Occurrence and Seasonal Variation of Picoplankton at Saiysad Freshwater in Taif City, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
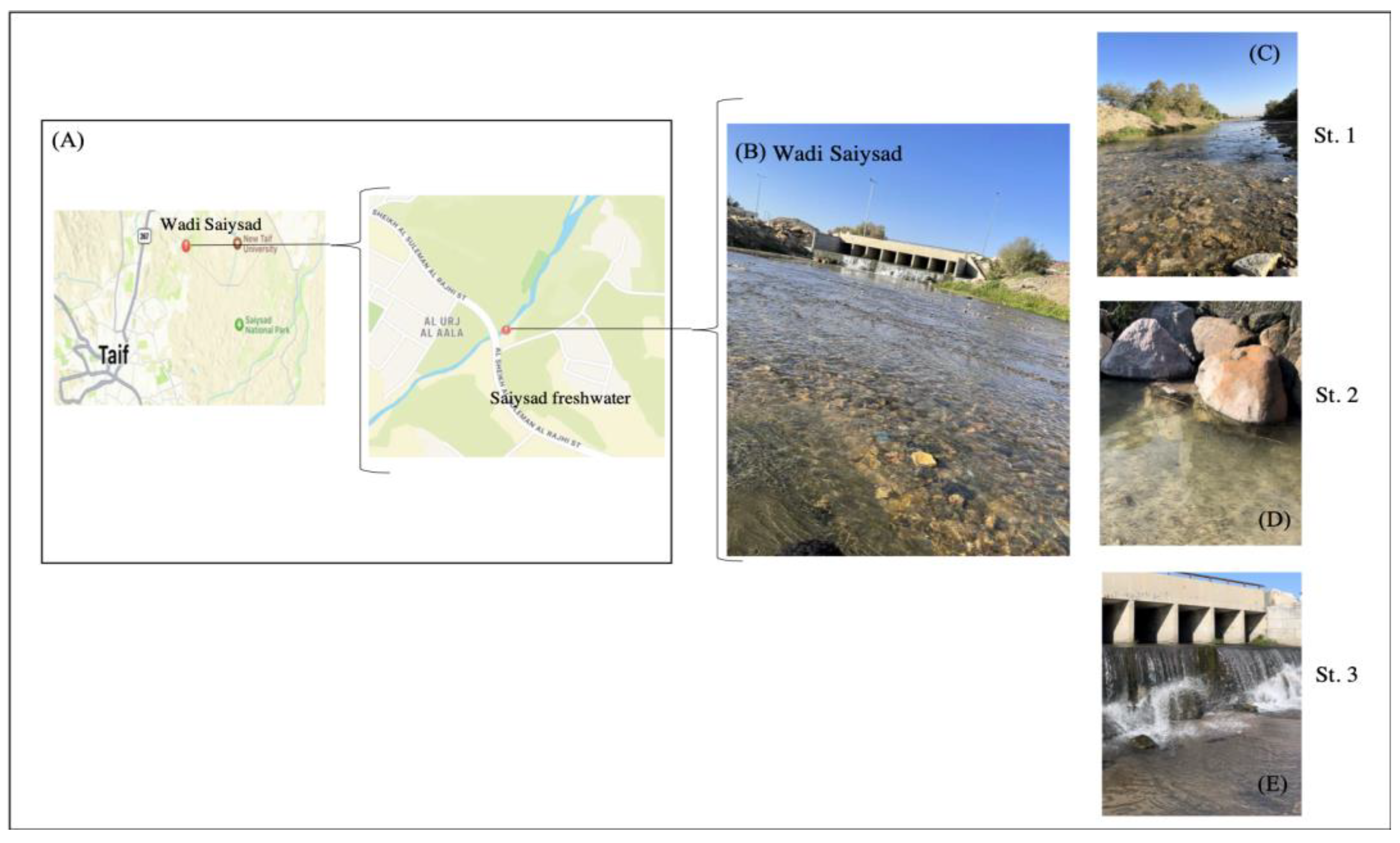
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Environmental Parameter Measurements
2.2. Flow Cytometric Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
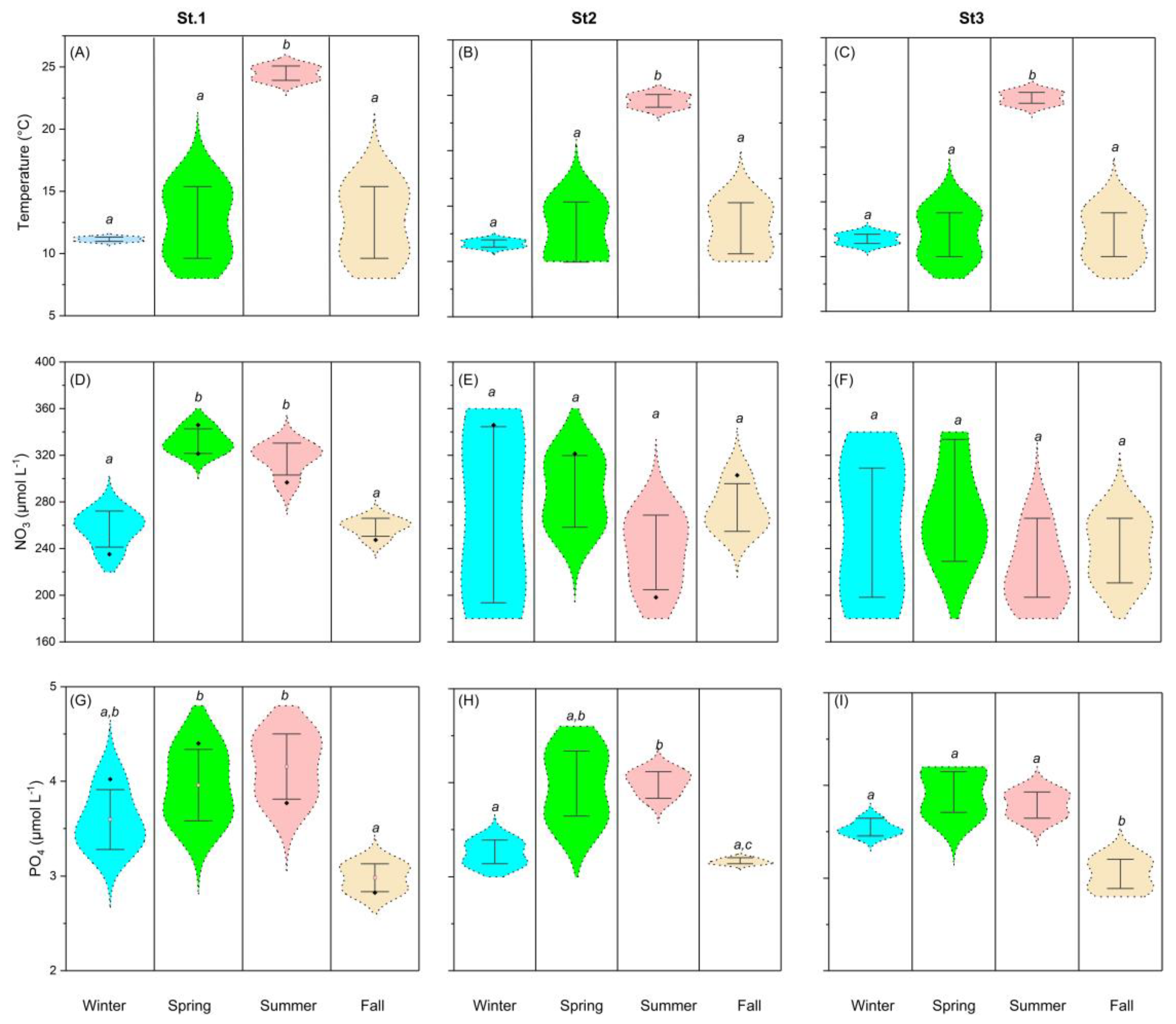
3.1. Seasonal and Spatial Variability in Hydrographic Conditions
3.2. Total and Size Fractionated Chlorophyll a Concentration
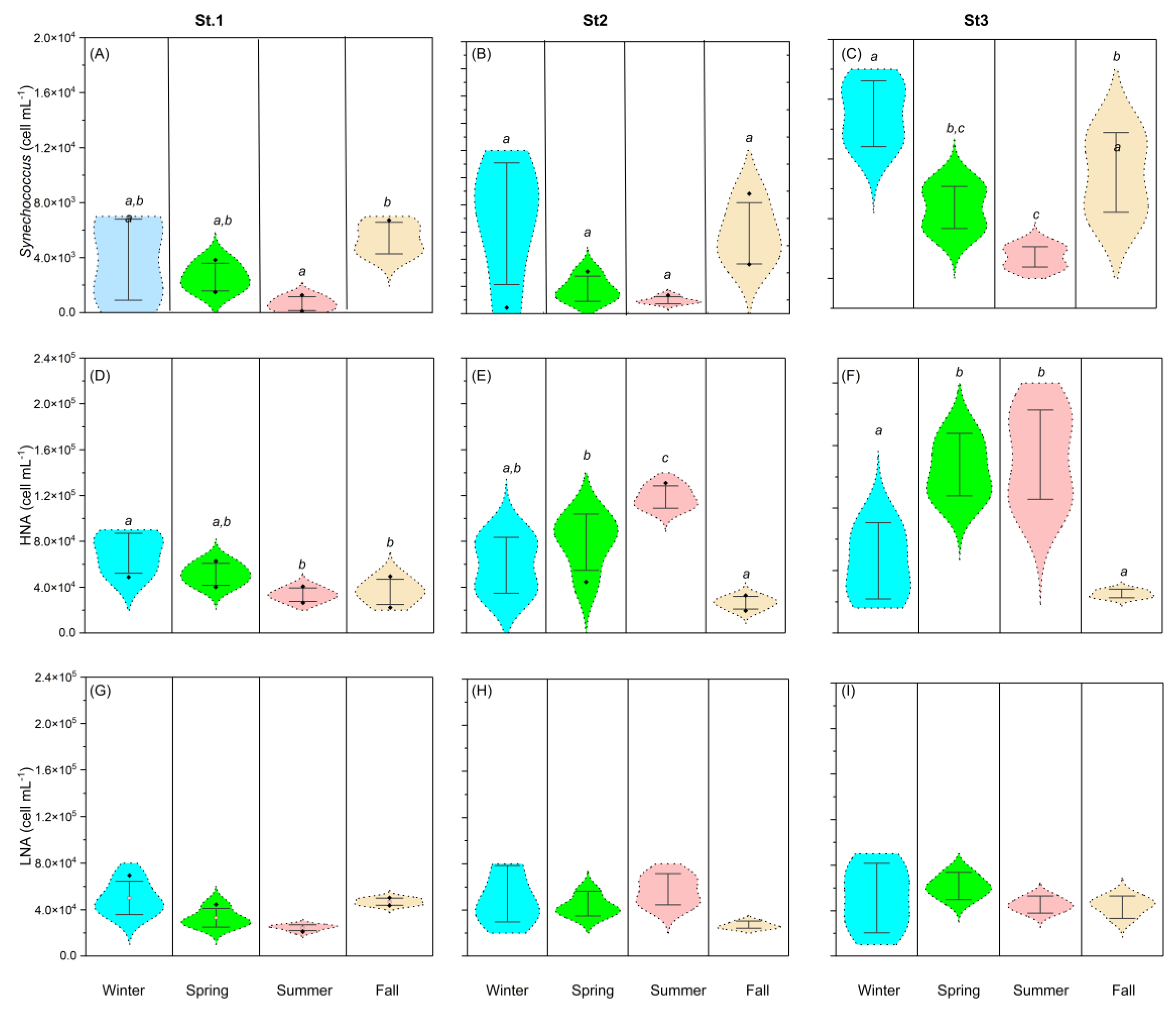
3.3. Seasonal and Spatial Variability Picoplankton Abundances
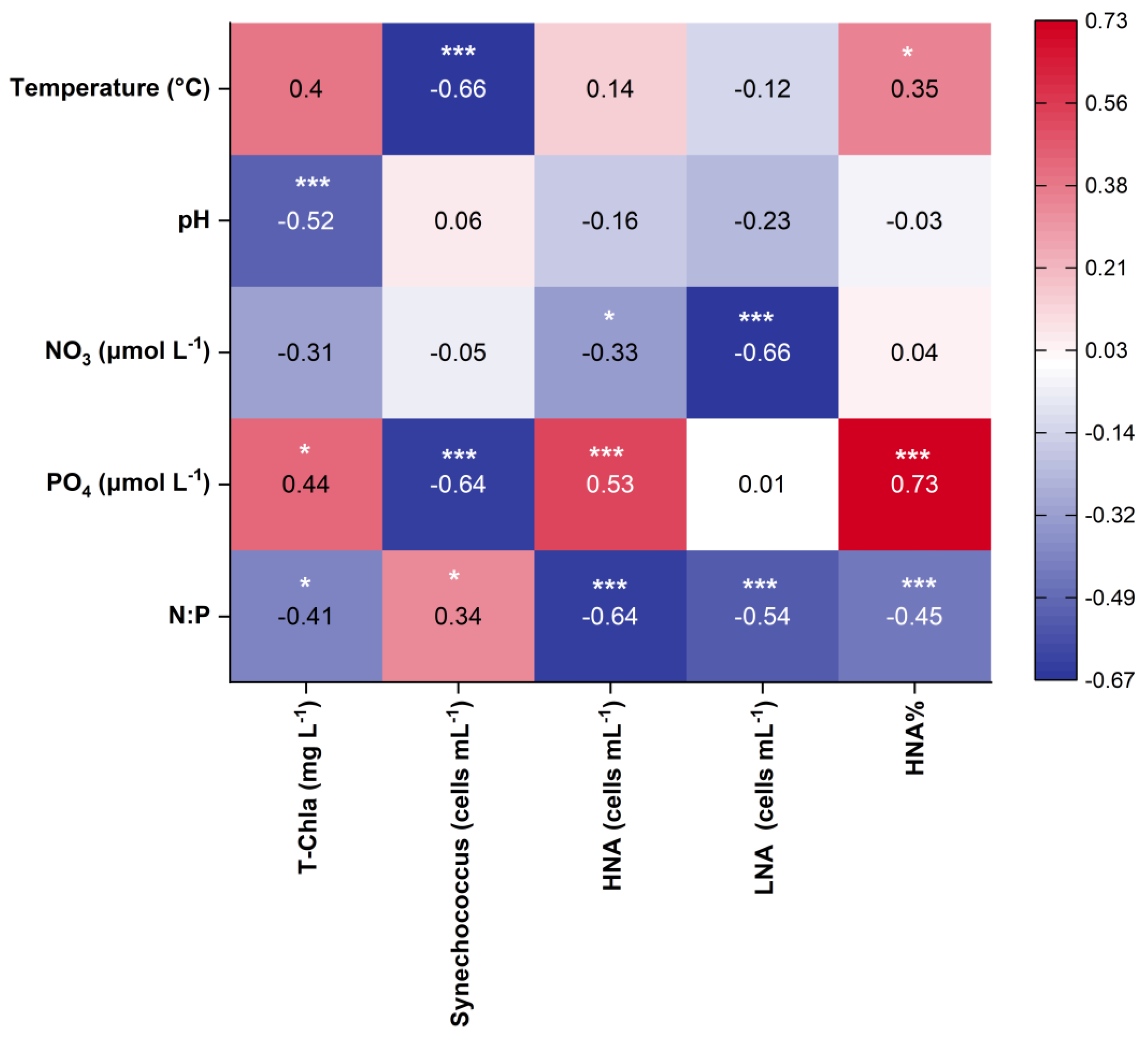
3.4. Relationships Between Environmental Variables and Picoplankton Abundances
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Planktonic Community Structure at Wadi Saiysad
4.2. Ecological and Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| St. 1 | Station 1 |
| St. 2 | Station 2 |
| St. 3 | Station 3 |
| NO3 | Nitrate |
| PO4 | Phosphate |
| N:P | Nitrate–phosphate ratio |
| Chl a | Chlorophyll a |
| TChl a | Total chlorophyll a |
| pChla | Picoplankton |
| nChla | Nanoplankton |
| mChla | Microplankton |
| HNA | High nucleic acid |
| LNA | Low nucleic acid |
| PE | Phycoerythrin |
| PerCP-Cy5-5 | Peridinin chlorophyll protein-Cyanine 5.5 |
| SSC | Side scatter signals |
References
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Solomun, M.K.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Zhao, W.; Kalantari, Z. Wetlands as nature-based solutions for water management in different environments. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambäck, P.A.; Dawson, L.; Geranmayeh, P.; Jarsjö, J.; Kačergytė, I.; Peacock, M.; Collentine, D.; Destouni, G.; Futter, M.; Hugelius, G.; et al. Tradeoffs and synergies in wetland multifunctionality: A scaling issue. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, C.; Boulton, A.J.; Courtwright, J.L.; Fritz, K.; May, C.L.; Walker, R.H.; Datry, T. Ecological research and management of intermittent rivers: An historical review and future directions. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1181–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, V.; Datry, T.; Marshall, J.; Barceló, D.; Dahm, C.N.; Ginebreda, A.; McGregor, G.; Sabater, S.; Tockner, K.; Palmer, M.A. Why Should We Care About Temporary Waterways? Science 2014, 343, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T.; Larned, S.T.; Tockner, K. Intermittent Rivers: A Challenge for Freshwater Ecology. BioScience 2014, 64, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larned, S.T.; Datry, T.; Arscott, D.B.; Tockner, K. Emerging concepts in temporary-river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaid, S.; Samraoui, B.; Thomas, J.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Schneider, W.; O’Connell, M. An overview of wetlands of Saudi Arabia: Values, threats, and perspectives. Ambio 2017, 46, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, S.; Grose, M.J.; Lake, P.S. Wadis as dryland river parks: Challenges and opportunities in designing with hydro-ecological dynamics. Landsc. Res. 2020, 45, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hammad, B.A.; Abd El-Salam, M.M. Monitoring Water Pollution Levels in Wadi Hanifa, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia and its Public Health Implications. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsabhan, A.H.; Perveen, K.; Alwadi, A.S. Heavy metal content and microbial population in the soil of Riyadh Region, Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Abubakar, I.R. Developing a sustainable water conservation strategy for Saudi Arabian cities. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Ashraf, M.W. The challenges and potential strategies of Saudi Arabia’s water Resources: A review in analytical way. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 20, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayboub, M. Water–Demand Management in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for Enhancement Environment. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2013, 14, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.O.; Mohammed, A.E.; Eltom, K.H. Metagenomic analysis of bacterial communities of Wadi Namar Lake, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3749–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, B.A.; Baig, M.B.; Najim, M.M.M.; Shah, A.A.; Alamri, Y.A. Water Scarcity Management to Ensure Food Scarcity through Sustainable Water Resources Management in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hetari, M.; Haider, H.; Ghumman, A.R.; Al-Salamah, I.S.; Thabit, H.