Abstract
The southern Gabès aquifer in southeastern Tunisia faces significant stress due to unsustainable groundwater extraction. This study employs a SEAWAT model to evaluate groundwater losses, salinization mechanisms, and the interaction between the confined aquifer and the Mediterranean Sea. The model, incorporating well pumping rates, regional freshwater inflows from the Matmata Mountain Range, and the Mediterranean Sea boundary, demonstrated high accuracy in simulating hydraulic heads. Findings reveal that regional inflow is only half of the current pumping rate, indicating unsustainable groundwater use. The study also assessed salinity dynamics by modeling the Mediterranean Sea as a constant head and salinity boundary. Results suggest limited exchange between the aquifer and the sea, challenging previous assumptions. While the immediate risks of salinization are low, continued over-extraction could compromise the aquifer’s long-term sustainability. This research highlights the need for stricter local groundwater management, offers insights into regional coastal aquifer interactions, and contributes to global discussions on managing stressed aquifer systems.
1. Introduction
Groundwater is a crucial resource, providing approximately 12 × 103 billion cubic meters (BCM) annually, with 986 BCM currently being utilized [1]. The primary uses of groundwater are distributed across agriculture (67%), domestic use (22%), and industry (11%) [2]. Groundwater supports more than 40% of global food production, underlining its importance in crop irrigation, potable water supply, and various industrial processes such as chemical manufacturing and energy production [3]. The rising demand for groundwater to meet the growing needs of economic and agricultural sectors places this vital resource under significant pressure, especially in coastal areas where salinization is a major concern. In coastal regions, the delicate balance between freshwater resources and seawater intrusion is of paramount concern. Several factors, including groundwater overexploitation, sea level rise, coastal storms, and the construction of seawalls can significantly impact the extent of seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers [4]. The higher density of seawater (1.025 g/cm3) compared to freshwater (1.0 g/cm3) causes seawater to intrude at the base of coastal aquifers when excessive groundwater extraction lowers the water table [5].
Seawater intrusion is a widespread issue in many countries due to factors such as sea level rise, excessive groundwater extraction, and peculiar geological features [6]. Numerous studies have documented groundwater salinity and mineralization in coastal regions worldwide, including Italy [7], Algeria [8], India [9], Western Australia [10], and Tunisia [11,12,13].
Groundwater salinization is a concerning environmental global issue, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Aquifer salinization is a process that can be driven by both natural and anthropogenic forcings [7,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Concurrent natural processes within the hydrological cycle, such as evapotranspiration, infiltration, and groundwater exchanges between coastal and inland aquifers, play a critical role by concentrating salts in the soil as water evaporates. This issue is particularly exacerbated in coastal regions because of the mixing processes between freshwater and saltwater [17,18]. Anthropogenic pressures on fresh groundwater resources, such as the excessive extraction of groundwater for agricultural and industrial purposes, further intensify this phenomenon by lowering the water table, often below the sea level. This leads to the concentration of dissolved salts in groundwater bodies [11,19,20]. The worsening groundwater salinization can also come from other processes within the hydrological cycle, such as a low amount of rainfall, which is usual in semi-arid and arid regions, limiting the natural dilution of salts [11]. Recent research has highlighted the importance of understanding the spatial distribution of groundwater salinity fluxes and the factors controlling them to support the sustainable management of coastal resources [21,22]. Given the increasing pressures from climate change, including rising temperatures and sea levels, and the depletion of surface water, managing the quantity and quality of groundwater resources has become critical [23]. To quantify salinization mechanisms and simulate seawater intrusion processes, density-dependent groundwater flow and solute transport models are required [13,24,25]. Models such as SUTRA, FEFLOW, and SEAWAT are available to simulate groundwater dynamics and contaminant pathways, addressing both groundwater-flow and transport equations [26]. Groundwater modeling provides a scientific approach to assess and predict the dynamics of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. It involves the integration of hydrological, geological, and chemical data to simulate the behavior of groundwater systems under various scenarios.
The southern Gabés aquifer in southeastern Tunisia serves as a critical water resource for the Gabés region’s agricultural, domestic, and industrial needs. However, the aquifer is under possible threat from seawater intrusion due to overexploitation and other factors, including halite dissolution, that exacerbate groundwater salinization [27]. The Gabès aquifer, like many coastal aquifers, faces challenges from seawater intrusion that could jeopardize the water quality for agricultural irrigation and other uses. This makes groundwater modeling an essential tool for understanding and mitigating seawater intrusion and ensuring the sustainable use of groundwater resources.
For the first time, a variable density SEAWAT model was conceived, discretized, and calibrated for the southern Gabès aquifer, with the aim to identify the extent of seawater intrusion, the factors driving groundwater salinization, and the potential mitigation strategies.
