Heavy Metal Removal from Produced Water Using Waste Materials: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Adsorbents
- (A)
- Gypsum
- (B)
- Neem leaves (Azadirachta indica), mandarin (Citrus reticulata) peels, and pistachio (Pistacia vera) shells
- (C)
- Dates pits (Phoenix dactylifera)
2.3. Synthetic Produced Water
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Characterization of the Adsorbents
2.6. Batch Sorption Tests
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Removal Efficiency of Different Adsorbents
3.2. Characterization of the Adsorbents
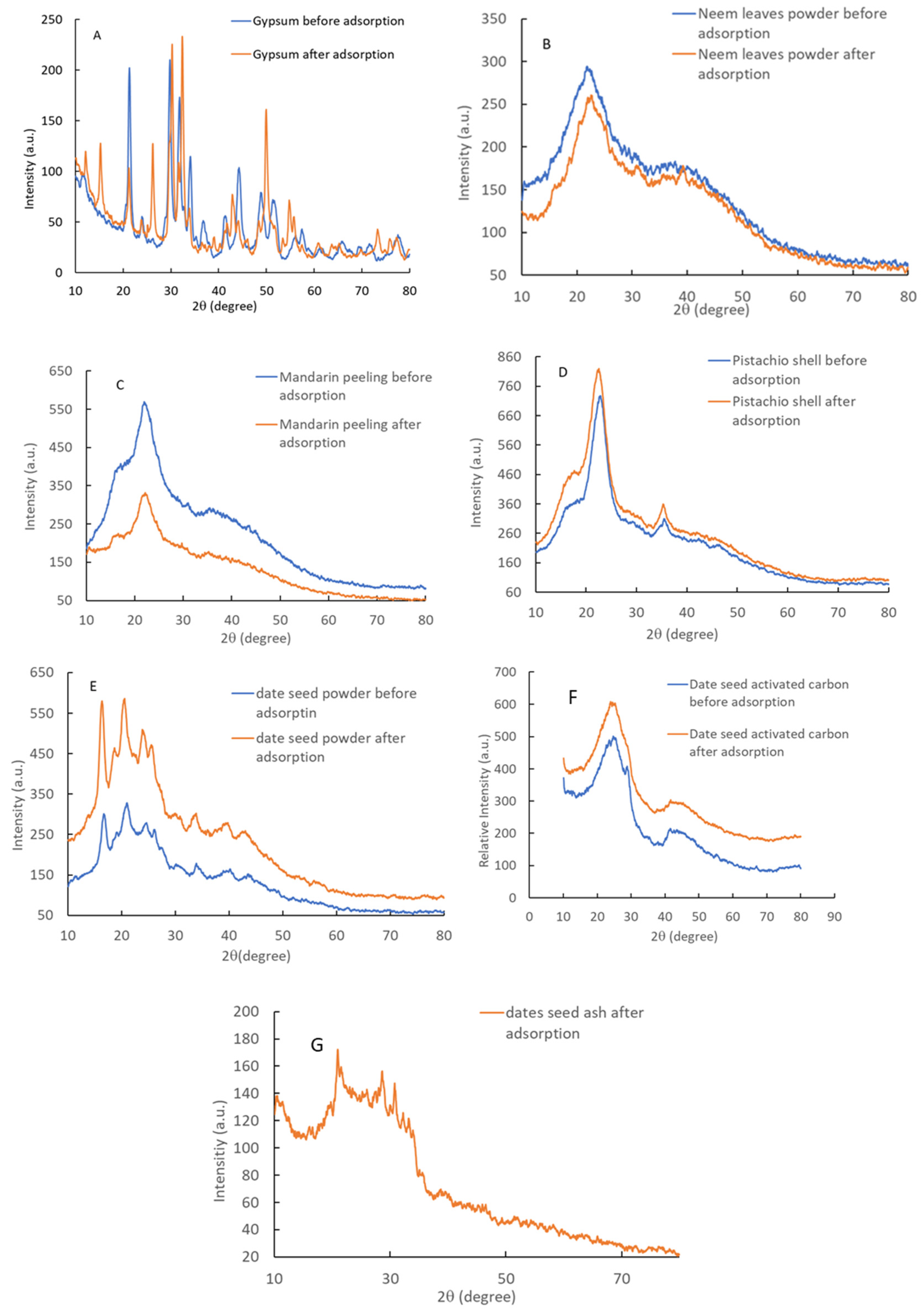
3.2.1. X-Ray Diffraction Patterns
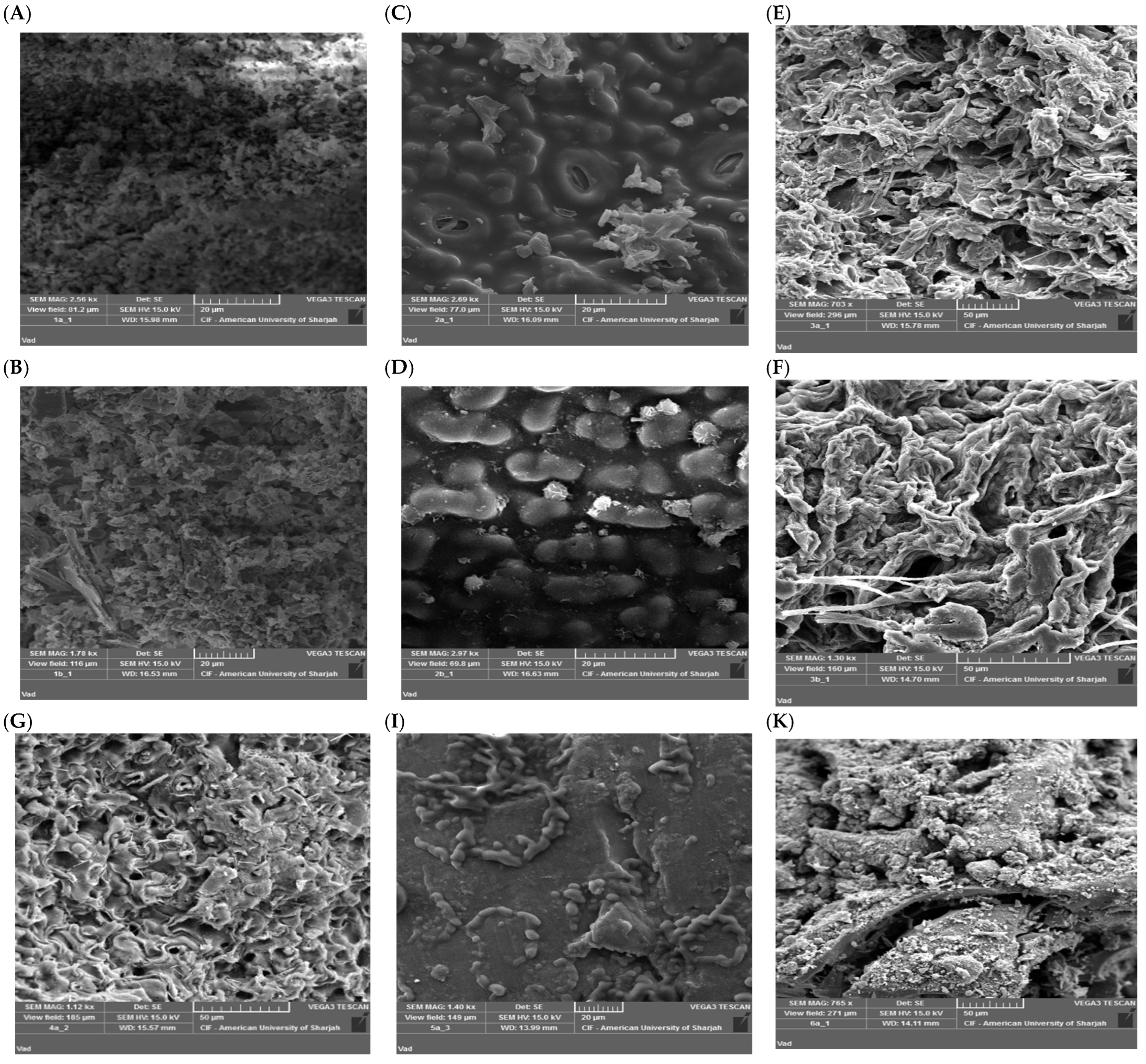
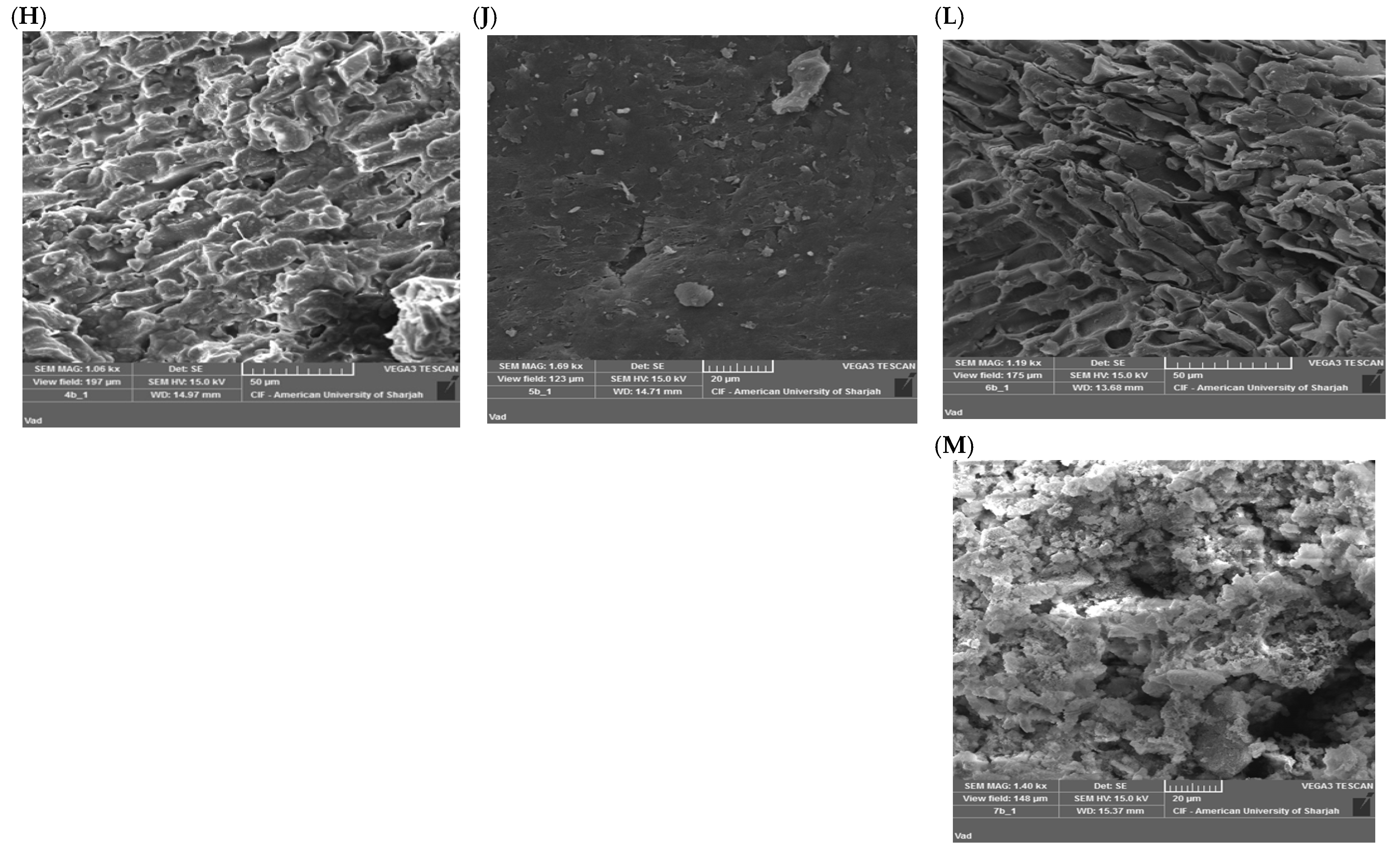
3.2.2. SEM Studies
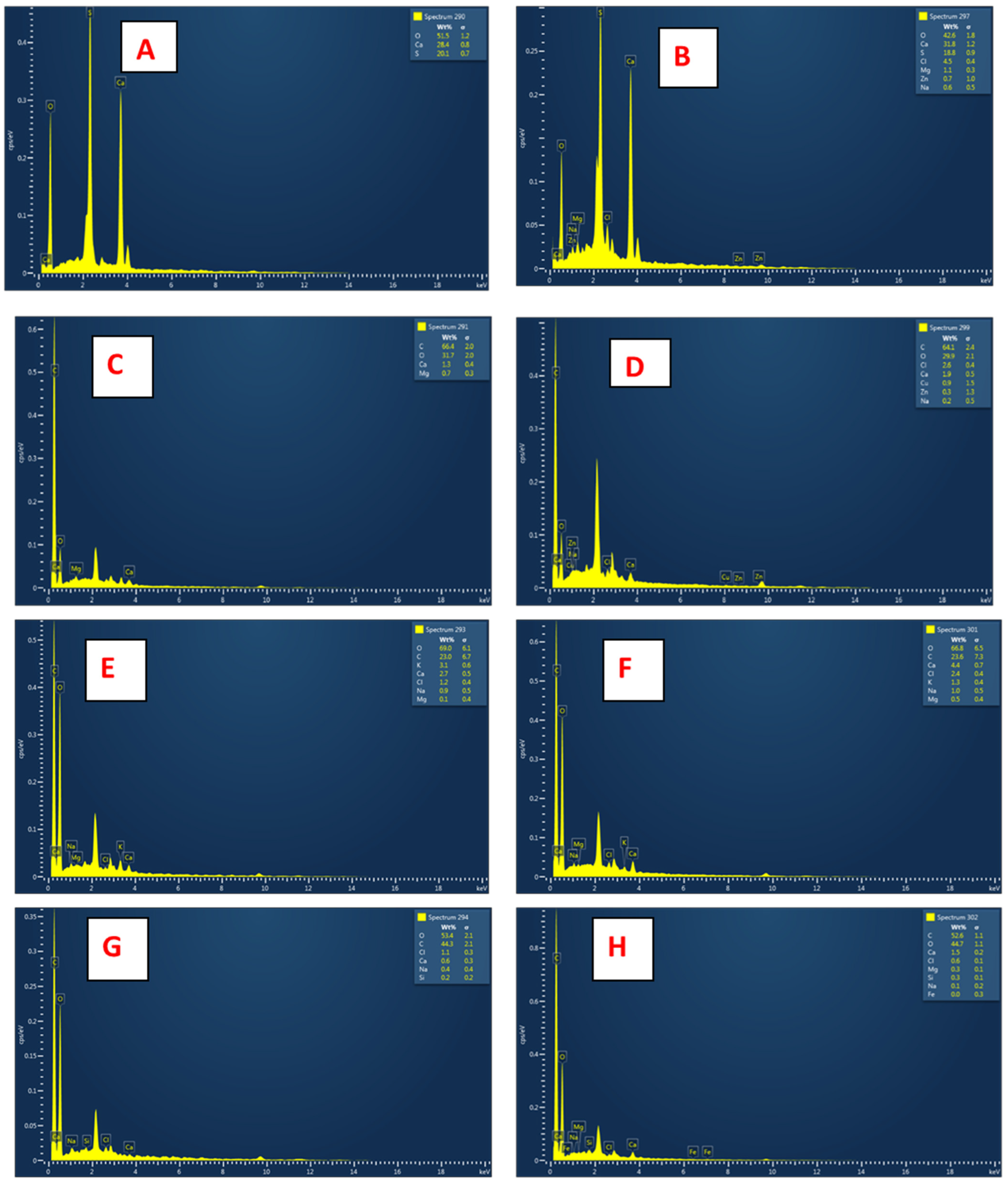
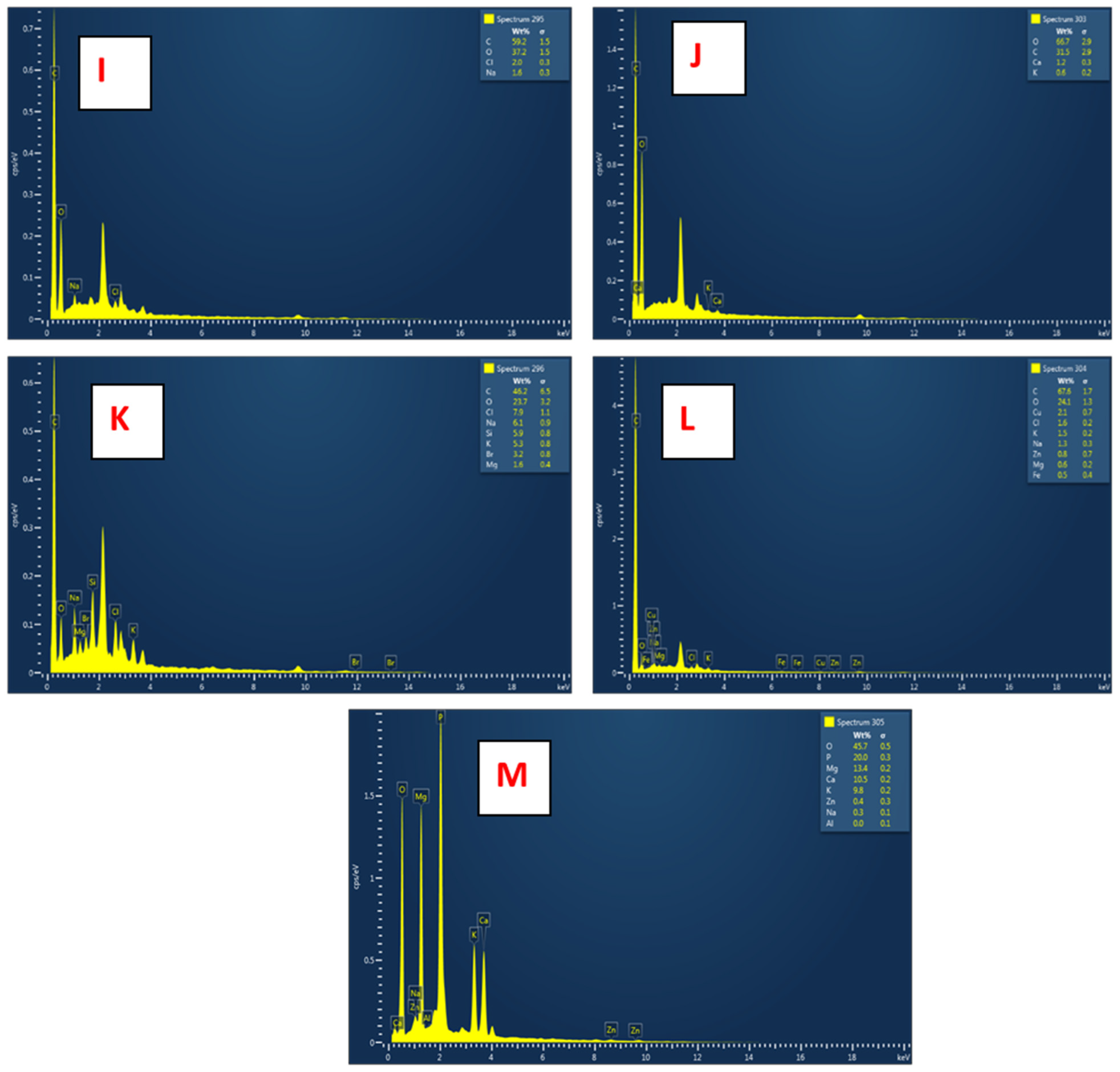
3.2.3. EDX Analyses
3.2.4. Characterization of Adsorbents and Link to Removal Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouafia, A.; Meneceur, S.; Chami, S.; Laouini, S.E.; Daoudi, H.; Legmairi, S.; Mohammed, H.A.M.; Aoun, N.; Menaa, F. Removal of hydrocarbons and heavy metals from petroleum water by modern green nanotechnology methods. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawoud, H.D.; Saleem, H.; Alnuaimi, N.A.; Zaidi, S.J. Characterization and treatment technologies applied for produced water in Qatar. Water 2021, 13, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, T.S.; Rialto, T.C.R.; Brito, J.F.D.; Micas, A.F.D.; Abe, F.R.; Savazzi, E.A.; Zanoni, M.B.; de Oliveira, D.P. Effects of water produced by oil segment on aquatic organisms after treatment using advanced oxidative processes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2021, 84, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Prigent, S.; Breuer, R. Integrated produced water management in a desert oilfield using wetland technology and innovative reuse practices. In Constructed Wetlands for Industrial Wastewater Treatment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Lin, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, P. Analysis of Regulatory Framework for Produced Water Management and Reuse in Major Oil- and Gas-Producing Regions in the United States. Water 2022, 14, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.; Vilcáez, J. Removal of toxic metals from petroleum produced water by dolomite filtration. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Aryanti, N.; Qudratun; Utomo, D.P. Oilfield produced water treatment to clean water using integrated activated carbon-bentonite adsorbent and double stages membrane process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patni, H.; Ragunathan, B. Recycling and re-usage of oilfield produced water—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Vaughan, J.; Boullemant, A.; Leong, T. The determination of trace mercury in environmental samples: A review. In Proceedings of the Chemeca 2013: Challenging Tomorrow, Brisbane, Australia, 29 September–2 October 2013; Engineers: Barton, ACT, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, M.S.M.; Abdel-shafy, H.I.; Ibrahim, A.M. Petroleum wastewater: Environmental protection, treatment, and safe reuse: An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119827. [Google Scholar]
- Hammod, N.; Al-Janabi, K.W.S.; Hasan, S.A.; Al-Garawi, Z.S. High pollutant levels of produced water around Al-Ahdab oil field in Wasit governorate (Iraq). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1853, 012004. [Google Scholar]
- Renu, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Myakala, H.; Koti, R.; Famurewa, A.C.; Madhyastha, H.; Vellingiri, B.; George, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (Lead, Chromium, Arsenic, Mercury, Nickel and Cadmium)—Induced hepatotoxicity—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothapalli, C.R. Differential impact of heavy metals on neurotoxicity during development and in aging central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 26, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, G.A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Jones, M.R.; Mann, K.K.; Nasir, K.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Ujueta, F.; Navas-Acien, A.; the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing. Contaminant metals as cardiovascular risk factors: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Oh, H.; Hoang, N.H.M.; Kim, M.-S. Association between heavy metals, high-sensitivity C-reaction protein and 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases among adult Korean population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-Y.; Lee, S.; Surenbaatar, U.; Lim, H.-J.; Kim, B.-G.; Eom, S.-Y.; Cho, Y.M.; Kim, W.J.; Yu, B.-C.; Lee, K.; et al. Association between levels of exposure to heavy metals and renal function indicators of residents in environmentally vulnerable areas. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, A.Y.; Leem, A.