Abstract
Relative permeability is a critical parameter governing multiphase fluid flow through porous media, significantly impacting recovery efficiency and CO2 sequestration potential in geological reservoirs. Accurately evaluating relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs remains challenging due to spatially variable porosity and permeability distributions. This study presents a novel intelligent prediction approach for evaluating water-CO2 relative permeability in heterogeneous porous media by integrating fluid properties, heterogeneity characteristics, and relative permeability measurements from uniform porous media. We established a comprehensive training dataset through systematic micromodel experiments that captured various heterogeneity patterns and fluid conditions. Using this dataset, we developed an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model that achieved exceptional accuracy with a Mean Squared Error below 0.0025. The model was then applied to predict relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs using site-specific relative permeability data obtained from core experiments as input parameters. To validate our approach, we incorporated the predicted relative permeability values into Computer Modelling Group (CMG) reservoir simulations of CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers. The simulation results demonstrated strong agreement with published literature, confirming the model’s predictive capability. This work provides a practical, efficient, and reliable methodology for predicting relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs, addressing a significant challenge in reservoir characterization and flow modeling.
1. Introduction
Global energy demands and climate change concerns have intensified interest in both efficient hydrocarbon recovery and secure carbon dioxide (CO2) sequestration in geological formations [1,2,3,4]. In both scenarios, the accurate characterization of multiphase fluid flow through porous media is essential for predicting reservoir performance and developing optimal operational strategies [5]. Relative permeability—a dimensionless measure describing the interference between fluid phases competing for the same flow pathways—stands as one of the most critical parameters governing these multiphase flow processes [6,7].
While relative permeability has been extensively studied in homogeneous systems [8,9], real-world geological formations exhibit significant heterogeneity across multiple scales [10]. These heterogeneities, manifested as spatial variations in porosity, permeability, wettability, and pore geometry, substantially influence multiphase flow behavior and consequently affect relative permeability relationships [11,12] and complicate the relative permeability characterizations [13,14]. At present, there are three widely used methods for studying the relative permeability of gas and water in reservoirs: experimental analysis, theoretical models, and numerical simulations. Firstly, experimental methods are widely used in testing the relative permeability of gas and water in reservoirs using nonsteady state methods, but their ability to reduce in-situ temperature conditions is still insufficient [15,16]. New technologies such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and CT three-dimensional scanning are used to improve experimental equipment, which can capture multiphase fluid displacement processes in real time and improve accuracy. For example, the prediction model based on NMR T2 distribution has been successfully applied in tight sandstone reservoirs, achieving non-destructive continuous permeability curve analysis. In addition, the development of high-temperature and high-pressure (150 °C, 50 MPa) experimental equipment has revealed phenomena such as the downward shift of the gas-water relative permeability curve and the displacement of the iso permeability point in carbonate reservoirs caused by the increase of confining pressure. [17]. Furthermore, these experimental methods are typically time-consuming, resource-intensive, and challenging to scale from core samples to field-scale applications [18,19].
In addition, there are theoretical models and numerical simulation methods. Existing models are mostly based on the extrapolation of two-phase data, but the assumptions vary and do not fully consider the real pore and fracture structures, which limits their universality. Numerical simulation breaks through the sample size limitation of physical experiments by combining on-site development data, dynamically depicting the changes in permeability during the harvesting process, but still needs to be verified in conjunction with experimental data. For example, microfluidic technology has shown potential in visualizing multiphase flow behavior, but its geological theoretical connections and application scenarios need to be expanded.
The limitations of traditional methods have spurred interest in developing alternative approaches for relative permeability estimation [20]. Recent advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence offer promising avenues for addressing this challenge [21,22]. Artificial intelligence methods achieve a rapid prediction and analysis of data features by deeply mining the mapping relationships between data. Especially adept at analyzing complex scenarios involving large-scale data, the efficiency of handling nonlinear problems is significantly better than traditional methods. In recent years, artificial intelligence methods such as deep learning have been widely applied in various scenarios such as oil and gas field development and carbon dioxide storage. These computational techniques can potentially identify complex patterns and relationships between reservoir properties and flow characteristics that might otherwise remain undetected through conventional analysis [23].
Data-driven models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) integrate geological parameters, dynamic development data, and environmental variables to construct a nonlinear relationship between permeability and reservoir conditions. Research has shown that such models have significantly better explanatory power (R2 > 0.8) for changes in permeability than traditional statistical methods and can capture the impact of key factors such as effective stress and fluid flow velocity on permeability and relative permeability. Foreign and local scholars have used artificial intelligence methods such as ANN and machine learning to analyze and predict the relative permeability transformation characteristics of different reservoir types, such as carbonate rocks and shale oil and gas reservoirs, greatly improving the efficiency of relative permeability analysis [24,25,26]. Ehsan Zeinedini (2022) [24] established a model to predict the relative permeability of gas condensate. The algorithm calculates the reservoir’s absolute and relative permeability versus different condensate ratios to gas. It can also be applied to different types of porous media and fluids. It does not need any experimental study to determine the empirical information about gas and condensate flow behavior [24]. Hanif F. Yoga (2024) extended the development of the relative permeability equation-of-state (kr-EoS) to create a predictive physically-constrained model using artificial neural networks (ANNs) [26].
Based on this, we present a novel approach to predict relative permeability in heterogeneous porous media by leveraging artificial neural networks (ANNs) [27] and integrating data from both micromodel experiments [28,29] and core analyses [30]. Our methodology uniquely bridges microscale observations with macroscale measurements to generate reliable relative permeability estimations that account for reservoir formation heterogeneity. The primary objectives of this research are to (1) develop a comprehensive dataset capturing heterogeneity effects on relative permeability, (2) construct and validate an ANN model for accurate prediction in heterogeneous media, and (3) demonstrate practical applicability through reservoir simulation of CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers. To validate our approach, we incorporated the predicted values into Computer Modelling Group (CMG) reservoir simulations of CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers. This methodology has significant implications for improving reservoir simulation accuracy, enhancing hydrocarbon recovery strategies, and optimizing carbon sequestration operations, which are crucial for meeting energy demands while mitigating climate change impacts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Micromodel Simulations
We design the hierarchical heterogeneous porous structure according to the pores found in actual geological reservoirs [3,4]. We respectively stagger 10 μm, 20 μm, and 40 μm radius circles with a 2 μm radial interval inside a 450 µm × 150 µm rectangle to generate the uniform pores, namely Con_Low, Con_Med, and Con_High, by using AutoCAD®. We permutate and combine the uniform pores to form the hierarchical heterogeneous porous structure, as illustrated in Figure 1a,b. The throat size is indicated by the narrowest interval between two circles in arbitrary directions, and the pore size is derived as the nearest circle center distance subtracting the circle diameter.
