Abstract
Lake Taihu, a large, shallow freshwater lake in China, has experienced severe eutrophication for decades under intense human activities occurring around cities. Through long-term water quality management since 1995, the eutrophication of Lake Taihu has been controlled. This review examines the eutrophication characteristics, source identification methods, and control measures in Lake Taihu. Phosphorus is a primary driver of eutrophication, correlating strongly with chlorophyll a. The lake exhibits significant temporal and spatial variability in nutrient dynamics, influenced by human activities and the climate. Historical data show fluctuating nutrient levels and persistent algal blooms despite government efforts. A critical assessment of various source apportionment methods, including statistical analysis, physical modeling, and empirical models, is presented to elucidate the relative contributions of different nutrient sources. These methods identify agricultural non-point and urban point sources as major external contributors, with sediment nutrient release as a significant internal source. Implemented controls, including wastewater treatment plants and non-point-source management, have had limited success. Increased sewage and sediment nutrients necessitate integrated watershed management. Future research should prioritize advanced source tracking, sediment dynamics, climate impacts, and integrated ecological models. Sustainable eutrophication management in Lake Taihu requires integrated science, policy, and public engagement to ensure ecosystem health.
1. Introduction
Nutrient enrichment in water bodies is a natural phenomenon that can occur in any aquatic system. However, this process is now being exacerbated on a global scale due to the escalating influx of human-derived nutrients in recent decades [1,2]. Lakes play an important role in maintaining a stable freshwater supply. The expansion of agriculture, industry, and urbanization has contributed to the significant discharge of nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, into water bodies, resulting in detrimental impacts on the ecological structures, functions, and esthetic value of lakes [3]. This alarming trend poses a serious threat to ecosystem health and the sustainability of human society [4,5], demanding immediate attention and intervention.
Under eutrophication, phytoplankton biomass exhibits pronounced growth, with cyanobacteria often dominating [6,7]. This leads to a significant increase in the concentration of chlorophyll a (Chl a) on the water surface, ultimately resulting in reduced light penetration [8]. Consequently, the growth and community structures of aquatic plants are adversely affected [9]. The excessive proliferation of cyanobacteria can deplete dissolved oxygen levels during the night, leading to a decline in fish populations [10]. Additionally, the reproduction of cyanobacteria is associated with the production of algae toxins that pose various risks to human health, ranging from mild skin irritation to gastrointestinal distress, liver ailments, neurological impairments, and even fatalities [11,12]. However, many lakes around the world exhibit significant eutrophication issues, such as Erie (America), Winnipeg (Canada), Peipsi (Estonia), Balaton (Hungary), Taihu (China), Kasumigaura (Japan), and Tana (Ethiopia) [1,13,14,15]. Globally, eutrophication has affected over 40% of lakes in recent years, posing a huge threat to aquatic systems [7]. In particular, the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms has garnered significant worldwide attention. In North America and Europe, the prevalence of cyanobacteria in nearly 60% of lakes has exhibited a substantial increase since the onset of the Industrial Revolution [16].
In China, there are 2693 natural lakes, with areas of over 1.0 km2 [17]. However, environmental challenges caused by eutrophication have become a substantial hindrance to China’s sustainable development [18]. Lake Taihu, as the third-largest freshwater lake in China, performs an array of pivotal functions, e.g., fishery support, transportation facilitation, tourism attraction, and flood control measures, while serving as a crucial drinking water source for the neighboring communities [19]. However, cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu have been observed with an increasing frequency since the late 1980s [20,21]. The deteriorating water quality, exacerbated by the surge in village enterprises within the Taihu Basin during the early 1990s, has elicited increased concern regarding eutrophication control. In 2007, a severe outbreak of cyanobacteria in Lake Taihu rendered approximately two million inhabitants incapable of accessing clean water. This spurred public awareness and scrutiny regarding the imperative for comprehensive eutrophication management strategies pertinent to Lake Taihu [22].
Since the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms in 1990, the Chinese government has prioritized the management of Lake Taihu, and stringent discharge limits for wastewater in the Taihu Basin have been in effect since 1999 [22]. After the outbreak of cyanobacterial blooms in 2007, the government launched a series of comprehensive water treatment plans, resulting in an unprecedented, intensive, and large-scale effort to control the eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu. The concentrations of nutrients in Lake Taihu exhibited a downward trajectory, although recent years have witnessed the resurgence of cyanobacterial blooms [23]. In 2017, the area affected by cyanobacterial blooms reached its maximum [24]. A number of strategies have been employed to mitigate the eutrophication issue in Lake Taihu, including wetland restoration [25], mechanical algae removal [26], and freshwater infusion from the Yangtze River [23]. However, the effectiveness of these strategies has been limited by a lack of understanding of the sources regarding lake eutrophication [5]. Ascertaining the sources of these nutrients should be regarded as the first step in mitigating eutrophication within the lake’s ecosystem [27]. The possibility of future large-scale blooming phenomena in Lake Taihu remains a concern [28].
As is the case for many large lakes [29], the issue of eutrophication in Lake Taihu has attracted the attention of researchers and become an interdisciplinary and comprehensive challenge [17]. This review summarizes the distinct characteristics and key issues associated with eutrophication in Lake Taihu, evaluates the methodology for the identification of nutrient pollution sources in the Taihu Basin, and assesses the efficacy of the source control and interception measures implemented over the years. Based on this, future research topics and remediation measures targeting eutrophication in Lake Taihu and other lakes around the world are discussed.
2. Characteristics of Eutrophication in Lake Taihu
Over the past few years, a multitude of studies have revealed that the occurrence, strength, and duration of cyanobacterial blooms in various aquatic environments worldwide are expected to rise due to increasing eutrophication and climate change [30]. Lake Taihu, as a typical large shallow lake, exhibits severe eutrophication. The dynamics of the nutrient concentrations and cyanobacterial blooms in the lake are regulated by complex interactions between several factors, including the economic development of the basin, pollution control measures, climate change, and hydrological conditions [3,31]. Hence, identifying the key pollutants that are related to cyanobacterial blooms, and analyzing the temporal and spatial characteristics of the eutrophication in Lake Taihu, are necessary to prevent the outbreak of cyanobacterial blooms and other potential hazards.
2.1. Characteristics of Nutrients
The underlying cause of eutrophication lies in the accumulation of nutrients. It is widely accepted among researchers that a nutrient concentration in water bodies that surpasses a specified threshold is necessary to trigger cyanobacterial blooms [15,32,33]. The “Guidelines for Lakes and Reservoirs Technical Guidelines—Nutrient Standards”, issued by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, stipulate that, when the concentrations of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) exceed 150 µg/L and 1 µg/L, respectively, the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms becomes likely [34]. It is now widely recognized that a TN level of >0.2 mg/L and a TP level of >0.02 mg/L indicate eutrophication in water bodies [35]. Compared to single pollution with nitrogen or phosphorus, the combined enrichment of nitrogen and phosphorus exhibits a more pronounced influence on the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms [36].