2. Study Area
2.1. Geographical and Climatic Overview
The current research focused on the southern region of Gabès, situated in the southeastern part of Tunisia. This area encompasses approximately 2465.3 km2, with geographic coordinates ranging from latitudes 33°54′40.8572″ N to 33°15′57.0200″ N, and longitudes 9°53′10.5381″ E to 10°35′46.6426″ E. Gabès is one of Tunisia’s primary groundwater reservoirs, featuring a variety of wadis such as Sourrag I and II, El Ferd, Zerkine, Zigzaou, and Ez Zeuss, originating from the Matmata Mountains (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The location of the model domain in the Gabès Gulf (black rectangle) and its main features, including active cells (not colored), inactive cells (light grey areas within the black rectangle), and constant heads cells (blue area within the black rectangle).
The climate in this region is predominantly Mediterranean, characterized by mild and humid winters, while becoming arid in summers because of the desertic climate elements. Annual precipitation is notably irregular and mostly scarce, averaging around 195 mm/year in the South Gabès plain and approximately 220 mm/year in the Matmata Mountains [11,28]. Temperature patterns reveal an annual average of about 21 °C, with peak temperatures reaching up to 33 °C in July. The hottest months, July and August, record average monthly temperatures of around 35 °C. Evaporation analysis indicates that August experiences the highest evaporation rates, with a maximum value of 197 mm, whereas December shows the lowest evaporation rates, approximately 123 mm [11,28].
The southern Gabès aquifer in southeastern Tunisia serves as a critical water source for most of the human activities in the area. This source of freshwater is threatened by several factors, for example: the rising (i) temperatures, which impact evapotranspiration processes within the local hydrological cycle; (ii) sea levels, increased in recent years; and (iii) the depletion of surface water, where managing the quantity and quality of groundwater resources has become critical [11,28].
Aquifer recharge provided by rainfall in Tunisia is extremely poor. Although northwestern Tunisia has a mean yearly rainfall of 700–1000 mm/year, the Gabès region is located in a much more arid area. The mean yearly amount of rainfall can be estimated between 0 and 300 mm/year [29], therefore the climate in the area is usually considered arid.
2.2. Geological and Hydrological Characteristics
The coastal plain of southern Gabès is characterized by a complex geological composition (Figure 2), spanning a dating period between the Upper Cretaceous and the Quaternary era. The Upper Cretaceous formations, observable to the west and north in areas including the Matmata, Hallouga, and Monncef mountains, predominantly consist of dolomites, limestones, fossiliferous marls, and gypsum clays [28,30]. The widespread Plio-Quaternary deposits in the study area mainly comprise gypsum clays with consolidated conglomerates. The Quaternary deposits are represented by continental detrital materials, including sands, clays, and conglomerates [11,30,31,32].
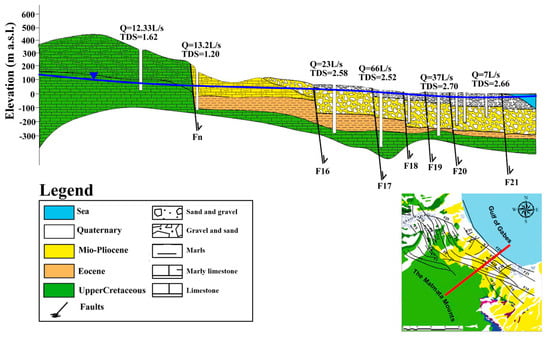
Figure 2.
Geological cross-sections of the study area and the main lithofacies are depicted by different colors.
The region’s groundwater system includes the phreatic (unconfined) aquifer within the Plio-Quaternary horizon and the confined aquifer within the Lower Senonian and Turonian carbonates. The unconfined aquifer is influenced by surface recharge and climatic variations, whereas the confined aquifer is characterized by significant fissuring and high transmissivity, indicating strong hydraulic connectivity. Tectonic activities profoundly influence the hydrodynamic behavior of these aquifers; this was witnessed by variations in the hydraulic head and of the hydrogeological parameters [28,30,31,32].
Hydrodynamic parameters were crucial for understanding groundwater flow dynamics. The transmissivity of the unconfined aquifer was approximately 4 × 10−3 m2/s, while for the confined aquifer, it ranged from 1 to 2 × 10−2 m2/s. The storage coefficients were 0.15 for the unconfined aquifer and 0.03 for the confined aquifer [33].
Groundwater extraction data indicated a significant increase over the past decades. Extraction volumes rose from approximately 50 MCM/y in 1970 to over 150 MCM/y in 2021, with the number of wells increasing from around 70 to more than 600.