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Chang, J.; Kang, Y.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Chung, K.S. Relationship between blood levels of heavy metals and lung function based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV-V. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, L.; Patel, T.N. Systemic impact of heavy metals and their role in cancer development: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynab, M.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Ameen, A.; Sharif, Y.; Ali, L.; Fatima, M.; Khan, K.A.; Li, S. Health and environmental effects of heavy metals. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.J.; Bansal, N.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Chromium in Environment, Its Toxic Effect from Chromite-Mining and Ferrochrome Industries, and Its Possible Bioremediation. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Coetzee, J.J.; Chirwa, E.M.N. In situ bioremediation of hexavalent chromium in presence of iron by dried sludge bacteria exposed to high chromium concentration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhokpande, S.R.; Deshmukh, S.M.; Khandekar, A.; Sankhe, A. A review outlook on methods for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 350, 127868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.A.K.; Kashifuddin, M. Adsorption Properties of Coriander Seed Powder (Coriandrum sativum): Extraction and Pre-concentration of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan Rao, R.; Rehman, F.; Kashifuddin, M. Removal of Cr(VI) from electroplating wastewater using fruit peel of Leechi (Litchi chinensis). Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 49, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of adsorption process for effective removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Ahmadi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Othmani, A.; Osagie, C.; Meskini, M.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Malloum, A.; Khanday, W.A.; Jacob, A.O.; et al. Recent advances on sustainable adsorbents for the remediation of noxious pollutants from water and wastewater: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hoang, T.K.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A critical and recent developments on adsorption technique for removal of heavy metals from wastewater-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saad, K.; El-Azazy, M.; Issa, A.A.; Al-Yafie, A.; El-Shafie, A.S.; Al-Sulaiti, M.; Shomar, B. Recycling of Date Pits Into a Green Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metals: A Fractional Factorial Design-Based Approach. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Joshi, P.; Gusain, R.; Khatri, O.P. Recent advances in adsorptive removal of heavy metal and metalloid ions by metal oxide-based nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214100. [Google Scholar]
- Haroon, H.; Butt, T.A.; Shah, J.A.; Ciobica, A.; Romila, L.E.; Burlui, V.; Bibi, H.; Bilal, M. Valorization of natural adsorbents for removing chromium (VI) from industrial wastewater: A review. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1608863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatiya, N.; Reshad, A.; Worku Negie, Z. Chemical Modification of Neem (Azadirachta indica) Biomass as Bioadsorbent for Removal of Pb2+ Ion from Aqueous Waste Water. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Chen, J. “Treating Waste with Waste”: Utilizing Phosphogypsum to Synthesize Porous Calcium Silicate Hydrate for Recovering of Fe2+ from Pickling Wastewater. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, L.; Durosinmi, S.O.; Jacob-Oricha, S.O.; Lau, S.Y.; Obayomi, K.S. Rapid and effective adsorption of selected heavy metals from battery wastewater using silicon-oxide nanoparticles derived rice husk. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; Davies, S.R. Review of potential technologies for the removal of dissolved components from produced water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1994, 72, 176–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dardor, D.; Al-Maas, M.; Minier-Matar, J.; Janson, A.; Sharma, R.; Hassan, M.K.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.A.; Adham, S. Protocol for Preparing Synthetic Solutions Mimicking Produced Water from Oil and Gas Operations. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 6881–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewa, A.M.; Amer, A.A.; Attallah, M.F.; Gad, H.A.; Al-Ahmed, Z.A.M.; Ahmed, I.A. Chemically Activated Carbon Based on Biomass for Adsorption of Fe(III) and Mn(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2023, 16, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, H.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Z. Study on the adsorption of Zn(II) and Cu(II) in acid mine drainage by fly ash loaded nano-FeS. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.A.