Although both nitrogen and phosphorus play crucial roles in the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms in lakes [37], it has been reported that the concentrations of TP in the water columns of eutrophic lakes often correspond to the levels of cyanobacterial blooms [38]. The significant correlation between the eutrophication status and TP concentration has been observed in many lakes worldwide [39,40,41,42,43,44]. A study showed that 90% of global lakes exhibit phosphorus retention [45]. In the case of Lake Taihu, TP has been identified as the primary factor influencing the spatial distribution of cyanobacterial blooms and thus requires prioritized attention in pollution control efforts [46]. As such, phosphorus has emerged as a paramount element in the preservation and ecological management of lakes [47].
Chl a serves as a key indicator in assessing water eutrophication and provides valuable insights for the identification of algal species and their abundance [48]. A strong positive correlation has been observed between the Chl a and TP concentrations in Lake Taihu, yielding a correlation coefficient (r) of 0.76 (p < 0.05). In contrast, some studies have found no evident relationship between TN and Chl a in many lakes, including Lake Taihu [3,15,49]. A possible explanation is that nitrogen is often not a primary limiting factor for cyanobacteria growth in some regions [46].
2.2. Temporal Heterogeneity
2.2.1. Historical Variation
Prior to the 1980s, the concentration of TN in Lake Taihu had reached approximately 60 μg/L [50]. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, the rapid development of township enterprises around Lake Taihu led to the production of a large amount of industrial wastewater. Because of the lack of centralized management in this sector, the generated wastewater was discharged into the water body without proper treatment. By 1981, 16.9% of Lake Taihu’s area was classified as eutrophic [51], triggering the occurrence of frequent cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay in the northern region of the lake and subsequently expanding northwestward [52]. The eutrophication of Lake Taihu progressed at an alarming rate after 1990 [50]. From 1991 to 1996, the annual average concentrations of TN, TP, and Chl a in Lake Taihu showed an initial upward trend. In 1995, the local government imposed mandatory control on wastewater discharge within the catchment area, and the eutrophication issue of Lake Taihu appeared to exhibit signs of recovery from 1996 onwards [53].
Unfortunately, the TN and TP concentrations in Lake Taihu have rebounded since 2001 [51]. In 2007, the annual average concentration of TN in the western waters reached its highest value, coinciding with the water supply crisis at Gong Bay [54]. Subsequently, the government intensified its pollution control efforts, leading to a decline in the TP concentrations in the rivers entering Lake Taihu [55]. From 2009 to 2017, the concentration of Chl a in Lake Taihu exhibited an upward trend. Assessment through satellite images indicated that there was no decreasing trend in the average level and maximum area of cyanobacterial blooms between 2007 and 2017. In fact, the largest area of bloom coverage was recorded in the lake in 2017, which was due to the synergistic effect of climate warming and nutrient enrichment [15]. Black patch events are unique ecological disasters caused by eutrophication in Lake Taihu. An analysis using field data from 2009 to 2017 revealed that, in 2017, the highest number of black patch events occurred (17), as well as the longest total occurrence time (47 d) and single duration (3.76 d). Correspondingly, the TP and TN loads in Lake Taihu reached their peaks during this year [56].
2.2.2. Seasonal Variation
The seasonal variations in the nutrient concentrations and cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu are strongly influenced by both the meteorological conditions and anthropogenic activities.
Drawing upon an analysis of monthly water quality data spanning 1985 to 2015, it was observed that the concentration of TN exhibited distinct seasonal patterns, with the highest levels occurring in March and April and the lowest in August and November [51]. The substantial reduction in nitrogen during the summer can be attributed to its absorption and utilization by cyanobacteria and a marked increase in denitrification capacity during the period of bloom [26,57]. In the northern region of Lake Taihu, serving as a primary inflow area, the nitrogen pollution pattern was found to be significantly influenced by the discharge of urban wastewater, spring fertilization practices, and land disturbance [58].
Researchers hold different opinions on the seasonal variations in the TP concentration. The study conducted by Dai et al. indicates that there was no significant seasonal variation in the TP concentration from 1985 to 2015 [51]. Zhang et al. analyzed the seasonal changes in phosphorus concentrations in the whole lake from 2005 to 2018 [59], and the result showed that TP reached its peak in summer, while the average values of TP in other seasons did not differ significantly. This does not mean that these research conclusions are contradictory, as the monitored TP includes phosphorus in organisms such as algae, and the algal reproduction status of water bodies in different years is greatly influenced by the water regime and meteorological conditions [60].
Regarding the nutrient composition in algae- and macrophyte-dominated regions of Lake Taihu, significant variations were observed among the different seasons. Lv et al. reported that nitrate nitrogen and organic phosphorus in algal-dominated regions were the predominant nutrients in winter, while, for the other seasons, particulate nitrogen and phosphorus dominated [32]. On the other hand, in macrophyte-dominated regions, particulate nitrogen and phosphorus prevailed during winter, whereas ammonia nitrogen and organic phosphorus were prominent during other seasons [32].
2.3. Spatial Heterogeneity
The pattern of Chl a distribution in Lake Taihu is intricately linked to the influx of river water and the presence of surrounding urban and industrial areas. The area division of Lake Taihu is shown in Figure 1. Most river inflows into Lake Taihu are from the western and northern sectors [49]. The water quality in these areas is largely impacted by industrial activities [61], resulting in a higher level of eutrophication compared to other regions [62]. The bay area, characterized by high nutrient loads and low water flow, becomes highly susceptible to cyanobacterial blooms. When examining different zones of Lake Taihu, it is evident that the highest frequency of cyanobacterial blooms occurs in the northwestern lake area and Meiliang Bay, followed by Zhushan Bay, Gong Bay, the central lake area, and the southwestern lake area, with the lowest frequency of cyanobacterial bloom occurrences in the eastern lake. Notably, from 2013 to 2017, there was a trend of an increase in the cyanobacterial bloom frequency spreading toward the central lake area [34].
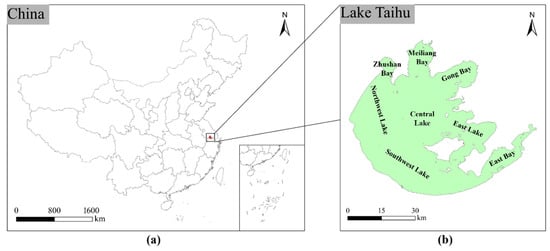
Figure 1.
Location of Lake Taihu (a) and dividing zones (b).
The spatial distribution of Chl a is also related to the lake flow dynamics caused by the wind. The prevailing southeasterly wind above Lake Taihu in summer and the resulting wind-driven current cause the surface layer of the lake to flow from southeast to northwest. Accordingly, Chl a and cyanobacteria accumulate in the northwest of Lake Taihu, and the spatial difference across the entire lake increase [63,64]. It has been observed that black patch events caused by cyanobacterial blooms mainly occur in the western coastal zone and northern part of Lake Taihu, such as Meiliang Bay and Gong Bay, rather than in the eastern lake [19,56].
