Abstract
Soil erosion poses a significant threat to natural resources and agricultural productivity in arid regions. This study applied the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model to simulate rainfall erosivity and soil erosion risk in the Wadi Allith basin, Saudi Arabia, using rainfall data from 2016 to 2018. The results demonstrated that the basin experienced a predominant slight level of erosion risk, with around 5 tons/ha annually. This study revealed that a very slight erosion risk was predominant in 2016 (97% of the basin area), 2017 (96%), and 2018 (95%), while less than 1% of the study area was exposed to severe erosion risks across all three years. An increasing trend in erosion severity was observed between 2016 and 2018, correlating with rising average annual rainfall amounts of 120 mm, 145 mm, and 155 mm. This underscores the importance of understanding how climatic factors influence soil stability, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity is typically a limiting factor. The successful application of Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and remote sensing tools integrating the various components of the RUSLE model showcases the effectiveness of these technologies in environmental monitoring and risk assessment. These tools facilitate a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to soil erosion, enabling researchers and policymakers to visualize erosion risk across the basin and prioritize areas for intervention. This study highlights the importance of ongoing soil erosion monitoring in arid environments such as the Wadi Allith basin, Saudi Arabia.
1. Introduction
In the last few decades, the drive to protect the environment and natural resources has received widespread focus not only in the scientific community but also among agricultural land management policymakers, water experts, and government agencies. This attention is partly due to the large-scale impacts of human activities on soil, water, and atmospheric resources. For example, about USD 44 billion is spent yearly to mitigate soil erosion-related problems in the US alone, while over 80% of soil problems are linked to soil erosion, which takes a high toll on crop productivity. In Saudi Arabia, soil degradation is a major environmental concern. To address threats such as desertification, soil degradation, and watershed inundation, there is an urgent need to find solutions to conserve natural resources [1].
Models are essential tools in hydrological research for representing the behavior of complex systems and sub-systems. Several models are available within the scientific community to evaluate soil erosion in watersheds [2,3]. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), developed in 1991, has been widely used for soil erosion prediction. Building on this foundation, the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) was designed as a more efficient, flexible, and advanced model for predicting yearly erosion rates in various watershed areas, particularly in ungauged catchments. [4,5].
Several models are available within the scientific community to evaluate soil erosion in watersheds. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), developed in 1991, takes front stage in terms of application for soil erosion prediction efforts [6,7,8,9]. This was followed by the Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (MUSLE) applied to quantify alluvium soil erosion triggered by an individual rainfall event, as formulated by Williams [10]. RUSLE is adaptable for yearly erosion rate prediction for various watershed areas, and it is more versatile when integrated with the local data of a watershed in ungauged catchments [1,11]. Therefore, in estimating soil loss for any given area, it is necessary to acquire all the above values. The Soil Loss Estimation Model for Southern Africa (SLEMSA) was also built following the USLE model, to estimate the loss of soil at regional scales in Africa [12]. SLEMSA demonstrates the adaptability of USLE-based models to various regions and provides a basis for applying a similar approach in the Wadi Allith basin [13]. By drawing on the regional adaptation experience of SLEMSA, this study can better refine the RUSLE-based models to suit the specific conditions of the Wadi Allith basin [2].
The impacts of rainfall erosion are significant in any basin, whether it occurs naturally or results from environmentally destructive human activities. In the upstream part of a basin, soil particles can be transported in the downstream direction by the actions of falling drops, leading to loss of fertile topsoil and exposing the sub-soil to further threats from subsequent rainfall events. Furthermore, at the downstream, the silting of reservoirs can be worsened by overland flow, which washes away loose soils from upstream, bare agricultural fields [14,15].
Rainfall erosivity, a key concept in soil erosion monitoring, refers to the susceptibility of soil aggregates to be displaced and moved within a watershed due to the impacts of rainfall and overland flow. The transfer of sediments within a watershed occurs at various scales and involves several physical laws to explain its phenomenon [16,17]. To better understand and address soil erosion challenges, there is a need for novel, precise, and accessible methods to measure soil erosion. The R-factor, which measures rainfall erosivity in the USLE model, accounts for the energy from rain hitting the soil surface and the movement of water over the land. Specifically, the rill and sheet erosion are added in the evaluation of the R-factor [18]. Gully formation is primarily dependent on runoff depth, as the erosive force of rainfall that triggers soil erosion occurs due to the direct impact of raindrops on the soil [19].