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Kulkarni, R.; Karri, R.R.; Koduru, J.R.; Chang, Y.-Y. Plasma-assisted MnO surface engineered activated carbon felt for enhanced heavy metal adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by Rice-husk-based activated carbon prepared by Dual-mode heating method. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2023, 6, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yao, R.; Yu, M.; Ye, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Tang, J.; Sun, J. Converting Waste into Treasure: Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using Iron-Modified Rice Straw Biochar. Toxics 2025, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.T.; Moneim, M.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; El-Ayaat, A.M.; Dardir, F.M. Effective removal of heavy metal ions (Pb, Cu, and Cd) from contaminated water by limestone mine wastes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Amin, M.T. Preparation of ZnMgAl-Layered Double Hydroxide and Rice Husk Biochar Composites for Cu(II) and Pb(II) Ions Removal from Synthetic Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Azanfire, B.-E.; Bulgariu, D.; Cimpoeşu, N.; Bulgariu, L. Efficient Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals on Kaolinite-Based Clay: Adsorption Characteristics, Mechanism and Applicability Perspectives. Water 2025, 17, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. Promising and Environmentally Friendly Removal of Copper, Zinc, Cadmium, and Lead from Wastewater Using Modified Shrimp-Based Chitosan. Water 2024, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skic, K.; Adamczuk, A.; Gryta, A.; Boguta, P.; Tóth, T.; Jozefaciuk, G. Surface areas and adsorption energies of biochars estimated from nitrogen and water vapour adsorption isotherms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Safitri, H.; Aini, W.D.; Farantino, R.; Ginting, S.B.; Rinovian, A.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Khairurrijal, K.; Taher, T.; Kusumaningrum, W.B.; et al. Biochar MMT ZnAl LDH composite materials derived from solid waste for heavy metal removal in artificial acid mine drainage. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya-Escobar, N.; Ospina-Acero, D.; Velásquez-Cock, J.A.; Gómez-Hoyos, C.; Guerra, A.S.; Rojo, P.F.G.; Acosta, L.M.V.; Escobar, J.P.; Correa-Hincapié, N.; Triana-Chávez, O.; et al. Use of Fourier Series in X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) for Estimation of Crystallinity in Cellulose from Different Sources. Polymers 2022, 14, 5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terinte, N.; Ibbett, R.; Schuster, K. Overview on native cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose I structure studied by X-ray diffraction (WAXD): Comparison between measurement techniques. Lenzing. Berichte 2011, 89, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Namasivayam, C.; Kavitha, D. IR, XRD and SEM studies on the mechanism of adsorption of dyes and phenols by coir pith carbon from aqueous phase. Microchem. J. 2006, 82, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluyamo Sunday, S.; Adekoya Mathew, A. Influence of Size Classifications on the Structural and Solid-State Characterization of Cellulose Materials. In Cellulose; Alejandro, R., María, E.E.M., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Kroatien, 2019; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, N.; Fathi, M. Entrapment of peppermint oil using cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 2018, 25, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, S.; Skillen, N.C.; Irvine, J.T.; Lawton, L.A.; Robertson, P.K. Cellulose II as bioethanol feedstock and its advantages over native cellulose. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Abu Judeh, A.; Hakeem, A.S.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Umar, Y.; Ahmad, A. Isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from date seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabili, A.; Fattoum, A.; Passas, R.; Elaloui, E. Extraction and characterization of cellulose from date palm seeds (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2016, 50, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, A.; Bharath, G.; Babu, K.R.; Taher, H.; Naushad, M.; Banat, F. Date seeds biomass-derived activated carbon for efficient removal of NaCl from saline solution. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Said, B.; Bacha, O.; Rahmani, Y.; Harfouche, N.; Kheniche, H.; Zerrouki, D.; Belkhalfa, H.; Henni, A. Activated carbon prepared by hydrothermal pretreatment-assisted chemical activation of date seeds for supercapacitor application. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 111012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ahmadi, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Kukkar, D.; Szulejko, J.E. The relative dominance of surface oxygen content over pore properties in controlling adsorption and retrograde behavior of gaseous toluene over microporous carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, C.; Tang, C.; Wei, J.; Liu, K.; Ma, J.; Yu, F.; Li, Y. Insights into the heavy metal adsorption and immobilization mechanisms of CaFe-layered double hydroxide corn straw biochar: Synthesis and application in a combined heavy metal-contaminated environment. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Singh, R.; Bhattacharya, G. Exploring the role of Azadirachta indica (neem) and its active compounds in the regulation of biological pathways: An update on molecular approach. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buasri, A.; Rochanakit, K.; Wongvitvichot, W.; Masa-Ard, U.; Loryuenyong, V. The Application of Calcium Oxide and Magnesium Oxide from Natural Dolomitic Rock for Biodiesel Synthesis. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, Z.; Di, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhu, X. Study on the effectiveness of sulfate-reducing bacteria to remove Pb(II) and Zn(II) in tailings and acid mine drainage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1352430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J.; Ding, N. Insight into different removal behaviors and mechanism of heavy metals via sulfate-loaded layered double oxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, B.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Song, S. Selective recovery of heavy metals from wastewater by mechanically activated calcium carbonate: Inspiration from nature. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Ji, H.-Y.; Ho, W.-F. Comparative Study of Cu Ion Adsorption by Nano-Hydroxyapatite Powder Synthesized from Chemical Reagents and Clam Shell-Derived Calcium Sources. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Bannon, D.I.; Wartelle, L.H. Retention of Heavy Metals by Carboxyl Functional Groups of Biochars in Small Arms Range Soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Adsorbent Type | Target Metals | Removal Efficiency (%) | Setup | Adsorbent Conc. | Adsorbate Conc. | Contact Time | Solution Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange peel (lignocellulosic) | Pb2+, Cu2+ | 70–95 | Batch | 1–10 g/L | 10–100 mg/L | 60–180 min | Synthetic | [29] |
| Neem sawdust (biomass) | Cr(VI) | ~80 | Batch | ~3 g/L | ~10 mg/L | 60 min | Synthetic (pH ~2) | [31] |
