Abstract
Heavy metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems is a critical environmental issue worldwide. In these ecosystems, the seston adsorbs heavy metals from the water and introduces them into the food web, causing potential environmental and health risks. This study analyses how heavy metals (Cd, Hg, Cr, Cu, Pb, Fe, and Mn) are distributed in the water and seston of the Tampamachoco Lagoon, an ecosystem affected by pollution from a thermoelectric plant and by hydrometeorological variability, both of which influence their concentrations. The relationships among metal distribution, physicochemical variables, and the influence of plant emissions in three seasons (rainy, northerly windstorms, and dry) were analyzed. The metal concentrations in seston (Fe > Mn > Pb > Cu > Cr > Hg) were up to four times higher than in the water column (Fe > Mn > Cr > Cd > Pb > Cu > Hg), emphasizing the key role of particulate matter in metal transport and bioavailability. Particularly, the Cd concentrations exceeded WHO thresholds by 527.6% in the water column during the rainy season, while Hg and Pb exceeded the thresholds of the Mexican criteria for the protection of marine aquatic life by 4.05% and 41.6%, respectively. Principal Component Analyses revealed distinct spatiotemporal distribution patterns for metals in water and seston, reflecting the combined effects of natural variability and anthropogenic inputs. The strong association between metals and seston indicates continued contamination and potential risks to aquatic ecosystems. These findings highlight the environmental impact of metals on seston and the need for monitoring to assess aquatic ecosystems’ health. Our results highlight the importance of understanding how metals are distributed between seston and water, and how climate variability affects pollutant redistribution patterns. We propose that water quality regulations need to be rethought and redirected towards the achievement of new strategic objectives that truly integrate the different pollutant sources whose final destination is water bodies, so as to protect and conserve biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Transitional ecosystems such as estuaries and coastal lagoons are among the most productive aquatic systems and are recognized worldwide for their ecological and economic importance [1]. Coastal lagoons receive high nutrient inputs from runoff and direct waste from human activities, increasing their high biological productivity and eutrophication processes [2]. Additionally, inputs of pollutants to coastal water bodies have increased in recent decades [3]. Among the diverse range of pollutants, metals are of particular interest due to their persistence in the environment, biogeochemical recycling, and risk to human health [4].
Seston includes all particles suspended in the water column, regardless of their nature or origin. Seston can be classified as bioseston (a biotic component: phytoplankton, zooplankton, bacteria, fungi, protozoa) and abioseston or tripton (an abiotic component: inert material, such as clay, silt, and detritus) [5]. Due to its high surface area/volume ratio, seston can adsorb trace metals dissolved in the water column [6,7,8]; therefore, it is considered to be a reservoir of trace metals [9]. The composition of seston (bioseston and abioseston) influences the interactions with trace metals in aquatic environments, as it determines the heterogeneity, complexity, and reactivity of the seston matrix with trace metals [10]. However, the chemical composition and characterization of seston are influenced by climatic variations, land use, seawater input, and water quality (pH, temperature, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, salinity), among others [11]. Once incorporated into seston, metals can be either transported to the sediment through diffusion, aggregation, and sedimentation or incorporated into the trophic webs via ingestion by filter feeders or detritivorous organisms. In this way, metals are transferred to higher trophic levels with an increase or decrease in their concentrations [12,13,14].
Studies in the coastal lagoon of Tampamachoco, located in the Gulf of Mexico, suggest that hydrometeorological forcings influence the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of potentially toxic metals. Through sediment resuspension, certain metals, such as Hg, may become bioavailable and biomagnified in the trophic web, highlighting seston as the primary source of metals’ incorporation into food chains [6]. Despite the recognized importance of evaluating the combined effects of natural and anthropogenic disturbances, including hydrometeorological variability, in the regulation of ecosystem biogeochemistry, there is limited information on processes that affect trace element distribution dynamics in subtropical coastal ecosystems subjected to contrasting seasonal climatic regimes (dry, northerly windstorms, and rainy seasons) [15]. Although several studies have described metal distribution patterns in seston in temperate coastal environments [16,17,18,19,20], information on this topic is scarce for subtropical coastal lagoons in general [21] and is unavailable for the Gulf of Mexico area. Hence, the importance of investigating the influence of hydrometeorological variability on the plume of atmospheric pollutants and the distribution patterns of trace metals in the seston of subtropical lagoons is evident.
In the area surrounding the Tampamachoco subtropical coastal lagoon, in the Gulf of Mexico coastal zone, pollutants, including metals, are emitted from a thermoelectric power plant located east of the lagoon. Local precipitation patterns, along with wind intensity and direction, define two dispersion routes (to the west and south) of these pollutants, which affect the lagoon and the city of Tuxpan [22]. In the lagoon, seston has been identified as the primary support of the food web [6]; therefore, assessing its capacity to accumulate trace metals and its role in the fluctuations of metal concentrations in the coastal lagoon is highly relevant. Furthermore, seston may play a critical role in the transfer of these metals to higher trophic levels. Given the above, the main objective of this study was to analyze the spatial and temporal distribution of trace metals (Hg, Pb, Cr, Cd, Fe, and Mn) in water and seston in Tampamachoco. Furthermore, this work examines the relationships between physicochemical factors and spatiotemporal patterns of trace metals in the lagoon, as well as the influence of hydrometeorological variability and the dispersion routes of the plume emitted by the Adolfo López Mateos thermoelectric power plant on the distribution of trace heavy metals in water and seston.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Tampamachoco Lagoon is located on the Gulf of Mexico slope, 9 km northeast of the city of Tuxpan, Veracruz (Figure 1). It has an elongated shape parallel to the coastline, with an area of 15 km2 (10.6 km long by 2.7 km wide) and a mean depth of 1.5 m [23]. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by a sandy bar called “Barra de Galindo”, where the “Adolfo López Mateos” thermoelectric plant is located. The Tampamachoco Lagoon (a Ramsar site) communicates with the Tamiahua Lagoon to the north, with the Tuxpan River to the south, and with the sea by an artificial channel in the Galindo Bar [6]. The local climate is warm and subhumid with summer rainfall (Aw’’z (e)), with a mean annual temperature of 24.2 °C and annual precipitation of 1350 mm [24]. It is characterized by three distinct climatic seasons: northerly windstorms (October to February), a dry season (November to May), and a rainy season (June to October), with marked changes in temperature, salinity, and nutrient concentration between these seasons. Three study sites were selected: Site 1 (E-1), located at the confluence of the Tuxpan River and the entrance of marine and freshwater currents; Site 2 (E-2), in front of the thermoelectric plant and communicating with the Tamiahua navigation channel; and Site 3 (E-3), in the northern part of the lagoon.
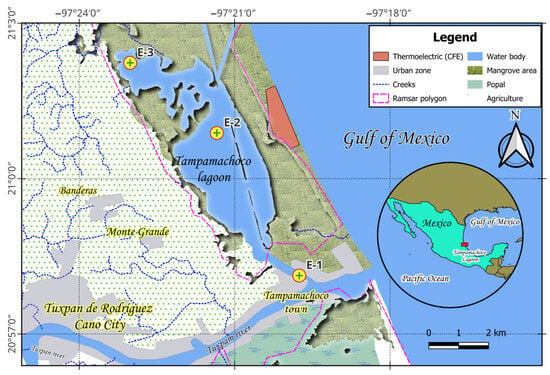
Figure 1.
Geographic location of the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon and study sites.