The primary aim of this study is to explore the relationship between rainfall erosivity and soil erosion levels in the Allith Basin of southwestern Saudi Arabia by integrating the RUSLE model with Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and remote sensing techniques. This comprehensive approach seeks to assess soil erosion risks in the context of long-term climatic data, with a focus on the effects of rainfall patterns on soil stability. This study contributes to the literature by providing a detailed analysis of soil erosion dynamics in an arid environment, offering insights into the spatial distribution of erosion risks, and demonstrating the effectiveness of combining the model with geospatial technologies for soil erosion assessment. The findings can help natural resource managers identify at-risk areas and guide appropriate land management strategies to preserve soil fertility and protect against degradation in this sensitive region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Allith basin is located around latitude 20.11° N and 21.14° N, longitude 40.19° E and 40.81° E (Figure 1). The study area is found in the south-western region of Saudi Arabia. It rises around the eastern corner to an elevation of 3000 m, above sea level; and at the western corner, the elevation slowly slopes into the red sea. The highest peak is found at Jabal Judah while the lowest region is concentrated around Allith town [20]. The study area is also notable with low-lying slopes of a large expanse, making it regarded principally as a plain. The mountainous regions of the study area are rugged and dissected with a main channel together with its tributaries [21].
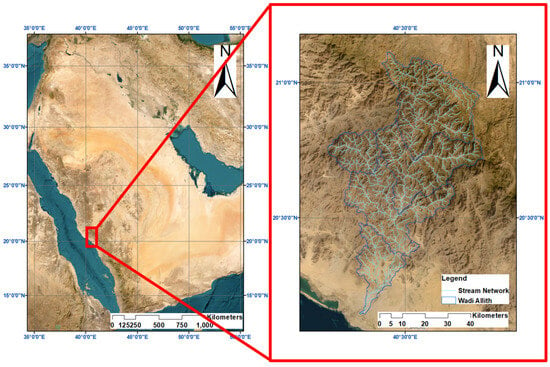
Figure 1.
Map showing the location of the study area.
2.2. Methodological Framework
The methodology used in this study is based on the recent findings of Ejaz et al. [2], and the adopted workflow is illustrated in Figure 2. The secondary data sources utilized include rainfall data derived from Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), soil characteristics, slope features, and information on current agricultural practices.
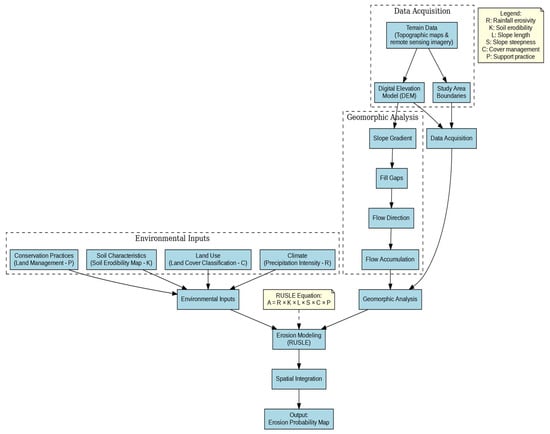
Figure 2.
Basic dataset creation and data processing flow chart.
The general RUSLE formula for calculating soil erosivity is given as follows:
A = R ∗ K ∗ LS ∗ C ∗ P
The units of A in the RUSLE are in tons per acre per year; R = the rainfall erosivity factor; K = is the soil erodibility factor; LS = the length of slope and the steepness factor; C = the crop management factor; and P = the support practices factor.
The steps followed in carrying out this study were to solve the equation. As shown in Equation (1) above, the methodology involved calculating the K, C, R, P, and LS factors. The results conducted from each factor were then integrated into a QGIS environment by overlaying the individual output maps for the component RUSLE factors. In determining the P-factor, it was decided to use the most frequent value (0.9), since the agricultural activity in the study area was not identifiable [2,22].
