Abstract
A survey of the hydrochemistry and isotopes of the Quaternary aquifer on the southern coast of Laizhou Bay provides new insights into the hydrodynamic and geochemical relationships between freshwater, seawater, and brine at different depths in coastal sediments. This study used a combination of groundwater level analysis, hydrochemistry, and isotopic methods to study the chemical characteristics of groundwater and the origin of groundwater recharge and salinity. Because the sedimentary structure of the area and the formation background of saltwater were important factors controlling the distribution of groundwater, we analyzed the distribution of groundwater in Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments. The variation of groundwater levels in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments in the saline–freshwater transition zone over time showed that the Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater flow directions differed in the saltwater–freshwater transition zone. From south to north in the study area, the hydrochemical types of groundwater in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments were as follows: HCO3-Ca (freshwater), SO4-Mg and HCO3-Ca (brackish water), Cl-Na·Mg (saltwater), and Cl-Na (brine). The results of the hydrochemical and isotopic studies indicated that the saltwater in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments and the brine in the Late Pleistocene sediments were the result of evaporation. The salinity of freshwater in the Holocene sediments was produced by rock weathering, while the salinity of freshwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments was not only derived from rock weathering, but was also affected by evaporation and precipitation. The salinity of brackish water in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments was derived from evaporation and precipitation. Ultimately, the origin of groundwater recharge in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments was atmospheric precipitation.
1. Introduction
Globally, climate change, rising sea levels, land use changes, and groundwater overexploitation have led to the severe intrusion of sea (salt) water into freshwater aquifers [1]. Coastal areas are usually the most densely populated areas [2,3,4]. With the development of the social economy and external factors such as climate change, the over-exploitation of groundwater and changes of land use types in coastal areas have undermined the dynamic balance of the original saltwater–freshwater interface and further exacerbated the degree of saltwater intrusion [5,6,7,8]. In China, underground saline water in the coastal zone is mainly distributed along the Bohai Sea coast, Jiaozhou Bay coast, Jiangsu coast, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta, among which the southern coast of Laizhou Bay is the most widely distributed [9]. Since the 1970s, a large amount of groundwater has been extracted in the process of rapid development in the region, resulting in the current problems, which were recognized by local authorities in 1976 [10]. Seawater (saltwater) intrusion has caused a reduction in freshwater resources and the abandonment of mining wells in coastal areas, which greatly restricts local social and economic development [5]. On the one hand, the salinity of coastal aquifers is caused by seawater (saltwater) intrusion. On the other hand, complex hydrogeochemical processes may also be involved. In this context, understanding the processes that control groundwater geochemical evolution and hydrodynamic processes has important implications for aquifer management.
Groundwater chemical characteristics in the natural environment are affected by factors such as the chemical composition of recharge water, water–rock interactions, solute transport, and evaporation [11,12]. A combination of chemical and isotopic indicators can be used to characterize the behavior of saltwater in the coastal groundwater cycle, determine the origin of groundwater salinity, characterize the groundwater salinization processes, and study migration at the saltwater–freshwater interface; this process is currently considered a good research method [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. For the multi-facies sedimentary strata on the south coast of Laizhou Bay, accurately describing the characteristics of aquifers and defining the process of brine formation are of great significance to research on the hydrochemical characteristics of the study area.
This study aims to investigate the evolution of saline groundwater through the Late Pleistocene and Holocene sediments. To this end, groundwater monitoring wells at different depths were set up to collect groundwater samples and obtain basic data for analysis and discussion. Stable isotope and hydrochemical methods were then used to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics, sources of recharging groundwater and salt in groundwater, and salinization mechanisms of groundwater. These results have important implications for the development and recharge management of intensively exploited coastal aquifers around the world and demonstrate the value of using isotopic metrics in conjunction with other hydrogeological information. The present results also have implications for the study of multiphase aquifer stratification.
2. Study Area
2.1. Location and Weather
The research area is located on the south coast of Laizhou Bay, Shandong Province, at a longitude of 118°32′~119°20′ and latitude of 36°41′ to 37°19′ (Figure 1). According to the Köppen–Geiger climate classification [20], the study area belongs to a subtropical humid climate (Cwa). The hottest month of the year is July, with a maximum of 40.4 °C, and the coldest month of the year is February, with a minimum of −19.5 °C. The annual average precipitation is 651 mm (1956–2016), mainly concentrated in June–September. The annual mean evaporation (E20 value) is 1834.0 mm (1956–2016).
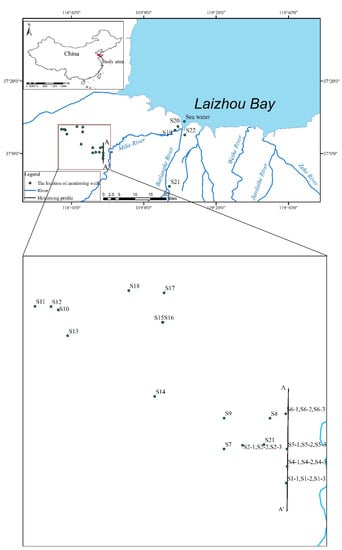
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area along with brine aquifer distribution and sampling wells. Line A−A’ is the hydrogeological section of Figure 2.
2.2. Hydrogeological Conditions
The aquifer in the study area is composed of river–lake facies, sea–land interaction facies, and loess accumulation due to the frequent interactions of the marine strata formed by three transgressive deposits since the Late Pleistocene with continental sand–gravel and mud layers. In the study area, the developed channels and numerous paleochannel sand bodies form numerous aquifers, and the aquifers are characterized by a complex multi-layered framework (Figure 2). Influenced by factors such as the depositional environment, paleogeography, and paleoclimatic conditions, especially the transgression–regression since the Late Pleistocene, there were differences in the lithology, hydraulic properties, and dynamic and hydrochemical characteristics of the aquifers during the formation of groundwater and aquifers in the study area. The aquifers are divided into Holocene groundwater (shallow groundwater) aquifers and Late Pleistocene groundwater (deep groundwater) aquifers [21,22].