2.2. Data Processing and Analysis of Hydrometeorological Variables
Information was obtained from CHIRPS (Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data) daily satellite estimates of precipitation (mm day−1), (https://data.chc.ucsb.edu/products/CHIRPS-2.0/, accessed on 1 May 2025), with 0.05° spatial resolution, for the period from January 2019 to December 2020. Additionally, the zonal and meridional components of the wind at 10 m height, with 0.1° spatial resolution, were obtained from ERA5-Land (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu, accessed on 1 May 2025). Pixel data were extracted from pixels that coincide with the location of the Tampamachoco Lagoon, thus obtaining a set of geospatial information that was concatenated into three-dimensional matrices and averaged monthly (mm month−1 for precipitation) for each climatic season of the study period. Subsequently, they were geospatially interpolated to 0.02° using the nearest-neighbor method. In addition, time series were obtained for the three characteristic climatic seasons: rainy (June–October 2019), northerly windstorms (October–February 2020), and dry (November–May 2020). Finally, maps of total monthly precipitation and wind roses were constructed for each climatic season.
Additionally, for the elaboration of the pollutant dispersion maps, the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) (https://www.ready.noaa.gov/hypub-bin/dispasrc.pl, accessed on 5 May 2025) software and meteorological data from NAM 12 Km (pressure, U.S., 05/2007-present) were used to model the dispersion of the plume emitted by the Adolfo López Mateos thermoelectric power plant. Modeling considered the three monitoring dates, namely, 13 October 2019, 19 January 2020, and 24 May 2020, to cover the study periods defined according to the influence of the wind direction. The first corresponds to the end of the rains and is influenced by northern winds; the second covers northerly windstorms (NWSs); and the third is the dry season, characterized by dominant southern and northern winds.
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
At each sampling site, the following environmental variables were recorded in situ: dissolved oxygen (DO, mg L−1), air and water temperature (°C), pH, and salinity (PSU), all measured at a 0.3 m depth with a multiparameter probe (Hydrolab Quanta, Kempten, Germany), and transparency using a Secchi disk. Three water and three seston samples were collected in duplicate during each season (a total of 18 samples) over the study period: rainy (RS, October 2019), northerly windstorms (WS, January 2020), and dry (DS, May 2020) seasons (nine water/seston samples in total). Seston samples were obtained using a 15 min horizontal trawl with a 300 µm mesh plankton net 15 cm in diameter and 30 cm in depth. The estimated volume of water was 15.5 m3 per tow, based on the net mouth area and the distance covered [25]. The samples were placed separately in HDPE flasks and transported to the laboratory under cold conditions. Once in the laboratory, water samples were tested for the following nutrients (mg L−1): total nitrogen (NT), ammoniacal nitrogen (NH4+), nitrates (NO3−), nitrites (NO2−), total phosphorus (PT), orthophosphates (PO43−), and sulfates (SO42−). Furthermore, total suspended solids (TSS, mg L−1) and color (Pt-Co) were determined in triplicate according to HACH DR3900 spectrophotometer (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA) techniques; while chlorides (Cl− mg L−1), calcium carbonate (CaCO3 mg L−1), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5, mg L−1), and fecal coliforms (MPN 100 mL−1) were determined following American Public Health Association techniques [26].
2.4. Metal Quantification
All water and seston samples were tested for metal concentrations (Cd, Hg, Cr, Cu, Pb, Fe, and Mn). To this end, all samples were digested in a Multiwave GO Anton-Paar (Anton-Paar, Graz, Austria) microwave oven according to EPA protocols. The samples were digested with 70% nitric acid (HNO3). For water samples, we added 9 mL of HNO3 to a 22.5 mL sample (Method 3051 [half-scale]); for seston samples, 9 mL of HNO3 was added to a 250 mg sample (Organic Method B). Subsequently, the samples were volumetrically diluted to 25 mL with deionized water. Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Fe, and Mn concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) (Agilent Technologies, Spectra AA 240 FS Santa Clara, CA, USA); Hg was measured by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (Agilent Technologies, Spectra 220 PSD120, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For quality control, the tests included standard calibration solutions of each metal and reagent blanks, which were processed following the same digestion and test protocol, with an average of three runs per sample considered in all cases. Additionally, for each batch of 5 samples, a duplicate and a reference standard were used as internal test controls, as well as CRM-SW-2006423 (simulated seawater standard; HPS, ZeptoMetrix, Buffalo, NY, USA) as a reference material. The recovery values of the selected metals ranged from 80 to 120%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) was <10% for all tests. Metal concentrations were expressed in mg L−1 for water samples and in mg kg−1 (dry weight) for seston samples.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Data on the physicochemical characteristics and metal concentrations in water and seston were tested for significant differences between study sites and seasons. First, each dataset was assessed for normality and homoscedasticity with the Shapiro–Wilk test. For non-parametric data, the Kruskal–Wallis test was applied, followed by Dunn’s post hoc test [27]. Principal Component Analyses (PCAs) were performed to identify the main factors or processes that explained the variability of the dataset, as well as the relationships between the variables analyzed. To this end, the data for environmental variables and metal concentrations were standardized using Ln(x + 1) to ensure that all transformed values were positive. One PCA was run for water, and another for seston, for each site and season. To reduce dimensionality, only variables with high factor loadings in the first two principal components were selected in the PCAs. To select the number of components to be retained in the analysis, we used a scree plot of the eigenvalues against the component number. We then identified the point of inflection where the rate of decrease in the explained variance noticeably slowed. Accordingly, we retained the components that appeared before this inflection point [28]. All statistical analyses were performed using XLSTAT software (XLSTAT software V. 2020.4.1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrometeorological Forcing and Dispersion of Atmospheric Pollutants
3.1.1. Hydrometeorology
Precipitation in the Tampamachoco Lagoon zone for the 2019 rainy season showed a decreasing latitudinal gradient in a northwest–southeast direction, from 580 mm month−1 to 500 mm month−1 (Figure 2a(1’)). Additionally, during this season, the wind predominantly blew from the southeast, with intensities of 5 m s−1, accompanied by a component from the northwest flowing at 3 m s−1; this latter component contributed humidity from the Tamiahua Lagoon and heavy rainfall in the north of the lagoon. On the other hand, the 2020 northerly windstorm season (Figure 2a(2’)) exhibited a decreasing precipitation gradient in the northeast–southwest direction, with values ranging from 198 mm month−1 to 184 mm month−1; the northern region of the lagoon recorded values close to 190 mm month−1. The wind direction in this season was predominantly from the northwest, with intensities between 1.1 m s−1 and 3 ms−1. Finally, the 2020 dry season (Figure 2a(3’)) allowed us to identify the maximum (>425 mm month−1) and minimum (<410 mm month−1) precipitation in the northern and southern regions of the lagoon, respectively. The predominant wind in this period blew from the northwest, with intensities between 1.1 m s−1 and 3 m s−1, and with a significant component from the east, with intensities between 3.1 m s−1 and 5 m s−1.
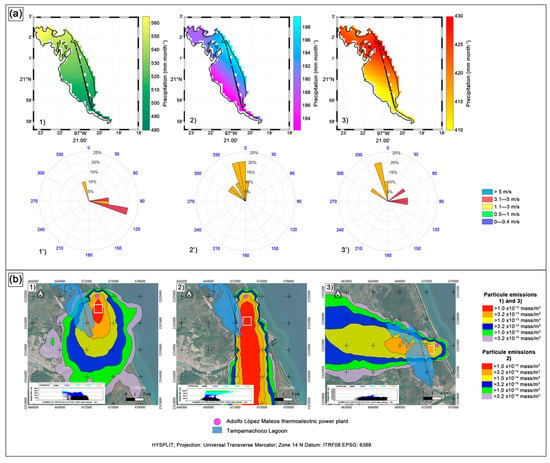
Figure 2.