To spatially integrate the slope, land use/land cover (LULC), and soil maps, the following steps were performed: all maps were preprocessed to ensure they shared the same coordinate system and spatial resolution. This involved reprojecting the maps into a geographical coordinate reference system (WGS-84) and resampling them to a consistent grid size using the Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW) algorithm for interpolation [23]. The slope map provided information on the terrain’s steepness, the LULC map identified different land use and vegetation types, and the soil map outlined soil types and their properties. Each map was linked to the corresponding factor. The slope map informed the LS-factor calculations, the LULC map contributed to the C-factor, and the soil map was essential for determining the K-factor. This integration allowed for a spatially explicit assessment of how each factor contributed to soil erosion risk.
By overlaying these maps in QGIS, a composite analysis was performed to combine the influence of slope, LULC, and soil properties on soil erosion. This involved calculating the combined effect of these factors across the study area, providing a detailed erosion risk assessment. Finally, after integrating all of the factors in QGIS, the final soil erosion risk map was generated by applying the RUSLE model. This map visually represented the spatial distribution of soil erosion risks, aiding in the identification of high-risk areas.
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
WorldClim Historical Monthly Weather data was downloaded and used to calculate the R-factor [24,25]. Erosive factor of the rain was derived from the GeoTif files of the rainfall data for 2016, 2017, and 2018, using the equation below, following Lee and Heo [26]:
R = 38.5 + 0.35P
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
To estimate the soil erodibility, FAO-UN Soil Map of the World (DSMW) data were used and the soil characteristics were applied to determine the K-factor in the QGIS environment [27]. The formula for calculating K-factor is given as follows:
where
KUSLE = Kw = fcsand ∗ fci-si ∗ forgc ∗ fhisand
ms is the sand fraction content (0.05–2.00 mm diameter) [%]; msilt is the silt fraction content (0.002–0.05 mm diameter) [%]; mc is the clay fraction content (<0.002 mm diameter) [%]; and orgC is the organic carbon (SOC) content [%].
2.3.3. Slope Length and Slope Steepness (LS)
Using the commonly available Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) as well as a digital elevation model (DEM), the LS-factor was derived with the help of an algorithm referred to as r.watershed in the GRASS GIS environment.
2.3.4. Crop Management Practices (C)
The C-factor was calculated by integrating remote sensing data, the red as well as the near-infrared bands, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) was derived by the method of semi-automatic classification (SCP) used to synchronize the Landsat data downloaded. The NDVI formula is given as follows:
The NDVI rescaling process was subsequently applied following [28] and the output was computed using the formula below with the QGIS raster calculator:
2.3.5. P-Factor (P)
Wadi Allith basin in Saudi Arabia has minimal or no significant agricultural activities where such support practices are implemented. Furthermore, the landscape is predominantly natural or has limited agricultural intervention, the influence of the P factor would be negligible, making its inclusion less relevant to the erosion risk assessment [22]. By omitting the P factor, this study can provide a clearer understanding of the baseline erosion risk due to factors like rainfall, soil properties, and terrain, which are more directly related to the natural environment of the Wadi Allith basin [29].
3. Results
The analysis of the RUSLE factors revealed varying levels of soil erosion risk across the Allith Basin from 2016 to 2018. The R-factor, calculated using historical rainfall data, showed fluctuations in the rainfall erosivity over the study period. The K-factor, derived from soil properties, indicated moderate soil erodibility across most of the basin. The LS-factor, based on slope characteristics, revealed gently sloping terrain with low erosion potential. The C-factor, determined through NDVI analysis, highlighted areas with sparse vegetation cover as being more susceptible to erosion. The P-factor was assumed to be 0.9 due to the lack of identifiable agricultural activities [30]. The integrated results demonstrated that the majority of the basin experienced slight erosion risk, with very slight erosion being predominant in all three years. However, a slight increasing trend in erosion severity was observed from 2016 to 2018, correlating with the increasing average annual rainfall amounts.
Figure 3 presents the rainfall erosivity factor (R) for the Allith Basin from 2016 to 2018. The results indicate that the rainfall erosivity varies spatially across the basin, with regions experiencing slight to severe erosivity levels. The temporal analysis of the rainfall data revealed fluctuations in R-values, reflecting changes in rainfall intensity and distribution over the study period [28].