3. Source Identification of Eutrophication in Lake Taihu
The sources and transport of nutrients in Lake Taihu can be summarized as in Figure 2. Non-point-source nutrients such as rural sewage, livestock manure, chemical fertilizers, etc., are transported to surface water via septic tanks and farmland. Other point-source nutrients (such as industrial wastewater and sanitary sewage) are partly transported to rivers after wastewater treatment. Then, the nutrients are introduced into Lake Taihu via inflowing rivers [65]. Moreover, the atmosphere and fisheries can also lead to nutrient input in Lake Taihu.
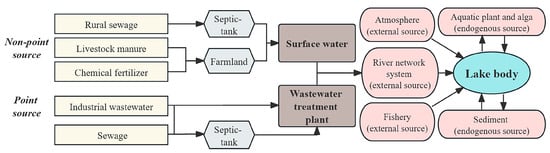
Figure 2.
Sources and transport of nutrients in Lake Taihu.
Due to the long-term eutrophication of Lake Taihu, the sediments within the lake mainly act as recipients of nutrients derived from external sources (e.g., sewage, livestock manure, fertilizers, and the atmosphere), as well as local sources (e.g., plankton and benthic plants). Over time, these sediments undergo a transition from nutrient “sinks” to significant nutrient “sources”, releasing substantial amounts of N and P under both undisturbed and disturbed conditions, and these releases bring new pollution challenges. As illustrated in Figure 2, the sources are categorized into two groups: external sources and endogenous sources.
The proliferation of cyanobacteria in Lake Taihu is influenced by a multitude of factors, with the excessive input of nutrients being a root cause. To effectively curb the growth of cyanobacteria in Lake Taihu, it is imperative to reduce the external load of nutrients [65,66,67]. Many methods have been developed to identify the nutrient sources and driving factors of eutrophication in Lake Taihu. The most noteworthy research studies conducted in recent years are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Studies on source identification of eutrophication in Lake Taihu.
Researchers have employed diverse models to identify the causes of lake eutrophication. The models can be categorized into several distinct modes of analysis, including multivariate statistical analysis, physical model analysis, empirical model analysis, and multidisciplinary comprehensive analysis.
3.1. Identification of External Pollution Using Multiple Analyses
3.1.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
With the water quality observation data, the results of multivariate statistical analysis have shown considerable potential in understanding the spatiotemporal patterns and source distribution of water eutrophication [76,77,78]. Principal component analysis, cluster analysis, and discriminant analysis have been extensively employed to evaluate the temporal and spatial variations in surface water, thereby enabling the inference of pollution sources of lakes [79,80,81].
Based on the water quality data of the outlets of rivers from 2006 to 2010, Chen et al. analyzed the potential pollution sources of two regions surrounding Lake Taihu through principal component analysis [82]. The results indicated that, in highly developed areas, most industrial and domestic wastewater was directly discharged into rivers. Therefore, the area was mainly affected by runoff related to industrial and domestic pollution, while the Tiaoxi River Basin, originating from mountainous and moderately developed rural areas, was affected by both point sources and non-point agricultural sources. In the northwestern area of Lake Taihu, where the eutrophication was the most severe, absolute principal component score–multiple linear regression and positive matrix factorization models were used to calculate the contribution rate of each pollution source. The results showed that agricultural non-point source pollution (26.6%) was the major contributor, followed by domestic sewage discharge (23.5%) [62].
Multivariate statistical analysis employs receptor models and dimensionality reduction techniques to identify the primary sources of pollution based on extensive water quality data. Various parameters, such as nutrients, organic matter, heavy metals, and other pollutants, are analyzed by this method, providing a comprehensive understanding of the pollution sources. However, the results obtained are limited to determining the contribution of overall pollution and are insufficient in precisely identifying the cause of water eutrophication.
3.1.2. Physical Model Analysis
Non-point-source pollutants, characterized by uncertain emissions from multiple outlets, play an important role in the eutrophication of water bodies. Due to the spatial and temporal variability in nutrient loads, non-point-source pollution has arbitrary and irregular processes and complex mechanisms [83]. Model simulation is a common approach to monitoring and evaluating non-point-source pollution. Physical and empirical models are two typical types of measures for such simulation. Physical models have been extensively employed to simplify the intricate natural processes involved in the generation and transformation of non-point-source pollutants [84,85,86]. The estimation of the loads of non-point-source pollutants is achieved through watershed models with hydraulic response simulations and receiving water models that simulate water quality and hydrodynamic transmissions [87].
In a study conducted in the southern part of the Taihu Basin, the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model was employed to analyze hydrological and water quality parameters. Agricultural fertilizers—specifically nitrogen and phosphorus carried by runoff—were identified as the primary non-point-source pollutants within the lake area. Thus, it is suggested to address the excessive application of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers and their synergistic impacts with manure, as these measures can significantly control nutrient pollution within the lake ecosystem [72]. In a study concerning Tianmu Lake (situated in the upper reaches of the Taihu Basin), using the Spatially Referenced Regressions On Watershed Attributes (SPARROW) model, variables such as the land cover, river length, runoff depth, and pond density were found to effectively explain 94% of the temporal and spatial variations in the TP load [88]. On average, ponds intercepted 24% of the phosphorus output from the watershed landscape. These findings underscore the profound importance of landscape characteristics in mitigating TP losses in environmentally sensitive hilly watersheds [88].
3.1.3. Empirical Model Analysis
Export coefficient models (ECMs) have been widely employed in studies of non-point-source pollution within large basins over the past two decades [89,90,91,92,93]. The initial ECM estimates the overall loss from diverse sources, such as land use, livestock, and rural activities, based on the nutrient load discharged from the watershed [94]. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in ECMs regarding parameterization and application scope [74]. Notably, to incorporate the influence of the distance between the source and sink on nutrient discharge (including hydrological, transport, and terrain impacts), the transmission [95], rainfall impact, and watershed loss coefficient have been introduced to the ECM [29].
Previous research on estimating ECM coefficients has relied on field experiments or investigations to determine nutrient load allocation across various pollution sources. While these studies increased the accuracy of the results, their limitations included small-scale watersheds and a reduced temporal scope. A study conducted in Xueyan Town, a first-grade protection zone of the Taihu Basin, during the rice-growing season of 2000 revealed that nitrogen emissions from farmland, village residents, town residents, and livestock contributed 72.7%, 18.9%, 7.2%, and 1.2%, respectively. Phosphorus emissions from these sources accounted for 56.2%, 18.9%, 22.2%, and 2.7%, respectively [96,97,98]. In 2004, it was observed that nitrate nitrogen and particulate nitrogen were the primary forms of nitrogen loss from dry land to water bodies in the Taihu Basin. Therefore, controlling these forms of nitrogen should be a priority. In this investigation, particulate phosphorus emerged as the major form of phosphorus loss, representing 76% of the total phosphorus [99]. Additionally, the land use composition significantly impacts nutrient outputs, as demonstrated in the Xitiaoxi watershed of the Taihu Basin, where an increase in the ratio of farmland to forest land was correlated with intensified nutrient outputs [100].