(a) Spatial and temporal distribution of cumulative precipitation patterns for the (1’) 2019 rainy season, (2’) 2020 northerly windstorm season, and (3’) 2020 dry season in the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon. (b) Dispersion of particulate emissions from the Adolfo Lopez Mateos thermoelectric power plant, determined using the HYSPLIT software. (1) Rainy season; (2) northerly windstorm season; (3) dry season.
3.1.2. Dispersion of Atmospheric Pollutants
The particulate plume emitted by the Adolfo López Mateos thermoelectric power plant on one of the representative rainy and northerly windstorm days (13 October 2019) dispersed towards the south of the lagoon, with particulate matter concentrations from >3.2 × 10−15 to >1 × 1012 mass/m3. In the horizontal projection (see the lower-left section of the map), the plume reaches the surface from the 1000 m layer and reaches heights of up to 2500 m (Figure 2b(1)) due to atmospheric dynamics. When these emissions come into contact with the water’s surface, SO2 and NOx solubilize and form sulfates, nitrites, and nitrates, with the latter two being nutrients that promote eutrophication [29]. The emissions of power plants generally provide several pollutants to the atmosphere due to the considerable volume of fossil fuels consumed annually. The emissions include a complex mixture of primary pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), and heavy metals of particular concern, such as mercury (Hg) [30]. Likewise, the particulate matter emitted by this thermoelectric plant contains trace metals (Pb, Ni, V, and Hg) [22].
The particulate emission plume of 19 January 2020, representative of the northerly windstorm season, spread beyond the southwestern area of the Tampamachoco Lagoon, with a southward dispersion direction and particulate matter concentrations ranging from >3.2 × 10−16 to >1 × 10−13 mass/m3. The horizontal projection shows that the particles reach the surface from the 3000 m layer and reach an altitude of 1200 m (Figure 2b(2)). This suggests that the gases (SO2 and NOX) and particles emitted by the thermoelectric plant probably come into contact with the lagoon water, which would promote the effect described above.
Particulate matter in the pollutant plume could cause an adverse impact because, unlike gases, particles containing heavy metals, such as Cd, Hg, Cr, Cu, Pb, Fe, and Mn, tend to settle more quickly. Due to their high toxicity, these metals pose a potential risk for both the organisms inhabiting the lagoon ecosystem and the surrounding human population [31]. Additionally, SO2 and NOx gases can lead to the formation of strong acids, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), lowering the pH of the water body [32]. During the dry season (24 May 2020), the emission plume was dispersed in a westerly direction, flowing over the northern and central parts of the Tampamachoco Lagoon (Figure 2b(3)), with particulate matter concentrations from >3.2 × 10−15 to >1 × 10−13 mass/m3. In the horizontal projection, the plume contacts the surface in the 2000 m layer and reaches a height of 4000 m. Therefore, it can be inferred that the emission also contacts the lagoon water.
Climate variability significantly impacts the transport, fate, and biogeochemical aspects of trace metals in coastal marine ecosystems. Zitoun et al. [33] stated that increased precipitation and extreme weather events can mobilize stored metals, while rising temperatures and acidification can alter the solubility, toxicity, and bioaccumulation processes of these elements. Furthermore, Li et al. [34] showed the relationship between climate and transport, highlighting the key factor in meteorological trends that are influenced by wind patterns and the wet deposition of trace metals driven by climate change at the regional and local levels, all of which can be depicted by atmospheric modeling.
3.2. Environmental Water Variables and Nutrient Distribution
The mean nutrient concentrations (minimum, maximum, and standard deviation) are shown in Table 1. The water temperature showed statistical differences (Kruskal–Wallis; p = 0.01) between the northerly windstorm and dry seasons (25.1 ± 0.4 °C vs. 30 ± 1.01 °C; Figure 3a). These values are within the mean range previously recorded for Tampamachoco (26.8–29.9 °C) and other coastal lagoons in the Gulf of Mexico, such as Alvarado, La Mancha, Grande and Chica, and Casitas [35]. Likewise, temporal differences in DO concentration were observed (Kruskal–Wallis; p = 0.01), with the highest values during the northerly windstorm season and the lowest in the dry season (Figure 3b). In contrast, although no significant differences were observed between seasons in terms of salinity and pH, temporal trends were detected. Salinity concentrations were lowest during the rainy season and highest in the dry season (26.5 PSU and 35 PSU, respectively; Figure 3c), highlighting the salinity-lowering influence of freshwater in the rainy season. On the other hand, the higher salinity values recorded during the dry season are consistent with those reported by Rivera-Guzmán et al. [35], who observed an increase in salinity in the Tampamachoco and La Mancha lagoons, associated with the dredging of navigation channels, which altered the balance between freshwater and seawater. For its part, pH had alkaline-to-neutral values (Figure 3d), with peak values in the northerly windstorm season (8.7 ± 0.14) and minimum values in the dry season (7.8 ± 0.11). These values are within the range reported for other Gulf of Mexico coastal lagoons [36,37]. During the dry season, the emission plume flows westward, reaching the northern and central areas of the lagoon (Figure 2), where SO2 and NOx gases (from plume emissions) may lead to the formation of strong acids, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), which likely contribute to the decrease in pH [32].

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of nutrient concentrations during the three sampling periods in the Tampamachoco Lagoon (rainy, northerly windstorms, and dry seasons).
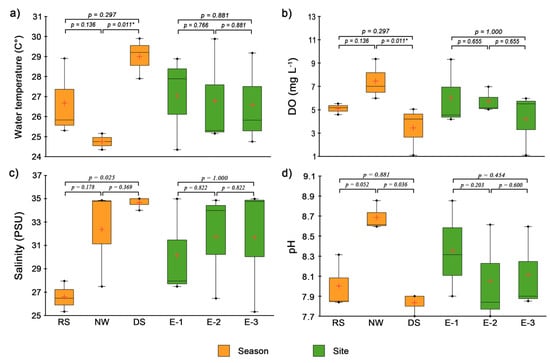
Figure 3.
Temporal and spatial variation in environmental variables determined in situ during the rainy, northerly windstorm, and dry seasons in the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon, Veracruz. (a) Water temperature, (b) Dissolved oxygen, (c) Salinity, and (d) pH. * Indicates statistical significance.
On the other hand, alkalinity, hardness, chlorides, total suspended solids (TSS), and fecal coliforms did not show significant differences between seasons (Kruskal–Wallis; p > 0.05). TSS was higher in the dry season and lower in the northerly windstorm season (61.5 vs. 7.5 mg L−1), with the northernmost zone returning the highest average value (38.5 mg L−1). Cl− values peaked in the dry season and dropped in the rainy season (16.907 g L−1 vs. 13.018 g L−1). During the dry season, higher chloride values indicate the influence of seawater [38]. In contrast, in the rainy season, the lower Cl− level is primarily due to dilution by freshwater runoff, which reduces the salinity of the lagoon. The mean hardness (CaCO3) ranged from 95 ± 3.5 mg L−1 in the rainy season to 40 ± 2 mg L−1 in the dry season. During the rainy season, increased watershed runoff can facilitate the transport of dissolved minerals, leading to a significant increase in calcium and magnesium concentrations in water bodies [39]. Concerning potential fecal sewage pollution, fecal coliforms are considered to be the most important indicators [40]. High concentrations of fecal coliforms are commonly associated with untreated sewage discharges, posing a risk to ecosystem health and public safety. According to the Mexican Official Standard NMX-AA-042-SCFI-2015 (https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/166147/nmx-aa-042-scfi-2015.pdf, accessed on 4 March 2025) the maximum concentration allowed in coastal lagoons for recreational and fishing activities is 240 NMP 100 mL−1. In the present study, the maximum values of coliforms were recorded in the rainy season (460 NMP 100 mL−1) at Sites E-2 and E-3, and in the dry season (1100 NMP 100 mL−1) at Site E-1. The higher concentration of fecal coliforms at Site E-1 is probably associated with domestic discharges from the Tuxpan River.