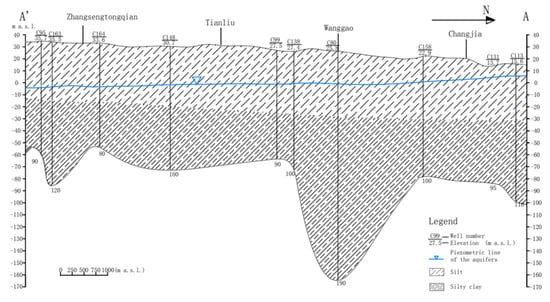
Figure 2.
Typical hydrogeological profile A-A’ and piezometric profile of the aquifers (1 March 2021) in study area.
The hydraulic properties of shallow groundwater in Holocene groundwater are phreatic and slightly confined water. Additionally, the bottom of the aquifer is buried at a depth of 25–30 m, and the salinity varies from less than 1 g/L to greater than 50 g/L [23]. According to the vertical hydrochemical characteristics, the water is divided into several types: an all-freshwater type, upper freshwater and lower saline types, and an all-saline type [21,24]. The burial depth of the top interface of the shallow saltwater is mainly controlled by the sedimentary environment of the ancient river, and the burial depth becomes smaller from the ancient river channel to the ancient river interchannel. The piedmont alluvial–pluvial fan is a whole freshwater area affected by groundwater runoff recharge in the southern piedmont. The thickness of the shallow freshwater sand layer is controlled by the ancient river channel and saltwater–freshwater interface. Areas with sand thickness greater than 5 m are generally distributed in a north–east direction, and areas with sand thickness greater than 15 m are mainly located in all freshwater areas. The groundwater flow direction is from south to north, which is roughly consistent with the direction of the terrain slope. Since the development level of groundwater in the area was relatively low before 1980, the groundwater level distribution at this time basically reflects the hydrodynamic field in its natural state [23,25]. From the southern piedmont to northern coastal areas, the shallow groundwater hydraulic gradient decreased from 1.4‰ to 0.2‰. Due to the continuous expansion of the groundwater funnel, the Holocene groundwater dynamic field underwent great changes, with the flow direction generally caused by the movement of the surrounding areas of the alluvial–proluvial fan to the center of the groundwater level drop funnel. Due to the continuous expansion of the groundwater funnel, the Holocene groundwater dynamic field has undergone great changes, with the flow direction likely emerging from the surrounding area of the alluvial–proluvial fan to the center of the groundwater funnel [24].
The top of the deep groundwater in Late Pleistocene sediments is buried at a depth of 25–30 m, and a cohesive soil aquifer with a relatively stable distribution and thickness of 5–10 m developed between the top of the aquifer in Late Pleistocene sediments and the overlying shallow aquifer [24]. Affected by the paleo-sedimentary environment, the groundwater in Late Pleistocene sediments is mainly saltwater. Under natural conditions, the groundwater runoff direction of the Late Pleistocene generally extends from south to north and ultimately drains into the Bohai Sea. Due to the overexploitation of groundwater, the scale of the funnel continues to expand, and the direction of the groundwater runoff changes [18]. Groundwater flows to the funnel from the south, north, and east, but mainly comes from the southern hills.
2.3. Environmental Issues
The environmental problems in the study area are mainly saltwater and brine intrusion, followed by seawater intrusion. The zoning of the hydrogeological environment in the study area is controlled by the Quaternary sedimentary environment. From the land area to the coast, there is a freshwater area, saltwater area, brine area, and brackish area. Here, brine is formed by evaporation, concentration, salt precipitation, and re-dissolution, mixing with freshwater, and the burial diagenesis of seawater is deposited in the formation. Seawater deposited in the formation is caused by Late Pleistocene seawater intrusion. The saltwater and brine intrusion in the study area was caused by the massive extraction of groundwater in the 1980s, leading the extraction of freshwater to exceed its recharge [23]. The groundwater level near the saltwater area drops, and when the freshwater level is lower than the water level of the saltwater wedge, the saltwater wedge will advance to the freshwater area until a new balance of saltwater and freshwater is formed. Due to socioeconomic development and human activities, groundwater has been over-exploited, leading to the formation of groundwater funnels, thereby intensifying salt–brine intrusion. In recent years, the seawater (saltwater) intrusion area in the Weibei Plain has shown an overall upward trend. According to a survey, the intrusion area in 1990 was 276.1 km2, in 2002 was 413 km2, and in 2011 was 762.8 km2 [26].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Groundwater Level Monitoring
Twelve monitoring wells containing water-level monitoring equipment (pressure water level gauges) were selected from Section A-A’ in the saltwater and freshwater transition zone to monitor the dynamic changes in groundwater levels (Figure 2). The monitoring time extended from 2021.3.1 to 2021.4.20. From inland to sea, monitoring wells were distributed in Houguhe Village (S1-1, S1-2, S1-3), Weiyuanzi Village (S4-1, S4-2, S4-3), Zhongbutou Village (S5-1, S5-2, S5-3), and Lijiazhuangzi Village (S6-1, S6-2, S6-3). The three monitoring wells in each village were distributed in a straight line (Figure 1 and Figure 2), and the adjacent monitoring wells were separated by 4 m to monitor the groundwater level of the shallow (0–30 m) and deep (30–100 m) aquifers. The monitoring wells were able to simultaneously monitor the Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater levels, and the monitoring data were updated every hour.