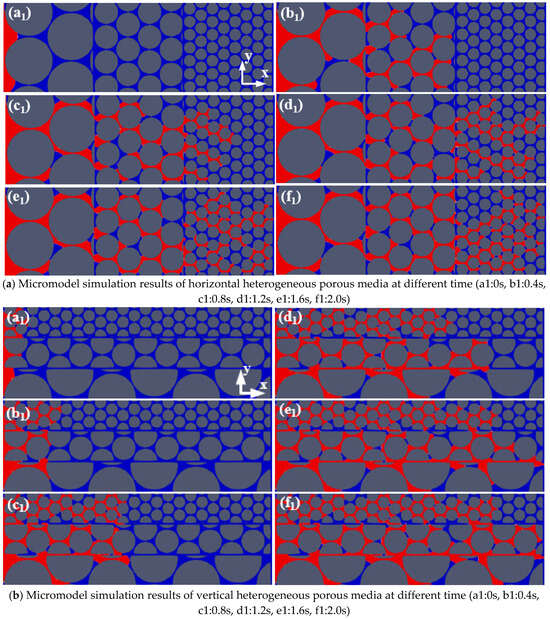
Figure 1.
Micromodel simulations of CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers, where red is the CO2 and blue is the water.
We propose a heterogeneity order, He, to quantitatively describe the heterogeneity of hierarchical heterogeneous porous structure. He is derived as Equation (1) [3,4], which takes the value and order of uniform pores into account.
where the subscripts 1st, 2nd and 3rd layers are ordered in the direction from inlet to outlet, and the subscript low refers to the layer with low PTR. Here, the coefficients of 0.5, 0.4, and 0.1 are weights configured to quantitatively distinguish the heterogeneous pores from each other. The weights themselves have no physical meaning, and their sum is 1. In this context, we ensure each heterogeneous pore has a unique corresponding He by leveraging the weights of 0.5, 0.4, and 0.1 (for example, if 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2 are used, the MLH and the LHM share the same He). Besides, we assign the element layer of the heterogeneous pores with a higher weight if it is closer to the CO2 inlet since the flow state in the second element layer is strongly related to the first layer, and the flow state in the third layer is dependent on the first and second layers. We set the weight of 0.5 for the first layer because there are no pressure drops exceeding 50% in the first layer in all cases.
We mesh the uniform and hierarchical heterogeneous porous structure by using the blockMesh and snappyHexMesh commands of OpenFOAM [31,32] (version 9). Specifically, we generate the background hexahedral meshes via blockMesh. We refine the background meshes with tetrahedral ones and remove the meshes outside the computational domain via snappyHexMesh. The mesh quality meets the numerical convergence criteria by checking with the checkMesh command. Detailed information on the meshing, boundaries, and solver settings is available on request from the authors.
2.2. Core Experiments
We conducted a series of core flooding experiments to obtain site-specific relative permeability data from actual heterogeneous reservoir samples [33]. The apparatus consisted of a high-pressure core holder capable of accommodating cylindrical core samples up to 10 cm in length and 3.8 cm in diameter. The system was equipped with precision pumps for injecting CO2 and water at controlled rates, pressure transducers at the inlet and outlet for differential pressure measurements, and a backpressure regulator to maintain reservoir-representative conditions.
The core samples used in this study, shown in Figure 2, were drilled directly from heterogeneous reservoir formations representative of potential CO2 sequestration sites. These cores exhibited visible heterogeneity with varying colors and textures, indicating different mineral compositions and pore structures throughout the samples. We collected cores from three distinct zones within the formation, characterized by different degrees of heterogeneity, as follows:
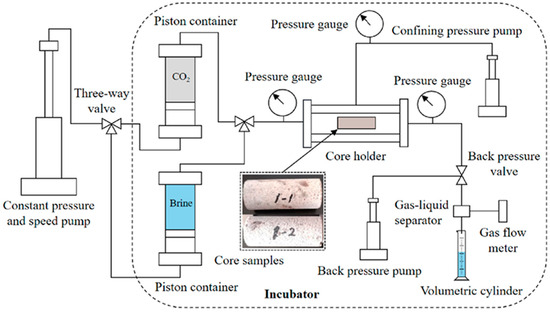
Figure 2.
Workflow of the core experiments for relative permeability measurements.
- (1)
- High heterogeneity zone—cores displayed prominent layering and significant variations in grain size distribution;
- (2)
- Medium heterogeneity zone—cores showed moderate variations in composition with some visible bedding planes;
- (3)
- Low heterogeneity zone—cores appeared more uniform but still contained subtle heterogeneous features.
Prior to relative permeability measurements, each core underwent comprehensive characterization, including porosity determination via helium porosimetry, absolute permeability measurement using water injection, and CT scanning to visualize internal heterogeneity structures. The porosity values ranged from 12% to 22%, while absolute permeability varied from 10 mD to 150 mD across the different samples, reflecting the inherent heterogeneity of the reservoir formation.
For the relative permeability measurements, we employed the steady-state method where CO2 and water were simultaneously injected into the cores at various fractional flow ratios. At each ratio, the injection continued until pressure stabilization and constant production rates were achieved, indicating steady-state conditions. The saturations were determined through material balance calculations, while the relative permeability values were computed using Darcy’s law for multiphase flow.
All experiments were conducted at pressure and temperature conditions representative of target saline aquifers for CO2 sequestration (12 MPa and 45 °C). The experimental conditions were carefully controlled to maintain CO2 in its supercritical state, simulating actual reservoir conditions during carbon sequestration operations. Additionally, we used synthetic water that matched the ionic composition of the formation water from the target reservoir to ensure realistic fluid-rock interactions.
2.3. Relative Permeability Acquisition
We use the JBN method [34,35] to acquire the relative permeability from the core experiments. Due to the compressibility of the gas, it is necessary to use the average volume flow rate to correct the flow rate at the outlet, as shown in Equation (2)
where Vt and Vt−1 are the cumulative productions of CO2 and water at the exit end of the core at moments t and t−1, mL, ∆Vb is the increased volume of water at the exit end of the core at moment t, mL, Pa is the atmospheric pressure, MPa, ∆P is the pressure difference between the two ends of the core, and ∆Vg is the increased volume of CO2 at the exit end of the core at moment t, mL.