Seasonal variations in nutrient levels are above the values reported for this lagoon [35,36,37]. The seasonal analysis showed an increase in the levels of nitrogenous compounds (NO2−, NO3−, and NH4+) from the dry season to the northerly windstorm and rainy seasons (Figure 4a,c,e). Furthermore, a gradient of increasing concentrations was detected from the mouth of the lagoon (E-1) towards the innermost part (E-3). This trend was also observed by Contreras et al. [36], who evaluated that the maximum nitrate and nitrite concentrations in 33 of the 39 coastal lagoons studied in the Gulf of Mexico and Pacific occurred in the rainy season. Likewise, Pérez-Rufaza et al. [41] recorded a positive correlation between the increase in nitrate concentration and the average accumulated precipitation, associating runoff from the drainage basin and excessive fertilizer use as the main sources of this nutrient. In the Tampamachoco Lagoon, the maximum accumulated precipitation occurred during the rainy season, approximately 580 mm month−1, with a latitudinal gradient in a northwest–southeast direction (Figure 2a). This gradient was reflected in increased nutrient levels in the northernmost areas of the lagoon, which are adjacent to cultivated pastures (Figure 1), facilitating nutrient inputs to the water body through runoff from agricultural areas in the region. In addition, atmospheric inputs may also contribute to the increase detected based on historical data before the year 2000 [36].
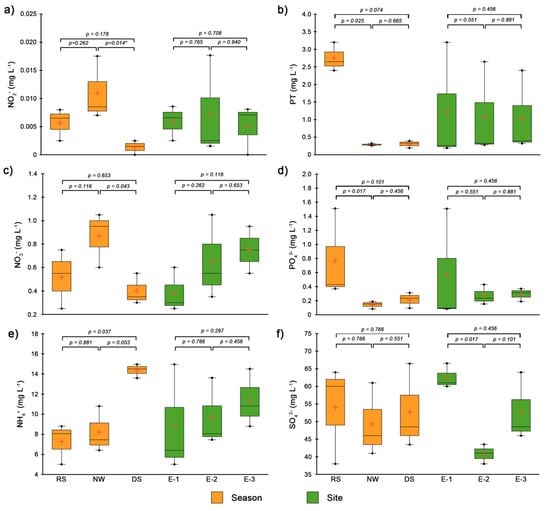
Figure 4.
Temporal and spatial variation in environmental variables and nutrients in the rainy, northerly windstorm, and dry seasons in the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon, Veracruz. (a) Nitrites, (b) Total Phosphorus, (c) Nitrates, (d) Orthophosphates, (e) Ammonium, and (f) Sulfates. * Indicates statistical significance.
Total phosphorus and orthophosphates were highest in the rainy season and lowest in the northerly windstorm season, reaching mean values of 2.53 mg L−1 and 0.40 mg L−1, respectively (Figure 4b,d). Particularly, in the spatial analysis, it was observed that Site E-1 had the highest orthophosphate values (1.51 mg L−1), indicating the influence of discharges from the Tuxpan River. Coastal lagoons with permanent connections to rivers and the adjacent oceanic shelf are subjected to a continuous exchange of materials, nutrients, and energy, with the drainage basin on one side and the ocean on the other, leading to conspicuous spatial gradients. In turn, seasonality in river discharges and particular watershed features contribute to the intra-annual variability in N, TP, and C inputs in shallow subtropical coastal bodies [42]. The total phosphorus and orthophosphate concentrations reported in this study are above those previously recorded in the lagoon, exceeding the range of average concentrations (0.47–0.95 mg L−1) for coastal lagoons in Mexico [43]. Phosphorus accumulation and leaching have been widely studied in recent decades, associating excessive inputs of phosphorus compounds from anthropogenic activities as one of the primary causes of eutrophication and algal blooms in receiving water bodies [44]. In the present study, in the rainy season, only Site E1 (mouth of the lagoon) reached values characteristic of eutrophic conditions. According to Gutiérrez-Mendieta & De la Lanza Espino [43], the increase in orthophosphate concentration is associated not only with anthropogenic discharges to rivers but also with the geomorphology and phosphate geochemistry of each lagoon system. The primary factors influencing the release of phosphorus (P) from sediments are sedimentation rates, tides, and anoxic reduction processes [45].
Sulfates (SO42−) did not show a clear seasonal variation pattern during the study period (Figure 4f), with a slight increase (61–66.5 mg L−1) observed at the mouth of the lagoon (Site E-1). According to Maurya and Kumari [46], the average sulfate concentration in the ocean is 2712 mg L−1, indicating that the origin of this anion in mangrove areas is mainly marine. The sulfate concentrations recorded in the present study are below those reported in estuaries with high evaporation rates and marine influence (5141.82–3855.45 mg L−1). However, the reported values are very similar to those observed in estuaries such as Laguna dos Patos, in southern Brazil, where the low sulfate concentration (64–86 mg L−1) observed in the winter is directly influenced by the intensity of freshwater discharges to the estuary from its tributaries [47].
3.3. Distribution of Dissolved Heavy Metals in Water and Seston
The metals measured in the water were found in the following order according to their concentration: Fe > Mn > Cr > Cd > Pb > Cu > Hg. The seasonal analysis did not reveal significant differences (Kruskal–Wallis; p > 0.05). In the spatial analysis, a gradient of decreasing Pb, Fe, and Mn concentrations was recorded from the innermost zone to the mouth of the lagoon (Figure 5). This pattern is very similar to that reported for several coastal lagoons, where the accumulation of metals in the inner portion corresponds to the increase in suspended particles, fine sludge, and organic matter, as well as to the increase in the cation-exchange capacity of the sediments [48]. Additionally, the study site associated with the thermoelectric plant (E-2) had the highest Hg levels during the rainy season. Previous studies in the lagoon reported that high Hg levels in aquatic organisms are associated with power plant emissions that reach the lagoon through wet and dry deposition [6,22]. Separately, the highest Cd and Cu concentrations were recorded in the rainy season at the site associated with discharges from the Tuxpan River and the inflow of marine currents (E-1) (Figure 5). These findings are consistent with those reported for the Pearl Estuary in southern China, where high concentrations of dissolved Cd and Cu were attributed to inputs from the river delta, which carried signals of anthropogenic origin (particularly Cd and Cu) influenced by industrial and waste effluents [49].
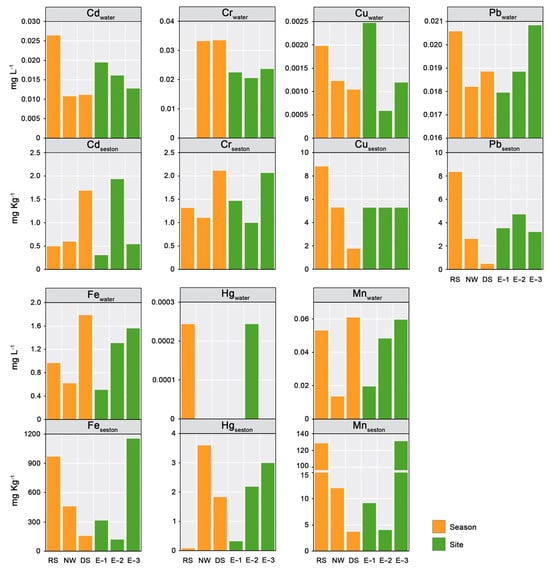
Figure 5.