3.2. Sampling
This study analyzed 36 groundwater samples, of which 22 were obtained from field sampling. The sampling locations in the study area are shown in Figure 1. The field sampling location of 22 groundwater samples was the transitional zone between saltwater and freshwater in Weifang City. Among them, 4 samples were taken from shallow agricultural irrigation wells, and 18 samples were taken from the monitoring wells able to monitor the groundwater levels of multiple aquifers. Fourteen groundwater samples were collected from the published literature [22,27,28], among which nine were from Taitou Town, Weifang City [22], and five were from Hanting District, Weifang City [27,28]. In total, 19 groundwater samples of Holocene groundwater, 16 samples of Late Pleistocene groundwater, and one seawater sample were used in this study. The groundwater samples were classified into four types based on salinity: freshwater, brackish water, saline water, and brine, with total dissolved solid (TDS) concentrations of <1, 1–10, 10–100, and >100 g/L, respectively.
3.3. Analytical Methods
The detection indicators of the groundwater samples included conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), pH, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, NO3−, HCO3−, Cl−, Sr, F−, Br−, I−, δ2H, δ18O, and Sr87/Sr86. During the sampling process, we used a syringe and 0.45 μm filter to filter the water sample and inject it into a pre-cleaned polyethylene plastic bottle. Then, we removed as many air bubbles as possible and sealed the bottle with tape to isolate the air. After sampling, the collected water samples were stored in a refrigerator at a temperature below 4 °C until analysis. At the same time, we used a portable multi-parameter water-quality analyzer to instantly determine routine physical and chemical indicators in the field, including pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and total dissolved solids (TDS).
The indoor detection indicators are all measured by the Groundwater Mineral Water and Environmental Monitoring Center of the Ministry of Land and Resources. Cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+) and Sr were determined using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES). The brand was Optima and the model was 8000. The samples to be tested were acidified to pH ≈ 2 with HNO3 solution prior to detection of the cations. Major anions (Cl−, Br−, NO3−, SO42−, and F−) were determined using an ion chromatograph (ICS-1500) from Thermo Fisher, USA. The chromatographic column used was an AS14 analytical column, and the data system was the Thermo Fisher chameleon chromatographic data system. The chromatographic analysis method can completely separate F−, Cl−, Br−, NO3−, and SO42− according to this peak sequence, and the high-concentration chloride peak shape did not affect the subsequent Br−, NO3−, or SO42− peaks. I− was measured using a CIC-D160-type ion chromatograph, and the brand of the instrument was Qingdao Shenghan. The characteristic of the measurement was the use of an amperometric detector, and the chromatographic column was an SH-AC-4-type chromatographic column. HCO3− was determined by titration. The charge balance error during the measurement of all samples was less than 8%.
⸹18O and ⸹2H were tested using a laser spectroscopic water isotope analyzer. The brand of the instrument was Picarro, and the model was 2130i. The analytical method was the optical cavity ring-down principle. The values of ⸹18O and ⸹2H were tested relative to VSMOW (Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water), hereafter expressed as ⸹ in units of ‰. The analytical accuracy of the long-term standard measurement of ⸹18O was ±0.2‰, and the analytical accuracy of ⸹2H was ±0.6‰. 87Sr/86Sr were tested using a multiple-receiver plasma mass spectrometer (MC-ICP-MS). The certified reference was NBS987. The precision for 87Sr/86Sr was 0.014‰. The 87Sr/86Sr ratio was exponential normalization correction using 88Sr/86Sr = 8.375209. The natural isotope ratio of krypton (83Kr/84Kr = 0.20175, 83Kr/86Kr = 0.66474) was used to deduct the interferences of krypton. The fractionation behaviors of rubidium and strontium were considered to be consistent, and the natural ratio of 85Rb/87Rb (85Rb/87Rb = 2.5926) was used to deduct the interference of 87Rb on 87Sr by measuring 85Rb. As long as the Rb/Sr was less than 0.01, the interference of rubidium can be completely deducted. The test results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of groundwater samples in the study area.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Groundwater Level
The groundwater levels of aquifers at different depths monitored by the monitoring wells distributed in Houguhe Village (S1-1, S1-2, S1-3), Weiyuanzi Village (S4-1, S4-2, S4-3), Zhongbutou Village (S5-1, S5-2, S5-3), and Lijiazhuangzi Village (S6-1, S6-2, S6-3) are shown in Figure 3. The locations of the monitoring wells mainly featured freshwater and brackish water, which are suitable for farming. The groundwater level generally declined after March 15, indicating that spring irrigation led to the massive exploitation of groundwater. From the inland to the ocean, during the monitoring period, the shallow groundwater level of the monitoring wells roughly increased sequentially, and the variation law of the deep groundwater level was different from that of the shallow layer, indicating that the flow direction of the groundwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments was different from that of groundwater in the Holocene sediments. At the same time, this result also shows that groundwater stratification monitoring is of great significance in identifying the hydrogeological characteristics of aquifers.
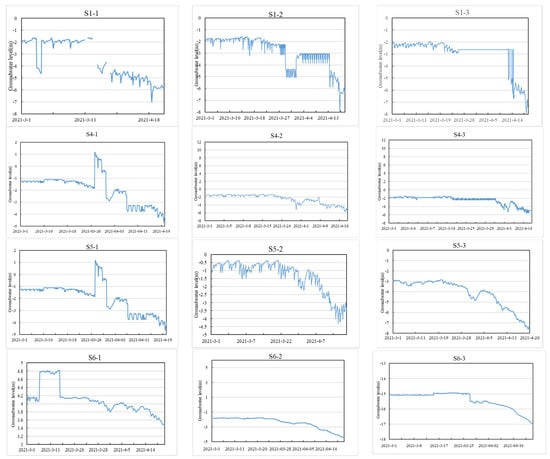
Figure 3.
Groundwater levels of aquifers at different depths changed over time in the saltwater and freshwater transition zone.