The CO2-water drainage relative permeability was calculated by Equation (3) using experimental data from the CO2 displacement water stage
where fb is the moisture content, is the dimensionless cumulative brine production, and is the dimensionless CO2 and brine production. The relative injection capacity I is defined as Equation (4),
where Q (t) and Q0 are the brine flow rate at the core outlet at the initial and t moments, respectively, mL/s, ∆P0 and ∆P (t) are the pressure difference between the two ends of the core at the initial and t moments, respectively, MPa. The relative permeability of CO2 and brine are derived from Equations (5) and (6),
where Krb and Krg are the relative permeability of brine and CO2, respectively, μb and μg are the viscosity of brine and CO2, respectively, mPa·s.
2.4. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model Set up
In this paper, we use the ANN model to construct a prediction model for the gas-water relative permeability of CO2 and brine. The specific process is as follows:
- (1)
- Building a dataset for model training through micromodel simulation and core experiments. Determining the input and output data, and the ratio of training and testing.
- (2)
- Training models separately for CO2 and brine to construct a prediction model for two-phase relative permeability.
- (3)
- Prediction of the relative permeability and validation of model accuracy.
The dataset for training our artificial neural network (ANN) model [36] was compiled from extensive micromodel experiments capturing various heterogeneity patterns and fluid conditions. We integrated relative permeability measurements across different contact angles (100°, 125°, and 150°) and heterogeneity configurations (LMH, MLH, LHM, HLM, MHL, and HML). The input data included the following critical parameters governing multiphase flow in heterogeneous porous media: relative permeability values from uniform porous media (RP_h_b, RP_m_b, RP_l_b, RP_h_c, RP_m_c, RP_l_c), heterogeneity order (He), contact angle (CA), fluid properties (Density_c, Density_b, Viscosity_c, Viscosity_b), interfacial tension (Gamma), and CO2 saturation (SCO₂). The output data is the relative permeability value of CO2 and brine obtained through calculation.
The models employed the MinMaxScaler for feature normalization to ensure that all input variables contributed proportionately to the learning process. The dataset was randomly shuffled and split into training (90%) and testing (10%) sets to evaluate model performance. The testing phase demonstrated exceptional accuracy with a Mean Square Error below 0.0025 for both CO2 and brine relative permeability predictions.
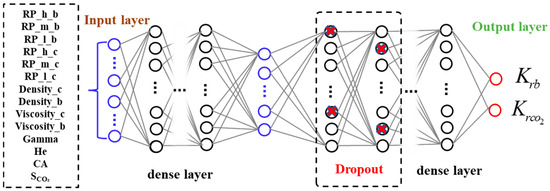
Figure 3.
Neural network framework of an artificial intelligence algorithm for predicting relative penetration.

Table 1.
The parameters of input and output.
For the relative permeability prediction of CO2, we developed a sequential neural network using TensorFlow and Keras frameworks. The architecture consisted of an input layer receiving 14 features, followed by a dense layer with 256 neurons. To prevent overfitting, we incorporated a dropout layer with a rate of 0.2. The subsequent layers included two dense layers with 64 and 16 neurons, respectively, both using ReLU activation functions. The output layer with a single neuron employed a ReLU activation function to ensure positive relative permeability predictions. The model was compiled using the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 1 × 10−3 and mean squared error (MSE) as the loss function. We implemented a learning rate reduction strategy using ReduceLROnPlateau, which monitored validation loss and decreased the learning rate by a factor of 0.5 after five epochs without improvement. The model was trained over 30 epochs with a batch size of 4 and a validation split of 0.1.
For the relative permeability prediction of brine, we employed a deeper neural network architecture to capture the more complex relationship between fluid properties and brine mobility in heterogeneous media. The model comprised an input layer receiving the same 14 features, followed by a dense layer with 4096 neurons and a dropout layer with a rate of 0.2. The subsequent layers included dense layers with 2048, 1024, 512, and 256 neurons, respectively, all using ReLU activation functions. The output layer with a single neuron also employed a ReLU activation function. This model was compiled with the same Adam optimizer and MSE loss function but was trained over 100 epochs with a larger batch size of 128 and a validation split of 0.25. The increased complexity and longer training period were necessary to achieve optimal predictive performance for brine relative permeability.
To systematically determine the optimal hyperparameters for the ANN model, we employed a grid search strategy combined with 5-fold cross-validation. Key parameters, including the number of hidden layers, neurons per layer, dropout rate, and activation functions, were rigorously tested. The search space was defined based on empirical studies, and model performance was evaluated using the validation R2. Final selections achieved higher accuracy than initial configurations while maintaining computational efficiency.
Once trained, the models were applied to predict relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs using site-specific data obtained from core experiments. The prediction process involved normalizing input features using the same scaling factors from the training phase, passing the normalized features through the trained neural networks, and then inverse-transforming the outputs to obtain the final relative permeability values. These predicted values were subsequently incorporated into Computer Modelling Group (CMG) reservoir simulations to validate our approach through comparison with published literature and experimental results.
3. Results
3.1. Relative Permeability of Micromodels
We analyzed the changes of relative permeability under two heterogeneous conditions, vertical and horizontal, with contact angles of 100, 125, and 150 degrees between CO2 and the brine. As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 100°, for horizontal heterogeneity, the relative permeability curves show distinct patterns across different heterogeneous configurations. In the LMH configuration (Figure 4a), the CO2 relative permeability reaches approximately 0.65 at maximum saturation, while the brine relative permeability decreases steadily with increasing CO2 saturation. The HLM configuration (Figure 4b) exhibits a lower maximum CO2 relative permeability around 0.5, indicating greater resistance to CO2 flow when high PTR regions are positioned first in the flow path. The MLH and MHL configurations (Figure 4c,d) show intermediate behavior, with maximum CO2 relative permeability values of approximately 0.58 and 0.53, respectively. In LHM and HML configurations (Figure 4e,f), we observe that the crossover points where CO2 and brine relative permeabilities are equal occur at different saturation values, suggesting that heterogeneity order significantly influences phase mobility.