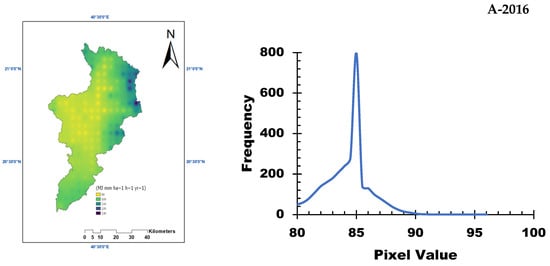
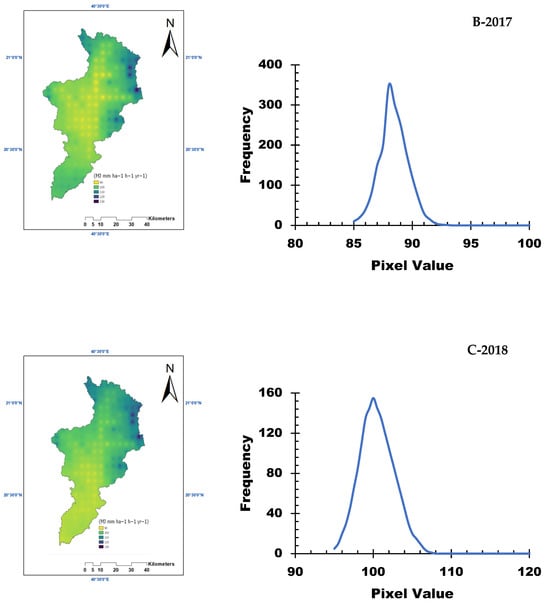
Figure 3.
Rainfall erosivity factor (R) for the study area from 2016 to 2018.
Figure 4 illustrates the soil erodibility factor (K) across the study area. Based on soil properties such as sand, silt, clay, and organic carbon content, the K-factor values were calculated. The results show that approximately 90% of the basin has moderate soil erodibility, indicating a moderate susceptibility to erosion under the influence of rainfall and runoff [30].
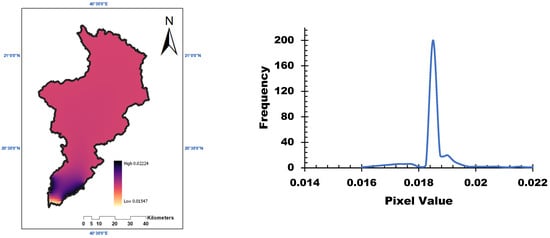
Figure 4.
Soil erodibility factor (K) measured in the study area.
The slope length and steepness factor (LS) are depicted in Figure 5. The LS factor was derived using a digital elevation model (DEM) and highlights the gently sloping nature of the terrain, with wide undulating areas characteristic of lowland terrain. These slope conditions contribute to lower erosion potential in the basin.
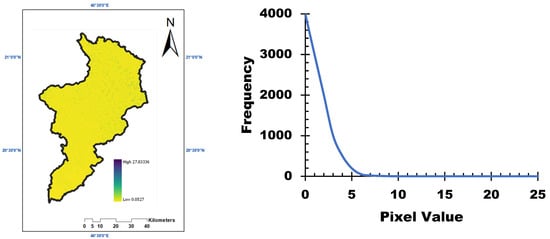
Figure 5.
Slope characteristics (LS) measured for the study area.
Figure 6 shows the NDVI values across the study area, which were used to calculate the crop management factor (C). NDVI values range from −1 to 1, with higher values indicating denser vegetation. The results indicate that most of the basins have low NDVI values, suggesting sparse vegetation cover and a higher susceptibility to soil erosion [28].
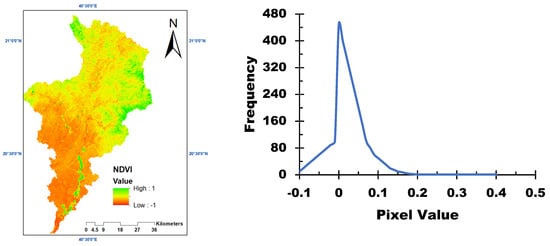
Figure 6.
NDVI calculated for the study area.
The spatial distribution of the C-factor is presented in Figure 7. The results show that the majority of the study area consists of bare soil, with sparse vegetation cover. This lack of protective ground cover increases the vulnerability of the soil to erosion during rainfall events. The spatial distribution of the C-factor (Figure 7), derived from NDVI values (Figure 6), provided insights into the impact of vegetation cover on soil erosion. Areas with dense vegetation exhibited higher NDVI values and lower soil erodibility, while regions with sparse or no vegetation cover showed lower NDVI values and higher susceptibility to erosion. This spatial variability in vegetation cover influenced the overall erosion risk across the basin, with bare soil areas being particularly vulnerable to erosion during rainfall events. The results emphasize the importance of vegetation in mitigating soil erosion and highlight the need for land management practices that promote vegetation growth and coverage to reduce erosion risks.