4.2. Hydrochemistry
4.2.1. Chemical Types
Table 1 shows that the variation range of TDS in the 35 groundwater samples was 375–132,300 mg/L, including freshwater, brackish water, and saline water in the Holocene sediments, as well as freshwater, brackish water, saline water, and brine in the Late Pleistocene sediments. In terms of horizontal distribution, the content of Na+, TDS, Cl−, and K+ gradually increased, and the content of Ca2+ and HCO3− gradually decreased from the inland to the sea. For vertical distribution, the groundwater samples located at different depths contained different ion concentrations. For example, S1-1, S1-2, and S1-3 were located at basically the same sampling point, whereas the TDS of S1-1 was significantly higher than that of S1-2 and S1-3. This is due to the different degrees of saltwater intrusion in different layers of the multiphase aquifer.
The piper triple line map presented in Figure 4 indicates the presence of many hydrochemical types of groundwater in the study area. The hydrochemical types of freshwater in the Holocene sediments and Late Pleistocene sediments were found to be mainly HCO3-Ca, while the hydrochemical types of brackish water in the Holocene sediments and Late Pleistocene sediments were mainly SO4-Mg and HCO3-Ca. The hydrochemical types of saline water in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene samples and brine in the Late Pleistocene were mainly Cl-Na. With an increase in the proportion of saltwater mixed into the fresh groundwater, the hydrochemical type of groundwater also changed. From land to coast, the hydrochemical type of groundwater water changed from a HCO3-Ca type with low salinity to a Cl-Na type with high salinity. This change in hydrochemical type was not only affected by saltwater intrusion, but was also closely related to water–rock interactions; for example, S3-1 was the HCO3-Ca phase with low salinity, which was affected by the dissolution process of dolomite–calcite and gypsum.
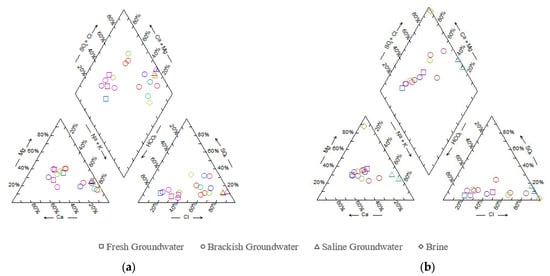
Figure 4.
Piper triple-line map of hydrochemical types of groundwater in (a) Holocene and (b) Late Pleistocene sediments.
4.2.2. Ion Correlation Analysis
A correlation analysis of ions can reflect the similarity of water chemical indicators and determine whether their corresponding sources are consistent; this method remains the most commonly used type of statistical analysis. The TDS value represented the content of dissolved substances in groundwater and can reveal the evolution law of groundwater [29]. In this paper, a correlation analysis of eight conventional ions (K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Na+, SO42−, NO3−, HCO3−, Cl−) along with TDS and pH was carried out using the SPSS 19.0 software. It can be seen from Table 2 that the TDS of the groundwater in the study area had a significant correlation with the main cations. The correlations were arranged in descending order as follows: Na+ > Mg2+ > K+ > Ca2+. TDS had a high correlation with Cl− and SO42−, but a significant negative correlation with HCO3− and NO3−, indicating that an increase in TDS was mainly related to the dissolution of rock salt and aluminosilicate. In addition, the correlation coefficient between TDS and Cl−, Na+ was the highest. This result showed a significant positive correlation and indicated that the contribution rate of Cl− and Na+ to TDS was the highest in coastal areas. PH was less correlated with major ions and TDS in this region. Na+, K+, and Mg2+ were all significantly correlated with SO42−, indicating that their sources were similar, and the dissolution of sulfate rock was the main source. The correlation coefficient of Ca2+ and Mg2+ was greater than 0.8, which was related to the dissolution of dolomite. There was a negative correlation observed between Ca2+ and HCO3−, which was caused by the precipitation of CaCO3. The correlation coefficients of K+ with Na+, Mg2+, SO42−, and Cl− in the groundwater samples were 0.979, 0.965, 0.937, and 0.98, respectively. The high correlation between K+ and major ions indicated that potassium was mainly produced by silicate weathering, rather than anthropogenic activities.

Table 2.
Pearson correlation coefficient of common ions.
The relationship among Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− is shown in Figure 5. The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− contents of freshwater in the Holocene sediments were 0.999, 0.966, 0.946, and 0.888, respectively. There was a strong positive correlation between Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl−. The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− of freshwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments were 0.928, −0.519, 0.823, and 0.393, respectively, with a strong positive correlation observed between Na+, Mg2+, and Cl−. This result indicated that the salt in the freshwater in the Holocene sediments came from rock weathering, while the salt in the freshwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments came from other processes.
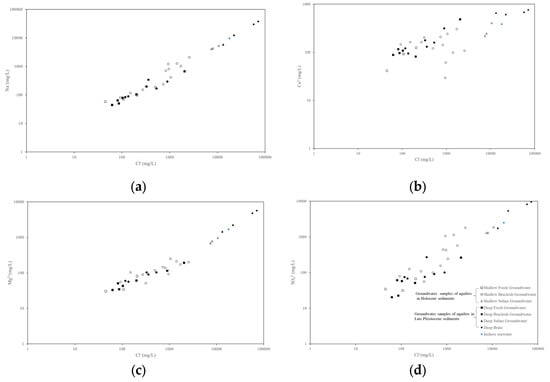
Figure 5.
Relationship between main ion ratios to (a) Na+ and Cl−; (b) Ca2+ and Cl−; (c) Mg2+ and Cl−; and (d) SO42− and Cl−.
The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− of the brackish water in the Holocene sediments were 0.920, −0.016, 0.723, and 0.864, respectively. There was a strong positive correlation between Na+, SO42−, and Cl−. The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− of the brackish water in the Late Pleistocene sediments were 0.933, 0.977, 0.966, and 0.603, respectively, with a strong positive correlation between Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Cl−. The salt in the brackish water in the Late Pleistocene sediments originated from the dissolution of evaporates, whereas the salt in the brackish water in the Late Pleistocene sediments was produced by other processes.