| Modified neem biomass (CMNB) | Pb2+ | ~85–90 | Batch | 0.9 g/L | 100 mg/L | 110 min | Synthetic | [32] |
| Date pits activated carbon | Pb2+, Cu2+, Fe2+ | >90 | Batch | 2–12 g/L | 1–10 mg/L | 1–120 min | Synthetic | [29] |
| Gypsum (phosphogypsum-derived) | Fe2+ | 99 | Batch | 0.8 g/L | 250 mg/L | 240 min | Real wastewater (pickling) | [33] |
| Rice husk silica nanoparticles | Pb2+, Fe3+ | 85 (Pb), 75 (Fe) | Batch | 60 mg/L | 100 mg/L | 45 min | Real wastewater (battery effluent) | [34] |
| Tea waste biomass | Cr3+, Cu2+ | 65–85 | Batch | 2–10 g/L | 10–100 mg/L | 60–150 min | Synthetic | [29] |
| Adsorbent | Removal Efficiency (%) ± SD; n = 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Fe | Pb | Zn | |||||
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | |
| Date ashes | 41 ± 2 | 98 ± 3 | 95 ± 4 | 91 ± 3 | 87 ± 3 | 85 ± 2 | 98 ± 3 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
| Date activated carbons | 88 ± 3 | 54 ± 2 | 82 ± 3 | 88 ± 2 | 78 ± 3 | 98 ± 3 | 96 ± 4 | 25 ± 1 | 34 ± 2 |
| Dried neem leaves | 62 ± 3 | 52 ± 3 | 49 ± 1 | 12 ± 1 | 31 ± 1 | 72 ± 2 | 90 ± 2 | 47 ± 2 | 30 ± 1 |
| Mandarin peels | 70 ± 1 | 61 ± 1 | 71 ± 3 | 15 ± 1 | 6 ± 0.5 | 78 ± 1 | 97 ± 2 | 62 ± 2 | 65 ± 2 |
| Dried date pits | 69 ± 2 | 30 ± 3 | 41 ± 1 | 5 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 1 | 77 ± 1 | 88 ± 3 | 37 ± 2 | 69 ± 2 |
| Gypsum | 15 ± 1 | 9 ± 2 | 18 ± 1 | 69 ± 2 | 81 ± 2 | 6 ± 0.5 | 18 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | 0 ± 0 |
| Pistachio shells | 41 ± 3 | 17 ± 1 | 34 ± 2 | 38 ± 1 | 38 ± 1 | 40 ± 1 | 66 ± 2 | 16 ± 1 | 12 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bansal, N.; Mortula, M.M.; Al-Asheh, S. Heavy Metal Removal from Produced Water Using Waste Materials: A Comparative Study. Water 2025, 17, 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182789
Bansal N, Mortula MM, Al-Asheh S. Heavy Metal Removal from Produced Water Using Waste Materials: A Comparative Study. Water. 2025; 17(18):2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182789
Chicago/Turabian StyleBansal, Neetu, Md Maruf Mortula, and Sameer Al-Asheh. 2025. "Heavy Metal Removal from Produced Water Using Waste Materials: A Comparative Study" Water 17, no. 18: 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182789
APA StyleBansal, N., Mortula, M. M., & Al-Asheh, S. (2025). Heavy Metal Removal from Produced Water Using Waste Materials: A Comparative Study. Water, 17(18), 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182789