When the export coefficients obtained from field investigations exceed a specific threshold, they can be applied to large-scale calculations, enabling expanded research coverage, enhanced pollution source identification, and accelerated data analysis [101]. Via an ECM, the total nutrient loads of TN and TP originating from industry, livestock farming, agriculture, household activities, and atmospheric deposition in the Taihu Basin in 2008 were estimated to be 33,043.2 t/a and 5254.4 t/a, respectively. Notably, household consumption exhibited the highest impact, accounting for 46% of the TN load and 47% of the TP load. Atmospheric deposition and agriculture contributed 18% and 15% of the TN load, respectively, while livestock farming was the second-largest contributor to the TP load, accounting for 32% [102]. Leveraging an ECM, a study estimated pollutant emissions from non-point sources in the rural areas of the south lake region and utilized the optimized maximum quantity of a pollutant program to determine the environmental capacity of water bodies in the small rural watershed. The findings supported the formulation of related measures for pollutant reduction [103].
3.1.4. Multidisciplinary Analysis
The limitations of simple ECMs in terms of accuracy have prompted researchers to incorporate geographic information systems (GISs) into pollution source accounting models to increase the precision in land use classification. The Agricultural Non-Point-Source Pollution Potential Index (APPI) system was developed to address this need. By considering factors such as the sediment production index, runoff index, human and animal load index, and chemical use index, the APPI system effectively quantifies non-point-source pollution. Research focused on Xueyan Town within the Taihu Basin revealed that rural residents contributed 33% of TP and 40% of TN, while residents in the town center contributed 25% of TP and 10% of TN [97]. The integration of a GIS with an ECM, along with the consideration of watershed-specific rainfall patterns, resulted in an improved model with excellent spatiotemporal suitability and generalization [104]. Based on GIS technology, a study integrated hydrological models into the ECM by using meteorological data, the watershed topography, land use, and river network data as inputs, thereby constructing the Monthly Export Coefficient Model (MECM). One significant achievement of this research is its monthly time scale, surpassing the prevalent annual time scale used in most ECM studies [105]. Zhou et al. used GIS spatial analysis capabilities to construct a semi-distributed export coefficient model, determining that the TN load from non-point sources in the entire Taihu Basin in 2011 was 398,100 t/year, with the corresponding TP load reaching 55,900 t/year [69]. Additionally, a spatial relationship model based on a GIS was developed in 2014 to describe the relationship among point sources, river segments, and catchments in the Taige Canal watershed of the Taihu Basin [106]. This model enables in-time source tracking triggered by predefined water quality thresholds, offering a fast response.
The MARINA-Lake model was recently developed to accurately assess nutrient inputs from river systems into the marine environment and to quantify nitrogen and phosphorus outputs from sub-basins to lakes [71]. Using this model, the Taihu Basin was divided into five sub-basins, and the pollution loads in each sub-basin were calculated by an ECM. The nutrient load discharged from each sub-basin into the lake was determined using the MARINA-Lake model, with the consideration of non-point-source losses, providing estimates that aligned closely with real values [5]. The Phosphorus Source Contribution Index (PSCI) model characterizes phosphorus sources, sinks, and transport in both horizontal and vertical directions within the lake, derived from a comprehensive three-dimensional hydrodynamic and water quality model. This model has been used to track the phosphorus sources of two drinking water intakes in Lake Taihu, and the results indicate that the internal phosphorus load in sediments is an important phosphorus source, with contribution rates of 47.1% and 30.4%, respectively [68]. Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have great potential in effectively identifying sources of eutrophication and pollution within Lake Taihu. Using 13 years of data, Hu et al. constructed six integrated machine learning models, and the results indicated that the TN concentration was primarily influenced by the endogenous load and incoming water quality [107], while TP was mainly affected by the endogenous load. The model shows potential in tracking and predicting pollution sources, aiding in the early warning and effective control of lake eutrophication [107].
3.2. Identification of Endogenous Pollution
It has been reported in many cases that, despite the extensive efforts being made to reduce external nutrient inputs, the decrease in the phosphorus concentration in the overlying water remains negligible [108,109]. This lack of reduction could be attributed to the release of phosphorus from sediment sources [23,110,111]. In this process, labile phosphorus in interstitial water is supplemented by sediment solids, subsequently becoming concentrated, and is released into the overlying water. Such release can be notably intensified during cyanobacterial blooms [112]. Furthermore, the occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms contributes to the accumulation of active organic matter and a decrease in the dissolved oxygen concentration. Consequently, nutrient release is enhanced in anoxic environments, leading to exacerbated algal growth and perpetuating a detrimental cycle [113]. As a shallow lake, Lake Taihu is heavily influenced by wind-induced disturbances, which also enhance the recycling efficiency of phosphorus [23]. As a result, the algal concentration in the lake sharply increases, further impeding the restoration process [70].
3.2.1. Nutrient Suspension Flux
Studies on endogenous phosphorus release loads have focused on simulating sediment suspension. By establishing a quantitative relationship between the wind speed and sediment suspension rate, it was calculated that the annual flux loads of TN and TP released from the sediments in Lake Taihu were 4577 t and 1101 t, respectively, accounting for 15.4% and 39.3% of the total sources [114]. Under static conditions, the diffusion-driven release of nutrients from sediment into the overlying water is primarily governed by concentration gradients, and these nutrients can be easily used by alga. The annual phosphorus release of Lake Taihu sediments measured without wind disturbances was estimated to be 899 t, and the annual nitrogen release was 10,000 t [115]. In contrast, the annual phosphorus release measured using diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) analysis was approximately 700 t [108]. These results indicate that endogenous release approximates one third of the external input. In fact, the intensity of dynamic nutrient release caused by wind and wave conditions is much higher than that under static conditions [23]. Although the annual flux of endogenous release might be offset by the sedimentation load [116], the rapid increase in nutrient concentrations in a water body during a short period of time can still trigger cyanobacterial blooms [114].
3.2.2. Relation to Sedimentary Organic Matter
The excessive endogenous phosphorus load in Lake Taihu primarily stems from the long-term accumulation of external phosphorus load in sediments [68]. Due to the presence of sedimentary organic matter (SOM), sediment acts as a reservoir for pollutants in the overlying water, and its association with Lake Taihu eutrophication has been well established [73]. The degradation of SOM, accompanied by nutrient release, is a key driver of eutrophication. Furthermore, the sources and composition of SOM significantly affect both the habitats of aquatic plants and the food quality of benthos organisms [95]. Researchers have employed the stable isotope analysis of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other elements in SOM [75,117,118], as well as the determination of the fatty acid composition [95,119], to identify the contributions of land, macrophytes, algae, and other sources to SOM in the lake.