The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− of the saline water in the Holocene sediments were 0.999, 0.999, 0.986, and 0.987, respectively. There was a strong positive correlation between Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl−. The Pearson correlation coefficients between the Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl− of the saline water in the Late Pleistocene sediments were 0.998, 0.836, 0.999, and 0.949, respectively. There was a strong positive correlation between Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, SO42−, and Cl−. It was previously suggested that the formation of saline water originated from the dissolution of evaporates [30,31].
4.2.3. Other Significant Constituents and Ratios
Cl/Br Ratios and Origin of Salt
The Cl/Br ratio can be used to determine the cause of groundwater salinization (TDS greater than 2–3 g/L) [32,33]. The Cl/Br ratio of seawater was found to be about 655 (Cl = 550 mmol/L, Br = 0.84 mmol/L, [34]) and had remained constant in all oceans since the Permian [35]. This value can, therefore, be used as a reference. According to the water evaporation test data, after 90% of the water in the standard seawater evaporated, the Cl− concentration remaining in the water was 194,000 mg/L. Moreover, NaCl had not yet precipitated, and the Cl/Br value was maintained at the seawater ratio. The Cl− concentration of the samples ranged from 45 to 71,336 mg/L, all of which were lower than 194,000 mg/L, so NaCl did not precipitate. If the high-salinity groundwater was the product of seawater evaporation and concentration, the corresponding Cl/Br value should have been maintained at the seawater ratio. However, the actual data indicated this was not the case. Thus, this groundwater was not formed after seawater evaporation and concentration [21,36]. Research showed that, since Br− was less compatible in precipitating salts, it was enriched relative to Cl− in residual brines. In contrast, precipitated salts were depleted in Br−, which caused the Cl/Br ratios to be high for water that dissolved halite [37].
Most of the groundwater samples of aquifers in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments had Cl/Br ratios below 655. Groundwater with a Cl− concentration of 1.30 mmol/L had the highest Cl/Br ratio of 863 (Figure 6). The dissolution of a small amount of rock salt from the unsaturated zone was the most likely mechanism of increase for the Cl/Br ratio. The Cl/Br ratio of saltwater and brine was 209–400 and showed relative invariance with an increase in the Cl− concentration. This result confirmed that evaporation was the main mechanism increasing the salinity of saline water and brine.
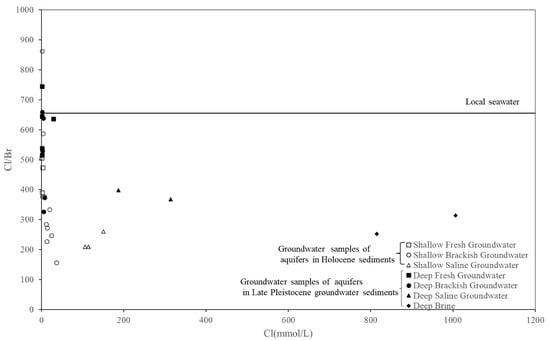
Figure 6.
Relationships between Br/Cl (mmol ratios) and Cl− (mmol/L).
The Cl/Br ratio of groundwater in the Holocene sediments with a TDS lower than 2 g/L was mostly lower than that of seawater, and the Cl/Br ratio range was larger than that of groundwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments, possibly due to the shallow burial depth of groundwater in the Holocene sediments and the introduction of bromine into groundwater via agricultural irrigation. As discussed by Thomas [17], the Cl/Br ratio in samples with a TDS below 2 g/L could not be used to identify the sources of salt in these samples.
NO3− and Cl−
The NO3− concentration in the groundwater was found to be closely related to human activities. The NO3− concentration in 28 groundwater samples was measured, and the NO3− concentration in 7 samples met relevant safety standards (20 mg/L) (Standards for Drinking Water Quality, GB5749-2006) [38] (Figure 7). The NO3− concentration of saline water and brine samples of aquifers in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments also met the safety standards, while only two brackish water samples of aquifers in Holocene sediments met the safety standards. The 21 groundwater samples that did not meet the safety standards were all from freshwater and brackish water in Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments, which indicated that the freshwater and brackish water in the study area suffered from serious groundwater nitrate pollution, primarily because agricultural planting areas were mainly distributed in freshwater and brackish water areas with low salinity, and the application of agricultural fertilizers represents the main source of nitrates in shallow groundwater. Fertilizers migrated to deep aquifers with precipitation infiltration and contaminated deep groundwater.
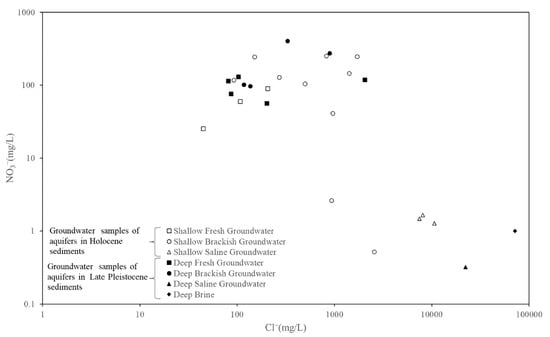
Figure 7.
Relationship between NO3− (mg/L) and Cl− (mg/L).