2.3. Hydrochemical Context
The region’s groundwater quality is a critical aspect of its hydrogeology. Previous studies indicate that the groundwater is susceptible to salinization, influenced by both natural processes and anthropogenic activities. The prevalence of gypsum and other soluble minerals in the geological formations contributes to the natural salinity of the aquifers [34]. Furthermore, excessive groundwater extraction for irrigation and other uses exacerbates the problem by lowering the water table and enhancing the intrusion of saline water from adjacent marine environments [35].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Integration
This study focused on the southern Gabès region, aiming to assess seawater intrusion and the groundwater balance of the confined aquifer, while the unconfined aquifer was not simulated, since it was not in direct hydraulic connection with the confined aquifer and had a lack of data, such as recharge and evapotranspiration rates. A multidisciplinary approach integrated a three-dimensional geological model, a groundwater flow model, Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM), water consumption analysis, irrigated agricultural systems, and oasis ecosystems. All data were incorporated into a Geographic Information System (GIS), encompassing harmonized geological maps and the details of the monitoring wells sampled. To this purpose, in September 2022, the TDS from 210 wells located in the confined aquifer was measured via a HANNA Instr. multi-parameter analyzer after purging the well for at least two well volumes.
3.2. Groundwater Flow Model Development
The groundwater flow model was constructed using SEAWAT, a three-dimensional variable density flow and transport model [36], included within the Processing Modflow 11 platform for pre-and post-processing [37]. This model solves the variable density groundwater flow equation for steady and transient states in confined and unconfined multilayered aquifers:
where is the gradient operator , is the is the fluid density (ML−3), is the specific discharge vector (L/T), is the density of water entering from a source or leaving through a sink (ML−3), is the volumetric flow rate per unit volume of aquifer representing sources and sinks (T−1), is the specific storage in terms of pressure (M−1LT2), P is the fluid pore pressure (ML−1T−2), is the effective porosity (-), C is the solute concentration (ML−3), and t is time (T).
3.3. Salinity Transfer Modeling
To assess the seawater intrusion risk, salinity transfer was incorporated into the groundwater flow model. The salinity transport equation used was:
where D is the hydrodynamic dispersion tensor along a principal direction (i,j) and component (L2T−1), is the groundwater velocity (LT−1), qs is the source/sink term (L3T−1), Cs is the concentration of the source/sink (ML−3), and R is a chemical reaction (if any).
3.4. Grid Design Conditions
The SEAWAT model designed to assess the southern Gabès confined aquifer’s interaction with the Mediterranean Sea utilized a meticulously structured grid of 136 rows and 130 columns, totaling approximately 17,500 active cells. This grid covered an area of 1508 km2 (43 × 41 km) and was aligned with the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system to ensure precise spatial accuracy. Within this grid, cells were designated as active if they fell within the model domain or in permeable geological units, while those outside the domain or in impermeable zones were set as inactive.
To accurately represent the topography of the southern Gabès region, the model incorporated data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with a resolution of 20 × 20 m. This high-resolution DEM was interpolated across the grid to capture the basin’s elevation profile, which is essential for defining surface boundary conditions and understanding the hydraulic gradients within the aquifer system.
Hydraulic conductivity (K) values for the lithological units were obtained from extensive pumping tests and informed by previous studies [33]. For the deep confined aquifer, the average hydraulic conductivity was determined to be 7.73 × 10−4 ± 3.00 × 10−4 m/s. This suggested a relatively homogeneous distribution of K, although localized variations were accounted for where data were available. The model incorporated a vertical anisotropy ratio of 1:10, indicating that the vertical hydraulic conductivity was significantly lower than the horizontal conductivity, consistent with standard practices in hydrogeological modeling [37].
Boundary conditions within the model were set using the general head boundary (GHB) package to represent the lateral contributions from adjacent basins. These contributions were based on hydraulic potential gradients and were crucial for simulating the dynamic inflows and outflows along the model’s edges. Additionally, the Mediterranean Sea was modeled as a constant head and salinity boundary to evaluate its potential impact on groundwater salinity and seawater intrusion. This approach allowed for a detailed assessment of how changes in sea level and groundwater extraction might influence salinization near the coast.
Groundwater extraction was simulated using the Well package, which distributed an average pumping rate across 173 wells scattered throughout the model domain (Figure 3). This distribution reflects current extraction practices and helps assess their impact on the aquifer system. The horizontal flow barrier (HFB) package was employed to simulate compressive faults with a thickness of 1 m and an initial hydraulic conductivity (K) of 1.0 × 10−9 m/s. These faults were modeled to analyze their potential role as flow barriers or preferential pathways, impacting groundwater flow direction and behavior. Consistent with the climatic setting of the area and considering that the aquifer within the modelled area was confined, we did not consider any atmospheric boundary conditions, hence we did not involve any recharge from rainfall.