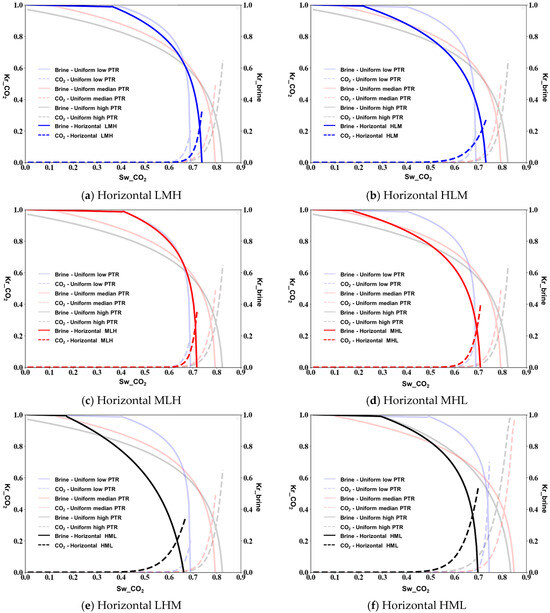
Figure 4.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of horizontal porous media at a contact angle of 100°.
As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 100°, for vertical heterogeneity, the gravity effects become more pronounced. The LMH vertical configuration (Figure 5a) shows enhanced CO2 relative permeability compared to its horizontal counterpart, reaching values up to 0.7, which can be attributed to the limited buoyancy-assisted upward migration of CO2. The HLM configuration (Figure 5b) displays a more restricted flow pattern with maximum CO2 relative permeability around 0.48. The vertical MLH and MHL arrangements (Figure 5c,d) show characteristic differences in the shapes of the curves, particularly in the mid-saturation range (0.4–0.6), where the slope of the CO2 relative permeability curve is steeper for MLH. The vertical LHM and HML configurations (Figure 5e,f) demonstrate how the positioning of different permeability zones affects the residual saturation values, with HML showing higher residual brine saturation.
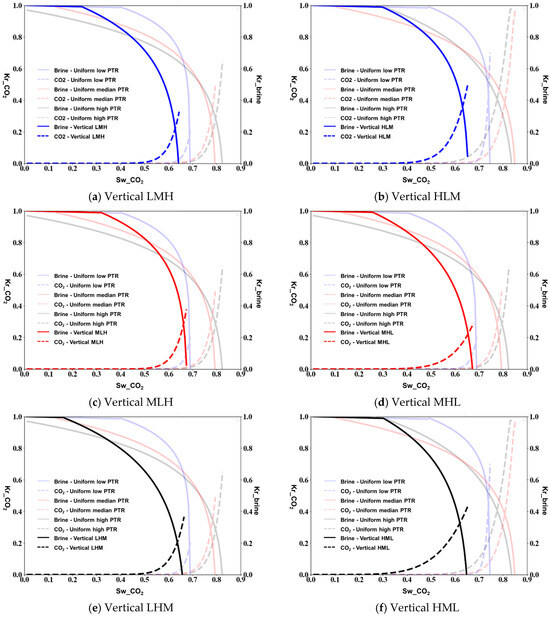
Figure 5.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of vertical porous media at a contact angle of 100°.
As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 125°, for horizontal heterogeneity, we observe an overall enhancement in CO2 relative permeability across all configurations due to increased CO2-wetting conditions. The LMH configuration (Figure 6a) shows a maximum CO2 relative permeability of approximately 0.72, while the HLM arrangement (Figure 6b) reaches about 0.6. The MLH and MHL configurations (Figure 6c,d) display maximum values of 0.65 and 0.62, respectively, with noticeably steeper curves in the middle saturation range compared to the 100° contact angle cases. The LHM and HML configurations (Figure 6e,f) show distinctive behavior with respect to the crossover point and endpoint relative permeabilities, with the HML arrangement exhibiting more favorable conditions for CO2 flow at higher saturations.
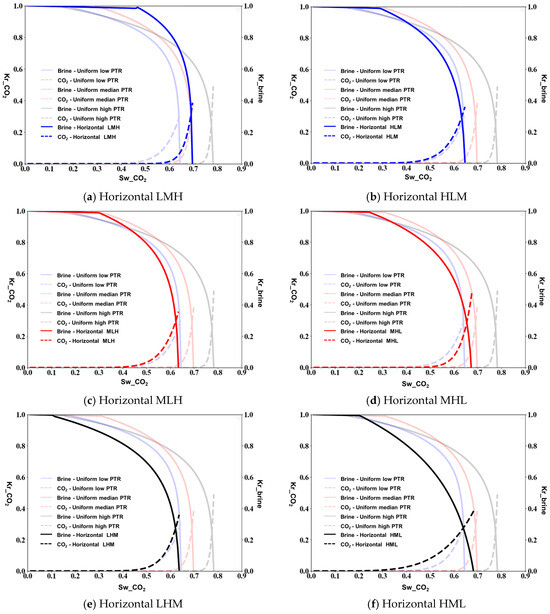
Figure 6.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of horizontal porous media at a contact angle of 125°.
As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 125°, for vertical heterogeneity, the combined effects of increased CO2-wetting and gravitational forces result in unique relative permeability patterns. The LMH vertical configuration (Figure 7a) demonstrates enhanced CO2 flow with maximum relative permeability reaching 0.75, while the HLM arrangement (Figure 7b) shows more restricted flow with a maximum value around 0.55. The vertical MLH and MHL configurations (Figure 7c,d) exhibit intermediate behavior with maximum CO2 relative permeability values of approximately 0.68 and 0.64, respectively. The vertical LHM and HML arrangements (Figure 7e,f) show characteristic differences in curve shapes, particularly in how rapidly the brine relative permeability decreases with increasing CO2 saturation.
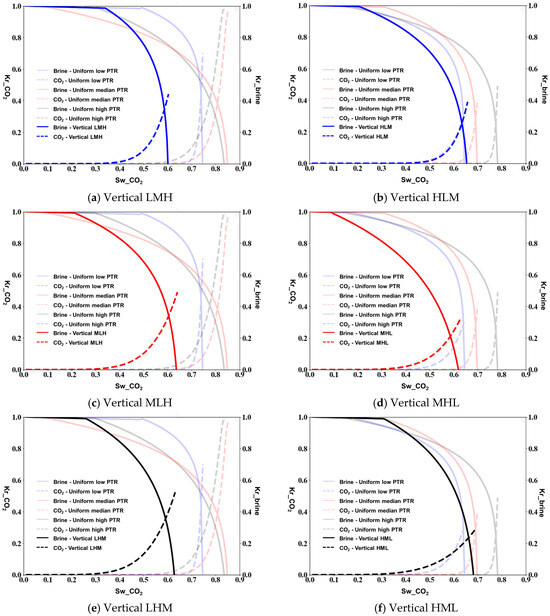
Figure 7.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of vertical porous media at a contact angle of 125°.