4.2.4. Hydrogeochemistry
The main water chemical components of the groundwater in the study area can be intuitively reflected by a Gibbs diagram [39]. This Gibbs diagram can be used not only to analyze the ion origins in surface water, but also to analyze the ion origins of groundwater. The Gibbs diagram used TDS versus Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) for anions and TDS versus Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) for cations, which is commonly used to explore the sources of salt in groundwater (e.g., rainfall, rock weathering, and evaporation concentration). Taking Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) as the abscissa axis and the logarithm of TDS as the ordinate axis, the hydrochemical data of the groundwater in the study area were projected on the Gibbs diagram. The result is shown in Figure 8. When precipitation controlled the origin of chemical components in the groundwater, the soluble ions in soil were introduced into the groundwater due to the leaching of precipitation. Additionally, the solubility of Na+ was higher than that of other ions, resulting in high Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) values and low TDS values in the groundwater. Moreover, the groundwater samples fall at the bottom of the Gibbs diagram. When rock weathering controlled the origin of chemical components in the groundwater, due to long-term weathering, Ca2+ and Mg2+ entered the groundwater through filtration. This resulted in lower Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) values and medium TDS values in the groundwater, with the groundwater samples falling in the middle region of the Gibbs diagram. When evaporation–precipitation or evaporation controlled the origin of chemical constituents in the groundwater, water evaporated, and Ca2+ and Mg2+ emerged from the solution. This resulted in higher Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) values and higher TDS values for the groundwater. These groundwater samples correspond to the upper portion of the Gibbs diagram.
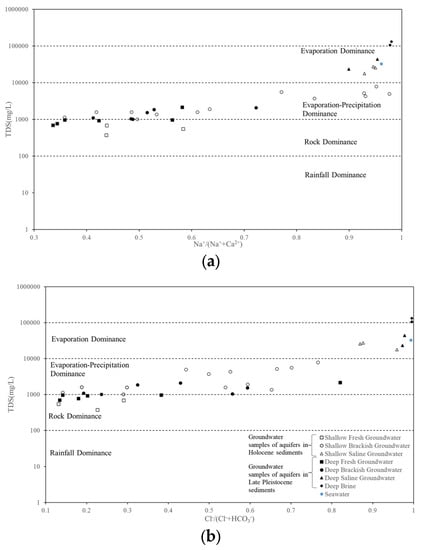
Figure 8.
Gibbs diagram of groundwater in the study area.
Figure 8 shows TDS versus Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) for anions and TDS versus Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) for cations. The TDS concentrations of freshwater in the Holocene sediments were all less than 1000 mg/L, indicating that they were all affected by rock weathering. The TDS concentrations of freshwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments were 100–10,000 mg/L, indicating that they were affected not only by rock weathering, but also by evaporation and precipitation. The TDS concentrations of brackish water in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments were 1000–10,000 mg/L, indicating that they were all affected by evaporative precipitation. The TDS concentrations of saline water and brine in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments were greater than 10,000 mg/L, which means that these concentrations were mainly affected by evaporation. Evaporation increased the water’s salinity by concentrating Na+ and Cl−. Meanwhile, TDS had a strong correlation with Na+ and Cl−.
4.3. Isotopic Characteristics
4.3.1. δ18O and δ2H Isotopes and Recharge Conditions
The global meteoric water line (GMWL) was δ2H = 8δ18O + 10. The local meteoric water line (LMWL: δ2H = 7.8δ18O + 6.3, n = 8, R2 = 0.78) was obtained based on the observed precipitation data for 1986–1990, obtained from the Yantai Station of the International Atomic Energy Agency’s Atmospheric Precipitation Isotope Observation Network (IAEA/WMO, 2006). Yantai Station had similar climatic and coastal conditions. The local evaporation line (Evaporation: δ2H = 4.4δ18O − 23.1) was obtained from Han et al. [17].
The test results for stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen showed that the variation range of δ18O in the groundwater samples was −9.2–3.8‰, and the variation range of δ2H was −66.0–29.1‰ (Figure 9). All values were lower than those of four seawater samples (one local seawater sample and three seawater samples from Han et al. [17]) (the variation range of δ18O was −2.3~−1.3‰, and δ2H was −27~−7‰). According to the stable isotope data, if the saline water (or brine) in the study area was the residue of seawater evaporation, the δ18O and δ2H values would be greater than the standard seawater values (the δ18O and δ2H values in standard seawater were both 0‰) [40]. However, the actual data presented lower values than those of the standard seawater and local seawater, distributed above and below the local atmospheric precipitation line, indicating that the main recharge of water in the groundwater in the study area mainly came from local precipitation. The burial depth of the Holocene groundwater was shallow and was significantly affected by the continuous recharge of precipitation. During the formation process of saltwater in the Late Pleistocene sediments, the groundwater received recharge from precipitation. However, with changes to the depositional environment, after the formation of a closed environment, the groundwater no longer received recharge from precipitation.
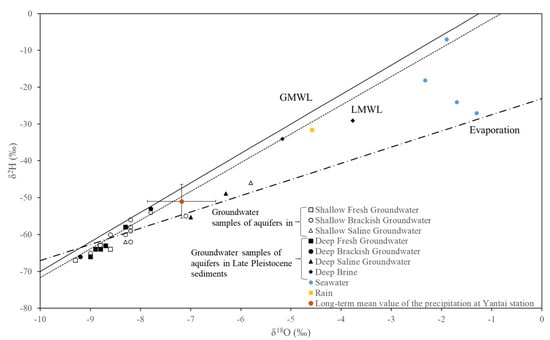
Figure 9.
δ18O (‰) versus δ2H (‰) relation of groundwater in the study area.
There were certain differences in the causes of groundwater salinization during different geological ages. The variation range of δ18O in the Late Pleistocene groundwater samples was −9.2–3.8‰, and the variation range of δ2H was −66.0−29.1‰. The variation range of δ18O in the Holocene groundwater samples was −9–−5.8‰, and the variation range of δ2H was −66.0–46.0‰. The freshwater and brackish water in the Late Pleistocene sediments and freshwater in the Holocene sediments were all distributed near LMWL. Moreover, some brackish water samples in the Holocene groundwater were farther from the LMWL and closer to the evaporation line, indicating that the buried depth of aquifer in Holocene sediments was shallow and obviously affected by evaporation.