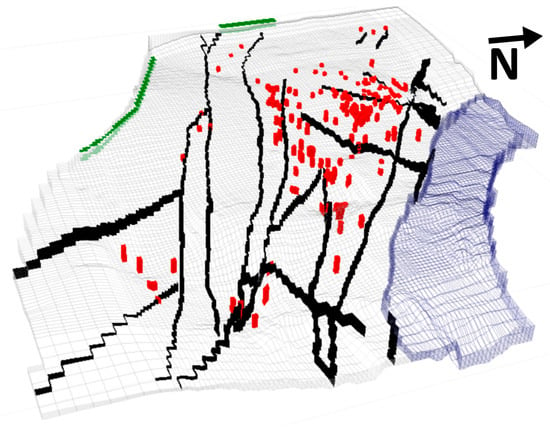
Figure 3.
The 3D discretization and boundary conditions of the confined aquifer: pumping wells (red); general head boundary, representing the inflow from the Matmata Mountains (green); the Mediterranean Sea, representing the outflow from the basin (blue); and HFB, representing the major faults (black). The vertical exaggeration is 1:10.
Model calibration involved an initial manual trial-and-error approach followed by automated calibration using the PEST tool [38]. This process adjusted key parameters, including hydraulic conductivity, GHB conductance, and the HFB equivalent K, to match simulated hydraulic heads with observed data from 161 observation wells distributed across the confined aquifer. Calibration performance was rigorously evaluated using metrics such as the index of agreement (I), mean error (ME), mean absolute error (MAE), determination coefficient (R2), and Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient (NSE) [39]. The detailed grid design and calibration process were critical for accurately simulating groundwater flow and salinity dynamics within the southern Gabès aquifer. This model provided essential insights for managing local groundwater resources, enhanced the regional understanding of aquifer behavior, and contributed to the global knowledge on addressing challenges related to seawater intrusion and groundwater depletion.
4. Results
The SEAWAT model simulations for the southern Gabès (TN) confined aquifer provided critical insights into the hydrogeological interactions between the aquifer system and the Mediterranean Sea. The comparison between observed and simulated hydraulic heads for the confined aquifers, as illustrated in Figure 4, indicated a generally good alignment, with data points scattered along the 1:1 line. However, a slight underestimation in the calculated heads was observed, with a mean error (ME) of approximately −0.58 m (Table 1). This error is considered acceptable given the broad piezometric range simulated, which exceeded 80 m. Despite this minor underestimation, the model’s performance metrics, including the index of agreement (I), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), and the determination coefficient (R2), were all robust, with values exceeding 0.8 and 0.9, respectively. The relatively large mean absolute error (MAE) observed in the calculated heads may be attributed to local variations in the hydraulic conductivity (K), which were not fully incorporated to maintain a streamlined model.
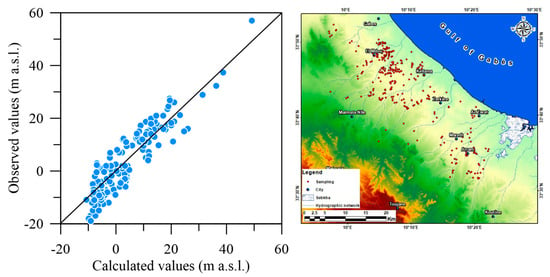
Figure 4.
Left panel: scatter diagram of the observed head (m) versus calculated head (m) values for the simulated confined aquifer. Right panel: position of the observation wells.

Table 1.
The model’s performance indicators.
The sensitivity analysis identified the equivalent hydraulic conductivity (K) of the horizontal flow barrier (HFB) as the most critical parameter affecting model accuracy. Calibration revealed that the initial assumption of faults as impermeable barriers was incorrect. Instead, the calibrated model indicated a much higher K value for the HFB, approximately 1.05 × 10−6 m/s, which was three orders of magnitude higher than the initial estimate. This significant increase suggests that faults in the region do not act as impermeable barriers, dividing the aquifer into independent zones. Rather, they function as conduits that concentrate and direct groundwater flow along their lengths, facilitating exchange between different aquifer zones. This finding is crucial, as it confirmed that faults in the region can act as drains with high K values, allowing significant interaction between the confined aquifers, thus influencing the overall groundwater flow dynamics.
The hydraulic head map of the confined aquifer (Figure 5) further elucidated the flow patterns within the system, showing hydraulic head values ranging from 60 m to −50 m. These values indicated a strong potential for inland drainage of Mediterranean Sea waters. The primary groundwater flow direction was observed to be from the south-west towards the north-east, originating from the Matmata mountain range. However, this natural flow regime was significantly altered by extensive groundwater pumping, particularly in the Mareth region. Here, the wells had created a large capture zone, resulting in a pronounced depression in the hydraulic head, effectively diverting groundwater flow away from the coast before it could reach the sea.