As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 150°, for horizontal heterogeneity, we observe a significant enhancement in CO2 mobility across all configurations due to the strongly CO2-wet conditions. The LMH configuration (Figure 8a) exhibits a maximum CO2 relative permeability of approximately 0.82, while the HLM arrangement (Figure 8b) reaches about 0.7. The MLH and MHL configurations (Figure 8c,d) show maximum values around 0.76 and 0.73, respectively, with notably different curvature patterns compared to the lower contact angle cases. The LHM and HML configurations (Figure 8e,f) demonstrate how increased CO2-wetting alters the balance between the phases, with crossover points shifted toward lower CO2 saturations, indicating preferential flow for CO2 even at lower saturations.
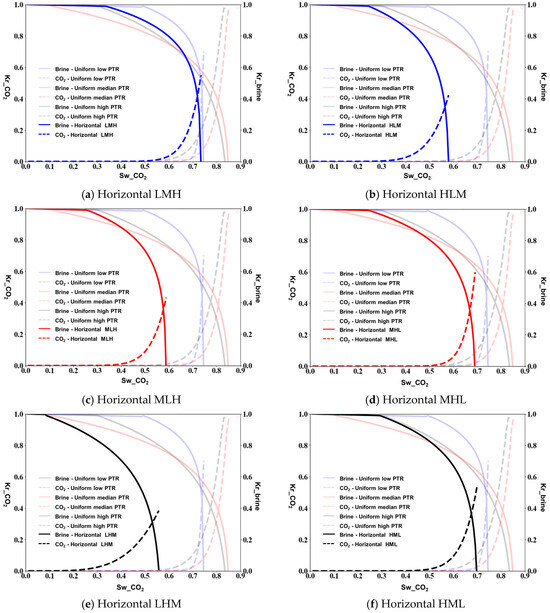
Figure 8.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of horizontal porous media at a contact angle of 150°.
As the contact angle between the CO2 and the brine is 150°, for vertical heterogeneity, the maximum benefit for CO2 mobility is observed. The LMH vertical configuration (Figure 9a) shows a remarkably high CO2 relative permeability approaching 0.85, while the HLM arrangement (Figure 9b) reaches about 0.75. The vertical MLH and MHL configurations (Figure 9c,d) exhibit maximum CO2 relative permeability values of approximately 0.8 and 0.78, respectively. The vertical LHM and HML arrangements (Figure 9e,f) demonstrate the most favorable conditions for CO2 flow, with the brine relative permeability decreasing more rapidly compared to all other contact angle scenarios.
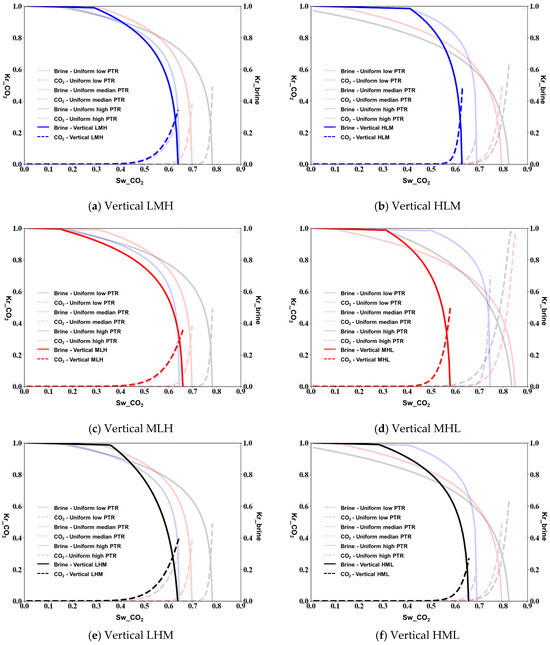
Figure 9.
Relative permeability measured from micromodel simulations of vertical porous media at a contact angle of 150°.
In summary, our micromodel results reveal several key trends: (1) increasing contact angle from 100° to 150° consistently enhances CO2 relative permeability across all heterogeneity configurations; (2) vertical arrangements generally provide more favorable conditions for CO2 flow compared to horizontal counterparts due to buoyancy effects; (3) the heterogeneity order (He) significantly influences relative permeability behavior, with LMH configurations consistently showing the highest CO2 mobility and HLM configurations the lowest; (4) the crossover points between CO2 and brine relative permeability curves shift toward lower CO2 saturations as the contact angle increases, indicating more favorable mobility conditions for CO2 under brine-wet conditions; and (5) the slope of the relative permeability curves in the mid-saturation range (0.4–0.6) varies considerably depending on both heterogeneity configuration and contact angle, which has important implications for displacement efficiency during CO2 injection.
3.2. The Accuracy of the Present Intelligence Model and Validation
The application of our intelligent model to predict relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs utilized site-specific data obtained from core experiments. Figure 10 presents the relative permeability curves acquired from core experiments for three different samples, showing variability in both shape and magnitude that reflects the inherent heterogeneity of the reservoir formation. These core-derived curves served as input parameters for our ANN model, which then generated comprehensive relative permeability predictions for the entire heterogeneous reservoir, as shown in Figure 11.
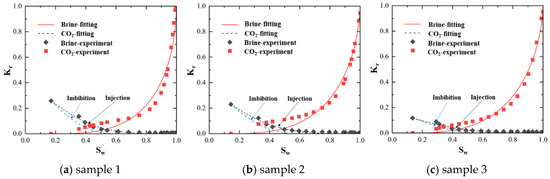
Figure 10.
The relative permeability curves were acquired from core experiments.
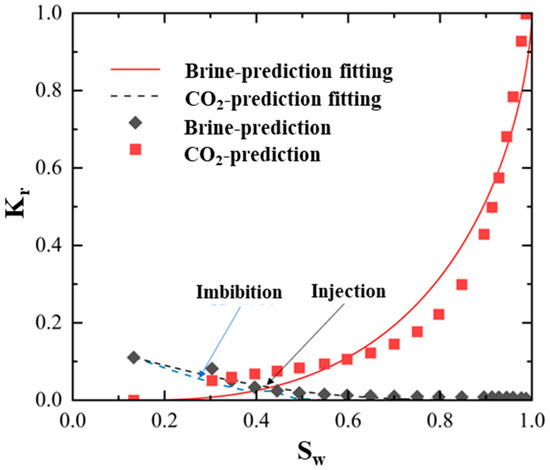
Figure 11.