Metal concentrations in water and seston in the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon.
The metals in seston showed the following order of concentration: Fe > Mn > Pb> Cu > Cr > Hg. No significant differences were observed between sites or seasons (Kruskal–Wallis; p > 0.05). The spatiotemporal analysis showed that, similar to the distribution pattern observed in water, during the rainy season, the highest Fe and Mn levels were observed at the innermost lagoon site (E-3), and the highest Pb levels were found at the site closest to the thermoelectric plant (E-2) (Figure 1). Likewise, the Cu concentrations were evenly distributed across the analyzed sites, with a slight increase in the rainy season. During the northerly windstorm and dry seasons, the highest Hg levels in seston were recorded in the central and northern parts of the lagoon (E-2 and E-3). Hg, particularly as Hg2+, is strongly adsorbed to organic particles, sulfides, and metal oxides present in the seston [50]. The difference in metal concentrations, up to four orders of magnitude higher in seston than in water, suggests the influence of point pollution sources (i.e., emissions from the thermoelectric plant) and local biogeochemical processes. Moreover, the aforementioned difference highlights the capacity of seston to adsorb or accumulate dissolved metals, as well as its role in regulating metal transfer across the trophic web. During northerly windstorms, the prevailing northern winds cause the emission plume to move southward. In contrast, during the dry season, it blows westward (Figure 2a(2’,3′)), encompassing a greater area over the lagoon and directly contributing to increased Hg levels in the seston. The wind velocity decreases during the dry season, promoting higher metal deposition. Additionally, these high concentrations could be related to the increase in water temperature (25.1 °C) and pH (8.7), since, according to Lazăr et al. [51], Hg concentrations are positively correlated with both factors. On the other hand, contrary to the spatiotemporal pattern observed in water, increased Cd (Site E-2) and Cr (E-3) concentrations were observed in seston during the dry season. Khan et al. [52] reported a correlation between Cd and Cr levels in wastewater, suggesting that a positive correlation between these two metals could be due to similar pollution levels, transport, and common sources. Industries such as steel mills and dyeing are the primary sources of heavy metals, including Cd, Cr, Pb, and Zn.
Our results highlight the strong seasonal variations in the concentrations of certain metals in seston, such as Pb, Cu, Mn, and Fe, which increase during the rainy season and reach their lowest concentrations during the dry season. Caetano and Vale [53] noted that the increase in metals in seston during the rainy season highlights the contribution of runoff from the catchment basin, which transports suspended terrestrial material. Yu et al. [38] highlighted the relevance of the adsorption and desorption of metals in particulate matter. The seston, comprising organic and inorganic particulate matter, is one of the main metal reservoirs, as it adsorbs metals through various mechanisms [9]. Particulate matter can provide binding sites for metal ions [54] and can also be adsorbed through electrostatic attraction and surface complexation reactions [55]. The contents and distribution of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter are primarily controlled by runoff input, hydrodynamic processes, and the interaction between seawater and freshwater in estuaries [21]. These adsorption processes may explain the higher concentration of metals in seston than in the water in the Tampamachoco Lagoon. The degree of adsorption of metals in seston also depends on their concentration in water [56], the surface area and composition of particulate matter [55], the presence of competing ions [57], and environmental conditions, such as pH [58]. In the case of the Tampamachoco Lagoon, the pH is neutral to slightly alkaline, so its influence is probably minimal. However, the differences in salinity between the rainy and dry seasons (26.5 mg L−1 vs. 35 mg L−1) suggest a possible competitive interaction of the metals adsorbed in seston with salinity in the dry season. This phenomenon could lead to the depletion of metals from the seston by competitive substitution, promoting their desorption. Meanwhile, when salinity decreases during the rainy season, adsorption processes are favored, particularly for Pb, Cu, Mn, and Fe.
Most of the analyzed metal concentrations in the water samples remained below the guideline limits established by the World Health Organization (Fe, 0.3 mg L−1; Mn, 0.2 mg L−1; Cr, 0.05 mg L−1; Cu, 2.0 mg L−1), indicating limited aquatic health or human exposure risks [59]. However, Cd, Pb, and Hg exceeded the recommended Mexican thresholds (Table 2), suggesting potential concerns related to chronic exposure. Therefore, further ecological risk assessment and source control measures are needed.

Table 2.
Heavy metal concentrations in water (mg L−1) and seston (mg kg−1) in different coastal lagoons around the world.
3.4. Effects Range Low (ERL) and Effects Range Median (ERM)
Although there are no international threshold levels specifically established for seston, international sediment guidelines are widely applied to assess pollutant levels in suspended particulate matter. In this study, the metal concentrations were within the ERL/ERM benchmarks, indicating a range between minimal ecological risk and occasional adverse effects [72]. Since no formal ERL/ERM estimates exist for Fe and Mn, their concentrations were evaluated against natural background ranges (Fe, 2000–100,000 mg kg−1; Mn, 2000–40,000 mg kg−1), suggesting no significant anthropogenic enrichment [73].
3.5. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Variability in Physicochemical Parameters and Metals in Water and Seston
In both analyses, we retained the first two PCs that appeared before the inflection point once the decrease rate in the explained variance dropped markedly (Supplementary Materials). Principal component analyses (PCAs) showed temporal and spatial variations in the environmental variables and metals measured in the water and seston samples (Figure 6a, b). For water samples, the first two PCA components explained 58.45% of the total variance, showing a marked spatiotemporal segregation. The dry season (DS) is on the left side (with the highest temperature, chloride, and salinity values), while the rainy (RS) and northerly windstorm (NW) seasons are on the right side (with the highest precipitation, dissolved oxygen, water hardness, and nitrates) (Figure 6a). In the spatial context, in the upper-right quadrant, regardless of the study season, Site E-1 (lagoon mouth) was associated with the highest Cd concentrations, and high DBO5 and DO levels were reached in RS and NW, respectively. This site recorded high transparency in the dry season.
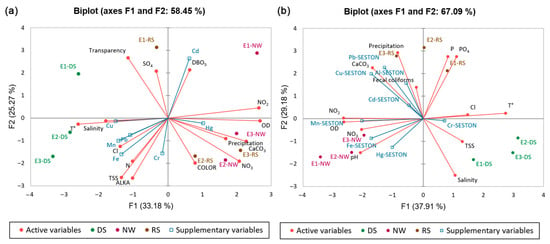
Figure 6.
Analysis of the distribution of environmental variables and metals in (a) water and (b) seston of the Tampamachoco coastal lagoon, including the sampling Sites E-1, E-2, and E-3, and the study seasons DS (dry season), NW (northerly windstorms), and RS (rainy season).