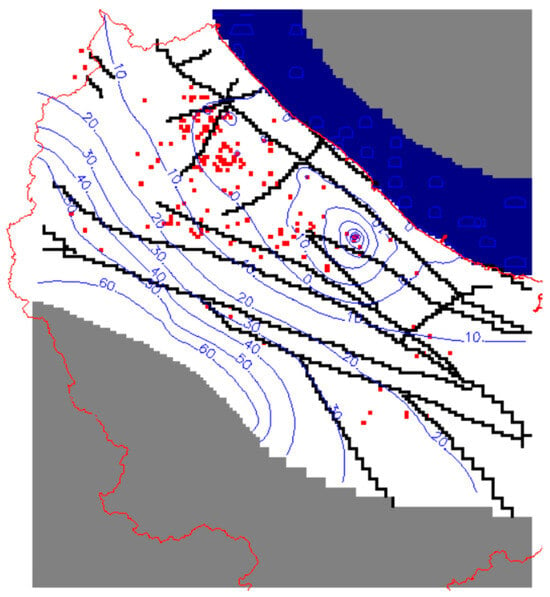
Figure 5.
Contours of the calculated groundwater heads in m a.s.l. for the confined aquifer in light blue. The grey areas are no flow cells; the deep blue area consists of constant head cells representing the Mediterranean Sea; the red polyline is the watershed boundary; the black lines are the HFB, representing the faults; and the red squares are pumping wells.
In scenarios where the HFB package was excluded from the model to simulate the hydrogeologic behavior of faults, the results were unsatisfactory. The simulated groundwater heads deviated significantly from the observed values near fault zones, either being too low or too high. This discrepancy underscored the critical role of faults in controlling groundwater flow within the aquifer system. Without accurately representing the faults as conduits for groundwater flow, the model could not achieve acceptable performance indicators, highlighting the importance of considering fault dynamics in regional groundwater models.
Additionally, the groundwater budget analysis for the southern Gabès confined aquifer in a steady-state condition revealed a balanced input and output flow, with a negligible discrepancy (Table 2). The contribution of the general head boundary (GHB) estimated by the model aligned with the constant head boundary (CHB), with only a minor portion of the groundwater outflowing as submarine discharge. However, the primary outflow of the aquifer system was due to groundwater extraction by wells.

Table 2.
The groundwater balance of the confined aquifer.
The analysis indicated that the current level of groundwater exploitation was unsustainable, as the regional groundwater flow from the Matmata mountain range was insufficient to support the extensive extraction. This unsustainable extraction resulted in a significant drawdown of the water table, approximately 10 m, observed in both the shallow and deep aquifers over recent decades [33].
Following the detailed analysis of hydraulic head dynamics and groundwater flow patterns, the focus shifted to evaluating the salinity distribution within the confined aquifer under different pumping scenarios. This assessment is crucial for understanding the impact of groundwater extraction on the aquifer’s water quality and its susceptibility to seawater intrusion. Figure 6 illustrates the calculated groundwater salinity contours for the confined aquifer under two distinct scenarios: one simulating the maximum pumping rates recorded in 2020, applied consistently over the entire simulation period (upper left panel), and the other incorporating the increasing pumping rates from 1970 to 2023 (upper right panel). In both scenarios, the model predicted the development of a substantial seawater wedge that extended several kilometers inland, suggesting a pronounced intrusion of saline water into the aquifer system. This intrusion was indicative of the pressure exerted by excessive groundwater extraction, which disrupts the natural balance between freshwater and seawater, leading to the inland migration of saline water. However, the observed salinities, depicted in the lower panel of Figure 6, tell a different story. Contrary to the model predictions, salinities in the range of 30–35 g/L were never detected in the field. The most saline groundwater, with concentrations ranging from 5 to 7.9 g/L, was located inland, rather than at the coast where one would expect the highest salinity levels due to seawater intrusion. This discrepancy between the observed and simulated salinities highlights a significant challenge in accurately modeling groundwater salinity in the region.
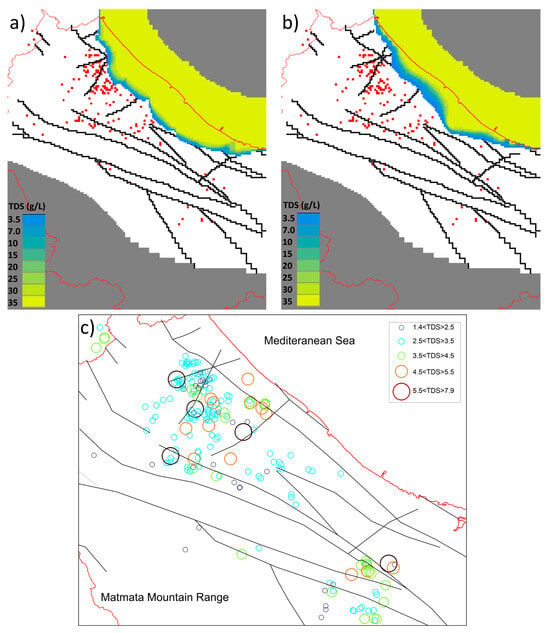
Figure 6.
