slum. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S. Surface Water-quality Modeling. In McGraw-Hill Series in Water Resources and Environmental Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://books.google.com.co/books?id=HHWNQgAACAAJ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Finkelman, R. Sources and Health Effects of Metals and Trace Elements in Our Environment: An Overview. In Metal Contaminants in New Zealand; Moore, T., Black, A., Centeno, J., Harding, J., Trumm, D., Eds.; Resolution Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005; pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gavis, J.; Ferguson, J.F. The Cycling of Mercury through the Environment. Water Res. 1972, 6, 989–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabelkova, J.; Kominkova, D. Trace Metals in the Bed Sediment of Small Urban Streams. Open Environ. Biol. Monit. J. 2012, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.; Allison, T. Partition Coefficients for Metals in Surface Water, Soil, and Waste. 2005. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P1000GHE.PDF?Dockey=P1000GHE.PDF (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Knightes, C.D. Modeling Mercury Transport and Transformation along the Sudbury River, Massachusetts (USA) with Implications for Regulatory Actions. 2009. Available online: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/01/471164.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Fang, T.-H.; Lien, C.-Y. Different Mercury Species Partitioning and Distribution in the Water and Sediment of a Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water 2021, 13, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C.; Pelletier, G. A Modeling Framework for Simulating River and Stream Water Quality. Documentation and Users Manual. 2003. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/389982473/Q2KDocumentation-1-pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Chapra, S.; Pelletier, G. Qual2k Documentation and User’s Manual; Civil and Environmental Engineering Dept., Tufts University: Medford, OR, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, L.A. (Universidad de Los Andes, Bogota, Colombia). Personal Communication, 2022.
- Sobol, I.M. Global Sensitivity Indices for Nonlinear Mathematical Models and Their Monte Carlo Estimates. Math Comput Simul 2001, 55, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).