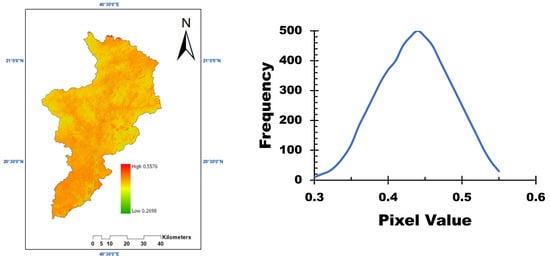
Figure 7.
Crop management (C) factor estimated for the study area.
Table 1 presents the calculated K-factor values for different soil types in the study area. The results show variations in soil erodibility based on soil characteristics such as sand, silt, clay, and organic carbon content.

Table 1.
K-factor calculation.
Average annual rainfall amounts recorded from the WorldClim data for 2016, 2017, and 2018 were estimated at 120-, 145-, and 155-mm yr−1, respectively. RUSLE was estimated by multiplying the component factors altogether. The results of the calculation are shown in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 while the interpretation of the erosion risk classes is summarized in Table 2. The resulting erosion risk classes are as follows: ERC 1 = very slight, ERC 2 = slight, ERC 3 = moderate, ERC 4 = severe, and ERC 5 = very severe [6,7].
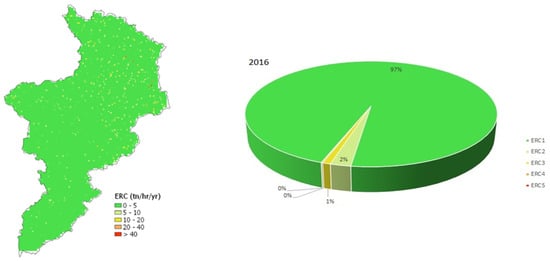
Figure 8.
Soil erosion risk map (left) and proportional distributions of erosion risk classes (right) of Allith basin in 2016.
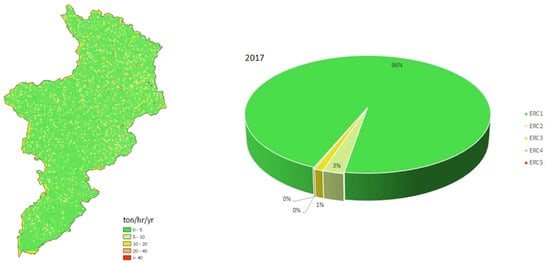
Figure 9.
Soil erosion risk map (left) and proportional distributions of erosion risk classes (right) of Allith basin in 2017.
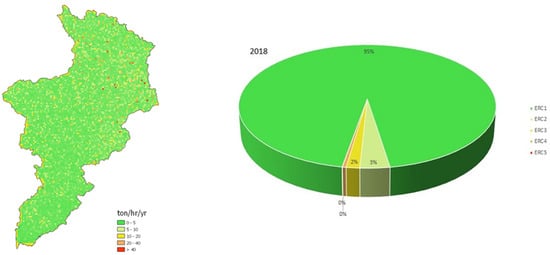
Figure 10.
Soil erosion risk map (left) and proportional distributions of erosion risk classes (right) of Allith basin in 2018.
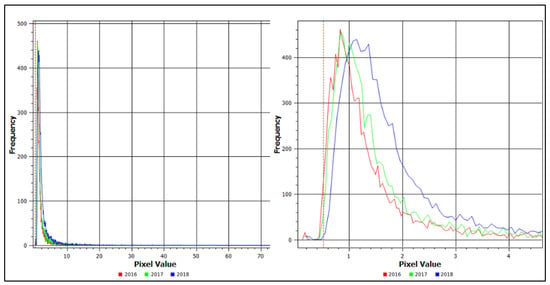
Figure 11.
Trend in ERC values for 2016, 2017, and 2018 before magnification (left) and after magnification (right).

Table 2.
Soil erosion classes and their interpretations following [7].