Contours of the calculated groundwater salinities for the confined aquifer, for the scenarios with maximum pumping rates recorded in 2020 used for the whole simulation time (upper left panel (a)), and increasing pumping rates over time from 1970 to 2023 (upper right panel (b)). Here the red line represents the watershed the red squares represent the pumping wells and the black lines the faults. The observed salinities are depicted in the lower panel (c).
The poor performance of the model in simulating groundwater salinity was further underscored by the model performance indicators, including the index of agreement (I), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), and the determination coefficient (R2). These indicators consistently failed to reach 0.2, even after increasing the apparent longitudinal dispersivity to 20 m, which represented the upper limit of physically based values for a model of this size [5]. The poor model performance suggests that there were unaccounted factors or complexities in the aquifer system that were not captured by the current modeling approach. Potential reasons for this could include heterogeneities in the aquifer materials, inaccuracies in the representation of fault dynamics, or unmodeled temporal variations in pumping rates and groundwater recharge.
These findings have important implications at multiple scales. Locally, the research highlights the urgent need for improved groundwater management strategies in southern Gabès to prevent further degradation of the water quality and to protect the aquifer from excessive seawater intrusion. Regionally, the study contributes to the broader understanding of the coastal aquifer dynamics in North Africa, where similar challenges of salinization and over-extraction are prevalent. The discrepancies between modeled and observed salinities indicate that further refinement of the model is necessary, potentially incorporating more detailed data on the spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity, the influence of geological structures, and the temporal dynamics of groundwater use. Addressing these challenges will be critical for developing more accurate predictive models that can guide sustainable groundwater management in the region and beyond.
5. Discussion
The tridimensional hydrogeological model developed for the southern Gabès confined aquifer aimed to achieve several key objectives: (i) to assess the extent of seawater intrusion into the aquifer, and (ii) to determine whether this intrusion had reached the inland pumping wells via preferential flow paths facilitated by geological faults. These objectives were critical to understanding how the current exploitation rate of about 3 m3/s affected the saline wedge’s structure and the potential seawater-groundwater interaction within the confined aquifer.
Modeling the confined aquifer, rather than the unconfined one, was justified by the fact that the majority of groundwater extraction in the region occurred in the confined aquifer, which is more productive and characterized by lower salinities compared to the unconfined aquifer. Phreatic wells, which are fewer and less monitored, have significantly lower pumping rates and do not impact the groundwater system as extensively as the confined aquifer wells [31]. Thus, focusing on the confined aquifer provided a clearer picture of the primary groundwater exploitation dynamics and allowed for a more robust analysis of its impact.
The numerical model demonstrated good accuracy in predicting groundwater heads, aligning well with the observed data and facilitating an accurate estimation of the groundwater budget. The mean error (ME) of approximately −0.58 m, while indicating a slight underestimation, fell within an acceptable range given the overall piezometric range of over 80 m. The model performance indicators, including the index of agreement (I), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE), and coefficient of determination (R2), consistently exceeded 0.9 and 0.8 respectively, reflecting a strong fit between observed and simulated heads [39]. Despite this success, the model’s performance in simulating groundwater salinities was less satisfactory, as shown by Figure 6 and corroborated by poor performance metrics for salinity (I, NSE, and R2 consistently below 0.2), even when longitudinal dispersivity was maximized [5].
The discrepancy in salinity results underscores a significant finding: the confined aquifer, as modeled, is not directly connected to the Mediterranean Sea. The simulations indicated that the hazardous salinization values did not encroach upon the pumping well areas. This suggests that while the constant head boundary (CHB) condition effectively simulates groundwater fluxes, the actual hydraulic connection to the Mediterranean Sea is located further from the coast [40]. This extensive shallow region implies that the confined aquifer may have a direct but distant hydraulic contact with the Mediterranean Sea floor, potentially hosting significant volumes of fresh to brackish groundwater.
Field investigations and the model also highlighted the critical role of geological faults in the area. These faults, identified through geological surveys and incorporated into the numerical model, function as vertical barriers to groundwater flow. They prevent significant vertical exchange between aquifer layers, effectively isolating the freshwater confined reservoir from direct seawater intrusion. This finding is consistent with other studies which have shown that faults can act as barriers or drains in aquifer systems, influencing the extent and direction of groundwater flow and contaminant movement [11,34,35].
The fact that high salinity values were not simulated in areas of active pumping wells, despite increasing pumping rates from 1970 to the present, supported the conclusion that the relatively high salinities found inland were likely due to relict seawater lenses or the dissolution of secondary gypsum. This phenomenon has been documented in other regions, where inland high salinities are attributed to historical seawater encroachment or mineral dissolution rather than ongoing seawater intrusion [41,42]
In conclusion, the model’s scenarios confirm that there is no direct connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the confined aquifer near the coastline. However, the risk of overexploitation remains significant. Continued extraction of freshwater could eventually lead to the inland advancement of the saline wedge, posing threats to future water resource management. This potential for saline intrusion into freshwater sources highlights the need for careful monitoring and management practices to safeguard the quality and sustainability of groundwater resources.