The intelligent model predicted relative permeability curves of a heterogeneous reservoir.
The predicted relative permeability curves exhibit several noteworthy characteristics: (1) the maximum CO2 relative permeability reaches approximately 0.68, consistent with the moderate to strong brine-wet conditions present in the reservoir; (2) the brine relative permeability displays a relatively steep decline with increasing CO2 saturation, indicating an efficient displacement of brine by CO2; (3) the crossover point occurs at a CO2 saturation of approximately 0.45, suggesting favorable mobility conditions for CO2 after moderate saturation is achieved; and (4) the curvature of the relative permeability functions captures the complex interplay between fluid properties and the heterogeneous pore structure.
These predicted relative permeability relationships represent a significant advancement over conventional approaches that might fail to capture the effects of spatial heterogeneity. By accounting for the influence of heterogeneity characteristics on multiphase flow behavior, our model provides more realistic relative permeability estimations that can be directly incorporated into reservoir simulations.
The accuracy of the intelligent model is manifested by the Mean Squared Error (MSE). For the accuracy of the training process, our ANN model achieved exceptional performance with an MSE below 0.0025 for both CO2 and brine relative permeability predictions. Figure 12 demonstrates the strong correlation between predicted and actual CO2 relative permeability values, with data points tightly clustered along the ideal 45° line, indicating high prediction accuracy across the entire range of saturation values. Similarly, Figure 13 shows excellent agreement between predicted and actual brine relative permeability values. The model’s high accuracy is attributed to several factors: (1) the comprehensive training dataset that captured various heterogeneity patterns and fluid conditions through systematic micromodel experiments, (2) the effective neural network architecture with appropriate hyperparameters, and (3) the integration of key physical parameters including fluid properties, heterogeneity characteristics, and relative permeability measurements from uniform porous media.
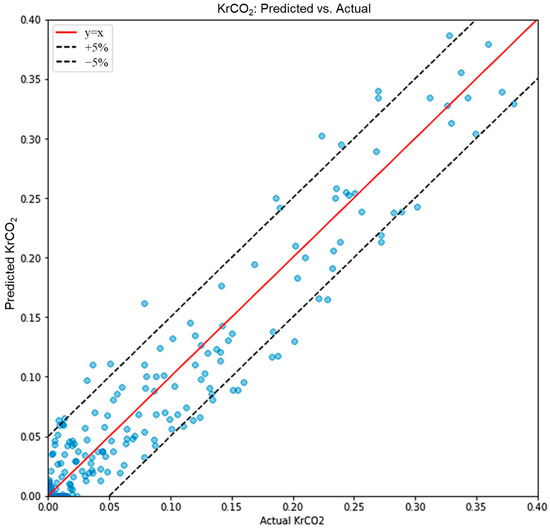
Figure 12.
The intelligent model accuracy manifested by predicted CO2 relative permeability vs. actual CO2 relative permeability.
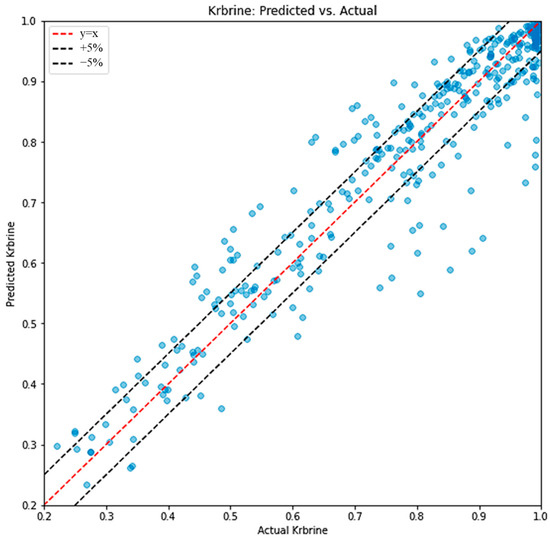
Figure 13.
The intelligent model accuracy manifested by predicted brine relative permeability vs. actual brine relative permeability.
The validation process further confirmed the model’s robust predictive capability, with validation MSE values closely matching those of the training process, indicating good generalization performance without overfitting. The model demonstrated particularly strong performance in predicting relative permeability in the mid-saturation range (0.3–0.7), which is most critical for practical applications in reservoir simulation.
3.3. Actual Field Application
The practical utility of our intelligent prediction approach was demonstrated through reservoir simulations of CO2 sequestration in a saline aquifer. Figure 14 presents the geological information of the actual reservoir and its reconstructed model in the CMG simulation platform. The heterogeneous nature of the reservoir is evident from the variable permeability distribution shown in the color scale.
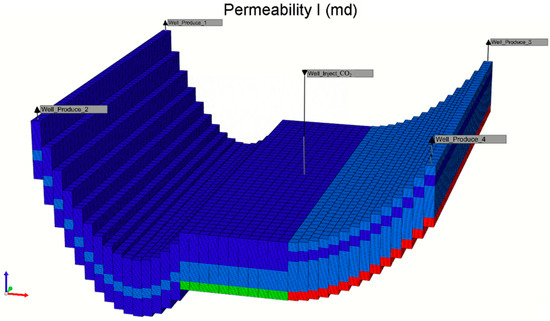
Figure 14.
The physical model of the actual heterogeneous reservoir.
Figure 15 illustrates the progression of CO2 injection and plume migration over a 30-year period, with snapshots at 5-year intervals. These simulation results, incorporating our predicted relative permeability relationships, show several important features: (1) the CO2 plume initially migrates upward due to buoyancy effects before spreading laterally beneath the caprock; (2) the plume shape and migration pattern are strongly influenced by the heterogeneous permeability distribution; (3) after 30 years of injection, the CO2 has spread across a substantial portion of the reservoir while remaining securely trapped beneath the impermeable caprock.