4.3.2. Sr and its Isotopic Characteristics
Figure 10a shows the relationship between the 87Sr/86Sr ratios and Sr2+. It can be seen in Figure 10a that the variation range of the 87Sr/86Sr ratios of freshwater and brackish water in the Late Pleistocene sediments was 0.712087–0.713595, and the variation range of the 87Sr/86Sr ratios of freshwater and brackish water in the Holocene sediments was 0.709337–0.713085. The 87Sr/86Sr ratios of freshwater and brackish water was higher than that of standard seawater (0.7092). In addition, Sr2+ had a relatively low concentration between 568 and 2512 ug/L. Since seawater had a lower strontium isotope ratio, but higher strontium content, it can be speculated that the main source of dissolved strontium in these groundwater samples was not from seawater intrusion. The Cenozoic Quaternary was the main exposed stratum in the study area, and the weathering of soil may be an important source of strontium, as reflected in the 87Sr/86Sr ratio characteristics of the groundwater. Further analysis found that the 87Sr/86Sr ratios of these groundwater samples were all greater than 0.710, which was in the range of silicate weathering, indicating that the recharge of these groundwater samples was probably controlled by silicates. Agriculture and other human activities may also be potential reasons for these high 87Sr/86Sr ratios. However, this contribution was difficult to quantify due to the variability of Sr2+ concentrations and 87Sr/86Sr ratios in fertilizers, but further evaluations were difficult because the specific type of fertilization used in the study area was unknown.
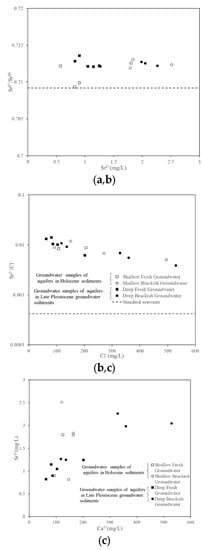
Figure 10.
Hydrochemical relationships between (a) Sr87/Sr86 and Sr2+ (mg/L); (b) Sr2+ and Cl− (mg/L); (c) Sr2+ and Ca2+ (mg/L).
In general, Cl− did not play an active role during ion exchange and Sr2+/Cl− was 0.42‰ in standard seawater [41]. Therefore, the Sr2+/Cl− ratios can be used to indicate the source of groundwater salinity [30,42]. The Sr2+/Cl− ratio in freshwater and brackish water was much higher than the Sr2+/Cl− ratio line in seawater (Figure 10b), which indicated that the groundwater salinity of the saline–freshwater transition zone did not come from seawater. The presence of significant amounts of strontium-containing minerals was not previously reported in this study area. Additionally, strontium in the area is released along with calcium and usually incorporated into calcite or aragonite matrices. As shown in Figure 10c, the positive correlation between Ca2+ and Sr2+ was 0.687, which also confirmed that Sr2+ was mainly the result of carbonate dissolution or precipitation.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the hydrochemical characteristics and salinity sources of the Quaternary aquifers at different depths on the southern coast of Laizhou Bay were studied by combining hydrochemistry and isotopic methods. This work provides new insights into the hydrodynamic and geochemical relationships between freshwater, seawater, and brine. The main findings were as follows.
In the saline and freshwater transition zone, the groundwater level in the upper layer of the monitoring well increased in sequence from south to north. The variation law of the groundwater level in the middle and deep layers was different from that in the upper layer, which indicated that the flow direction of Late Pleistocene groundwater was different than that of Holocene groundwater and that the stratified monitoring of groundwater was very important.
From south to north, the hydrochemical types of Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments in the study area were as follows: HCO3-Ca (freshwater), SO4-Mg and HCO3-Ca (brackish water), and Cl-Na (saltwater and brine). The correlation analysis of ions showed that the observed increase in TDS was mainly related to the dissolution of rock salt and aluminosilicate, with Cl− and Na+ contributing the most to TDS. The sources of Na+, K+, Mg2+, and SO42− were similar, with the dissolution of sulfate rocks found to be main source. Na+ and K+ were mainly the result of silicate weathering, rather than anthropogenic supplementation. The analysis of the Cl/Br ratios showed that the Cl/Br ratios can determine the source of saline water and brine. Additionally, previous studies showed that evaporation was the main mechanism that increased the salinity of saline water and brine. The analysis of the NO3−/Cl− ratios revealed high concentrations of nitrate in the freshwater and brackish water areas of the study zone, indicating that these areas were greatly affected by human activities.
The analysis of the Gibbs diagram showed that the salinity of freshwater in the Holocene was the result of rock weathering, while the salinity of freshwater in the Late Pleistocene was not only derived from rock weathering, but was also affected by evaporation and precipitation. The salinity of brackish water in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments was derived from evaporation and precipitation. The salinity of saline water in the Holocene and Late Pleistocene sediments and brine in the Late Pleistocene sediments was mainly affected by evaporation, which was consistent with the results of the Cl/Br ratio analysis.
The analysis of the δ18O /δ2H ratio showed that the recharge of the groundwater in the study area mainly came from precipitation. The study area was mainly dominated by the intrusion of saline and brine, with evaporation found to play an important role in the salinization of the groundwater. The analysis of the 87Sr/86Sr ratio showed that soil weathering may be an important source of strontium in groundwater and that the recharge of these groundwater samples was likely controlled by silicates. Agriculture and other human activities may be other potential reasons for the high 87Sr/86Sr ratio observed in the present study.