The formation of authigenic phosphorus mainly occurs through organic matter mineralization and apatite precipitation, as indicated by the oxygen isotope ratios of phosphate [75]. In both estuaries and open waters, the proportion of land organic matter in sediments (46.8%~55.0%) exceeds those of algal sources (13.8%~23.4%) and macrophytes (20.0%~30.0%) [117]. This finding aligns with the evaluation results regarding organic matter sources in sediments in different zones of Lake Taihu, suggesting a substantial contribution from terrigenous matter [118].
By utilizing source-specific fatty acid biomarkers, the contributions of different potential sources of organic matter in the western region of Lake Taihu were evaluated, with terrestrial plants being identified as the primary source [95]. The eutrophication status of Lake Taihu significantly impacts the sources and composition of organic matter. Increased eutrophication leads to a higher contribution of aquatic organic matter sources compared to terrestrial sources [119], further supporting the positive feedback relationship between organic matter accumulation and lake eutrophication. To mitigate the impact of endogenous pollution on the eutrophication of Lake Taihu, it is crucial to not only control nutrient release from the sediment to the overlying water but also to reduce the concentrations and total amounts of pollutants in the sediment.
4. Source Control of Eutrophication in Lake Taihu
During the 1990s, the local government invested billions of Chinese Yuan each year to combat eutrophication in Lake Taihu [120]. A long-term fixed-point water quality monitoring system was implemented in Lake Taihu, leading to the significant accumulation of extensive and intricate datasets [109,121]. Moreover, a large-scale investment in ecological environment protection and restoration projects commenced in 2000 [122]. Since 2007, comprehensive treatment measures have been implemented in the Taihu Basin, including the establishment of new wastewater treatment facilities, the closure of chemical-intensive and highly polluting factories, the establishment of cyanobacteria salvaging sites and water–algae separation stations surrounding the lake, and sediment remediation efforts, as well as wetland protection and restoration initiatives [56]. The control of water pollution in Lake Taihu has exerted a notable influence on the spatiotemporal distribution of nutrient concentrations [24]. By 2017, significant reductions in nutrient indices were observed in the rivers surrounding the lake and the lake itself, with 12 of the 15 major rivers meeting or surpassing the Class III water quality standard [123]. Remarkable achievements in nutrient concentration (NH4+-N, TN, TP) control were witnessed in most of the studied areas. Notably, source-targeted interventions demonstrated greater efficacy regarding ecosystem restoration in comparison to those focusing on pollution reduction [122].
4.1. Control of Non-Point-Source Pollution
Non-point-source pollution poses a significant threat to water quality in various global regions, bringing challenges in effective management and mitigation efforts (Adu and Kumarasamy). The Environmental Protection Law of China, enacted in 1989, established guidelines regarding strengthening rural environmental protection, adopting agricultural inputs (such as pesticides and fertilizers), and advancing the concept of agricultural non-point-source pollution control. However, the effective collection and treatment of wastewater, such as domestic wastewater, in the rural area, as well as township industrial wastewater, agricultural wastewater, and livestock farming wastewater, are still lacking. Wetlands or ponds have been widely employed globally to intercept non-point pollution [23], and the captured nutrients can be viably utilized if appropriately recycled [124]. However, the current pollution load of Lake Taihu surpasses the environmental capacity of the surrounding wetlands, leading to a delay in non-point-source pollution control. Moreover, climate change in the future is predicted to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme rainstorms, intensifying the challenge of mitigating non-point-source pollution and cyanobacterial blooms [125].
The source of non-point pollution in the Taihu Basin has undergone changes due to the rapid development of agriculture. The fruit, vegetable, and tea planting system has surpassed the rice planting system and become the major contributor to nitrogen and phosphorus losses in farmland [126]. Therefore, optimizing the planting structure of fruit, vegetables, tea, and rice, as well as the fertilization strategy, is important in reducing and controlling agricultural non-point-source pollution in the Taihu Basin [127,128].
Freshwater aquaculture in the Taihu Basin accounts for over 85% of inland fishery in China [129]. However, there is a lack of systematic control over the aquaculture wastewater around Lake Taihu. The supervision and management of livestock and poultry farms since 2001 has not effectively reduced eutrophication in many water bodies in China [130]. To address these issues, a case study was conducted on a town in the Taihu Basin with three non-point pollution sources: crop farming, livestock, and aquaculture. The results showed that reusing all livestock wastewater and manure together with partial aquaculture wastewater is the most effective method to control non-point-source pollution in the Taihu Basin, considering cost-effectiveness among the studied four scenarios [131].
4.2. Control of Point-Source Pollution
The expansion of wastewater treatment infrastructure constitutes the primary strategy to reduce the amounts of nutrients transported from point sources to Lake Taihu. During 2007 to 2020, the wastewater treatment facilities in the Taihu Basin expanded from 129 to 312 plants [132]. Meanwhile, discharge limits for pollutants in sewage are becoming increasingly stringent [133]. In 2018, the nearby provinces issued more stringent local standards than the National Discharge Standards (GB 18918-2002) [134] for sewage treatment plants and required corresponding technological upgrading to promote water resource protection [59].
Although point-source pollution has been effectively controlled, the water quality of Lake Taihu is still far from the expected level [40,135]. After the implementation of the Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants (GB 18918-2002), the sewage treatment plants in China had already reduced their nutrient loads by around half; however, the load of pollutants discharged to the water bodies has increased compared with the 1980s because of the increase in the total sewage volume [136]. From 2008 to 2018, the average annual TN export to Lake Taihu was around 40,000~50,000 t, and that of TP was around 2000 t [23]. The lack of sewage treatment facilities and the low efficiency of existing facilities still exist [137]. The inappropriate industrial structure and distribution and the dominance of secondary industries, especially considering the excessive pollutant emissions from the effluents of sewage treatment plants, also lead to the severe pollution of river tributaries and poor water quality in the Lake Taihu area [120,138].
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
This review has synthesized the current understanding of eutrophication dynamics and source identification in Lake Taihu, a critical freshwater resource facing substantial environmental challenges. The escalating influx of human-derived nutrients has exacerbated eutrophication globally, with Lake Taihu serving as a prominent case study. Our analysis reveals that phosphorus emerges as the key driver of eutrophication in Lake Taihu, exhibiting a strong correlation with Chl a concentrations. The lake’s nutrient dynamics are characterized by significant temporal and spatial heterogeneity, influenced by both anthropogenic activities and meteorological conditions. Historical trends indicate fluctuating nutrient concentrations and cyanobacterial bloom occurrences, despite government-led control efforts. The resurgence of blooms highlights the complex interplay among factors governing eutrophication in this large, shallow lake.
The effective management of Lake Taihu’s eutrophication necessitates a comprehensive understanding of nutrient sources. This review has evaluated various methodologies, including multivariate statistical analysis, physical models, empirical models, and multidisciplinary approaches integrating GISs and machine learning. These methods have collectively identified agricultural non-point-source pollution and urban point-source discharges as major external nutrient contributors. Furthermore, the role of sediment nutrient release as an endogenous source, influenced by sedimentary organic matter and wind-induced resuspension, is increasingly recognized.