On the other hand, in the lower-right quadrant, Sites E-2 (site close to the power plant) and E-3 (northernmost area) showed high Hg and Cr concentrations, respectively, in the NW and RS seasons, along with high nitrogen (NO3− y NO2−), CaCO3, precipitation, and color, particularly in the RS. In contrast, during the DS season, these sites (E-2 and E-3) (lower-left quadrant) showed high concentrations of Mn and Fe, followed by Pb and Cu, as well as high salinity, chlorides, total nitrogen, TSS, and alkalinity levels. The marked release of metals such as Mn and Fe from sediments in river-margin ecosystems has been associated with the continuous supply of particulate matter [74]. In sediments, dissolved Fe and Mn are produced through the reductive dissolution of Fe and Mn oxides, which is influenced by the degradation of organic matter and the production of reducing compounds, such as sulfides [75]. Regarding the patterns observed in RS and NW, Pan et al. [76] associated the increase in pollutant and nutrient loads (nitrogen, total phosphorus, and orthophosphates) with runoff. Rainfall promotes the input of materials from the catchment basin and suspended materials from tributaries, which can also confer a particular color to the water [77]. Particles and gases emitted by the Adolfo López Mateos power plant, including fine particles (PM2.5 and PM10) and trace metals (Pb, Ni, V, and Hg), can enter water bodies through wet deposition during the rainy and northerly windstorm seasons [22]. During this process, gases such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) released in the emission plume are solubilized in water and form sulfates, nitrites, and nitrates [29]. In turn, agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, along with improper household waste disposal, can increase the concentrations of metals such as Cd [78]. In the present study, the Cd concentrations at the lagoon mouth were higher than those recorded in the interior, evidencing that the Tuxpan River is a significant source of cadmium pollution at this site. Additionally, the association of this metal with BOD5 (an indicator of high organic matter content) suggests that the source of pollution is related to organic inputs from wastewater.
On the other hand, the PCA of the metal distribution in seston (Figure 6b) showed marked seasonal segregation between the analyzed sites, with an explained variance of 67.09% in the first two principal components. In the RS (upper quadrants), Sites E-2 and E-3 were associated with the highest Pb, Cu, Al, and Cd concentrations in seston, and with high values of precipitation, CaCO3, and fecal coliforms. Similarly, during this season, Site E-1 was associated with high concentrations of total phosphorus and orthophosphates, indicating that the Tuxpan River is a likely source of phosphorus inputs to the lagoon. On the other hand, in the NW, the three study sites (lower-left quadrant) were associated with high Hg, Fe, and Mn levels in seston, along with the highest values of DO, pH, NO2−, and NO3−. Meanwhile, during the dry season, the three study sites were associated with high Cr levels in seston, with high values of SST, salinity, Cl−, and water temperature. The enrichment of nutrients such as phosphorus has been reported to be frequently associated with terrestrial runoff and the discharge of industrial and household wastes [40]. The human population near the Tampamachoco Lagoon has doubled in the past 20 years, and the population of the largest city in the sub-basin has almost tripled due to its proximity to the Port of Tuxpan [35]. Several studies have highlighted the role of seston in the distribution and transport of heavy metals, particularly as a carrier of Al, Cu, Cr, Cd, Pb, and Hg [6]. Sediment resuspension and transport have been analyzed in correlation with wind intensity [79]. In shallow water bodies, light winds produce waves that cause sediment resuspension [80]. This is particularly the case in Tampamachoco, which has a mean depth of 1.5 m [23].
One of the most significant contributions to this field is the identification of seston as a central factor in the trophic transfer of pollutants [6]. Therefore, effective metal pollution management in the lagoon requires an integrated strategy that combines pollution prevention, source identification, ecological risk assessment, and remediation. Given that the main source of metal input is the emissions plume from the thermoelectric plant, it is essential to transition to a combined-cycle plant powered by natural gas. Additionally, a restoration plan should incorporate adaptive management, allowing remediation actions to evolve based on continuous monitoring and evaluation [81].
Particulate matter in the pollutant plume could cause an adverse impact because, unlike gases, particles containing heavy metals, such as Cd, Hg, Cr, Cu, Pb, Fe, and Mn, tend to settle more quickly. Due to their high toxicity, these metals pose a potential risk for both the organisms inhabiting the lagoon ecosystem and the surrounding human population [31]. Additionally, SO2 and NOx gases can lead to the formation of strong acids, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), lowering the pH of the water body [32]. During the dry season (24 May 2020), the emission plume was dispersed in a westerly direction, flowing over the northern and central parts of the Tampamachoco Lagoon (Figure 3c), with particulate matter concentrations from >3.2 × 10−15 to >1 × 10−13 mass/m3. In the horizontal projection, the plume contacts the surface in the 2000 m layer and reaches a height of 4000 m. Therefore, it can be inferred that the emission also contacts the lagoon water.
The study of heavy metals in seston is relevant in coastal areas, characterized by high levels of particulate material and metal discharges from natural and anthropogenic sources. Since seston plays a fundamental role as the base of the food web, serving as a primary source for filter-feeding organisms, pollutants associated with seston can be readily transferred through the food chain, with potential implications for biomagnification across trophic levels. Therefore, monitoring the metal concentrations in seston is critical for understanding ecosystem health and potential risks to higher consumers (including commercially important species and humans) [9,22].
4. Conclusions
The heavy metals evaluated in the present study (Hg, Pb, Cr, Cd, Fe, and Mn) exhibited marked spatial and temporal variations in water. Although no statistically significant differences were found in seston, seasonal trends were evident. The highest Pb, Fe, and Mn concentrations in water and seston were recorded in the innermost part of the lagoon, likely due to the accumulation of suspended particles and sediments. The spatial distribution of Hg suggests that it is associated with thermoelectric plant emissions, while Cd and Cu are related to industrial and household waste effluents from Tuxpan River discharges. In the Tampamachoco Lagoon, the maximum precipitation occurred during the rainy season, producing a latitudinal gradient that led to increased nutrient levels in the northernmost areas, associated with agricultural runoff. In addition, atmospheric inputs associated with emissions from the thermoelectric plant can increase the concentrations of metals and nitrogen oxides (NOx). In particular, the higher Hg concentrations in seston during the northerly windstorm season could result from the deposition of particulate matter from pollutant emissions associated with stationary sources, biogeochemical processes, and sediment resuspension. Moreover, the rise in fecal coliforms at the site, directly influenced by river inputs, indicates pollution from household sources. This wastewater may also contribute to nutrient enrichment (e.g., phosphorus) in the lagoon system. In the present study, the metal concentrations were up to four orders of magnitude higher in seston than in water, demonstrating a high affinity of metals for seston, and highlighting the role of adsorption processes in their distribution. These findings have important ecological, biogeochemical, and toxicological implications, as seston (being at the base of the trophic web) plays a key role in metals’ transfer to higher trophic levels through ingestion and biomagnification, posing potential risks to ecosystem health. Therefore, this study highlights the importance of incorporating seston into the assessment of aquatic ecosystems.
5. Future Perspectives
Despite the existence of a water quality monitoring network in Mexico, where different parameters are measured, there is poor coordination with other monitoring networks, e.g., air quality. Hence, the potential effects of atmospheric pollutants on water are neither considered nor linked to the emission sources. Water quality regulations have always been designed for the control of wastewater pollutants. However, given the current dynamics, pollutants can reach water bodies through different pathways. Thus, water quality regulations need to be rethought to integrate the different pollution sources. In this sense, our findings highlight the role of seston as a reservoir of pollutants that has not been specifically considered in the monitoring of water bodies. Additionally, these results identified atmospheric pollutant emissions as a source that impacts water bodies, along with the influence of hydrometeorological variability on the input of pollutants to the lagoon. Therefore, it is mandatory to establish new models for environmental monitoring.