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Development of a Water Quality Management Model for Dry Rivers in Arid Regions: Application on Wadi Rumah, Saudi Arabia. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Quality and groundwater contamination of Wadi Hanifa, central Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqel, H.; Sannan, N.; Al-Hunaiti, A.; Fodah, R. Integrated water quality dynamics in Wadi Hanifah: Physical, chemical, and biological perspectives. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaibani, A.M. Hydrogeology and hydrochemistry of a shallow alluvial aquifer, western Saudi Arabia. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Issa, A.; Ebied, A. Interaction between Phytoplankton and Zooplankton in Some Freshwater Bodies in Relation to Some Ecological Factors in Taif, KSA. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2017, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Mahmoud, H.; Habashy, M.; El-Wakeil, K.A. Effect of sewage disposal in some torrents streams on zooplankton community structure. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Mahmoud, H.M.; Abd El-Wakeil, K.F. Community Structure of Zoobenthos in Some Freshwater Bodies in Taif, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2014, 2, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Stern, R.F.; Atkinson, A.; Best, M.; Bresnan, E.; Creach, V.; Devlin, M.; Holland, M.; Ostle, C.; Schmidt, K.; et al. The silent majority: Pico- and nanoplankton as ecosystem health indicators for marine policy. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, X.; Dang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Sui, X. Picoplankton Groups and Their Responses to Environmental Factors in Small Cascade Hydropower Stations. Water 2025, 17, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, M.; Gasol, J.; Izaguirre, I.; Unrein, F. Picoplankton abundance and cytometric group diversity along a trophic and latitudinal lake gradient. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 68, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callieri, C. Picophytoplankton in Freshwater Ecosystems: The Importance of Small-Sized Phototrophs. Freshw. Rev. 2008, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, N.; Huete-Stauffer, T.M.; Calleja, M.L.; Irigoien, X.; Morán, X.A.G. Seasonal variability and vertical distribution of autotrophic and heterotrophic picoplankton in the Central Red Sea. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, S. Viability and niche segregation of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus cells across the Central Atlantic Ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biller, S.J.; Berube, P.M.; Lindell, D.; Chisholm, S.W. Prochlorococcus: The structure and function of collective diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasol, J.M.; Zweifel, U.L.; Peters, F.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Hagström, Å. Significance of Size and Nucleic Acid Content Heterogeneity as Measured by Flow Cytometry in Natural Planktonic Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4475–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, R.R.; Coe, A.; Kettler, G.C.; Martiny, A.C.; Frias-Lopez, J.; Zinser, E.R.; Chisholm, S.W. Temporal dynamics of Prochlorococcus ecotypes in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, K.R.; Seuthe, L. Seasonal microbial processes in a high-latitude fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard): I. Heterotrophic bacteria, picoplankton and nanoflagellates. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Díaz, A.; Morán, X. Seasonal dynamics of picoplankton in shelf waters of the southern Bay of Biscay. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 42, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.; Kalff, J. The contribution of picophytoplankton in marine and freshwater systems of different trophic status and depth. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminot, A.; Rey, F. Standard procedure for the determination of chlorophyll a by spectroscopic methods. ICES Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2002, 112, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kamphake, L.J.; Hannah, S.A.; Cohen, J.M. Automated analysis for nitrate by hydrazine reduction. Water Res. 1967, 1, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasol, J.M.; Morán, X.A.G. Flow Cytometric Determination of Microbial Abundances and Its Use to Obtain Indices of Community Structure and Relative Activity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 159–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolás Ruiz, N.; Suárez Alonso, M.L.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R. Contributions of dry rivers to human well-being: A global review for future research. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadou, W.S.; Sulieman, A.M.E.-H.; Alshammari, N.; Snoussi, M.; Alanazi, N.A.; Alshammary, A.; Al-Azmi, M. Water quality assessment of the surface and groundwater from Wadi Al-Adairey, Hail, Saudi Arabia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebied, A.-B.; Issa, A.; Awad, M. Micro Flora Associated with Freshwater Medicinal Leeches in Taif City, Saudi Arabia. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2018, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borics, G.; Abonyi, A.; Salmaso, N.; Ptacnik, R. Freshwater phytoplankton diversity: Models, drivers and implications for ecosystem properties. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updhyay, D.; Shukla, K.; Mishra, A.; Shukla, S. Freshwater Phytoplankton: The Significant Ecosystems Services Provider in Aquatic Environment; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, P.; Mahajan, D.; Thakur, K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Brar, B.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, A.K. A review on plankton as a bioindicator: A promising tool for monitoring water quality. World Water Policy 2024, 10, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuRand, M.D.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W. Phytoplankton population dynamics at the Bermuda Atlantic Time-series station in the Sargasso Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 1983–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partensky, F.; Blanchot, J.; Lantoine, F.; Neveux, J.; Marie, D. Vertical structure of picophytoplankton at different trophic sites of the tropical northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1996, 43, 1191–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.W.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwirglmaier, K.; Jardillier, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Mazard, S.; Garczarek, L.; Vaulot, D.; Not, F.; Massana, R.; Ulloa, O.; Scanlan, D.J. Global phylogeography of marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus reveals a distinct partitioning of lineages among oceanic biomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkov, M.V.; Allen, J.I.; Fuchs, B.M. Coexistence of dominant groups in marine bacterioplankton community—A combination of experimental and modelling approaches. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2004, 84, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, X.; Bode, A.; Suárez, L.; Nogueira, E. Assessing the relevance of nucleic acid content as an indicator of marine bacterial activity. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 46, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, P.; Casamayor, E.; Courties, C.; Catala, P.; Parthuisot, N.; Lebaron, P. Activity and diversity of bacterial cells with high and low nucleic acid content. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 33, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaron, P.; Servais, P.; Agogué, H.; Courties, C.; Joux, F. Does the High Nucleic Acid Content of Individual Bacterial Cells Allow Us To Discriminate between Active Cells and Inactive Cells in Aquatic Systems? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.; Calleja, M.L.; Huete-Stauffer, T.M.; Ivetic, S.; Ansari, M.I.; Viegas, M.; Morán, X.A.G. Low Abundances but High Growth Rates of Coastal Heterotrophic Bacteria in the Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Kim, C.; Nagata, T. Vertical and Seasonal Variations of Bacterioplankton Subgroups with Different Nucleic Acid Contents: Possible Regulation by Phosphorus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5828–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, M.B.; Alotibi, Y.; Straquadine, G.S.; Alataway, A. Water Resources in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Challenges and Strategies for Improvement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Otaibi, N. Occurrence and Seasonal Variation of Picoplankton at Saiysad Freshwater in Taif City, Saudi Arabia. Water 2025, 17, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182788
Al-Otaibi N. Occurrence and Seasonal Variation of Picoplankton at Saiysad Freshwater in Taif City, Saudi Arabia. Water. 2025; 17(18):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182788
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Otaibi, Najwa. 2025. "Occurrence and Seasonal Variation of Picoplankton at Saiysad Freshwater in Taif City, Saudi Arabia" Water 17, no. 18: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182788
APA StyleAl-Otaibi, N. (2025). Occurrence and Seasonal Variation of Picoplankton at Saiysad Freshwater in Taif City, Saudi Arabia. Water, 17(18), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182788