6. Conclusions
This study on the southern Gabès confined aquifer has provided critical insights into the hydrogeological dynamics of this essential groundwater resource. The calibration of a robust numerical model to assess salinization processes, enabled results to reveal that the groundwater salinities observed in the wells tapping the confined aquifer were not due to direct seawater intrusion. The model simulations confirmed that seawater did not reach the inland areas where primary pumping wells are located. Instead, geological faults acted as crucial vertical flow barriers, preventing significant seawater intrusion and effectively safeguarding the aquifer’s freshwater resources. This study also identified that the relatively high salinity levels inland were primarily due to trapped relict seawater and gypsum dissolution, rather than ongoing marine influence. These findings are significant not only for local water management, guiding sustainable extraction practices, but also for regional and global contexts, offering valuable insights into the management of coastal aquifers under similar conditions. As water scarcity intensifies worldwide, the methodologies and conclusions drawn from this research could be useful for developing effective strategies to protect and sustainably manage groundwater resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C. and K.W.; methodology, N.C. and K.W.; software, N.C. and M.S.; validation, N.C., Y.H. and S.B.; formal analysis, K.W.; investigation, K.W.; data curation, K.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W. and B.H.; writing—review and editing, N.C., M.S., B.H., Y.H. and S.B.; visualization, N.C.; supervision, Y.H. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data and models will be available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Villholth, K.G. Groundwater Trends, Challenges and Solutions—From Global to Local; Grundfos Groundwater Days Aarhus Waterworks: Aarhus, Denmark, 2016; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Gun, J. Groundwater and Global Change: Trends, Opportunities and Challenges; UN World Water Assessment Program, WWDR: Perugia, Italy, 2012; 38p. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.; Tyson, G.; Konikow, L.; Custodio, E.; Villholth, K.G.; van der Gun, J.; Klingbeil, R. Food Security and Groundwater; Strategic Overview Series; International Association of Hydrogeologists: Vetralla, Italy, 2015; 6p. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, J.; Allen, D.M. Assessing the Risk of Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, H.D. Seawater Intrusion. In Modeling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport; Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantelon, J.A.; Guimond, J.A.; Robinson, C.E.; Michael, H.A.; Kurylyk, B.L. Vertical Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers Driven by Episodic Flooding: A Review. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR032614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombani, N.; Osti, A.; Volta, G.; Mastrocicco, M. Impact of Climate Change on Salinization of Coastal Water Resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, Y.; Hadji, R.; Redhaounia, B.; Zighmi, K.; Bâali, F.; El Gayar, A. Climate Impact on Surface and Groundwater in North Africa: A Global Synthesis of Findings and Recommendations. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2018, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, P.; Farooq, S.H. Seawater Intrusion in the Coastal Aquifers of India—A Review. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costall, A.R.; Harris, B.D.; Teo, B.; Schaa, R.; Wagner, F.M.; Pigois, J.P. Groundwater Throughflow and Seawater Intrusion in High Quality Coastal Aquifers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wederni, K.; Alaya, M.; Missaoui, R.; Hamed, Y. Assessment of Groundwater Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Salinization Intrusion in Coastal Arid Area (South Gabes, South-East Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 200, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Allouche, N.; Bouri, S.; Aljuaid, A.M.; Hachicha, W. Assessment of Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers Using Multivariate Statistical Analyses and Hydrochemical Facies Evolution-Based Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughariou, E.; Allouche, N.; Ben Brahim, F.; Nasri, G.; Bouri, S. Delineation of groundwater potentials of Sfax region, Tunisia, using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio, and weights of evidence models. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 14749–14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Hashemi, H.; Bouri, S. The consequences of saline irrigation treatments on soil physicochemical characteristics. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2018, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-M.; Yeh, H.-D. Spectral Approach to Seawater Intrusion in Heterogeneous Coastal Aquifers. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M.; Gervasio, M.P.; Busico, G.; Colombani, N. Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Driving Groundwater Resources Salinization for Agriculture Use in the Campania Plains (Southern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 144033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, S.L.; Greskowiak, J.; Oude Essink, G.H.; Massmann, G. Understanding Climate Change and Anthropogenic Impacts on the Salinization of Low-Lying Coastal Groundwater Systems. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, J.