The evolution of source identification techniques underscores the shift from traditional methods to more sophisticated, spatially explicit assessments. ECMs provide valuable insights into nutrient loads from various sources, while physical models such as SWAT and SPARROW enhance our understanding of hydrological and water quality processes. Multidisciplinary approaches, incorporating GISs and machine learning, offer improved accuracy and predictive capabilities. Notably, the application of AI has shown promise in identifying complex relationships between nutrient concentrations and environmental factors.
Despite substantial investments in wastewater treatment plants and non-point-source pollution control, Lake Taihu continues to experience eutrophication challenges. The increasing volume of sewage discharge and the legacy of nutrient accumulation in sediments necessitate a paradigm shift towards integrated watershed management. Future research should prioritize the following: (a) refined source tracking—further refine source tracking methodologies, particularly for non-point-source pollution, using advanced techniques like stable isotope analysis and high-resolution spatial modeling; (b) sediment dynamics—enhance the understanding of sediment nutrient release mechanisms and develop effective sediment remediation strategies; (c) climate change impacts—investigate the impacts of climate change on nutrient loading and cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in Lake Taihu; (d) integrated modeling—develop integrated models that couple hydrological, water quality, and ecological processes to simulate the complex interactions within the lake ecosystem; (e) AI applications—expand the application of deep learning architectures for predictive modeling and eutrophication monitoring.
Ultimately, achieving the sustainable management of Lake Taihu’s eutrophication requires a holistic approach that integrates scientific research, policy implementation, and public engagement. This review provides a foundation for future efforts aimed at restoring and protecting this vital aquatic ecosystem.
Author Contributions
K.C., conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, and data curation; B.X., investigation, resources, and supervision; Y.L., validation and data curation; R.Z., validation; X.G., conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, visualization, and final draft preparation; X.C., conceptualization, writing—review and editing, project administration, supervision, and funding acquisition; D.S., conceptualization, supervision, and project administration; K.H., conceptualization and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2021ZY78), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC3200604), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52170023 and 51878048).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the funding organizations for the support of this paper. We also acknowledge the help from editors and anonymous reviewers who have helped to improve the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ayele, H.S.; Atlabachew, M. Review of characterization, factors, impacts, and solutions of Lake eutrophication: Lesson for lake Tana, Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14233–14252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.M.d.S.; Azevedo, M.T.d.P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.d.O.; Honda, R.Y.; Corrêa, B. Toxic cyanobacteria and microcystin concentrations in a public water supply reservoir in the Brazilian Amazonia region. Toxicon 2005, 45, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Gao, G. Long-term MODIS observations of cyanobacterial dynamics in Lake Taihu: Responses to nutrient enrichment and meteorological factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Strokal, M.; Burek, P.; Kroeze, C.; Ma, L.; Janssen, A.B.G. Excess nutrient loads to Lake Taihu: Opportunities for nutrient reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinçon-Leite, B.; Casenave, C. Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; Hall, N.S.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Wu, Y.; Rossignol, K.L.; Dong, L.; McCarthy, M.J.; Joyner, A.R. Controlling Cyanobacterial Blooms in Hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China: Will Nitrogen Reductions Cause Replacement of Non-N2 Fixing by N2 Fixing Taxa? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.; She, X.; Kong, D.; Xue, K.; Li, Y. Algal Blooms in Lake Taihu: Earlier Onset and Extended Duration. Harmful Algae 2025, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, A.; Bird, D.F.; Prairie, Y.T.; Lawrence, J.F. Empirical study of cyanobacterial toxicity along a trophic gradient of lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, R.; Pearman, J.K.; Atalah, J.; Waters, S.; Vandergoes, M.J.; Howarth, J.D.; Thomson-Laing, G.; Thompson, L.; Wood, S.A. A taxonomy-free diatom eDNA-based technique for assessing lake trophic level using lake sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.N.; Wellen, C.; Parsons, C.T.; Taylor, W.D.; Arhonditsis, G.; Chomicki, K.M.; Boyd, D.; Weidman, P.; Mundle, S.O.C.; Cappellen, P.V.; et al. Understanding and managing the re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Knowledge gaps and research priorities. Freshw. Sci. 2019, 38, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Liu, J.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, K.; Deng, J. Why Lake Taihu continues to be plagued with cyanobacterial blooms through 10 years (2007–2017) efforts. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, Z.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Leavitt, P.R.; Bunting, L.; Buchaca, T.; Catalan, J.; Domaizon, I.; Guilizzoni, P.; Lami, A.; McGowan, S.; et al. Acceleration of cyanobacterial dominance in north temperate-subarctic lakes during the Anthropocene. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of Lake Waters in China: Cost, Causes, and Control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Qin, B. A critical review of the development, current hotspots, and future directions of Lake Taihu research from the bibliometrics perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12811–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jia, Y.; Li, E.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Song, L. Soil-Based Treatments of Mechanically Collected Cyanobacterial Blooms from Lake Taihu: Efficiencies and Potential Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13370–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Xu, X.; Kong, F.; Zhang, S.; Kong, W.; Hao, J.; Shang, L. Two-Decade Reconstruction of Algal Blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Q.; Liu, P.-W. Strategy of water pollution prevention in Taihu Lake and its effects analysis. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B. Shallow lake limnology and control of eutrophication in Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1229–1243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Lin, P. Spatio-temporal dynamics of water quality and eutrophication in Lake Taihu, China. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.L. A new indices system for evaluating ecological-economic-social performances of wetland restorations and its application to Taihu Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 295, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liuyan, Y.; Lin, X.; Aijun, M.; Xi, B. Nitrogen removal by denitrification during cyanobacterial bloom in Lake Taihu. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend-Small, A.; McCarthy, M.J.; Brandes, J.A.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gardner, W.S. Stable isotopic composition of nitrate in Lake Taihu, China, and major inflow rivers. In Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes with Special Reference to Lake Taihu, China; Qin, B., Liu, Z., Havens, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Gao, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, N.; Dong, F.; Shi, W. How successful are the restoration efforts of China’s lakes and reservoirs? Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Naren, T. Mapping Taihu Basin research: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Rev. 2021, 29, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y. Profound Changes in the Physical Environment of Lake Taihu From 25 Years of Long-Term Observations: Implications for Algal Bloom Outbreaks and Aquatic Macrophyte Loss. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 4319–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.-W.; Yao, X.; Zhang, B.-H.; Gao, G.; Shao, K.-Q. Temporal-spatial distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Lake Taihu based on geostatistical analysis. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Variation and Environmental Driving Forces Analyses of Algal Blooms in Taihu Lake Based on Multi-Source Satellite and Land Observations. Water 2020, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, Y.; Stoffella, P.J.; Phlips, E.J.; Powell, C.A. Nitrogen versus phosphorus limitation of phytoplankton growth in Ten Mile Creek, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Steinman, A.D.; Oudsema, M.; Hassett, M.; Xie, L. The influence of nutrients limitation on phytoplankton growth and microcystins production in Spring Lake, USA. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Gan, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ding, R.; Liu, G.; Wu, J.; et al. A novel indicator for defining plain urban river network cyanobacterial blooms: Resource use efficiency. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhu, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gu, Z. Estimation of the algal-available phosphorus pool in sediments of a large, shallow eutrophic lake (Taihu, China) using profiled SMT fractional analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, M.C.; Ugaya, C.M.L.; de Almeida Neto, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.B. Regionalized phosphorus fate factors for freshwater eutrophication in Bahia, Brazil: An analysis of spatial and temporal variability. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, M.; Gábor, S.; Piroska, K.; Gábor, K.; János, T.; Tamás, K.; Péter, T.; Krisztián, H.; Piroska, P.; Péter, S.; et al. Soluble phosphorus content of Lake Balaton sediments. J. Maps 2022, 18, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xi, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. The eutrophication and its regional heterogeneity in typical lakes of China. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2018, 42, 854–864. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Jesna, P.K.; Ramya, V.L.; Mol, S.S.; Panikkar, P.; Vijaykumar, M.E.; Sarkar, U.K.; Das, B.K. Phosphorus fractions in the sediment of a tropical reservoir, India: Implications for pollution source identification and eutrophication. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 749–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E.M. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. Cyanobacterial organic matter (COM) positive feedback aggravates lake eutrophication by changing the phosphorus release characteristics of sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Peñuelas, J.; Huang, J.; Sardans, J.; Jiang, Q.; Finlay, J.C.; Britten, G.L.; Follows, M.J.; et al. Imbalance of global nutrient cycles exacerbated by the greater retention of phosphorus over nitrogen in lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, P.; Ni, T. Response of cyanobacterial bloom risk to nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in large shallow lakes determined through geographical detector: A case study of Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R. Phosphorus control is critical to mitigating eutrophication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11039–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Zhu, G.; Cai, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Quantifying the dependence of cyanobacterial growth to nutrient for the eutrophication management of temperate-subtropical shallow lakes. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Gao, M.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Increase in chlorophyll-a concentration in Lake Taihu from 1984 to 2021 based on Landsat observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B. Progress and prospect on the eco-environmental research of Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 445–455. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Qian, P.; Ye, L.; Song, T. Changes in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in Lake Taihu, 1985–2015. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 935–943. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, B.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M.T. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M. Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: An 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to Climatic Variability and Lake Management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xia, Y.; Ti, C.; Shan, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X. Thirty years of experience in water pollution control in Taihu Lake: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Gao, M.; Wen, L.; Yao, M.; Nie, Q. Occurrence characteristics of black patch events and their influencing factors in Lake Taihu during 2009 and 2017. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1196–1205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ti, C.; Shan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, L.; Yan, X. Nitrogen Removal Capacity of the River Network in a High Nitrogen Loading Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ye, C. Response of the nitrogen load and its driving forces in estuarine water to dam construction in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31458–31467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, R.; Feng, G.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lv, Y. Spatial and temporal variations in algal phosphorus in Taihu Lake. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J. Main factors driving inter-annual variability of chlorophyll-a and the influence of future climate on chlorophyll-a in Lake Taihu. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 1332–1341. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Dai, J.; Huang, T. Response of the photosynthetic activity and biomass of the phytoplankton community to increasing nutrients during cyanobacterial blooms in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.F.; Li, Y.M.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Yin, B. Validation of a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Highly Turbid Eutrophic Water of Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Ding, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G.; Xu, H.; Li, W.; Dong, B.; Luo, L. Field Observation of Different Wind-Induced Basin-Scale Current Field Dynamics in a Large, Polymictic, Eutrophic Lake. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6945–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining Critical Nutrient Thresholds Needed to Control Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; de Jager, V.C.L.; Janse, J.H.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Mooij, W.M. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: Implications for Lake Taihu (China). Water Res. 2017, 119, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Chen, Q.; Hu, L.; Shi, W. Tracking Nitrogen Sources, Transformation, and Transport at a Basin Scale with Complex Plain River Networks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5396–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, R.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Yang, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, R.; Liao, K.; Huang, J. A modelling framework to track phosphorus sources of the drinking water intakes in a large eutrophic lake. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z. Estimation of Nutrient Export Loads in Taihu Lake Watershed Based on the Export Coefficient Model. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2014, 36, 678–683. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.J.; Koh, H.L.; Mohd, M.H.; Teh, S.Y. Assessing the role of internal phosphorus recycling on eutrophication in four lakes in China and Malaysia. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Kroeze, C.; Wang, M.; Bai, Z.; Ma, L. The MARINA model (Model to Assess River Inputs of Nutrients to seAs): Model description and results for China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Chen, Y.-X.; Jilani, G.; Shamsi, I.H.; Yu, Q.-G. Model AVSWAT apropos of simulating non-point source pollution in Taihu lake basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omesová, M.; Helešic, J. Organic matter and fine grains as possible determinants of spatial and seasonal variability in bed sediment fauna: A case study from a Hercynian gravel stream. Limnologica 2010, 40, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.D.; Sun, J.H.; Hua, G.F.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, H. Runoff characteristics and non-point source pollution analysis in the Taihu Lake Basin: A case study of the town of Xueyan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15029–15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Li, Q.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Liu, E.; Yu, J.; Fang, H.; Li, H.; Jaisi, D.P. Identifying sources and cycling of phosphorus in the sediment of a shallow freshwater lake in China using phosphate oxygen isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, H.; Jia, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, C. Principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analyses of arsenic groundwater geochemistry in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Geochemistry 2015, 75, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyar, N.; Hatvani, I.G.; Székely, I.K.; Herzig, A.; Dinka, M.; Kovács, J. Application of multivariate statistical methods in determining spatial changes in water quality in the Austrian part of Neusiedler See. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.B.; Ahluwalia, A.S.; Jindal, R.; Sharma, C. Water Quality Assessment of Some Freshwater Bodies Supporting Vegetation in and Around Chandigarh (India), Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2013, 5, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, X.; Wu, Q.; Pan, B.; Du, Y.; Feng, Q. Application of Composite Water Quality Identification Index on the water quality evaluation in spatial and temporal variations: A case study in Honghu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4237–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, D.; Oh, J.-M. Runoff characteristics of non-point pollutants caused by different land uses and a spatial overlay analysis with spatial distribution of industrial cluster: A case study of the Lake Sihwa watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Das, P. Assessment of water quality index using cluster analysis and artificial neural network modeling: A case study of the Hooghly River basin, West Bengal, India. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Cao, W.; Bo, Y.; Shang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhou, F. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Source Identification of Water Pollution in Lake Taihu (China). Water 2016, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Tang, L.; Yang, D. Spatial and temporal variability of nitrogen load from catchment and retention along a river network: A case study in the upper Xin’anjiang catchment of China. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 47, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoy, G.A.; Jenkinson, R.W.; Robertson, D.M.; Saad, D.A. Nutrient delivery to Lake Winnipeg from the Red—Assiniboine River Basin–A binational application of the SPARROW model. Can. Water Resour. J./Rev. Can. Ressour. Hydr. 2016, 41, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Liao, Q.; Hong, Q.; Gong, Y. An overview of research on agricultural non-point source pollution modelling in China. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.K.; Akhtar, T.; Ghimire, U.; Rudra, R.P.; Goel, P.K.; Shukla, R.; Daggupati, P. Can-GLWS: Canadian Great Lakes Weather Service for the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) modelling. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, J.T.; Kumarasamy, M.V. Assessing Non-Point Source Pollution Models: A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pueppke, S.G.; Li, H.; Geng, J.; Diao, Y.; Hyndman, D.W. Modeling phosphorus sources and transport in a headwater catchment with rapid agricultural expansion. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yu, W.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, F.; Shen, Z. Development of regional pollution export coefficients based on artificial rainfall experiments and its application in North China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malve, O.; Tattari, S.; Riihimäki, J.; Jaakkola, E.; Voβ, A.; Williams, R.; Bärlund, I. Estimation of diffuse pollution loads in Europe for continental scale modelling of loads and in-stream river water quality. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.H.; Melack, J.M. Modeling Nutrient Export From Coastal California Watersheds. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Duan, L.; Bai, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, B. Improved export coefficient model for identification of watershed environmental risk areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 34649–34668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Shen, Z. Dynamic export coefficient model for evaluating the effects of environmental changes on non-point source pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnes, P.J. Evaluation and management of the impact of land use change on the nitrogen and phosphorus load delivered to surface waters: The export coefficient modelling approach. J. Hydrol. 1996, 183, 323–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, W.; Fujibayashi, M.; Nomura, M.; Nishimura, O.; Li, X. Predominance of terrestrial organic matter in sediments from a cyanobacteria- blooming hypereutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, G. Quantity of Nitrogen from Non-Point Source Pollution in Taihu Lake Catchment. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2003, 22, 150–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Quantification of non-point sources phosphorus pollution in key protection area of Taihu Lake. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 15, 136–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.Y.; Wang, X.R.; Zhu, J.G. Quantification and Index of Non-Point Source Pollution in Taihu Lake Region with GIS. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Duan, Z.; Xia, S. Quantification of non-point pollution from uplands in Taihu Lake Catchment. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 26, 40–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Li, H. Estimation of nutrient export coefficient from different land use types in Xitiaoxi Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 1–4+34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yang, L. Research advances of export coefficient model for non-point source pollution. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 755–761. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Modeling Nutrient Release in the Tai Lake Basin of China: Source Identification and Policy Implications. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, P. Non-point Pollution Control of Rural Watersheds in South Taihu Lake Basin. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 230–235. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, G.; Li, H. Estimated nutrient export loads based on improved export coefficient model in Xitiaoxi Watershed. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 668–672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Gao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Estimation of nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Xitiaoxi catchment using PCRaster software. Adv. Water Sci. 2012, 23, 80–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bi, J.; Zhang, X.-X.; Fang, Q.; Qi, Y. In-time source tracking of watershed loads of Taihu Lake Basin, China based on spatial relationship modeling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22085–22094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Du, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Xu, X.; Li, W. Source identification and prediction of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of Lake Taihu by an ensemble machine learning technique. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, M.; Gong, M.; Fan, X.; Qin, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, S.; Jin, Z.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, C. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Hall, N.S.; Zhu, M. Long-term nutrient trends and harmful cyanobacterial bloom potential in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2017, 787, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SØNdergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Skov, C.; Van Nes, E.H.; Roijackers, R.; Lammens, E.; Portielje, R.O.B. Lake restoration: Successes, failures and long-term effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, W. Effect of algal blooms outbreak and decline on phosphorus migration in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Xu, H.; Deng, J. Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Pang, Y.; Hu, K. Research on nutrient pollution load in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17829–17838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Gao, G.; Gu, B. Estimation of internal nutrient release in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Sci. China Ser. D 2006, 49, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhao, H.; Fang, M. Sediment-water exchange capacity of total phosphorus in Taihu Lake caculated by mass budget model. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 1992, 13, 83–84+97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Han, R.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, G. Isotopic evidence revealing spatial heterogeneity for source and composition of sedimentary organic matters in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Ji, M.; Wang, G.; Han, R.; Ma, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, J. Estimating sedimentary organic matter sources by multi-combined proxies for spatial heterogeneity in a large and shallow eutrophic lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Li, W.; Fujibayashi, M.; Nomura, M.; Sakamaki, T.; Nishimura, O.; Li, X. Feedback of threshold via estimating sources and composition of sedimentary organic matter across trophic gradients in freshwater lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. In Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes with Special Reference to Lake Taihu, China; Qin, B., Liu, Z., Havens, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; He, G.; Han, J.; Wang, T. Multivariate Analysis of Interactions Between Phytoplankton Biomass and Environmental Variables in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Gaüzère, P.; García Molinos, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H.; Brown, L.E.; Xu, J. Mitigation of urbanization effects on aquatic ecosystems by synchronous ecological restoration. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Xu, F.; Gao, Y.; Xiang, L.; Mao, X. Variations of water quality of the major 22 inflow rivers since 2007 and impacts on Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 1167–1174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, R.; Fu, B. Mitigation of nonpoint source pollution in rural areas: From control to synergies of multi ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W. Changing Rainfall Patterns Over the Western Lake Erie Basin (1975–2017): Effects on Tributary Discharge and Phosphorus Load. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Ji, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Pan, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W. Changes in planting structure and nitrogen and phosphorus loss loads of farmland in Taihu Lake region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 1230–1238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.; Ren, P.-a. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Xing, G. Maintaining rice yield and reducing N pollution by substituting winter legume for wheat in a heavily-fertilized rice-based cropping system of southeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 202, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Study on calculation of representative aquaculture pollution discharging coefficients in the Taihu Lake basin within Jiangsu Province. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 1330–1336. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, J.; Butterly, C.R.; Chen, Q.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, X. Effects of fertilizer types on nitrogen and phosphorous loss from rice-wheat rotation system in the Taihu Lake region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 285, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Xie, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, F. Optimization of pollutant reduction system for controlling agricultural non-point-source pollution based on grey relational analysis combined with analytic hierarchy process. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Lin, Y.; Cao, C.; Huang, M.; Zheng, B. A comprehensive assessment of upgrading technologies of wastewater treatment plants in Taihu Lake Basin. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.D.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. Water crisis, environmental regulations and location dynamics of pollution-intensive industries in China: A study of the Taihu Lake watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18918-2002; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/swrwpfbz/200307/t20030701_66529.shtml (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Hu, L.; Hu, W.; Zhai, S.; Wu, H. Effects on water quality following water transfer in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qin, J. Investigation of crucial measures for Taihu lake basin source administration. Jiangsu Water Resour. 2016, 4, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, S.; Lindley, S. Customizing the coefficients of urban domestic pollutant discharge and their driving mechanisms: Evidence from the Taihu Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H. Ammonia volatilization from a Chinese cabbage field under different nitrogen treatments in the Taihu Lake Basin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 38, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).