Therefore, the current monitoring plan should be redirected towards the achievement of new strategic objectives that truly integrate the different pollutant sources that reach water bodies, so as to protect and conserve biodiversity and aquatic ecosystems. Behmel et al. [82] indicated that one approach to optimize the monitoring objectives is to assess whether new problems have emerged that need to be addressed. The challenges that have been reviewed in the present study include the changing climatic conditions, atmospheric pollutants not previously considered to impact water bodies, and a component of aquatic ecosystems (seston) rarely considered to influence pollutant transfer processes. Therefore, we strongly recommend reviewing water quality monitoring policies to link them with atmospheric monitoring.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17131929/s1. Figure S1. Explained variance of each PC showing the inflection point and decrease in explained variance. (a) For the PCA of seston, (b) For the PCA of water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.-M., E.L.-L., H.A.B.-H. and J.E.S.-D.; methodology, A.R.-M., E.L.-L., H.A.B.-H. and J.E.S.-D.; software, A.R.-M., H.A.B.-H. and E.M.-A.; validation, A.R.-M.; formal analysis, A.R.-M.; investigation, A.R.-M., E.L.-L., H.A.B.-H., S.A.-G., R.C.-D., J.E.S.-D. and E.M.-A.; resources, H.A.B.-H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R.-M.; writing—review and editing, A.R.-M., E.L.-L., H.A.B.-H., S.A.-G., R.C.-D., E.M.-A. and J.E.S.-D.; visualization, A.R.-M. and E.L.-L.; supervision, E.L.-L.; project administration, H.A.B.-H.; funding acquisition, H.A.B.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado, grant number 20254770-PRORED, and the APC was funded by the Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request to the corresponding author, due to institutional restrictions related to the confidentiality of information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Vieira, L.R.; Morgado, F.; Nogueira, A.J.; Soares, A.M.; Guilhermino, L. Integrated multivariate approach of ecological and ecotoxicological parameters in coastal environmental monitoring studies. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Morkune, R.; Marcos, C.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Razinkovas-Baziukas, A. Can an oligotrophic coastal lagoon support high biological productivity? Sources and pathways of primary production. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 153, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; He, X.; Wu, X. Geological evolution of offshore pollution and its long-term potential impacts on marine ecosystems. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarska, D.; Kiedrzyńska, E.; Jaszczyszyn, K. A global perspective on the nature and fate of heavy metals polluting water ecosystems, and their impact and remediation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 54, 1436–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duysak, Ö.; Uğurlu, E. Trace Metal Concentrations in the Seston of the Gulf of İskenderun (Turkey, North-Eastern Mediterranean). Thalassas 2020, 36, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Márquez, A.; Aguíñiga-García, S.; Morales-García, S.S.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E. Temporal distribution patterns of metals in water, sediment, and components of the trophic structure in a tropical coastal lagoon of the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61643–61661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Yang, K. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment, northeast Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showell, M.A.; Gaskin, D.E. Partitioning of cadmium and lead within seston of coastal marine Waters of the Western Bay of Fundy, Canada | Enhanced Reader. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1992, 22, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Severini, M.D.; Villagran, D.M.; Biancalana, F.; Berasategui, A.A.; Spetter, C.V.; Tartara, M.N.; Menendez, M.C.; Guinder, V.A.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Heavy Metal Concentrations Found in Seston and Microplankton from an Impacted Temperate Shallow Estuary along the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 335, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, P.; Souza, C.M.M.A.; Rezende, C.E. Linking major nutrients (C, H, N, and P) to trace metals (Fe, Mn, and Cu) in lake seston in southern Brazil. Limnology 2007, 8, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Xu, H. Qualitative Dynamics of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Changjiang Estuary from Geostationary Ocean Color Images: An Empirical, Regional Modeling Approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Marini, M.E.; Soto-Jiménez, M.F.; Páez-Osuna, F. Trophic relationships and transference of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in a subtropical coastal lagoon food web from SE Gulf of California. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Marini, M.E.; Molina-García, A.; Martínez-Durazo, Á.; Páez-Osuna, F. Trace metal trophic transference and biomagnification in a semiarid coastal lagoon impacted by agriculture and shrimp aquaculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5323–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara-Marini, M.E.; Soto-Jiménez, M.F.; Páez-Osuna, F. Mercury transfer in a subtropical coastal lagoon food web (SE Gulf of California) under two contrasting climatic conditions. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Soto, M.C.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Basterretxea, G. Seasonal variation and sources of dissolved trace metals in Maó Harbour, Minorca Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, L.L.; Nemirovskaya, I.A. Spatial distribution of microelements in the seston of the White Sea. Oceanology 2007, 47, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirak, A.; Yılmaz, H.A.; Keskin, F.; Şahin, Y.; Akpolat, O. Investigation of heavy metal content in the suspended particulate matter and sediments of inner Gokova Bay and creeks. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7113–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, R.E. Concentrations of dissolved and suspended particulate Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in surface waters around the coasts of England and Wales and in adjacent seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.N.; van Geen, A.; Lee, B.G.; Cloern, J.E. Metal uptake by phytoplankton during a bloom in South San Francisco Bay: Implications for metal cycling in estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.F.; Flegal, A.R. Lead in marine planktonic organisms and pelagic food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ahmed, M.K.; Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; et al. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in suspended particles in the Sundarban mangrove river, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala-Cortés, M.; Barrera-Huertas, H.A.; Sedeño-Díaz, J.E.; López-López, E. Impact of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) from a Thermoelectric Power Plant on Morpho-Functional Traits of Rhizophora mangle L. Leaves. Forests 2023, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezcua, F.; Bellgraph, B. Fisheries Management of Mexican and Central American Estuaries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Austria-Ortíz, G.M.; Reyes-Márquez, A.; López-López, E.; Aguíñiga-García, S.; López-Martínez, J. Temporal variability (1966–2020) of the fish assemblage and hydrometeorology of the Tampamachoco Lagoon, Veracruz, Mexico: Pre-and during COVID-19 scenario. In Environmental Resilience and Transformation in Times of COVID-19; Ramanathan, A.L., Sabarathinam, C., Arriola, F., Prasanna, M.V., Kumar, P., Jonathan, M.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.; Wiebe, P.; Lenz, J.; Skjoldal, H.R.; Huntley, M. (Eds.) ICES Zooplankton Methodology Manual; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. WIREs Comp. Stats. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency-EPA. Óxidos de Nitrógeno (NOx): ¿Por qué y Cómo se Controlan? Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttncatc1/cica/files/fnoxdocs.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Iniciativa Climática de México. Estudio sobre la Influencia de la Central Termoeléctrica de Tula, Hidalgo, en la Calidad del Aire Regional. 2021, pp. 1–32. Available online: https://www.iniciativaclimatica.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Central-Termoele%CC%81ctrica-Tula.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Pabón, S.E.; Benítez, R.; Sarria, R.A.; Gallo, J.A. Gallo. Water contamination by heavy metals, analysis methods and removal technologies. A review. Entre Cienc. Ing. 2020, 14, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Ecología y Cambio Climático. Análisis del Estado del Arte Sobre el Depósito Atmosférico en México y su Relación con el Cambio Climático. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/410254/INFORME_FINAL_EADAM_V3_INECC.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Zitoun, R.; Marcinek, S.; Hatje, V.; Sander, S.G.; Völker, C.; Sarin, M.; Omanović, D. Climate change driven effects on transport, fate and biogeochemistry of trace element contaminants in coastal marine ecosystems. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, J.; Yang, M.; Meng, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhou, H.; Tong, L.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, X.; et al. Atmospheric wet deposition of trace metal elements: Monitoring and modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Guzmán, N.E.; Moreno-Casasola, P.; Ibarra-Obando, S.E.; Sosa, V.J.; Herrera-Silveira, J. Long term state of coastal lagoons in Veracruz, Mexico: Effects of land use changes in watersheds on seagrasses habitats. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 87, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, F.; Castañeda, O.; Torres-Alvarado, R.; Gutiérrez, F. Nutrientes en 39 lagunas costeras mexicanas. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1996, 44, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Espinosa, F.; Warner, B.G. Ecosystem characteristics and management considerations for coastal wetlands in Mexico. Hydrobiologia 2004, 511, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Ji, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y. Adsorption-desorption characteristics of typical heavy metal pollutants in submerged zone sediments: A case study of the Jialu section in Zhengzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 96055–96074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Ghosh, S.; Satpathy, K.K.; Bhattacharya, B.D.; Sarkar, S.K.; Mishra, P.; Raja, P. Water quality assessment of the ecologically stressed Hooghly River Estuary, India: A multivariate approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Campillo, S.; Fernández-Palacios, J.M.; García-Lacunza, A.; García-Oliva, M.; Ibañez, H.; Navarro-Martínez, P.C.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Quispe-Becerra, J.I.; et al. Long-term dynamic in nutrients, chlorophyll a, and water quality parameters in a coastal lagoon during a process of eutrophication for decades, a sudden break and a relatively rapid recovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Gómez, I.; Villalobos-Zapata, G.J.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A. Spatial and Temporal Hydrological Variations in the Inner Estuaries of a Large Coastal Lagoon of the Southern Gulf of Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Mendieta, F.; de la Lanza Espino, G. Physicochemical Characterization of Mexican Coastal Lagoons, Current Status, and Future Environmental Scenarios. In Mexican Aquatic Environments; Ibáñez, A.L., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, T.; Tian, S.; Wang, L.; Holm, P.E.; Hansen, H.C.B. High-resolution imaging of labile phosphorus and its relationship with iron redox state in lake sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.T.; Rezanezhad, F.; O′Connell, D.W.; Van Cappellen, P. Sediment phosphorus speciation and mobility under dynamic redox conditions. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3585–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.; Kumari, R. Spatiotemporal variation of the nutrients and heavy metals in mangroves using multivariate statistical analysis, Gulf of Kachchh (India). Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Marques, D.; Costa, P.G.; Souza, G.M.; Cardozo, J.G.; Barcarolli, I.F.; Bianchini, A. Selection of biochemical and physiological parameters in the croaker Micropogonias furnieri as biomarkers of chemical contamination in estuaries using a generalized additive model (GAM). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacerda, L.D. Biogeochemistry of Heavy Metals in Coastal Lagoons; Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Lin, W.; Yang, X.; Zhai, W.; Dai, M.; Chen, C.T.A. Occurrences of dissolved trace metals (Cu, Cd, and Mn) in the Pearl River Estuary (China), a large river-groundwater-estuary system. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 50–51, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Uria, F.; Morales-Belpaire, I.; Achá, D.; Pouilly, M. Particulate mercury and particulate organic matter in the Itenez basin (Bolivia). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, N.N.; Simionov, I.A.; Petrea, Ș.M.; Iticescu, C.; Georgescu, P.L.; Dima, F.; Antache, A. The influence of climate changes on heavy metals accumulation in Alosa immaculata from the Danube River Basin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.N.; Nafees, M.; Imtiaz, M. Assessment of industrial effluents for heavy metals concentration and evaluation of grass (Phalaris minor) as a pollution indicator. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, M.; Vale, C. Trace-element Al composition of seston and plankton along the Portuguese coast. Acta Oecol. 2003, 24, S341–S349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xia, D.; Jiang, X.; Fu, D.; Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.B. Enhanced bioreduction of iron and arsenic in sediment by biochar amendment influencing microbial community composition and dissolved organic matter content and composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 311, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: Influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Isa, Z.M. Heavy metal transport with adsorption for instantaneous and exponential attenuation of concentration. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Che, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Fu, Z. Adsorption and desorption of heavy metals at water sediment interface based on bayesian model. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Shen, L.Q.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Rosas, P.I.; Báez, A.; Belmont, R. Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) as an indicator of heavy metal pollution in Gulf of Mexico lagoons. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 1983, 20, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, F.S.; Botello, A.V. Metales pesados en la zona costera del Golfo de Mexico y Caribe Mexicano: Una Revision. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2012, 8, 47–61. Available online: https://www.revistascca.unam.mx/rica/index.php/rica/article/view/29312 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Bejarano-Ramirez, I.; Jurado, J.M.; Muñiz-Valencia, R.; Alcázar, A.; Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; Olivos-Ortiz, A.; Rangel, O. Comparative study of As, Cd, Cu, Cr, Mg, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn concentrations between sediment and water from estuary and port. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, E.O. Physico-chemical parameters and heavy metal contents of water from the Mangrove Swamps of Lagos Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria. Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-García, S.S.; de Acacia Pérez-Escamilla, P.; Sujitha, S.B.; Godwyn-Paulson, P.; Zúñiga-Cabezas, A.F.; Jonathan, M.P. Geochemical elements in suspended particulate matter of Ensenada de La Paz Lagoon, Baja California Peninsula, Mexico: Sources, distribution, mass balance and ecotoxicological risks. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, J.; Kremling, K. Trace element fluxes in the northeast Atlantic deep ocean. Deep Sea Res. I 1999, 46, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Colla, N.S.; Negrin, V.L.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Botté, S.E. Dissolved and particulate metals dynamics in a human impacted estuary from the SW Atlantic. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 166, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sudarshan, M.; Jonathan, M.P.; Sarkar, S.K.; Thakur, S. Spatial and seasonal distribution of multi-elements in suspended particulate matter (SPM) in tidally dominated Hooghly river estuary and their ecotoxicological relevance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12658–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suja, S.; Kessarkar, P.M.; Fernandes, L.L.; Kurian, S.; Tomer, A. Spatial and temporal distribution of metals in suspended particulate matter of the Kali estuary. India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chan, F. Spatial distribution and correlation characteristics of heavy metals in the seawater, suspended particulate matter and sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CE-CCA-001/89; CECA Criterios Ecológicos de Calidad del Agua. Diario Oficial de la Fedaración: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 1989.
- Lace, A.; Cleary, J. A Review of Microfluidic Detection Strategies for Heavy Metals in Water. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman Michael, F. NOAA Screening Quick Reference Tables. 1999. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/9327 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Lenstra, W.K.; van Helmond, N.A.; Żygadłowska, O.M.; van Zummeren, R.; Witbaard, R.; Slomp, C.P. Sediments as a Source of Iron, Manganese, Cobalt and Nickel to Continental Shelf Waters (Louisiana, Gulf of Mexico). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 811953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J. Geochemistry of Marine Sediments; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.P.; Wang, Y.S. Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of trace elements at 10 sites in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolin, E.C.; Távora, J.; Fernandes, E.H.L. Long-Term Variability on Suspended Particulate Matter Loads from the Tributaries of the World’s Largest Choked Lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 836739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyere, E.Y.; Adu-Boahen, K.; Boateng, I.; Dadson, I.Y.; Boanu, N.Y.; Kyeremeh, S. Analysis of ecological health status of the Muni Lagoon: Evidence from heavy metal content in its water and fish samples. Geo 2023, 10, e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Echeandía, J.; Bernárdez, P.; Sánchez-Marín, P. Trace metal level variation under strong wind conditions and sediment resuspension in the waters of a coastal lagoon highly impacted by mining activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.O.; Coco, G. Review of wave-driven sediment resuspension and transport in estuaries. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 77–117. [Google Scholar]
- Deepwater Horizon (DWH) Natural Resource Damage Assessment Trustees. Monitoring and Adaptive Management Procedures and Guidelines Manual Version 2.0. Appendix to the Trustee Council Standard Operating Procedures for Implementation of the Natural Resource Restoration for the DWH Oil Spill. December 2021. Available online: http://www.gulfspillrestoration.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Behmel, S.; Damaur, M.; Ludwing, R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Water quality monitoring strategies—A review and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 15, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).