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Nolte, A.; Boving, T.B. Saltwater Intrusion Into Coastal Aquifers In The Contiguous United States—A Systematic Review Of Investigation Approaches And Monitoring Networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncibi, K.; Hadji, R.; Hamdi, M.; Mokadem, N.; Abbes, M.; Khelifi, F.; Zighmi, K.; Hamed, Y. Application of the Analytic Hierarchy Process to Weight the Criteria Used to Determine the Water Quality Index of Groundwater in the Northeastern Basin of the Sidi Bouzid Region, Central Tunisia. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2020, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fogg, G.E.; Pauloo, R.A. Groundwater Basin Openness and Sustainability. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Xia, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, S.; Wang, G. Spatial Distribution Of Groundwater Quality in the Coastal Plain and Its Relationship with Land Use and Seawater Intrusion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Impact of Climate Change on Multi-Objective Management of Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Karst Aquifers in Zhoushuizi District of Dalian City, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 2329–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemer, Z.; Khaldaoui, F.; Benaissa, Z.; Belaroui, A.; Tebbouche, M.Y.; Ydri, A. Hydrogeophysical Investigation of Aquifer Parameters and Seawater Intrusion: A Case Study from Eastern Mitidja Plain, Algeria. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.D.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. (Eds.) Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods and Practices; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 1999; 91p. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Bouri, S. Subsurface Drainage System Performance, Soil Salinization Risk, and Shallow Groundwater Dynamic under Irrigation Practice in an Arid Land. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.D. Modelling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2010; pp. 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, A.; Sogut, A.R. Hydrochemical and statistical study of the groundwater salinization in the region of Gabes in Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoui, M.; Agoubi, B. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk using AVI, SPI, and RGPI indexes: Applied to southern Gabes aquifer system, Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50881–50894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béjaoui, B.; Ismail, S.B.; Othmani, A.; Hamida, O.B.A.B.H.; Chevalier, C.; Feki-Sahnoun, W.; Harzallah, A.; Hamida, N.B.H.; Bouaziz, R.; Dahech, S.; et al. Synthesis review of the Gulf of Gabes (eastern Mediterranean Sea, Tunisia): Morphological, climatic, physical oceanographic, biogeochemical and fisheries features. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, S. Study of Brittle Tectonics in the Saharan Platform and Atlas (Southern Tunisia): Evolution of Stress Paleo-Fields and Implications Geodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, State University Tunis II, Tunis, Tunisia, 1995; p. 486. [Google Scholar]
- Rouatbi, R. Contribution to the Hydrogeological Study of the Buried Karst of Gabes-South. 3rd Cycle Thesis, BIRH, Tunis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 1967; 235p. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkarim, B.; Telahigue, F.; Agoubi, B. Assessing and Delineation of Groundwater Recharge Areas in Coastal Arid Area Southern Tunisia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J.F.; Jarraya Horriche, F.; Ghoudi, R. Numerical Groundwater Flow Modeling for Managing the Gabes Jeffara Aquifer System (Tunisia) in Relation with Oasis Ecosystems. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Brahim, F.; Msaddki, H.; Bouri, S. Groundwater Quality Index Mapping for Irrigation Purposes in the “El Hezma-El Hmila” (Medenine, Tunisia). CLEAN Soil Air Water 2022, 50, 2100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Yahyaoui, N.; Bousnina, S.; Ben Brahim, F.; Allouche, A.; Faiedh, H.; Bouri, S.; Hachicha, W.; Aljuaid, A.M. Using a Mamdani Fuzzy Inference System Model (MFISM) for Ranking Groundwater Quality in Agri-Environmental Context: Case of the Hammamet-Nabeul Shallow Aquifer (Tunisia). Water 2021, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, C.D.; Thorne, D.T.; Dausman, A.M.; Sukop, M.C.; Guo, W. SEAWAT Version 4: A Computer Program for Simulation of Multi-Species Solute and Heat Transport; Techniques and Methods Book 6; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; Chapter A22; p. 39.
- Chiang, E. User Guide for Processing Modflow Version 11: A Graphical User Interface for MODFLOW, GSFLOW, MODPATH, MT3D, PEST, SEAWAT, and ZoneBudget. Simcore Software. 2022. 334p. Available online: https://www.simcore.com/wp/processing-modflow-11/ (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Doherty, J. PEST-Model-Independent Parameter Estimation, Version 12. Watermark Computing: Corinda, Australia, 2010. Available online: http://www.pesthomepage.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Cinkus, G.; Mazzilli, N.; Jourde, H.; Wunsch, A.; Liesch, T.; Ravbar, N.; Chen, Z.; Goldscheider, N. When Best Is the Enemy of Good–Critical Evaluation of Performance Criteria in Hydrological Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 2397–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMODnet Bathymetry Consortium. EMODnet Digital Bathymetry (DTM 2022). EMODnet Bathymetry Consortium, 2022. Available online: https://doi.org/10.12770/ff3aff8a-cff1-44a3-a2c8-1910bf109f85 (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Bachtouli, S.; Abidi, M.; Comte, J.C.; Zairi, M. Potential for fresh submarine groundwater occurrence in an arid Mediterranean region: The case of Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 32, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M. Modeling stochastic saline groundwater occurrence in coastal aquifers. Wat. Res. 2023, 235, 119885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).