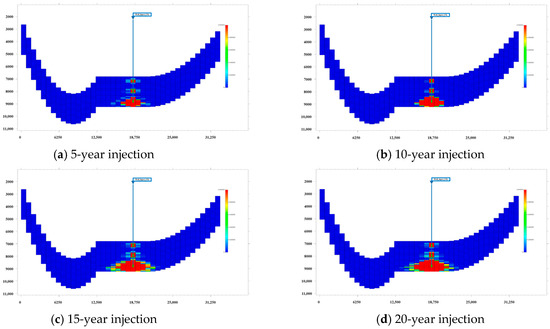
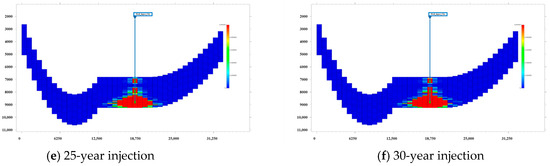
Figure 15.
The simulation of CO2 sequestration in the actual heterogeneous reservoir by integrating the predicted relative permeability.
Validation against published literature [37,38] demonstrated that our simulation results of temporal CO2 saturation variation deviate by only 3% from previously reported values for similar geological settings. Furthermore, the predicted CO2 distribution patterns and migration duration align closely with literature reports, with ultimate CO2 storage capacities reaching 94% of experimental results, as shown in Figure 16. This strong agreement confirms the predictive capability of our approach and its practical applicability for CO2 sequestration projects in heterogeneous reservoirs.
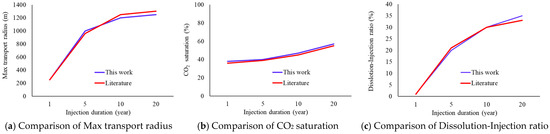
Figure 16.
Comparison between the results of this article and the published literature [37,38].
To validate the reliability of the AI-predicted relative permeability curves under realistic reservoir conditions, we integrated the predicted curves into a numerical simulator to model CO2 injection processes. The simulated results—including CO2 saturation profiles and maximum transport radius—were compared against field-monitored data from analogous CO2 sequestration projects. For instance, the predicted relative permeability curves yielded a transport radius with a relative error of less than 5%. Similarly, CO2 saturation distributions aligned closely with historical monitoring data (R2 > 0.90). This consistency demonstrates that the AI-derived parameters preserve physical rationality and effectively replicate reservoir dynamics, thereby indirectly verifying the accuracy of the proposed method.
4. Discussion
The intelligent prediction method established in this paper utilizes machine learning to identify patterns in cross-scale experimental data, thereby addressing the limitations of experimental, theoretical analysis, and numerical simulation methods. The integration of micromodel experiments, which can be conducted more rapidly than core floods while still capturing essential physics, with core-scale measurements provides a more efficient pathway to relative permeability prediction.
Despite the promising results, several limitations of our approach warrant discussion. First, the training dataset, while comprehensive, cannot capture the full range of heterogeneity patterns encountered in natural reservoirs. Future work should focus on expanding the training dataset to include a wider variety of geological settings and heterogeneity configurations. Second, the current model assumes that the input parameters adequately characterize the relevant heterogeneity. More sophisticated heterogeneity descriptors, possibly derived from advanced imaging techniques or geostatistical methods, could further enhance the model’s predictive capability. Third, our validation focused primarily on CO2-brine systems relevant to carbon sequestration. Additional validation for other fluid systems, particularly those with more complex phase behavior such as three-phase flow or flow involving non-Newtonian fluids, would strengthen the model’s applicability.
The application of our model to CO2 sequestration scenarios reveals several important insights. The strong agreement between our simulated results and published literature validates not only the predictive capability of our model but also its practical utility for carbon storage projects. Accurate prediction of relative permeability directly influences estimates of CO2 injectivity, plume migration, and ultimate storage capacity—all critical parameters for project planning and risk assessment.
Furthermore, our approach allows for a more rapid evaluation of potential storage sites by reducing the need for expensive and time-consuming laboratory experiments. This efficiency gain could accelerate the implementation of carbon sequestration projects, contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
An important consideration for practical implementation is the significant gap between laboratory conditions used in our experiments and actual reservoir conditions in the field. While our model has demonstrated strong predictive capability under controlled laboratory settings, several factors may affect its performance in real-world carbon sequestration projects. These include variations in pressure and temperature conditions that can alter CO2-brine interfacial properties, the presence of formation minerals that may interact with injected CO2, causing precipitation or dissolution, geomechanical effects such as stress-dependent permeability changes, and long-term chemical reactions not captured in short-duration experiments. Future work should focus on validating our approach under conditions that more closely approximate reservoir environments, potentially through pilot-scale studies or by incorporating these complex physicochemical interactions into the modeling framework. This validation will be crucial for accurately predicting long-term storage behavior and optimizing injection strategies in full-scale carbon sequestration operations.
5. Conclusions
The novel intelligent prediction approach developed in this study offers a robust solution for evaluating relative permeability in heterogeneous porous media. Our methodology uniquely integrates multiscale properties—bridging microscale experiments, core-scale measurements, and field-scale applications—to create a comprehensive predictive framework. This multiscale integration represents a significant advancement over conventional approaches that typically operate at discrete scales.
Our intelligent model demonstrated exceptional predictive accuracy, achieving a Mean Squared Error below 0.0025 when tested against experimental measurements. The model successfully captured the complex relationships between fluid properties, heterogeneity characteristics, and relative permeability behavior across different spatial scales.
When the predicted relative permeability was incorporated into CMG simulations of heterogeneous reservoirs, the CO2 sequestration deviated by only 3% from published literature values. Besides, the model predicted CO2 distribution and the migration duration align with the literature report and the ultimate CO2 storage capacities within 94% of experimental results.
In conclusion, this intelligent multiscale prediction methodology addresses a fundamental challenge in reservoir characterization by providing an efficient approach for predicting relative permeability in heterogeneous reservoirs. The framework has significant implications for both academic research, advancing our understanding of multiphase flow dynamics, and industrial implementation, offering tools for site screening and risk assessment in geological carbon storage operations. By bridging laboratory experiments with field-scale predictions, our methodology can accelerate the deployment of carbon sequestration technologies while improving their effectiveness. This approach extends to various reservoir types and fluid systems, contributing valuable insights to both scientific inquiry and practical carbon sequestration implementation.