Table 2 summarizes the soil erosion classes and their interpretations based on the RUSLE model. The erosion risk classes range from very slight (0–5 tons/hectare/year) to very severe (>40 tons/hectare/year), providing a clear framework for categorizing and understanding the erosion risks in the basin.
Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 provide the soil erosion risk maps for the Allith Basin for the years 2016, 2017, and 2018, respectively. The maps show the spatial distribution of erosion risk classes across the basin. In 2016, a very slight erosion risk was predominant (97% of the basin area), while in 2017 and 2018, this decreased slightly to 96% and 95%, respectively. The proportional distributions of erosion risk classes indicate a gradual increase in moderate and severe erosion risks over the three-year period.
Figure 11 illustrates the trend in erosion risk class (ERC) values for 2016, 2017, and 2018. The results show a clear increasing trend in erosion severity from 2016 to 2018, which correlates with the increasing average annual rainfall amounts recorded during the study period [31].
4. Discussion
This study provides valuable insights into the soil erosion dynamics in arid environments like the Allith Basin. The findings indicate that while the majority of the basin is subject to moderate erosion risks, isolated areas with severe erosion require targeted management strategies. The relationship between increasing rainfall and erosion severity underscores the importance of understanding how climatic factors influence soil stability, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity is a limiting factor. The increase in rainfall not only highlights the variability of climatic conditions but also emphasizes the potential for more severe erosion events as rainfall patterns shift due to climate change [31]. Furthermore, the successful application of Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and remote sensing tools, integrating the various components of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE), showcases the effectiveness of these technologies in environmental monitoring and risk assessment. These tools facilitate a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to soil erosion, enabling researchers and policymakers to visualize erosion risk across the basin and prioritize areas for intervention [1,30].
Soil erosion in arid regions is a complex process influenced by multiple interacting factors, including rainfall intensity, soil properties, terrain characteristics, and land cover. In the Allith Basin, the combination of low slope gradients and moderate soil erodibility contributes to the predominantly low erosion risk levels observed in this study [32]. However, the presence of areas with severe erosion risk highlights the need for localized management approaches. The spatial distribution of erosion risk can be attributed to variations in these factors across the basin. For instance, areas with higher rainfall erosivity and lower vegetation cover are more prone to erosion. This spatial variability emphasizes the importance of high-resolution data and geospatial technologies in accurately assessing and addressing soil erosion risks [33,34].
The estimated average soil loss in the basin (~5 tons/ha/year) aligns closely with prior studies in similar hyper-arid settings: Bahrawi et al. [1] reported 3–7 tons/ha/year in Wadi Yalamlam (Saudi Arabia) under comparable rainfall (100–150 mm/year), while Ejaz et al. [2] documented 3–8 tons/ha/year in Wadi Baysh using identical geospatial-model integration. The dominance of very slight erosion (95–97% of the basin) corroborates the regional patterns where sparse vegetation and low rainfall constrain soil loss, as observed in arid African basins [15,22]. Notably, the observed escalation in erosion severity with rising annual rainfall (2016–2018) mirrors the trends in climate-sensitive erosion dynamics reported in semi-arid Ethiopia [35,36]. Discrepancies with humid-region studies (e.g., >20 tons/ha/year in Chen et al. [30] and Elhag et al. [37]), underscore the climatic modulation of the model outputs, emphasizing the necessity of context-specific calibration. These comparisons validate this study’s methodology while situating its findings within broader RUSLE-based research on arid-land erosion processes.
The model, when combined with GIS and remote sensing, offers a powerful framework for predicting and mapping soil erosion risks in data-scarce regions like the Allith Basin [11]. The model’s ability to integrate multiple factors provides a holistic view of erosion dynamics, which is crucial for developing effective soil conservation strategies. However, the accuracy of the model depends on the quality and resolution of input data. In this study, the use of historical rainfall data and soil property maps from various sources introduced some uncertainties. Future research could enhance the model’s accuracy by incorporating more detailed and localized data, such as higher-resolution rainfall measurements and soil samples collected specifically from the study area [1].