Author Contributions
Y.C.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, formal analysis, funding acquisition; X.C.: supervision, conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, resources, data curation, writing—reviewing and editing, project administration, funding acquisition; Q.G.: methodology, resources; C.T.: investigation; D.L.: resources, data curation; D.X.: investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partly supported by the Optional Project of Water Resources Research Institute of Shandong Province (Grant SDSKYZX202101) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (Grant ZR2021MD086).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and/or analyzed in the current study are not publicly available due to further dissertation writing, but are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chang, C.M.; Yeh, H.D. Spectral approach to seawater intrusion in heterogeneous coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefelnasr, A.; Sherif, M. Impacts of seawater rise on seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. Ground Water 2014, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; Javadi, A. Incorporating the concept of equivalent freshwater head in successive horizontal simulations of seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 464–465, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.H.; Ataie-Ashtianiab, B.; Simmonsab, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, H.; Mahmoodzadeh, D.; Ataieashtiani, B.; Simmonset, C.T. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheril, M.M.; Singh, V.P. Effect of climate change on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Processes 1999, 13, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.F.A.A.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Maity, J.P.; Alias, Y.; May, R.; Alborsh, H. A study on the impact of anthropogenic and geogenic factors on groundwater salinization and seawater intrusion in Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine: An integrated multi-techniques approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 156, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hu, B.X.; Xu, Z.X.; Li, X.; Tong, J.X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.X.; Miao, J.J.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Numerical simulation of seawater intrusion to coastal aquifers and brine water/freshwater interaction in south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 215, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.C. Some changes of resources and environment caused by seawater intrusion. Environmental Sciences 1991, 12, 62–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Carol, E.; Kruse, E.; Mas-Pla, J. Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of ground water salinization process on the coastal plain of Samborombón Bay, Argentina. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Samie, S.G.A.; Badawy, H.A. Factors controlling mechanics of groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in the Quaternary aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergelson, G.; Nativ, R.; Bein, A. Salinization and dilution history of groundwater discharging into the Sea of Galilee, the Dead Sea Transform, Israel. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, K.S.; Koh, D.C.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.G.; Park, W.B.; Koh, G.W.; Woo, N.C. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: A case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea. J. Hydrol. 2003, 270, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, S.; Reynolds, D.A.; Le Gal, L.C. A field study of hydraulic, geochemical and stable isotope relationships in a coastal wetlands system. J. Hydrol. 2005, 315, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M.A.; Hauser, S.; Povinec, P.P. Stable isotopes of water as a tool to study groundwater-seawater interactions in coastal south-eastern Sicily. J. Hydrol. 2009, 364, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Kohfahl, C.; Song, X.F.; Xiao, G.Q.; Yang, J.L. Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay. China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Q. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Boschetti, T.; Petitta, M.; Tallini, M. Stable isotope (H2, O18 and Sr87/Sr86) and hydrochemistry monitoring for groundwater hydrodynamics analysis in a karst aquifer (Gran Sasso, Central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.Y.; Andreas, M. Linking human-biometeorological thermal conditions with the KöppenGeiger climate classification updated–The Example of China. In Proceedings of the ICUC9—9th International Conference on Urban Climate jointly with 12th Symposium on the Urban Environment, Toulouse, France, 20–24 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.F.; Wang, R.J.; Xu, S.N.; Li, W.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Mei, J.J.; Ding, Z.L.; Yang, P.J. Hydrogeochemistry and stable isotopes of groundwater from Shouguang, Laizhou and Longkou in the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 801–817. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.F.; Wang, R.J.; Xu, S.N.; Li, W.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Mei, J.J.; Ding, Z.L.; Yang, P. J.Hydrogeochemistry and stable isotopes characteristic of brine in Laizhou Bay. Geol. Rev. 2016, 62, 343–352. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.X. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies for salt water intrusion on the south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Ground Water 2000, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. The Evolution of Ground-Saline Water and Process Mechanism of Saline Water Intrusion in Southern Laizhou Bay; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Miao, J.J.; Bill, X.H.; Liu, H.W.; Zhang, H.X.; Ma, Z. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21073–21090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.H.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhang, J. Analysis on dynamic changes of salt water intrusion in Northern Weibei Plain in south Laizhou Bay. Shandong Land Resour. 2014, 9, 39–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y.J. Hydrochemical characteristics and functions of groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay based on the multivariate statistical analysis approach. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.; Hou, G.H. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, s607–s608, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.F.; Zou, X.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.L.; Sun, L.L. Heavy metal contents analysis and potential ecological risk appraisal to sediments of large and medium-scaled reservoirs in Guangdong Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 11, 801–817. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, J.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Darling, W.; Ma, J.; Pang, Z.; Young, A.A. Conceptual model of recharge to southeastern Badain Jaran Desert groundwater and lakes from environmental tracers. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3519–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Ma, J.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Kipfer, R.; Darbyshire, D.P.F. Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin, North West China. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 2148–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R.; Fifield, L.K. Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: An example from the southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Chem. Geol. 2006, 231, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, F.J.; Custodio, E. Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer to identify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, M.G. Extensive and rapid changes in seawater chemistry during the Phanerozoic: Evidence from Br contents in basal halite. Terra Nova 2003, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drever, J.I. The Geochemistry of Natural Waters: Surface and Groundwater Environments; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Usiglio, M.J. Etudes sur la composition de leau de la Mediterranee et sur lexploitation des sels quelle contient. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1849, 27, 172–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mazor, E. Chemical and Isotopic Groundwater Hydrology; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- GB5749–2006. Standards for Drinking Water Quality. National Standard of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China; 2006; pp. 1–10.
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Gat, J.; Frochlich, K.F.O. Isotopes in the water cycle: Past, present and future of a developing science. J. Paleolimnol. 2007, 38, 621–622. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Saiki, M. Strontium concentrations and strontium-chlorinity ratios in seawater of the North Pacific and the adjacent seas of Japan. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 27, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X. Cl/Br ratios and chlorine isotope evidences for groundwater salinization and its impact on groundwater arsenic, fluoride and iodine enrichment in the Datong basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).