Author Contributions
J.W.: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. J.L.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. X.L.: Investigation. Y.Z.: Visualization. H.S.: Supervision and Resources, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52274027) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2022M713204).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PTR | Pore-throat ratio |
| PV | Pore volume |
| LMH | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with low, median and high pore-throat ratio |
| LHM | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with low, high and median pore-throat ratio |
| MLH | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with median, low and high pore-throat ratio |
| MHL | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with median, high and low pore-throat ratio |
| HLM | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with high, low and median pore-throat ratio |
| HML | The heterogeneous porous structure hierarchically assembled by uniform pore blocks with high, median and low pore-throat ratio |
| He | The heterogeneity order, which quantitatively indicates the heterogeneity of the hierarchical heterogeneous porous structure |
References
- Bachu, S. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2015, 40, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, S.M.; Cole, D.R. CO2 Sequestration in Deep Sedimentary Formations. Elements 2008, 4, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yue, M. Microscopic regulation mechanisms of pore heterogeneity and flow conditions on CO2 residual trapping and sequestration capacity. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 013108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.; Xie, Z.; Du, S.; Zhou, Y.; Song, H. Reducing energy consumption and enhancing trapping and capacity of CO2 sequestration: The effects of pore heterogeneity and fluid properties. Energy 2024, 304, 132088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krevor, S.; Blunt, M.J.; Benson, S.M.; Pentland, C.H.; Reynolds, C.; Al-Menhali, A.; Niu, B. Capillary trapping for geologic carbon dioxide storage—From pore scale physics to field scale implications. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2015, 40, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, R.H. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Honarpour, M.; Koederitz, L.; Harvey, A.H. Relative Permeability of Petroleum Reservoirs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarabadi, M.; Piri, M. Relative permeability hysteresis and capillary trapping characteristics of supercritical CO2/brine systems: An experimental study at reservoir conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 52, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.B.; Bachu, S. Drainage and Imbibition Relative Permeability Relationships for Supercritical CO2/Brine and H2S/Brine Systems in Intergranular Sandstone, Carbonate, Shale, and Anhydrite Rocks. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2008, 11, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltermann, C.E.; Gorelick, S.M. Heterogeneity in sedimentary deposits: A review of structure-imitating, process-imitating, and descriptive approaches. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2617–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Menhali, A.; Niu, B.; Krevor, S. Capillarity and wetting of carbon dioxide and brine during drainage in Berea sandstone at reservoir conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 7895–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, D.N.; Santamarina, J.C. Water-CO2-mineral systems: Interfacial tension, contact angle, and diffusion-Implications to CO2 geological storage. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 15355–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Samper, J.; Wolfsberg, A.; Levitt, D. Identification of relative conductivity models for water flow and solute transport in unsaturated bentonite. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2008, 33, S177–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; McPherson, B.; Pan, F.; Dai, Z.; Moodie, N.; Xiao, T. Impact of three-phase relative permeability and hysteresis models on forecasts of storage associated with CO2-EOR. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1109–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.; Bossler, D.; Bossler, V.N. Calculation of Relative Permeability from Displacement Experiments. Trans. AIME 1959, 216, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, J.; Bodi, T.; Szucs, P.; Civan, F. Convenient formulae for determination of relative permeability from unsteady-state fluid displacements in core plugs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2002, 36, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijic, A.; LaForce, T.C.; Muggeridge, A.H. CO2 injectivity in saline aquifers: The impact of non-Darcy flow, phase miscibility, and gas compressibility. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 4163–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.; Oedai, S.; Ott, H. Displacement and mass transfer between saturated and unsaturated CO2–brine systems in sandstone. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2013, 12, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.A.; Blunt, M.J.; Krevor, S. Multiphase Flow Characteristics of Heterogeneous Rocks From CO2 Storage Reservoirs in the United Kingdom. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krevor, S.C.M.; Pini, R.; Zuo, L.; Benson, S.M. Relative permeability and trapping of CO2 and water in sandstone rocks at reservoir conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirian, E.; Dejam, M.; Chen, Z. Performance forecasting for polymer flooding in heavy oil reservoirs. Fuel 2018, 216, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, D.; Lu, D.; Yang, J. Research on the reconstruction method of porous media using multiple-point geostatistics. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2010, 53, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Rai, C.S.; Sondergeld, C.H.; Devegowda, D. Rock Typing in Eagle Ford, Barnett, and Woodford Formations. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2018, 21, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinedini, E.; Dabir, B.; Dadvar, M. Integrating computational fluid dynamic, artificial intelligence techniques, and pore network modeling to predict relative permeability of gas condensate. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, R.; Simjoo, M.; Chahardowli, M. Low salinity water flooding: Estimating relative permeability and capillary pressure using coupling of particle swarm optimization and machine learning technique. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoga, H.F.; Russell, T.J.; Purswani, P. Predictive Model for Relative Permeability Using Physically-Constrained Artificial Neural Networks. SPE J. 2024, 29, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemifar, F.; Blois, G.; Kyritsis, D.C.; Christensen, K.T. Quantifying the flow dynamics of supercritical CO2–water displacement in a 2D porous micromodel using fluorescent microscopy and microscopic PIV. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 95, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lao, J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y. Underground hydrogen storage in reservoirs: Pore-scale mechanisms and optimization of storage capacity and efficiency. Appl. Energy 2023, 337, 120901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, R.; Benson, S.M. Capillary pressure heterogeneity and hysteresis for the supercritical CO2/water system in a sandstone. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 108, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasak, H. OpenFOAM: Open source CFD in research and industry. Int. J. Nav. Arch. Ocean. 2009, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Raeini, A.Q.; Blunt, M.J.; Bijeljic, B. Modelling two-phase flow in porous media at the pore scale using the volume-of-fluid method. J. Comput. Phys. 2012, 231, 5653–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Song, Z.; Pan, B.; Ming, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, H. Research on CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers with different relative permeability considering CO2 phase conditions. Energy 2024, 313, 133739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.M.; Watson, A.T. Accuracy of JBN Estimates of Relative Permeability: Part 2—Algorithms. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1984, 24, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.M.; Watson, A.T. Accuracy of JBN Estimates of Relative Permeability: Part 1—Error Analysis. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1984, 24, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Bai, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, B. Characterizing CO2 plume migration in multi-layer reservoirs with strong heterogeneity and low permeability using time-lapse 2D VSP technology and numerical simulation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2020, 92, 102880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Liu, T.; Wei, N.; Ma, X.; Jin, X.; Fu, L. Classification and assessment methodology of carbon dioxide geological storage in deep saline aquifers. China Geol. 2023, 50, 943–951. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).