The implications of this study extend beyond the Allith Basin, offering insights applicable to other arid and semi-arid regions facing similar challenges of soil erosion and degradation. The methodology employed demonstrates a cost-effective and efficient approach to soil erosion assessment that can be adapted to different geographical contexts. By identifying areas at higher risk of erosion, resource managers can prioritize these regions for targeted interventions, such as implementing soil conservation practices, promoting sustainable land-use policies, and enhancing vegetation cover [24,25]. Additionally, the findings highlight the importance of long-term monitoring and modeling to track changes in erosion patterns and assess the effectiveness of management strategies over time. This study contributes to the broader goal of preserving soil fertility and mitigating environmental degradation in sensitive arid environments.
Wadi Allith basin’s minimal agricultural activity, described as <5% cultivated land [38,39], and the absence of erosion-control practices [32] combined with its predominantly natural, non-managed landscape (97% bare soil/sparse vegetation) aligns with the RUSLE guidelines for regions lacking conservation measures [8,22], justifying the negligible P-factor.
While the RUSLE model itself is well-established, this research introduces methodological advancements in its application to arid environments, leveraging remote sensing, GISs, and climate data to address gaps in soil erosion science. The integration of spatiotemporal analysis, arid-specific parameterization, and policy-focused outputs represents a novel contribution to sustainable land management in water-scarce regions globally.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
This study on simulating soil erosion risks in the Allith Basin, Saudi Arabia, from 2016 to 2018 provides valuable insights into the dynamics of soil erosion in arid environments. The findings indicate that the majority of the basin is subject to moderate erosion risks, suggesting that while erosion is a concern, it can spread across the region based on the rainfall intensities. However, the identification of isolated areas with severe erosion highlights the need for targeted management strategies to mitigate these risks. One of the key observations from the analysis is the notable trend of increasing severity of soil erosion risk correlating with rising average annual rainfall. This relationship underscores the importance of understanding how climatic factors influence soil stability, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity is typically a limiting factor. The increase in rainfall not only underscores the variability in climatic conditions but also emphasizes the potential for more severe erosion events as rainfall patterns shift due to climate change. Furthermore, the successful application of Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and remote sensing tools integrating the various components of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) showcases the effectiveness of these technologies in environmental monitoring and risk assessment. These tools facilitate a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to soil erosion, enabling researchers and policymakers to visualize erosion risk across the basin and prioritize areas for intervention.
Finally, it is recommended to conduct a detailed assessment of the spatial extent for each severity class and present the results as a percentage of the total watershed area for each soil-loss severity level. Strengthening the analysis in this way would provide clearer insights into the distribution of soil loss within the watershed and enhance the overall understanding of soil erosion dynamics in the region. Additionally, future research could explore the temporal variations in soil erosion risk by incorporating more detailed and localized data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E. and M.H.H.; methodology, M.E. and S.O.; validation, M.E., L.Z. and R.E.; formal analysis, M.E. and K.D.; investigation, M.E.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E.; writing—review and editing, M.E., M.H.H., S.O., R.E., L.Z. and K.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), President’s International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI), grant number 2021VEA0007.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study is either open or public. The datasets generated or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bahrawi, J.A.; Elhag, M.; Aldhebiani, A.Y.; Galal, H.K.; Hegazy, A.K.; Alghailani, E. Soil erosion estimation using remote sensing techniques in Wadi Yalamlam Basin, Saudi Arabia. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9585962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, N.; Elhag, M.; Bahrawi, J.; Zhang, L.; Gabriel, H.F.; Rahman, K.U. Soil Erosion Modelling and Accumulation Using RUSLE and Remote Sensing Techniques: Case Study Wadi Baysh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabani, A.; Adem, E.; Elfeki, A.; Farran, M.M.; Shults, R.; Elhag, M. Hydrogeological mapping of fracture networks using earth observation data to improve rainfall–runoff modeling in arid mountains, Saudi Arabia. Open Geosci. 2024, 16, 20220679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadore, E.; Bronders, J.; Batelaan, O. Hydrological modelling of urbanized catchments: A review and future directions. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Caloiero, T.; Mehta, D.J.; Singh, K. Comprehensive overview of flood modeling approaches: A review of recent advances. Hydrology 2023, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains: Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The New Assessment of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Berndt, H. Sediment yield prediction based on watershed hydrology. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinka, M.O. Quantification of soil erosion and sediment yield for ungauged catchment using the RUSLE model: Case study for Lake Basaka catchment in Ethiopia. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2020, 25, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocking, M.; Elwell, H. Soil erosion hazard in Rhodesia. Rhod. Agric. J. 1973, 70, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sestras, P.; Mircea, S.; RoȘCA, S.; Bilașco, Ș.; Sălăgean, T.; Dragomir, L.O.; Herbei, M.V.; Bruma, S.; Sabou, C.; Marković, R. GIS based soil erosion assessment using the USLE model for efficient land management: A case study in an area with diverse pedo-geomorphological and bioclimatic characteristics. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2023, 51, 13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.; Shahin, M. Erosion and sedimentation in drainage basins and in storage reservoirs. In Water Resources and Hydrometeorology of the Arab Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 333–367. [Google Scholar]
- Elhag, M.; Hidayatulloh, A.; Bahrawi, J.; Chaabani, A.; Budiman, J. Using inconsistencies of wadi morphometric parameters to understand patterns of soil erosion. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, L.J.; Turnbull, L.; Wainwright, J.; Bogaart, P. Sediment connectivity: A framework for understanding sediment transfer at multiple scales. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, S. A review on the research advances in groundwater–surface water interaction with an overview of the phenomenon. Water 2023, 15, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, A. Soil Erosion–Causes and Effects. Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science; University of Mysore: Mysore, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts, factors and control. Catena 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, F.; Hames, A. Comparison of four classification methods to extract land use and land cover from raw satellite images for some remote arid areas, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Earth sciences 2009, 20, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishi, M.; Bahrawi, J.; Elfeki, A. Empirical equations for flood analysis in arid zones: The Ari-Zo model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, B.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Ebabu, K.; Meshesha, D.T.; Tsubo, M.; Masunaga, T.; Fenta, A.A. Determining C-and P-factors of RUSLE for different land uses and management practices across agro-ecologies: Case studies from the Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Phys. Geogr. 2021, 42, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M. Evaluation of DEM interpolation techniques for characterizing terrain roughness. Catena 2021, 198, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.; Osborn, T.J.; Lister, D.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations–the CRU TS3. 10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Heo, J.-H. Evaluation of estimation methods for rainfall erosivity based on annual precipitation in Korea. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.; Arnold, J.; Kiniry, J.; Williams, J. Erosion Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation; Texas Agricultural Eksperiment Station: College Station, TX, USA, 2000.
- Durigon, V.; Carvalho, D.; Antunes, M.; Oliveira, P.; Fernandes, M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhu, Z.; Yue, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, F.; Guo, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, M. Soil erosion assessment by RUSLE with improved P factor and its validation: Case study on mountainous and hilly areas of Hubei Province, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Niu, R.-q.; Li, P.-x.; Zhang, L.-p.; Du, B. Regional soil erosion risk mapping using RUSLE, GIS, and remote sensing: A case study in Miyun Watershed, North China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.A.; Kavian, A. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and soil erosion in field plots. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajabaa, S.; Masoud, M.; Al-Amri, N. Flash flood hazard mapping based on quantitative hydrology, geomorphology and GIS techniques (case study of Wadi Al Lith, Saudi Arabia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, J.L.; Singh, V.P.; de Lima, M.I.P. The influence of storm movement on water erosion: Storm direction and velocity effects. Catena 2003, 52, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Lei, T.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, X. Velocity of water flow along saturated loess slopes under erosion effects. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategekimana, Y.; Allam, M.; Meng, Q.; Nie, Y.; Elhag, M. Quantification of soil losses along the coastal protected areas in Kenya. Land 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, W.G. Resilience in the face of ecological challenges: Strategies for integrating environmental considerations into social policy planning in Africa. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M.; Kojchevska, T.; Boteva, S. EPM for soil loss estimation in different geomorphologic conditions and data conversion by using GIS. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 221, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, A.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Elhag, M.; Alatar, A.A.; Abbadi, G.A.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Arif, I.A.; Baeshen, A.A.; Eid, E.M. Remote sensing of 10 years changes in the vegetation cover of the northwestern coastal land of Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3169–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noamen, B.; Hamza, M.H.; Slama, T.; Sebei, A.; Ouerghi, S.; Elsheikh, R.; Rebai, N.; Hasanean, H.; Almazroui, M.; Elhag, M. Assessment of Machine Learning Techniques in Mapping Land Use/Land Cover Changes in a Semi-Arid Environment. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).